Choosing Your How To Make Die Cuts: Key Specs to Compare in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to make die cuts
In the competitive landscape of modern manufacturing, understanding how to make die cuts efficiently can be a game changer for B2B buyers. As businesses across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek innovative solutions for product design and production, the challenge of sourcing the right cutting technology becomes paramount. This comprehensive guide not only demystifies the die-cutting process but also explores various types of dies, their applications, and the intricacies of supplier vetting.
International buyers face unique challenges, from navigating local regulations to assessing the quality and cost-effectiveness of materials. By providing insights into the latest technologies and techniques, this guide empowers decision-makers to make informed choices tailored to their specific needs. Whether you are producing packaging, textiles, or custom components, understanding the nuances of die-cutting will enhance your operational efficiency and product quality.
Furthermore, we delve into cost considerations, helping you to balance budget constraints with the demand for precision and reliability. With a focus on actionable strategies and practical solutions, this resource is designed to equip you with the knowledge necessary to thrive in the global market. Embrace the opportunity to optimize your production processes and elevate your business offerings by mastering the art of die cutting.
Understanding how to make die cuts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel Rule Dies | Made from steel rules, ideal for precise cuts. | Packaging, Labels, Textiles | Pros: Durable, cost-effective for high volumes. Cons: Longer lead times. |
| Rotary Dies | Use a rotating cylinder for continuous cutting. | High-volume production runs | Pros: Efficient for large batches. Cons: High initial setup cost. |
| Laser Cutting Dies | Utilize laser technology for intricate designs. | Prototyping, Custom Projects | Pros: High precision, flexible design changes. Cons: Slower for mass production. |
| Custom Foam Dies | Simple, homemade dies often for low-volume tasks. | Crafting, Small Businesses | Pros: Low cost, quick to produce. Cons: Limited durability and precision. |
| Hydraulic Dies | Heavy-duty dies for stamping and shaping materials. | Automotive, Aerospace | Pros: Extremely powerful, suitable for thick materials. Cons: Expensive and requires specialized equipment. |
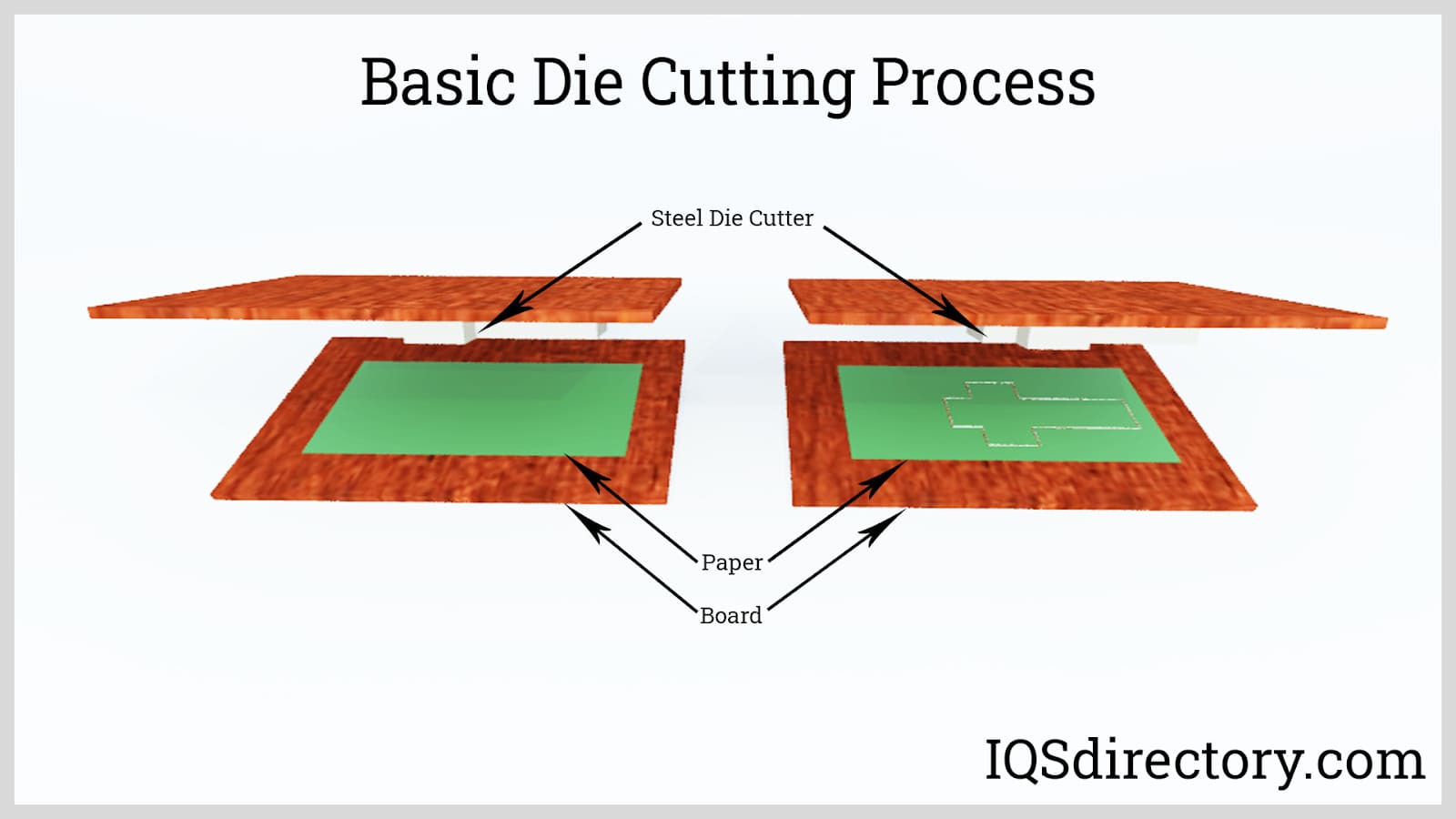
What Are Steel Rule Dies and Their B2B Benefits?
Steel rule dies are crafted from thin steel strips, making them a popular choice for applications requiring precision cuts. They are primarily used in packaging, label production, and textiles, where accuracy is paramount. For B2B buyers, the advantages of steel rule dies include their durability and cost-effectiveness for high-volume production. However, the downside is that they often come with longer lead times, which may not suit businesses needing rapid turnaround.
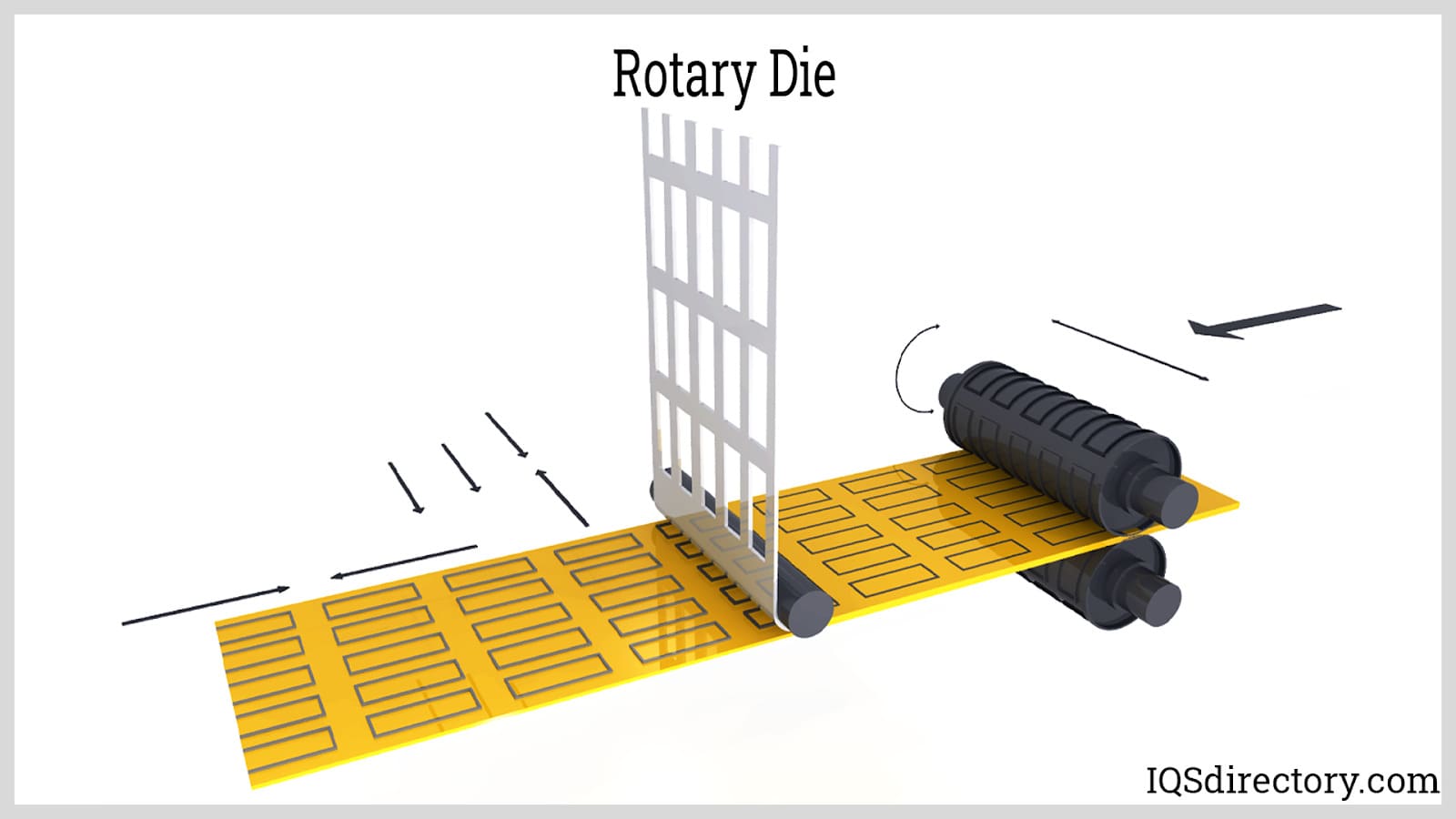
How Do Rotary Dies Enhance Production Efficiency?
Rotary dies are designed for high-speed production, employing a rotating cylinder to continuously cut materials. This method is particularly beneficial for businesses engaged in high-volume production runs, such as packaging and labels. The main advantages of rotary dies include their efficiency and ability to handle large batches. However, the initial setup costs can be significant, making them more suitable for companies that can justify the investment through volume sales.
Why Choose Laser Cutting Dies for Precision Projects?
Laser cutting dies leverage advanced laser technology to achieve intricate designs and precise cuts. They are ideal for prototyping and custom projects where detail is crucial. B2B buyers benefit from the high precision and flexibility that laser cutting offers, allowing for quick design changes without the need for new dies. However, the process can be slower for mass production, which may affect overall output for businesses focused on high volumes.
What Are the Advantages of Using Custom Foam Dies?
Custom foam dies are typically homemade and best suited for low-volume tasks, such as crafting or small business applications. They are easy to produce and cost-effective, making them appealing for startups or individual projects. While the advantages include rapid production and low costs, buyers should consider the limitations in durability and precision, which may not meet the standards required for more demanding industrial applications.
How Do Hydraulic Dies Support Heavy-Duty Applications?
Hydraulic dies are designed for heavy-duty applications, capable of stamping and shaping various materials. They are widely used in industries such as automotive and aerospace, where the need for strength and precision is critical. The primary benefits of hydraulic dies include their immense power and suitability for thick materials. However, they come with high costs and require specialized equipment, making them a significant investment for businesses that need robust solutions for heavy manufacturing tasks.

Illustrative image related to how to make die cuts
Key Industrial Applications of how to make die cuts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how to make die cuts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Packaging | Custom packaging for consumer goods | Enhanced brand differentiation and product protection | Material compatibility, precision cutting requirements |
| Automotive | Die-cut parts for vehicle interiors | Cost savings through reduced waste and improved efficiency | Supplier reliability, compliance with safety standards |
| Electronics | Die-cut components for circuit boards | Improved assembly speed and reduced labor costs | Material sourcing, precision tolerance, and lead times |
| Textiles | Custom fabric shapes for fashion and upholstery | Increased design versatility and reduced manual labor | Fabric type compatibility, cutting precision, and durability |
| Pharmaceuticals | Die-cut labels and packaging for medications | Enhanced compliance with regulations and improved branding | Regulatory compliance, material safety, and print quality |
How is Die Cutting Used in Packaging Applications?
In the packaging industry, die cutting is crucial for creating custom shapes and sizes that enhance the presentation of consumer goods. Businesses can develop unique packaging designs that not only attract customers but also provide necessary protection during transport. For international buyers, understanding local regulations regarding packaging materials and sustainability is vital, as well as ensuring that the die-cut processes align with their production capabilities to minimize waste and maximize efficiency.
What Role Does Die Cutting Play in the Automotive Sector?
The automotive industry utilizes die-cutting to produce precise parts for vehicle interiors, such as foam padding and insulation materials. This method allows manufacturers to reduce waste and improve production efficiency by creating parts that fit perfectly without additional trimming. Buyers from different regions must consider the availability of materials that comply with safety standards and the need for reliable suppliers who can deliver consistent quality in high-volume orders.
How is Die Cutting Applied in Electronics Manufacturing?
In electronics, die cutting is essential for producing components for circuit boards, such as insulators and spacers. The precision of die-cut parts ensures that assemblies are faster and less labor-intensive, which can significantly cut costs. Buyers should focus on sourcing materials that meet specific electrical properties and tolerances, as well as ensuring that suppliers can provide quick turnaround times to keep pace with rapidly evolving technology.
How Does Die Cutting Benefit the Textile Industry?
Die cutting in textiles enables manufacturers to create custom shapes for fashion items and upholstery with minimal manual labor. This process not only increases design flexibility but also ensures consistent quality across large production runs. When sourcing die-cutting services, businesses must assess the compatibility of cutting techniques with various fabric types, as well as the durability of the final products to withstand wear and tear.
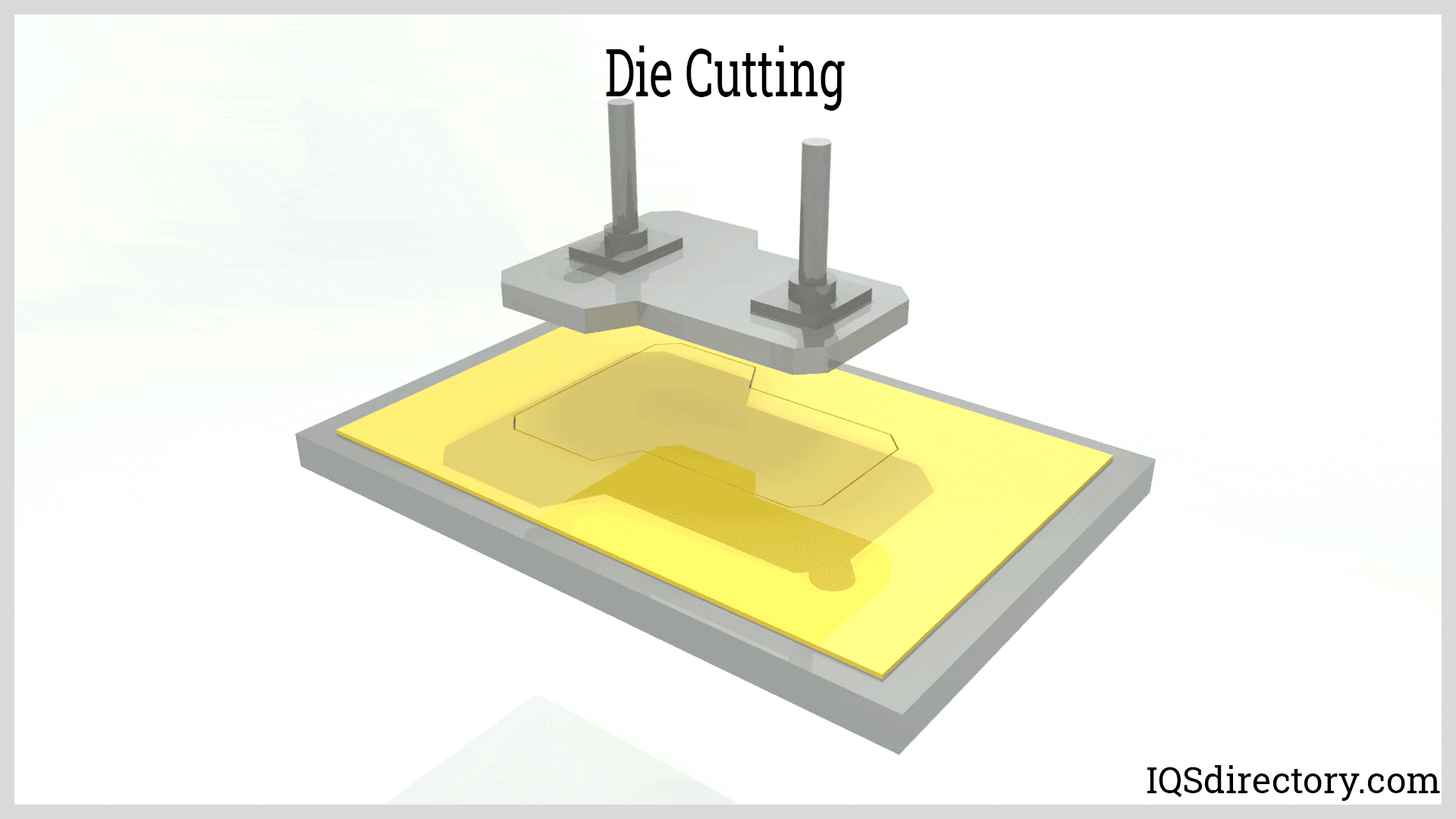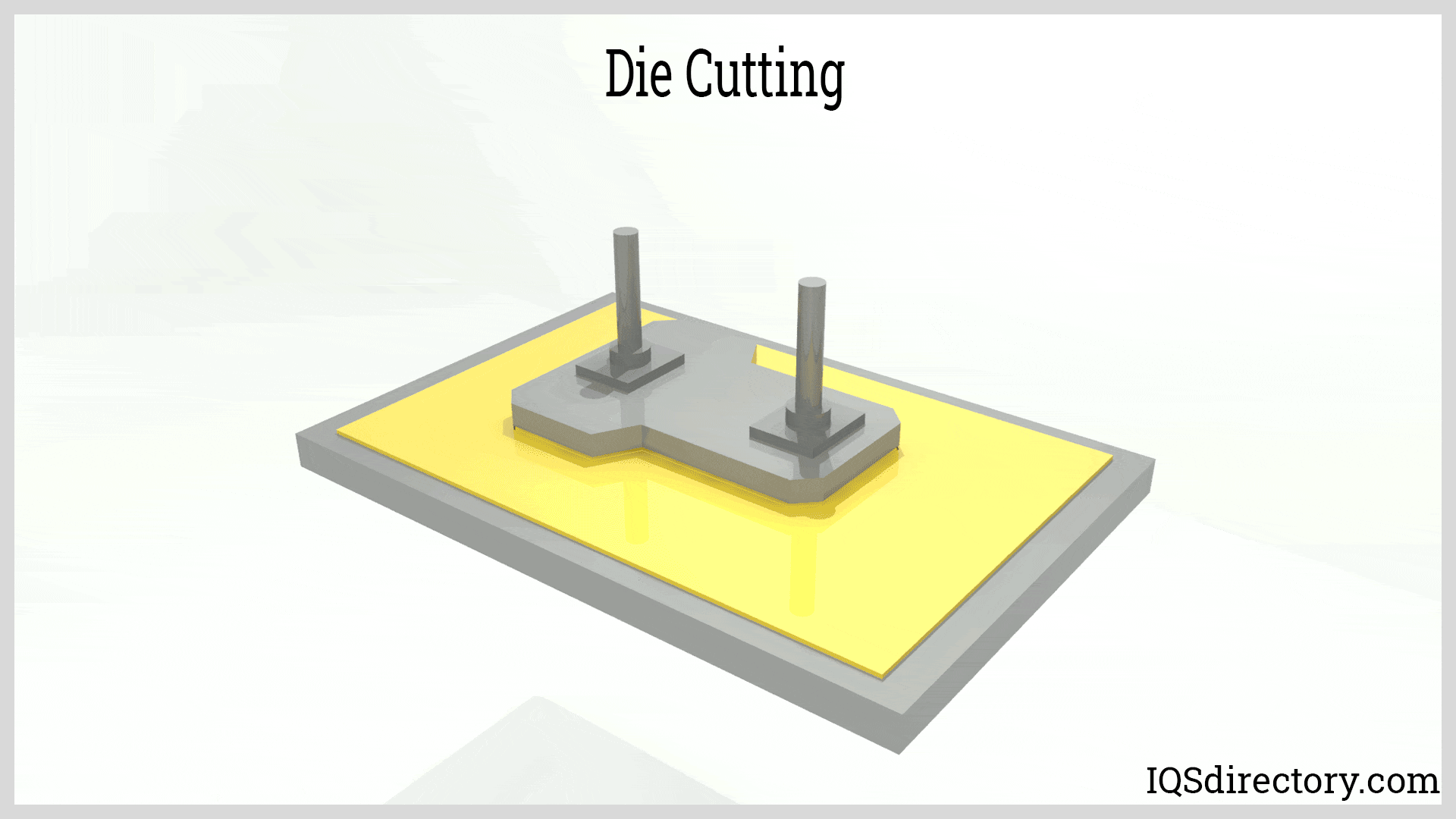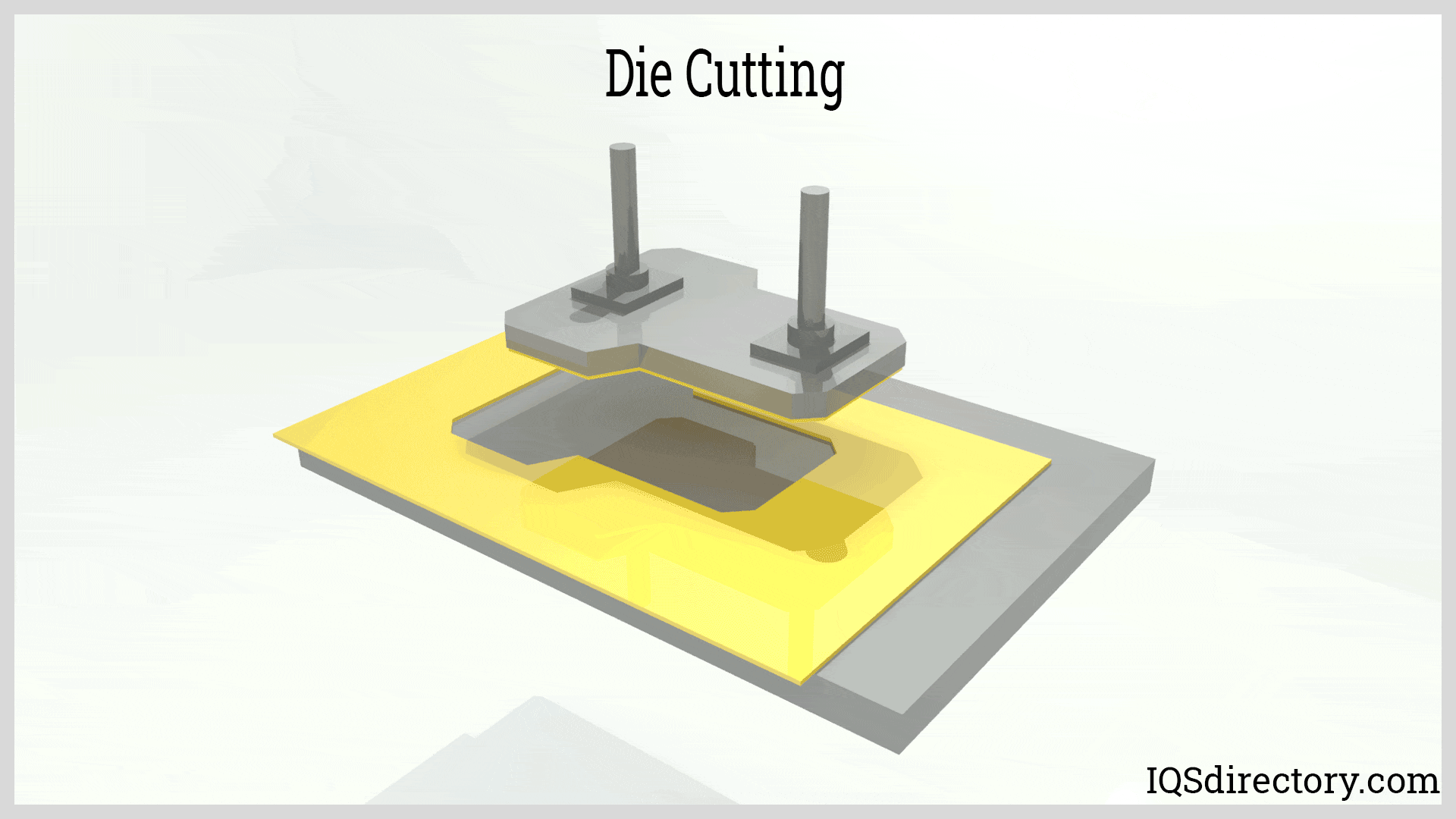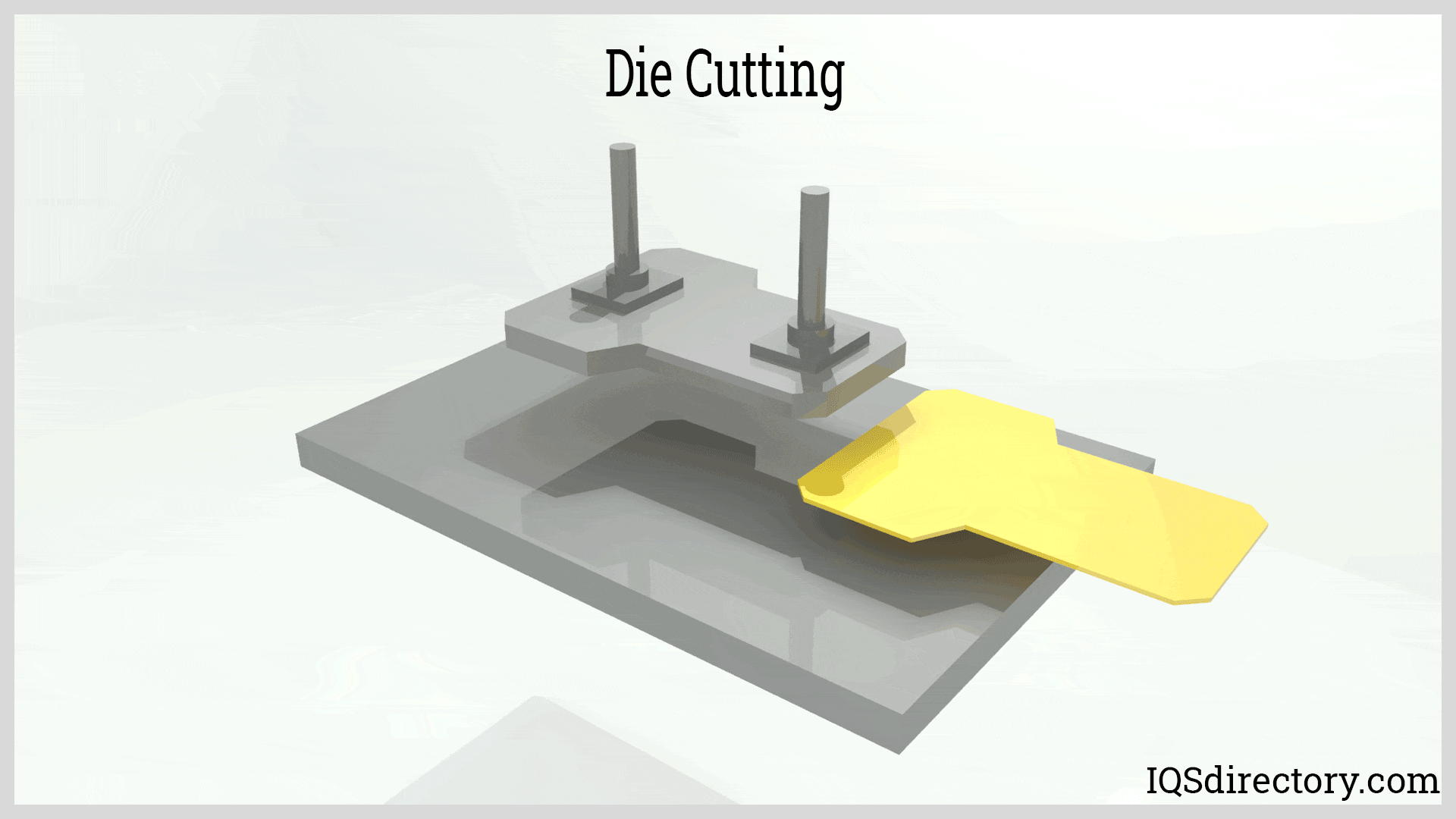
Illustrative image related to how to make die cuts
Why is Die Cutting Important in the Pharmaceutical Sector?
In the pharmaceutical industry, die cutting is used for producing labels and packaging that comply with strict regulatory requirements. This process enhances branding while ensuring that products are clearly marked for safety and efficacy. International buyers must prioritize suppliers who understand local regulations, can provide high-quality printing, and ensure that materials are safe for medical use, as these factors are critical in maintaining compliance and consumer trust.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to make die cuts’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: High Costs of Professional Die Production
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face the challenge of high costs associated with outsourcing die cutting to professional manufacturers. For companies producing low to medium quantities of products, the expense of custom dies can significantly impact profitability. This is especially true for businesses in regions with limited access to cost-effective manufacturing solutions, such as parts of Africa and South America. Buyers often find themselves in a dilemma: either invest heavily in custom dies or rely on manual cutting methods, which can be time-consuming and inefficient.
The Solution: To address this issue, businesses should consider investing in DIY die-making processes. For instance, creating simple dies using readily available materials like metal cans can significantly reduce costs. By following a structured approach—gathering the right tools, designing a pattern, and assembling the die with precision—companies can produce their own cutting dies tailored to specific needs without incurring high costs. Additionally, they can explore local suppliers for materials and tools to ensure timely access and lower shipping costs. Utilizing training resources and workshops can also equip teams with the necessary skills to enhance their die-making capabilities, thus optimizing production and saving costs.
Illustrative image related to how to make die cuts
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Cutting Quality and Precision
The Problem: Another common pain point is the inconsistency in cutting quality and precision when using homemade dies. Many businesses, particularly those dealing with intricate designs or high-volume production, find that homemade solutions often lead to uneven cuts, resulting in wasted materials and time. This is particularly critical for industries like packaging and textiles, where accuracy is paramount for maintaining product quality and meeting customer expectations.
The Solution: To improve cutting quality, businesses should invest in measuring and calibration tools to ensure that their dies are made with precision. Implementing a systematic approach to die design, such as using software for digital modeling, can help in creating accurate patterns. Additionally, sharpening blades before use and regularly maintaining the dies are vital practices that can enhance cutting efficiency and consistency. Establishing a quality control process that involves checking the first few cuts for accuracy before full production can also help identify issues early on, allowing for adjustments to be made and ensuring a higher quality output.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Scaling Production with Die Cuts
The Problem: As businesses grow, they often encounter difficulties in scaling their die-cutting operations. The transition from small-scale production to larger volumes can be challenging, especially when relying on manual die-making methods or limited equipment. This is a significant concern for companies in emerging markets that may lack access to advanced machinery or sufficient technical expertise, leading to delays and inefficiencies in production.

Illustrative image related to how to make die cuts
The Solution: To effectively scale production, businesses should consider investing in semi-automated die-cutting machines that can accommodate larger volumes while maintaining flexibility in design changes. Partnering with local manufacturers or suppliers can also provide access to affordable machinery that meets specific production needs. Additionally, companies can explore forming strategic alliances with other businesses to share resources and equipment, thereby reducing individual investment costs. Training staff on the use of new technologies and implementing lean manufacturing principles can further streamline operations, ensuring that the transition to larger-scale production is both smooth and efficient.
By addressing these common pain points with actionable solutions, B2B buyers can enhance their die-cutting processes, reduce costs, and improve overall production efficiency, ultimately leading to greater competitiveness in their respective markets.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to make die cuts
When selecting materials for die cutting, it’s essential to consider the specific requirements of the application, including the type of media being cut, the complexity of the design, and the intended end-use. Here, we analyze four common materials used in die cutting, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
Illustrative image related to how to make die cuts
What Are the Key Properties of Steel in Die Cutting?
Steel, particularly high-carbon steel, is a popular choice for die cutting due to its durability and ability to retain sharp edges. It typically withstands high pressure and temperature, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Steel dies can be heat-treated to enhance hardness, which is critical for cutting tougher materials.
Pros: Steel dies are highly durable and can produce a large number of cuts before needing replacement. They offer excellent precision, which is essential for complex designs.
Cons: The initial cost of steel dies can be high, and they require specialized manufacturing processes, which can lead to longer lead times. Additionally, they may be prone to corrosion if not properly maintained.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with a wide range of materials, including paper, cardboard, and thin metals. However, buyers must ensure that the steel grade meets specific industry standards, such as ASTM A681 for tool steels.
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Die Cutting Material?
Aluminum is increasingly popular in die cutting applications due to its lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion. It is easier to machine compared to steel, which can reduce manufacturing complexity and lead times.
Pros: Aluminum dies are lighter, making them easier to handle and operate. They also have good thermal conductivity, which can be advantageous in certain cutting processes.
Cons: While aluminum is less expensive than steel, it may not offer the same level of durability, especially for high-volume cutting tasks. It can wear down faster than steel, leading to more frequent replacements.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for cutting softer materials like paper and plastics. International buyers should consider compliance with standards like ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions to ensure quality.
Illustrative image related to how to make die cuts
What Are the Advantages of Using Polymer-Based Materials for Die Cuts?
Polymer-based materials, such as nylon and polyurethane, are often used for die cutting due to their flexibility and ease of fabrication. These materials can be molded into various shapes, making them ideal for custom applications.
Pros: They are lightweight and can be produced at a lower cost than metal dies. Their flexibility allows for intricate designs without the risk of breaking.
Cons: Polymer dies may not be suitable for high-pressure applications and can wear out quickly when cutting harder materials. They also have lower heat resistance compared to metals.
Impact on Application: These materials are best for cutting softer substrates like paper and textiles. Buyers in regions with varying climates, such as Africa and the Middle East, should consider the thermal stability of polymers to avoid deformation.
How Do Composite Materials Enhance Die Cutting Applications?
Composite materials, which combine different materials to leverage their strengths, are gaining traction in die cutting. These can include combinations of metals and polymers or layered materials designed for specific applications.
Pros: Composites can offer a balance of durability and flexibility, making them versatile for various applications. They can also be engineered to meet specific performance criteria.
Cons: The complexity of manufacturing composite dies can lead to higher costs and longer production times. Additionally, ensuring consistent quality can be challenging.
Impact on Application: Composites are suitable for cutting a range of materials, including both soft and hard substrates. International buyers should ensure compliance with relevant standards, such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Die Cuts
| Material | Typical Use Case for how to make die cuts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty cutting for metals and plastics | High durability and precision | Higher initial cost and corrosion risk | High |
| Aluminum | Cutting softer materials like paper | Lightweight and easy to machine | Less durable than steel | Medium |
| Polymer | Cutting textiles and soft substrates | Cost-effective and flexible | Limited pressure resistance | Low |
| Composite | Custom applications for varied materials | Versatile performance | Higher manufacturing complexity | Medium to High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of material options for die cutting, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to make die cuts
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Die Cuts?
The manufacturing of die cuts involves several critical stages, each essential for ensuring precision and quality. Understanding these stages is crucial for B2B buyers looking to optimize their supply chain and product outcomes.
How Is Material Prepared for Die Cuts?
The first step in die cut manufacturing is material preparation. This involves selecting the appropriate substrate, which could range from paper and cardboard to plastics and metals. The choice of material directly impacts the die’s performance, so it’s important to consider factors like thickness, flexibility, and intended end use.
Once the material is selected, it must be cut to size and treated if necessary. For instance, materials may need to be pre-treated to improve adhesion or enhance cutting precision. This stage may also include testing the material’s compatibility with the intended die cutting technique, ensuring that it can withstand the stresses of the cutting process.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of Die Cuts?
After material preparation, the next stage is forming, where the actual die cutting occurs. Various techniques can be employed, depending on the complexity and volume of the production run:
-
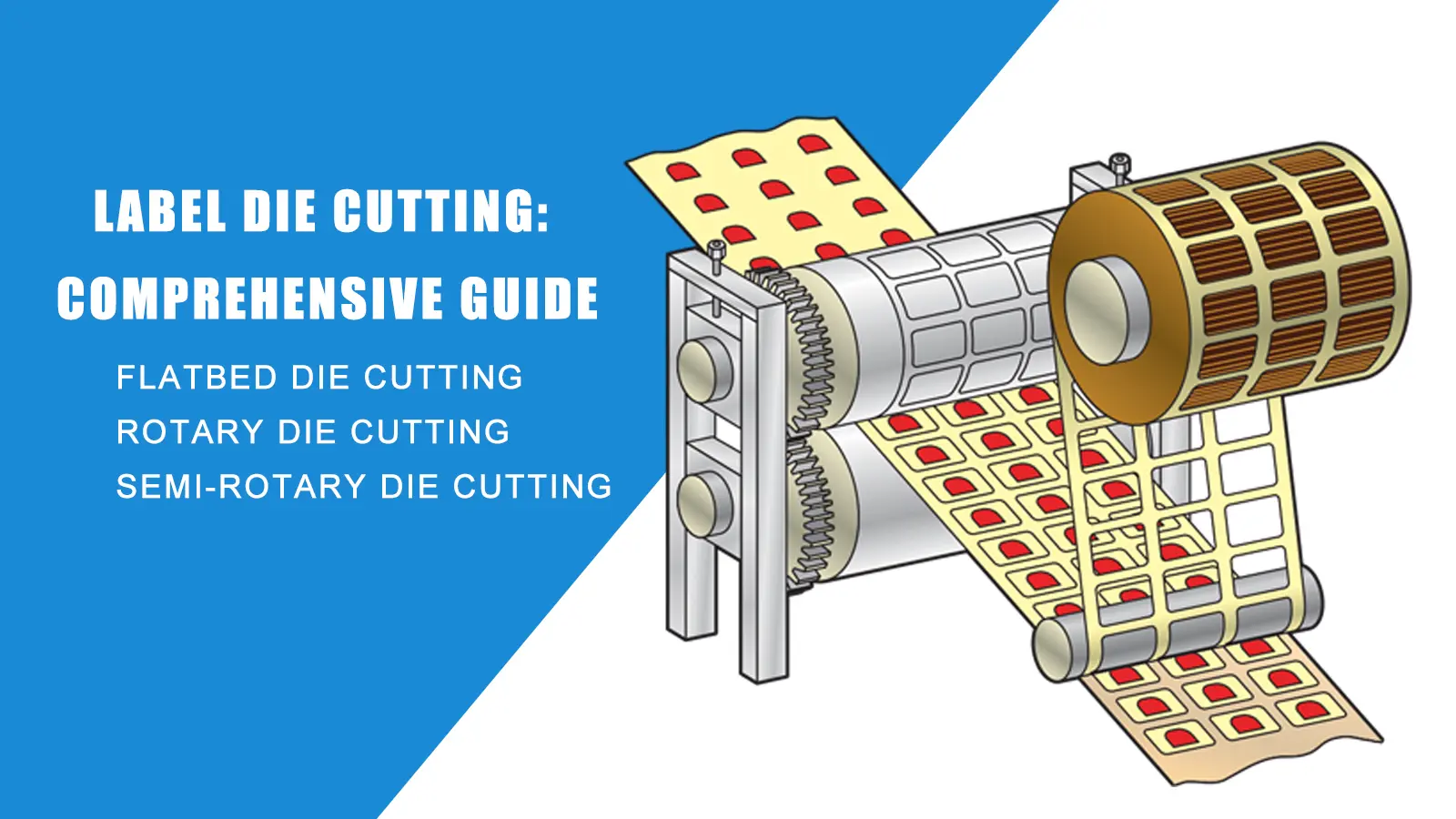
Rotary Die Cutting: This method uses cylindrical dies to cut materials continuously, making it ideal for high-volume production. It’s particularly effective for flexible materials like labels and packaging.
-
Flatbed Die Cutting: Utilizing flat dies, this technique is suitable for thicker materials and intricate designs. It’s often used in the production of custom shapes and prototypes.
-
Laser Cutting: For high precision and intricate designs, laser cutting is favored. This technique is versatile and can cut through a variety of materials, making it perfect for custom applications.
-
Waterjet Cutting: This method uses high-pressure water streams to cut materials, ideal for thick substrates that require a clean cut without fraying.
Each of these techniques has its advantages and disadvantages, influencing cost, lead time, and the overall quality of the die cuts produced.
How Are Die Cuts Assembled and Finished?
Once the die cuts are formed, they must be assembled and finished. Assembly can involve several processes, such as gluing, laminating, or stitching, depending on the product’s final design. This stage is crucial for ensuring that all components fit together seamlessly and meet design specifications.
Finishing processes may include die-cutting additional features like perforations, scoring, or embossing. Quality checks during this stage are vital to ensure that the product meets aesthetic and functional requirements. For example, products intended for retail display must not only be functional but also visually appealing.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Die Cuts?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the die-cutting process, ensuring that products meet international and industry-specific standards. B2B buyers should be familiar with these QA measures to assess supplier reliability and product quality effectively.
Which International Standards Should Be Considered?
One of the most recognized international standards for quality management is ISO 9001. This standard outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS) and emphasizes customer satisfaction, process efficiency, and continuous improvement. Suppliers that adhere to ISO 9001 demonstrate a commitment to maintaining quality throughout their manufacturing processes.
In addition to ISO 9001, industry-specific standards such as CE marking for products sold in Europe or API standards for certain industrial applications may also apply. Understanding these certifications can help B2B buyers ensure that the products they procure meet regulatory requirements and industry benchmarks.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints play a crucial role in maintaining product integrity throughout the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials before they enter the production process. Ensuring that materials meet predefined standards is critical to preventing defects in the final product.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, regular checks should be conducted to monitor the quality of the products being produced. This includes verifying dimensions, ensuring proper alignment, and assessing the performance of cutting techniques.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection is conducted after the die cuts are completed. This involves testing the finished products against specifications to ensure they meet quality standards. Common tests include dimensional accuracy, strength tests, and visual inspections for defects.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential for establishing trust and ensuring product reliability. Here are effective strategies for conducting due diligence:
Illustrative image related to how to make die cuts
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality control processes and adherence to standards. This can be done through on-site visits or remote assessments.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed QC reports can offer transparency regarding a supplier’s quality management practices. These reports should outline inspection methods, results, and any corrective actions taken.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control measures. This can be particularly useful for international transactions, where language and cultural barriers may complicate direct communication.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of specific nuances related to quality control in international trade. Factors such as local regulations, cultural differences, and logistical challenges can impact the procurement process.
Understanding the regulatory landscape in the supplier’s country is crucial. For instance, certain materials may require specific certifications for importation. Additionally, buyers should consider the supplier’s ability to communicate effectively in English or other relevant languages, as this can facilitate smoother transactions and clearer quality expectations.
By keeping these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in mind, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their supply chain efficiency and product quality in the competitive die-cutting market.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to make die cuts’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers interested in procuring the necessary resources and expertise for making die cuts. Understanding the die-cutting process is essential, especially for businesses in industries such as packaging, textiles, and manufacturing. By following these steps, you can ensure a streamlined process for sourcing the right materials and suppliers.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clearly outline your technical requirements for die cuts. This includes dimensions, material types (e.g., paper, metal), and complexity of designs. Understanding these specifications will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and prevent costly errors down the line.
- Consider the Material: Different materials require specific die-cutting techniques. For instance, cutting metal may necessitate more robust dies than cutting paper.
- Precision Requirements: Determine how precise your cuts need to be, as this will influence the type of die and equipment you’ll need.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in die-cutting services or materials. Use industry-specific directories, trade shows, and online platforms to compile a list of candidates.
- Evaluate Supplier Experience: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your specific industry.
- Check Reviews and Testimonials: Seek feedback from other businesses to assess reliability and quality.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Ensuring that your suppliers meet industry standards and certifications is crucial. This step guarantees that the materials and processes used are compliant with safety and quality regulations.
- ISO Certifications: Suppliers with ISO certifications demonstrate a commitment to quality management.
- Compliance with Local Regulations: Verify that suppliers adhere to regulations specific to your region, especially if you are sourcing internationally.
Step 4: Request Samples
Before placing a large order, request samples of the die cuts or materials to evaluate quality and performance. This step allows you to assess how well the supplier meets your technical specifications.
- Test for Durability: Ensure the samples can withstand the intended use without degradation.
- Check Precision: Verify that the samples meet your dimensional requirements.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, lead times, and payment terms. Establishing favorable terms can significantly affect your budget and project timeline.
- Bulk Discounts: Discuss potential discounts for larger orders to optimize costs.
- Payment Flexibility: Consider negotiating payment terms that align with your cash flow needs.
Step 6: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Effective communication is essential throughout the sourcing process. Establish clear lines of communication with your supplier to facilitate quick resolution of any issues.
- Regular Updates: Request regular progress updates during production to stay informed about timelines.
- Point of Contact: Designate a specific individual from both parties for consistent communication.
Step 7: Plan for Quality Assurance
Implement a quality assurance plan to monitor the die-cutting process and the final products. This is critical to ensure that the outputs consistently meet your specifications.
- Inspection Protocols: Develop protocols for inspecting die cuts upon receipt.
- Feedback Mechanism: Establish a system for providing feedback to the supplier for continuous improvement.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing die cuts effectively, ensuring high-quality outcomes and successful supplier partnerships.
Illustrative image related to how to make die cuts
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to make die cuts Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Making Die Cuts?
When sourcing die cuts, B2B buyers must consider multiple cost components that contribute to the overall pricing structure. The primary cost elements include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts costs. Common materials for die cuts include steel, aluminum, and various plastics. The thickness and quality of these materials will affect both price and performance, with higher-quality materials generally yielding longer-lasting dies.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely based on the region and skill level required for die-making. In regions like Africa and South America, labor may be less expensive, but this can also affect the precision and quality of the die cuts produced. Skilled labor is essential for intricate designs, which can drive up costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these overheads, making it crucial to evaluate suppliers based on their operational efficiencies.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be significant, especially for custom dies. Tooling costs can vary based on complexity and precision requirements. Buyers should assess whether the tooling is reusable for future projects to maximize return on investment.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that die cuts meet specified standards incurs additional costs. Investing in robust QC processes can prevent costly errors down the line, making it a worthwhile expenditure for buyers focused on long-term efficiency.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary based on the supplier’s location and the shipping method chosen. For international buyers, understanding Incoterms is crucial, as they dictate who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and liability during transit.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and profit. This margin can be influenced by market competition, demand, and the supplier’s reputation.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Die Cut Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of die cuts, particularly in international B2B transactions:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) often lead to volume discounts. Buyers should consider ordering larger quantities if feasible to reduce per-unit costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs typically incur higher costs due to the additional time and resources required for production. Standardized designs might be more cost-effective.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: High-quality materials may cost more initially but can lead to reduced maintenance and replacement costs. Certifications for materials can also add to costs but may be necessary for specific industries.
-
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers with a strong reputation may charge more but often provide higher quality and reliability. Conducting thorough supplier evaluations can help identify the best balance between cost and quality.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping can greatly impact overall costs. Different Incoterms can shift responsibilities and costs between the buyer and supplier, affecting the total landed cost.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing Die Cuts?
B2B buyers should adopt several strategies to optimize their sourcing of die cuts:
-
Negotiation: Always engage in negotiations. Suppliers may have flexibility in pricing, especially for larger orders or long-term contracts.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Analyze the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just initial pricing. Consider long-term costs associated with quality, durability, and maintenance.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. For instance, sourcing from suppliers in regions with lower labor costs can be advantageous, but ensure that quality standards are met.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and potential discounts on future orders.
-
Conduct Market Research: Stay informed about market trends and pricing fluctuations to make informed purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
Prices for die cuts can fluctuate based on market conditions, material availability, and specific project requirements. It is advisable to obtain multiple quotes and conduct thorough supplier evaluations to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to make die cuts With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternatives for Die Cuts
When it comes to creating custom shapes and designs in materials like paper, cardboard, or thin metal, die cutting is a popular method. However, various alternatives can also achieve similar results, each offering unique advantages and disadvantages. This section compares die cutting with two viable alternatives: laser cutting and manual cutting with tools like X-Acto knives. Understanding these options is crucial for B2B buyers looking to optimize their production processes while balancing cost, efficiency, and precision.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | How To Make Die Cuts | Laser Cutting | Manual Cutting (X-Acto Knives) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision; bulk production suited | Extremely high precision; intricate designs | Lower precision; best for small batches |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; long-term savings | Higher initial investment; variable operational costs | Low cost; minimal investment required |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires setup of dies; moderate complexity | Requires specialized machinery; training needed | Very easy to implement; no special equipment needed |
| Maintenance | Regular upkeep of dies required | High maintenance of laser equipment | Minimal maintenance; occasional blade replacements |
| Best Use Case | High-volume production of consistent shapes | Complex, intricate designs; prototyping | Low-volume, detailed work; one-off projects |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
How To Make Die Cuts
Die cutting is a method that uses custom-made dies to cut materials into specific shapes. This approach is particularly beneficial for high-volume production, where consistency and precision are paramount. While the initial investment in creating the die may seem significant, the long-term savings in labor and material efficiency can be substantial. However, die cutting may not be the best option for small runs or highly intricate designs, where setup costs may outweigh the benefits.
What Are the Advantages of Laser Cutting?
Laser cutting utilizes focused laser beams to cut through materials with high precision. This method is excellent for intricate designs and allows for quick adjustments without the need for physical dies. While the initial investment in laser cutting equipment can be high, the versatility and precision it offers make it a worthy consideration for companies needing flexibility in design. However, the operational costs can vary significantly based on material and machine wear, which may pose challenges for budget-conscious businesses.
Why Consider Manual Cutting with X-Acto Knives?
Manual cutting with tools like X-Acto knives is the most accessible alternative, requiring minimal investment and no specialized machinery. This method is ideal for low-volume projects or prototypes where speed and cost are more critical than precision. However, the labor-intensive nature of manual cutting can lead to inconsistencies and a higher likelihood of errors. It is best suited for small, detailed work rather than large-scale production, making it less efficient for businesses focused on high output.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the right method for creating die cuts depends on your specific production needs and budget constraints. For high-volume and precision-oriented projects, die cutting remains a strong contender. However, if your projects require flexibility and intricate designs, investing in laser cutting technology may be advantageous. On the other hand, for small-scale, detailed work, manual cutting with X-Acto knives can provide an affordable and straightforward solution. By evaluating the performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases of each method, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to make die cuts
What Are the Key Technical Properties Important for Making Die Cuts?
Understanding the technical properties involved in die cuts is crucial for B2B buyers. These specifications not only influence the quality and efficiency of the die-cutting process but also impact the overall production costs and timelines.
Material Grade: Why Does It Matter?
The material grade of the cutting die directly affects its durability and cutting efficiency. Common materials include steel, aluminum, and various composites. Higher-grade materials can withstand more pressure and last longer, which is essential for high-volume production runs. For instance, a die made from high-carbon steel can maintain sharpness longer than one made from lower-grade materials, reducing the frequency of replacements and downtime.
Tolerance: How Precise Does It Need to Be?
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from specified dimensions in the die’s design. In die cutting, tighter tolerances are crucial for applications requiring precise cuts, such as in the automotive or aerospace industries. For B2B buyers, understanding the necessary tolerance levels can help ensure that products fit together correctly, minimizing waste and rework.
Die Height: What Is Its Impact on Production?
Die height is the thickness of the die and affects how deep the cutting blades penetrate the material. A properly calibrated die height ensures that the cutting process is efficient and consistent across all units produced. For buyers, understanding this property can help in selecting dies that align with their production capabilities and material types.
Blade Sharpness: Why Should You Care?
The sharpness of the cutting blades is a critical factor in achieving clean cuts and reducing the force required for cutting. Dull blades can lead to increased wear on the die and can compromise the quality of the final product. This is particularly important for businesses that prioritize quality in their offerings, as poor cuts can lead to increased returns or customer dissatisfaction.

Illustrative image related to how to make die cuts
Press Type: What Are Your Options?
Different types of presses can be used for die cutting, including hydraulic, mechanical, and digital presses. Each type has its advantages and limitations, impacting speed, precision, and the types of materials that can be processed. B2B buyers should consider the press type in relation to their production needs and the materials being used to ensure optimal performance.
What Are the Common Trade Terms in the Die Cutting Industry?
Navigating the die cutting industry requires familiarity with specific jargon that can influence purchasing and production decisions.
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is vital for B2B buyers, as it can affect sourcing, quality assurance, and warranty considerations.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the minimum quantity of products that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it can significantly impact inventory management and production costs. Knowing the MOQ helps companies plan their purchasing strategies effectively.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing for specific products or services. For B2B buyers, issuing RFQs is an essential step in obtaining competitive pricing and ensuring that they receive the best value for their investment.

Illustrative image related to how to make die cuts
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand shipping responsibilities, risk transfers, and costs, ensuring smoother transactions across borders.
Lead Time: What Should You Expect?
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is essential for effective production planning and inventory management, allowing companies to meet their deadlines and customer expectations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions in the die-cutting industry, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and product quality.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to make die cuts Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing the Die Cuts Sector?
The global die-cutting market is witnessing robust growth, primarily driven by advancements in manufacturing technologies and increasing demand for customized packaging solutions. Key trends shaping this sector include the integration of automation and digitalization into die-cutting processes, which enhance efficiency and reduce production costs. Moreover, the rise of e-commerce has amplified the need for unique packaging, prompting manufacturers to explore innovative die-cut designs that cater to diverse consumer preferences.
In regions like Africa and South America, where manufacturing capabilities are evolving, local businesses are increasingly looking to source die-cut solutions that offer flexibility and customization without the high costs associated with traditional die-making. This shift is particularly evident in Brazil and Vietnam, where manufacturers are investing in both in-house die-cutting capabilities and partnerships with specialized suppliers. The emergence of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT and AI, is also influencing how businesses approach die-cutting, allowing for better tracking of production processes and optimization of material usage.

Illustrative image related to how to make die cuts
Furthermore, sustainability is becoming a critical factor in the sourcing decisions of international buyers. As companies strive to align with global sustainability goals, there is a growing demand for environmentally friendly die-cutting materials and processes. This includes the use of recycled materials and eco-friendly adhesives, which are gaining traction across various markets.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Die Cuts Sector?
Sustainability has become a pivotal concern for businesses worldwide, significantly influencing sourcing strategies in the die cuts sector. The environmental impact of traditional manufacturing processes, including high energy consumption and waste generation, has prompted companies to seek greener alternatives. Ethical sourcing practices are now essential for maintaining brand reputation and meeting the expectations of socially conscious consumers.
International buyers, particularly from Europe and the Middle East, are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability. This includes sourcing materials with recognized ‘green’ certifications, such as FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) for paper products or using biodegradable plastics. Additionally, manufacturers are exploring innovative die-cutting techniques that minimize material waste and improve energy efficiency, thereby reducing their overall carbon footprint.
As businesses strive to create ethical supply chains, transparency in sourcing is critical. Companies are investing in technologies that enhance traceability, ensuring that every component of the die-cutting process meets environmental and ethical standards. This shift not only helps in compliance with regulations but also fosters customer loyalty and enhances market competitiveness.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Die Cutting in the B2B Context?
The evolution of die cutting dates back to the early 19th century, with its roots in the leather and textile industries. Initially, die-cutting processes were labor-intensive and time-consuming, requiring skilled craftsmen to create molds and cut materials manually. However, with the industrial revolution and advancements in machinery, die cutting transformed into a more efficient and automated process.
By the mid-20th century, die cutting had expanded into various sectors, including packaging, automotive, and electronics, as manufacturers sought to enhance production efficiency and product customization. The introduction of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology in the late 20th century revolutionized the industry, allowing for precise cutting and the ability to produce intricate designs with minimal waste.
Today, die cutting is an integral part of the manufacturing landscape, with ongoing innovations in technology and materials driving its evolution. As B2B buyers seek customizable and sustainable solutions, the die cuts sector continues to adapt, ensuring it meets the dynamic demands of international markets.
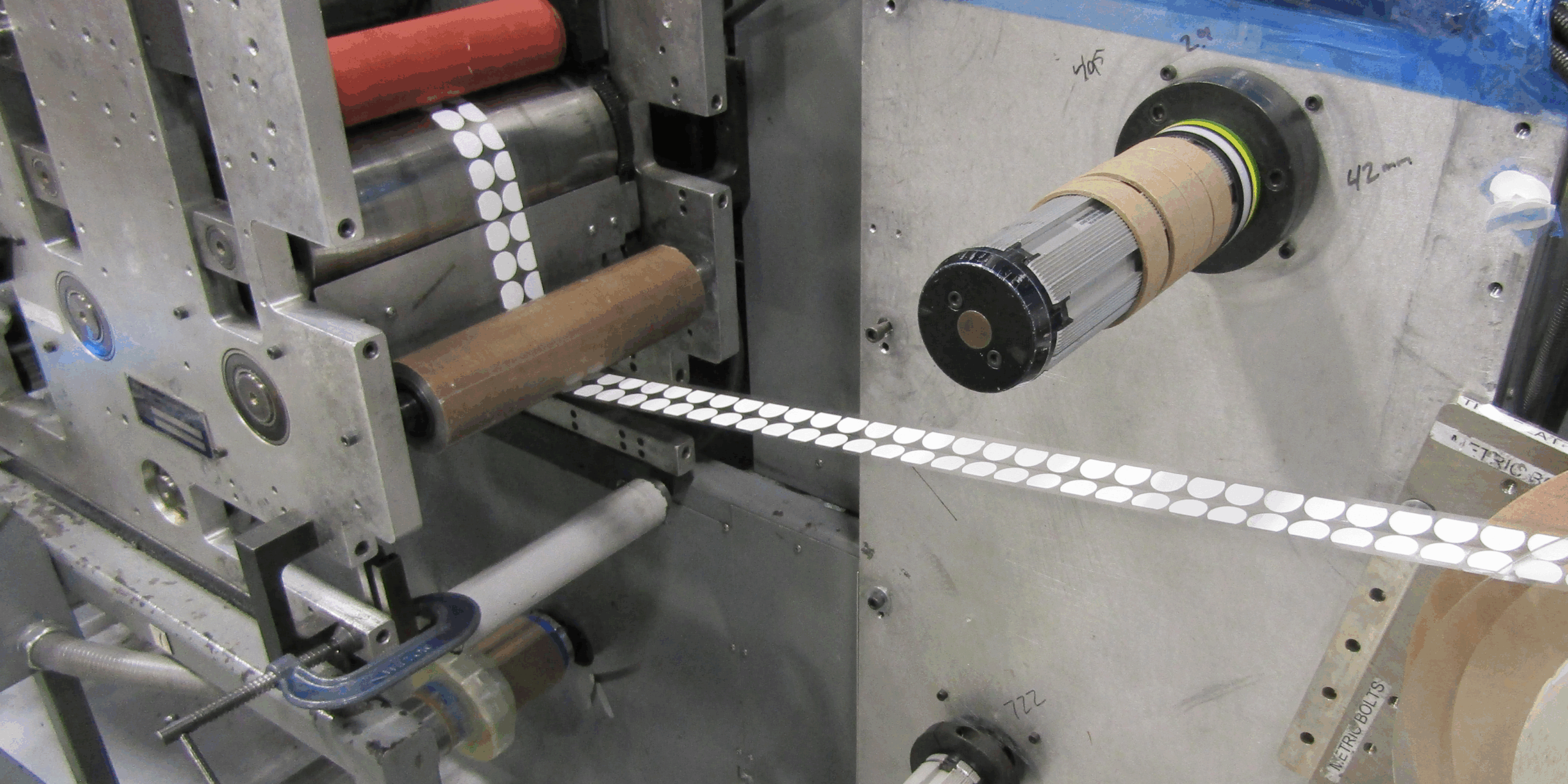
Illustrative image related to how to make die cuts
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to make die cuts
-
How do I solve issues with die-cut precision in my production?
To address precision issues in die-cutting, ensure that your dies are sharpened correctly and that you are using the right materials for your intended application. If you require ultra-precise dimensions, consider investing in professionally made dies rather than homemade ones. Regular maintenance and testing of your cutting equipment can also help maintain accuracy. Additionally, using a reliable foam base can improve the consistency of cuts. For complex designs, consider using CAD software to create exact specifications before manufacturing the die. -
What is the best material for making dies for different applications?
The best material for making dies largely depends on the application. For paper products, aluminum or steel is commonly used due to its durability and ability to produce clean cuts. For cutting softer materials, such as foam or fabric, a less rigid material may suffice. When working with metal, it’s critical to ensure that the blades are set in a robust frame to withstand pressure during operation. Always evaluate the specific requirements of your project before selecting materials to ensure optimal performance. -
What factors should I consider when sourcing die-cutting suppliers internationally?
When sourcing die-cutting suppliers, consider their production capabilities, quality certifications, and experience in your specific industry. Evaluate their ability to meet your customization needs and minimum order quantities (MOQs). Look for suppliers who provide transparent communication and have a proven track record of timely deliveries. Conducting thorough background checks and requesting samples can also help assess their reliability. Additionally, check their compliance with international trade regulations to avoid future complications. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) in die-cutting processes?
To ensure quality assurance in die-cutting, establish clear quality control protocols that include regular inspections of raw materials, in-process checks, and final product evaluations. Work with suppliers who offer transparent QA processes and are willing to provide documentation such as certificates of conformity. Implement a feedback loop with your supplier to address any quality concerns promptly. Utilizing technology, such as automated measurement tools, can also enhance accuracy and consistency in production. -
What payment terms should I negotiate with die-cutting suppliers?
When negotiating payment terms with die-cutting suppliers, consider factors such as order size, supplier reputation, and your cash flow needs. Common payment terms include net 30, 60, or 90 days, but you may also explore options like partial upfront payments or letter of credit for larger orders. Ensure that the payment method is secure and offers protection against non-delivery or quality issues. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can also facilitate more favorable payment terms in the long run. -
What are the common logistical challenges in die-cutting operations?
Logistical challenges in die-cutting operations can include shipping delays, customs clearance issues, and managing inventory levels. To mitigate these challenges, work closely with reliable logistics providers who understand international shipping regulations. Use efficient inventory management systems to keep track of stock levels and plan for demand fluctuations. Additionally, having contingency plans for unforeseen delays can help maintain production schedules and minimize disruptions. -
How do minimum order quantities (MOQs) affect my sourcing strategy for die cuts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can significantly impact your sourcing strategy, especially if you are a smaller business or testing new products. High MOQs may require you to invest more upfront, which can strain cash flow. When negotiating with suppliers, consider discussing flexibility in MOQs, especially for initial orders or prototypes. This can allow you to assess product viability without overcommitting resources. Additionally, collaborating with other businesses to meet MOQs can be a strategic approach. -
What customization options should I consider for die cuts?
Customization options for die cuts can include various shapes, sizes, and materials tailored to your specific needs. Consider the complexity of your designs and whether you need unique features like embossing or cutting multiple layers. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to explore their capabilities in producing custom dies. Additionally, inquire about their design process and whether they can assist in creating prototypes to visualize the final product before full-scale production.
Top 9 How To Make Die Cuts Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Instructables – Homemade Cutting Dies
Domain: instructables.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Homemade cutting dies designed for cutting paper; materials needed include floral foam, metal food cans, tin snips, Gorilla glue, needlenose pliers, leather gloves (optional), Dremel tool or handheld drill, clamps or vice, grinding/sharpening attachment, ruler; process involves cutting can pieces, sharpening blades, laying out the die pattern, bending blades, and ensuring all blades are set to the…
2. Tonic Studios – Die Cutting Solutions
Domain: tonic-studios.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Die: A piece of metal with a raised edge used to cut shapes out of card with pressure. Available in various shapes and sizes for cutting butterflies, layers, words, letters, and box outlines. Can cut card, paper, thin craft foam, metal, and some fabrics.
Die Cutting: A process similar to using a cookie-cutter, but requires a die cutting machine to apply pressure for cutting shapes from cardstock…
3. Reddit – Custom Die-Cut Envelope Prints
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Custom die-cut prints for envelopes; requires custom dies for cutting and creasing/scoring; process includes die cutting, letterpress, folding, and assembly; flexibility in using various papers; Cricut or Silhouette devices suggested for cutting and scoring; laser cutter recommended for high detail; cost for a small envelope die estimated at $125.
4. Zip’emate – Personal Cutter
Domain: scrapbook.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Zip’emate personal cutter, uses slim metal or wood dies, purchased for $25, brand new. Custom die options mentioned include wooden based Steel rule dies (costing $25-45), chemical etch dies, and wooden shapes from craft stores like Michaels or AC Moore. Companies mentioned for custom dies: Ellison, Accucut, Criss-Cross.com.
5. Crafty Chica – Electric & Hand Crank Die Cutting Machines
Domain: craftychica.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Electric die cutting machines: Empress by Anna Griffin Inc., Gemini by Crafter’s Companion. Hand crank machines: Big Shot by Sizzix, Sidekick by Ranger, Tonic Tangerine, Crossover II by Maker’s Movement, Marquise by Diamond Press. Electric cutting machines: Cricut Explore Air 2, Cricut Maker, Silhouette Cameo, Brother Scan and Cut. Features: Electric machines use pressure with metal dies; hand cra…
6. The Cultivated Creative – Cricut Maker
Domain: thecultivatedcreative.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Cricut Maker, HP452 printer, Printswell Fulfillment services, Heavyweight Cardstock 100lb
7. Spellbinders – Die Cutting Tools
Domain: spellbindersblog.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: S4-809 Starstruck Dies, S4-810 Strands Dies, S4-812 Sunburst Dies, SBS-017 French Text Rubber Stamp, PL-001 Spellbinders Platinum Die Cutting and Embossing Machine.
8. Sizzix – Vagabond II Die Cutting Machine
Domain: hopalongstudio.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Sizzix Vagabond II Die Cutting Machine, Sizzix Vagabond II Cutting Platform & Plates, Memory Box Mini Golf Cart Die, Surfaces: Leigon Yupo, White Cardstock, Ranger Alcohol Ink: Gunmetal, Aquamarine, Tranquil, Deception, Crimson, Mushroom, Foil Tape, Size 0 Synthetic Paint Brush, 99% Alcohol, Paper towels.
9. Interwell – Die Cutting Guide & Stationery Products
Domain: interwell.cn
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Die Cutting Guide: Process, Tools, and Applications. Key product details include: 1. Types of Notebooks: Hardcover Notebook, Spiral Journals, Leather Notebook, Cute Notebooks, Marble Journal, Pocket Notebook, Pop it Notebook, Composition Notebook. 2. Stationery Products: Sticky Notes, Ballpoint Pens, Pencils, Pencil Cases, Stationery Set, Erasers, Highlighters, Rulers, Pencil Sharpener. 3. Die Typ…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to make die cuts
In conclusion, strategic sourcing for die cuts offers substantial benefits to businesses looking to optimize production processes and reduce costs. By understanding the intricacies of die making—from selecting appropriate materials to employing precise cutting techniques—buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency. It is crucial to evaluate suppliers not only on cost but also on their ability to deliver quality and reliability, especially in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Investing in high-quality die cuts ensures that your products maintain a competitive edge, while also accommodating the unique demands of your target market. As the global marketplace continues to evolve, leveraging partnerships with skilled manufacturers and suppliers will be vital for innovation and sustainability.
Looking ahead, we encourage international B2B buyers to explore new sourcing opportunities and stay informed about advancements in die-cutting technologies. Engaging with local and global suppliers will not only streamline your production but also foster collaboration that can lead to groundbreaking solutions in your industry. Start your journey towards smarter sourcing today and unlock the full potential of your business.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to how to make die cuts
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.