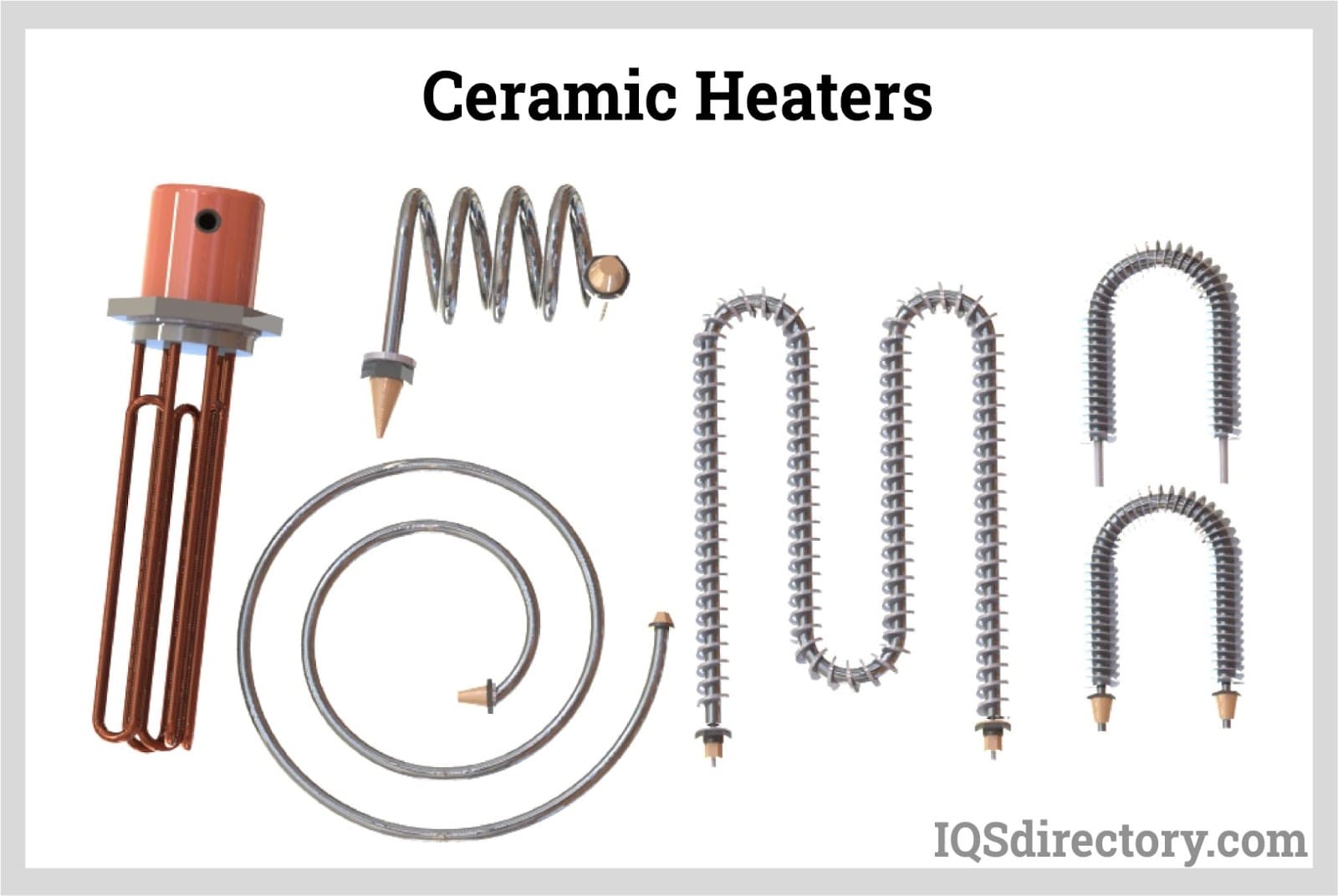
Choosing Your How Do Ceramic Heaters Work: Key Specs to Compare in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how do ceramic heaters work
In an increasingly competitive global market, understanding how ceramic heaters work is essential for businesses seeking efficient and effective heating solutions. As international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, you face the challenge of sourcing heating equipment that not only meets your operational needs but also aligns with budget constraints and energy efficiency goals. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of ceramic heaters, offering insights into their working mechanisms, various types, and diverse applications across industries.
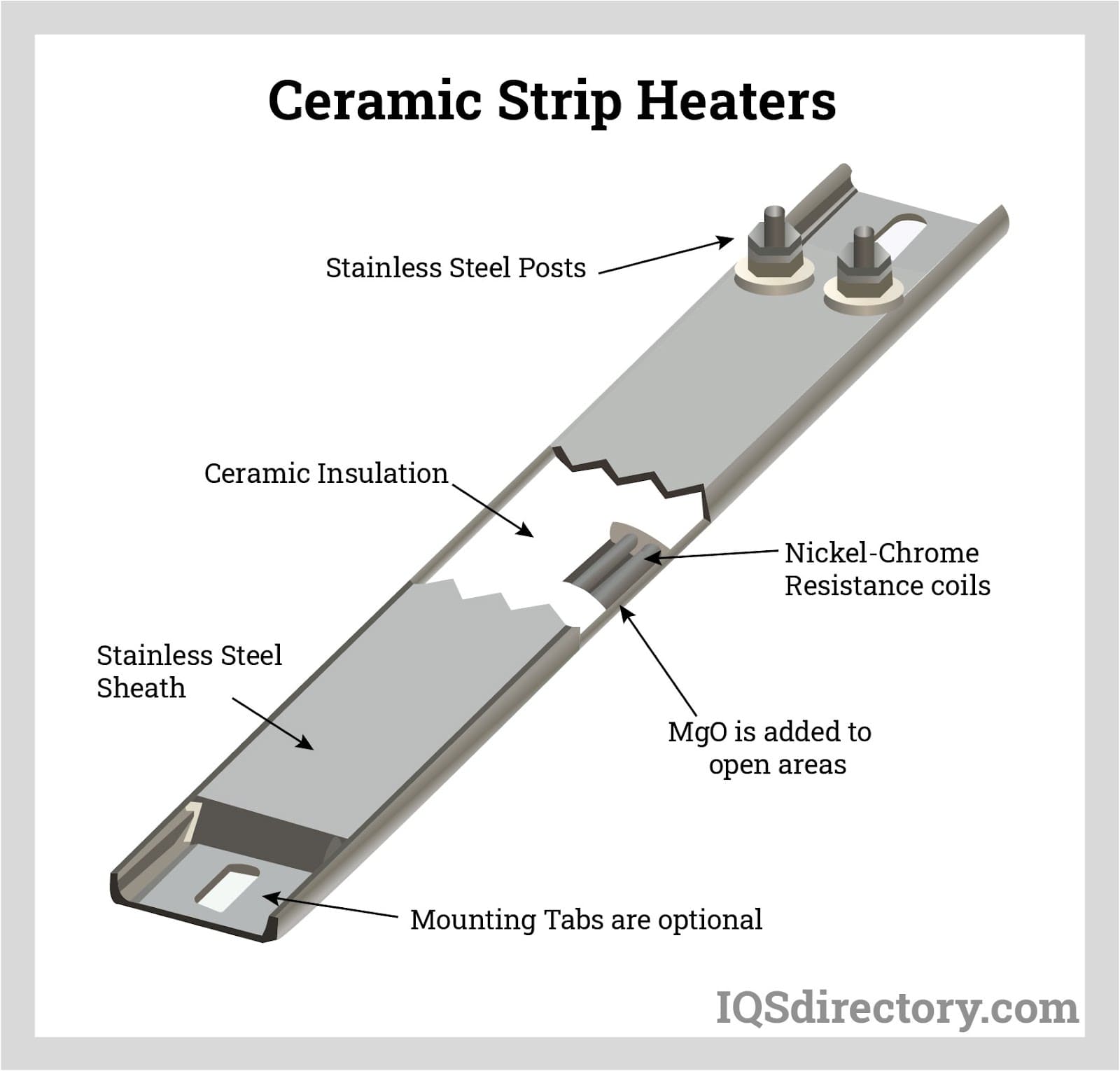
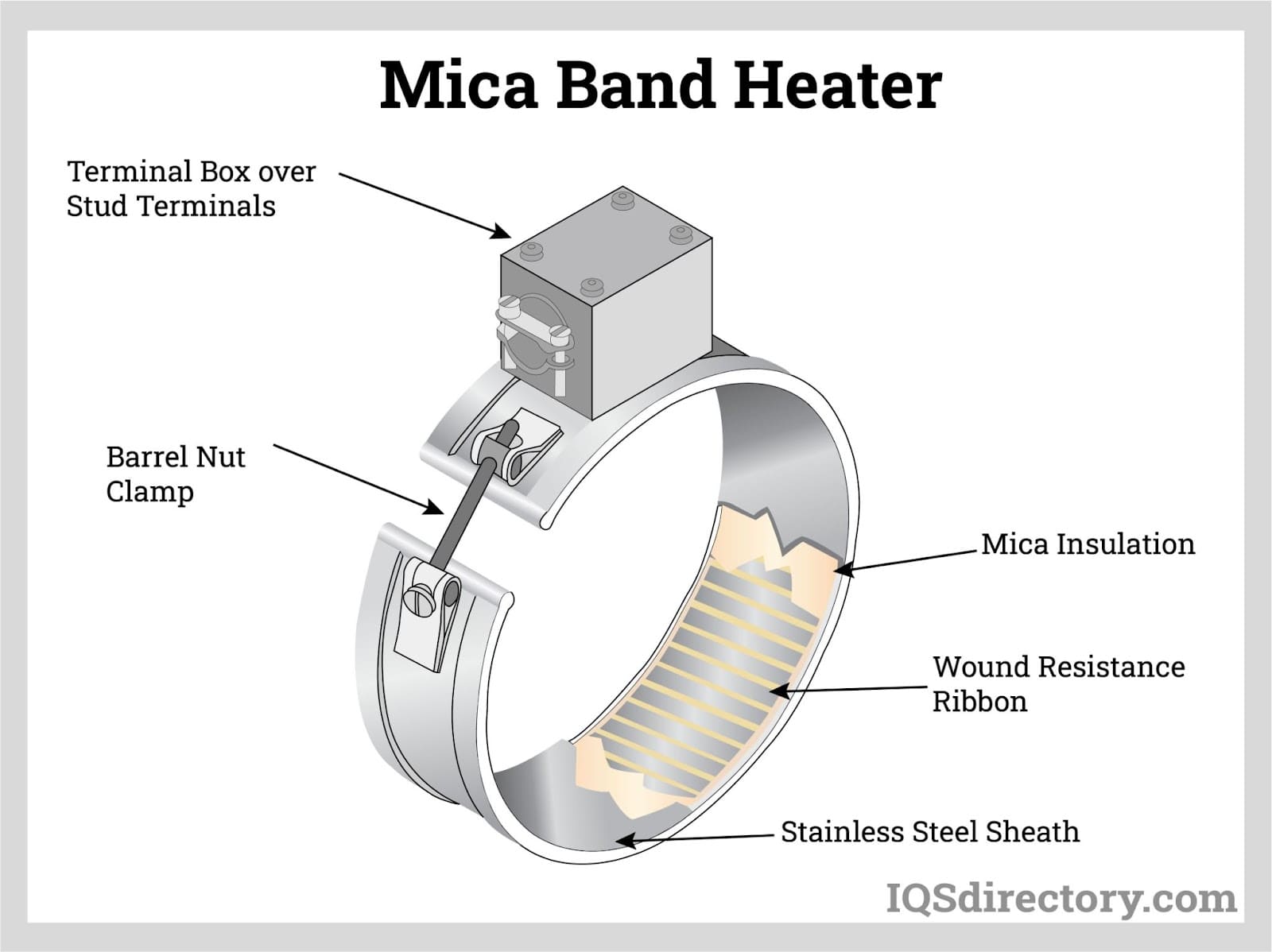
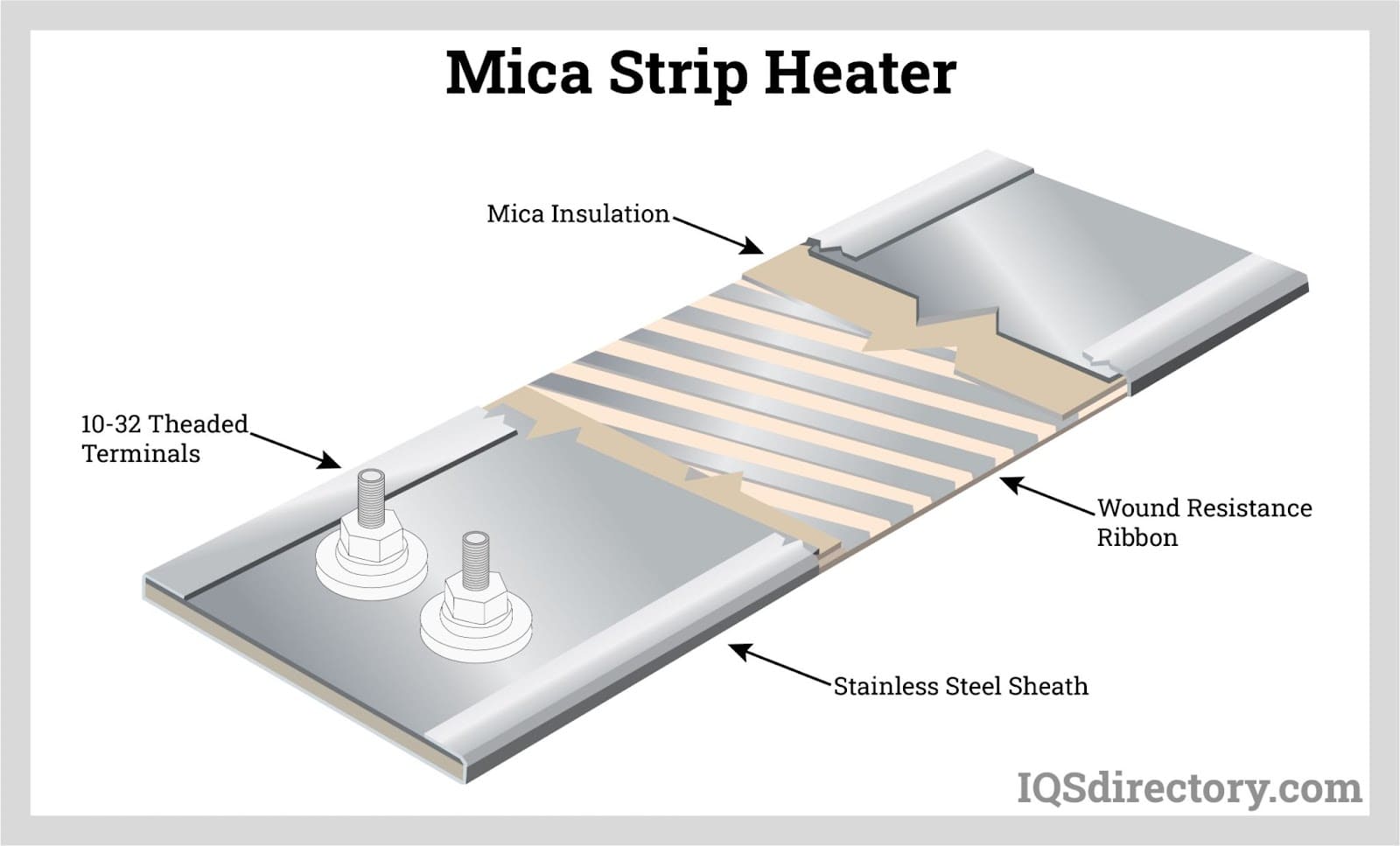
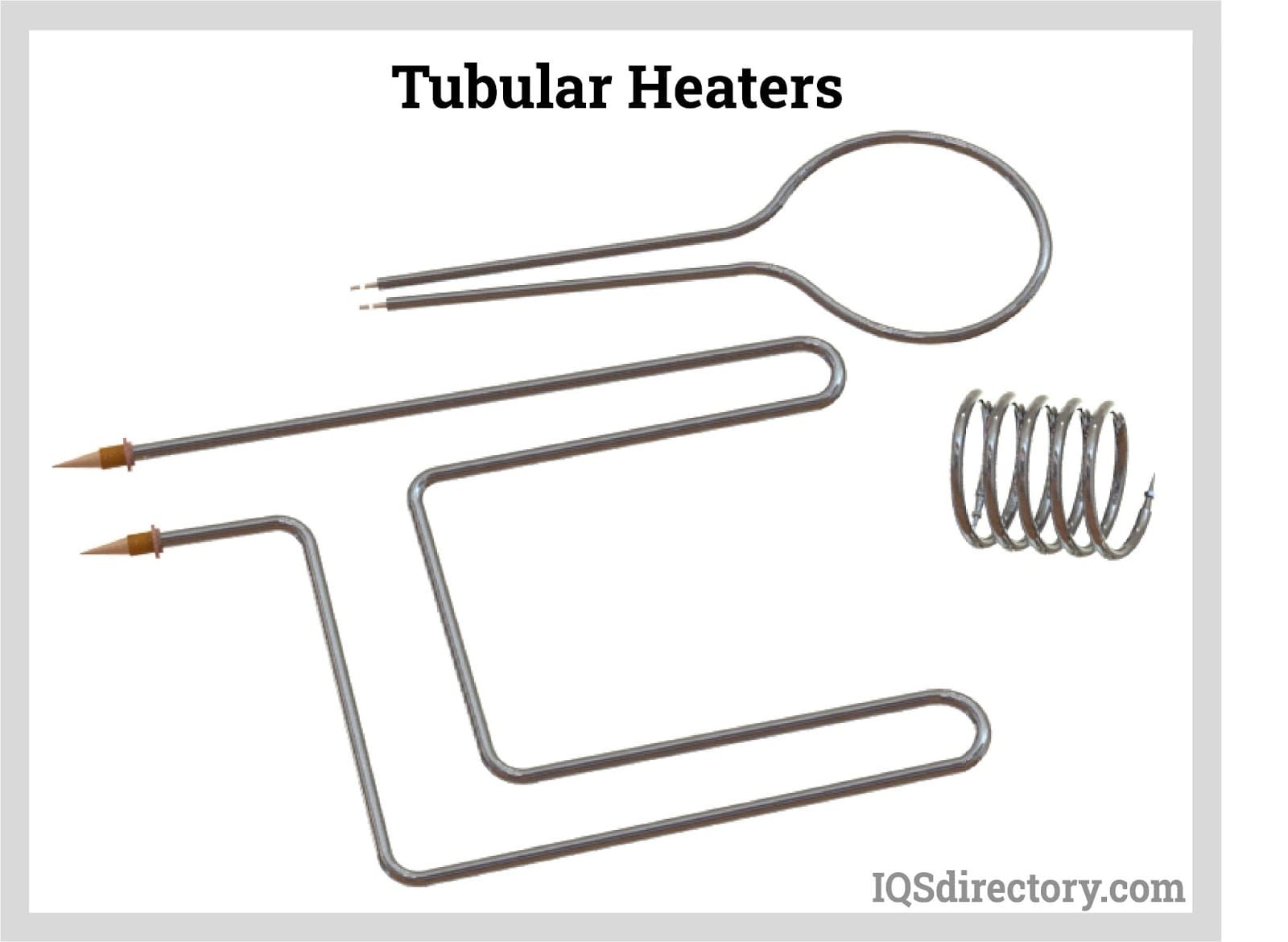
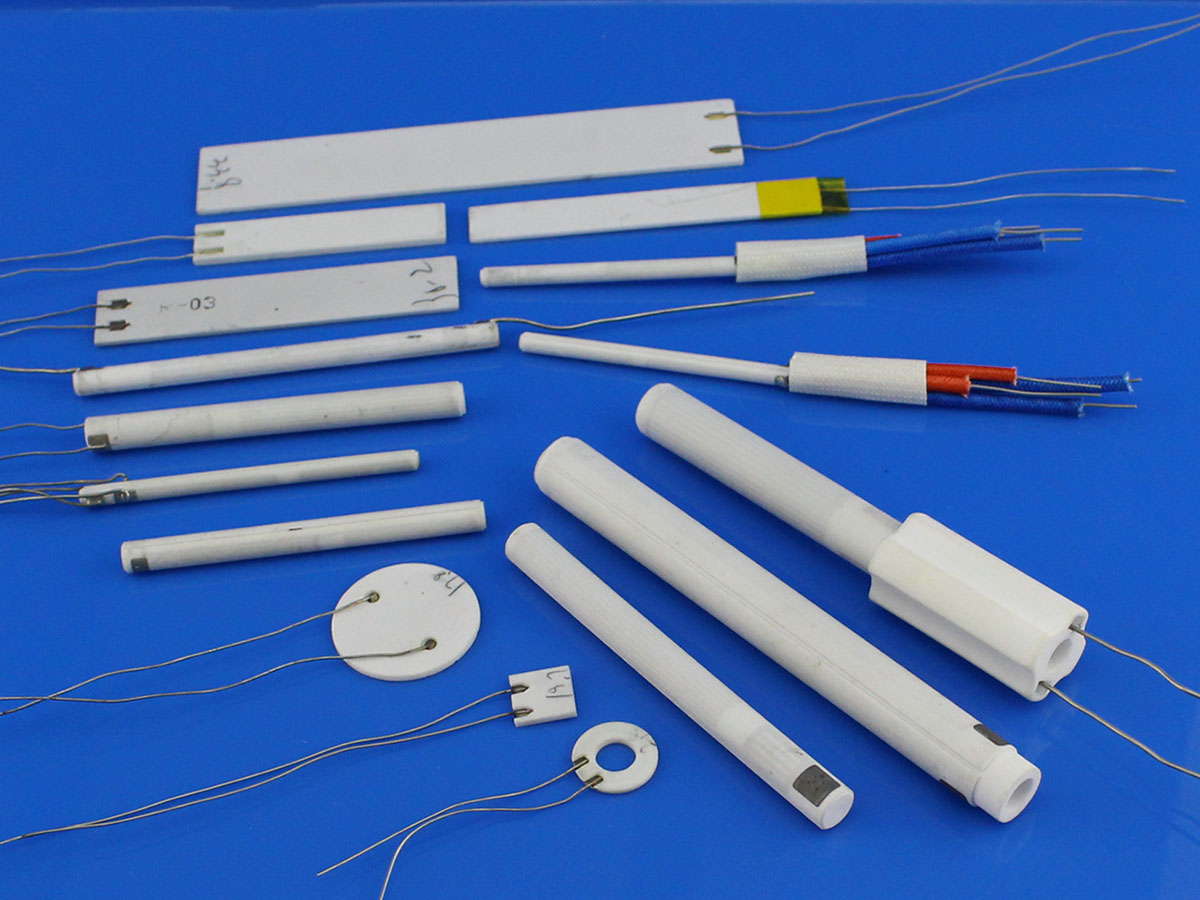
Throughout this guide, we will explore the different types of ceramic heaters, such as band heaters, cartridge heaters, and immersion heaters, and their suitability for various settings—from industrial applications to residential use. We will also provide actionable tips for vetting suppliers, understanding cost structures, and assessing energy efficiency ratings. By equipping yourself with this knowledge, you can make informed purchasing decisions that optimize your heating solutions while minimizing operational costs.
Ultimately, this guide serves as your go-to resource for navigating the complexities of ceramic heater technology, empowering you to enhance your business operations and ensure a comfortable environment for your workforce, whether in manufacturing plants, offices, or remote locations.
Understanding how do ceramic heaters work Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Band Heaters | Clamps onto objects, combining radiant and conductive heating. | Industrial machinery, plastics processing | Pros: Effective for localized heating; versatile. Cons: Limited to specific applications; requires secure mounting. |
| Cartridge Heaters | Cylindrical design for precise internal heating. | Injection molding, metal processing | Pros: High precision; efficient for small spaces. Cons: Installation complexity; limited to specific applications. |
| Flexible Heaters | Made of bendable materials, adaptable to various surfaces. | Automotive, electronics, aerospace | Pros: Space-saving; customizable shapes. Cons: Potentially higher costs; durability concerns in harsh environments. |
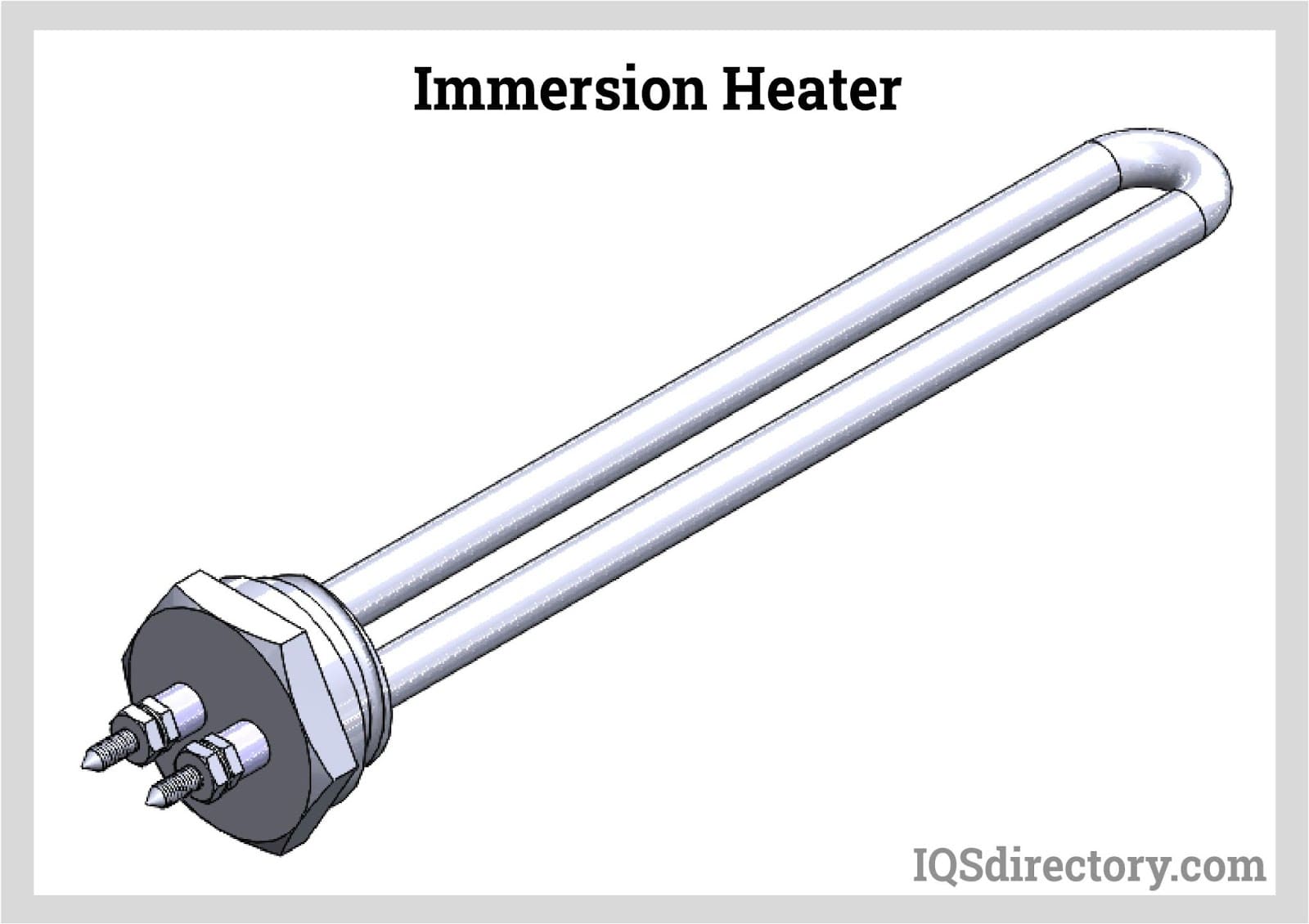
| Immersion Heaters | Directly inserted into liquids for rapid heating. | Chemical processing, food production | Pros: Fast and efficient; suitable for large volumes. Cons: Risk of corrosion; requires careful handling. |
| Radiant Heaters | Emit heat through infrared radiation for direct warmth. | Warehouses, large retail spaces | Pros: Energy-efficient; low maintenance. Cons: Limited effectiveness in open spaces; initial cost can be high. |
What Are the Characteristics of Band Heaters and Their B2B Suitability?
Band heaters are designed to provide external heat to cylindrical objects through a combination of radiant and conductive heating. Their clamping mechanism makes them particularly suitable for industrial applications, such as machinery and plastics processing, where localized heating is essential. B2B buyers should consider the heater’s mounting requirements and ensure compatibility with the machinery in use, as improper installation can lead to inefficiencies or safety hazards.
How Do Cartridge Heaters Offer Precision Heating in B2B Applications?
Cartridge heaters are cylindrical heating elements that fit into pre-drilled holes, providing targeted heat for various materials. They are commonly used in applications like injection molding and metal processing, where precise temperature control is crucial. Buyers should assess the heater’s watt density and material compatibility, as these factors influence performance and longevity in demanding industrial environments.
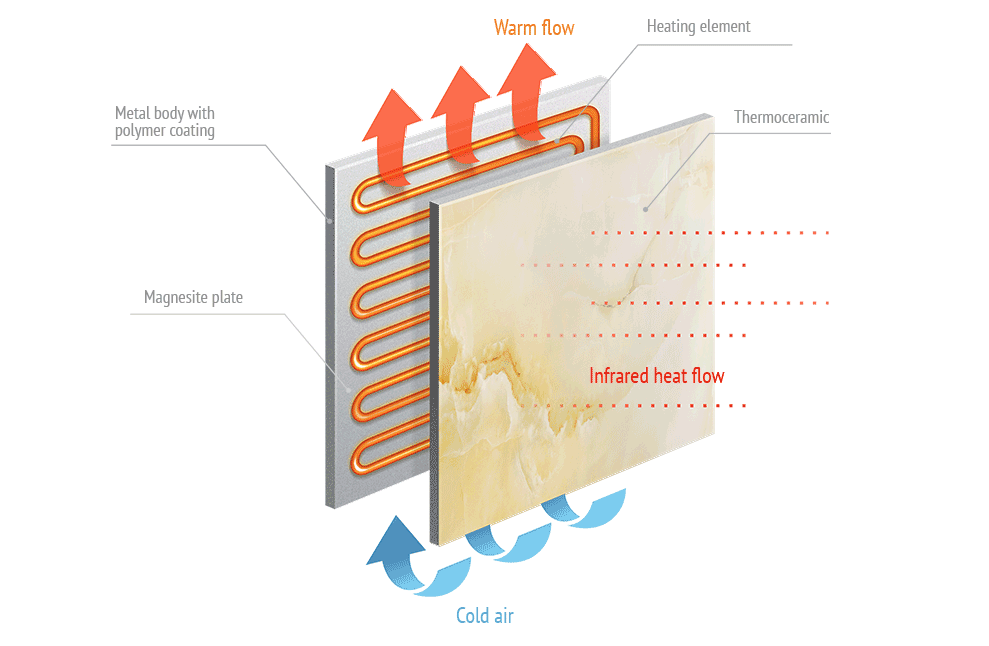
Illustrative image related to how do ceramic heaters work
What Makes Flexible Heaters Unique for Diverse B2B Uses?
Flexible heaters are notable for their ability to conform to various surfaces, making them ideal for applications in automotive, electronics, and aerospace industries. Their customizable shapes allow for efficient heating in tight spaces. However, buyers should consider the material durability and potential costs, as flexible heaters may require more investment compared to traditional heating solutions, particularly in harsh operational environments.
Why Choose Immersion Heaters for Rapid Liquid Heating Needs?
Immersion heaters are designed for direct heating of liquids, making them essential in industries like chemical processing and food production. Their rapid heating capabilities are advantageous for large volumes of liquid. When purchasing, B2B buyers must evaluate the materials used in the heater to prevent corrosion and ensure safety, as well as consider the installation requirements to avoid mishaps during operation.
How Do Radiant Heaters Provide Efficient Heating Solutions?
Radiant heaters utilize infrared radiation to warm objects and people directly, making them effective in large spaces like warehouses and retail environments. Their energy efficiency and low maintenance requirements appeal to businesses looking to reduce operational costs. However, buyers should be aware of their limitations in open areas and the initial investment required, which may affect budget considerations for large-scale installations.
Illustrative image related to how do ceramic heaters work
Key Industrial Applications of how do ceramic heaters work
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how do ceramic heaters work | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Process heating in injection molding and die-casting | Enhanced efficiency and reduced cycle times | Ensure compatibility with existing machinery and safety standards |
| Food & Beverage | Heating equipment for food processing and storage | Improved food safety and quality control | Look for energy-efficient models with easy maintenance |
| Automotive | Component heating in vehicle assembly and paint curing | Faster production times and improved finish quality | Consider size and portability for integration in production lines |
| Pharmaceuticals | Heating in laboratory equipment for chemical reactions | Precise temperature control for better outcomes | Evaluate reliability and compliance with industry regulations |
| Textile Industry | Heating elements for fabric drying and curing processes | Increased throughput and reduced energy consumption | Check for durability and performance in high-temperature settings |
How Are Ceramic Heaters Applied in Manufacturing Processes?
In the manufacturing sector, ceramic heaters are extensively used for process heating in injection molding and die-casting applications. These heaters provide rapid and uniform heating, which is critical for maintaining the quality of molded parts. By reducing cycle times, businesses can enhance production efficiency and lower operational costs. For international buyers, ensuring compatibility with existing machinery and adherence to safety standards is essential for seamless integration.
What Role Do Ceramic Heaters Play in the Food & Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage industry, ceramic heaters serve as essential components in heating equipment for food processing and storage. Their ability to provide consistent and controlled heating helps maintain food safety and quality, which is crucial in this sector. Businesses can benefit from energy-efficient models that reduce operational costs. Buyers should prioritize heaters that are easy to maintain and comply with health regulations to ensure safe food handling.
How Are Ceramic Heaters Utilized in the Automotive Sector?
Ceramic heaters are pivotal in the automotive industry for component heating during assembly and paint curing processes. They enable faster production times while ensuring an improved finish quality on vehicle surfaces. For B2B buyers, considering the size and portability of these heaters is vital for effective integration into existing production lines. Additionally, the safety features of ceramic heaters can mitigate risks associated with high-temperature operations.
Why Are Ceramic Heaters Important in Pharmaceuticals?
In pharmaceutical manufacturing, ceramic heaters are crucial for laboratory equipment that requires precise temperature control for chemical reactions. The ability to maintain specific temperature ranges enhances the reliability of experimental outcomes and product quality. Buyers in this sector should evaluate the reliability of heaters and their compliance with industry regulations to ensure consistent performance and safety in sensitive environments.
How Do Ceramic Heaters Benefit the Textile Industry?
In the textile industry, ceramic heaters are employed in fabric drying and curing processes, significantly increasing throughput while reducing energy consumption. Their efficient heating capabilities enable faster production cycles, which is vital in a competitive market. When sourcing, buyers should focus on the durability of heaters and their performance in high-temperature settings to ensure longevity and reliability in demanding operational conditions.
Illustrative image related to how do ceramic heaters work
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how do ceramic heaters work’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding Energy Efficiency in Ceramic Heaters
The Problem: B2B buyers, particularly those in industries such as manufacturing or construction, often face challenges in understanding the energy efficiency of different heating solutions. Many may be uncertain about how ceramic heaters compare to traditional heating methods in terms of energy consumption and cost-effectiveness. This lack of clarity can lead to misguided purchasing decisions that impact operational costs and sustainability goals.
The Solution: To address this concern, buyers should conduct thorough research on the energy efficiency ratings of ceramic heaters, which typically range between 85-90%. Engaging with suppliers who provide detailed product specifications can help clarify how these heaters convert electrical energy into heat through resistive heating. Additionally, utilizing tools such as energy calculators or software that simulates heating scenarios can aid in comparing the operational costs of ceramic heaters against other heating solutions. Buyers should also seek testimonials or case studies from other businesses that have successfully integrated ceramic heaters into their operations, providing real-world insights into their efficiency and savings.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Safety Features in Portable Ceramic Heaters
The Problem: In sectors where safety is paramount, such as hospitality or healthcare, B2B buyers must ensure that any heating solution they choose is equipped with adequate safety features. Concerns arise over the risks associated with portable ceramic heaters, such as overheating or fire hazards, particularly in environments where they might be moved frequently or used in less supervised areas.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize sourcing ceramic heaters that include built-in safety mechanisms, such as tilt detection technology and automatic shut-off features. When evaluating options, buyers can request detailed information about safety certifications and standards that the heaters comply with, ensuring that they meet industry-specific regulations. Additionally, conducting a risk assessment before implementation can help identify potential hazards in the intended use environment, allowing businesses to choose heaters that are both effective and safe. Regular training for staff on the safe use of portable heaters can further mitigate risks.
Illustrative image related to how do ceramic heaters work
Scenario 3: Navigating the Versatility of Ceramic Heaters for Different Applications
The Problem: Many businesses may struggle with determining the right type of ceramic heater for their specific application, whether it’s for a small workshop, a large warehouse, or a temporary heating solution for outdoor events. The diverse range of ceramic heater models can lead to confusion, causing buyers to hesitate in making a decision that meets their heating needs effectively.
The Solution: To navigate this challenge, B2B buyers should start by clearly defining their heating requirements, including the space dimensions, intended use, and any specific features needed (e.g., fan-assisted models for larger areas). Engaging with suppliers who offer customization options can also lead to tailored solutions that fit unique operational demands. Buyers can benefit from arranging product demonstrations or trials to evaluate the performance of various ceramic heaters in their actual environment. Furthermore, leveraging online resources such as comparison charts or expert reviews can provide deeper insights into the best ceramic heater models suited for different scenarios, enhancing the decision-making process.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how do ceramic heaters work
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Ceramic Heaters?
Ceramic heaters utilize a combination of materials that contribute to their efficiency, safety, and performance. Understanding these materials from a B2B perspective is crucial for international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Here, we analyze four common materials used in ceramic heaters: ceramic, metal, insulation materials, and electronic components.
How Does Ceramic Material Influence Heater Performance?
Ceramic is the primary material used for the heating elements in ceramic heaters. Its key properties include high thermal conductivity and excellent resistance to thermal shock. Ceramics can withstand high temperatures (typically up to 1,200°C) without degrading, making them suitable for a variety of heating applications.
Pros: Ceramics are durable and can operate at high temperatures without risk of melting or deformation. They are also generally resistant to corrosion and oxidation, which enhances their longevity.
Cons: The manufacturing process can be complex and costly, particularly for high-quality ceramics. Additionally, ceramics can be brittle, which may pose challenges in environments where mechanical shock or vibration is prevalent.
Impact on Application: The compatibility of ceramic materials with various heating media (like air or liquids) ensures they are versatile in application across different industries, from residential heating to industrial processes.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM or DIN is essential. Buyers in regions like Nigeria or Vietnam may also need to consider local manufacturing capabilities and the availability of high-quality ceramics.
What Role Does Metal Play in Ceramic Heaters?
Metals, particularly copper and aluminum, are often used in the construction of the heating coils that work alongside ceramic plates. These metals have excellent electrical conductivity, which is crucial for efficient heat generation.
Pros: Metals are generally more cost-effective and easier to manufacture than ceramics. They also provide good mechanical strength and can be easily shaped into various configurations.
Cons: Metals can corrode over time, especially in humid or corrosive environments, which may limit their lifespan compared to ceramics. They also have lower thermal resistance, which can affect efficiency.

Illustrative image related to how do ceramic heaters work
Impact on Application: The choice of metal can influence the heater’s performance, especially in environments with varying temperatures and humidity levels.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for metals that comply with local corrosion resistance standards, especially in regions with high humidity, such as parts of South America and the Middle East.
How Do Insulation Materials Affect Heater Safety and Efficiency?
Insulation materials, often made from fiberglass or other composites, are critical for ensuring safety and energy efficiency in ceramic heaters. They prevent heat loss and protect users from burns.
Pros: Good insulation materials can withstand high temperatures and provide excellent thermal resistance, enhancing the overall efficiency of the heater.
Cons: Some insulation materials may degrade over time, especially under prolonged exposure to high temperatures, which can lead to safety concerns.
Impact on Application: Proper insulation is essential for maintaining safe surface temperatures, particularly in residential applications where safety is a priority.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with safety standards is crucial, particularly in regions with stringent regulations. Buyers should ensure that insulation materials meet local fire safety codes.
What About Electronic Components in Ceramic Heaters?
Electronic components, including thermostats and control systems, are integral to the functionality of ceramic heaters. These components help regulate temperature and ensure safe operation.
Pros: Modern electronic components enhance the efficiency and usability of ceramic heaters, allowing for features like programmable timers and energy-saving modes.
Cons: The complexity of electronic components can lead to higher manufacturing costs and potential reliability issues if not sourced from reputable suppliers.
Impact on Application: Advanced electronic features can improve user experience and energy efficiency, making ceramic heaters more appealing in competitive markets.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should prioritize suppliers that adhere to international electronic standards to ensure compatibility and reliability.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Ceramic Heaters
| Material | Typical Use Case for how do ceramic heaters work | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ceramic | Heating elements in various heater types | High thermal conductivity | Brittle, complex manufacturing | Medium |
| Metal | Heating coils and electrical connections | Cost-effective, strong | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Insulation Materials | Safety and energy efficiency | Excellent thermal resistance | Potential degradation over time | Medium |
| Electronic Components | Temperature regulation and control | Enhances usability and efficiency | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials used in ceramic heaters, offering valuable insights for B2B buyers looking to make informed decisions in their purchasing processes.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how do ceramic heaters work
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Ceramic Heaters?
The manufacturing process of ceramic heaters involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets quality and efficiency standards. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to source reliable ceramic heating solutions.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Ceramic Heater Production?
The process begins with the selection and preparation of materials. The primary component is the ceramic itself, often made from a combination of aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, or other ceramic compounds known for their excellent thermal conductivity and resistance to thermal shock.
In addition to ceramics, conductive metals such as copper or nickel are used for the heating elements. These metals are prepared through processes like cutting, shaping, and cleaning to ensure they are free from impurities that could affect performance.
How Is the Forming Process Conducted for Ceramic Heaters?
Once the materials are ready, the forming process takes place. This typically involves shaping the ceramic into plates or other forms that will be used in the heating element. Common techniques include:
- Pressing: This technique involves placing ceramic powder into molds and applying pressure to form the desired shape.
- Casting: Liquid ceramic materials can be poured into molds to achieve intricate designs or specific dimensions.
- Sintering: The formed ceramics are then subjected to high temperatures in a kiln, which fuses the particles together, enhancing the material’s strength and thermal properties.
The forming process is crucial, as any defects at this stage can lead to inefficiencies or failures in the final product.
What Steps Are Involved in the Assembly of Ceramic Heaters?
The assembly stage combines the various components into a complete ceramic heater. This involves attaching the ceramic plates to the metal coils that conduct heat.

Illustrative image related to how do ceramic heaters work
During assembly, manufacturers often utilize:
- Welding or Soldering: This secures the metal components together.
- Insulation Application: Ensuring that electrical components are insulated to prevent short circuits and enhance safety.
- Integration of Safety Features: Many ceramic heaters include built-in safety mechanisms such as thermostats and tilt detection systems, which are integrated during this phase.
This stage is critical for ensuring that the heater operates efficiently and safely.
How Is the Finishing Process Executed for Ceramic Heaters?
After assembly, the ceramic heaters undergo a finishing process. This includes:
- Surface Treatment: This may involve glazing the ceramic for improved aesthetics and durability.
- Quality Checks: Initial inspections for physical defects, ensuring that the assembly is secure and that safety features are operational.
- Final Testing: Each unit is typically tested for performance, checking that it reaches the required temperature and operates within safety parameters.
What Are the Quality Assurance Processes for Ceramic Heaters?
Quality assurance is integral to the manufacturing of ceramic heaters, ensuring that the products meet international and industry-specific standards.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with several key international standards that govern the quality of ceramic heaters:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is essential for manufacturers aiming to deliver consistent quality.
- CE Certification: Particularly important in Europe, this certification indicates that the product meets health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Relevant for industries that require precise heating solutions, such as oil and gas.
Compliance with these standards not only ensures product quality but also facilitates smoother import and export processes, especially for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are established at various stages of the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Regular inspections during the manufacturing process help identify issues early, reducing waste and rework.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough examination of the finished product ensures it meets all specifications and performance requirements.
Establishing these checkpoints is vital for maintaining high-quality production standards and minimizing defects.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Ceramic Heaters?
To ensure that ceramic heaters meet performance and safety standards, manufacturers employ various testing methods, including:
- Thermal Testing: Assessing the heater’s ability to reach and maintain the desired temperature efficiently.
- Electrical Testing: Ensuring that the electrical components function correctly and safely.
- Safety Testing: Verifying that built-in safety features, such as overheat protection and tilt sensors, operate as intended.
These tests are critical in validating the heater’s reliability and safety before it reaches the market.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of their suppliers to ensure they receive reliable products.
What Are Effective Methods for Conducting Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is a key strategy for verifying quality control practices. Buyers should consider:
- On-Site Inspections: Visiting the manufacturing facility to assess processes, equipment, and adherence to quality standards.
- Reviewing Quality Documentation: Requesting quality assurance reports, inspection records, and certifications to understand the supplier’s compliance with international standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent quality inspectors to conduct assessments and provide unbiased reports on the supplier’s practices.
These methods help buyers build confidence in their supplier’s ability to deliver high-quality ceramic heaters.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must navigate additional complexities in quality control. Factors such as local regulations, import/export standards, and cultural differences in manufacturing practices can impact quality assurance.
- Understanding Local Regulations: Buyers should familiarize themselves with the regulatory landscape in the supplier’s country to ensure compliance with local standards.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Building strong relationships with suppliers through understanding and respect for their manufacturing culture can enhance communication and quality outcomes.
By being aware of these nuances, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and establish strong partnerships with reliable ceramic heater manufacturers.
Illustrative image related to how do ceramic heaters work
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how do ceramic heaters work’
The following guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in understanding and sourcing ceramic heaters effectively. This step-by-step checklist will help you navigate the procurement process, ensuring you choose the right product and supplier for your specific needs.
Step 1: Understand the Working Principle of Ceramic Heaters
Ceramic heaters operate on the principle of resistive heating, where an electric current passes through a ceramic plate, generating heat. This understanding is crucial as it informs you about the efficiency and effectiveness of the heater. Look for ceramic materials that offer high thermal conductivity and resistance, which enhance heating performance.
Step 2: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, clearly outline your technical requirements. Consider factors such as the desired heating capacity, size, and energy efficiency ratings. This clarity will guide you in selecting models that meet your operational needs and will aid in discussions with suppliers.
- Heating Capacity: Determine the BTU or wattage required for your space.
- Energy Efficiency: Aim for models with efficiency ratings between 85-90%.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet suppliers before making a commitment. Assess their reputation, product range, and customer feedback. Request case studies or testimonials from businesses similar to yours to gauge their experience and reliability.

Illustrative image related to how do ceramic heaters work
- Supplier Profiles: Review their history, expertise, and product offerings.
- References: Ask for references from other B2B clients to validate their claims.
Step 4: Verify Compliance with Safety Standards
Safety is paramount when sourcing heating equipment. Ensure that the ceramic heaters comply with international safety standards, such as CE, UL, or IEC certifications. This verification minimizes risks associated with electrical hazards and enhances product reliability.
- Safety Features: Look for built-in safety features such as tilt detection and overheat protection.
- Certification Documentation: Request copies of compliance certificates from suppliers.
Step 5: Assess Energy Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
Evaluate the energy efficiency of ceramic heaters against their operational costs. Given their ability to heat quickly and maintain warmth, these heaters can be more economical in the long run. Compare energy consumption rates and expected lifespan to ensure you are making a sound investment.
- Operational Costs: Estimate electricity costs based on usage patterns.
- Lifespan Analysis: Investigate the average lifespan of different models.
Step 6: Consider Portability and Versatility
If you require flexibility, assess the portability of ceramic heaters. Many models are lightweight and designed for easy relocation, which can be beneficial for businesses with varying heating needs across different locations.
- Design Features: Look for compact designs that are easy to move.
- Multi-Use Capability: Consider models that offer both heating and cooling functions for year-round use.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have identified potential suppliers and products, enter into negotiations regarding pricing, delivery timelines, and warranty terms. Clear agreements on these aspects can prevent future disputes and ensure a smooth procurement process.
Illustrative image related to how do ceramic heaters work
- Pricing Structures: Inquire about bulk purchasing discounts or financing options.
- Warranty Coverage: Understand the warranty terms to protect your investment.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can confidently procure ceramic heaters that meet their specific needs, ensuring both efficiency and safety in their operations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how do ceramic heaters work Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Ceramic Heaters?
Understanding the cost structure of ceramic heaters is essential for B2B buyers aiming to optimize their procurement strategies. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
Materials: The primary materials used in ceramic heaters are ceramic plates, metal coils, and various electronic components. The quality of these materials significantly impacts both the heater’s performance and its price. High-quality ceramics offer better thermal conductivity and durability but come at a premium.
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely based on the manufacturing location. Countries with lower labor costs, such as Vietnam or certain regions in Africa, may offer more competitive pricing. However, it’s crucial to consider the skill level of the workforce, as higher expertise can lead to superior product quality.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can lower these costs, which can be passed on to buyers.
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for ceramic heaters can be significant, especially for custom designs. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs and whether these are factored into the unit price or charged separately.
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that the heaters meet safety and performance standards. While this can add to the overall cost, it is essential for ensuring product reliability and customer satisfaction.
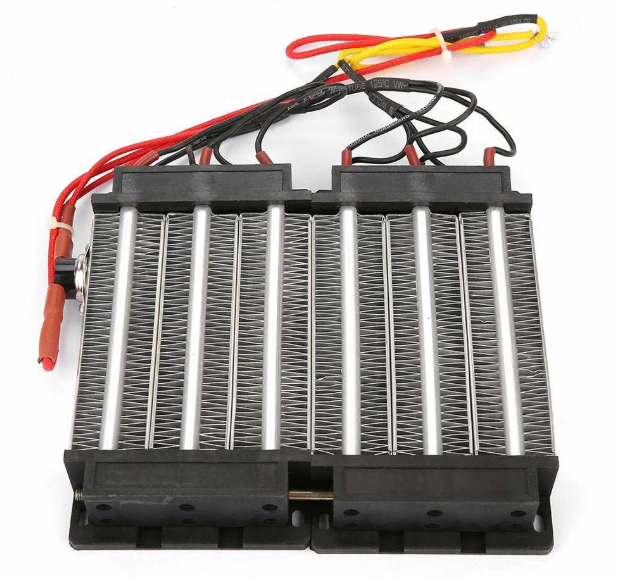

Illustrative image related to how do ceramic heaters work
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary depending on the supplier’s location and the buyer’s destination. International buyers must consider import duties and shipping fees when calculating total costs.
Margin: The profit margin applied by manufacturers can differ based on market competition, brand reputation, and perceived product value. Buyers should aim to negotiate favorable terms that align with their budget and quality expectations.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Ceramic Heater Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of ceramic heaters, particularly for international B2B buyers.
Volume/MOQ: Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ) can significantly impact pricing. Larger orders often come with discounts, so buyers should evaluate their needs carefully to maximize cost efficiency.
Specs/Customization: Customized ceramic heaters tailored to specific applications typically incur additional costs. Buyers should balance the need for customization against the potential for increased pricing.
Materials: The choice of materials not only affects performance but also pricing. Buyers should explore options that meet their specifications without compromising budget constraints.
Quality/Certifications: Heaters that meet international quality standards or have certifications (e.g., CE, UL) may come at a higher price. However, these certifications can enhance marketability and compliance with regulations, making them worth the investment.
Supplier Factors: Establishing relationships with reliable suppliers can influence pricing. Long-term partnerships may yield better pricing and terms compared to one-off transactions.
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial for international buyers. These terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, impacting overall costs.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Sourcing Ceramic Heaters?
B2B buyers should employ strategic approaches to ensure they secure the best deals on ceramic heaters.
Illustrative image related to how do ceramic heaters work
Negotiation: Always engage in negotiations. Suppliers often have flexibility in pricing, especially for bulk orders or long-term contracts. Building a rapport can also lead to better terms.
Cost-Efficiency: Focus on the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the upfront price. Consider factors like energy efficiency, maintenance costs, and lifespan, which can affect long-term expenses.
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East may face unique challenges such as fluctuating exchange rates and import tariffs. It’s advisable to conduct thorough market research and consult with local experts to navigate these complexities effectively.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices: Pricing for ceramic heaters can vary widely based on specifications, supplier, and market conditions. It is essential for buyers to obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing tailored to their specific requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how do ceramic heaters work With Other Solutions
Introduction: What Are the Alternatives to Ceramic Heaters?
When considering heating solutions, businesses must evaluate various options to determine which technology best meets their operational needs. Ceramic heaters are known for their energy efficiency, rapid heating capabilities, and safety features. However, there are several alternatives available, each with unique characteristics that may suit different applications. This analysis will compare ceramic heaters with immersion heaters and infrared heaters, providing insights into their performance, cost, implementation, and maintenance.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | How Do Ceramic Heaters Work | Immersion Heaters | Infrared Heaters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Efficient, quick heating with good thermal conductivity | Highly effective for heating liquids quickly | Direct heating, quick response time |
| Cost | Affordable to purchase and operate | Generally low initial cost, but can be energy-intensive | Moderate initial cost, energy-efficient |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple plug-and-play design; portable | Requires installation in tanks or containers | Easy to install; often requires mounting |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; occasional cleaning required | Requires regular maintenance to prevent scale build-up | Minimal maintenance; usually self-cleaning |
| Best Use Case | Small to medium spaces, portable heating | Industrial applications for liquid heating | Spot heating in large areas or outdoor settings |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Immersion Heaters: What Are Their Benefits and Drawbacks?
Immersion heaters are designed to heat liquids by directly submerging a heating element in the fluid. This method is effective for applications requiring rapid heat transfer, such as in industrial processes or large tanks. The advantages include a low initial cost and straightforward functionality. However, immersion heaters can be energy-intensive, especially if not adequately insulated, leading to higher operational costs over time. Regular maintenance is necessary to prevent mineral buildup, which can affect efficiency.
Infrared Heaters: How Do They Compare?
Infrared heaters work by emitting infrared radiation that heats objects directly in their path, rather than warming the air. This technology allows for quick heating and is particularly effective in large spaces or outdoor areas. The installation is relatively simple, and they are often energy-efficient, especially in applications where immediate heat is required. However, the initial investment can be moderate, and infrared heaters may not be suitable for heating entire rooms uniformly, as they are more effective for targeted heating.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Heating Solution for Your Business
Selecting the appropriate heating solution depends on various factors, including the specific application, energy efficiency, and budget constraints. Ceramic heaters offer a balanced combination of efficiency, safety, and portability, making them suitable for diverse environments. Immersion heaters excel in liquid heating applications but require careful maintenance, while infrared heaters are ideal for quick, localized heating. B2B buyers should assess their operational needs, space constraints, and cost considerations to determine which heating technology aligns best with their objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how do ceramic heaters work
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Ceramic Heaters?
1. Material Grade
Ceramic heaters primarily utilize high-grade ceramic materials that exhibit excellent thermal conductivity and resistive properties. The specific grade of ceramic impacts the heater’s efficiency and durability. For B2B buyers, selecting the right material grade ensures optimal performance and longevity in industrial applications, reducing maintenance costs and enhancing reliability.
2. Heating Element Efficiency
The efficiency of a ceramic heater is typically rated between 85-90%. This percentage indicates how effectively the heater converts electrical energy into heat. A higher efficiency rating signifies lower energy consumption and operational costs, making it an essential specification for businesses focused on sustainability and cost-effectiveness.
3. Temperature Control Range
This specification refers to the range of temperatures a ceramic heater can achieve and maintain. Understanding the temperature control range is critical for B2B buyers as it dictates the heater’s suitability for specific applications, whether for industrial processes or environmental comfort in commercial spaces.

Illustrative image related to how do ceramic heaters work
4. Size and Power Output
Ceramic heaters come in various sizes and power outputs, often measured in watts. The size and power output determine the heater’s capacity to warm a given area. For businesses, selecting the appropriate size and power ensures efficient heating without overspending on energy costs, making it an essential consideration in procurement.
5. Safety Features
Modern ceramic heaters are equipped with various safety features, such as tilt detection and overheat protection. These features are crucial for minimizing risks in commercial settings. B2B buyers should prioritize heaters with robust safety mechanisms to protect their workforce and equipment, reducing liability and potential downtime.
What Are the Common Trade Terms in the Ceramic Heater Industry?
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
In the context of ceramic heaters, an OEM refers to a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is vital for B2B buyers looking for custom solutions or specific branding, as it influences product quality and support.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For ceramic heaters, knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their purchasing strategies, manage inventory effectively, and negotiate better terms with suppliers, particularly in bulk buying scenarios.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent by a buyer to potential suppliers requesting pricing information for specific products or services. In the ceramic heater market, submitting an RFQ allows companies to compare costs and features across multiple suppliers, ensuring they receive competitive pricing and value.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized terms used in international trade that outline the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B buyers to navigate the complexities of international shipping and logistics effectively, ensuring smooth transactions.
5. Warranty and Support Terms
Warranty and support terms define the conditions under which a product is guaranteed against defects and the level of service provided by the manufacturer. B2B buyers should carefully review these terms for ceramic heaters to ensure they receive adequate support and protection for their investment, ultimately influencing the total cost of ownership.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing ceramic heaters, ensuring they choose solutions that align with their operational needs and budgetary constraints.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how do ceramic heaters work Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Influencing Ceramic Heaters?
The ceramic heater market is witnessing significant growth driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient heating solutions across various sectors. Key global drivers include a shift towards sustainable energy sources, rising energy costs, and a growing awareness of the environmental impact of traditional heating methods. In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, businesses are increasingly seeking alternatives that not only reduce operational costs but also minimize their carbon footprint.
Emerging trends in B2B sourcing for ceramic heaters include the integration of smart technology and automation. Modern ceramic heaters are being designed with features such as Wi-Fi connectivity, smart thermostats, and open window detection systems, enhancing their usability and efficiency. Additionally, the rise of flexible heating solutions, such as portable ceramic heaters for industrial applications, is reshaping market dynamics. B2B buyers are increasingly looking for products that offer high heat output in compact designs, catering to diverse applications from residential spaces to commercial settings.
Furthermore, global supply chains are adapting to local market needs, with manufacturers in emerging markets focusing on affordability without compromising on quality. For international buyers, especially in regions like Nigeria and Vietnam, sourcing ceramic heaters with robust performance at competitive prices is crucial. Establishing partnerships with local suppliers can enhance supply chain efficiency and reduce lead times, providing a strategic advantage in a competitive marketplace.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Sourcing of Ceramic Heaters?
Sustainability has become a critical consideration in the B2B landscape, significantly influencing the sourcing of ceramic heaters. With the global push towards reducing greenhouse gas emissions, ceramic heaters, known for their energy efficiency, are positioned as a favorable alternative to traditional heating methods. Their ability to heat up quickly and maintain temperature with minimal energy waste makes them an attractive option for businesses seeking to lower their operational costs while adhering to environmental regulations.
Moreover, ethical sourcing practices are gaining traction among international buyers. Companies are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate transparency in their production processes and adhere to sustainability standards. The use of ‘green’ certifications, such as Energy Star or ISO 14001, is becoming a prerequisite for procurement decisions. Buyers in markets like South America and Europe are particularly inclined to partner with manufacturers who implement eco-friendly materials and processes in their ceramic heater production.
The emphasis on sustainability extends beyond product efficiency to encompass the entire supply chain. Businesses are seeking suppliers who can provide information on the lifecycle of their products, ensuring that materials used in ceramic heaters are responsibly sourced. This shift not only helps companies comply with regulatory requirements but also enhances their brand reputation, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
What Is the Historical Context of Ceramic Heaters in B2B Markets?
The evolution of ceramic heaters dates back to the early 20th century when advancements in electrical engineering made electric heating a viable option. Initially, these heaters were primarily used in residential settings; however, their versatility and efficiency quickly led to broader industrial applications. The introduction of ceramic materials revolutionized heating technology, allowing for better heat retention and distribution.
Over the decades, the design and functionality of ceramic heaters have evolved significantly. The integration of safety features, such as tilt detection and overheat protection, has increased their appeal in both consumer and industrial markets. As energy efficiency became a priority in the late 20th century, ceramic heaters emerged as a sustainable alternative, paving the way for innovations that cater to modern heating demands.
Today, ceramic heaters are a staple in various industries, from manufacturing to hospitality, reflecting a rich history of adaptation and innovation. Understanding this evolution is vital for B2B buyers as they navigate the current landscape, ensuring they select products that not only meet their immediate needs but also align with future trends in energy efficiency and sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how do ceramic heaters work
-
How do ceramic heaters generate heat efficiently?
Ceramic heaters utilize a process known as resistive heating, where an electric current passes through a ceramic conductor. The ceramic material has high thermal resistance, which allows it to generate significant heat as the current struggles to pass through. This heat is then distributed into the surrounding air, providing quick and effective warmth. Their efficiency often ranges from 85-90%, making them a cost-effective heating solution for both residential and industrial applications. -
What are the advantages of using ceramic heaters in industrial applications?
Ceramic heaters offer several advantages for industrial use, including rapid heating, energy efficiency, and a compact design. They heat up quickly, which minimizes energy waste, and can maintain a high heat output relative to their size. Additionally, they feature safety mechanisms like overheat protection and tilt detection, making them suitable for various industrial environments, including workshops and manufacturing facilities. -
How do I choose the right ceramic heater for my business needs?
When selecting a ceramic heater, consider factors such as the size of the area you need to heat, energy efficiency ratings, and specific features like thermostats or timers. For larger spaces, models with fans are beneficial for air circulation. Additionally, assess the heater’s safety features, portability, and whether it meets your local regulatory requirements, especially if you’re sourcing from international suppliers. -
What should I look for when vetting suppliers of ceramic heaters?
To ensure you select a reliable supplier, research their reputation, customer reviews, and industry certifications. Confirm their production capabilities, lead times, and quality assurance processes. Request samples to evaluate the product quality firsthand and inquire about their compliance with international safety and environmental standards. Establish communication to gauge their responsiveness and willingness to address your specific needs. -
Can I customize ceramic heaters to meet specific requirements?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for ceramic heaters. This can include modifications in size, heating capacity, design features, and even branding. When discussing customization, clearly outline your specifications and requirements to ensure the supplier can meet your needs. It is also advisable to confirm any additional costs or changes in lead times associated with customized orders. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for ceramic heaters?
MOQs for ceramic heaters can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the specific model. Generally, MOQs may range from 50 to several hundred units. It’s essential to discuss your order needs upfront with potential suppliers to determine their capabilities and flexibility regarding MOQs. If you’re testing a new market or product line, ask if they offer lower MOQs for initial orders. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing ceramic heaters internationally?
Payment terms can vary by supplier but typically include options like upfront payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, and balance payment prior to shipping. It’s crucial to negotiate favorable terms that align with your cash flow and risk management strategies. Consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services, especially for larger transactions, to safeguard your investment. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when importing ceramic heaters?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed specifications and compliance documentation from your supplier. Consider conducting factory audits or arranging third-party inspections to verify product quality before shipment. Establish clear performance and safety standards in your purchase agreement and discuss the process for handling defects or returns. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can also facilitate better communication regarding quality concerns.
Top 3 How Do Ceramic Heaters Work Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. IQS Directory – Ceramic Heaters
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Ceramic heaters are electric heaters featuring a Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) ceramic element that produces heat through resistive heating. They are known for their substantial electrical resistance and thermal transfer capabilities, making them efficient in producing and conducting heat. Ceramic heaters can be made from pure ceramic or composite materials that include both metal and cer…
2. High-Rated Ceramic Space Heater – Efficient Heating Solution
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: High-rated ceramic space heater, purchased for around $30 on Amazon, designed to heat up to 200 square feet, used in a 290 square foot trailer. Features include half power mode to reduce strain on electrical outlets and prevent overheating, as well as tilt turn-off protection.
3. De’Longhi – Ceramic Fan Heater
Domain: delonghi.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: This company, De’Longhi – Ceramic Fan Heater, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how do ceramic heaters work
Ceramic heaters present a compelling solution for diverse heating needs across various industries. Their efficiency, rapid heating capabilities, and safety features make them an attractive option for businesses looking to optimize energy use while ensuring comfort. By leveraging resistive heating through ceramic plates, these devices not only heat quickly but also maintain energy efficiency, with performance ratings often between 85-90%. This is particularly advantageous for sectors operating in regions with variable climates, such as Africa and South America, where adaptable heating solutions can significantly enhance operational effectiveness.
Strategic sourcing of ceramic heaters can yield significant cost savings and operational benefits. As international B2B buyers, particularly from the Middle East and Europe, it’s crucial to partner with reputable suppliers who understand regional heating requirements and compliance standards. Investing in high-quality ceramic heaters will not only meet immediate heating demands but also align with sustainability goals, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Looking ahead, the demand for versatile and energy-efficient heating solutions is set to rise. Businesses should actively explore partnerships that prioritize innovation and sustainability. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your operations with ceramic heaters and stay ahead in the competitive landscape.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.