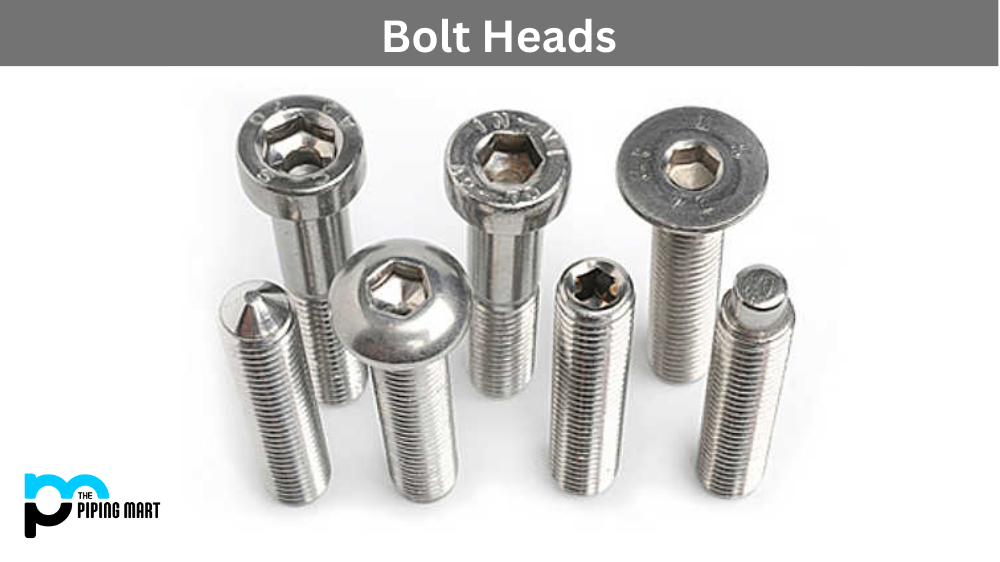
Choosing Your Different Types Of Bolt Heads: Key Specs to Compare in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for different types of bolt heads
In today’s global market, sourcing the right types of bolt heads can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers. With the vast array of options available, from hex bolts to socket screws, understanding the specifications, applications, and compatibility of each type is critical to ensuring project success. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of different bolt head types, detailing their unique features, uses, and the materials they are commonly made from.
Moreover, we delve into essential considerations such as supplier vetting processes, pricing strategies, and best practices for quality assurance, enabling buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs. Whether you are operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, this guide equips you with the knowledge necessary to navigate the complexities of the fastener market confidently. By understanding the nuances of bolt heads, you can streamline your procurement process, reduce costs, and enhance the reliability of your assemblies.
Ultimately, this resource aims to empower B2B buyers to not only select the right fasteners but also foster long-term relationships with suppliers who align with their operational goals. Engage with this guide to unlock insights that can transform your sourcing strategy and elevate your business’s competitive edge in a diverse marketplace.
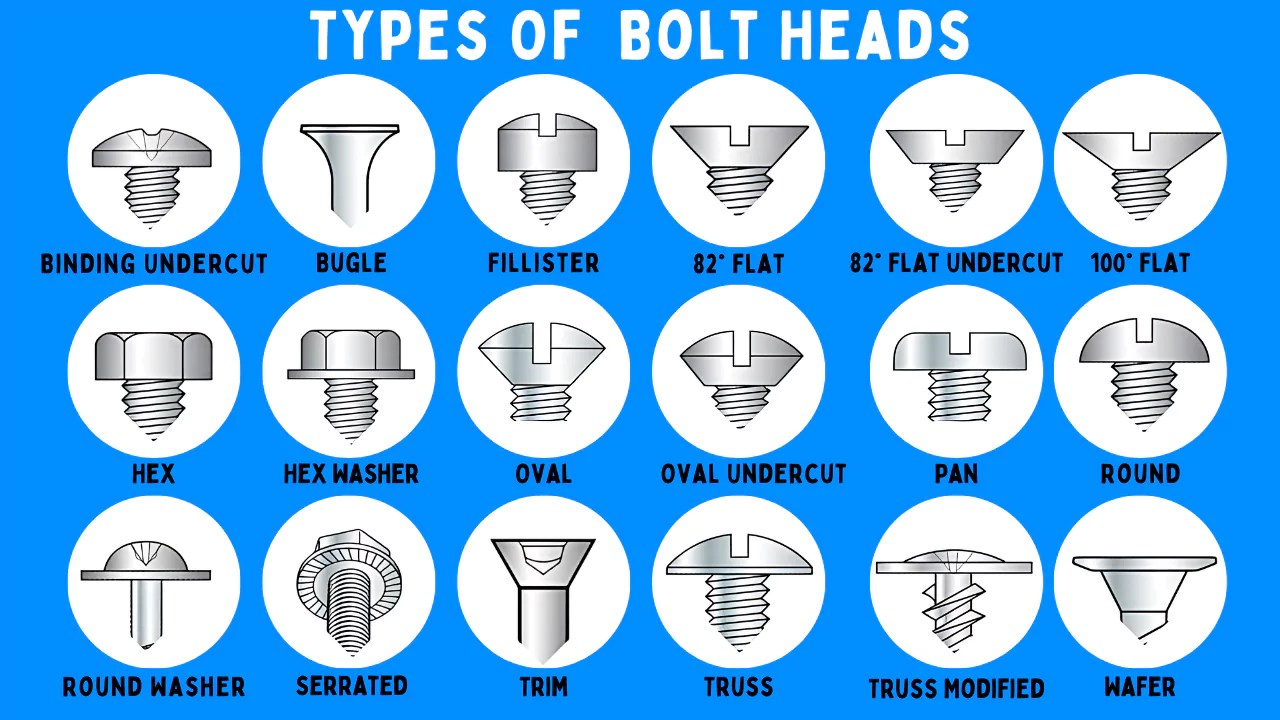
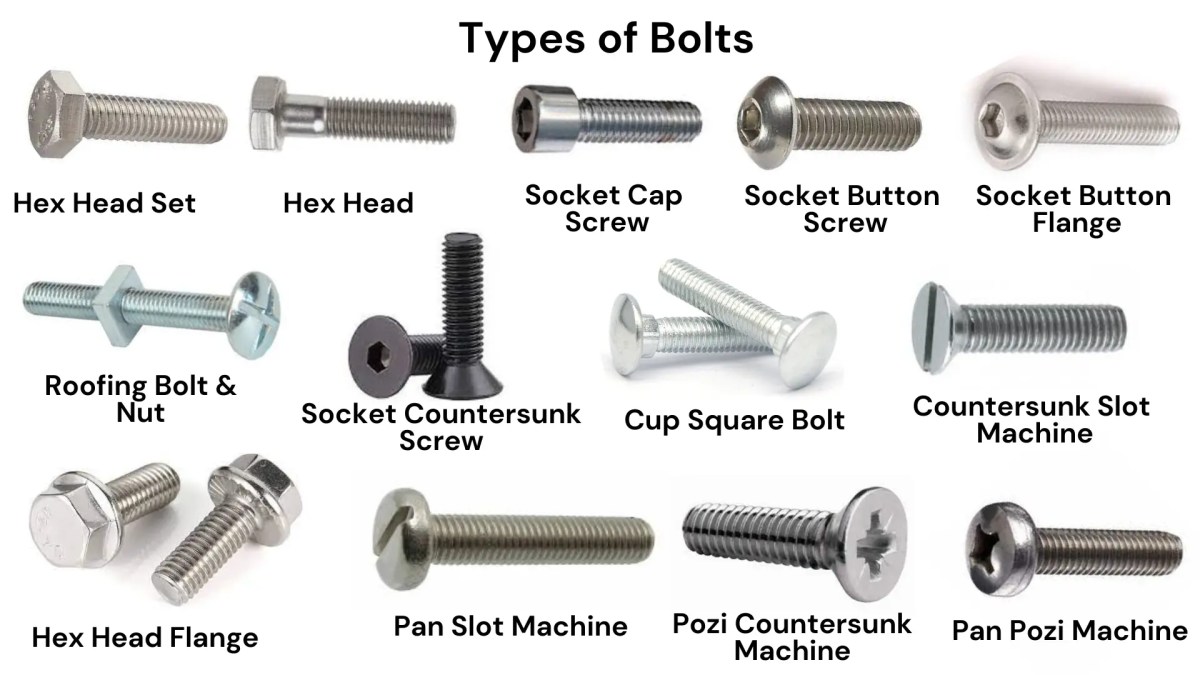
Understanding different types of bolt heads Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hex Head Bolt | Hexagonal head shape; requires a wrench for fastening | Construction, machinery, automotive | Pros: High torque capability; versatile. Cons: Requires tools for installation. |
| Socket Cap Bolt | Cylindrical head with hex socket drive; low profile design | Automotive, electronics, industrial | Pros: Compact design; less prone to stripping. Cons: Requires specific Allen wrench. |
| Carriage Bolt | Rounded head with a square neck; designed for smooth surfaces | Woodworking, construction | Pros: Prevents spinning during installation. Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
| Flange Bolt | Integrated flange under the head; distributes load | Heavy machinery, structural applications | Pros: Reduces the need for separate washers. Cons: May be bulkier than standard bolts. |
| Eye Bolt | Circular ring at the head; used for lifting or anchoring | Marine, construction, rigging | Pros: Ideal for securing ropes or chains. Cons: Limited load capacity compared to other bolts. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Hex Head Bolts?
Hex head bolts are characterized by their six-sided heads, which provide a secure grip for wrenches and sockets. This design allows for high torque application, making them suitable for heavy-duty fastening in construction, automotive, and machinery sectors. When purchasing hex head bolts, buyers should consider material strength, corrosion resistance, and compatibility with nuts. Their versatility and reliability make them a preferred choice, although they require specific tools for installation.
How Do Socket Cap Bolts Stand Out in B2B Applications?
Socket cap bolts feature a low-profile cylindrical head with a hex socket drive, making them ideal for tight spaces where traditional wrenches cannot fit. Commonly used in automotive and electronic applications, they offer a clean aesthetic and reduced risk of stripping due to their design. Buyers should evaluate the required Allen wrench size and the bolt’s material for durability. While they provide a strong fastening option, their specific drive type may limit tool compatibility.
What Makes Carriage Bolts Suitable for Woodworking?
Carriage bolts are easily identifiable by their rounded heads and square necks, which lock into place when installed, preventing rotation. This feature makes them particularly effective for securing wood connections in construction and woodworking projects. When considering carriage bolts, buyers should assess the length, diameter, and material to ensure they meet the project’s needs. Their unique design simplifies installation, though their usage is somewhat limited to specific applications.
Illustrative image related to different types of bolt heads
Why Choose Flange Bolts for Heavy Machinery?
Flange bolts are distinguished by their built-in flange that acts as a washer, distributing the load evenly across the surface. This feature is especially beneficial in heavy machinery and structural applications where load-bearing capacity is crucial. Buyers should focus on the bolt’s grade and material to ensure it can withstand operational stresses. While flange bolts reduce the need for additional washers, their bulkier design may not be suitable for all applications.
In What Scenarios Are Eye Bolts Most Effective?
Eye bolts come with a circular ring at the head, designed for attaching ropes or chains, making them ideal for lifting and securing applications in marine, construction, and rigging environments. Buyers should consider the load rating and material, especially in corrosive environments. Although eye bolts are versatile for anchoring, their load capacity is generally lower compared to other bolt types, which is a critical factor in their selection for specific tasks.
Key Industrial Applications of different types of bolt heads
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of different types of bolt heads | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Use of hex bolts in structural frameworks | Ensures stability and safety in building projects | Material certifications, load capacity specifications |
| Automotive | Socket screws for engine assembly and components | Provides reliable fastening under high vibration conditions | Compliance with automotive standards, corrosion resistance |
| Manufacturing | Elevator bolts in conveyor systems for material handling | Enhances operational efficiency and safety in production | Durability under load, compatibility with existing systems |
| Energy | Flange bolts in wind turbine installations | Critical for structural integrity in renewable energy setups | Resistance to environmental conditions, availability of sizes |
| Aerospace | Eye bolts for rigging and securing equipment in aircraft | Ensures safety and compliance with aviation regulations | Weight specifications, material grade certifications |
How are Different Types of Bolt Heads Used in Key Industries?
In the construction industry, hex bolts are extensively utilized in structural frameworks to provide reliable fastening and stability. These bolts are essential for ensuring the safety of buildings and infrastructures, particularly in seismic zones. For international buyers, sourcing high-quality hex bolts with the right load capacity and material certifications is crucial to meet local building codes and safety standards.
In the automotive sector, socket screws play a vital role in engine assembly and various components. Their design allows for secure fastening that can withstand high vibrations common in vehicle operation. Buyers need to ensure that these screws comply with automotive industry standards and exhibit corrosion resistance to maintain vehicle longevity, especially in diverse climates found in regions like Africa and South America.
The manufacturing industry often employs elevator bolts in conveyor systems to facilitate the efficient movement of materials. These bolts are designed to handle substantial loads and provide a secure connection. Businesses must consider the durability of elevator bolts under continuous use and their compatibility with existing systems, ensuring a seamless integration into production lines.
In the energy sector, particularly with wind turbine installations, flange bolts are critical for maintaining structural integrity. These bolts distribute loads effectively, preventing failures in harsh environmental conditions. International buyers must focus on sourcing flange bolts that can withstand specific environmental factors, such as extreme temperatures and humidity, to ensure long-term reliability.
Finally, in the aerospace industry, eye bolts are essential for rigging and securing equipment on aircraft. They must meet stringent safety regulations to ensure the safety of passengers and cargo. Buyers need to prioritize weight specifications and material grade certifications to comply with aviation standards, which can vary significantly across different regions, including Europe and the Middle East.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘different types of bolt heads’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Bolt Head for Specific Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with identifying the most suitable bolt head type for their specific applications. For instance, in industries like construction or manufacturing, the choice of bolt head can significantly affect assembly efficiency and structural integrity. A buyer might face challenges when needing to select between hex bolts, socket screws, or carriage bolts, particularly when considering factors such as load distribution, accessibility, and torque specifications. This confusion can lead to project delays, increased costs, and even safety hazards if the wrong type is used.
Illustrative image related to different types of bolt heads
The Solution: To overcome this issue, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of their project requirements before sourcing bolt heads. Begin by assessing the materials being joined and the load conditions they will encounter. For example, if high torque is required and space is limited, socket screws may be the best option due to their compact design and ease of installation with an Allen wrench. Conversely, if the application demands higher load-bearing capacity, hex bolts might be preferable. Utilizing comprehensive fastener selection tools available online can also streamline this process. Furthermore, collaborating with suppliers who offer technical support can provide valuable insights into the best practices for bolt head selection tailored to specific applications.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Quality and Performance of Bolt Heads
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the inconsistency in quality and performance of bolt heads from different suppliers. Variability in manufacturing processes can lead to discrepancies in dimensions, material properties, and finishing treatments, which may compromise the integrity of the final assembly. This inconsistency can result in increased failure rates, unplanned maintenance, and warranty claims, ultimately affecting the buyer’s reputation and bottom line.
The Solution: To mitigate this risk, buyers should prioritize sourcing bolt heads from reputable suppliers who adhere to strict quality control standards and certifications. Requesting detailed product specifications and material test reports before making a purchase can help ensure compliance with industry standards. Additionally, establishing long-term relationships with trusted suppliers can foster better communication regarding quality expectations and allow for joint problem-solving when issues arise. Implementing a robust inspection process upon receipt of materials can further safeguard against quality inconsistencies, ensuring that only high-quality fasteners are used in production.
Scenario 3: Complex Installation Challenges with Bolt Heads
The Problem: Installation difficulties can arise from using the wrong bolt head type, particularly in environments where accessibility is restricted or when specific tools are unavailable. For instance, a buyer might choose a bolt with a slotted head but find that the installation requires a specialized driver that is not readily available on-site. This can lead to increased labor costs, project delays, and frustration among the installation team.
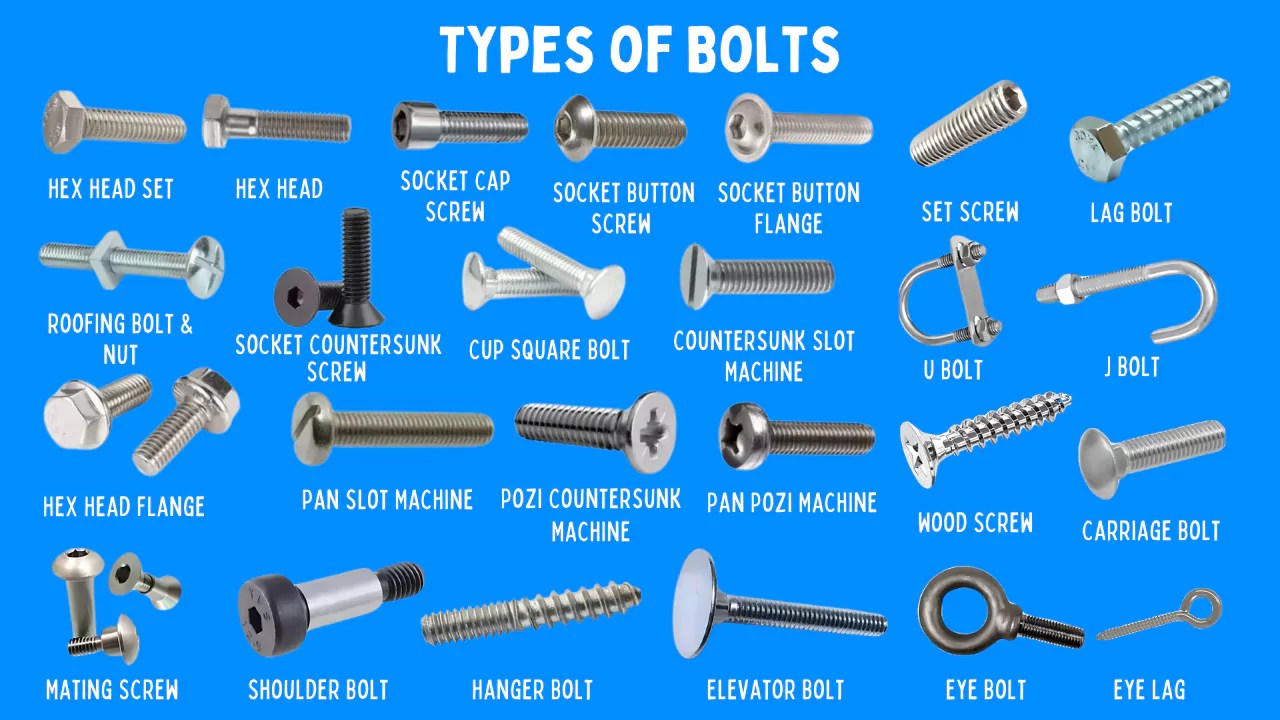
Illustrative image related to different types of bolt heads
The Solution: To address these challenges, it is crucial for buyers to consider the installation environment and available tools when selecting bolt head types. Conducting a site assessment before procurement can help identify potential obstacles and tool requirements. For situations requiring frequent adjustments or where space is limited, opting for bolt heads that accommodate versatile drive types, such as combination or star drives, can simplify installation. Additionally, investing in a comprehensive toolkit that includes various drivers can enhance flexibility and efficiency during installation. Providing training for installation teams on the nuances of different bolt head types and their respective installation methods can further improve overall project execution.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for different types of bolt heads
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used for Bolt Heads?
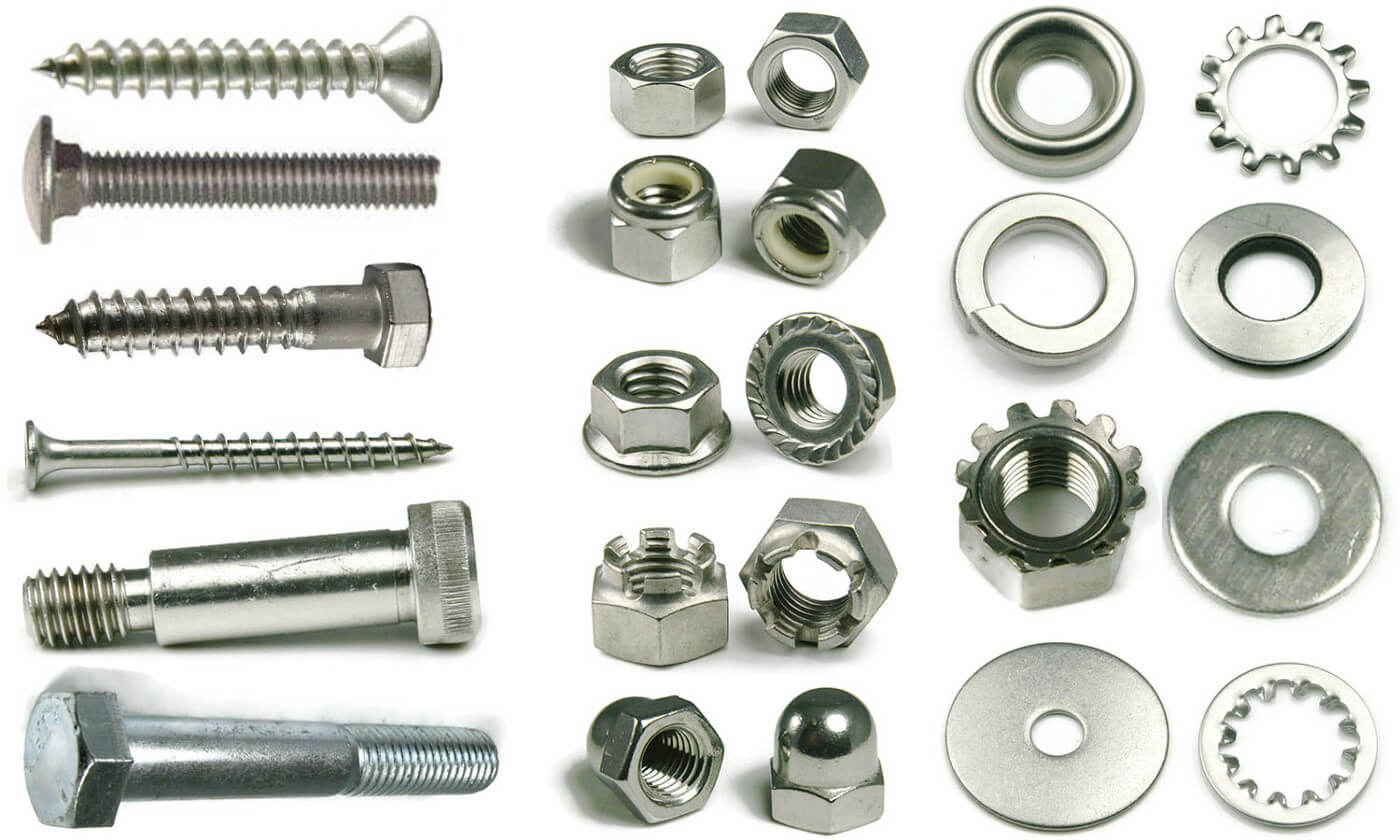
When selecting materials for bolt heads, several factors influence their performance and suitability for specific applications. Here, we analyze four common materials: carbon steel, stainless steel, brass, and aluminum. Each material offers distinct properties that cater to different operational needs.
How Does Carbon Steel Perform in Bolt Head Applications?
Carbon steel is widely used due to its excellent strength and hardness. It has a high tensile strength, making it ideal for applications requiring strong fastening capabilities. However, carbon steel is prone to corrosion, which can limit its use in humid or corrosive environments unless properly coated or treated.
Pros: High strength, cost-effective, widely available.
Cons: Susceptible to rust and corrosion, may require additional coatings.
Impact on Application: Suitable for structural applications in dry environments but less ideal for outdoor or marine applications without protective coatings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A307 or DIN 933 is crucial, particularly in regions like Europe where stringent quality measures are enforced.

Illustrative image related to different types of bolt heads
What Advantages Does Stainless Steel Offer for Bolt Heads?
Stainless steel is favored for its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. It maintains its strength at elevated temperatures and is less likely to rust, making it suitable for outdoor and marine applications. Stainless steel bolt heads often come in various grades, such as 304 and 316, which offer varying levels of corrosion resistance.
Pros: Excellent corrosion resistance, high-temperature tolerance, and aesthetic appeal.
Cons: Generally more expensive than carbon steel, can be more challenging to machine.
Impact on Application: Ideal for applications in harsh environments, such as chemical processing or coastal areas.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for compliance with ASTM A193 or JIS B 1180 standards, especially in regions like Brazil and Germany, where quality assurance is paramount.
Why Choose Brass for Bolt Heads in Specific Applications?
Brass is known for its excellent machinability and corrosion resistance, particularly in marine environments. It is non-magnetic and has good electrical conductivity, making it suitable for electrical applications. However, brass is softer than steel, which may limit its use in high-stress applications.
Pros: Good corrosion resistance, excellent machinability, and aesthetic appeal.
Cons: Lower tensile strength compared to steel, higher cost.
Impact on Application: Best suited for decorative applications or low-stress environments, such as electrical fittings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM B16 or similar standards is essential, particularly in regions with strict regulations on materials.
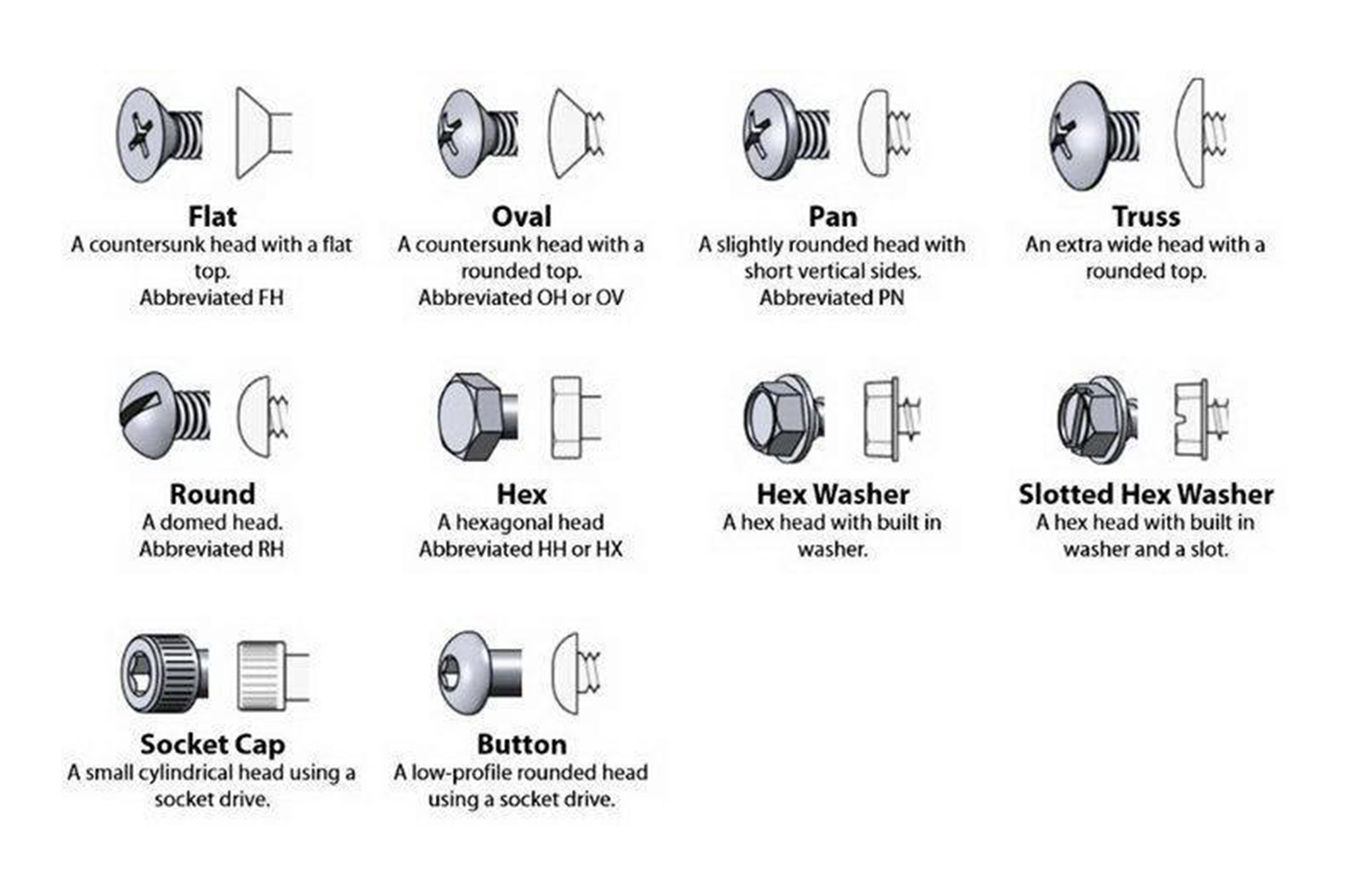
Illustrative image related to different types of bolt heads
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Bolt Head Design?
Aluminum is lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making it a popular choice for applications where weight is a critical factor. It has good thermal and electrical conductivity, but its strength is lower than that of steel. Aluminum bolt heads are often used in aerospace and automotive applications.
Pros: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and good thermal properties.
Cons: Lower strength compared to steel, can be more expensive.
Impact on Application: Ideal for applications in the aerospace and automotive industries where weight savings are crucial.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM B211 or DIN EN 573 is important, especially in the aerospace sector in Europe.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Bolt Heads
| Material | Typical Use Case for different types of bolt heads | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Structural applications in dry environments | High strength and cost-effective | Prone to corrosion without coating | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Marine and chemical processing applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and machining difficulty | High |
| Brass | Electrical fittings and decorative applications | Good machinability and corrosion resistance | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
| Aluminum | Aerospace and automotive applications | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength than steel | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of various materials used for bolt heads, enabling informed purchasing decisions tailored to specific application needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for different types of bolt heads
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Bolt Heads?
The manufacturing process for bolt heads involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure precision and quality. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Illustrative image related to different types of bolt heads
-
Material Preparation: The initial stage involves selecting the appropriate materials, typically carbon steel, stainless steel, or alloy steel, depending on the desired properties of the bolt head. The material is cut into manageable sizes, often in the form of rods or bars, and subjected to processes like heat treatment to enhance its mechanical properties.
-
Forming: This stage is crucial as it shapes the raw material into the desired bolt head configuration. Techniques such as cold heading, die stamping, and forging are commonly employed. Cold heading is particularly favored for its efficiency in producing high volumes with minimal waste, where the material is deformed into the required shape without the application of heat. Die stamping and forging may be used to produce complex geometries or heavier-duty components.
-
Assembly: Once the heads are formed, they may need to be assembled with other components, such as washers or nuts, especially for specialized bolt types. This stage ensures that all parts fit together seamlessly to meet design specifications.
-
Finishing: The final manufacturing stage involves surface treatments, such as galvanizing, anodizing, or coating, to enhance corrosion resistance and improve aesthetic appeal. This step not only protects the bolt but also ensures compliance with industry standards for various applications.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Bolt Head Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of bolt heads to ensure that they meet international standards and customer specifications. The following key components are integral to the QA process:
-
Adherence to International Standards: Compliance with standards such as ISO 9001 is essential for maintaining a quality management system. This certification demonstrates a commitment to quality across all manufacturing processes. Industry-specific standards like API (American Petroleum Institute) for oil and gas applications or CE marking for European markets further ensure that bolt heads meet safety and performance requirements.
-
Quality Control Checkpoints: The QA process involves several critical checkpoints:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing checks are conducted to monitor key parameters such as dimensional accuracy and surface finish. This may include using precision measuring instruments and visual inspections.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the manufacturing process is complete, the final products undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet all specifications. This may include tensile testing, hardness testing, and non-destructive testing methods like ultrasonic or magnetic particle inspection.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Bolt Head Quality Assurance?
Testing methods play a crucial role in confirming the integrity and performance of bolt heads. Commonly used methods include:
-
Tensile Testing: Measures the material’s strength and ductility by applying a tensile load until failure. This test provides critical data on the bolt’s ability to withstand operational stresses.
-
Hardness Testing: Assesses the surface hardness of the bolt, which is indicative of its wear resistance and durability. Techniques like Rockwell or Brinell hardness tests are frequently employed.
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or dye penetrant inspection are utilized to detect internal flaws or surface cracks without damaging the bolt. These methods are essential for ensuring the reliability of bolts in critical applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, especially those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is vital for ensuring product reliability and compliance. Here are some effective strategies:

Illustrative image related to different types of bolt heads
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting thorough audits of potential suppliers is one of the most effective ways to assess their quality assurance practices. Audits should evaluate their adherence to international standards, the integrity of their QA processes, and their production capabilities.
-
Requesting Quality Assurance Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed QA documentation, including test results, inspection reports, and certifications. This transparency allows buyers to evaluate the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturing process and the quality of the finished products. These inspections can help ensure compliance with international standards and provide an additional layer of confidence in the supplier’s capabilities.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various quality control and certification nuances when sourcing bolt heads. Understanding these aspects is crucial for successful procurement:
-
Regional Standards Compliance: Different regions may have specific standards and certifications that must be met. For instance, European buyers often require CE marking, while those in North America may prioritize ASTM standards. Familiarizing oneself with these requirements is essential for compliance.
-
Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Buyers should be aware of the cultural and regulatory differences that may impact quality control practices. In regions with stringent regulations, such as Germany, suppliers may have more robust QA processes than in other markets.
-
Language Barriers: Language differences can pose challenges in understanding quality documentation and standards. Buyers should ensure that suppliers provide documentation in a language they comprehend, or consider employing translation services.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for bolt heads is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on key stages of production, rigorous quality control measures, and effective supplier verification strategies, buyers can ensure they source high-quality, reliable fasteners for their applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘different types of bolt heads’
In the fast-paced world of B2B procurement, sourcing the right bolt heads is crucial for ensuring the integrity and performance of your projects. This practical sourcing guide provides a step-by-step checklist to help you navigate the complexities of selecting different types of bolt heads, allowing you to make informed purchasing decisions that align with your operational needs.

Illustrative image related to different types of bolt heads
1. Identify Your Project Requirements
Understanding your specific project requirements is the first step in sourcing bolt heads. Determine the load-bearing capacity, environmental conditions, and the materials being joined. This ensures you select the appropriate bolt head type, whether it be hex, socket, or another style, tailored to the demands of your application.
2. Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical specifications for the bolt heads you need. This includes dimensions, thread type, material (e.g., stainless steel, carbon steel), and finish (e.g., galvanized, coated). Accurate specifications will prevent costly mistakes and ensure compatibility with other components in your assembly.
3. Research Different Bolt Head Types
Familiarize yourself with the various bolt head types available in the market. Common options include hex heads, socket heads, and flange bolts, each offering distinct advantages for different applications. Understanding these types will help you select the best fit for your project, enhancing performance and reliability.
4. Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Assess their manufacturing capabilities and track record in delivering quality products on time, as this will impact your supply chain efficiency.
5. Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that your chosen suppliers meet relevant industry standards and certifications. Look for compliance with international quality standards such as ISO 9001 or specific industry regulations. This verification process mitigates risks associated with substandard products and enhances confidence in your procurement decisions.

Illustrative image related to different types of bolt heads
6. Request Samples for Testing
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the bolt heads for testing. This step allows you to evaluate their performance under actual conditions relevant to your application. Testing samples can reveal potential issues early on, saving you time and resources in the long run.
7. Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve selected a supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, lead times, and payment terms. Clear communication about your expectations and requirements will establish a mutually beneficial relationship. Ensure all agreements are documented to avoid misunderstandings in the future.
By following this checklist, you can streamline your sourcing process for bolt heads, ensuring that you select the right components for your projects while building reliable supplier relationships. This proactive approach not only enhances project outcomes but also contributes to overall operational efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for different types of bolt heads Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components Involved in Sourcing Different Types of Bolt Heads?
When sourcing various types of bolt heads, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The main cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts the cost. Common materials for bolt heads include carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel. Stainless steel, while more expensive, offers superior corrosion resistance and longevity, making it a preferred choice for outdoor or industrial applications.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly based on the manufacturing location. Countries with lower labor costs may offer more competitive pricing; however, this can come at the expense of quality or lead times. Skilled labor is necessary for high-precision manufacturing processes, which can elevate costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, including utilities, maintenance, and factory management. In regions with higher operational costs, these expenses can significantly influence the final pricing of bolt heads.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, particularly for custom or specialized bolt head designs. This cost is typically amortized over the production run, meaning larger orders can result in lower per-unit costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are essential to ensure product reliability and compliance with industry standards. The costs associated with QC, including testing and inspection, should be factored into the overall pricing.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary greatly depending on the distance and method of transport. International buyers must consider both freight costs and the potential for tariffs or customs duties, which can add to the total cost.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary widely based on market conditions and competition. Understanding the supplier’s pricing strategy can help buyers negotiate better deals.
What Influences the Pricing of Bolt Heads in International Markets?
Several factors influence the pricing of bolt heads, especially in the international market:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can affect pricing. Larger orders often lead to bulk discounts, making it crucial for buyers to assess their needs accurately.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific material requirements can lead to increased costs. Buyers should ensure that any customization aligns with their project requirements to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet international quality standards or possess certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) typically command higher prices. Buyers should assess the necessity of these certifications based on their application.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more but can offer better assurance of product performance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is essential for pricing clarity. These terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping, which can affect overall costs significantly.
What Negotiation Tips Can Help Buyers Achieve Cost-Efficiency?
B2B buyers should consider the following tips to enhance negotiation outcomes and cost-efficiency:
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the purchase price, consider the long-term costs associated with the product, including maintenance, replacement, and disposal. This perspective can guide purchasing decisions.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If feasible, consolidate orders to meet MOQs and secure better pricing. This strategy can reduce costs per unit and improve cash flow.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better terms and pricing flexibility. Regular communication can also provide insights into market trends and potential savings.
-
Research Market Trends: Staying informed about market conditions, including material costs and supply chain disruptions, can provide leverage during negotiations. Knowledge of competitor pricing can also strengthen a buyer’s position.
What Pricing Nuances Should International Buyers Consider?
For international buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several pricing nuances should be considered:
-
Currency Fluctuations: Exchange rate volatility can impact pricing. Buyers should consider hedging strategies or negotiate prices in stable currencies.
-
Customs and Duties: Understanding the implications of tariffs and customs regulations can prevent unexpected costs. It’s advisable to engage with logistics experts to navigate these complexities effectively.
-
Cultural Considerations: Different regions may have varying negotiation styles and expectations. Being aware of these cultural nuances can facilitate smoother discussions and foster better relationships.
Disclaimer
The prices mentioned herein are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Always consult with multiple suppliers to obtain the most accurate pricing tailored to your unique needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing different types of bolt heads With Other Solutions
Introduction
When selecting fastening solutions, B2B buyers must consider various factors that impact performance, cost, and suitability for specific applications. While different types of bolt heads serve critical roles in assembly and fastening, there are alternative solutions that may offer competitive advantages depending on the context. This analysis compares traditional bolt heads with two viable alternatives: rivets and adhesive bonding, providing insights to help buyers make informed decisions.
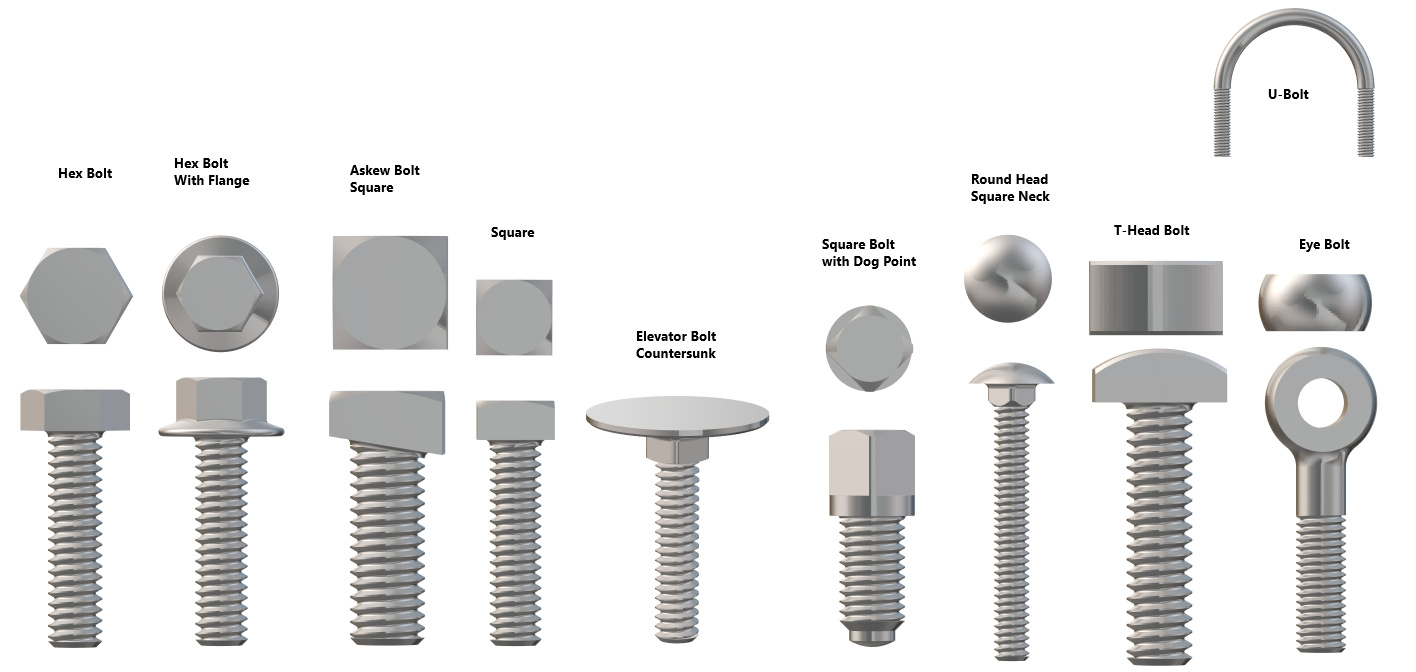
Illustrative image related to different types of bolt heads
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Different Types of Bolt Heads | Rivets | Adhesive Bonding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength and reliability; suitable for dynamic loads | Very strong in shear; best for static loads | Excellent for uniform stress distribution; limited in load-bearing |
| Cost | Moderate cost; requires nuts and washers | Generally lower cost; no nuts required | Variable; depends on type and application, can be cost-effective in large volumes |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires tools for installation; straightforward but labor-intensive | Simple installation; requires special tools for certain types | Requires surface preparation; curing time can delay assembly |
| Maintenance | Can be disassembled for maintenance; reusable | Permanent; cannot be removed without destruction | Permanent; removal can be challenging and damaging |
| Best Use Case | Mechanical assemblies, heavy machinery | Aircraft, automotive, and structural applications | Lightweight materials, electronic components, and where aesthetics are important |
Detailed Breakdown
Rivets
Rivets are permanent mechanical fasteners that create a strong joint by deforming the rivet’s tail after insertion, securing the components together. They excel in shear strength, making them ideal for applications where static loads are prevalent, such as in aerospace and automotive industries. However, rivets cannot be easily removed or replaced without damaging the surrounding materials, which can complicate maintenance and repairs. Additionally, the installation process may require specific tools, particularly for blind rivets.
Adhesive Bonding
Adhesive bonding involves using adhesives to join materials, providing a uniform distribution of stress across the bonding surface. This method is particularly useful for lightweight materials and applications where aesthetics are essential, such as in electronics and furniture manufacturing. While adhesive bonding can be cost-effective in large volumes, it requires careful surface preparation and curing time, which can delay production schedules. Additionally, while adhesives can be very strong, they may not be suitable for high-load applications or environments subject to extreme conditions.
Conclusion
Choosing the right fastening solution requires a comprehensive assessment of project requirements, including load characteristics, environmental conditions, and long-term maintenance considerations. Different types of bolt heads offer significant advantages in terms of strength and reusability, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. However, alternatives like rivets and adhesive bonding may provide cost or implementation benefits in specific scenarios. By analyzing the pros and cons of each option, B2B buyers can select the most effective fastening solution tailored to their unique needs.
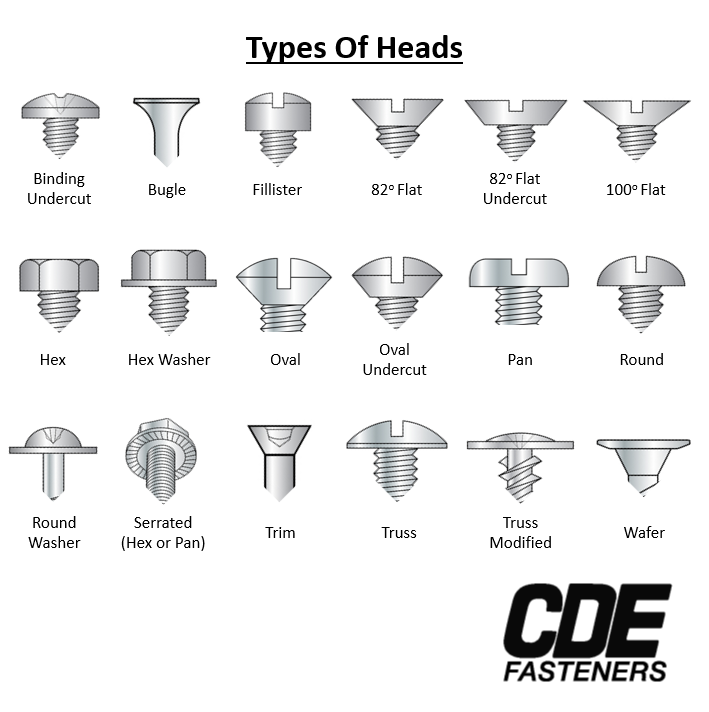
Illustrative image related to different types of bolt heads
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for different types of bolt heads
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Different Bolt Heads?
Understanding the critical specifications of bolt heads is essential for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing products for manufacturing or construction projects. Here are some key properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material grade of a bolt head determines its strength, corrosion resistance, and suitability for specific applications. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel, each offering distinct properties. For instance, stainless steel bolts are ideal for marine environments due to their corrosion resistance, while carbon steel is often used in structural applications due to its strength and cost-effectiveness. Selecting the right material grade ensures durability and longevity, reducing the need for frequent replacements. -
Thread Specifications
The thread type and pitch are crucial for ensuring compatibility with nuts and other threaded components. Common thread types include UNC (Unified National Coarse), UNF (Unified National Fine), and metric threads. The choice of thread affects the ease of assembly and the load-bearing capacity of the joint. Understanding thread specifications helps buyers ensure that components fit together seamlessly, minimizing assembly time and potential failures. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance defines the permissible limits of variation in a physical dimension. In the context of bolt heads, this includes diameter, length, and thread pitch. Precise tolerances are vital for applications requiring tight fits, such as in machinery and automotive sectors. Poor tolerance can lead to misalignment or failure of the assembly, impacting overall performance and safety. Buyers should request tolerance specifications to ensure compliance with industry standards. -
Coating and Finish
The coating on bolt heads can significantly influence their performance, especially in harsh environments. Common coatings include zinc plating, hot-dip galvanizing, and powder coating, each providing varying degrees of corrosion resistance. Selecting the appropriate finish helps in prolonging the life of the bolts and ensuring they perform well under specific environmental conditions. Buyers should consider the application when evaluating coating options. -
Load Capacity
Load capacity indicates how much weight a bolt can safely support without failure. This specification is critical in construction and heavy machinery applications, where the safety and stability of structures depend on the integrity of the fasteners used. Understanding load capacity allows buyers to select bolts that meet or exceed the requirements of their specific applications, ensuring safety and reliability.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Bolt Heads?
Familiarity with industry jargon can enhance communication and negotiation between buyers and suppliers. Here are some common terms that B2B buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of bolts, buyers often source OEM parts to ensure compatibility with existing systems. Understanding OEM specifications helps in making informed purchasing decisions. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for budgeting and inventory management, as it can impact the overall cost of procurement. Buyers should evaluate their needs against MOQs to optimize their purchasing strategy. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers requesting price quotes for specific products or services. Including detailed specifications for bolt heads in an RFQ ensures that suppliers provide accurate pricing and lead times, facilitating better decision-making. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is essential for managing shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities associated with bolt head procurement across borders. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. This metric is vital for project planning and can vary significantly based on supplier capacity and logistics. Buyers should factor in lead times when scheduling production to avoid delays.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring the right bolt heads are sourced for their specific applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the different types of bolt heads Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Affecting Bolt Head Sourcing?
The global fastener market, particularly for different types of bolt heads, is witnessing significant transformations driven by technological advancements, economic shifts, and changing consumer preferences. Key drivers include the rapid industrialization in emerging markets like Africa and South America, where infrastructure development is gaining momentum. In Europe, particularly in Germany, there is a strong push towards automation and smart manufacturing, which increases the demand for precision-engineered fasteners.
Current B2B sourcing trends are increasingly focused on digital platforms that facilitate easier access to suppliers and products. E-commerce platforms are becoming vital for international buyers, allowing them to compare prices, quality, and lead times effectively. Additionally, the rise of Industry 4.0 technologies is enabling manufacturers to optimize production processes, leading to innovations in bolt head designs and materials. Buyers should pay attention to emerging materials such as high-strength steel and corrosion-resistant alloys, which enhance the performance of bolt heads in demanding applications.

Illustrative image related to different types of bolt heads
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Changing the Bolt Head Industry?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of B2B operations, especially in the fastener sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, is under scrutiny. International buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adopt sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and implementing eco-friendly manufacturing processes.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as businesses are held accountable for their supply chains. Certifications like ISO 14001 and adherence to international labor standards are becoming essential for suppliers looking to attract B2B buyers. The use of green certifications can provide assurance that the materials used for bolt heads are sourced responsibly, contributing to a company’s overall sustainability goals. This focus on ethical sourcing not only mitigates risks but also enhances brand reputation, which is increasingly significant for buyers in competitive markets.
What Is the Historical Context of Bolt Head Development?
The evolution of bolt heads can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where rudimentary fastening methods were employed for construction and machinery. As industrialization progressed in the 19th century, the need for standardized fasteners became evident, leading to the development of various bolt head designs to meet specific applications. Innovations such as the hexagonal head and the socket cap head emerged to improve torque application and ease of installation.
Today, the fastener industry continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements and the demand for more efficient, high-performance products. Modern manufacturing techniques such as cold heading and powder metallurgy have significantly enhanced the precision and durability of bolt heads, enabling them to meet the rigorous demands of various industries, from automotive to construction. Understanding this historical context helps international buyers appreciate the complexities of sourcing high-quality bolt heads suited to their specific needs.
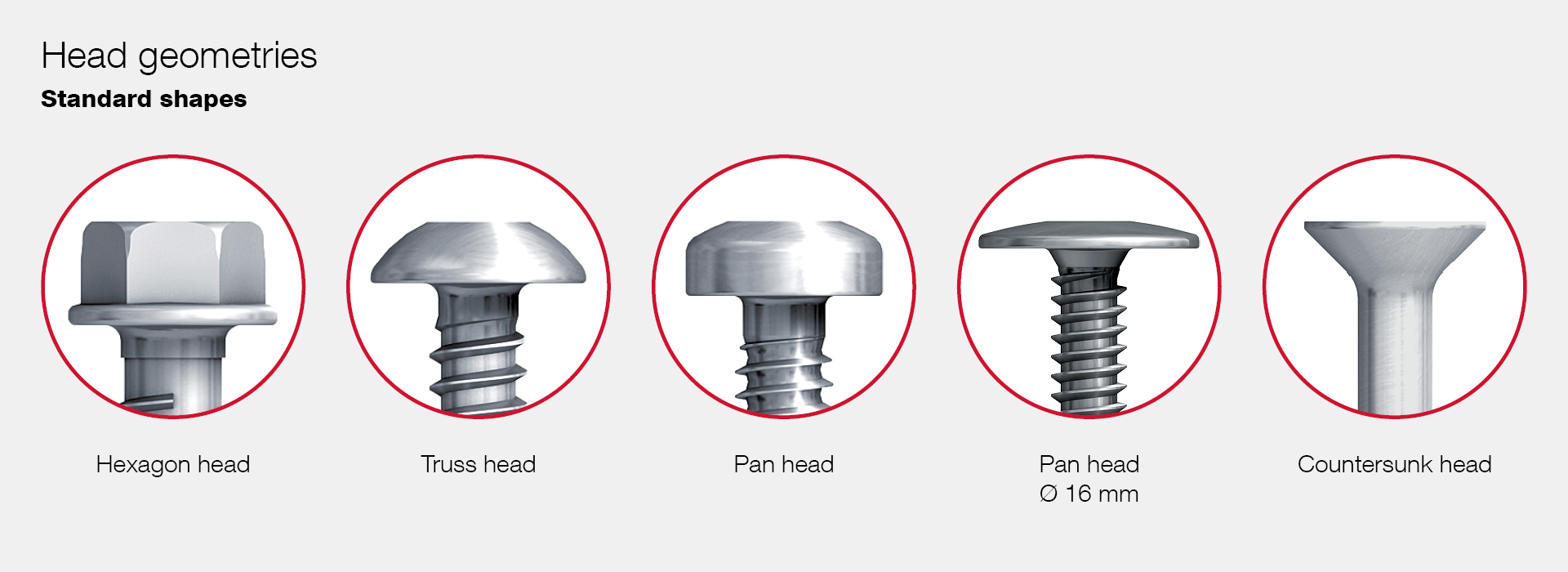
Illustrative image related to different types of bolt heads
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of different types of bolt heads
1. How do I choose the right bolt head type for my project?
Selecting the appropriate bolt head type depends on several factors, including the material being fastened, the environment, and the application. For instance, hex bolts are ideal for high-torque applications, while socket screws offer better accessibility in tight spaces. Additionally, consider the aesthetic requirements and whether the head type will be exposed. Understanding the specific needs of your project can guide you to the best choice, ensuring both functionality and longevity.
2. What are the advantages of using hex head bolts over other types?
Hex head bolts are favored for their strength and ease of use. They provide a larger surface area for wrenching, allowing for higher torque application without stripping. Their design also minimizes slippage, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Moreover, hex head bolts are widely available and compatible with various nuts and washers, which simplifies sourcing and assembly processes, especially in international markets.
3. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for bolt heads when sourcing internationally?
Minimum order quantities for bolt heads can vary significantly based on the supplier, material, and manufacturing processes involved. Typically, MOQs can range from 100 to several thousand pieces. When negotiating with suppliers, inquire about their flexibility on MOQs, especially if you are testing a new product line or project. Additionally, consider the potential for bulk discounts if you plan to order larger quantities in the future.
4. How can I ensure the quality of bolt heads from international suppliers?
To ensure quality, start by vetting suppliers through certifications such as ISO or ASTM standards, which indicate adherence to international manufacturing practices. Request samples for testing before committing to larger orders, and consider conducting third-party quality inspections if feasible. Establish clear quality assurance protocols in your purchasing agreements, including specifications for materials, dimensions, and performance criteria.
5. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing bolt heads internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely depending on the supplier’s location and credibility. Common arrangements include letters of credit, advance payments, or net payment terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60 days). It is advisable to negotiate terms that protect your interests while ensuring the supplier’s confidence. Research local payment practices and consider using secure payment platforms to mitigate risks associated with international transactions.
6. How do I handle logistics and shipping for bolt head orders?
Effective logistics management is crucial when importing bolt heads. Coordinate with suppliers to understand their shipping options and lead times. Consider the total landed cost, which includes shipping fees, customs duties, and potential tariffs. Engage a reliable freight forwarder who can assist with documentation and customs clearance, ensuring compliance with regulations in your destination country.
7. Are custom bolt head designs available, and what is the process?
Yes, many suppliers offer custom bolt head designs to meet specific project requirements. The process typically involves submitting detailed specifications, including dimensions, materials, and any unique features. Collaborate closely with the supplier’s engineering team to refine your design, and be prepared for potential prototyping phases. Custom designs may require larger MOQs and longer lead times, so plan accordingly.
8. What factors should I consider when sourcing bolt heads from different regions?
When sourcing bolt heads internationally, consider factors like regional manufacturing capabilities, material availability, and local standards. Additionally, assess the political and economic stability of the supplier’s country, as these can impact production and delivery timelines. Communication styles and time zone differences may also influence collaboration. Building strong relationships with suppliers in target regions can enhance reliability and ease of doing business.
Top 6 Different Types Of Bolt Heads Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Bolt Depot – Fasteners & Screws
Domain: boltdepot.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Fastener Categories: Wood Screws (WS), Machine Screws (MS), Thread Cutting Machine Screws, Sheet Metal Screws (SMS), Self Drilling Screws, Hex Bolts (HHMB or HXBT), Carriage Bolts, Lag Bolts, Flange Bolts, Socket Screws, Eye Bolts, Eye Lags, U-Bolts, J-Bolts, Shoulder Bolts, Elevator Bolts, Sex Bolts, Mating Screws, Hanger Bolts, Set Screws. Head Styles: Flat (FH), Oval (OH or OV), Pan (PN), Truss…
2. Reddit – Bolt Head Replacement Guide
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The bolt head in question is typically used with metal or plastic knobs, featuring wings that are pressed into the knob material for a friction fit to prevent slippage. It is suggested to replace the bolt with one of the same length and threading, possibly with a thumb screw head. The original design is identified as a flange bolt, which had a plastic handle formed around the head during manufactu…
3. Digi-Key – Common Fastener Head Types
Domain: forum.digikey.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: This company, Digi-Key – Common Fastener Head Types, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. Screw Types – Key Advantages and Disadvantages
Domain: diy.stackexchange.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Different types of screws include Phillips, flat, hex (Allen), star (Torx), and Robertson. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages:
– Slotted (flat) screws are cheap and easy to manufacture but prone to slipping and stripping.
– Phillips screws are self-centering and allow for powered screwdrivers but can cam-out under high torque.
– Robertson (square) and Allen (hex) screws can handle m…
5. TFG USA – Diverse Bolt Solutions
Domain: tfgusa.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Different types of bolts include Hex Bolts, Carriage Bolts, Lag Bolts, U-Bolts, Eye Bolts, J-Bolts, Anchor Bolts, Shoulder Bolts, Elevator Bolts, Tension Control Bolts (TC Bolts), Flange Bolts, and Plow Bolts. Bolt drives include Hex Drive, Slotted Drive, Phillips Drive, Torx Drive, Square Drive (Robertson), and External Hex Drive. Common bolt head styles are Hex Head, Countersunk Head, Dome or Bu…
6. GC Fasteners – Common Bolt and Screw Heads
Domain: gcfasteners.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Common Types of Bolt and Screw Heads: 1. Pan Heads: Large surface area for easy grip with slotted or flat drivers; recommended for new designs. 2. Round Heads: Previously popular but largely replaced by pan heads; not recommended for new designs. 3. Fillister Heads: Smaller diameter than round heads, allowing for more pressure application; deeper slots for assembly close to flanges. 4. Truss Heads…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for different types of bolt heads
In navigating the diverse landscape of bolt heads, B2B buyers must prioritize strategic sourcing to enhance operational efficiency and product reliability. Understanding the unique characteristics of various bolt head types—such as hex, socket cap, and truss—enables businesses to select the most suitable fasteners for their specific applications, thus reducing the risk of assembly failures. Additionally, sourcing high-quality materials from reputable suppliers ensures durability and compliance with international standards, which is particularly crucial for markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
The ongoing evolution of manufacturing technologies and the increasing emphasis on sustainability present both challenges and opportunities for international buyers. As industries shift toward more eco-friendly practices, sourcing from suppliers who prioritize sustainable materials and processes will not only enhance corporate responsibility but also improve market competitiveness.
As we look to the future, it is vital for B2B buyers to remain proactive in their sourcing strategies. Engage with suppliers who can provide innovative solutions and insights tailored to your specific industry needs. By doing so, you can ensure that your projects are not only successful but also positioned for long-term growth and sustainability.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.