Choosing Your Edible Wax: Key Specs to Compare in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for edible wax
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing high-quality edible wax can present significant challenges for international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With diverse applications ranging from fruit coatings to chocolate finishes and even cosmetics, understanding the nuances of edible wax—its types, sourcing methods, and quality standards—is crucial for maintaining product integrity and consumer trust.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of edible wax, providing an in-depth exploration of various types such as Carnauba, Candelilla, and beeswax, along with their respective applications in the food industry and beyond. We will cover essential factors like supplier vetting processes, pricing strategies, and regulatory considerations to equip buyers with the knowledge necessary for informed purchasing decisions.
By navigating through this guide, B2B buyers will gain insights that empower them to identify reliable suppliers, evaluate product quality, and optimize their supply chains. As the edible wax market continues to evolve, being well-informed will not only enhance your product offerings but also position your business for long-term success in a global marketplace.
Understanding edible wax Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carnauba Wax | Derived from Brazilian palm leaves, high melting point | Coating fruits, chocolates, and candies | Pros: Natural, biodegradable; Cons: Higher cost |
| Candelilla Wax | Plant-based, derived from Candelilla shrubs | Coatings, cosmetics, and food products | Pros: Vegan, good gloss; Cons: Limited availability |
| Beeswax | Natural wax produced by honeybees, unique flavor and aroma | Cheese coatings, candies, and cosmetics | Pros: Natural, antimicrobial; Cons: Allergen risk |
| Paraffin Wax | Mineral-based, widely available, cost-effective | Food packaging and coatings | Pros: Inexpensive, versatile; Cons: Non-biodegradable |
| Microcrystalline Wax | Soft, flexible, and sticky, derived from petroleum | Food coatings, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals | Pros: Excellent adhesion; Cons: Synthetic origin |
What are the Key Characteristics of Carnauba Wax for B2B Buyers?
Carnauba wax is renowned for its high melting point and glossy finish, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and visual appeal. It is commonly used in the coating of fruits, chocolates, and candies, enhancing their shelf life and aesthetic value. B2B buyers should consider sourcing high-quality Carnauba wax to ensure superior product performance. However, its higher cost compared to other waxes may be a factor in pricing strategies.
How Does Candelilla Wax Stand Out for Food Industry Applications?
Candelilla wax, derived from the Candelilla shrub, is a popular choice for vegan products due to its plant-based origin. It is commonly utilized in food coatings, cosmetics, and various food products, providing a desirable gloss and texture. B2B buyers should assess the availability of Candelilla wax, as its supply can be limited. Additionally, its compatibility with vegan formulations can be a significant selling point in certain markets.
Why is Beeswax Considered a Versatile Option for Edible Applications?
Beeswax is a natural product with unique flavor and aroma, widely used in cheese coatings, candies, and cosmetics. Its antimicrobial properties make it an excellent choice for food preservation. B2B buyers should be aware of potential allergen risks associated with beeswax, as some consumers may have sensitivities. However, its natural origin and effectiveness in extending product shelf life can justify its inclusion in premium product lines.
What Advantages and Disadvantages Does Paraffin Wax Offer to Buyers?
Paraffin wax is a mineral-based wax that is both cost-effective and versatile, making it a popular choice for food packaging and coatings. Its affordability allows for broader application across various industries. However, B2B buyers should consider its environmental impact, as paraffin wax is not biodegradable. This factor may influence purchasing decisions, particularly in markets with a growing emphasis on sustainability.
How Can Microcrystalline Wax Enhance Product Quality in Edible Goods?
Microcrystalline wax is characterized by its soft, flexible nature and excellent adhesion properties, making it suitable for food coatings, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. Its ability to provide a protective barrier while maintaining product integrity is a key selling point. B2B buyers should evaluate the synthetic origin of microcrystalline wax against their product positioning, as some consumers prefer natural alternatives.
Key Industrial Applications of edible wax
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Edible Wax | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food & Beverage | Coating Fruits | Extends shelf life and enhances appearance | Ensure compliance with food safety regulations; sourcing from reputable suppliers. |
| Dairy Products | Cheese Coating | Prevents spoilage and moisture loss | Select waxes that are food-grade and suitable for specific cheese types. |
| Confectionery | Chocolate Coating | Improves texture and reduces melting | Focus on waxes that are compatible with various chocolate formulations. |
| Personal Care & Cosmetics | Edible Massage Candles | Provides dual use as a moisturizer and massage oil | Look for natural ingredients to cater to health-conscious consumers. |
| Packaging | Food Packaging Wax | Offers waterproofing and extends product freshness | Consider sustainability and biodegradability of waxes used in packaging. |
How is Edible Wax Used in the Food and Beverage Industry?
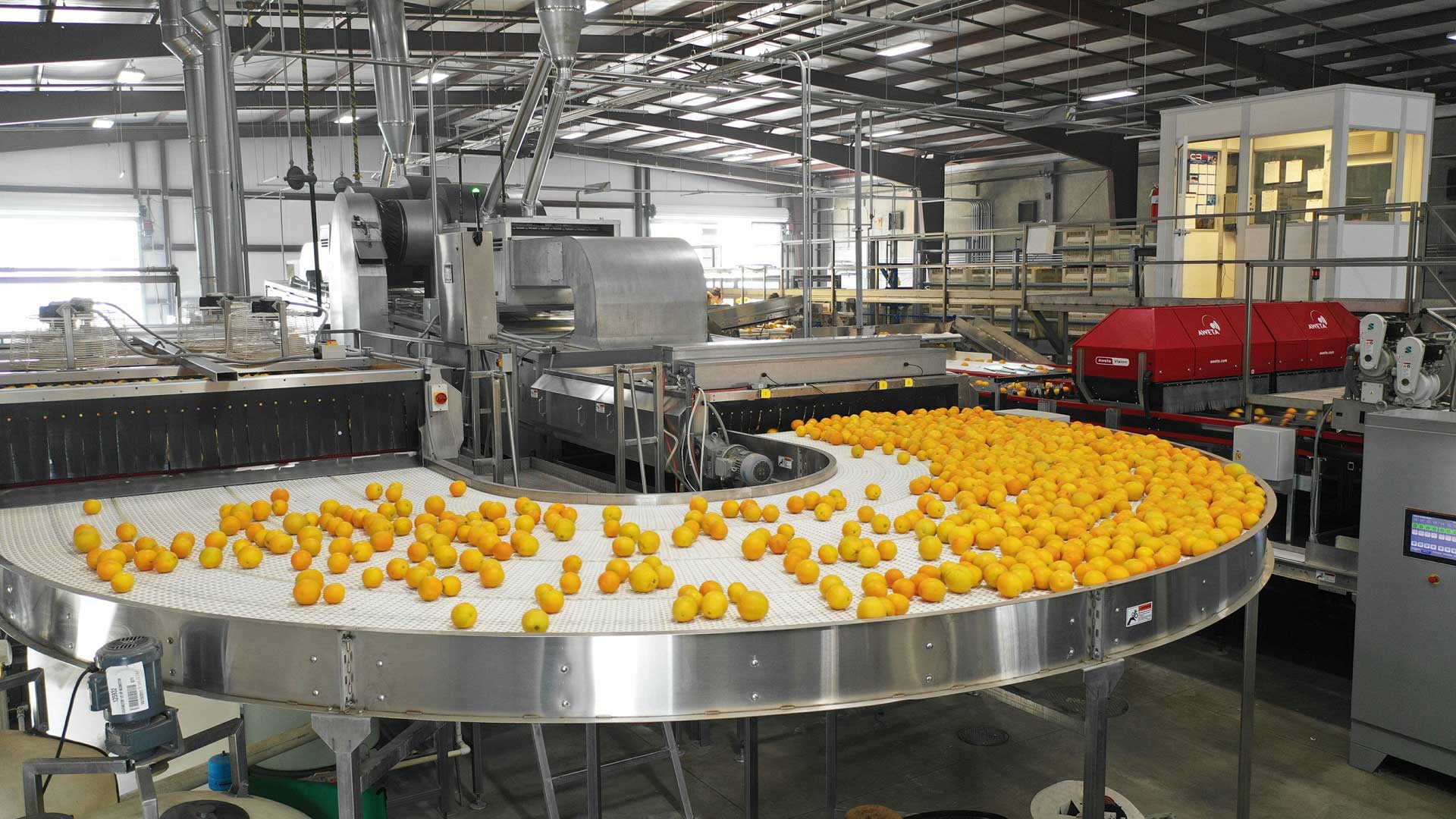
In the food and beverage sector, edible wax is primarily used for coating fruits. This application not only enhances the visual appeal of fruits but also plays a crucial role in retaining moisture, thereby extending their shelf life. For international buyers, especially from regions with varying climate conditions, sourcing edible wax that complies with local food safety standards is paramount. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who can guarantee the wax’s food-grade status and provide documentation for regulatory compliance.
What Role Does Edible Wax Play in Dairy Products?
For dairy products, particularly cheese, edible wax serves as a protective coating that prevents spoilage and moisture loss. This application has been a long-standing practice, with wax colors indicating different cheese varieties. B2B buyers in this sector need to ensure that the wax used is specifically formulated for cheese and adheres to food safety regulations. Additionally, sourcing high-quality wax can enhance the consumer experience by maintaining the cheese’s flavor and texture.
How is Edible Wax Beneficial in Confectionery?
In the confectionery industry, edible wax is often used in chocolate coatings to improve texture and reduce melting. This application is particularly popular in markets like the United States, while being less common in Europe, where regulations may differ. Buyers should focus on sourcing waxes that are compatible with various chocolate formulations, ensuring that they meet both quality and regulatory standards in their respective markets.
What Are the Applications of Edible Wax in Personal Care and Cosmetics?
Edible wax is gaining popularity in personal care products, such as edible massage candles, which melt into a moisturizing oil. This unique application allows businesses to offer multifunctional products that appeal to health-conscious consumers. For B2B buyers, it is essential to source waxes that contain natural ingredients, as this trend is increasingly favored by consumers seeking vegan and cruelty-free options. Ensuring that the wax meets cosmetic-grade standards is also crucial for product safety.
How Does Edible Wax Enhance Food Packaging Solutions?
In the realm of packaging, edible wax is utilized to create waterproof coatings for food items, significantly extending their freshness. This innovative application is particularly relevant in sustainable packaging solutions, where biodegradable options are in high demand. B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing waxes that are not only effective but also eco-friendly, aligning with global trends towards sustainability. Understanding the specific requirements for various food products can further enhance the effectiveness of packaging solutions.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘edible wax’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing High-Quality Edible Wax for Food Products
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle to find reliable suppliers of high-quality edible wax that meets regulatory standards. This challenge is particularly acute for companies in the food industry, where the safety and quality of ingredients directly impact product integrity and consumer trust. Many suppliers may offer edible waxes, but they often lack transparency regarding sourcing, quality control, and certifications. This can lead to inconsistent product quality, increased production costs, and potential compliance issues with food safety regulations.

Illustrative image related to edible wax
The Solution: To effectively source high-quality edible wax, buyers should begin by researching suppliers with established reputations in the food industry. Look for suppliers that provide comprehensive documentation, including certificates of analysis, safety data sheets, and compliance with food safety regulations like FDA or EU standards. Engaging in direct communication with suppliers can help clarify their production processes and ingredient sourcing. Additionally, consider requesting samples for testing before committing to larger orders. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers who prioritize quality and transparency can significantly reduce risks associated with product recalls or customer complaints.
Scenario 2: Understanding the Functional Benefits of Different Types of Edible Wax
The Problem: Many B2B buyers are unaware of the functional differences between various types of edible wax, such as Carnauba, Candelilla, and beeswax. This lack of knowledge can lead to improper application in food products, affecting texture, shelf life, and overall consumer satisfaction. For example, a buyer may choose a wax based solely on cost, not realizing that a higher-quality option could enhance the product’s performance and appeal.
The Solution: To make informed decisions about which type of edible wax to use, buyers should invest time in understanding the unique properties and applications of each wax type. For instance, Carnauba wax is known for its high melting point and glossy finish, making it ideal for coating fruits and candies, while Candelilla wax offers a vegan alternative with similar properties. Conducting thorough research or consulting with ingredient specialists can provide insights into how each wax interacts with other ingredients and its effects on product stability. Furthermore, utilizing pilot testing phases can help assess the performance of different waxes in real-world applications, ensuring that the chosen product aligns with business goals and consumer expectations.

Illustrative image related to edible wax
Scenario 3: Navigating Regulatory Compliance for Edible Wax Use
The Problem: Regulatory compliance is a significant concern for B2B buyers in the edible wax market. Different countries and regions have varying regulations regarding the use of food-grade waxes, and failing to comply can result in hefty fines, product recalls, and damage to brand reputation. This issue is especially pressing for businesses operating in multiple markets, such as those in Africa, South America, Europe, and the Middle East.
The Solution: To navigate regulatory compliance effectively, buyers should familiarize themselves with the specific laws governing edible wax in each target market. This may include understanding the food additive codes, permissible levels of certain waxes, and labeling requirements. Engaging with legal experts or regulatory consultants can provide tailored guidance based on the company’s operational landscape. Additionally, establishing a robust compliance program that includes regular training for employees on regulations and best practices can help mitigate risks. Buyers should also maintain thorough documentation of all ingredient sourcing and usage, which will be beneficial during audits or inspections, ensuring that the business is always prepared for regulatory scrutiny.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for edible wax
What are the Key Properties of Common Edible Wax Materials?
When selecting edible wax for various applications, it is crucial to understand the properties and characteristics of the materials available. The most common edible waxes include Carnauba wax, Candelilla wax, Beeswax, and Microcrystalline wax. Each material has unique properties that affect performance, cost, and suitability for specific applications.

Illustrative image related to edible wax
Carnauba Wax: What Makes It Stand Out?
Carnauba wax, derived from the leaves of the Brazilian palm tree, is known for its high melting point (approximately 82-86°C) and excellent gloss. Its strong film-forming capabilities and resistance to moisture make it ideal for coating fruits and confections. However, it can be more expensive than other waxes, which may be a consideration for budget-conscious buyers. Additionally, its hardness can complicate processing, requiring careful temperature control during manufacturing.
Impact on Application: Carnauba wax is particularly effective in applications requiring a high-gloss finish and moisture barrier, such as fruit coatings and chocolate products. It is compliant with international food safety standards, making it suitable for markets in Europe and North America.
Candelilla Wax: What are Its Advantages and Limitations?
Candelilla wax, sourced from the leaves of the Candelilla plant, has a lower melting point (approximately 68-73°C) compared to Carnauba wax. This makes it easier to work with during manufacturing. It offers a good balance of hardness and flexibility, making it suitable for various applications, including candy coatings and cosmetic products. However, its availability can be inconsistent due to environmental factors affecting the Candelilla plant, potentially impacting supply chains.
Impact on Application: Candelilla wax is often used in vegan products, appealing to a growing market segment. It meets several international standards, including those set by the FDA and EU, making it a reliable choice for B2B buyers in regions such as Africa and South America.
Beeswax: Why is It a Popular Choice?
Beeswax is a natural wax produced by honeybees and has been used for centuries in food preservation and cosmetics. Its melting point ranges from 62-65°C, which allows for easy incorporation into various formulations. Beeswax is known for its natural antibacterial properties, making it an excellent choice for applications requiring food safety. However, it is generally more expensive than plant-based waxes and may not be suitable for vegan products.
Impact on Application: Beeswax is widely accepted in many markets, including Europe, where consumers often prefer natural ingredients. However, buyers must consider the ethical implications of sourcing beeswax, as sustainability practices can vary.

Illustrative image related to edible wax
Microcrystalline Wax: When is it Most Effective?
Microcrystalline wax is a petroleum-derived wax that offers excellent flexibility and adhesion properties. With a melting point of around 60-80°C, it is versatile in various applications, including food packaging and coatings. Its lower cost and ease of processing make it attractive for manufacturers. However, being petroleum-based, it may not appeal to consumers seeking natural or organic products.
Impact on Application: Microcrystalline wax is often used in food packaging and as a coating for confections, providing a durable barrier against moisture and air. Compliance with international standards, such as those set by ASTM and JIS, is essential for B2B buyers in regions like the Middle East and Europe.
Summary Table of Edible Wax Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for edible wax | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carnauba Wax | Fruit coatings, chocolate products | High melting point and excellent gloss | Higher cost and processing complexity | High |
| Candelilla Wax | Candy coatings, vegan products | Easier to work with, good flexibility | Inconsistent availability | Medium |
| Beeswax | Food preservation, cosmetics | Natural antibacterial properties | Higher cost, not vegan | High |
| Microcrystalline Wax | Food packaging, confection coatings | Excellent flexibility and adhesion | Petroleum-based, may not appeal to all consumers | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the strategic material selection for edible waxes, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and market requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for edible wax
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Edible Wax?
The manufacturing of edible wax involves several critical stages, ensuring the final product meets safety and quality standards. These stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: Sourcing and Processing Raw Materials
The first step in manufacturing edible wax is sourcing high-quality raw materials. Common sources include plant-based waxes such as Carnauba and Candelilla, as well as beeswax. Each raw material undergoes rigorous selection to ensure it meets food safety standards. This phase may involve washing, drying, and grinding materials to prepare them for subsequent processes. For instance, Carnauba wax is extracted from the leaves of the Copernicia prunifera palm, which requires careful harvesting and processing to maintain its properties.
Forming: Techniques for Shaping Edible Wax Products
Once the raw materials are prepared, the forming stage begins. This can involve melting the wax and blending it with other ingredients, such as oils or flavorings, to achieve desired characteristics. Techniques such as molding or extrusion are commonly used. For example, melted wax can be poured into molds to create specific shapes for applications like edible massage candles. Temperature control is crucial during this stage to prevent degradation of the wax and ensure the final product retains its quality.
Assembly: Combining Components for Functional Products
In the assembly phase, different components are combined to create the final product. For edible wax, this could involve mixing various wax types or adding additional ingredients like colors and fragrances. For instance, an edible massage candle may include a blend of hemp seed oil and soy wax, which provides moisturizing properties while also enhancing the product’s usability. Careful attention is given to the ratios and mixing times to ensure uniformity and effectiveness.
Finishing: Quality Control and Packaging
The finishing stage encompasses the final touches and quality assurance checks before the product is packaged. This may involve cooling, cutting, or polishing the wax products, depending on their intended use. Proper packaging is essential to maintain the integrity of edible wax products, with considerations for moisture and light exposure. Labels must comply with international standards, including ingredient disclosure and usage instructions.
How Is Quality Assurance Managed Throughout the Edible Wax Manufacturing Process?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the edible wax manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet international safety standards and consumer expectations. Key quality assurance protocols include compliance with ISO 9001 and relevant industry-specific certifications.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for Edible Wax?
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized standard for quality management systems, applicable to various industries, including food production. Compliance with this standard indicates that a manufacturer has established processes for consistent quality and customer satisfaction. Additionally, edible wax products may require adherence to specific regional regulations, such as CE marking in Europe or FDA approval in the United States, particularly if they are incorporated into food products.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are essential for maintaining product integrity throughout the manufacturing process. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet predefined specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring production processes in real time helps identify and rectify any deviations from quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The final product undergoes comprehensive testing before packaging, ensuring it meets all safety and quality criteria.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used?
Various testing methods are employed to assess the quality of edible wax products. These may include:
- Physical Testing: Assessing properties such as melting point, viscosity, and texture to ensure consistency and performance.
- Chemical Testing: Analyzing for contaminants or impurities, including pesticide residues or heavy metals, which is crucial for food safety.
- Microbiological Testing: Ensuring products are free from harmful bacteria or pathogens, particularly if the wax is intended for direct food contact.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers looking to source edible wax should take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of potential suppliers.

Illustrative image related to edible wax
What Are the Best Practices for Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is a crucial method for assessing the quality management systems in place. Buyers should request access to audit reports, certifications, and any third-party inspections conducted on the manufacturing facility. These audits should focus on compliance with international standards and the effectiveness of quality control measures.
How Can Buyers Request Quality Assurance Documentation?
Buyers should request comprehensive quality assurance documentation from suppliers, including:
- Certificates of Analysis (CoA): These documents detail the results of quality testing performed on batches of wax, providing transparency into product quality.
- Compliance Certificates: Evidence of compliance with relevant food safety and quality standards, such as ISO certifications or local regulations.
- Traceability Documentation: Information on the sourcing of raw materials, which can help ensure the sustainability and safety of the products.
What Are the Unique QC Considerations for International Buyers?
International buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate varying quality standards and regulations. It’s crucial to be aware of:
- Regional Regulations: Different countries may have specific regulations governing edible products. For instance, EU regulations may require more stringent testing compared to other regions.
- Cultural Preferences: Understanding regional preferences for product characteristics, such as flavor or texture, can influence quality expectations.
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for edible wax, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they source high-quality products that meet their needs and those of their customers.

Illustrative image related to edible wax
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘edible wax’
Introduction
This sourcing guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers interested in procuring edible wax. As the demand for food-grade waxes increases across various industries—from agriculture to confectionery—understanding how to effectively source these materials is crucial. This guide will help you navigate the complexities of selecting the right edible wax, ensuring quality, compliance, and suitability for your specific applications.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before you begin sourcing edible wax, clearly outline your technical requirements. Consider factors such as the type of wax (e.g., Carnauba, Candelilla, or beeswax), desired properties (e.g., melting point, texture), and application (e.g., fruit coating, chocolate, or confectionery). Defining these specifications ensures that you narrow your focus to suppliers who can meet your specific needs.
Step 2: Research Regulatory Compliance
Ensure that the edible wax you intend to procure complies with local and international food safety regulations. This includes checking for certifications like FDA approval in the U.S. or EFSA regulations in Europe. Compliance is essential not only for legal reasons but also for maintaining product quality and safety standards.
- Key Certifications to Look For:
- FDA approval for food-grade products.
- EU regulations compliance (E-number classifications).
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they meet your requirements. Request company profiles, references, and case studies from other clients, especially those within your industry or region. A reliable supplier should demonstrate a strong track record of quality and service.
- Considerations:
- Look for suppliers with experience in your specific application.
- Verify the quality management systems they have in place.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request samples of the edible wax for testing. This step is crucial for assessing the wax’s performance in your specific application, such as its melting point, texture, and compatibility with other ingredients. Testing samples can prevent costly mistakes down the line.
Step 5: Assess Pricing and Payment Terms
Evaluate the pricing structure of the edible wax and understand the payment terms being offered. While it’s important to find a competitive price, consider the total cost of ownership, including shipping and handling fees, as well as potential discounts for bulk orders.
- Negotiation Tips:
- Inquire about long-term contracts for better pricing.
- Ask about payment plans that could ease cash flow.
Step 6: Review Logistics and Supply Chain Capabilities
Assess the logistics and supply chain capabilities of your chosen suppliers. Ensure they have the infrastructure to deliver your edible wax consistently and on time. Delays in supply can disrupt your production line and affect your business reputation.
- Key Logistics Factors:
- Transportation methods and lead times.
- Availability of emergency stock or backup suppliers.
Step 7: Establish a Quality Control Plan
Finally, establish a quality control plan that outlines how you will monitor the quality of the edible wax received. This includes setting up regular inspections and testing protocols to ensure that the wax meets your specifications and regulatory requirements consistently.
By following this checklist, you can streamline the sourcing process for edible wax and make informed decisions that align with your business needs.

Illustrative image related to edible wax
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for edible wax Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Edible Wax Sourcing?
When sourcing edible wax, it is essential to understand the various cost components involved in the production and supply chain. Key cost factors include:
-
Materials: The primary ingredient costs can vary significantly based on the type of wax being sourced, such as Carnauba, Candelilla, or beeswax. Each type has different market prices influenced by availability, harvesting methods, and processing requirements.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both the workforce involved in the extraction and processing of wax and any skilled labor required for quality control (QC) and packaging. Geographic location plays a critical role in labor expenses, with some regions offering lower wages than others.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes all indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing practices can help minimize these overhead costs.
-
Tooling: The costs related to the machinery and tools used for processing edible wax must be factored in. Investment in high-quality, efficient equipment may lead to lower long-term costs but can increase initial capital expenditures.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring the wax meets food safety standards and certifications incurs additional costs. Rigorous QC processes may be necessary to comply with regulations, especially when exporting to different countries.
-
Logistics: Transportation, warehousing, and handling costs can add significant expenses, particularly for international shipments. The choice of shipping methods and routes can greatly influence overall logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a profit margin to cover their operational costs and ensure sustainability. This margin can vary widely based on market competition and supplier reputation.
What Influences Pricing in Edible Wax Procurement?
Several factors influence the pricing of edible wax in the B2B marketplace:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often come with discounts, as suppliers benefit from economies of scale. Understanding a supplier’s MOQ can help buyers negotiate better terms.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom formulations or specific quality requirements can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their needs to avoid unexpected price hikes.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality waxes with certifications (e.g., organic, vegan) may command premium prices. Buyers should evaluate whether these certifications align with their product requirements and target market.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, production capacity, and geographic location can all impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer reliability, while emerging suppliers might be more cost-effective but pose risks.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) affect pricing by determining who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and liability. Understanding these terms can help buyers make informed decisions regarding total costs.
What Tips Can Help B2B Buyers Optimize Their Edible Wax Procurement?
To navigate the complexities of edible wax sourcing, international B2B buyers can adopt several strategies:
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage in discussions regarding pricing, MOQ, and payment terms. Building a good relationship with suppliers can lead to better deals and flexibility.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider logistics, storage, and potential wastage costs. A lower upfront price may not always translate to overall savings.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Different regions may have varying price standards due to local economic conditions and regulations. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should research regional market trends to ensure competitive pricing.
-
Stay Informed: Regularly monitor market trends and supply chain disruptions that could affect pricing. Being proactive can help buyers anticipate changes and adapt their sourcing strategies accordingly.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
Prices for edible wax can fluctuate based on market dynamics, supplier negotiations, and other factors. It is crucial for buyers to conduct thorough market research and engage with multiple suppliers to obtain the most accurate and favorable pricing for their specific needs.
Illustrative image related to edible wax
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing edible wax With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Edible Wax
In the food and cosmetic industries, edible wax serves as a versatile option for coating and preserving products. However, various alternatives exist that can achieve similar results, each with its unique benefits and limitations. Understanding these alternatives can help international B2B buyers select the most suitable solution for their specific applications, considering factors like performance, cost, and ease of implementation.
Comparison Table of Edible Wax and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Edible Wax | Plant-Based Coatings | Shellac |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent moisture retention; enhances appearance | Good moisture retention; natural look | Provides a glossy finish; good barrier properties |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to sourcing and processing |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple application; requires minimal training | Easy to apply; requires some knowledge of plant materials | More complex; requires specific application techniques |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Low maintenance | Moderate maintenance; can degrade over time |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for fruits and chocolates | Suitable for fruits and vegetables | Ideal for confectionery and certain dairy products |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Plant-Based Coatings
Plant-based coatings, derived from natural ingredients such as starches and proteins, are increasingly popular due to their sustainability and effectiveness. These coatings provide good moisture retention, helping to extend the shelf life of fresh produce. Additionally, they impart a natural look, appealing to health-conscious consumers. However, they may require a specific application process that necessitates some training for staff, and their performance can vary based on environmental conditions.
Shellac
Shellac, a natural resin secreted by the lac bug, is another alternative that offers a glossy finish and excellent barrier properties. It is commonly used in the confectionery industry to provide shine and protect products from moisture. While shellac is effective, it comes at a higher cost than edible wax and may require more complex application techniques. Additionally, shellac is not suitable for vegan products, which could limit its market appeal.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between edible wax and its alternatives, B2B buyers should consider their specific product requirements and market demands. Factors such as performance, cost, ease of implementation, and maintenance will significantly influence the decision. For example, companies focused on sustainability may prefer plant-based coatings, while those seeking a traditional finish might opt for shellac. Ultimately, aligning the chosen solution with the target market’s preferences and product specifications will lead to the best outcomes.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for edible wax
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Edible Wax for B2B Buyers?
Understanding the technical properties of edible wax is essential for B2B buyers who want to ensure product quality and compliance. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material grade indicates the quality and purity of the wax. For edible applications, it is crucial to use food-grade waxes such as Carnauba (E903), Candelilla (E902), and Beeswax (E901). Each grade has specific regulatory approvals and safety standards, impacting their suitability for various food products. Buyers should always verify that suppliers provide documentation confirming compliance with food safety regulations. -
Melting Point
The melting point is significant as it determines how the wax behaves during application. For instance, edible waxes used for coating fruits typically have a melting point close to body temperature, allowing for easy application without compromising the food’s integrity. Buyers should consider the melting point when selecting wax for applications like chocolate coatings or fruit preservation to ensure optimal performance. -
Viscosity
Viscosity measures the thickness or resistance to flow of the wax when melted. This property is critical for applications such as glazing fruits or confectionery. A lower viscosity allows for better spreadability, while a higher viscosity can create thicker coatings. B2B buyers should assess viscosity based on their specific application needs to achieve desired results. -
Shelf Life
The shelf life of edible wax indicates how long the product can maintain its quality without degradation. Factors such as storage conditions and exposure to light can affect this property. Longer shelf life is often preferred, as it minimizes waste and ensures that products remain viable for longer periods, which is particularly important for international shipping and storage. -
Chemical Composition
Understanding the chemical composition is vital for compliance and safety. Edible waxes can contain various fatty acids, esters, and other compounds that can affect taste, texture, and stability. Buyers should request a detailed composition breakdown to avoid allergens or substances that may affect their products. -
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with local and international food safety standards is a must for edible waxes. B2B buyers should ensure that the waxes meet relevant regulations, such as those set by the FDA in the U.S. or EFSA in Europe. Documentation proving compliance is essential for avoiding legal issues and ensuring product safety.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Edible Wax Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can enhance communication and facilitate smoother transactions. Here are some essential trade terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
In the context of edible wax, an OEM refers to a company that produces wax products that are then marketed under another brand’s name. Understanding OEM relationships helps buyers navigate supplier options and negotiate terms for private labeling. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for buyers looking to manage inventory and costs effectively. Higher MOQs may be beneficial for pricing but can lead to excess stock if demand is uncertain. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers asking for pricing and terms for a specific quantity of edible wax. Submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare offers and negotiate better deals based on their needs. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping, insurance, and duties. Familiarity with Incoterms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) is essential for B2B buyers to clarify shipping responsibilities and costs. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to delivery. Understanding lead time helps businesses plan their production schedules and inventory management, ensuring they have enough stock to meet market demand. -
Certification
Certification pertains to the official recognition that a product meets specific standards or regulations. For edible wax, certifications may include organic, vegan, or non-GMO labels. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with relevant certifications to ensure product integrity and consumer trust.
By understanding these properties and terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing edible wax, ensuring quality, compliance, and efficiency in their operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the edible wax Sector
How Are Global Drivers Influencing the Edible Wax Market?
The edible wax market is witnessing significant growth driven by various global factors, including increasing consumer awareness regarding food safety, product aesthetics, and the demand for natural, plant-based ingredients. With health-conscious consumers on the rise, edible waxes derived from sources like Carnauba and Candelilla are gaining traction, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. These waxes not only enhance the visual appeal of fruits and vegetables but also extend their shelf life, making them essential for producers looking to meet export standards.
Emerging technologies in the sourcing landscape, such as blockchain for traceability and AI for supply chain optimization, are transforming how businesses engage with edible wax suppliers. International B2B buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that can provide transparency in sourcing practices and product origins. Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce platforms has simplified the procurement process, allowing buyers from diverse markets to access a wider range of edible wax products with comparative ease.
In Europe and Brazil, regulatory compliance regarding food safety and additives is becoming stricter, prompting manufacturers to prioritize food-grade certifications. This trend is crucial for buyers in these regions as they navigate the complexities of local regulations and consumer preferences, ensuring they source compliant and high-quality edible waxes.

Illustrative image related to edible wax
What Role Does Sustainability Play in the Edible Wax Supply Chain?
Sustainability is a growing concern within the edible wax sector, particularly as businesses aim to reduce their environmental impact. Ethical sourcing practices are paramount, with an increasing number of suppliers adopting sustainable farming methods for raw materials like Carnauba and Candelilla. This not only helps in conserving biodiversity but also supports local communities involved in the harvesting process.
B2B buyers are now prioritizing suppliers with ‘green’ certifications, such as USDA Organic and Fair Trade, which validate sustainable practices. These certifications are becoming essential differentiators in a competitive market, as they signal to consumers that a brand is committed to ethical sourcing and environmental responsibility. Additionally, integrating biodegradable packaging solutions into the supply chain is gaining traction, helping to further reduce the ecological footprint associated with edible wax products.
Moreover, the transition towards renewable energy sources in production facilities is another trend that aligns with sustainability goals. Buyers are encouraged to evaluate potential suppliers based on their energy practices and waste management strategies, ensuring they align with the broader movement towards sustainability in the food industry.
How Has the Edible Wax Market Evolved Over Time?
The history of edible wax can be traced back to natural waxes used for coating fruits to enhance their appearance and extend shelf life. Initially, these practices were based on traditional methods, with wax coatings being applied manually. Over time, advancements in technology and processing have led to the development of food-grade waxes that are safe for human consumption, including synthetic options that offer enhanced functionality.
In recent years, the edible wax market has evolved significantly, driven by consumer demand for transparency and quality. The introduction of stringent food safety regulations has compelled manufacturers to invest in research and development, resulting in more effective and safer edible wax formulations. This evolution has not only expanded the application of edible waxes in various food products, such as chocolates and cheeses, but has also positioned them as vital components in modern food preservation strategies.
As the market continues to grow, international B2B buyers must stay informed about the latest trends and technologies to make informed sourcing decisions that align with both consumer demands and regulatory requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of edible wax
-
How do I ensure the quality of edible wax from suppliers?
To guarantee the quality of edible wax, conduct thorough supplier vetting. Request certifications such as FDA approval or EU food safety standards to confirm compliance with regulations. Additionally, ask for samples to evaluate the wax’s texture, melting point, and taste. Engage in third-party testing to validate the supplier’s claims about their products. Establish clear quality assurance agreements that outline specifications, testing protocols, and acceptable quality limits to ensure consistency in your supply chain. -
What are the key applications of edible wax in the food industry?
Edible wax is primarily used for coating fruits and vegetables to enhance appearance and extend shelf life by retaining moisture. It’s also utilized in cheese coatings, providing protection against mold and moisture loss. In confectionery, edible wax is used to create glossy finishes on chocolates and candies. Additionally, it serves as a binding agent in products like chewing gum, offering texture and stability. Understanding these applications can help you target your sourcing efforts effectively. -
What should I consider when selecting a supplier for edible wax?
When choosing a supplier for edible wax, evaluate their reputation, industry experience, and production capabilities. Check for certifications relevant to food safety and quality standards. Assess their ability to meet your specific requirements, such as customization options and minimum order quantities (MOQs). Additionally, consider their logistics capabilities, including shipping times and costs, especially if sourcing from international suppliers. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can lead to better terms and reliability. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for edible wax?
Minimum order quantities for edible wax can vary significantly based on the supplier and type of wax. Generally, MOQs range from 100 kg to several tons, depending on production capabilities and market demand. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for smaller orders, especially for first-time buyers or samples. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with suppliers to negotiate terms that align with your business requirements while ensuring cost-effectiveness. -
What payment terms are common for international B2B transactions of edible wax?
Common payment terms for international B2B transactions often include options like advance payment, letter of credit, or net 30/60 days after delivery. Advance payment may be required for first-time orders or smaller suppliers, while letters of credit provide security for both parties. It’s essential to clarify payment terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings. Consider negotiating favorable terms based on your purchasing history and order size, which can enhance your cash flow management. -
How can I customize edible wax for my specific product needs?
Customization of edible wax can include variations in color, flavor, and texture based on your product requirements. Discuss your needs with potential suppliers to explore available options. Some suppliers may offer tailored formulations or blends to meet specific applications, such as vegan or organic waxes. Be prepared to share detailed specifications and any regulatory requirements to ensure compliance. Collaborating closely with your supplier can lead to innovative solutions that differentiate your products in the market. -
What are the logistics considerations when importing edible wax?
When importing edible wax, consider logistics aspects such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Choose a shipping method that balances cost and delivery time, like sea freight for larger shipments or air freight for urgent needs. Ensure compliance with international food safety regulations to avoid customs delays. It’s also advisable to work with a freight forwarder experienced in food products to navigate the complexities of cross-border shipping and ensure smooth delivery. -
How do I handle regulatory compliance for edible wax in different regions?
Regulatory compliance for edible wax varies by region, requiring a thorough understanding of local food safety standards. For instance, in the EU, edible waxes must comply with regulations like the EU Food Additives Regulation. Research the specific requirements for the regions you are targeting, such as labeling, safety testing, and permissible ingredients. Collaborate with suppliers who are knowledgeable about these regulations to ensure your products meet all necessary compliance standards, thereby minimizing the risk of legal issues.
Top 4 Edible Wax Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Edible Wax Candy
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Food-grade paraffin wax and 100% beeswax are mentioned as edible waxes used in wax candy.
2. Earthly Body – Edible Massage Candle
Domain: shop.earthlybody.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “Earthly Body Edible Massage Candle”, “flavor”: “Strawberry”, “size”: “4 oz”, “price”: “$18.99”, “subscription_price”: “$18.04”, “key_benefits”: [“3-in-1 formula (candle, oil, moisturizer)”, “Nourishes and smooths skin”, “Safe for tasting and licking off skin”], “burn_time”: “up to 30 hours”, “ingredients”: [“Hydrogenated Vegetable Oil”, “Glycine Soja Oil”, “Aroma (Flavor)”, “Cann…
3. Zhang Catherine – DIY Wax Candy
Domain: zhangcatherine.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: DIY Wax Candy made with food-grade wax (paraffin or beeswax), sweetened with sugar or corn syrup, flavored with extracts, and colored with food coloring. Essential tools include a candy thermometer, double boiler or microwave-safe bowl, molds, and a spatula. Optional extras are decorative sprinkles or edible glitter. The process involves melting the wax, adding sweeteners and flavors, coloring, po…
4. Facebook – Edible Paraffin Wax
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Facebook – Edible Paraffin Wax, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for edible wax
In today’s competitive landscape, the strategic sourcing of edible wax represents a pivotal opportunity for international B2B buyers seeking to enhance product quality and sustainability. Edible waxes, derived from natural sources such as Carnauba and Candelilla, not only serve as effective coatings for fruits and cheeses but also play a crucial role in extending shelf life and improving product aesthetics. Understanding the diverse applications of edible wax across various sectors—including food preservation, confectionery, and cosmetics—can drive innovation and differentiation in your product offerings.
As you navigate the sourcing process, prioritize suppliers that emphasize quality, compliance with food safety standards, and sustainable practices. This will not only ensure that you meet regulatory requirements but also resonate with increasingly eco-conscious consumers.
Looking ahead, the demand for edible wax is anticipated to grow, fueled by trends towards natural ingredients and clean-label products. Now is the time to engage with reliable suppliers and explore new partnerships that can bolster your supply chain. Embrace the potential of edible wax to not only enhance your product line but also contribute to a more sustainable future in the global marketplace.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

Illustrative image related to edible wax