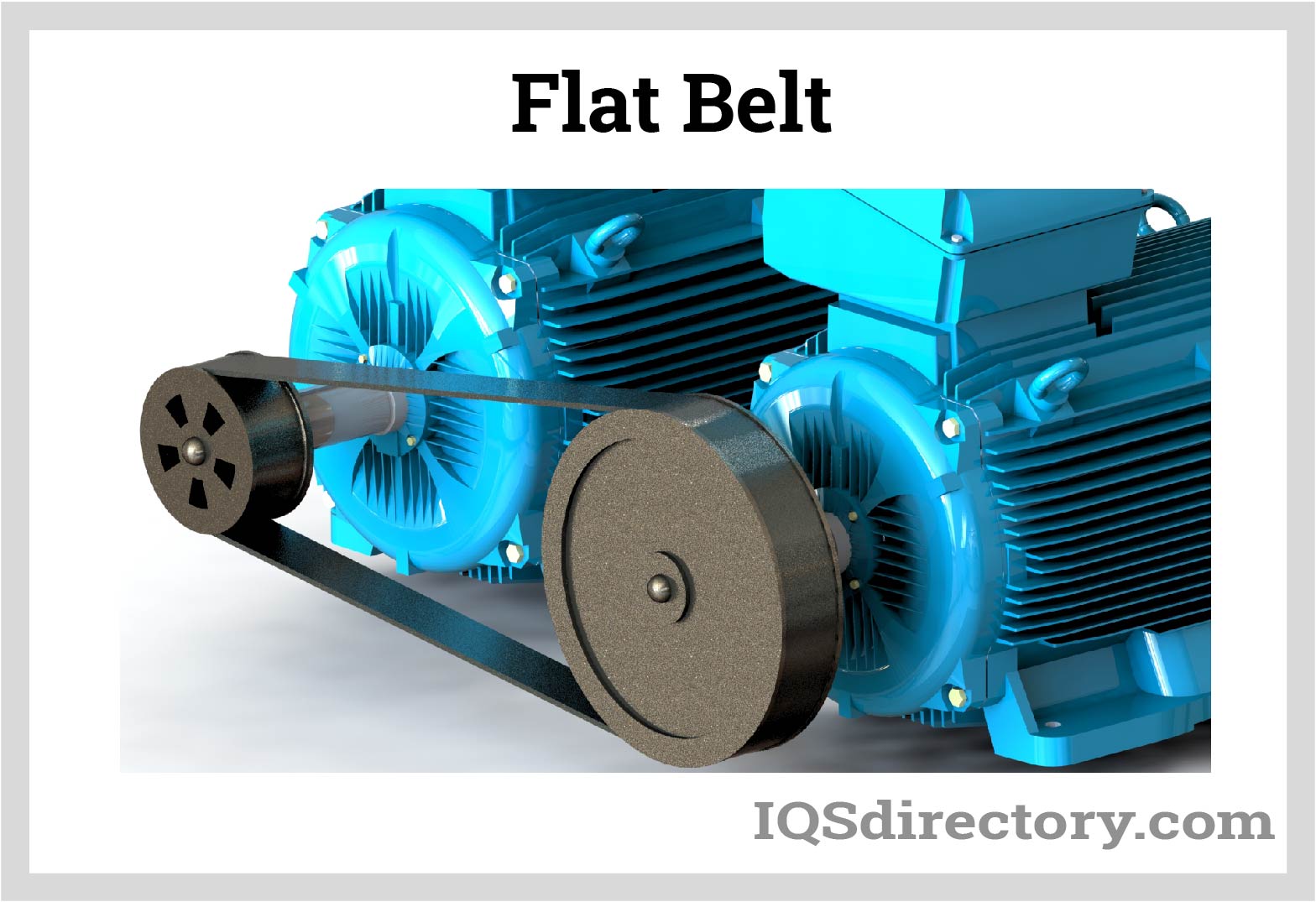
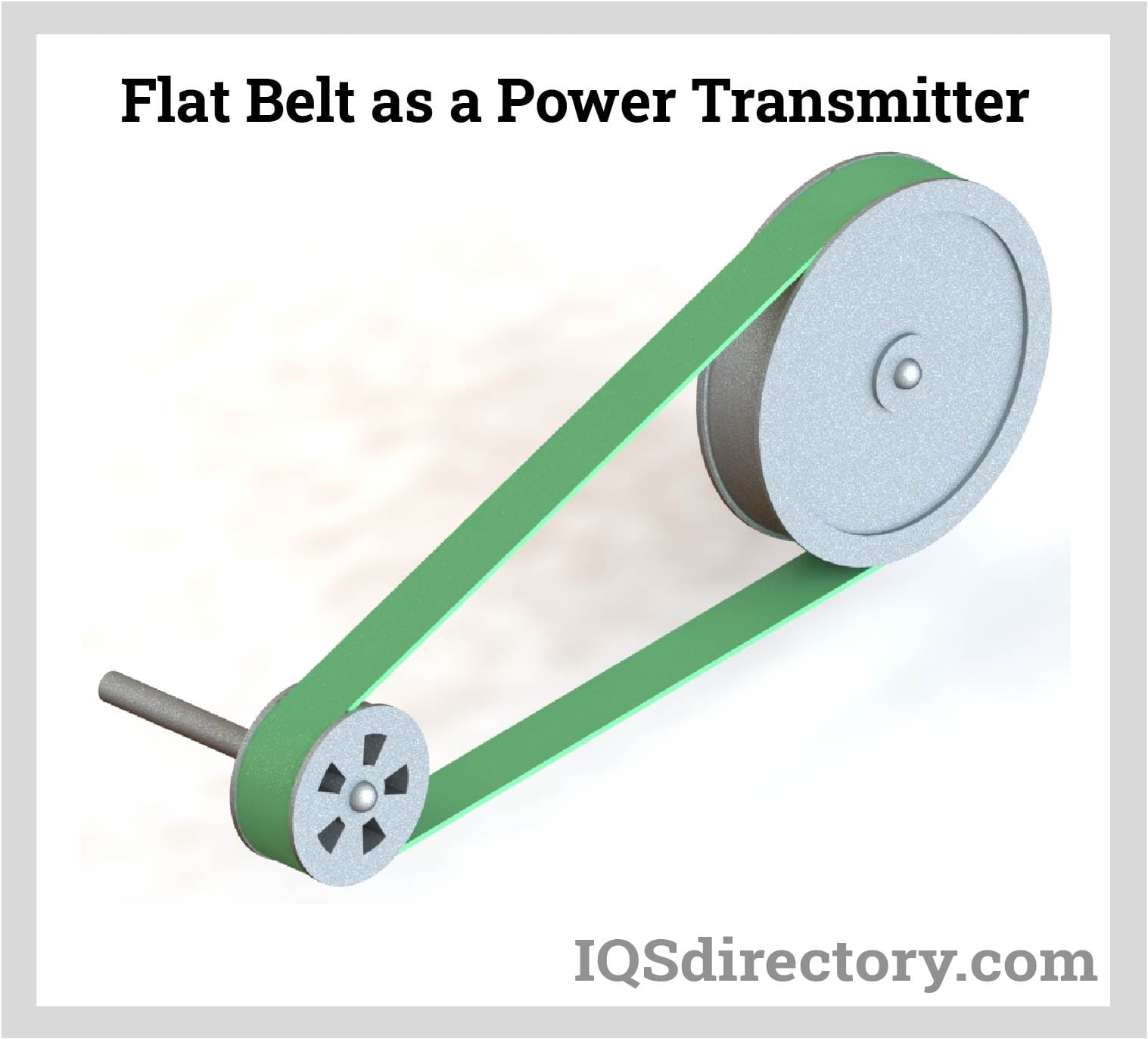
Choosing Your Flat Belts: Key Specs to Compare in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for flat belts
In the complex landscape of industrial operations, sourcing flat belts can pose significant challenges for businesses aiming to enhance their conveyance systems. Understanding the intricacies of flat belts—including their types, applications, and performance characteristics—is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This guide serves as an invaluable resource, equipping decision-makers with the insights needed to navigate the global market effectively.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we will delve into various types of flat belts, exploring their unique benefits and applications across diverse industries. Buyers will gain a clear understanding of how to vet suppliers, ensuring that they select partners who meet stringent quality and service standards. Additionally, we will address cost considerations, enabling businesses to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational budgets.
By providing a thorough analysis of the flat belt market, this guide empowers B2B buyers to optimize their sourcing strategies, reduce downtime, and enhance productivity. Whether you’re based in Nigeria or Vietnam, leveraging the information within will facilitate smarter investments in flat belt technology, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and competitive advantage in your industry.
Understanding flat belts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Flat Belts | Uniform thickness, smooth surface | Assembly lines, packaging machinery | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile. Cons: Limited grip on steep inclines. |
| Textured Flat Belts | Textured surface for enhanced grip | Material handling, conveyor systems | Pros: Improved traction, reduced slippage. Cons: Higher cost than standard belts. |
| Reinforced Flat Belts | Additional layers for increased strength | Heavy-duty applications, mining | Pros: Excellent durability, longer service life. Cons: Heavier, may require more power to operate. |
| Antistatic Flat Belts | Designed to dissipate static electricity | Electronics manufacturing, clean rooms | Pros: Reduces risk of static discharge. Cons: Can be more expensive. |
| Oil & Chemical Resistant | Special materials that withstand harsh substances | Food processing, chemical industries | Pros: Enhanced longevity in harsh environments. Cons: Limited flexibility compared to standard belts. |
What are Standard Flat Belts and Their Applications?
Standard flat belts are characterized by their uniform thickness and smooth surface, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. These belts are commonly used in assembly lines and packaging machinery where consistent performance is required. When purchasing standard flat belts, businesses should consider factors such as the belt’s length, width, and material compatibility with their machinery to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
How Do Textured Flat Belts Enhance Performance?
Textured flat belts feature a specially designed surface that provides enhanced grip, making them ideal for material handling and conveyor systems. The textured design reduces slippage, especially on inclined surfaces, which is crucial for maintaining productivity in operations. Buyers should evaluate the level of grip required for their specific applications and consider the cost versus the performance benefits when choosing textured flat belts.
What Makes Reinforced Flat Belts Suitable for Heavy-Duty Use?
Reinforced flat belts are constructed with additional layers, offering increased strength and durability. These belts excel in heavy-duty applications, such as mining and heavy machinery operations, where they face significant wear and tear. When selecting reinforced flat belts, businesses must assess the load requirements and the operating environment, as these belts can be heavier and may require more power for operation.
Why Choose Antistatic Flat Belts for Sensitive Environments?
Antistatic flat belts are specifically designed to dissipate static electricity, making them essential for industries like electronics manufacturing and clean rooms. The ability to minimize static discharge is critical in preventing damage to sensitive components. Buyers should consider the specific antistatic properties required for their applications, as well as the potential higher costs associated with these specialized belts.
How Do Oil & Chemical Resistant Flat Belts Benefit Industries?
Oil and chemical-resistant flat belts are made from materials that can withstand exposure to harsh substances, making them suitable for food processing and chemical industries. These belts enhance longevity in challenging environments, reducing the frequency of replacements. When purchasing, businesses should ensure that the chosen belt meets the specific resistance requirements for the substances they handle, balancing durability with flexibility needs.
Key Industrial Applications of flat belts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Flat Belts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Assembly Line Conveyance | Enhanced efficiency and reduced downtime | Durability, compatibility with existing systems |
| Food Processing | Conveyor Systems for Food Transport | Improved hygiene and reduced contamination risk | FDA compliance, material safety, temperature tolerance |
| Textile Industry | Fabric Handling and Transport | Smooth operation and minimized fabric damage | Material flexibility, length and width specifications |
| Mining and Quarrying | Material Transport Systems | High durability and resistance to harsh conditions | Weather resistance, tensile strength, custom sizes |
| Packaging | Automated Packaging Lines | Increased productivity and operational efficiency | Customization for specific packaging types, reliability |
How are Flat Belts Used in Manufacturing Assembly Lines?
In the manufacturing sector, flat belts are integral to assembly line conveyance systems. They facilitate the smooth transportation of components between different production stages, enhancing overall efficiency. Flat belts reduce downtime due to their robust construction and minimal maintenance needs. Buyers should consider the compatibility of flat belts with existing machinery, ensuring that the dimensions and materials meet specific operational requirements, particularly in regions where equipment may vary significantly.
What Role Do Flat Belts Play in Food Processing?
In food processing, flat belts are utilized in conveyor systems that transport food items safely and efficiently. Their smooth surfaces minimize the risk of contamination, while textured surfaces provide a secure grip for various food products. Compliance with food safety regulations is crucial, so buyers must ensure that the materials used are FDA-approved and capable of withstanding the specific temperature ranges typical in food processing environments, particularly in regions with varying climate conditions.
How are Flat Belts Beneficial for the Textile Industry?
The textile industry employs flat belts for the handling and transport of fabrics throughout the production process. Their ability to provide a gentle yet secure grip helps prevent fabric damage and misalignment during movement. When sourcing flat belts for textile applications, businesses should focus on the flexibility and length of the belts to accommodate different fabric types and machinery configurations, ensuring optimal performance.
Why are Flat Belts Essential in Mining and Quarrying?
In the mining and quarrying industries, flat belts are crucial for transporting heavy materials across challenging terrains. Their durability and resistance to wear and tear make them ideal for harsh environments where reliability is paramount. Buyers in this sector need to prioritize sourcing belts that offer high tensile strength and weather resistance to withstand extreme conditions and maintain operational continuity.
How Do Flat Belts Enhance Packaging Operations?
Flat belts are commonly used in automated packaging lines, where they facilitate the swift movement of products through various packaging stages. Their ability to maintain speed and efficiency directly contributes to increased productivity. When sourcing flat belts for packaging, businesses should consider customization options to align with specific packaging types and ensure long-term reliability in high-throughput environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘flat belts’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Sourcing the Right Flat Belt Size
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle with sourcing flat belts that fit specific machinery requirements. Often, buyers either overestimate or underestimate the dimensions needed, leading to inefficiencies or operational downtime. For instance, a manufacturing facility in Nigeria may have older equipment that requires a unique flat belt size no longer in production. This can result in significant delays as they search for compatible replacements, ultimately impacting production schedules and costing the business time and money.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should implement a systematic approach to measuring and documenting the specifications of their existing flat belts. This includes not just length and width, but also the thickness and material type. A reliable supplier can offer custom solutions or maintain a catalog of hard-to-find sizes. Buyers are encouraged to establish relationships with multiple suppliers who specialize in flat belts to ensure they have access to a wider range of products. Additionally, using digital tools or software for inventory management can help track belt specifications more efficiently, reducing the likelihood of errors in ordering.
Scenario 2: Short Lifespan of Flat Belts in Harsh Environments
The Problem: In industrial settings, especially in regions like South America and the Middle East, flat belts are often exposed to extreme temperatures, dust, and chemicals. These harsh conditions can lead to accelerated wear and tear, resulting in frequent replacements and increased operational costs. A textile factory in Vietnam, for example, may find that their flat belts degrade rapidly due to moisture and heat, causing unexpected production halts.
The Solution: To address this challenge, buyers should prioritize sourcing flat belts designed for durability in extreme conditions. This involves selecting materials that are resistant to the specific environmental factors present in their operations. For instance, belts made from polyurethane or specially treated rubber can withstand higher temperatures and exposure to chemicals. Additionally, establishing a routine maintenance schedule can help identify wear early, allowing for timely replacements before a breakdown occurs. Suppliers should provide guidance on the best products for specific applications, and companies can benefit from training their staff on the correct installation and care procedures to prolong the lifespan of flat belts.

Illustrative image related to flat belts
Scenario 3: Inefficient Power Transmission Leading to Increased Energy Costs
The Problem: Inefficient power transmission is a common pain point for B2B buyers using flat belts. If a flat belt is not properly aligned or if it is too worn, it can lead to slippage and increased energy consumption. This is particularly problematic in manufacturing facilities in Europe, where energy costs are a significant part of operational expenses. A factory relying on outdated flat belts may notice spikes in their energy bills, which can eat into profit margins.
The Solution: Buyers should invest in regular assessments of their flat belt systems to ensure proper alignment and tension. Utilizing advanced monitoring systems can help identify issues such as slippage before they escalate. When sourcing flat belts, buyers should consider options that are engineered for optimal power transmission, such as those with specialized surface textures that enhance grip. Additionally, conducting a full system audit to understand the energy dynamics of their conveyor systems can reveal potential inefficiencies. Training operators on best practices for installation and maintenance can further ensure that flat belts function at peak efficiency, helping to lower energy costs over time.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for flat belts
When selecting materials for flat belts in various industrial applications, it is crucial to understand the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material. This knowledge helps B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in flat belt manufacturing.
What Are the Key Properties of Polyurethane Flat Belts?
Polyurethane is a popular choice for flat belts due to its excellent wear resistance and flexibility. It can operate effectively in a temperature range of -30°C to 80°C, making it suitable for various environments. Polyurethane also exhibits good chemical resistance, particularly against oils and greases, which is essential in industrial settings.

Illustrative image related to flat belts
Pros and Cons: The primary advantage of polyurethane flat belts is their durability, which translates to a longer service life and reduced maintenance costs. However, they can be more expensive than other materials, which may be a consideration for budget-sensitive projects. Additionally, while they offer good flexibility, they may not perform well under extreme temperatures exceeding their rated limits.
Impact on Application: Polyurethane belts are ideal for applications involving light to medium loads, particularly in food processing, packaging, and material handling. Their resistance to oils makes them suitable for environments where lubrication is prevalent.
How Does Rubber Compare as a Material for Flat Belts?
Rubber is another widely used material for flat belts, known for its excellent grip and elasticity. It can handle a temperature range of -20°C to 70°C and is highly resistant to abrasion and wear, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Pros and Cons: The main advantage of rubber flat belts is their high tensile strength and flexibility, allowing them to handle heavy loads effectively. However, they can be prone to degradation from UV exposure and certain chemicals, which may limit their lifespan in specific environments. Additionally, rubber belts can be less cost-effective than other materials, particularly in regions where raw rubber prices fluctuate.
Impact on Application: Rubber belts are commonly used in mining, agriculture, and heavy machinery applications, where durability and load-bearing capacity are critical. Their excellent grip makes them suitable for inclined or vertical applications.
What Are the Benefits of Polyester Flat Belts?
Polyester is known for its high tensile strength and dimensional stability, making it a reliable choice for flat belts. It operates effectively within a temperature range of -40°C to 120°C and offers good resistance to moisture and chemicals.

Illustrative image related to flat belts
Pros and Cons: Polyester belts are lightweight and easy to handle, which simplifies installation and maintenance. However, they can be more expensive than rubber and polyurethane options. Their performance may also be affected by exposure to UV light, which can lead to deterioration over time.
Impact on Application: Polyester flat belts are suitable for applications in textile manufacturing, packaging, and assembly lines, where precision and reliability are paramount.
How Does Nylon Perform as a Material for Flat Belts?
Nylon flat belts are known for their excellent abrasion resistance and flexibility. They can operate in a temperature range of -40°C to 100°C and are resistant to many chemicals, making them versatile for various applications.
Pros and Cons: The key advantage of nylon belts is their ability to withstand high impacts and loads, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, they can absorb moisture, which may affect their performance in humid environments. Additionally, nylon belts can be more expensive than other materials, impacting budget considerations.
Illustrative image related to flat belts
Impact on Application: Nylon flat belts are often used in conveyor systems, packaging, and material handling applications, where durability and flexibility are essential.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Flat Belts
| Material | Typical Use Case for flat belts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane | Food processing, packaging, material handling | Excellent wear resistance and flexibility | Higher cost, limited extreme temperature tolerance | Medium |
| Rubber | Mining, agriculture, heavy machinery | High tensile strength and grip | Prone to UV degradation, higher cost | Medium |
| Polyester | Textile manufacturing, assembly lines | High tensile strength and dimensional stability | More expensive, UV exposure sensitivity | High |
| Nylon | Conveyor systems, packaging, material handling | Excellent abrasion resistance and flexibility | Moisture absorption, higher cost | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for B2B buyers, enabling them to choose the most suitable flat belt material based on their specific application requirements and operational environments.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for flat belts
What Are the Main Stages of Flat Belt Manufacturing?
The manufacturing of flat belts involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets industry standards and customer specifications. Here’s a breakdown of the primary manufacturing processes:
Material Preparation
The first stage of manufacturing flat belts involves selecting the appropriate raw materials. Common materials include rubber, polyurethane, and various synthetic compounds, chosen for their durability, flexibility, and resistance to wear. During this stage, materials are thoroughly inspected for quality to ensure they meet predefined specifications. This may involve checking for consistency in thickness, elasticity, and other physical properties.
Forming Techniques: How Are Flat Belts Shaped?
Once the materials are prepared, they undergo forming processes. These techniques typically include extrusion and calendering.
-
Extrusion: This method involves forcing the raw material through a die to create a continuous flat belt of the desired width and thickness. The extrusion process allows for uniform thickness and the integration of various additives for enhanced performance.
-
Calendering: In this process, the raw material is passed through a series of rollers to achieve the desired thickness and finish. Calendering is particularly effective for creating belts with specific surface textures, which can enhance grip and reduce slippage during operation.
Assembly: How Are Flat Belts Constructed?
After forming, the belts are assembled. This may involve cutting the extruded or calendered material to specific lengths and joining the ends to create a loop. Common joining techniques include:
- Mechanical Joining: Utilizing clips or fasteners to secure the ends of the belt.
- Adhesive Joining: Using industrial adhesives to bond the ends, ensuring a seamless connection that can withstand high tension and stress.
Each assembly method has its advantages, and the choice often depends on the application and operational requirements of the flat belt.
Finishing Processes: What Steps Ensure Quality?
The final stage of manufacturing flat belts involves finishing processes that enhance their performance and longevity. This includes applying surface treatments to improve grip and resistance to environmental factors such as heat and chemicals. Additionally, belts may undergo a curing process, especially those made from rubber, which helps enhance their durability.

Illustrative image related to flat belts
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Flat Belts?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the manufacturing of flat belts to ensure that they perform reliably under various industrial conditions. Here are some key aspects of QA for flat belts:
What International Standards Apply to Flat Belt Manufacturing?
To ensure quality and reliability, many manufacturers adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a company consistently meets customer and regulatory requirements, which is crucial for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers.
Other relevant certifications may include:
- CE Marking: This indicates compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Particularly for belts used in oil and gas applications, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards ensures safety and performance.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are vital throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that each flat belt meets quality standards. Key checkpoints include:

Illustrative image related to flat belts
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials before they enter production. Ensuring that materials meet specified standards helps prevent defects later in the process.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing inspections are conducted to monitor the production process. This may involve testing the consistency of the material, checking dimensions, and verifying the performance of machinery.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the belts are assembled, a final inspection is conducted. This includes testing for flexibility, durability, and resistance to wear. Common testing methods include tensile strength tests, abrasion resistance tests, and fatigue tests.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is essential. Here are actionable steps buyers can take:
What Audits and Reports Should Buyers Request?
Buyers should request detailed quality assurance reports from potential suppliers, including:
-
Audit Reports: Regular internal and external audits should be conducted to assess compliance with quality standards. Buyers can request copies of these reports to understand the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Certificates of Compliance: Suppliers should provide certifications that verify adherence to relevant international and industry-specific standards.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Confidence?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes. These inspections can be scheduled at various stages of production, offering buyers peace of mind that their orders meet the required specifications before shipment.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International Buyers?
International B2B buyers face unique challenges regarding quality control, particularly concerning logistics, cultural differences, and varying standards. Here are some nuances to consider:
-
Understanding Local Regulations: Buyers must familiarize themselves with the regulatory landscape of both their own country and that of the supplier. Compliance with local safety and quality regulations is crucial for successful importation.
-
Language Barriers: Communication can sometimes be challenging due to language differences. Ensuring that quality control documentation is available in a language that all parties understand can help mitigate misunderstandings.
-
Cultural Differences: Attitudes towards quality and business practices can vary significantly between regions. Establishing clear expectations and maintaining open lines of communication can foster better relationships with suppliers.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols associated with flat belts, B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘flat belts’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in procuring flat belts effectively. Given their critical role in various industrial applications, a structured approach to sourcing ensures that you select the right product and supplier to meet your operational needs. This checklist will help you navigate the complexities of purchasing flat belts, ensuring quality, compatibility, and cost-effectiveness.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for your flat belts before beginning your search. Consider factors such as width, length, material type, and the specific application environment.
– Material Considerations: Determine if you need belts made from rubber, polyurethane, or other materials based on durability and flexibility.
– Performance Metrics: Identify the load capacity, temperature resistance, and any specific surface texture requirements for optimal performance.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers with a strong reputation in the flat belt market. Look for manufacturers and distributors that specialize in your required specifications.
– Supplier Credentials: Check for certifications and industry standards compliance, such as ISO or ANSI, which indicate reliability and quality.
– Market Presence: Consider suppliers with a proven track record and customer testimonials, particularly those serving similar industries or regions.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Offerings
Review the product range and options offered by potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your specific needs. A diverse portfolio often indicates a supplier’s capability to address various applications.
– Customization Options: Inquire about the ability to customize belts for unique applications, which can enhance performance and longevity.
– Product Samples: Request samples to assess quality and compatibility with your existing systems before making a bulk purchase.

Illustrative image related to flat belts
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Before finalizing your decision, ensure that your selected supplier holds the necessary certifications that reflect their commitment to quality and safety.
– Quality Assurance: Look for certifications that align with international standards to ensure the flat belts meet stringent quality requirements.
– Sustainability Practices: Consider suppliers that adhere to environmentally friendly practices, which can enhance your company’s sustainability profile.
Step 5: Assess Pricing and Payment Terms
Evaluate the pricing structures of your shortlisted suppliers and understand their payment terms. This step is crucial to ensure that you are making a financially sound decision.
– Total Cost of Ownership: Consider not just the initial purchase price but also potential maintenance costs and lifespan of the belts.
– Flexible Payment Options: Look for suppliers that offer flexible payment terms, such as installment plans or discounts for bulk orders, which can improve cash flow management.
Step 6: Establish Communication Channels
Set up clear communication channels with your chosen supplier to facilitate a smooth procurement process. Effective communication helps prevent misunderstandings and delays.
– Point of Contact: Ensure you have a dedicated contact person who understands your requirements and can address any issues promptly.
– Feedback Mechanism: Establish a feedback mechanism for post-purchase support, enabling you to report issues or request assistance as needed.
Step 7: Plan for Delivery and Installation
Finally, coordinate the delivery and installation process to minimize operational downtime. Understanding logistics is key to ensuring that your flat belts are integrated smoothly into your systems.
– Delivery Timelines: Discuss lead times and shipping methods to ensure timely arrival.
– Installation Support: Inquire if the supplier offers installation support or guidance, which can help streamline the setup process and reduce potential errors.
By following this comprehensive checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the sourcing process for flat belts, ensuring they make informed decisions that support their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for flat belts Sourcing
When sourcing flat belts, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing elements is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This guide will break down the various cost components involved in flat belt sourcing, the influencers on pricing, and provide actionable tips for buyers.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Flat Belts Sourcing?
-
Materials: The primary cost component for flat belts is the raw materials used in their production, which typically include rubber, PVC, polyurethane, and various fabrics. The choice of material directly impacts durability, flexibility, and performance, which can influence the overall pricing.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages paid to workers involved in the manufacturing process. This can vary significantly based on geographic location, local labor laws, and the complexity of the production process.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these costs, thereby lowering the final price of the belts.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are associated with the machinery and molds used to produce flat belts. Custom tooling for specialized designs can increase upfront costs, but may yield long-term savings through increased production efficiency.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that flat belts meet industry standards necessitates investment in quality control processes. This includes testing materials and finished products, which can add to the overall cost but is essential for maintaining reliability and safety.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely depending on the origin of the flat belts and the destination. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and import/export duties should be considered when evaluating logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin on top of their production costs. This margin can vary based on market competition, brand reputation, and the uniqueness of the product.
What Influences Pricing for Flat Belts?
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Pricing often decreases with higher order volumes. Suppliers may offer better rates for bulk purchases, making it essential for buyers to consider their inventory needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications such as size, width, and material can significantly affect pricing. Standard sizes may be more economical, while customized belts will likely incur additional charges.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (such as ISO or FDA compliance) can increase costs but may offer better performance and longevity, which are crucial for minimizing downtime.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and service level can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their proven track record, while newer entrants may offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping (Incoterms) can affect the total cost. Buyers should understand whether costs include freight, insurance, and duties, as these can add significantly to the final price.
How Can Buyers Negotiate for Better Pricing on Flat Belts?
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: Consider consolidating orders to meet minimum quantities for discounts. Negotiating for tiered pricing based on order size can yield significant savings.
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the upfront cost but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, downtime, and replacement. A higher initial investment in quality belts can result in lower TCO.
-
Research Market Rates: Being informed about the average market rates for flat belts can provide leverage in negotiations. Buyers should compare quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
-
Assess Supplier Relationships: Building long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service. Regular communication and loyalty can result in favorable terms over time.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: For international buyers, sourcing from local suppliers can reduce logistics costs and lead times, potentially offsetting higher material costs.
Disclaimer on Pricing
It is important to note that the prices for flat belts can fluctuate based on market conditions, currency exchange rates, and supplier pricing strategies. Buyers should seek updated quotes to ensure they are working with current pricing data.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing flat belts With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Flat Belts in Conveyance Systems
In the realm of industrial conveyance systems, flat belts are a popular choice due to their efficiency and versatility. However, businesses often seek alternative solutions that can meet specific operational needs, whether through different technologies or methods. This analysis explores flat belts alongside two viable alternatives: roller conveyors and modular belts, allowing B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their unique requirements.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Flat Belts | Roller Conveyors | Modular Belts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency in power transmission | Excellent for heavy loads | Versatile, can handle various products |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment | Higher upfront costs | Variable costs based on configuration |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple installation | Requires more space and setup | Moderate complexity, but customizable |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, long service life | Moderate maintenance needs | Higher maintenance depending on design |
| Best Use Case | Light to medium loads, assembly lines | Heavy-duty applications, warehousing | Diverse applications, including food processing |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
1. Roller Conveyors
Roller conveyors utilize a series of rollers to transport goods, making them an excellent choice for heavy loads. They excel in high-capacity environments, such as warehouses and distribution centers, where items need to be moved efficiently over long distances. However, roller conveyors typically have a higher initial investment and require more space for installation. Maintenance can also be moderate, as the rollers may require periodic lubrication and replacement.

Illustrative image related to flat belts
2. Modular Belts
Modular belts consist of interlocking plastic or metal pieces, allowing for flexibility in design and application. They are particularly advantageous in industries such as food processing, where hygiene and easy cleaning are paramount. Modular belts can handle various product sizes and weights, but they tend to have a higher maintenance requirement due to the complexity of their design. Their costs can vary significantly based on configuration, making them a potentially more expensive option for some operations.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the right conveyance solution, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including performance needs, budget constraints, and the specific application environment. Flat belts offer a balanced solution for light to medium loads with low maintenance requirements, while roller conveyors are ideal for heavier items but come with higher costs. On the other hand, modular belts provide flexibility and hygiene but may require more upkeep. Understanding these dynamics will empower buyers to make strategic decisions that align with their operational goals and enhance productivity in their respective industries.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for flat belts
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Flat Belts That B2B Buyers Should Know?
When sourcing flat belts for industrial applications, understanding the technical properties is essential for ensuring compatibility and performance. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Flat belts are typically made from materials such as rubber, polyurethane, or leather. The choice of material affects durability, flexibility, and resistance to wear. For instance, rubber belts are known for their excellent grip and flexibility, making them ideal for high-tension applications. Understanding the material grade helps B2B buyers select the right belt for specific operational needs.
2. Width and Length Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in dimensions. Flat belts come in various widths (e.g., 50mm, 70mm, 100mm) and lengths (e.g., 900mm, 1200mm). A precise tolerance ensures that the belt fits properly on pulleys, enhancing performance and reducing the risk of slippage or wear. Buyers must consider these specifications to avoid operational disruptions.
3. Temperature Resistance
Flat belts must operate under varying environmental conditions, including temperature extremes. Different materials have specific temperature ranges where they perform optimally. For instance, polyurethane belts can withstand higher temperatures than rubber belts. Assessing temperature resistance is crucial for applications in industries like food processing or metalworking, where heat can affect performance.
4. Load Capacity
Load capacity indicates the maximum weight that a flat belt can handle without failing. This specification is vital for B2B buyers who need to ensure that their chosen belt can support the operational demands of their machinery. Selecting a belt with an appropriate load capacity prevents premature wear and potential breakdowns, leading to reduced maintenance costs.
5. Surface Texture
The surface texture of a flat belt can significantly influence its grip and friction properties. Textured surfaces offer better traction, which is essential for applications that involve incline or decline movement. Understanding the surface characteristics helps buyers choose belts that enhance operational efficiency and safety.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Flat Belt Industry?
Familiarizing yourself with industry terminology can facilitate smoother communication and transactions. Here are some essential terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of flat belts, OEMs provide high-quality components that meet specific requirements, ensuring compatibility with existing machinery. B2B buyers should prioritize OEM products to guarantee reliability and performance.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ denotes the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers, especially when sourcing flat belts, as it impacts inventory management and cost. Suppliers may have different MOQs based on the product type or material, so negotiating terms that align with your operational needs is essential.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to solicit price proposals from suppliers. When purchasing flat belts, submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare prices, terms, and specifications from multiple vendors. This process helps ensure that buyers receive competitive offers and can make informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is vital for B2B buyers, as they clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. For flat belt procurement, knowing the applicable Incoterms can help avoid misunderstandings and unexpected costs.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement processes, ensuring they select the right flat belts for their operational requirements.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the flat belts Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Flat Belts Sector?
The flat belts market is experiencing significant growth driven by increasing industrial automation and the demand for efficient material handling solutions. Globally, industries such as automotive, food processing, and packaging are increasingly adopting flat belts due to their versatility and durability. In emerging markets like Nigeria and Vietnam, there is a burgeoning demand for reliable conveyor systems, fueled by rapid industrialization and urbanization. Additionally, advancements in materials science are leading to the development of high-performance flat belts that offer enhanced durability and efficiency.
Another key trend is the integration of smart technologies within flat belt systems. IoT-enabled sensors are being utilized to monitor belt conditions in real-time, allowing for predictive maintenance and minimizing downtime. This trend is particularly appealing to B2B buyers in regions like South America and the Middle East, where operational efficiency can significantly impact profitability. Furthermore, customization is becoming increasingly important; suppliers are now offering tailored solutions to meet specific operational requirements, catering to the diverse needs of international buyers.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the Flat Belts Sector?
Sustainability has become a paramount concern for businesses globally, and the flat belts sector is no exception. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and materials used in flat belts is under scrutiny, prompting buyers to seek suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices. Ethical sourcing and transparency in the supply chain are critical factors for B2B buyers, particularly in Europe and North America, where regulatory frameworks are increasingly stringent.
Buyers are increasingly looking for flat belts made from recycled or eco-friendly materials, as well as products that have certifications such as ISO 14001, which signifies adherence to effective environmental management systems. Sustainable practices not only enhance brand reputation but can also lead to cost savings through improved efficiency and reduced waste. As a result, international buyers must engage with suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability and provide clear documentation of their sourcing and manufacturing processes.
What Is the Historical Context of Flat Belts in Industrial Applications?
Flat belts have a rich history that dates back to the early days of industrialization. Initially used in simple machinery to transmit power, their design has evolved significantly over the decades. Early flat belts were made from leather or fabric, but advancements in synthetic materials have led to modern belts that are more durable and efficient. The introduction of high-strength polymers and innovative manufacturing techniques has allowed flat belts to become integral components in various sectors, from manufacturing to agriculture.
Today, flat belts serve not just as a means of power transmission but as crucial elements in enhancing productivity and operational efficiency. Their evolution reflects broader trends in manufacturing and technology, making them a vital consideration for B2B buyers seeking reliable and effective solutions for their operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of flat belts
-
1. How do I solve issues with flat belt slippage?
To mitigate flat belt slippage, ensure that the tension is appropriately adjusted. An insufficiently tensioned belt can lead to inadequate grip on pulleys. Additionally, check the surface of the belt and pulleys for wear or contamination, as these factors can also contribute to slippage. Consider using belts with textured surfaces for enhanced grip. Regular maintenance and inspection are crucial to preventing slippage and extending the life of the belt. -
2. What is the best flat belt material for my application?
The choice of flat belt material depends on several factors, including load capacity, operating environment, and the nature of the goods being transported. Common materials include rubber, polyurethane, and leather, each offering unique advantages. For instance, rubber belts are durable and provide good grip, while polyurethane belts are resistant to abrasion and chemicals. Assessing your specific application requirements will guide you in selecting the most suitable material. -
3. How can I customize flat belts to fit my machinery?
Customization options for flat belts often include alterations in width, length, and material. Many suppliers offer bespoke solutions tailored to specific machinery requirements. When discussing customization with suppliers, provide detailed specifications, including dimensions, load requirements, and environmental conditions. This ensures that the final product meets your operational needs. Collaborating closely with the manufacturer can lead to optimal performance and efficiency in your application. -
4. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for flat belts?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on factors such as belt type and material. Typically, MOQs may range from a few units to hundreds, depending on the manufacturer’s production capabilities. It’s advisable to inquire directly with potential suppliers to understand their specific MOQs and whether they offer flexibility for smaller orders, especially for initial trials or smaller-scale operations. -
5. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing flat belts internationally?
Payment terms can differ based on the supplier’s policies and the buyer’s location. Common options include upfront payments, net 30 or 60 days, and letters of credit for larger transactions. It’s essential to negotiate payment terms that align with your cash flow and risk management strategies. Ensure clarity on any applicable fees, currency exchange rates, and payment methods accepted by the supplier to avoid complications. -
6. How can I vet suppliers of flat belts effectively?
Vetting suppliers involves assessing their experience, reputation, and product quality. Start by researching their business history, customer reviews, and certifications. Request samples to evaluate the quality of their flat belts. Additionally, consider their production capacity, delivery timelines, and after-sales support. Engaging with existing customers for testimonials can provide valuable insights into the supplier’s reliability and service level. -
7. What quality assurance measures should I expect for flat belts?
Reputable manufacturers should have robust quality assurance protocols in place. This includes testing belts for durability, flexibility, and performance under various conditions. Ask suppliers about their quality control processes, including any relevant certifications (e.g., ISO). Request documentation of test results and warranties to ensure that the flat belts meet industry standards and are suited for your specific applications. -
8. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing flat belts?
When importing flat belts, factor in shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations for your destination country. Choose a reliable freight forwarder familiar with international trade to streamline the shipping process. Ensure that all documentation, including invoices and customs declarations, is accurate to avoid delays. Additionally, consider the total landed cost, including shipping, tariffs, and handling fees, to make informed purchasing decisions.
Top 9 Flat Belts Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. McMaster – Made-to-Order Flat Belts
Domain: mcmaster.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, McMaster – Made-to-Order Flat Belts, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. Weinig USA – Flat Belts
Domain: tooling.weinigusa.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Weinig USA – Flat Belts, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Megadyne Group – Flat Belts
Domain: megadynegroup.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Flat belts provide reliable movement for goods and components in commercial and industrial conveyance systems, such as assembly lines. Advantages include efficiency, durability, productivity, safety, and simplicity. Applications include compressors, conveyors, machine tools, and industrial equipment. Key products include: 1. Rubber Megaflat Flat Belt – Available in knitted, unsupported, and woven …
4. MISUMI – Flat Belts
Domain: us.misumi-ec.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Flat belts are a type of drive belt traditionally used to transmit power between pulleys in mechanical systems. They have a flat surface, allowing for efficient power transfer and reducing slippage. Commonly made from materials like rubber or synthetic compounds, flat belts are widely used in various applications, such as conveyor systems, industrial machinery, and automotive engines. They provide…
5. IQS Directory – Flat Belts
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Flat belts are essential components in power transmission, crafted from materials such as rubber, synthetic composites, or leather. They have a flat cross-sectional form with a trapezoidal contour, reducing slippage and increasing power transmission efficiency. Key types of flat belts include: 1. Rubber Belts – Offer elasticity, abrasive resistance, and superior grip; suitable for high-speed and h…
6. Forbo – Siegling Extremultus Flat Belts
Domain: forbo.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Siegling Extremultus flat belts are high efficiency flat belts designed for easy handling and superb tracking at high speeds. They enhance power transmission and conveying across various industries. The product range includes five lines with different tension members and coatings, allowing for a wide choice of types for sophisticated, cost-saving designs and efficient operation. Key types include …
7. Ammeraal Beltech – RAPPLON® High Performance Flat Belts
Domain: ammeraalbeltech.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: RAPPLON® High Performance Flat Belts are high-quality Power Transmission Belts suitable for various industries including Airports, Food, Metal, Textile, Wood, Automotive, Logistics, Recycling, Tobacco, Coating & Lamination, Carton, Paper & Packaging Materials, and Building Materials. They feature classic nylon core belting and special fabric constructions for low tensions and thermoplastic inner l…
8. Fenner – Lightweight Flat Belting Solutions
Domain: fenner.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Lightweight flat belting designed for various industrial applications, offering flexibility and durability. Available in a range of materials and constructions to suit specific needs. Suitable for use in food processing, packaging, and other industries requiring lightweight and flexible belting solutions.
9. Flywheel Supply – Flat Leather Belting
Domain: flywheel-supply.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Flat leather belting, 1/8″ thick, sold by the foot. Available sizes: 1/2″ (SKU#2756), 3/4″ (SKU#2757), 7/8″ (SKU#2758), 1″ (SKU#2759), 1 1/4″ (SKU#2760), 1 3/8″ (SKU#2761), 1 1/2″ (SKU#2762). Durable power transmission belting made from high-quality oak-tanned leather, designed for high loads and continuous use. Ideal for steam engines, line shaft machinery, and historical equipment. Optional laci…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for flat belts
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Flat Belt Procurement?
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of flat belts is essential for optimizing operational efficiency and ensuring long-term cost-effectiveness. By leveraging the advantages of flat belts—such as their durability, low maintenance requirements, and superior power transmission—international B2B buyers can enhance the reliability of their conveyance systems. The ability to source high-quality flat belts from reputable suppliers ensures that companies can maintain productivity while minimizing downtime.
Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers who offer not only competitive pricing but also comprehensive support services. Engaging in strategic sourcing allows businesses to negotiate better terms, access innovative products, and secure a steady supply chain, which is particularly vital in today’s dynamic market environment.
As we look to the future, investing in strategic sourcing for flat belts will empower your business to adapt to evolving industry demands. Take action today by evaluating your current suppliers and exploring new partnerships that can drive your operational success. The journey to enhanced efficiency and reliability starts with informed sourcing decisions.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to flat belts
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.