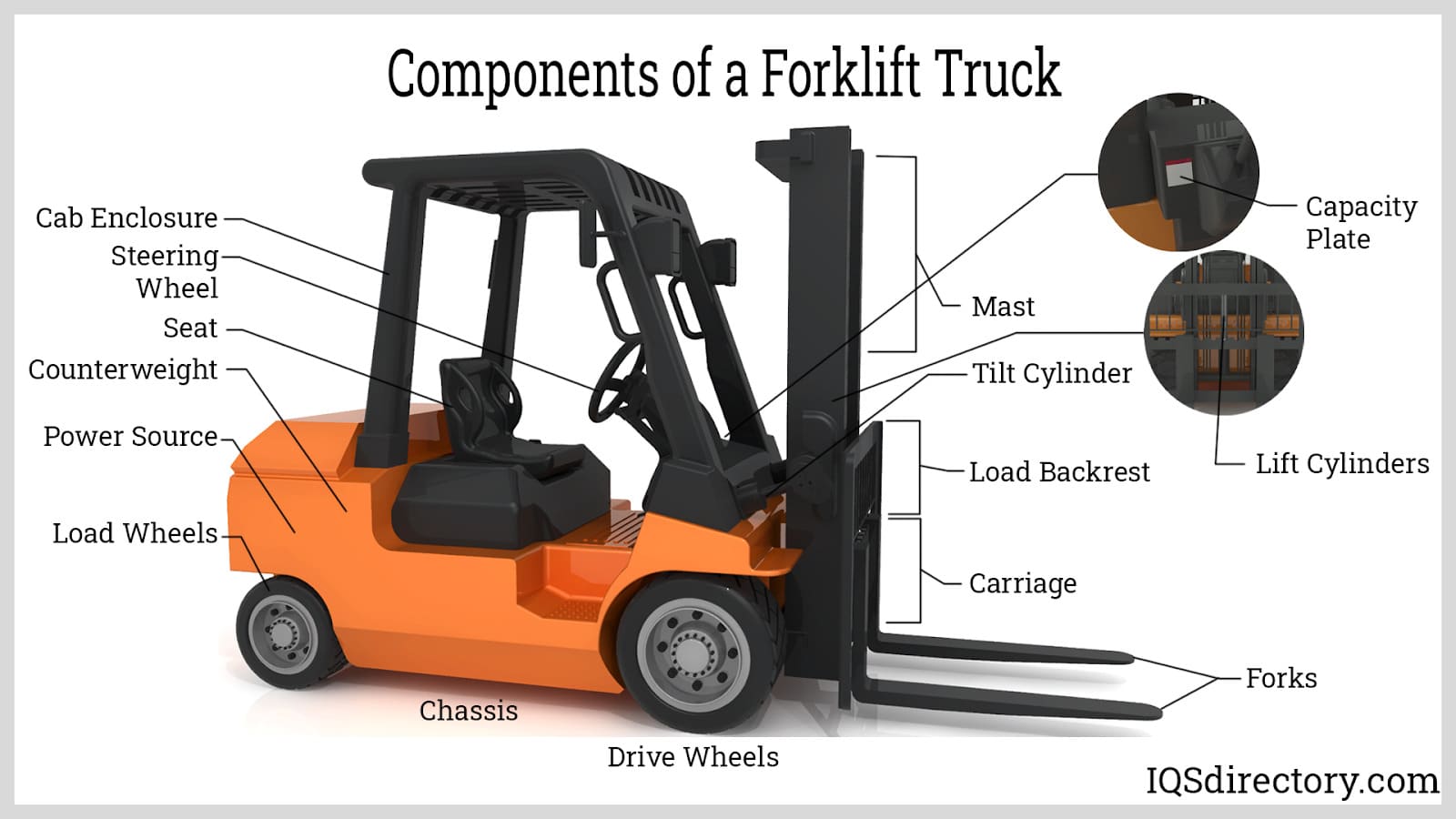
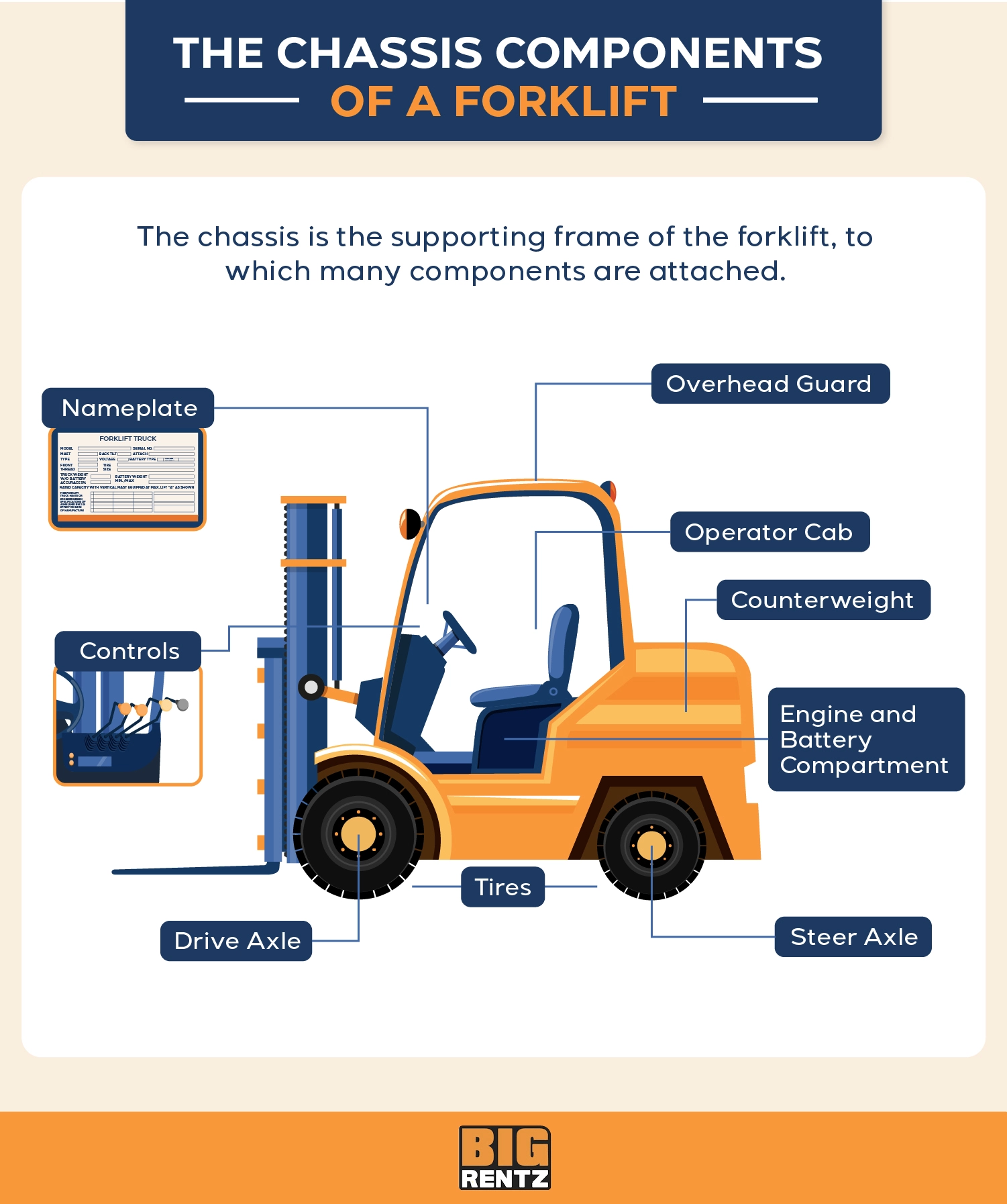
Choosing Your Components Of A Forklift Truck: Key Specs to Compare in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for components of a forklift truck
In the competitive landscape of material handling, sourcing high-quality components for forklift trucks presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to expand, understanding the intricacies of forklift components—from the mast and chassis to essential attachments—is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, detailing various types of forklift components, their applications, and the critical factors to consider when selecting suppliers.
Navigating the complexities of the global market requires an informed approach to purchasing decisions. With insights into supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and potential applications of different forklift types, this guide empowers buyers to make strategic choices that align with their business needs. Whether you’re operating in a warehouse in Germany or managing a construction site in Nigeria, understanding the functionalities and specifications of forklift components will enhance your ability to select the right equipment for your operations.
By leveraging the information provided, B2B buyers can streamline their procurement processes, ensuring they acquire reliable and efficient forklift components that support their operational goals. Dive into this guide to unlock actionable insights that will help you navigate the global market with confidence.
Understanding components of a forklift truck Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Counterbalance Forklift | Rear counterweight for stability; versatile for heavy loads | Warehousing, distribution, manufacturing | Pros: High lifting capacity; good maneuverability. Cons: Requires adequate space for operation. |
| Reach Truck | Extended forks for narrow aisles; designed for vertical lifting | Warehouses, narrow aisle storage | Pros: Excellent for maximizing vertical space. Cons: Limited outdoor use; lower weight capacity. |
| Rough Terrain Forklift | Large, rugged tires; higher ground clearance | Construction sites, outdoor applications | Pros: Stability on uneven terrain; versatile. Cons: Less maneuverable in tight spaces. |
| Telehandler | Extendable boom for versatile lifting; can reach higher elevations | Construction, agriculture | Pros: Multi-functional; can handle various attachments. Cons: Requires specialized training. |
| Warehouse Forklift | Compact design; cushioned tires for smooth surfaces | Indoor storage, factories | Pros: Ideal for tight spaces; easy to operate. Cons: Limited outdoor capability. |
What Are the Characteristics of Counterbalance Forklifts?
Counterbalance forklifts are designed with a rear counterweight that offsets the load being lifted at the front. This configuration allows for the safe lifting of heavy loads, making them ideal for various applications in warehousing, distribution, and manufacturing. When considering a counterbalance forklift, buyers should evaluate the lifting capacity and the available space for maneuvering, as these forklifts require ample room to operate effectively.
How Do Reach Trucks Maximize Space in Warehouses?
Reach trucks are specialized for narrow aisle operations, featuring extended forks that allow them to reach deep into racking systems. This design is particularly advantageous for warehouses looking to maximize vertical storage space. Buyers should consider the height of their racking systems and the lift capacity needed when selecting a reach truck, as these vehicles are optimized for indoor use and may not perform well on uneven outdoor surfaces.
Why Choose Rough Terrain Forklifts for Construction Sites?
Rough terrain forklifts are built with large, rugged tires and increased ground clearance, enabling them to navigate challenging outdoor conditions such as loose gravel or rocky landscapes. They are commonly used on construction sites and in agricultural applications where stability is crucial. Buyers should assess the terrain they will be operating in and consider the trade-off between stability and maneuverability when selecting this type of forklift.
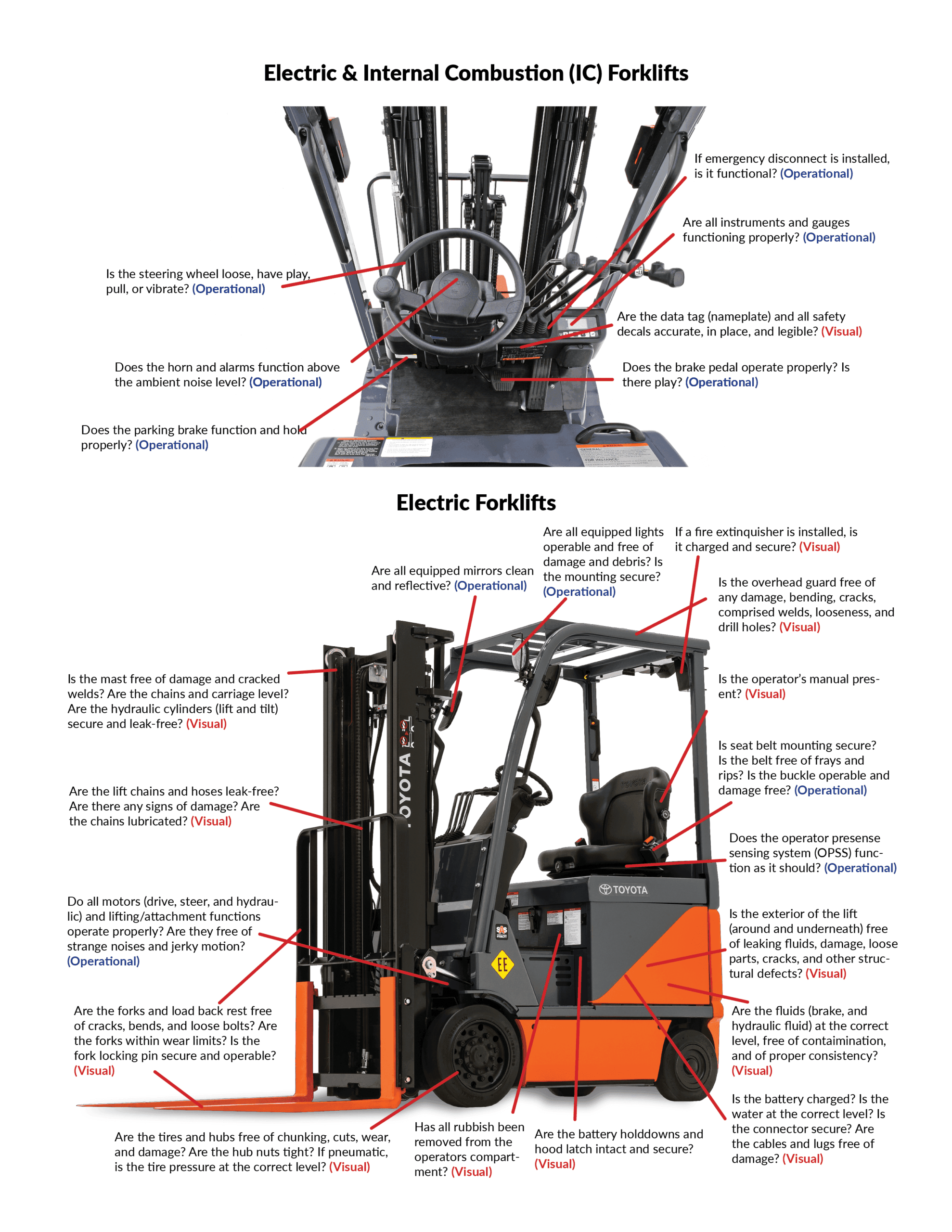
Illustrative image related to components of a forklift truck
What Advantages Do Telehandlers Offer in Various Industries?
Telehandlers, or telescopic handlers, feature an extendable boom that allows for versatile lifting capabilities, including reaching high elevations. They can be equipped with a variety of attachments, making them suitable for construction and agricultural tasks. However, buyers should be aware that operating a telehandler requires specialized training, and they should evaluate the specific lifting needs of their projects to ensure the right model is selected.
How Do Warehouse Forklifts Enhance Efficiency in Indoor Operations?
Warehouse forklifts are designed for indoor use, featuring a compact design and cushioned tires that provide stability on smooth surfaces. They excel in maneuvering within tight spaces, making them ideal for factories and storage facilities. When purchasing a warehouse forklift, businesses should consider the layout of their operations and the types of loads they will be handling to ensure optimal efficiency and safety.
Key Industrial Applications of components of a forklift truck
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of components of a forklift truck | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Warehousing & Logistics | Use of electric forklifts with advanced control systems | Increased efficiency in inventory management | Focus on battery life, maintenance support, and operational costs |
| Construction | Heavy-duty forklifts for transporting materials on-site | Improved safety and productivity in rugged terrains | Ensure compliance with local safety regulations and terrain adaptability |
| Agriculture | Rough-terrain forklifts for moving crops and supplies | Enhanced productivity and reduced manual labor | Look for specialized attachments for handling diverse agricultural loads |
| Manufacturing | Forklift attachments for assembly line operations | Streamlined processes and reduced downtime | Assess compatibility with existing equipment and required load capacities |
| Retail | Warehouse forklifts for stock replenishment and order picking | Faster turnaround times and improved customer service | Evaluate the forklift’s maneuverability in confined spaces and load capacity |
How Are Forklift Components Used in Warehousing & Logistics?
In warehousing and logistics, electric forklifts equipped with advanced control systems are essential for managing inventory. These forklifts allow operators to navigate tight spaces while efficiently lifting and transporting goods. By optimizing space and reducing the time taken for stock management, businesses can achieve significant cost savings. Buyers should consider battery life, maintenance support, and total operational costs when sourcing these components, especially in regions with varying power supply reliability.
What Role Do Forklifts Play in Construction?
Heavy-duty forklifts are crucial in the construction sector for transporting materials across job sites. Their robust design enables them to operate efficiently on rugged terrains, enhancing both safety and productivity. These forklifts can handle large loads, minimizing the risk of workplace accidents and delays. When sourcing, companies should ensure that the equipment complies with local safety regulations and can adapt to the specific conditions of their construction sites.
How Are Forklifts Beneficial in Agriculture?
In agriculture, rough-terrain forklifts are employed to move crops and supplies across uneven fields. Their specialized tires and powerful lifting capabilities allow them to operate effectively in challenging environments, significantly enhancing productivity and reducing the need for manual labor. Buyers should look for forklifts with attachments tailored for agricultural use, ensuring they can handle various load types and sizes, which is particularly important in diverse agricultural markets.
What Advantages Do Forklifts Offer in Manufacturing?
In manufacturing, forklifts equipped with various attachments streamline assembly line operations. These components facilitate quick loading and unloading of materials, reducing downtime and increasing throughput. Businesses benefit from improved operational efficiency and reduced labor costs. When sourcing, it’s vital to assess the compatibility of attachments with existing equipment and ensure they meet specific load capacity requirements to maintain production efficiency.
How Do Forklifts Enhance Retail Operations?
In retail, warehouse forklifts play a key role in stock replenishment and order picking. Their ability to quickly move goods from storage to the sales floor enhances customer service by ensuring products are readily available. This leads to faster turnaround times and improved sales. Buyers should evaluate the maneuverability of forklifts in confined retail spaces and the load capacities required to meet their operational demands effectively.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘components of a forklift truck’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Maintenance Costs for Forklift Components
The Problem:
B2B buyers, particularly in industries reliant on forklifts, often face the challenge of escalating maintenance costs associated with forklift components. Components like hydraulic systems, drive axles, and tires can wear out quickly, especially in high-use scenarios. This not only disrupts operational efficiency but also leads to unexpected downtime, which can be costly. In regions with limited access to reliable suppliers or service centers, sourcing quality replacement parts can become a logistical nightmare, further complicating the situation.

Illustrative image related to components of a forklift truck
The Solution:
To effectively manage maintenance costs, B2B buyers should prioritize building relationships with reputable suppliers who specialize in high-quality forklift components. Establishing a maintenance schedule that aligns with the operational demands of your business is crucial; this may include regular inspections and timely replacements of wear-prone parts like tires and hydraulic seals. Investing in telematics can provide insights into component wear and performance, allowing for predictive maintenance. Additionally, consider sourcing OEM parts or certified aftermarket components to ensure compatibility and durability, ultimately reducing long-term costs.
Scenario 2: Understanding Forklift Component Compatibility Issues
The Problem:
One common pain point for buyers is the challenge of ensuring component compatibility across different forklift models. With various manufacturers producing forklifts with distinct specifications, purchasing parts that do not fit can lead to additional expenses and project delays. This problem is particularly acute for businesses operating a fleet with diverse forklift types, making it difficult to standardize parts and maintenance practices.
The Solution:
To avoid compatibility issues, B2B buyers should maintain a comprehensive inventory of their fleet’s specifications, including model numbers, component sizes, and any aftermarket modifications. Before purchasing components, consult with manufacturers or authorized dealers to confirm compatibility. Creating a centralized database of parts and their specifications can streamline the procurement process and help in quickly identifying suitable replacements when needed. Additionally, consider investing in modular components that offer flexibility across multiple models, thus simplifying maintenance and reducing costs.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Operator Safety with Forklift Components
The Problem:
Safety concerns related to forklift operation are paramount, especially regarding components like the overhead guard, brakes, and operator cab design. Many buyers struggle to ensure that their forklifts are equipped with the latest safety features, which can lead to accidents and injuries on the job site. In regions with varying safety regulations, keeping up with compliance can also be a daunting task, particularly for international operations.
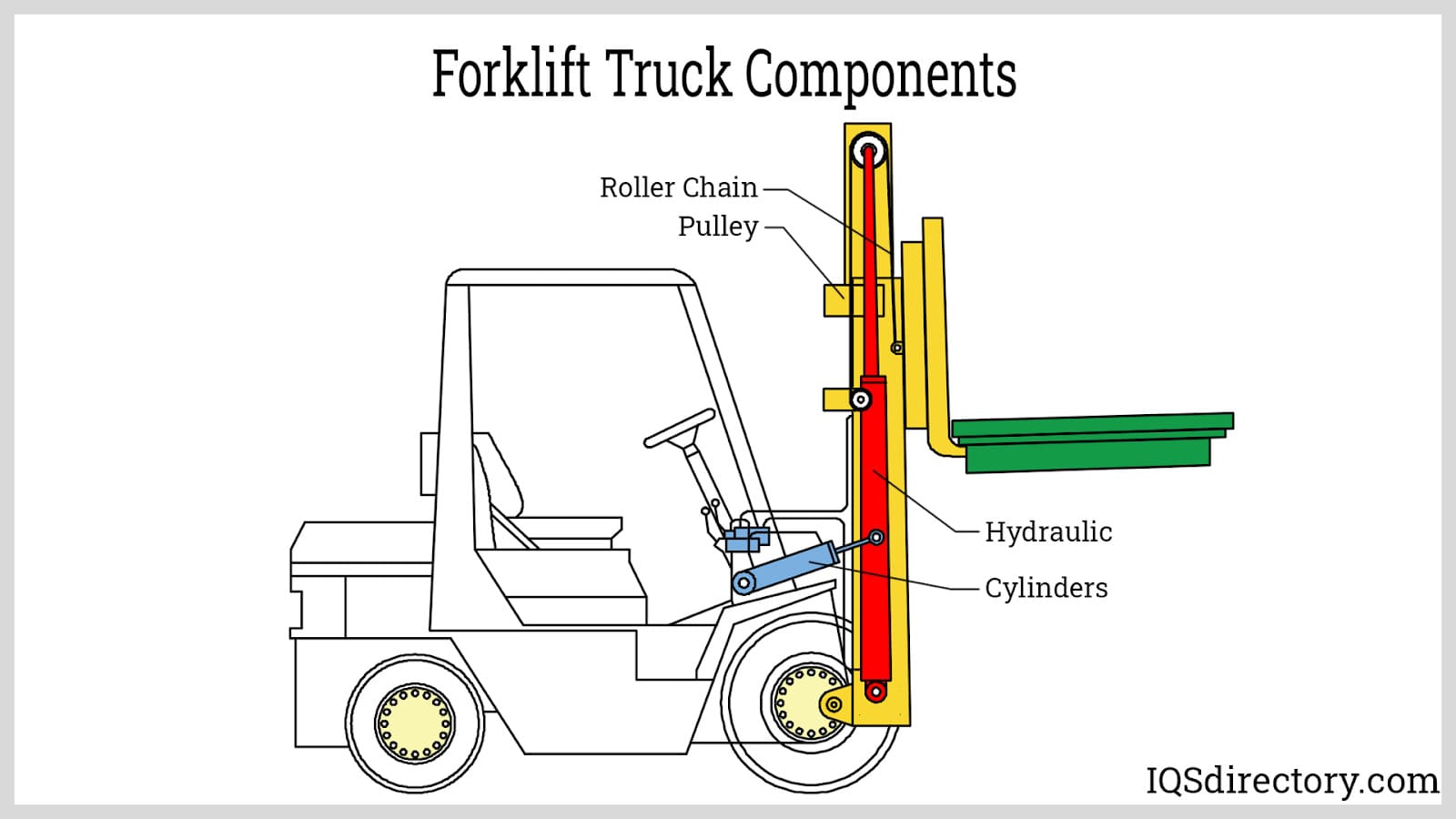
Illustrative image related to components of a forklift truck
The Solution:
B2B buyers should prioritize safety by conducting thorough assessments of their forklift fleet, focusing on critical components that impact operator safety. Regularly scheduled safety audits and training sessions can help reinforce the importance of equipment checks and proper operation. Engaging with suppliers who provide updated safety features or retrofitting options for existing forklifts can enhance safety compliance. Furthermore, staying informed about local and international safety regulations will ensure that your operations meet necessary standards, minimizing liability and enhancing employee well-being. Investing in operator training that emphasizes the importance of utilizing safety components effectively can also lead to a safer work environment.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for components of a forklift truck
What Are the Key Materials Used in Forklift Components?
When selecting materials for forklift components, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. The choice of material directly impacts the performance, durability, and overall cost-effectiveness of the forklift. Below, we analyze four common materials used in forklift manufacturing: steel, aluminum, rubber, and composite materials.
How Does Steel Perform in Forklift Component Manufacturing?
Steel is the most widely used material in forklift construction, particularly for the chassis, forks, and masts. Its high tensile strength allows it to withstand significant loads and stresses. Steel also exhibits excellent durability and can be treated for enhanced corrosion resistance, making it suitable for various environments.
Pros: Steel is highly durable, cost-effective, and readily available. It can be manufactured into complex shapes and sizes, making it versatile for different forklift designs.
Cons: The primary drawback of steel is its weight, which can affect the forklift’s overall efficiency and fuel consumption. Additionally, untreated steel is susceptible to rust, especially in humid or corrosive environments.
Impact on Application: Steel’s strength makes it ideal for heavy-duty applications, but it may require additional treatments or coatings for environments with high humidity or exposure to chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM for steel grades is crucial. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should consider local availability and the cost of transporting steel, while European buyers may prioritize compliance with DIN standards.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Forklift Design?
Aluminum is increasingly used in forklift design due to its lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion. It is often found in components like the operator cab and certain mast sections.
Pros: The lightweight property of aluminum enhances fuel efficiency and maneuverability. It is also resistant to rust, which is beneficial in humid environments.
Cons: Aluminum typically has a lower tensile strength compared to steel, making it less suitable for heavy-duty applications. It is also more expensive, which can affect the overall cost of the forklift.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is ideal for applications requiring lighter loads and improved fuel efficiency, but it may not be suitable for high-capacity forklifts.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific aluminum grades and their compliance with international standards. In regions like the Middle East, where high temperatures can affect material properties, selecting the right aluminum alloy is critical.
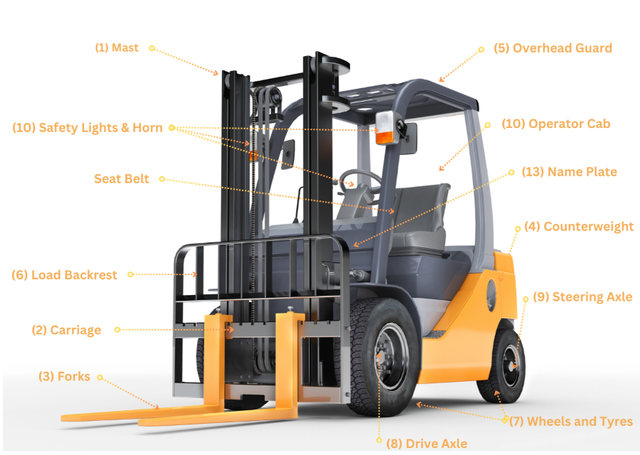

Illustrative image related to components of a forklift truck
How Important Is Rubber in Forklift Operations?
Rubber is primarily used for forklift tires, which are crucial for traction and stability. The type of rubber used can vary based on the intended application, such as pneumatic tires for outdoor use or cushion tires for indoor settings.
Pros: Rubber provides excellent shock absorption and traction, making it suitable for various terrains. Pneumatic tires can navigate rough surfaces, while cushion tires are ideal for smooth, indoor operations.
Cons: Rubber tires can wear out quickly, especially in abrasive environments, leading to higher maintenance costs. Additionally, they may not perform well in extreme temperatures.
Impact on Application: The choice between pneumatic and cushion tires significantly affects the forklift’s operational efficiency and suitability for specific tasks.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider local climate conditions and terrain when selecting rubber tires. Compliance with safety standards for tire performance is also essential.
What Advantages Do Composite Materials Offer for Forklift Components?
Composite materials are becoming popular for specific forklift components, such as load backrests and certain attachments. They combine materials like fiberglass and resins to create lightweight yet strong components.
Pros: Composites are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and can be molded into complex shapes. They also offer good thermal and electrical insulation properties.
Cons: The primary limitation is the cost, as composite materials can be significantly more expensive than traditional materials. Additionally, they may not be suitable for all structural applications due to lower tensile strength.
Impact on Application: Composites are ideal for non-structural components where weight savings are essential, but their use in load-bearing applications may be limited.
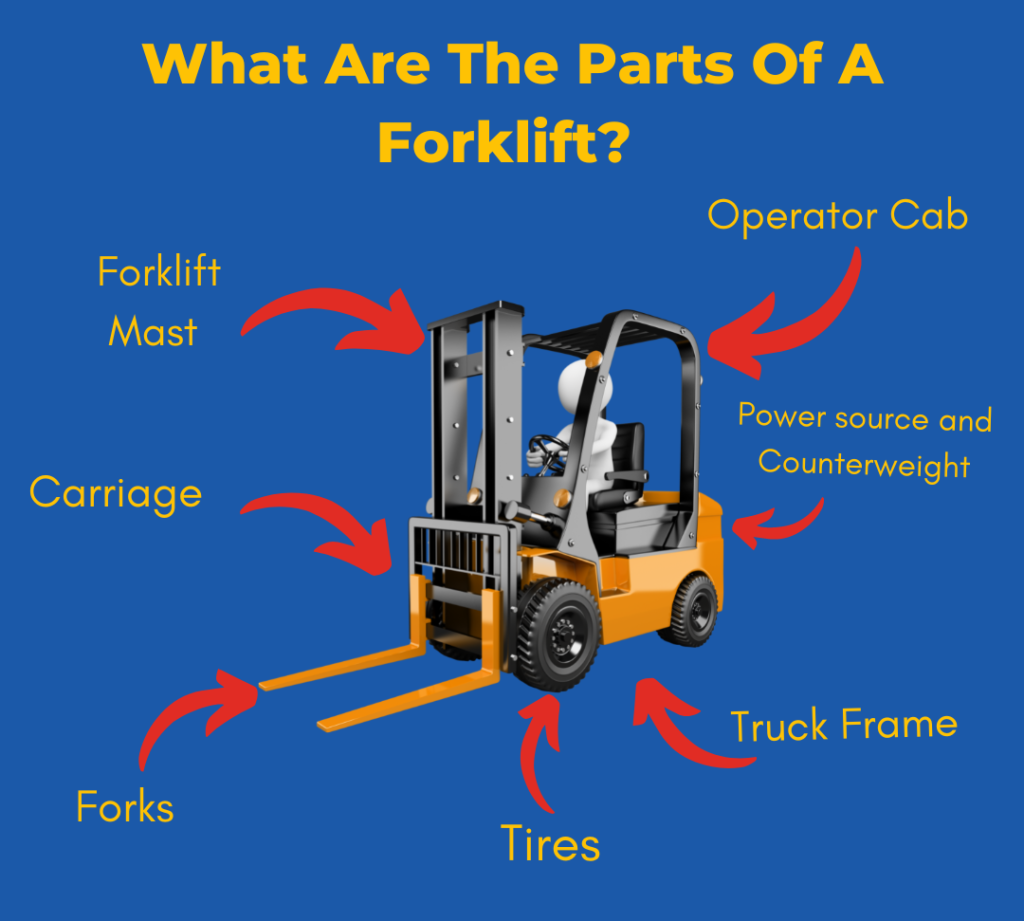
Illustrative image related to components of a forklift truck
Considerations for International Buyers: Understanding the specific composite materials and their certifications is vital, especially in regions with stringent safety regulations.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Forklift Components
| Material | Typical Use Case for components of a forklift truck | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Chassis, forks, masts | High durability and strength | Heavy weight, rust susceptibility | Medium |
| Aluminum | Operator cab, mast sections | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Lower tensile strength, higher cost | High |
| Rubber | Tires (pneumatic and cushion) | Excellent traction and shock absorption | Quick wear in abrasive environments | Medium |
| Composite | Load backrests, attachments | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, limited structural use | High |
This material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of materials used in forklift components, ensuring informed decision-making for their specific operational needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for components of a forklift truck
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Forklift Truck Components?
The manufacturing process of forklift components is intricate, involving several critical stages that ensure the final product meets industry standards and customer expectations.
Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. This involves selecting high-quality materials that are suitable for the specific components being produced, such as steel for structural parts or rubber for tires. Suppliers often provide certifications for these materials, which can include chemical composition reports and mechanical property tests. This phase may also involve cutting, machining, or treating the materials to achieve the desired specifications.
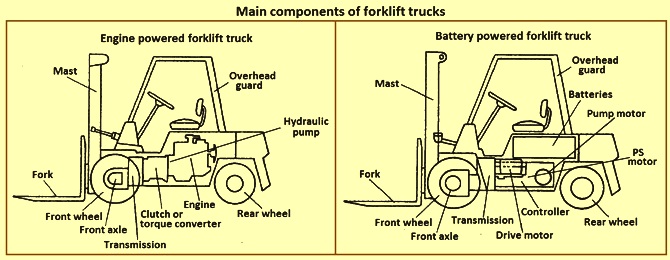
Illustrative image related to components of a forklift truck
Forming Techniques Used in Forklift Component Manufacturing
Once the materials are prepared, various forming techniques are employed. For example, components such as the chassis and mast may undergo processes such as stamping, forging, or welding.
- Stamping: Used for creating flat parts like the overhead guard, stamping involves pressing a flat sheet of metal into a specific shape.
- Forging: This technique uses compressive forces to shape metal, ideal for components that require high strength, such as axles.
- Welding: Critical for assembling parts, welding joins metal components together, ensuring structural integrity and durability.
These forming techniques are selected based on the component’s design, function, and required strength.
How Are Forklift Components Assembled?
After individual components are formed, the assembly stage begins. This phase involves fitting together various parts such as the engine or battery, operator cab, and mast.
- Sub-assembly: Often, smaller assemblies are created first—such as the hydraulic system for lifting—before being integrated into the main assembly.
- Final Assembly: During this stage, all components are brought together, and quality checks are conducted to ensure proper fit and function. This includes alignment tests and torque specifications for bolts and screws.
The assembly process may vary depending on the type of forklift being manufactured, whether it’s electric or combustion-powered, and the specific design requirements.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Forklift Components?
The finishing process is vital for enhancing the durability and appearance of forklift components. Common techniques include:
- Coating: Components are often coated with protective finishes like powder coating or paint to prevent corrosion and improve aesthetics.
- Surface Treatment: Processes such as anodizing or galvanizing may be applied to increase wear resistance and longevity.
- Quality Polishing: Some parts may require polishing to ensure smooth surfaces, especially those involved in high-friction applications.
These finishing touches not only improve the look of the forklift but also extend its operational lifespan.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Forklift Components?
Quality assurance (QA) is crucial in the manufacturing of forklift components to ensure safety, reliability, and compliance with international standards.
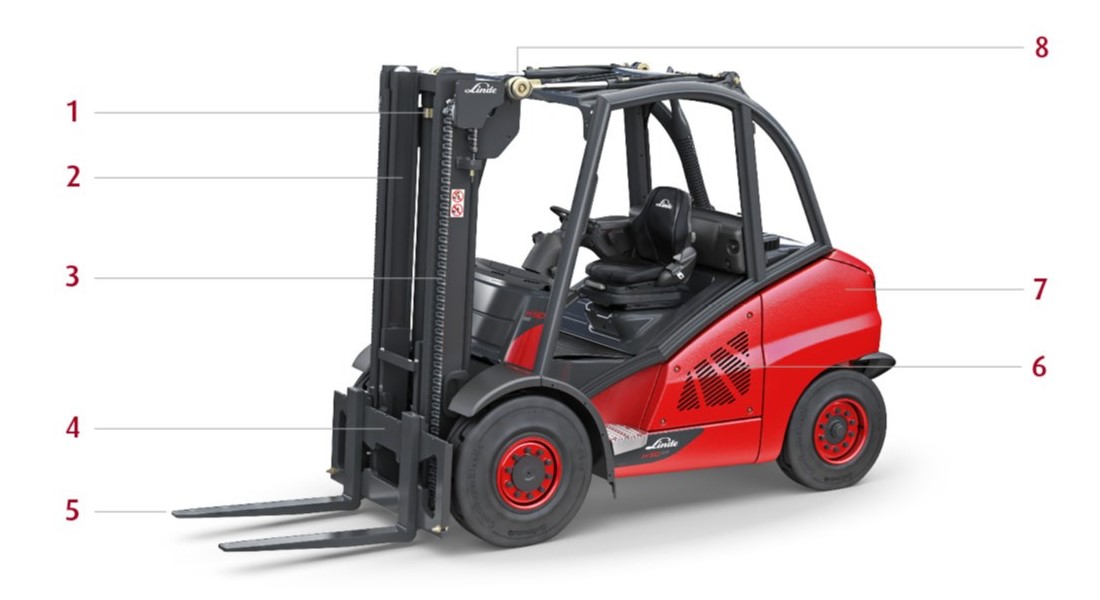

Illustrative image related to components of a forklift truck
Understanding International Standards for Forklift Component Quality
One of the most recognized standards is ISO 9001, which outlines the criteria for a quality management system. Companies seeking ISO 9001 certification must demonstrate their ability to consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking in Europe and API standards for certain components are also critical. CE marking indicates compliance with European safety standards, while API certification is essential for components like hydraulic systems.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) is implemented at various checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): QC checks during the manufacturing process verify that components are being produced according to established specifications.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, a comprehensive inspection ensures that the finished product meets all quality and safety standards before shipment.
Common testing methods include tensile strength tests, fatigue tests, and dimensional inspections. These tests help ensure that components can withstand the operational demands placed upon them.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is paramount.
What Are Effective Methods for Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to evaluate a manufacturer’s quality control practices. This can include:
- On-site Audits: Visiting the manufacturing facility to assess processes, equipment, and working conditions.
- Reviewing Quality Documentation: Requesting access to quality control records, including inspection reports, certifications, and compliance documentation.
How Important Are Third-Party Inspections?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality management systems. This includes:
- Pre-shipment Inspections: Ensuring that products meet the required specifications before they are shipped.
- Random Sampling: Verifying the quality of random samples from a production batch to ensure consistency.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
B2B buyers must navigate various nuances in quality control when sourcing components internationally. These include understanding local regulations, adapting to different quality standards, and considering logistical challenges.
Navigating Compliance and Standards in Different Regions
Buyers should be aware that compliance requirements may vary significantly between regions. For instance, European buyers will need to ensure that suppliers meet CE marking requirements, while those in Africa may have different local certifications.

Illustrative image related to components of a forklift truck
Understanding these standards will help buyers mitigate risks and ensure that the components they procure are not only compliant but also suitable for their operational needs.
Conclusion
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for forklift components are comprehensive and vital for delivering safe, reliable, and high-quality products. B2B buyers must engage rigorously with suppliers, leveraging audits, third-party inspections, and a clear understanding of international standards to ensure they are making informed purchasing decisions. By prioritizing these factors, buyers can enhance their operational efficiency and maintain competitive advantage in their respective markets.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘components of a forklift truck’
In the competitive landscape of international B2B procurement, sourcing forklift truck components requires a structured approach to ensure quality, compatibility, and cost-effectiveness. This guide provides a practical checklist for buyers looking to procure these essential parts effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by outlining the specific technical requirements for the forklift components you need. This includes understanding the type of forklift (electric, diesel, etc.), load capacity, and intended operating environment (indoor vs. outdoor). Clear specifications help streamline the sourcing process and ensure compatibility with existing equipment.
- Consider factors such as:
- Load capacity and dimensions
- Required safety features
- Environmental considerations (e.g., temperature, humidity)
Step 2: Research Reputable Suppliers
Identifying reliable suppliers is crucial for maintaining quality standards. Look for companies with a strong reputation in the industry, particularly those that specialize in forklift components. Conduct thorough research to assess their market presence and customer feedback.
- Key indicators to evaluate:
- Years of experience in the industry
- Positive reviews and testimonials from previous clients
- Availability of a comprehensive product range
Step 3: Request Detailed Product Information
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed product catalogs and specifications. This includes technical drawings, material certifications, and warranty information. Understanding the product in detail will help you make informed purchasing decisions.
- Ensure you check for:
- Compliance with industry standards (ISO, ANSI)
- Detailed descriptions of materials used
- Compatibility with your existing forklift models
Step 4: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Verify that your chosen suppliers have the necessary certifications and comply with relevant regulations. This step is vital for ensuring that the components meet safety and performance standards.
- Look for certifications such as:
- ISO 9001 for quality management
- CE marking for compliance with European safety standards
- Local certifications relevant to your region
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Service
Quality after-sales support can significantly impact your overall satisfaction and operational efficiency. Inquire about the availability of technical support, spare parts, and maintenance services.
- Consider the following:
- Response times for support requests
- Availability of replacement parts
- Training or guidance offered for installation and operation
Step 6: Compare Pricing and Payment Terms
Before finalizing your purchase, compare pricing from multiple suppliers. Ensure that you understand the payment terms, including any potential discounts for bulk orders or long-term contracts. Transparency in pricing helps avoid unexpected costs later on.
Illustrative image related to components of a forklift truck
- Focus on:
- Total cost of ownership (including shipping and duties)
- Payment flexibility and options
- Potential for long-term partnership discounts
Step 7: Finalize Your Order and Review Delivery Logistics
Once you have selected a supplier, confirm your order and review the logistics for delivery. Ensure that you have a clear understanding of the expected delivery timeline and any associated shipping costs.
- Important considerations include:
- Shipping methods and timelines
- Customs clearance processes if importing
- Inspection and acceptance criteria upon delivery
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline the procurement process for forklift truck components, ensuring that they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for components of a forklift truck Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Forklift Truck Component Sourcing?
When sourcing components for forklift trucks, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the pricing of forklift components. High-strength steel, for instance, is often used for chassis and masts due to its durability, whereas rubber or polyurethane is common for tires. Material costs can fluctuate based on market demand and availability, influencing overall pricing.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass wages for skilled workers involved in manufacturing and assembly. Regions with lower labor costs may offer more competitive pricing, but this can vary based on local economic conditions and regulations.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs related to production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce these costs, which may be passed on to buyers.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific components can add to initial costs. However, investing in high-quality tooling can improve production efficiency and reduce long-term costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that components meet safety and performance standards, especially critical in the heavy equipment industry. Enhanced QC measures may increase upfront costs but can prevent costly failures and liability issues down the line.
-
Logistics: Transporting components from suppliers to manufacturers or directly to buyers involves shipping, handling, and storage costs. These can vary significantly based on distance, shipping methods, and volume.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market competition, brand reputation, and service offerings.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Forklift Component Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of forklift components, including:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often qualify for bulk pricing discounts. Understanding the supplier’s MOQ can help buyers negotiate better rates, especially for large-scale operations.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom components tailored to specific operational needs can significantly increase costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the potential for increased expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Components that meet international quality standards or possess certifications may command higher prices. However, investing in certified components can enhance safety and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and service capabilities can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital for international buyers. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can influence total costs and responsibilities for shipping and insurance.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for B2B Buyers in Forklift Component Sourcing?
To maximize cost-efficiency when sourcing forklift components, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Rather than focusing solely on upfront costs, evaluate the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational, and disposal costs. This approach ensures that buyers invest in components that provide long-term value.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Different regions may have varying pricing structures due to local labor costs, material availability, and economic conditions. For instance, suppliers in Europe may have different pricing strategies compared to those in Africa or South America.
-
Negotiate Terms: Always negotiate payment terms, delivery schedules, and warranties. Flexible payment options can improve cash flow, while favorable delivery terms can enhance operational efficiency.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and improved communication, ultimately benefiting the sourcing process.
Conclusion
While the costs associated with sourcing forklift truck components can vary widely, a thorough understanding of the cost structure and pricing influencers allows buyers to make informed decisions. By focusing on long-term value and leveraging negotiation strategies, international B2B buyers can optimize their sourcing efforts to achieve significant cost savings. Always consider that prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, and obtaining multiple quotes is advisable for the best outcomes.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing components of a forklift truck With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Forklift Truck Components
In the realm of material handling, forklift trucks are commonly utilized for their efficiency and versatility. However, various alternative solutions exist that can fulfill similar roles, especially in diverse working environments. This section examines how the components of a forklift truck compare against other viable options, providing B2B buyers with insights to make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Components Of A Forklift Truck | Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) | Hand Pallet Trucks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High load capacity; versatile for various tasks | Efficient for repetitive tasks; limited load capacity | Manual lifting; best for light loads |
| Cost | Higher initial investment; ongoing maintenance costs | Moderate investment; lower operating costs over time | Low initial cost; minimal maintenance |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires operator training and infrastructure | Requires integration into existing systems | Simple to use; no training needed |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed; complex systems | Low maintenance; self-diagnostic features | Minimal maintenance; easy repairs |
| Best Use Case | Heavy-duty lifting and transportation | Automated processes in warehouses | Manual handling of lighter loads in tight spaces |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)?
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) present a modern alternative to traditional forklift trucks. They excel in environments where repetitive tasks are prevalent, such as warehouses and manufacturing facilities. Pros include improved efficiency, reduced labor costs, and increased safety since AGVs can operate without human intervention. However, their limitations include higher upfront costs and a need for significant infrastructure adjustments, which may not be feasible for all businesses.
How Do Hand Pallet Trucks Compare to Forklift Trucks?
Hand pallet trucks, or manual pallet jacks, are another alternative that can be particularly effective for small to medium-sized operations. They are cost-effective, easy to maneuver, and require little to no training for operators. Their primary drawback is the limited load capacity and reliance on human strength, making them unsuitable for heavy-duty tasks. In environments where heavy lifting is not required, hand pallet trucks can be a practical solution.

Illustrative image related to components of a forklift truck
Making the Right Choice: Which Solution Is Best for Your Business?
When deciding between forklift truck components and alternative solutions, B2B buyers should assess their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and the physical environment in which the equipment will be used. Factors such as load weight, frequency of use, and available workforce will significantly influence the choice. For instance, companies handling heavy loads may find forklifts indispensable, while those focusing on lighter loads and cost-efficiency might opt for hand pallet trucks. Ultimately, the best solution will align with both operational requirements and financial considerations, ensuring productivity and safety in material handling processes.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for components of a forklift truck
When considering the procurement of forklift truck components, it’s essential to understand their technical specifications and the industry terminology that accompanies them. This knowledge not only aids in making informed purchasing decisions but also ensures compatibility and efficiency in operations.
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Forklift Truck Components?
-
Load Capacity
The load capacity indicates the maximum weight a forklift can safely lift. This specification is crucial for buyers as it directly impacts the forklift’s suitability for specific tasks. Understanding load capacity helps ensure compliance with safety regulations and prevents equipment damage. -
Mast Height
Mast height refers to the vertical reach of the forklift’s lifting mechanism. It is essential for operations in environments with height restrictions, such as warehouses with low ceilings. Buyers must assess the required lift height based on their operational needs to avoid inefficiencies or accidents. -
Fork Length
The length of the forks affects the type of loads a forklift can handle. Standard fork lengths usually range from 36 to 48 inches, but extensions are available for larger items. Selecting the appropriate fork length ensures stability during lifting and transport, reducing the risk of load spills. -
Tire Type
The type of tires—pneumatic or cushion—determines the forklift’s operational environment. Pneumatic tires provide better traction on uneven outdoor surfaces, while cushion tires are ideal for smooth indoor surfaces. Choosing the right tire type is vital for maximizing performance and safety in various terrains. -
Engine Type
Forklifts can be powered by internal combustion engines (gasoline, diesel, propane) or electric batteries. The choice of engine affects operational costs, maintenance needs, and environmental impact. Buyers should consider the nature of their operations and local regulations when selecting an engine type. -
Turning Radius
The turning radius is the smallest circular turn a forklift can make. This specification is particularly important in tight spaces, such as narrow aisles in warehouses. A smaller turning radius enhances maneuverability, making it a key consideration for operational efficiency.
Which Trade Terms Are Commonly Used in Forklift Component Procurement?
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts that are used in the manufacturing of a product. In the forklift industry, OEM parts are often preferred for their guaranteed compatibility and quality. Buyers should consider OEM parts for reliability and optimal performance. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers to manage inventory costs effectively. Suppliers often set MOQs to ensure production efficiency, so buyers should negotiate terms that align with their operational needs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used by buyers to solicit price bids from suppliers. It specifies the required components and quantities, allowing suppliers to provide accurate pricing. Utilizing RFQs helps buyers compare offers and make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms
Incoterms are a set of international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and obligations, facilitating smoother transactions across borders. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period between placing an order and receiving the goods. For forklift components, understanding lead time is critical for project planning and inventory management. Buyers should account for lead time when scheduling equipment availability to prevent operational disruptions. -
Warranty
A warranty is a guarantee provided by the manufacturer regarding the quality and longevity of a product. In the forklift industry, warranties protect buyers against defects and provide assurance of the component’s reliability. Evaluating warranty terms can significantly impact long-term operational costs.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of forklift truck procurement with greater confidence, ensuring they make choices that align with their operational requirements and business goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the components of a forklift truck Sector
What are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Impacting Forklift Components?
The forklift components market is experiencing significant transformation driven by several global factors. Increased demand for efficient material handling solutions in sectors like logistics, manufacturing, and construction is propelling growth. Emerging markets in Africa, South America, and the Middle East are witnessing rapid industrialization, leading to heightened requirements for forklifts and their components. This is particularly evident in countries like Nigeria and Brazil, where infrastructure projects are booming.
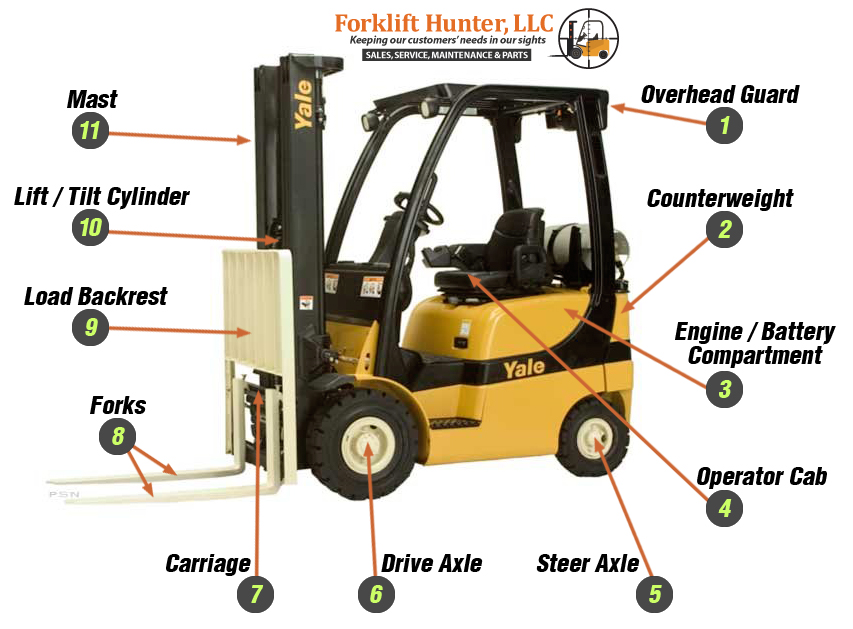
Illustrative image related to components of a forklift truck
In terms of technology, the integration of IoT and AI into forklift systems is enhancing operational efficiency and safety. Smart forklifts equipped with sensors and data analytics are becoming more common, allowing for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce is pushing companies to optimize their supply chains, driving demand for forklifts with advanced capabilities such as higher lifting capacities and better maneuverability.
Sourcing trends are also evolving, with a growing emphasis on local suppliers to reduce lead times and transportation costs. International buyers are increasingly prioritizing partnerships with manufacturers that offer customization options tailored to specific regional needs. This trend is particularly relevant for B2B buyers in Europe, where stringent regulations around safety and emissions are influencing purchasing decisions.
How is Sustainability Shaping the Sourcing of Forklift Components?
Sustainability is no longer a peripheral concern; it is at the forefront of the sourcing strategy for forklift components. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the lifecycle of forklift components is under scrutiny. Buyers are increasingly demanding transparency regarding the sourcing of raw materials and the sustainability practices of their suppliers.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Companies are looking for suppliers who adhere to fair labor practices and environmentally responsible sourcing. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and OHSAS 18001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are becoming crucial benchmarks for assessing suppliers.
Illustrative image related to components of a forklift truck
Moreover, the use of ‘green’ materials is gaining traction. Components that are manufactured using recycled materials or that are designed for easy disassembly at the end of their lifecycle are becoming preferred choices. This aligns with the circular economy model, which many companies are now adopting to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency.
How Have Forklift Components Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of forklift components has been marked by technological advancements and changing market needs. Initially, forklifts were predominantly powered by internal combustion engines, which limited their use to outdoor environments. However, the introduction of electric forklifts has opened new avenues for indoor applications, particularly in warehouses and distribution centers.
Over the years, components like the mast, forks, and drive systems have undergone significant upgrades, focusing on enhancing lifting capacities and improving safety features. The advent of advanced materials has also contributed to making forklifts lighter and more efficient. As automation continues to reshape industries, the development of smart forklifts equipped with sensors and connectivity features is poised to redefine the future landscape of forklift components.
In conclusion, understanding the market dynamics, sustainability considerations, and historical context of forklift components equips international B2B buyers with the insights needed to make informed purchasing decisions. Emphasizing efficiency, safety, and ethical practices will not only enhance operational performance but also contribute to a more sustainable future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of components of a forklift truck
-
How do I choose the right components for my forklift?
Choosing the right components for your forklift depends on various factors, including the type of loads you handle, the operating environment, and the specific applications you require. Assess the weight capacity, lift height, and type of terrain (e.g., indoor or outdoor) to determine the best fit. Consider the forklift’s configuration, such as counterbalance or reach trucks, and evaluate the available attachments for specialized tasks. Engaging with suppliers who understand your operational needs can also provide valuable insights into optimal component selection. -
What are the best suppliers for forklift components in international markets?
Identifying reliable suppliers for forklift components requires thorough research and vetting. Look for suppliers with a solid reputation, positive reviews, and experience in your specific market region. Trade platforms, industry trade shows, and local business directories can be useful resources. Ensure that the supplier adheres to international quality standards and regulations, and consider their ability to provide after-sales support, warranty services, and timely deliveries. Establishing relationships with multiple suppliers can also mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for forklift components?
Minimum order quantities for forklift components can vary significantly depending on the supplier, component type, and your specific needs. Many manufacturers set MOQs to optimize production efficiency and reduce costs. It’s essential to communicate your requirements clearly with potential suppliers. Some may offer flexibility on MOQs for first-time orders or bulk purchases, while others might have strict policies. Always negotiate terms that align with your purchasing strategy and budget constraints. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing forklift components internationally?
Payment terms for international transactions can differ widely based on the supplier, country, and order size. Common arrangements include advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Establishing clear terms upfront is crucial to avoid misunderstandings. It’s advisable to choose payment methods that provide security and recourse options, such as escrow services or trade finance solutions. Additionally, factor in currency exchange risks and potential tariffs when budgeting for your purchases. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for forklift components?
To ensure quality assurance for forklift components, start by partnering with suppliers that comply with international quality standards such as ISO 9001. Request detailed product specifications, certifications, and testing reports before making a purchase. Consider conducting factory audits or inspections to assess production processes and quality control measures. Additionally, establish a clear return policy and warranty terms to protect your investment against defective components. Regularly reviewing supplier performance can help maintain quality over time. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing forklift components?
When sourcing forklift components internationally, logistics plays a critical role in ensuring timely delivery and cost efficiency. Consider factors such as shipping methods (air vs. sea), transit times, customs clearance, and import regulations in your country. Collaborate with logistics providers experienced in handling heavy equipment components to navigate potential challenges. Also, factor in storage and handling costs upon arrival, and ensure that your supply chain is resilient to disruptions. -
Can forklift components be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many forklift components can be customized to meet specific operational needs. Suppliers often offer options for tailored configurations, such as different mast heights, fork lengths, and specialized attachments. When seeking customization, clearly communicate your requirements and intended applications to the supplier. Keep in mind that customization may affect lead times and costs, so it’s essential to weigh the benefits against potential delays in procurement. -
What are the common challenges in sourcing forklift components internationally?
Common challenges in sourcing forklift components internationally include language barriers, cultural differences, and varying regulatory standards. Additionally, logistical issues such as shipping delays, customs complications, and fluctuating currency rates can pose significant hurdles. To mitigate these challenges, establish strong communication with suppliers, invest in understanding local regulations, and build a network of reliable logistics partners. Conducting thorough market research and due diligence before finalizing any agreements will also help minimize risks.
Top 3 Components Of A Forklift Truck Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Logisnext Americas – Forklift Mast and Cylinder Solutions
Domain: logisnextamericas.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Mast: Vertical support for raising/lowering loads; types include Duplex (2 stages), Triplex (3 stages), Quad (4 stages). Lift Cylinder: Powers vertical movement of the mast, hydraulically operated. Tilt Cylinder: Controls tilt movement of the carriage and forks. Forklift Carriage Assembly: Platform for mounting objects, includes forks and load backrest. Forks: Used to transport loads, available in…
2. Southern Lift – Forks
Domain: southernlift.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: 1. Forks: Essential for lifting, supporting, and carrying loads. Types include shaft mounted, bolt-on, block, coil, lumber, drum, roller, scale, telescopic, tire, offset, inset, corrugated, inverted, peek-a-book, quick detach, gypsum, folding, rotator, anti-slip, tip plate, two hitch, stainless steel, boat forks.
2. Carriage: Comprises forks and load backrest, stabilizing the lifted load and preve…
3. National Dispatching – Forklift
Domain: nationaldispatching.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: A forklift is a motor-powered industrial truck designed to lift and move large, heavy objects, typically pallets and boxes, within warehouses and docking sites. Key components of a forklift include: 1. Chassis: Contains the counterweight for balance, engine and battery compartment, operator compartment with controls, and wheels/tires. 2. Counterweight: Ensures proper weight distribution to prevent…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for components of a forklift truck
In navigating the complexities of forklift truck components, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal approach for international B2B buyers. Understanding the integral roles of various parts—from the engine or battery to the lift cylinders and mast systems—enables businesses to make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and safety. By prioritizing quality suppliers and evaluating the total cost of ownership, companies can optimize their procurement strategies, ensuring that their forklifts are not only functional but also reliable and durable.
As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to evolve, the demand for advanced forklift solutions is on the rise. Buyers are encouraged to embrace innovative sourcing strategies that leverage local insights while considering global supply chain dynamics. Engaging with reputable manufacturers and suppliers can lead to mutually beneficial partnerships, fostering growth and resilience in a competitive landscape.
Looking ahead, the future of forklift components will be shaped by technological advancements and sustainability trends. By staying informed and agile, businesses can position themselves to capitalize on emerging opportunities, ensuring their operations remain robust and efficient. Take the next step in your sourcing journey—explore partnerships that align with your goals for innovation and excellence.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.