Choosing Your Electroless Nickel Plating: Key Specs to Compare in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electroless nickel plating
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing effective electroless nickel plating solutions presents a significant challenge for B2B buyers across the globe. As industries increasingly seek durable, corrosion-resistant coatings for components ranging from automotive parts to electronic devices, understanding the nuances of electroless nickel plating becomes crucial. This comprehensive guide addresses the diverse types of electroless nickel plating, their applications, and the intricate details of supplier vetting and cost considerations, ensuring that you make informed purchasing decisions.
Navigating the global market can be daunting, particularly for buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria. Each of these markets presents unique demands and regulations that can complicate the sourcing process. This guide empowers international buyers by providing actionable insights into identifying reputable suppliers, understanding pricing models, and evaluating the quality of plating services.
By delving into the technical specifications and best practices of electroless nickel plating, you will be better equipped to select the right solutions for your business needs. Whether you’re looking to enhance the performance of existing products or expand your manufacturing capabilities, this guide serves as your essential resource for navigating the complexities of the electroless nickel plating market.
Understanding electroless nickel plating Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Electroless Nickel | Basic nickel plating with good corrosion resistance | Automotive, aerospace, and industrial components | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile. Cons: Limited wear resistance. |
| High-Phosphorus Electroless Nickel | Higher phosphorus content for improved corrosion resistance | Marine applications, chemical processing | Pros: Excellent corrosion resistance. Cons: More expensive than standard. |
| Low-Phosphorus Electroless Nickel | Lower phosphorus content, better wear resistance | Tooling, machinery parts | Pros: Superior hardness and wear resistance. Cons: Less corrosion resistance compared to high-phosphorus. |
| Electroless Nickel Composite | Nickel combined with other materials (e.g., PTFE) | Electronics, medical devices | Pros: Enhanced properties (e.g., reduced friction). Cons: More complex application process. |
| Electroless Nickel with Teflon | Nickel layer with Teflon for low friction applications | Food processing, packaging machinery | Pros: Non-stick properties, excellent release. Cons: Limited to specific applications due to unique properties. |
What Are the Characteristics of Standard Electroless Nickel Plating?
Standard electroless nickel plating is characterized by its autocatalytic process, which allows for uniform coating without the need for electrical current. This type is commonly used across various industries due to its cost-effectiveness and versatility. It provides good corrosion resistance, making it suitable for automotive and aerospace components. Buyers should consider the thickness and uniformity of the coating, as well as the potential for limited wear resistance in high-friction applications.
How Does High-Phosphorus Electroless Nickel Differ from Standard Options?
High-phosphorus electroless nickel contains a higher phosphorus content, which significantly enhances its corrosion resistance. This variation is ideal for marine applications and chemical processing environments where exposure to harsh conditions is common. While it offers superior protection, it comes at a higher cost compared to standard options. B2B buyers should evaluate the specific environmental factors their components will face to determine if the investment in high-phosphorus plating is justified.
What Benefits Does Low-Phosphorus Electroless Nickel Provide?
Low-phosphorus electroless nickel plating is designed to provide enhanced wear resistance, making it suitable for tooling and machinery parts that experience significant friction. This variation sacrifices some corrosion resistance for improved hardness, which can be crucial in heavy-duty applications. Buyers should assess the trade-off between wear resistance and corrosion protection based on their operational needs and the specific environments in which the components will be used.
What Are the Advantages of Electroless Nickel Composite Coatings?
Electroless nickel composite coatings involve combining nickel with other materials, such as PTFE, to enhance specific properties. These coatings are particularly beneficial in electronics and medical devices, where unique performance characteristics are required. While they offer advantages like reduced friction and improved durability, the application process can be more complex. B2B buyers must consider the added value of these enhanced properties against the potential for increased costs and application challenges.
In What Situations Is Electroless Nickel with Teflon Most Effective?
Electroless nickel with Teflon is specifically designed for applications that require low friction and non-stick properties, such as in food processing and packaging machinery. This combination ensures that surfaces remain clean and functional, reducing maintenance needs. However, the unique properties of this coating limit its applicability to certain industries. Buyers should carefully assess whether their specific application warrants the use of this specialized coating to ensure they are making a sound investment.
Key Industrial Applications of electroless nickel plating
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of electroless nickel plating | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Coating of engine components | Enhanced corrosion resistance and wear protection | Compliance with aerospace standards and certifications |
| Automotive | Plating of engine parts and fuel injectors | Improved durability and performance | Need for high-quality finishes and adherence to OEM specifications |
| Oil & Gas | Protection of drilling equipment | Extended equipment lifespan and reduced maintenance costs | Sourcing from suppliers with experience in harsh environments |
| Electronics | Plating of connectors and circuit boards | Enhanced conductivity and corrosion resistance | Consistency in plating thickness and quality assurance |
| Medical Devices | Coating surgical instruments | Increased biocompatibility and resistance to wear | Regulatory compliance and stringent quality control measures |
How is Electroless Nickel Plating Utilized in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace industry, electroless nickel plating is crucial for coating engine components, such as turbine blades and casings. This process provides enhanced corrosion resistance and wear protection, which are vital in high-stress environments. For international buyers, especially in regions like the Middle East and Europe, compliance with aerospace standards such as AS9100 is critical. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers can meet these stringent requirements to maintain safety and reliability in their operations.
What Role Does Electroless Nickel Plating Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
Electroless nickel plating is commonly used in the automotive sector to plate engine parts and fuel injectors. This application enhances durability and performance by providing a uniform coating that protects against corrosion and wear. B2B buyers from Africa and South America should prioritize suppliers who can deliver high-quality finishes that meet OEM specifications. Additionally, understanding the plating thickness and its impact on component performance is essential for optimizing engine efficiency.
How Does Electroless Nickel Plating Benefit the Oil & Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas sector, electroless nickel plating is applied to drilling equipment to protect against harsh environmental conditions. This process extends the lifespan of components and significantly reduces maintenance costs. Buyers in this industry should consider sourcing from suppliers with expertise in handling equipment designed for extreme conditions, ensuring that the plating can withstand high pressures and corrosive substances commonly found in drilling operations.

Illustrative image related to electroless nickel plating
Why is Electroless Nickel Plating Important for Electronics?
Electroless nickel plating is vital for the electronics industry, particularly for plating connectors and circuit boards. The process enhances conductivity and provides corrosion resistance, which is essential for the longevity and reliability of electronic components. International buyers, especially in Europe and the Middle East, should focus on suppliers that can guarantee consistency in plating thickness and quality assurance to avoid potential failures in electronic applications.
How is Electroless Nickel Plating Used in Medical Devices?
In the medical device sector, electroless nickel plating is applied to surgical instruments to improve biocompatibility and resistance to wear. This application is crucial for ensuring patient safety and instrument longevity. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers adhere to regulatory compliance and implement stringent quality control measures to meet the high standards required in the medical field. This is particularly important for international buyers looking to export medical devices across borders.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electroless nickel plating’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Maintaining Consistent Nickel Levels in Plating Solutions
The Problem: One of the most significant challenges faced by B2B buyers in the electroless nickel plating process is maintaining the nickel concentration in the plating bath. When the nickel levels drop below 80%, the plating bath can crash, rendering it ineffective. This scenario is particularly concerning for manufacturers who rely on consistent quality in their plating for components that are critical to their operations. A sudden failure in the bath can lead to production delays, increased costs, and potential loss of business due to unmet delivery timelines.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, it is essential to implement a robust monitoring system for the nickel concentration in the plating solution. B2B buyers should invest in software or tools that help track nickel credits and provide reminders for replenishment. This involves calculating the surface area of the parts being plated and determining the necessary replenishment intervals based on usage. For example, if a part requires 1,500 nickel credits for plating, buyers should have a clear plan for when and how much replenisher to add, ensuring that they never fall below the critical threshold. Additionally, regular training for staff on the importance of nickel levels and how to manage them effectively can further enhance operational efficiency.
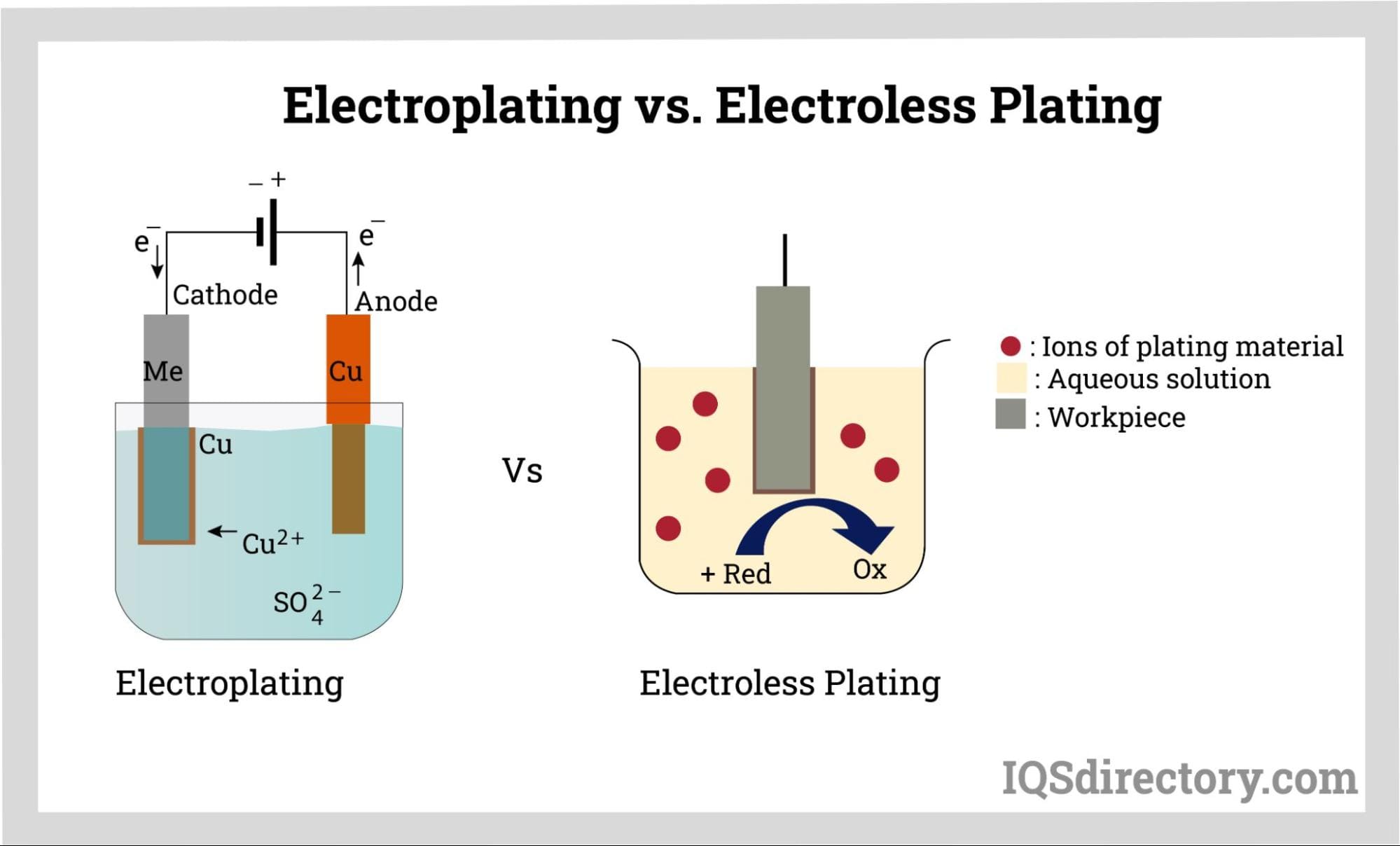
Illustrative image related to electroless nickel plating
Scenario 2: Challenges with Maximum Load in Electroless Plating
The Problem: Buyers often encounter difficulties when plating larger parts due to the maximum load limitations of their electroless nickel plating kits. Each kit has a specific maximum area that can be effectively plated, and exceeding this can result in an incomplete or failed plating process. This limitation can lead to frustration and wasted resources, particularly for companies that manufacture larger components, such as automotive parts or industrial machinery.
The Solution: To navigate the constraints of maximum load, B2B buyers should assess their production needs and select an appropriate electroless nickel plating kit that accommodates their typical part sizes. If larger components are frequently plated, investing in larger-scale plating systems capable of handling increased load is advisable. Alternatively, buyers can consider segmenting larger parts into smaller, manageable pieces that fit within the maximum load parameters. This approach not only ensures a successful plating process but also maintains the integrity and quality of the finished product. Collaborating with suppliers who can provide guidance on optimal plating practices for larger parts can further enhance this process.
Scenario 3: Complications in the Plating Process for Non-Conductive Materials
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the challenge of plating non-conductive materials. Electroless nickel plating relies on an autocatalytic reaction, which requires the presence of a conductive substrate to initiate the plating process. This can be a significant barrier for companies looking to enhance the corrosion resistance of non-metal components or non-conductive substrates, such as plastics or ceramics, leading to limited application possibilities.

Illustrative image related to electroless nickel plating
The Solution: To effectively plate non-conductive materials, buyers should consider the use of a conductive primer or intermediary layer that can facilitate the autocatalytic reaction necessary for electroless nickel plating. These conductive coatings can be applied to the surface of non-conductive parts before plating, allowing for a successful and uniform nickel application. Additionally, exploring advanced techniques such as plasma treatment or metallization processes can create a conductive surface suitable for electroless plating. Working closely with suppliers who specialize in innovative plating solutions will provide buyers with insights and products tailored to their specific needs, enabling them to expand their capabilities and improve product offerings.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electroless nickel plating
What Are the Key Materials for Electroless Nickel Plating?
Electroless nickel plating is a versatile process that can enhance the performance and longevity of various substrates. Understanding the properties and applications of different materials is crucial for international B2B buyers to make informed decisions. Below, we analyze four common materials used in electroless nickel plating, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from diverse regions.
How Does Steel Perform in Electroless Nickel Plating?
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high strength and durability. When electroless nickel plated, it exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in harsh environments. The temperature rating can reach up to 600°F, making it suitable for high-temperature applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of using steel is its cost-effectiveness and availability. However, it is susceptible to rust if not properly treated before plating, which can complicate the manufacturing process. Additionally, the weight of steel can be a disadvantage in applications requiring lightweight materials.
Impact on Application: Steel components plated with electroless nickel are commonly used in automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery. They are compatible with various media, including oils and chemicals, enhancing their versatility.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with ASTM standards for steel plating and consider local regulations regarding material sourcing and environmental impact. In regions like Africa and South America, where steel is widely available, the cost advantage is significant.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Electroless Nickel Plating?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and offers good corrosion resistance. When electroless nickel plated, it can withstand temperatures up to 300°F and provides a smooth finish ideal for aesthetic applications.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum makes it suitable for applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in aerospace. However, the cost of aluminum can be higher than steel, and it may require additional pre-treatment processes to ensure proper adhesion of the nickel layer.
Impact on Application: Electroless nickel plating on aluminum is often used in the electronics and automotive industries, where lightweight components are essential. Its compatibility with various media, including fuels and solvents, makes it a preferred choice.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must be aware of the specific pre-treatment requirements for aluminum and ensure compliance with international standards like JIS or DIN. In markets such as the Middle East, where lightweight materials are favored, aluminum’s benefits are particularly appealing.
Why Is Copper a Consideration in Electroless Nickel Plating?
Key Properties: Copper has excellent electrical conductivity and thermal properties. Electroless nickel plating enhances its corrosion resistance and can improve its mechanical properties.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its conductivity, making it ideal for electrical applications. However, copper can be more expensive and may require careful handling to avoid oxidation before plating.

Illustrative image related to electroless nickel plating
Impact on Application: Copper components plated with electroless nickel are commonly used in electrical connectors and circuit boards. They are compatible with various media, including water and oils, which broadens their application range.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that copper components meet relevant electrical standards and consider the cost implications of sourcing high-quality copper. In regions like Europe, where electrical standards are stringent, compliance is crucial.
How Does Zinc-Plated Steel Compare in Electroless Nickel Plating?
Key Properties: Zinc-plated steel offers good corrosion resistance and is often used in environments where exposure to moisture is common. The temperature rating is lower than that of untreated steel, typically around 200°F.
Pros & Cons: The primary benefit of zinc-plated steel is its affordability and availability. However, it may not provide the same level of durability as other materials, and the zinc layer can affect the adhesion of the nickel plating.

Illustrative image related to electroless nickel plating
Impact on Application: This material is often used in construction and automotive applications where cost is a significant factor. Its compatibility with various media, including water, makes it versatile.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify the quality of the zinc plating and ensure compliance with local regulations. In regions like Nigeria, where cost is a primary concern, zinc-plated steel can be a practical choice.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Electroless Nickel Plating
| Material | Typical Use Case for electroless nickel plating | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Automotive and industrial machinery | High strength and durability | Susceptible to rust if untreated | Low |
| Aluminum | Aerospace and electronics | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost and pre-treatment needed | Medium |
| Copper | Electrical connectors and circuit boards | Excellent conductivity | More expensive and requires handling | High |
| Zinc-Plated Steel | Construction and automotive applications | Affordable and widely available | Lower durability and adhesion issues | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for B2B buyers considering electroless nickel plating. By understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of various materials, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific application needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electroless nickel plating
The manufacturing process of electroless nickel plating involves several critical stages that ensure the quality and performance of the final product. For B2B buyers, understanding these stages is essential for assessing supplier capabilities and ensuring that the products meet their specific needs.
What Are the Main Stages of Electroless Nickel Plating Manufacturing?
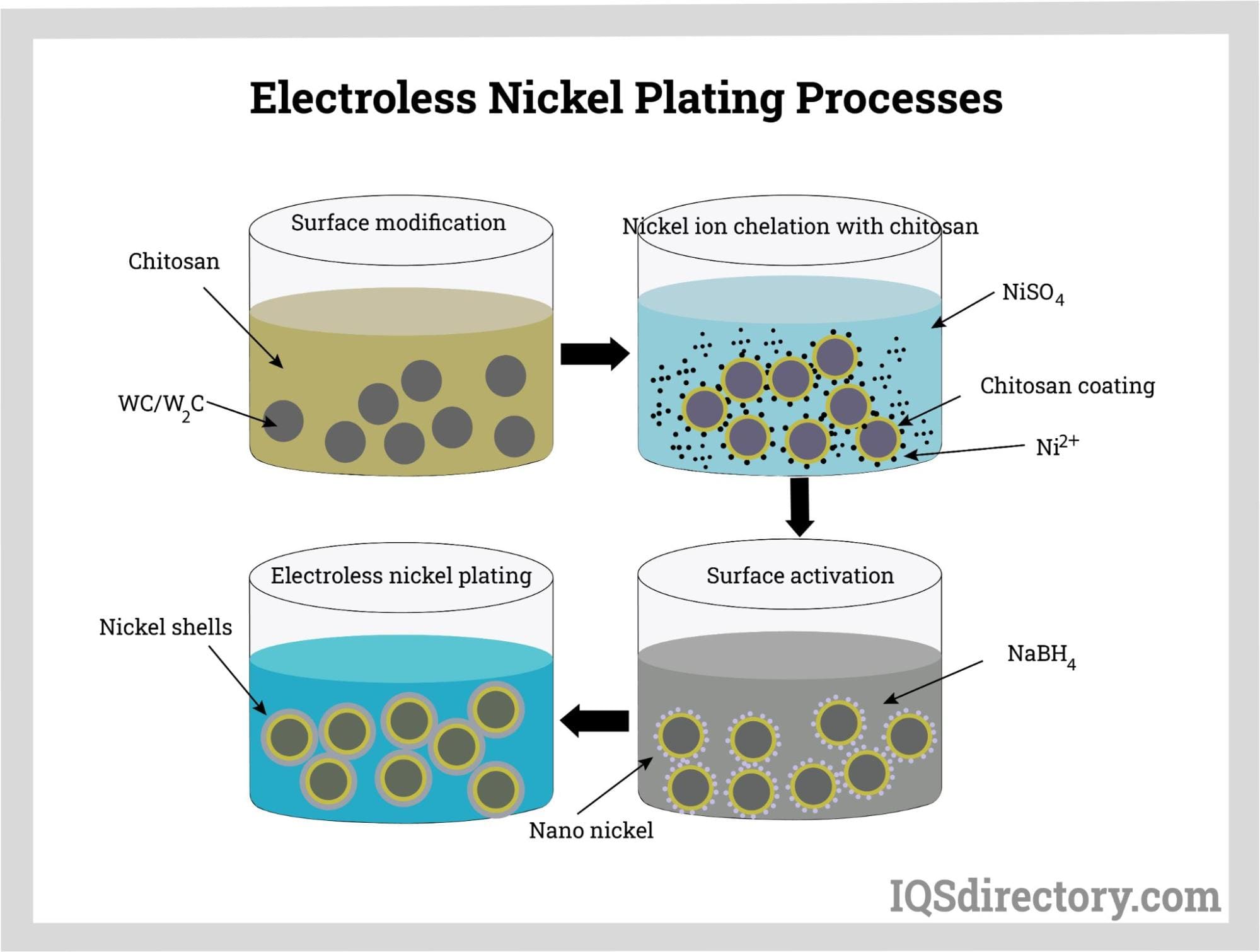
1. Material Preparation
The first stage in the manufacturing process involves preparing the substrate material. This typically includes cleaning and degreasing the surface to remove contaminants that could interfere with the plating process. Common methods for cleaning include ultrasonic cleaning, chemical etching, or abrasive cleaning. For parts made from copper or copper alloys, a preliminary step may involve creating a conductive layer to initiate the autocatalytic reaction necessary for the plating process.
2. Plating Bath Preparation
Once the materials are clean, the next step is preparing the electroless nickel plating bath. This involves mixing the nickel solution according to specific ratios, ensuring that the nickel concentration remains above 80% to avoid bath failure. The solution is then heated to the required temperature, typically around 195°F (90°C). Maintaining the correct temperature and chemistry in the bath is crucial, as it directly affects the uniformity and thickness of the nickel coating.
3. Plating Process
During the plating process, parts are immersed in the electroless nickel solution. The duration of immersion depends on the desired thickness of the nickel layer, which can range from a few microns to several hundred microns. The autocatalytic reaction deposits nickel uniformly over the surface, ensuring comprehensive coverage even in complex geometries. Continuous monitoring of the nickel credits used during the plating is essential to maintain the solution’s effectiveness.
4. Finishing
After plating, the parts undergo finishing processes such as rinsing, drying, and sometimes additional treatments like passivation or polishing. These steps enhance the corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal of the final product. Proper drying techniques are crucial to avoid water spots or oxidation, which can compromise the nickel layer.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into the Electroless Nickel Plating Process?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of the electroless nickel plating process. It involves several checkpoints and testing methods to ensure that the final product meets international and industry-specific standards.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who comply with international quality management standards such as ISO 9001. This certification ensures that the manufacturing processes are consistently monitored and improved. Additionally, industry-specific standards like CE marking for products sold in the European Union and API standards for oil and gas applications are crucial for ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Electroless Nickel Plating?
Quality control in electroless nickel plating typically includes the following checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials and chemicals for compliance with specifications before they are used in production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring occurs during the plating process to check for parameters such as temperature, nickel concentration, and immersion time. Any deviations can lead to defects in the coating.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the plating process, parts are subjected to final inspections and tests to ensure they meet the required specifications. This may include thickness measurements, adhesion tests, and visual inspections for defects.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance?
Several testing methods are employed to verify the quality of electroless nickel plating, including:
-
Thickness Measurement: Common techniques include X-ray fluorescence (XRF) and magnetic induction methods to assess the nickel layer thickness accurately.
-
Adhesion Testing: Methods such as tape tests or scratch tests are used to evaluate how well the nickel plating adheres to the substrate.
-
Corrosion Resistance Testing: Salt spray tests and cyclic corrosion tests help determine the durability of the coating under various environmental conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Measures?
When sourcing electroless nickel plating services, buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control measures of potential suppliers. This includes:
-
Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers to assess their adherence to quality management systems and manufacturing processes. This provides insight into their operational capabilities and commitment to quality.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports that outline the results of testing and inspections performed during the manufacturing process. This transparency helps buyers assess the reliability of the supplier.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures. This is particularly important for international buyers who may not be able to visit suppliers in person.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control in electroless nickel plating is essential. Buyers should consider:
-
Cultural Differences: Different regions may have varying standards and expectations for quality. Establishing clear communication regarding quality requirements can mitigate misunderstandings.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Buyers must ensure that suppliers are compliant with both local and international regulations, which may vary significantly across regions.
-
Logistical Challenges: Consider the potential for delays in shipping or customs clearance, which can affect the timely delivery of quality products. Ensuring that suppliers have robust logistics and supply chain practices can help alleviate these concerns.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with electroless nickel plating, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and quality expectations. This knowledge not only enhances supplier relationships but also contributes to the overall success of their projects.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electroless nickel plating’
The following guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure electroless nickel plating services or products. This step-by-step approach will help ensure that your sourcing process is efficient and effective, enabling you to meet your technical requirements while ensuring supplier reliability and quality.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for your electroless nickel plating project. Consider factors such as the substrate material, desired thickness, and specific application needs. Having precise specifications will facilitate better communication with potential suppliers and help ensure that the final product meets your performance standards.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in electroless nickel plating. Look for companies with a strong reputation in the industry, particularly those with experience serving your specific market or region. Utilize online directories, trade shows, and industry publications to compile a list of potential candidates.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that potential suppliers possess relevant certifications and compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 or RoHS. Certifications not only demonstrate a commitment to quality management but also ensure that the products meet necessary safety and environmental regulations. Request documentation to support their certifications and compliance claims.
Step 4: Assess Quality Control Processes
Investigate the quality control measures employed by the supplier. Inquire about their testing procedures, inspection protocols, and any third-party audits they may undergo. A robust quality control system is critical to ensuring that the electroless nickel plating meets your specifications and industry standards.
- Key considerations:
- Ask for details on their quality assurance processes.
- Request samples of previous work to evaluate quality.
Step 5: Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
Once you have narrowed down your list of suppliers, request quotes for your specific project. Ensure that the quotes include a detailed breakdown of costs, including any additional fees for setup, shipping, or special requirements. Comparing multiple quotes will allow you to gauge the market rate and make informed decisions.
Step 6: Check References and Reviews
Request references from previous clients to gain insights into the supplier’s reliability, service quality, and overall performance. Look for reviews or testimonials online, particularly from businesses in your industry or region. This feedback can provide valuable information regarding the supplier’s ability to deliver on time and adhere to quality standards.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Finalize Contracts
Before finalizing any agreements, engage in negotiations to clarify terms such as delivery timelines, payment conditions, and warranty provisions. Ensure that all aspects of the agreement are documented in a contract to avoid misunderstandings later. A well-structured contract protects both parties and establishes a clear framework for the business relationship.

Illustrative image related to electroless nickel plating
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing process for electroless nickel plating, ensuring that they partner with reliable suppliers who can meet their technical and quality requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electroless nickel plating Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of electroless nickel plating is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This section provides a comprehensive analysis of the cost components, price influencers, and actionable tips for buyers looking to optimize their sourcing strategies.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Electroless Nickel Plating?
The total cost of electroless nickel plating comprises several components:
-
Materials: The primary materials include nickel salts, reducing agents, and other chemicals necessary for the plating process. The quality and source of these materials significantly influence the overall cost.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for managing the plating process, maintaining quality control, and ensuring the proper handling of hazardous materials. Labor costs can vary widely depending on local wage rates and the complexity of the plating operation.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility management. Efficient operations can help minimize overhead costs.
-
Tooling: The creation and maintenance of tooling, such as fixtures and tanks for plating, are critical. The initial investment in high-quality tooling can reduce long-term costs by improving efficiency.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous testing and inspection processes are vital to ensure that the plating meets industry standards. The costs associated with QC can add up, particularly for specialized applications requiring certifications.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling of materials and finished products must be factored into the total cost. International shipping can introduce additional complexities and expenses, especially with varying customs regulations.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and risks. This margin can vary based on market conditions and supplier relationships.
How Do Volume and Customization Affect Pricing?
Several factors influence the pricing of electroless nickel plating services:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Higher order volumes often lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk orders, so negotiating for larger quantities can be beneficial.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom projects requiring specific thicknesses, finishes, or additional treatments can increase costs. Clear communication of specifications upfront can help avoid unexpected charges.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of high-quality materials and compliance with specific industry certifications (e.g., ISO) can impact pricing. Suppliers that provide certifications may charge a premium but can offer greater assurance of quality.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can significantly influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may command higher prices but can also reduce risks related to quality and delivery.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. The choice between FOB (Free on Board), CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), or other terms can alter the total cost of ownership and should be carefully considered during negotiations.
What Are the Best Tips for B2B Buyers in Electroless Nickel Plating?
-
Negotiate Wisely: Engage in negotiations with a clear understanding of your requirements and budget. Don’t hesitate to ask for discounts on larger orders or inquire about flexible payment terms.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the initial price but the TCO, which includes maintenance, longevity, and potential rework costs. A lower upfront price may lead to higher long-term expenses if quality is compromised.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for Different Regions: Different markets may exhibit distinct pricing trends based on local economic conditions, labor costs, and material availability. For example, suppliers in Europe may have higher labor costs compared to those in Africa, which could influence pricing structures.
-
Request Sample Runs: Before committing to large orders, request sample runs to evaluate quality and service. This can help mitigate risks associated with new suppliers.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
The prices associated with electroless nickel plating can vary significantly based on the factors outlined above. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing and optimal sourcing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electroless nickel plating With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to Electroless Nickel Plating
In the realm of surface finishing, electroless nickel plating (ENP) is often chosen for its unique properties, such as uniform coating and corrosion resistance. However, various alternatives may also meet specific requirements based on performance, cost, and application needs. This section explores a few viable alternatives to ENP, allowing B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their operational contexts.
| Comparison Aspect | Electroless Nickel Plating | Zinc Plating | Hard Chrome Plating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent corrosion resistance, uniform thickness, and good wear resistance | Moderate corrosion resistance, offers sacrificial protection | High hardness, excellent wear resistance, but lower corrosion resistance |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial cost due to chemical management | Generally low cost, widely available | Higher cost due to complex processes and environmental regulations |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires precise chemical management and monitoring | Simple application process, suitable for various substrates | Complex setup and requires skilled operators |
| Maintenance | Requires constant monitoring and replenishment of chemicals | Minimal maintenance; can be done in-house | High maintenance due to environmental compliance and equipment upkeep |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, automotive, and electronics where durability and uniformity are crucial | Fasteners, automotive components, and less critical applications | Heavy machinery, automotive parts, and applications requiring high wear resistance |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Zinc Plating as an Alternative?
Zinc plating is a popular alternative to electroless nickel plating, primarily due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of implementation. It offers a decent level of corrosion resistance by creating a sacrificial layer, meaning that the zinc will corrode before the underlying metal. This makes zinc plating a suitable choice for fasteners and automotive components where cost constraints are critical. However, it may not provide the same level of durability or uniformity as ENP, especially in demanding environments.
How Does Hard Chrome Plating Compare to Electroless Nickel Plating?
Hard chrome plating is another alternative that excels in wear resistance and hardness, making it ideal for applications in heavy machinery and automotive parts. The process involves electroplating chromium onto a substrate, resulting in a tough surface that can withstand significant wear and tear. However, hard chrome plating often comes with higher costs and complexity, including stringent environmental regulations. Additionally, while it provides excellent surface hardness, its corrosion resistance is typically inferior to that of electroless nickel plating, which may limit its use in certain applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Surface Finishing Solution?
When selecting the appropriate surface finishing solution, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including the specific performance requirements, budget constraints, and the operational environment of the components in question. Electroless nickel plating may be the best option for applications demanding high durability and corrosion resistance, while zinc plating offers a cost-effective solution for less critical components. Hard chrome plating could be ideal for applications where wear resistance is paramount, despite its higher costs and complexity. By weighing these factors carefully, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business needs and operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electroless nickel plating
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Electroless Nickel Plating?
Electroless nickel plating is a sophisticated process that demands a deep understanding of various technical properties to ensure optimal results. Here are some critical specifications relevant to B2B buyers:
1. Material Grade
Electroless nickel plating can be classified into different grades, such as low-phosphorus (2-4% phosphorus) and high-phosphorus (up to 10% phosphorus). Low-phosphorus grades offer excellent corrosion resistance and hardness, making them suitable for aerospace and automotive applications. High-phosphorus grades, on the other hand, provide enhanced wear resistance and are ideal for applications in harsh environments. Understanding the material grade helps businesses select the right type for their specific needs, impacting product longevity and performance.
2. Thickness Tolerance
The thickness of the nickel coating can range from 0.0002 inches to over 0.002 inches, depending on the application. Tighter tolerances are crucial in industries like electronics, where precision is vital. Buyers should consider the required thickness to ensure that the plated parts meet industry standards, which can affect performance and compliance with regulatory requirements.
3. Adhesion Strength
The adhesion strength of the electroless nickel coating to the substrate is critical for performance. A strong bond minimizes the risk of delamination under stress or exposure to corrosive environments. Adhesion testing, such as cross-hatch adhesion tests, can help determine if the coating will withstand operational demands. Buyers need to assess adhesion strength to avoid costly failures in their applications.
4. Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is one of the primary benefits of electroless nickel plating. The coating serves as a protective layer against oxidation and chemical attack. Buyers should evaluate corrosion resistance ratings, often measured through salt spray tests, to ensure that the coating will provide adequate protection for the intended application, particularly in industries such as oil and gas.
5. Surface Finish
The surface finish of electroless nickel plating can significantly impact the aesthetic and functional qualities of the final product. A smoother surface finish can enhance the part’s appearance and reduce friction in mechanical applications. Understanding the desired surface finish helps in selecting the right plating process and parameters to meet client specifications.

Illustrative image related to electroless nickel plating
What Are Common Trade Terms Associated with Electroless Nickel Plating?
Navigating the world of electroless nickel plating involves familiarizing oneself with industry-specific terminology. Here are several essential terms that B2B buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of electroless nickel plating, buyers often seek OEM services to ensure that their specifications are met for parts used in larger assemblies. Understanding OEM relationships can help in sourcing high-quality components.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is vital for B2B buyers, as understanding MOQ can affect inventory management and cost structures. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with their production needs and budget constraints.

Illustrative image related to electroless nickel plating
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price offers from suppliers. In the electroless nickel plating industry, RFQs help businesses obtain competitive pricing and terms for their plating needs. A well-defined RFQ can streamline procurement processes and ensure that all necessary specifications are included.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to understand shipping, insurance, and customs duties related to electroless nickel plating services. Knowledge of these terms can help in negotiating contracts and avoiding misunderstandings.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the finished product. In the context of electroless nickel plating, lead times can vary based on the complexity of the plating process and the supplier’s capacity. Buyers should consider lead times when planning production schedules to avoid delays in their supply chain.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and industry standards, ultimately enhancing their competitive advantage.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electroless nickel plating Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in Electroless Nickel Plating?
The electroless nickel plating market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for corrosion resistance and wear protection across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics. The shift towards high-performance coatings is particularly notable in emerging markets such as Africa and South America, where industrial expansion is accelerating. In the Middle East, the focus on infrastructure development is propelling demand for durable materials, including electroless nickel-plated components. European markets are increasingly adopting advanced coatings to meet stringent regulatory standards and improve product longevity.

Illustrative image related to electroless nickel plating
Key trends shaping the market include the rise of automation in plating processes and the integration of digital technologies for better monitoring and quality control. Companies are increasingly leveraging data analytics and IoT solutions to enhance their plating operations, ensuring consistency and reducing waste. Furthermore, the push towards localized sourcing has gained traction, as businesses seek to mitigate supply chain disruptions and reduce shipping costs. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers in regions like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria, where local suppliers are being prioritized for their ability to provide timely and cost-effective solutions.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Practices in Electroless Nickel Plating?
Sustainability has emerged as a critical factor in the sourcing of electroless nickel plating materials. As companies face growing pressure from consumers and regulators to adopt environmentally friendly practices, the focus on ethical sourcing and the environmental impact of plating processes has intensified. Electroless nickel plating is inherently more sustainable than traditional electroplating methods due to its lower energy consumption and waste generation. However, the sourcing of raw materials must also align with sustainability goals.
International buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with environmental standards and possess certifications such as ISO 14001. The use of ‘green’ chemicals in plating processes is becoming a priority, with many companies opting for environmentally friendly alternatives that do not compromise performance. Additionally, the adoption of closed-loop systems in plating operations helps minimize waste and promote resource efficiency. By prioritizing suppliers committed to sustainability, B2B buyers can enhance their brand reputation and meet the demands of eco-conscious customers.
What Is the Historical Context of Electroless Nickel Plating in B2B Markets?
Electroless nickel plating has its roots in the mid-20th century, initially developed as an alternative to traditional electroplating methods. Its unique autocatalytic process allows for uniform coating on complex geometries and non-conductive surfaces, making it an attractive option for various applications. Over the decades, advancements in chemical formulations and process technologies have significantly improved the performance characteristics of electroless nickel coatings, including hardness, corrosion resistance, and adhesion.
As industries began to recognize the benefits of electroless nickel plating, its adoption spread globally, particularly in sectors where durability and performance are paramount. Today, it is widely used in diverse applications, from automotive parts to electronic components, reflecting its evolution from a niche technology to a mainstream solution in the B2B marketplace. The ongoing development of advanced materials and processes continues to drive innovation in this field, making it essential for international buyers to stay informed about the latest trends and technologies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electroless nickel plating
-
How do I solve issues with electroless nickel plating bath stability?
To maintain the stability of your electroless nickel plating bath, ensure that the nickel concentration remains above 80% of its initial level. Regularly monitor the nickel credits using a balance sheet to track usage during plating. Implement a replenishment schedule based on the surface area of the parts being plated, adding replenisher as needed to prevent the bath from crashing. Consistent temperature control at approximately 195°F is also critical to sustaining the autocatalytic reaction necessary for effective plating. -
What is the best supplier for electroless nickel plating solutions?
The best supplier for electroless nickel plating solutions will depend on your specific requirements, including volume, customization options, and delivery capabilities. Look for suppliers with a strong reputation in the industry, proven track records, and experience in international shipping, especially to your region. Ensure they provide technical support and resources, such as guidance on bath management and replenishment, to help you maximize the efficiency of your plating process. -
How can I customize my electroless nickel plating order?
Customization options for electroless nickel plating can include variations in coating thickness, surface finish, and chemical formulations tailored to specific applications. To initiate customization, communicate your requirements clearly to potential suppliers, detailing the intended use of the plated parts, desired specifications, and any industry standards that must be met. A good supplier will work with you to develop a tailored solution, often providing samples for testing before full production. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for electroless nickel plating services?
Minimum order quantities for electroless nickel plating services can vary significantly among suppliers. Factors influencing MOQ include the type of parts being plated, the complexity of the plating process, and the supplier’s production capabilities. Generally, it’s advisable to inquire directly with suppliers about their specific MOQ policies and negotiate terms that suit your business needs, especially if you are looking for a pilot run or smaller-scale production. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing electroless nickel plating?
Payment terms for electroless nickel plating orders often vary by supplier and can depend on factors such as order size, customer relationship, and creditworthiness. Common practices include upfront deposits (typically 30-50%), with the balance due upon delivery or prior to shipment. For larger orders, suppliers may offer flexible financing options or extended payment terms. Always clarify payment conditions before finalizing agreements to ensure alignment with your cash flow management. -
How do I ensure quality assurance in electroless nickel plating?
To ensure quality assurance in electroless nickel plating, select suppliers who adhere to recognized industry standards and certifications (such as ISO 9001). Request detailed documentation regarding their quality control processes, including inspection methods and testing protocols for thickness, adhesion, and corrosion resistance. Establish clear specifications and expectations in your contracts and consider conducting periodic audits or reviews to monitor compliance with quality standards throughout the production process. -
What logistics considerations should I take into account when sourcing electroless nickel plating?
When sourcing electroless nickel plating, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations in your region. Engage suppliers who have experience with international shipping to ensure timely and cost-effective delivery. Be aware of potential tariffs and import duties that may apply to plated parts. Additionally, discuss packaging requirements to protect your products during transit and minimize the risk of damage. -
What are the environmental regulations affecting electroless nickel plating?
Environmental regulations surrounding electroless nickel plating can vary by country and region, particularly concerning waste disposal and chemical handling. Familiarize yourself with local and international regulations that govern the use of hazardous materials, including nickel and other chemicals involved in the plating process. Suppliers should provide Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) and comply with environmental standards, ensuring that their processes minimize environmental impact and adhere to legal requirements.
Top 6 Electroless Nickel Plating Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Caswell Plating – Electroless Nickel Plating Kits
Domain: caswellplating.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Electroless Nickel Plating Kits
2. US Chrome – Electroless Nickel Plating
Domain: uschrome.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Electroless Nickel Plating provides a microcrystalline to amorphous nickel-phosphorous alloy coating that enhances corrosion resistance. Offered in three phosphorus content weights: Low Phosphorus (1-4%), Mid Phosphorus (5-9%), and High Phosphorus (10-12%). Thickness range of 12 to 25 microns (0.0005” to 0.001”). Features include uniform thickness, heat resistance up to 540°C (1000°F), good durabi…
3. HCS Plating – Electroless Nickel Coating
Domain: hcsplating.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Electroless Nickel Plating:
– No electric current required; uses natural chemical reactions.
– Provides even coating on irregular shapes.
– Applicable to various base materials (conductive and non-conductive).
– Reaches hidden surfaces of complex parts.
– Better corrosion resistance due to coating consistency.
– Cost-effective due to no electricity usage and less nickel waste.
– Customizabl…
4. Advanced Plating Technologies – Electroless Nickel Plating
Domain: advancedplatingtech.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Electroless Nickel Plating services provided by Advanced Plating Technologies (APT) comply with MIL-C-26074, ASTM B733, and AMS 2404. APT offers loose-piece barrel, rack, and vibratory electroless nickel plating on various metallic substrates, including ferrous, cupreous, aluminum alloys, and exotic alloys. The process involves codepositing a nickel-phosphorous alloy without external electrical cu…
5. ENS Technology – Electrolytic Nickel Plating Solutions
Domain: enstechnology.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Electrolytic Nickel Plating:
– Types: Type I (dull nickel plating, sulfamate nickel solution, ductile, used for soldering/brazing) and Type II (bright nickel plating, chrome-like finish, used for aesthetics and wear resistance).
– Phosphorous content: Low (1-3%, uncommon), Medium (4-9%, excellent corrosion protection, most common), High (10-13%, withstands corrosive materials, used in semiconduct…
6. Surface Technology – Electroless Nickel Plating
Domain: surfacetechnology.co.uk
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Electroless Nickel Plating (ENP) is a nickel-alloy coating deposited by chemical reduction without electric current. It typically contains 2 to 14% phosphorus; higher phosphorus content increases corrosion resistance but decreases hardness. Common thickness ranges from 25-75 micrometers, with high phosphorus ENP exceeding 75 micrometers. ENP provides excellent corrosion resistance against salt wat…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electroless nickel plating
Why Is Strategic Sourcing Crucial for Electroless Nickel Plating?
In summary, strategic sourcing is essential for businesses looking to leverage electroless nickel plating for its unique advantages, such as superior corrosion resistance and uniform coating on complex geometries. By establishing strong relationships with reliable suppliers, companies can ensure consistent quality, competitive pricing, and timely delivery of plating materials and services. This proactive approach not only minimizes risks associated with supply chain disruptions but also enhances operational efficiency.
How Can International Buyers Capitalize on Electroless Nickel Plating Trends?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the growing demand for advanced surface finishing technologies presents a significant opportunity. By investing in electroless nickel plating, businesses can meet stringent industry standards and customer expectations while enhancing product longevity and performance.
What’s Next for the Electroless Nickel Plating Market?
As the global market evolves, staying informed about advancements in plating technologies and sourcing strategies will be vital. We encourage buyers to engage with industry experts, attend trade shows, and explore partnerships that can offer innovative solutions. Embrace the future of electroless nickel plating and position your business for success by making informed sourcing decisions today.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.