Choosing Your Cold Headed Fasteners: Key Specs to Compare in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cold headed fasteners
In the ever-evolving landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing cold headed fasteners poses a unique challenge for B2B buyers. With increasing demand for high-quality, durable components, businesses must navigate a complex market filled with various suppliers, material specifications, and production techniques. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, delving into the types of cold headed fasteners available, their diverse applications across industries, and crucial supplier vetting processes.
By providing insights into cost considerations, production capabilities, and technological advancements, this guide empowers international B2B buyers—particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Germany and Nigeria—to make informed purchasing decisions. Understanding the nuances of cold heading manufacturing not only aids in selecting the right fasteners but also enhances overall supply chain efficiency and product quality.
As you explore this guide, you will uncover actionable strategies for optimizing your fastener sourcing, ensuring that you partner with reliable suppliers who meet your specific needs. Whether you are looking to reduce costs, enhance product performance, or innovate your fastener solutions, the insights provided will equip you with the knowledge necessary to thrive in today’s competitive market.
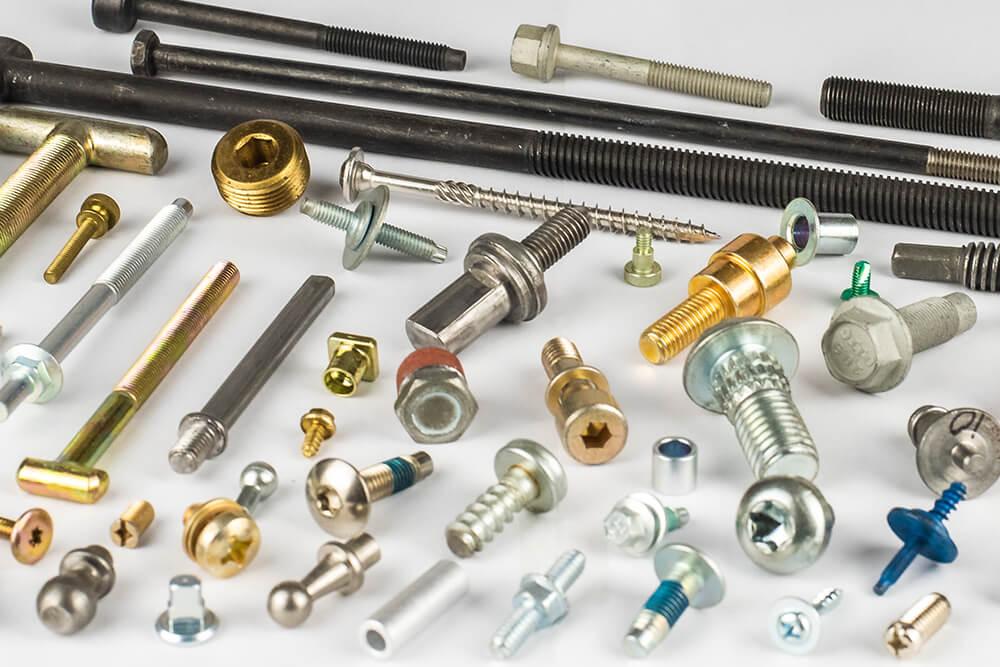
Understanding cold headed fasteners Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hex Head Bolts | Six-sided head design for easy wrench grip; high torque capacity | Automotive, machinery assembly | Pros: Versatile; high strength. Cons: May require additional hardware for specific applications. |
| Socket Head Screws | Cylindrical head with hexagonal recess; compact design | Electronics, furniture, and machinery | Pros: Space-efficient; allows for higher torque. Cons: Requires specific tools for installation. |
| Carriage Bolts | Round head with square neck; prevents rotation during tightening | Wood and metal construction | Pros: Easy installation; secure hold. Cons: Limited to specific applications; less aesthetic appeal. |
| Self-Drilling Screws | Drill point eliminates pre-drilling; fast assembly | Roofing, metal sheeting, and construction | Pros: Time-saving; reduces labor costs. Cons: Not suitable for all materials; may require specific drill sizes. |
| Studs | No head; threaded on both ends; versatile fastening solution | Structural applications, machinery assembly | Pros: Flexible in applications; allows for adjustable tension. Cons: May require additional nuts and washers for complete assembly. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Hex Head Bolts?
Hex head bolts are characterized by their six-sided heads, which provide a strong grip for wrenches, making them ideal for high-torque applications. Commonly used in automotive and machinery assembly, these fasteners can handle significant loads. When purchasing hex head bolts, buyers should consider the material grade and finish to ensure compatibility with their specific application, as these factors affect strength and corrosion resistance.
Illustrative image related to cold headed fasteners
Why Choose Socket Head Screws for Your Projects?
Socket head screws feature a cylindrical head with a hexagonal recess, allowing for a compact design that is particularly beneficial in tight spaces. These fasteners are widely used in electronics and machinery due to their ability to withstand high torque without stripping. B2B buyers should evaluate the screw’s material and coating to ensure durability and longevity in their applications.
What Makes Carriage Bolts Ideal for Construction?
Carriage bolts are identified by their round head and square neck, which prevents the bolt from turning once installed. This feature makes them particularly effective in securing wood and metal structures. They are easy to install and provide a secure hold, making them a preferred choice in construction projects. Buyers should consider the bolt’s diameter and length to match their specific structural needs.
How Do Self-Drilling Screws Improve Efficiency?
Self-drilling screws are designed with a drill point that allows them to penetrate materials without pre-drilling. This feature significantly reduces assembly time and labor costs, especially in roofing and metal sheeting applications. However, buyers should ensure that these screws are suitable for the materials being fastened, as they may not be effective in all situations.
Why Are Studs a Versatile Fastening Solution?
Studs are unique fasteners that lack a head and are threaded on both ends, allowing for a versatile fastening solution in various applications. Commonly used in structural assembly, they provide adjustable tension and can be paired with nuts and washers for secure fastening. When purchasing studs, buyers should consider the length and thread specifications to ensure they meet their project requirements effectively.
Key Industrial Applications of cold headed fasteners
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of cold headed fasteners | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine assembly and vehicle body components | Enhanced strength and durability, reduced weight | Material specifications, tight tolerances, and volume needs |
| Construction | Structural steel connections | Cost-effective, high-speed production for large projects | Compliance with local standards, corrosion resistance |
| Electronics | Circuit board assembly | Precision fastening for reliability in electronic devices | Customization options, compatibility with various materials |
| Aerospace | Aircraft structural components | Lightweight, high-strength fasteners for safety | Certifications (e.g., AS9100), material traceability |
| Machinery Manufacturing | Heavy machinery assembly | Increased efficiency and reduced waste in production | Bulk purchasing options, lead times, and delivery logistics |
How Are Cold Headed Fasteners Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, cold headed fasteners are integral to engine assembly and vehicle body components. They provide enhanced strength and durability while contributing to weight reduction, which is crucial for fuel efficiency. International buyers, particularly from regions like Europe and South America, should consider material specifications and tight tolerances to ensure compatibility with automotive standards. Additionally, the ability to produce large volumes quickly can significantly streamline production timelines.

Illustrative image related to cold headed fasteners
What Role Do Cold Headed Fasteners Play in Construction?
Cold headed fasteners are widely utilized in construction for structural steel connections. Their ability to be produced cost-effectively and at high speeds makes them ideal for large-scale projects. Buyers in Africa and the Middle East should focus on compliance with local building codes and standards, as well as the corrosion resistance of fasteners to ensure longevity in various environmental conditions. The reduced raw material waste associated with cold heading also aligns with sustainable construction practices.
How Are Cold Headed Fasteners Essential in Electronics?
In the electronics industry, cold headed fasteners are crucial for circuit board assembly, providing precision fastening that ensures reliability in electronic devices. For buyers, particularly in Europe, customization options are vital to meet specific design requirements and material compatibility. The fasteners must be able to withstand various environmental factors, such as temperature fluctuations and moisture, making sourcing from reputable suppliers with robust quality assurance processes essential.
Why Are Cold Headed Fasteners Important in Aerospace?
In aerospace applications, cold headed fasteners are used in aircraft structural components due to their lightweight and high-strength properties, which are critical for safety and performance. Buyers must prioritize suppliers that hold relevant certifications, such as AS9100, to ensure compliance with stringent aerospace industry standards. Material traceability is also essential to maintain safety and quality throughout the manufacturing process.
How Do Cold Headed Fasteners Benefit Machinery Manufacturing?
For heavy machinery assembly, cold headed fasteners enhance efficiency and reduce waste in production processes. Their ability to be manufactured in bulk allows for significant cost savings, which is particularly beneficial for manufacturers in regions like South America and Africa. Buyers should evaluate lead times and delivery logistics to ensure that they can meet production schedules without delays, while also considering the potential for customized fastener designs to fit specific machinery requirements.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cold headed fasteners’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Achieving Tight Tolerances
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face challenges when sourcing cold headed fasteners that require exceptionally tight tolerances. Many manufacturers may promise precision, but the reality can fall short, leading to parts that do not fit properly or perform as expected. This not only impacts the quality of the final product but also increases costs due to rework or replacement. Buyers in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery are particularly sensitive to these issues, as even minor deviations can lead to failures or safety concerns.
The Solution:
To overcome this challenge, buyers should prioritize suppliers with a proven track record in manufacturing cold headed fasteners to stringent specifications. When sourcing, request detailed documentation on the manufacturing process, including inspection reports and quality assurance measures. Look for suppliers who utilize advanced cold heading technologies, as these are better equipped to maintain tight tolerances throughout production. Additionally, consider engaging in a collaborative design process with your supplier. This allows for the adjustment of specifications early on, ensuring that the fasteners are tailored to your exact requirements. Establishing a strong relationship with your supplier can also facilitate better communication and quicker resolutions to any potential issues.
Scenario 2: High Costs Due to Inefficient Sourcing
The Problem:
Cost is a significant concern for B2B buyers, especially when dealing with cold headed fasteners. Many companies find themselves paying more than necessary due to inefficient sourcing practices, such as relying on multiple suppliers for different components. This not only inflates costs but can also complicate logistics and increase lead times. Buyers in regions with fluctuating raw material prices, like Africa or South America, may find it particularly challenging to manage budgets effectively.
The Solution:
To reduce costs, buyers should consider consolidating their sourcing strategy by partnering with a single supplier capable of providing a wide range of cold headed fasteners. This approach simplifies procurement and can lead to volume discounts. Furthermore, buyers should engage in market research to identify suppliers that offer competitive pricing without compromising quality. Establishing long-term contracts can also provide price stability, protecting against market volatility. Finally, leveraging technology such as digital procurement platforms can streamline the sourcing process, allowing for real-time comparisons of pricing and availability across multiple suppliers.

Illustrative image related to cold headed fasteners
Scenario 3: Inadequate Knowledge of Material Properties
The Problem:
Many B2B buyers lack a comprehensive understanding of the material properties of the cold headed fasteners they require. This can lead to selecting fasteners that are not suitable for their specific applications, causing premature failures or performance issues. For instance, buyers in the construction or manufacturing industries may inadvertently choose a fastener made from a material that cannot withstand the environmental conditions or loads it will face, leading to costly downtime and repairs.
The Solution:
To address this knowledge gap, buyers should invest time in understanding the various materials used in cold headed fasteners and their specific properties. Engaging with suppliers who provide educational resources or technical support can be invaluable. Additionally, conducting material compatibility assessments for the intended application can help ensure that the chosen fasteners meet the necessary performance criteria. Buyers should also consider collaborating with engineers or materials scientists when specifying fasteners for critical applications. This proactive approach not only improves the reliability of the fasteners but also enhances overall project success and reduces the risk of costly mistakes.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cold headed fasteners
What Materials Are Commonly Used for Cold Headed Fasteners?
When selecting materials for cold headed fasteners, it is crucial to consider the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material. This analysis focuses on four common materials: carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and brass. Each material has unique characteristics that can significantly impact the performance and suitability of the fasteners in various applications.
How Does Carbon Steel Perform as a Material for Cold Headed Fasteners?
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its high tensile strength and hardness. It typically has a temperature rating up to 300°C and can withstand moderate pressure.

Illustrative image related to cold headed fasteners
Pros & Cons: The advantages of carbon steel include its cost-effectiveness and excellent durability, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. However, it has limited corrosion resistance unless treated, which can lead to premature failure in corrosive environments.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel fasteners are commonly used in automotive and construction applications where strength is critical. However, they may not be suitable for environments with high humidity or exposure to chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of local corrosion challenges and consider coatings or treatments. Compliance with standards such as ASTM A307 or DIN 933 is essential for ensuring quality.
What Are the Benefits of Using Stainless Steel in Cold Headed Fasteners?
Key Properties: Stainless steel is renowned for its excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand temperatures up to 800°C.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and ability to maintain structural integrity in harsh environments. However, it is generally more expensive than carbon steel and can be more challenging to machine, which may increase manufacturing complexity.

Illustrative image related to cold headed fasteners
Impact on Application: Stainless steel fasteners are ideal for applications in the food processing, marine, and chemical industries where corrosion resistance is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe, particularly Germany, often prefer stainless steel due to stringent quality standards. Compliance with standards like ASTM A193 or JIS B 1180 is critical for ensuring product reliability.
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Material for Cold Headed Fasteners?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has good corrosion resistance, with a temperature rating of around 150°C.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum fasteners is their lightweight nature, which is beneficial in applications where weight reduction is essential. However, they have lower tensile strength compared to steel, making them less suitable for high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum fasteners are often used in aerospace and automotive industries where weight savings are crucial.
Considerations for International Buyers: In regions like the Middle East, where temperature fluctuations can be extreme, buyers should consider the specific aluminum alloy used to ensure performance. Compliance with standards such as ASTM B211 is important for quality assurance.
What Role Does Brass Play in Cold Headed Fasteners?
Key Properties: Brass offers good corrosion resistance and has a temperature rating of up to 200°C. It is also known for its excellent machinability.

Illustrative image related to cold headed fasteners
Pros & Cons: Brass fasteners are durable and resistant to corrosion, making them suitable for electrical applications. However, they are typically more expensive than carbon steel and may not be suitable for high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Brass is commonly used in plumbing and electrical applications due to its conductivity and resistance to corrosion.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from South America should ensure that brass fasteners comply with local standards like ASTM B16. As brass can be more expensive, it’s essential to evaluate the cost versus performance benefits.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Cold Headed Fasteners
| Material | Typical Use Case for cold headed fasteners | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Automotive, construction | Cost-effective and durable | Limited corrosion resistance | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, marine, chemical | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive | Lightweight and good corrosion resistance | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
| Brass | Plumbing, electrical | Good corrosion resistance and machinability | More expensive, not for high-stress | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used in cold headed fasteners, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional considerations.

Illustrative image related to cold headed fasteners
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cold headed fasteners
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Cold Headed Fasteners?
The manufacturing of cold headed fasteners involves a series of well-defined stages that ensure the production of high-quality components. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a critical role in determining the efficiency, precision, and durability of the final product.
How Is Material Prepared for Cold Heading?
Material preparation begins with selecting the appropriate wire material, typically steel, stainless steel, or alloyed metal, based on the specifications required for the fasteners. The wire is drawn to the desired diameter and then fed into a cold heading machine.
Before the wire can be processed, it undergoes rigorous quality checks to ensure it meets the required specifications. This includes verifying the chemical composition and mechanical properties. The wire is then cut into slugs that will be used in the forming process. The precision in this stage is crucial, as variations can lead to inconsistencies in the final product.
What Techniques Are Used During the Forming Stage?
The forming stage is where the actual shaping of the fasteners occurs. Cold heading machines employ a series of dies and hammers to shape the slugs into the desired forms. Key techniques used in this process include:
- Upsetting: This technique involves compressing the slug to increase its diameter while reducing its height. It is commonly used to create the heads of fasteners.
- Extrusion: There are two types of extrusion—forward and backward. Forward extrusion lengthens the material while reducing its diameter, whereas backward extrusion creates internal cavities.
These techniques allow for the rapid production of fasteners with tight tolerances, often achieving precision within ±0.002 inches. The efficiency of the cold heading process significantly reduces waste, with minimal material loss compared to traditional machining methods.
How Does the Assembly Process Work for Cold Headed Fasteners?
Post-forming, some fasteners may require assembly, especially if they consist of multiple components or need additional features such as threads or knurling. Secondary operations, which are typically performed after the initial cold heading, include:
- Thread Rolling: This process forms threads on the fasteners using a rolling technique, which enhances the strength of the threads compared to cutting.
- Drilling and Tapping: Necessary for creating holes or internal threads that enable fastening.
- Heat Treatment: This process improves the mechanical properties of the fasteners, increasing their strength and wear resistance.
These operations ensure that the fasteners meet specific application requirements, providing the necessary functionality and reliability.

Illustrative image related to cold headed fasteners
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Used for Cold Headed Fasteners?
Finishing techniques enhance both the appearance and performance of cold headed fasteners. Common finishing processes include:
- Plating: Applying a protective layer to prevent corrosion and improve aesthetic appeal.
- Grinding and Polishing: This ensures smooth surfaces, which are crucial for functional applications.
- Metal Finishing: This includes various treatments that can improve resistance to environmental factors and wear.
Effective finishing not only extends the lifespan of fasteners but also ensures they meet industry-specific standards.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential in Cold Headed Fastener Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) in the manufacturing of cold headed fasteners is paramount, particularly for international B2B buyers who demand reliability and performance. The QA process typically follows several key standards and checkpoints.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers comply with international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. Other industry-specific certifications may include:
- CE Marking: Essential for fasteners sold in the European market, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Certification: Relevant for fasteners used in the oil and gas industry, ensuring they meet stringent safety and performance criteria.
Compliance with these standards not only assures quality but also enhances a supplier’s credibility in international markets.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Fastener Manufacturing?
The QA process typically includes three primary checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process is essential. This includes checking dimensions, tolerances, and surface finishes to catch any issues early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection occurs after production, ensuring that the finished fasteners meet all specifications and quality standards before shipping.
These checkpoints are critical in identifying defects and ensuring that only high-quality products reach the market.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify a supplier’s quality control processes:
- Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers helps assess their adherence to quality standards and manufacturing processes.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports, including test results and compliance certificates, provides insight into the supplier’s quality assurance practices.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s manufacturing and quality control processes.
These measures are particularly important for international buyers from diverse regions, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, who may face varying regulatory standards and quality expectations.

Illustrative image related to cold headed fasteners
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider Regarding Quality Control?
International B2B buyers must navigate the complexities of varying quality standards and regulations across different regions. For instance, European markets may have stricter regulations compared to those in Africa or South America. Understanding these nuances is essential for ensuring compliance and minimizing risks associated with product quality.
Additionally, language barriers and differing business practices can complicate communication with suppliers. Establishing clear expectations and maintaining open lines of communication can mitigate these challenges and foster stronger supplier relationships.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for cold headed fasteners are intricate and vital to ensuring product reliability. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and secure high-quality fasteners that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cold headed fasteners’
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, sourcing cold headed fasteners requires a strategic approach. This checklist serves as a practical guide for B2B buyers to ensure they procure high-quality fasteners that meet their specific needs. Follow these steps to streamline your sourcing process and enhance your supply chain efficiency.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes dimensions, tolerances, materials, and any specific performance standards your fasteners must meet.
– Considerations: Identify whether you need standard or custom configurations and if secondary operations like threading or plating are required.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reputable suppliers who specialize in cold headed fasteners. Look for companies with a proven track record and positive customer reviews.
– Key Actions: Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to compile a list of potential suppliers. Pay attention to their experience in your specific industry sector.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify the certifications and quality management systems of potential suppliers. This ensures they adhere to industry standards and regulations, which is crucial for maintaining product quality and safety.
– Certifications to Look For: ISO 9001, AS9100, or any relevant regional certifications that pertain to your industry.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Before placing a bulk order, request samples or prototypes of the cold headed fasteners you require. This step allows you to assess the quality and suitability of the products for your applications.
– Evaluation Criteria: Check for dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and overall workmanship. Ensure the samples meet your defined specifications.
Step 5: Assess Production Capabilities
Inquire about the supplier’s production capabilities to ensure they can meet your volume requirements and delivery timelines. Understanding their manufacturing processes can also provide insight into their efficiency and reliability.
– Questions to Ask: What is their production capacity? Can they accommodate both large and small orders? How do they handle rush orders?
Step 6: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you’ve identified a suitable supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. This is critical to establishing a mutually beneficial partnership.
– Tip: Be clear about your budget constraints but also consider the value of quality and reliability over the lowest price.

Illustrative image related to cold headed fasteners
Step 7: Finalize Your Order and Establish Communication Channels
After agreeing on terms, finalize your order and establish clear communication channels with your supplier. Ensure that both parties understand the expectations for order fulfillment and ongoing support.
– Best Practices: Set up regular check-ins during the production process and establish a point of contact for any inquiries or issues that may arise.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing process for cold headed fasteners, ensuring they secure high-quality products that meet their specific manufacturing needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cold headed fasteners Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Cold Headed Fasteners?
When considering sourcing cold headed fasteners, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and procurement. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly impacts costs. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and specialized alloys. Prices can fluctuate based on market demand and availability, which is critical for international buyers to monitor.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both skilled machine operators and support staff. In regions with higher labor costs, such as Western Europe, manufacturers may pass these expenses on to buyers. Conversely, sourcing from regions with lower labor costs can provide savings, but may come with trade-offs in quality or lead times.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes facility costs, utilities, and administrative expenses associated with production. Efficient operations can lead to lower overhead costs, which can be beneficial for buyers seeking competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can be a significant upfront investment. The complexity of the fastener design often dictates tooling costs. Buyers should inquire about tooling amortization over production runs to understand how this affects unit pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that fasteners meet required specifications often involves rigorous QC processes. While this can increase costs, it is essential for maintaining product integrity, particularly in sectors like automotive or aerospace.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary widely, especially for international buyers. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties should be considered when evaluating total costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure business viability. Understanding typical margins in the cold headed fastener market can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
How Do Pricing Influencers Impact Cold Headed Fasteners Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of cold headed fasteners, including volume requirements, specifications, materials, quality certifications, supplier characteristics, and Incoterms.
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often qualify for bulk pricing discounts, which can significantly reduce per-unit costs. Buyers should assess their needs carefully to leverage economies of scale.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific tolerances can increase costs due to the need for specialized tooling and longer production times. Buyers should balance their requirements with cost implications.
-
Materials: The choice of material not only affects the price but also the performance and durability of the fasteners. High-performance materials may come at a premium, which can impact overall sourcing costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Fasteners that require industry-specific certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) may incur additional costs. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who can provide the necessary documentation to avoid potential compliance issues.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer greater assurance in terms of quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping. The chosen terms can affect total landed costs, including freight and insurance.
What Are Essential Tips for Negotiating Cold Headed Fastener Prices?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should adopt strategic approaches to ensure cost-effectiveness in sourcing cold headed fasteners.
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage in discussions about pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Flexibility in these areas can lead to more favorable pricing arrangements.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also factors like maintenance, durability, and potential delays. A lower upfront cost might lead to higher long-term expenses if the quality is subpar.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware that prices may vary significantly based on regional markets, currency fluctuations, and geopolitical factors. Local suppliers may offer advantages in terms of logistics and support.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service. Consider long-term partnerships that can provide stability and predictability in sourcing.
Disclaimer on Indicative Pricing
Pricing for cold headed fasteners can vary widely based on numerous factors, including market conditions, specific buyer requirements, and supplier capabilities. It is advisable for buyers to seek multiple quotes and conduct thorough due diligence before making purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cold headed fasteners With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Cold Headed Fasteners
In the fastener industry, selecting the right solution is crucial for operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Cold headed fasteners are well-regarded for their precision and efficiency, but there are alternative manufacturing methods worth considering. Each method has its unique strengths and weaknesses, which can significantly impact the final product’s performance, cost, and suitability for specific applications. Below, we compare cold headed fasteners with two viable alternatives: machined fasteners and stamped fasteners.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Cold Headed Fasteners | Machined Fasteners | Stamped Fasteners |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength, tight tolerances | Moderate strength, variable tolerances | Moderate strength, good for high volume |
| Cost | Lower due to reduced material waste | Higher due to material removal and waste | Cost-effective for high-volume production |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized machinery | Versatile, widely available | Simple setup, but limited to specific shapes |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, durable | Moderate maintenance, dependent on machine type | Low maintenance, but die wear can be an issue |
| Best Use Case | High volume, custom shapes | Custom, intricate designs | High volume, simple shapes |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
1. Machined Fasteners
Machined fasteners are produced by removing material from a solid block or bar through various machining processes, such as turning, milling, or drilling. This method allows for intricate designs and tight tolerances, making it suitable for applications requiring high precision. However, the machining process typically generates significant material waste—up to 60%—and can be more time-consuming than cold heading. While machined fasteners are versatile and can be customized, they often come at a higher cost, making them less ideal for high-volume production runs.
2. Stamped Fasteners
Stamped fasteners are created using a stamping process where metal sheets are cut and formed into desired shapes. This method is generally faster and more cost-effective for large production runs, making it a popular choice for mass-produced components. Stamped fasteners can achieve reasonable strength levels, but their precision is typically lower than cold headed or machined fasteners. Additionally, the initial setup for stamping dies can be costly and time-consuming. However, once established, the production rates are high, making stamped fasteners ideal for simple shapes in high-volume applications.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Fastener Solution
When selecting the appropriate fastener solution, B2B buyers must consider their specific needs, including production volume, design complexity, and cost constraints. Cold headed fasteners excel in high-volume applications requiring custom shapes and tight tolerances, offering superior material efficiency. Machined fasteners are ideal for intricate designs but come at a higher cost and lower production speed. Stamped fasteners provide a cost-effective solution for high-volume needs but may lack the precision required for more complex applications. By evaluating these factors, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and budget.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cold headed fasteners
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Cold Headed Fasteners?
When sourcing cold headed fasteners, understanding their technical properties is crucial for ensuring product quality and compatibility with your applications. Here are several critical specifications that you should consider:
1. Material Grade
Cold headed fasteners are often manufactured from various materials, including carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloys. The material grade affects the fastener’s strength, corrosion resistance, and overall performance. For example, ASTM A193 B7 is commonly used for high-strength bolts, while A2 stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance. Selecting the right material grade is essential for applications in industries such as automotive, construction, and aerospace, where durability and reliability are paramount.

Illustrative image related to cold headed fasteners
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from specified dimensions in a fastener’s manufacturing process. Cold headed fasteners can achieve tight tolerances, typically within ±0.002 inches. This precision is vital for ensuring a proper fit in assemblies, reducing the risk of failure due to improper alignment or insufficient load-bearing capabilities. Tighter tolerances can also lead to less need for secondary machining, which can reduce overall production costs.
3. Surface Finish
The surface finish of cold headed fasteners can influence their performance and aesthetic appeal. Common finishes include zinc plating, black oxide, and passivation. A proper surface finish can enhance corrosion resistance, reduce friction, and improve the fastener’s overall lifespan. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate surface finish is critical based on the operating environment and specific application requirements.
4. Strength Grade
Fasteners are often categorized by their strength grade, which indicates the tensile strength and load-bearing capacity of the fastener. Common strength grades for cold headed fasteners include Grade 5, Grade 8, and ASTM A325. Understanding the strength grade is crucial for ensuring that the fasteners can withstand the mechanical loads they will encounter in service, especially in high-stress applications.
5. Diameter and Length
The diameter and length of cold headed fasteners are critical specifications that directly affect their performance in applications. These dimensions must meet the requirements of the assembly they are designed for, as incorrect sizes can lead to structural failure. B2B buyers should ensure that suppliers can provide fasteners in a wide range of sizes to accommodate various project needs.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Cold Headed Fasteners Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can enhance communication and negotiations with suppliers. Here are some essential trade terms to know:

Illustrative image related to cold headed fasteners
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces components that are used in another company’s end product. In the context of cold headed fasteners, understanding whether a supplier is an OEM can help assess their quality standards and production capabilities, which is particularly important for large-scale projects.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. This term is crucial for B2B buyers, as it affects budgeting and inventory management. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers determine whether a supplier can meet their needs without excess inventory costs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. For B2B buyers, creating a detailed RFQ can facilitate accurate and competitive quotes, ensuring that you receive the best value for your investment in cold headed fasteners.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized terms used in international trade to define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms helps mitigate risks and misunderstandings in global transactions, making them essential for B2B buyers operating across borders.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the products. Understanding lead times is critical for project planning and ensuring that fasteners arrive when needed to avoid delays in production schedules.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing cold headed fasteners, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and product quality.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cold headed fasteners Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends for Cold Headed Fasteners?
The cold headed fasteners market is influenced by several global drivers that shape its dynamics. A significant factor is the increasing demand for high-strength, lightweight materials in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction. As manufacturers seek to optimize performance and reduce costs, the cold heading process becomes increasingly attractive due to its efficiency and minimal waste generation. Furthermore, advancements in automation and Industry 4.0 technologies are revolutionizing the manufacturing landscape, enabling faster production cycles and enhanced precision in cold headed fasteners.
B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should also be aware of emerging sourcing trends. The adoption of digital platforms for procurement is gaining traction, allowing buyers to streamline sourcing processes and access a broader range of suppliers. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on local sourcing to mitigate supply chain disruptions, particularly in light of recent global events. This trend is especially pertinent for international buyers looking to ensure a consistent supply of cold headed fasteners while minimizing transportation costs.
Another key trend is the customization of fasteners to meet specific application requirements. Suppliers are increasingly offering tailored solutions, such as unique head shapes and multi-part assemblies, which can enhance the overall performance of products. This shift toward customization underscores the importance of collaboration between buyers and manufacturers to achieve optimal results.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Cold Headed Fasteners?
The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is a critical concern for B2B buyers today. The cold heading process is inherently more sustainable than traditional machining methods, producing significantly less waste and utilizing raw materials more efficiently. However, buyers should also consider the ethical dimensions of their supply chains. Ensuring that suppliers adhere to ethical labor practices and environmental regulations is essential for building a responsible brand image.
Sustainable sourcing practices are becoming increasingly important, with many buyers seeking suppliers who can provide ‘green’ certifications or use eco-friendly materials. For instance, sourcing fasteners made from recycled metals can reduce the overall carbon footprint and contribute to a circular economy. Additionally, buyers should inquire about suppliers’ commitment to reducing their environmental impact, such as implementing energy-efficient manufacturing processes or using renewable energy sources.

Illustrative image related to cold headed fasteners
As the market evolves, the importance of sustainability and ethical sourcing in the cold headed fasteners sector will only continue to grow. Buyers who prioritize these values will not only enhance their corporate responsibility but also position themselves favorably in a market that increasingly favors sustainability-conscious companies.
How Has the Cold Heading Process Evolved Over Time?
The cold heading process has undergone significant evolution since its inception, adapting to meet the changing demands of various industries. Originally developed to produce basic fasteners, advancements in technology have enabled manufacturers to create increasingly complex components with high precision. The introduction of computerized controls and advanced tooling has allowed for tighter tolerances and improved production speeds.
Moreover, the expansion of applications for cold headed parts beyond traditional fasteners has opened new markets. Today, cold heading is utilized in a variety of sectors, including electronics, medical devices, and renewable energy, highlighting its versatility and the continuous innovation within the field. As industries evolve, the cold heading process is likely to keep pace, offering new solutions that meet the dynamic needs of international B2B buyers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cold headed fasteners
-
How do I ensure the quality of cold headed fasteners from suppliers?
To ensure the quality of cold headed fasteners, conduct thorough supplier vetting. Request certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management systems. Additionally, ask for product samples and conduct quality assurance tests like tensile strength and corrosion resistance. Establish a clear quality control protocol in your contract, including inspection stages and acceptance criteria. Regular audits of your suppliers can also help maintain consistent quality levels over time. -
What factors should I consider when selecting a cold headed fastener supplier?
When selecting a supplier for cold headed fasteners, consider their manufacturing capabilities, lead times, and certifications. Evaluate their experience in your industry and their ability to meet specific requirements, including customization options. Check for reliable logistics and shipping practices, especially for international orders. Additionally, assess their customer service responsiveness and willingness to accommodate your needs, such as minimum order quantities (MOQs) and payment terms. -
What are the common customization options available for cold headed fasteners?
Customization options for cold headed fasteners include variations in size, shape, and material. Suppliers can accommodate specific head shapes, thread types, and surface treatments based on your requirements. Discuss your needs with potential suppliers to understand their capabilities in creating custom tooling and unique configurations. Always verify their ability to deliver prototypes or samples for approval before proceeding with large orders to ensure that the final products meet your specifications. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for cold headed fasteners?
Minimum order quantities for cold headed fasteners can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on the complexity of the fastener. Generally, MOQs range from 1,000 to 10,000 pieces for standard fasteners. Custom fasteners may have higher MOQs due to the tooling and setup costs involved. It’s essential to discuss your project requirements with suppliers to find a mutually beneficial arrangement that meets your needs without excessive inventory costs. -
What payment terms are commonly offered for international purchases of cold headed fasteners?
Payment terms for international purchases of cold headed fasteners typically include options such as advance payment, letter of credit, or net terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60). Many suppliers may require a deposit upfront, especially for custom orders. It’s crucial to negotiate favorable terms that align with your cash flow requirements while ensuring the supplier’s confidence in fulfilling the order. Always document the agreed terms in your purchase agreement to avoid misunderstandings. -
How does logistics affect the sourcing of cold headed fasteners internationally?
Logistics plays a critical role in sourcing cold headed fasteners internationally, influencing lead times, shipping costs, and overall supply chain efficiency. Consider the supplier’s location and their shipping capabilities, including options for air or sea freight. Understanding customs regulations and potential tariffs in your country is essential to avoid delays and unexpected costs. Collaborating with a logistics partner familiar with international trade can streamline the process and ensure timely delivery. -
What quality assurance measures should be in place for cold headed fasteners?
Quality assurance measures for cold headed fasteners should include incoming material inspections, in-process quality checks, and final product evaluations. Implementing a system of documentation, such as batch records and inspection reports, is vital for traceability. Collaborate with your supplier to establish clear acceptance criteria and testing protocols. Regular audits and feedback loops can enhance the quality control process and help identify areas for improvement. -
How can I address specific technical challenges when sourcing cold headed fasteners?
To address technical challenges when sourcing cold headed fasteners, maintain open communication with your supplier about your specific needs and potential issues. Collaborate on design modifications and material selection to overcome challenges like strength requirements or environmental factors. Engaging with engineering support from the supplier can provide insights into best practices and innovative solutions. Additionally, investing in prototype testing can help identify problems early in the process, ensuring a smoother production run.
Top 6 Cold Headed Fasteners Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Grandeur Fasteners – Custom Cold Heading Fasteners
Domain: grandeurfasteners.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Grandeur Fasteners specializes in cold heading processes to manufacture custom fasteners. Key product details include: 1. Cold heading process: Forming metal wire into specified shapes at room temperature using dies, hammers, and punches. 2. Capabilities: Tight tolerances (+/- .002″), high-speed production rates, large volume capabilities, and reduced raw material waste. 3. Product range: Standard…
2. B&D Cold Headed Products – High Strength Fasteners
Domain: bdcoldheadedproducts.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: B&D Cold Headed Products is a U.S. manufacturer of high strength cold-formed bolts, studs, pins, and other metal fasteners. Key product categories include:
– Threaded Bolts & Screws: Wheel Bolts, Hex Bolts & Screws, Square Head Bolts & Screws, Hex Flange Bolts, Plow Bolts, Shoulder Bolts, Carriage & Timber Bolts, Other Bolts & Screws.
– Threaded Studs: Double End Studs, Hex Studs, Continuous Thr…
3. BCEPI – Cold Heading Fasteners
Domain: bcepi.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Cold heading is a manufacturing process for fasteners using non-heated metal blanks, often made from materials like carbon steel, brass, aluminum, and stainless steels. Key advantages include higher production rates, improved consistency and accuracy, reduced scrap material, and the ability to create a wide range of shapes and sizes. Cold heading reduces material costs by over 50% and lowers overa…
4. TFG USA – Cold Heading Solutions
Domain: tfgusa.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Cold heading is a high-speed metal forming process that shapes parts at room temperature without the need for heat. It is primarily used for forming the heads on fasteners like bolts, screws, rivets, and nails. Key advantages include minimal waste, faster production, stronger parts, reduced costs, and the ability to simplify multi-piece assemblies. Cold heading supports sustainable manufacturing b…
5. Fastco Industries – Cold Headed Bolts and Screws
Domain: fastcoindustries.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Cold Headed Bolts and Screws Manufacturer, High Quality. Specializes in custom cold heading manufacturing. Products include cold heading studs, rivets, pins, bolts, and screws. Materials used: Carbon Steel (1010-1015-1018-1022-1038-1045-10B21), Alloy Steel (1541-4037-4135-4140-B16), Stainless Steel (302-304-316-410-430), High Nickel Alloy Stainless Steel (A286-431). Sizes range from M3 to M18 and …
6. Level 1 Fasteners – Cold Headed Fasteners
Domain: level1fasteners.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Cold heading process forms shapes without heat; fasteners sizes #2-56 to .875 DIA up to 7″ in length; manufacturing rods, headed bolts, and screws; heading styles include hex head, double hex head, button cap, socket cap, and flat socket cap; commonly used materials: K500, 400 Monel, 304, 316, 4140, 8740; benefits include large quantity production, tight tolerances, reduced material waste, reduced…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cold headed fasteners
In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing, the strategic sourcing of cold headed fasteners presents an invaluable opportunity for international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By leveraging the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of the cold heading process, companies can significantly reduce raw material waste while achieving tighter tolerances and improved physical properties in their products.
Key takeaways include the capability to produce high volumes with minimal waste, the potential for custom tooling to meet unique specifications, and the versatility of cold headed fasteners across various applications. As global supply chains become increasingly complex, embracing a strategic sourcing approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also fosters stronger supplier relationships, ensuring reliability and quality in fastener procurement.
Looking ahead, as technological advancements continue to shape the manufacturing industry, now is the time for B2B buyers to reassess their sourcing strategies. Engaging with experienced suppliers who specialize in cold headed fasteners can unlock new avenues for innovation and cost savings. Take the next step in your sourcing journey—explore the benefits of cold heading today to secure a competitive edge in your market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.