Choosing Your 4 Way Solenoid Valve: Key Specs to Compare in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for 4 way solenoid valve
In the dynamic landscape of industrial automation, sourcing the right 4-way solenoid valve can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. With varying specifications, applications, and supplier reliability, navigating this complex market is crucial to ensuring operational efficiency and reliability. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, detailing the diverse types of 4-way solenoid valves available, their applications across different industries, and essential criteria for vetting suppliers.
As businesses in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including Nigeria and Saudi Arabia) seek to enhance their automation processes, understanding the nuances of these valves becomes imperative. The guide empowers buyers with insights into cost considerations, performance metrics, and maintenance requirements, enabling informed purchasing decisions that align with specific operational needs.
By providing actionable information and expert recommendations, this resource aims to demystify the complexities of the global market for 4-way solenoid valves, ensuring that B2B buyers are equipped to make strategic investments that drive productivity and innovation in their operations. Whether you’re looking to enhance your supply chain or streamline your production processes, this guide will be your trusted companion in navigating the intricacies of solenoid valve procurement.
Understanding 4 way solenoid valve Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4/2-Way Solenoid Valve | Four ports, two positions; typically used for double-acting cylinders | Pneumatic actuators, robotics | Pros: Simple design, cost-effective. Cons: Limited control compared to 5/2-way valves. |
| 4/3-Way Solenoid Valve | Four ports, three positions; allows for more complex control scenarios | Automation systems, packaging | Pros: Greater control flexibility. Cons: More complex and potentially higher cost. |
| Direct-Operated 4-Way Valve | Directly actuated by the solenoid; no pilot pressure needed | Small machinery, medical devices | Pros: Fast response time, compact design. Cons: Limited to lower flow rates. |
| Pilot-Operated 4-Way Valve | Uses pilot pressure to operate; suitable for larger systems | Heavy machinery, industrial automation | Pros: Handles higher flow rates, reliable in larger systems. Cons: Requires more maintenance. |
| Manual Override 4-Way Valve | Features a manual override for maintenance and testing | Maintenance operations, emergency systems | Pros: Allows for manual control, enhances safety. Cons: Adds complexity and potential failure points. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of 4/2-Way Solenoid Valves?
4/2-way solenoid valves are characterized by their four ports and two operational positions, making them ideal for controlling double-acting cylinders in various applications. These valves are commonly used in pneumatic actuators and robotics, where straightforward control is essential. When considering a purchase, buyers should evaluate the valve’s compatibility with their existing systems and its ability to meet specific operational requirements. While they offer a cost-effective solution, their limited control capabilities compared to more complex valve types may be a drawback for certain applications.
How Do 4/3-Way Solenoid Valves Enhance Control in Automation Systems?
4/3-way solenoid valves feature four ports and three positions, providing enhanced control in automation systems. This design allows for more complex control scenarios, making them suitable for applications in packaging and assembly lines where precise positioning is crucial. When purchasing, businesses should consider the increased flexibility and control these valves offer, despite their potentially higher cost and complexity. This type of valve is particularly advantageous for operations requiring frequent adjustments or multiple control states.
Why Choose Direct-Operated 4-Way Valves for Smaller Machinery?
Direct-operated 4-way valves are actuated directly by the solenoid, eliminating the need for pilot pressure. This makes them suitable for smaller machinery and medical devices where space is limited, and quick response times are essential. Buyers should assess the valve’s flow rate and response characteristics to ensure it meets their operational needs. While these valves are compact and efficient, their limitations in handling higher flow rates should be considered when selecting the appropriate valve type.
What Benefits Do Pilot-Operated 4-Way Valves Offer for Heavy Machinery?
Pilot-operated 4-way valves utilize pilot pressure to facilitate operation, making them ideal for heavy machinery and industrial automation applications. They can manage higher flow rates and are generally more reliable in larger systems. When purchasing, businesses should evaluate the valve’s maintenance requirements and the compatibility of pilot pressure with their existing setups. Although these valves provide robust performance in demanding environments, they may require more frequent maintenance compared to simpler valve designs.
How Do Manual Override 4-Way Valves Improve Safety in Maintenance Operations?
Manual override 4-way valves incorporate a manual control feature that allows operators to bypass automated controls during maintenance or emergencies. This capability enhances safety in operations where immediate manual control is necessary. Buyers should consider the added complexity and potential failure points associated with this feature, as it can impact overall system reliability. However, the ability to manually control the valve can be invaluable in ensuring system functionality during critical operations, making it a worthwhile investment for many businesses.

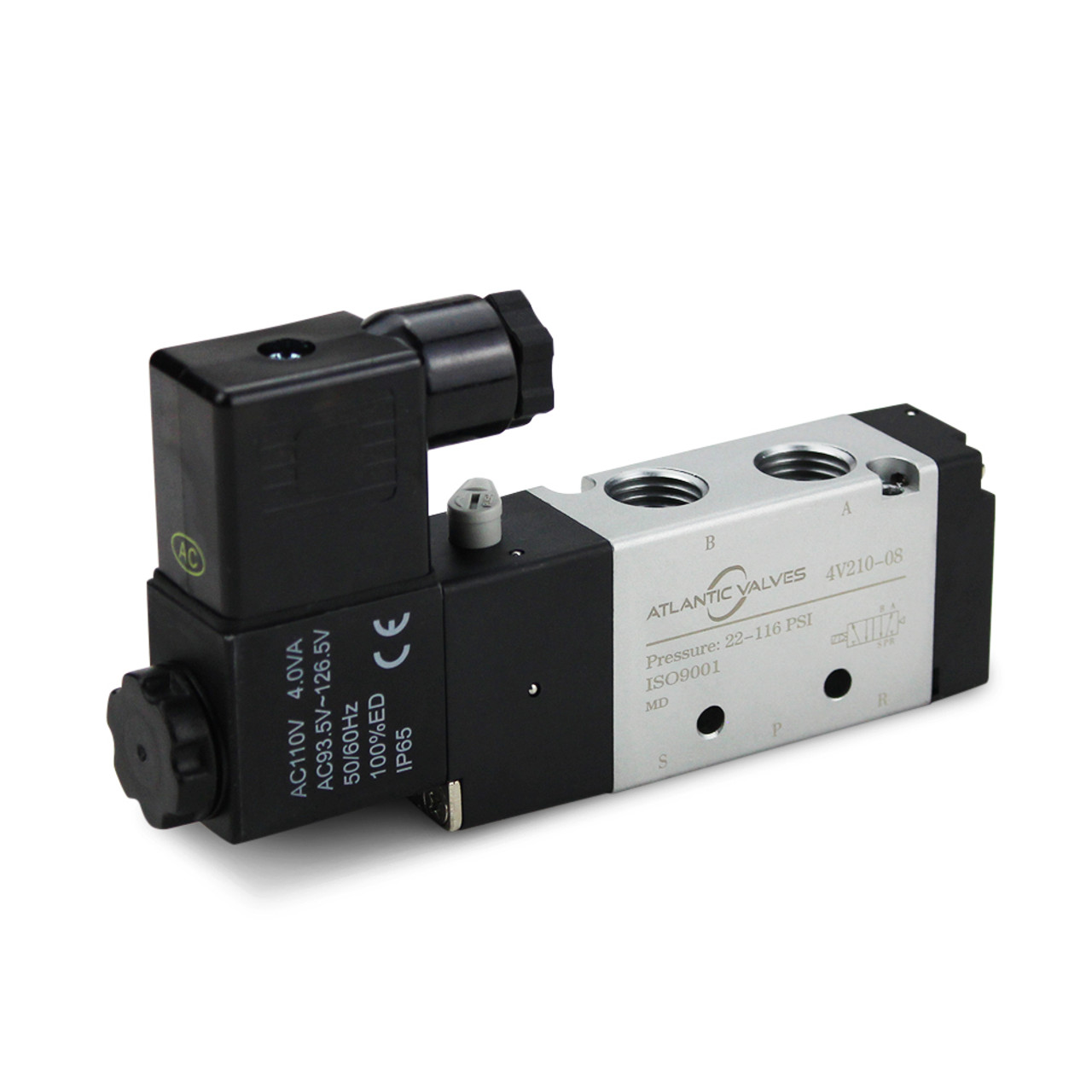
Illustrative image related to 4 way solenoid valve
Key Industrial Applications of 4 way solenoid valve
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of 4 way solenoid valve | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Control of pneumatic actuators in assembly lines | Increased automation efficiency and reduced downtime | Quality certifications, compatibility with existing systems, and supplier reliability |
| Automotive | Operation of double-acting cylinders in testing rigs | Enhanced testing accuracy and faster cycle times | Temperature and pressure ratings, response time, and availability of spare parts |
| Food and Beverage | Regulation of liquid flow in bottling plants | Improved product consistency and reduced waste | Compliance with food safety standards, material compatibility, and maintenance support |
| Oil and Gas | Control of valves in pipeline systems | Enhanced safety and operational reliability | Corrosion resistance, pressure specifications, and supplier support in remote locations |
| HVAC Systems | Regulation of airflow in climate control systems | Energy efficiency and improved environmental control | Energy ratings, adaptability to varying pressure conditions, and responsiveness to control signals |
How is the 4 Way Solenoid Valve Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, 4-way solenoid valves play a crucial role in controlling pneumatic actuators on assembly lines. They enable precise movement of double-acting cylinders, which are essential for tasks such as lifting, positioning, and fastening components. By automating these processes, manufacturers can significantly increase efficiency and reduce downtime. International buyers should consider sourcing valves that meet quality certifications and are compatible with existing machinery to ensure seamless integration.
What Role Does the 4 Way Solenoid Valve Play in Automotive Testing?
In automotive applications, 4-way solenoid valves are integral to the operation of double-acting cylinders in testing rigs. These valves allow for controlled movement and testing of various components, ensuring that vehicles meet safety and performance standards. The ability to enhance testing accuracy and reduce cycle times is vital in a competitive market. Buyers should focus on sourcing valves that can withstand rigorous testing conditions, including specific temperature and pressure ratings.
How Does the 4 Way Solenoid Valve Benefit the Food and Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage sector, 4-way solenoid valves are used to regulate liquid flow in bottling plants. Their precision ensures that products are filled consistently, reducing waste and improving overall product quality. Compliance with stringent food safety standards is paramount for international buyers in this industry. Therefore, sourcing valves made from food-grade materials and those that offer reliable maintenance support is critical.
What is the Importance of 4 Way Solenoid Valves in Oil and Gas Operations?
In the oil and gas industry, 4-way solenoid valves control the flow of fluids in pipeline systems. They enhance safety and operational reliability by managing pressure and flow effectively. Given the harsh environments in which these valves operate, buyers must prioritize sourcing options that offer corrosion resistance and high-pressure specifications. Additionally, suppliers should provide robust support, especially for operations in remote locations.
How Do 4 Way Solenoid Valves Improve HVAC Systems?
In HVAC systems, 4-way solenoid valves regulate airflow to ensure optimal climate control. By allowing for precise adjustments in air distribution, they contribute to energy efficiency and enhanced comfort levels. Buyers in this sector should seek valves with high energy ratings and adaptability to varying pressure conditions to maximize performance. Responsiveness to control signals is also a key consideration for effective climate management.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘4 way solenoid valve’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Performance Due to Sizing Issues
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter challenges when selecting the correct size of a 4-way solenoid valve for their applications. An undersized valve can lead to insufficient flow rates, resulting in slow actuator response times and inefficiencies in production processes. Conversely, an oversized valve may lead to excessive energy consumption and increased operational costs. This sizing inconsistency often stems from a lack of clear specifications and understanding of the specific application requirements, leading to frustration and potential financial losses.
The Solution: To overcome sizing issues, buyers should begin by conducting a thorough analysis of their system requirements, including the flow rate, pressure, and the specific pneumatic devices being controlled. Utilizing manufacturer catalogs and detailed specifications can provide insights into the appropriate valve sizes. Engaging with suppliers who offer expert consultation services can also aid in selecting the right valve. Additionally, consider using flow calculators or simulation software to predict performance based on various valve sizes. This proactive approach ensures optimal performance and energy efficiency in the long run.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Maintenance and Troubleshooting
The Problem: A common pain point for businesses using 4-way solenoid valves is the complexity of maintenance and troubleshooting. When a valve fails or operates incorrectly, it can halt production and lead to costly downtime. Many buyers struggle to identify the root cause of these issues, whether it’s due to electrical failures, improper installation, or wear and tear of the valve components. This lack of clarity can lead to prolonged downtime and increased repair costs.
The Solution: To address maintenance challenges, buyers should implement a preventive maintenance schedule that includes regular inspections and testing of solenoid valves. Training staff on how to recognize early signs of failure—such as unusual sounds, leaks, or inconsistent operation—can also be beneficial. Furthermore, investing in valves with diagnostic features, such as built-in sensors that monitor performance, can provide real-time data to help identify issues before they lead to failure. Documenting maintenance procedures and creating a troubleshooting guide can streamline the repair process and minimize downtime.
Scenario 3: Limited Knowledge on Valve Variants and Applications
The Problem: Many international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, may face challenges stemming from a limited understanding of the different variants of 4-way solenoid valves and their appropriate applications. This lack of knowledge can lead to purchasing the wrong type of valve, resulting in compatibility issues and inadequate system performance. Without a clear understanding of the differences between options like 4/2-way and 4/3-way valves, buyers may struggle to make informed decisions.
The Solution: Buyers should invest time in educating themselves about the various types of 4-way solenoid valves and their specific applications. Manufacturers often provide detailed product literature, including application guides and technical datasheets, which can serve as valuable resources. Additionally, attending industry workshops, webinars, or trade shows can enhance understanding and provide networking opportunities with experts. Collaborating with suppliers who offer comprehensive product training and support can also empower buyers to make informed decisions, ensuring they select the right valve for their specific needs and applications.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for 4 way solenoid valve
When selecting materials for 4-way solenoid valves, it is essential to consider the specific requirements of the application, including environmental conditions, media compatibility, and regulatory standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of these valves: brass, stainless steel, aluminum, and plastic. Each material has its unique properties, advantages, and drawbacks, which can significantly impact performance and suitability for various applications.
What Are the Key Properties of Brass in 4-Way Solenoid Valves?
Brass is a popular choice for solenoid valve construction due to its excellent machinability and corrosion resistance, particularly in environments with moderate temperatures and pressures. Brass valves typically have a temperature rating of up to 150°C (302°F) and can handle pressures up to 10 bar (145 psi).
Pros and Cons: Brass is durable and relatively cost-effective, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. However, it can be susceptible to dezincification in certain corrosive environments, which may compromise its integrity over time.
Impact on Application: Brass is compatible with various media, including air, water, and certain oils, but may not be suitable for aggressive chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM or DIN, particularly when using brass valves in corrosive environments.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in 4-Way Solenoid Valves?
Stainless steel is renowned for its superior corrosion resistance and strength, making it ideal for harsh environments and high-pressure applications. It can withstand temperatures exceeding 200°C (392°F) and pressures up to 20 bar (290 psi).
Pros and Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and resistance to corrosion, which makes it suitable for a variety of aggressive media, including acids and solvents. However, it is more expensive than brass and can be more challenging to machine.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel valves are often used in industries such as food processing and pharmaceuticals, where hygiene and material integrity are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for certifications that confirm compliance with international standards, such as JIS for Japanese markets or EN standards in Europe.
What Are the Benefits of Using Aluminum in 4-Way Solenoid Valves?
Aluminum is lightweight and has good corrosion resistance, making it a suitable choice for applications where weight is a concern. Aluminum valves typically operate effectively at temperatures up to 120°C (248°F) and pressures around 8 bar (116 psi).
Pros and Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum allows for easier installation and reduced shipping costs. However, it is less durable than brass or stainless steel and may not perform well in high-pressure applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for air and water applications but may not be ideal for aggressive chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that aluminum valves meet relevant standards for pressure and temperature ratings, especially in regions with strict safety regulations.
Why Are Plastics Used in 4-Way Solenoid Valves?
Plastic materials, such as PVC or polycarbonate, are increasingly used in solenoid valves due to their excellent chemical resistance and lightweight properties. They can typically handle temperatures up to 80°C (176°F) and pressures around 6 bar (87 psi).
Pros and Cons: The main advantage of plastic valves is their resistance to a wide range of chemicals, making them ideal for corrosive environments. However, they have lower pressure and temperature ratings compared to metals, which limits their application scope.
Impact on Application: Plastic valves are commonly used in chemical processing and water treatment applications where metal corrosion is a concern.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the selected plastic material complies with local regulations and standards, particularly in industries that require stringent safety measures.
Summary Table of Material Selection for 4-Way Solenoid Valves
| Material | Typical Use Case for 4 way solenoid valve | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brass | General industrial applications | Cost-effective and durable | Susceptible to dezincification | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Superior corrosion resistance | Higher cost and machining complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight applications, air/water systems | Lightweight and easy to install | Lower durability and pressure rating | Medium |
| Plastic | Chemical processing, water treatment | Excellent chemical resistance | Limited pressure and temperature ratings | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for 4-way solenoid valves, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for 4 way solenoid valve
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of 4-Way Solenoid Valves?
The manufacturing of 4-way solenoid valves involves several key stages, ensuring that these critical components meet high standards of performance and reliability. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for 4-Way Solenoid Valves?
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. Typically, high-grade metals such as brass, stainless steel, or aluminum are selected for their durability and resistance to corrosion. The materials undergo rigorous inspections to verify their quality and specifications before being cut or shaped.
Advanced techniques such as laser cutting or CNC machining are commonly employed to ensure precision in shaping the components. For instance, solenoid coils are often made from copper wire, which is wound to specific standards to achieve optimal electromagnetic performance.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming 4-Way Solenoid Valves?
The forming process involves shaping the raw materials into the desired components of the valve. Techniques like stamping and forging are frequently used to create the valve body and other critical parts. During this phase, attention to detail is crucial, as even minor defects can affect the valve’s functionality.
Illustrative image related to 4 way solenoid valve
The components are often subjected to heat treatment to enhance their mechanical properties. This process increases strength and durability, ensuring that the solenoid valve can withstand various operational conditions.
How Are 4-Way Solenoid Valves Assembled?
Assembly is a vital stage where all the individual parts come together to form the complete solenoid valve. This process typically involves:
- Integrating the solenoid coil: The coil is mounted onto the valve body, with precise alignment to ensure effective electromagnetic actuation.
- Sealing and O-rings: The use of high-quality seals and O-rings prevents leaks and ensures that the valve maintains its integrity under pressure.
- Final assembly: All components, including the spool and springs, are carefully assembled. Automated assembly lines may be employed to enhance speed and accuracy.
Quality checks are often performed during assembly to catch any discrepancies early on.
What Finishing Processes Are Involved in 4-Way Solenoid Valve Manufacturing?
Finishing processes aim to enhance the valve’s appearance and functionality. This stage includes surface treatments like anodizing, powder coating, or plating to improve corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
Additionally, final inspections are conducted to ensure that all dimensions meet specifications and that there are no visible defects. This is crucial for maintaining high standards in manufacturing, especially for international buyers who may have stringent quality requirements.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of 4-way solenoid valves, particularly for international B2B transactions. The following international standards are relevant:
- ISO 9001: This standard ensures that manufacturers maintain a quality management system that meets customer and regulatory requirements. It emphasizes continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
- CE Certification: For products sold in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For valves used in the oil and gas industries, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is essential.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is an integral part of the manufacturing process. The following checkpoints are commonly implemented:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials and components are inspected upon receipt to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular checks are performed to monitor production processes and ensure that they remain within tolerances.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of the finished product is conducted before it is packaged and shipped. This includes functional testing to verify that the valve operates correctly.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must take steps to ensure that their suppliers adhere to strict quality control measures. Here are actionable strategies:
- Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. Buyers should look for adherence to ISO 9001 and other relevant certifications.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide detailed quality reports that outline their QC processes, inspection results, and compliance with international standards.
- Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality practices and the products being manufactured.
What QC and Certification Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control and certification:
- Local Regulations: Each region may have unique regulatory requirements that must be met. For instance, certain countries may require additional certifications beyond ISO or CE marking.
- Cultural Differences in Quality Expectations: Understanding the cultural context of your supplier can be critical. Some regions may prioritize different aspects of quality, such as reliability over speed of delivery.
- Communication of Standards: Clear communication of quality standards and expectations is vital. Buyers should ensure that suppliers understand their requirements and can meet them consistently.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing 4-way solenoid valves, ensuring they receive products that meet their operational needs and compliance standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘4 way solenoid valve’
This practical sourcing guide provides a structured checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure a 4-way solenoid valve. By following these steps, you can ensure that you make informed decisions that align with your operational needs and standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes the valve’s pressure rating, size, and the specific application it will serve, such as controlling double-acting cylinders. Understanding these specifications will help you filter suppliers and products that meet your operational demands.
Step 2: Research Industry Standards and Certifications
Verify that the solenoid valves comply with relevant industry standards and certifications. Look for certifications such as ISO, CE, or UL, which indicate adherence to safety and quality standards. This step is crucial as it ensures the reliability and safety of the components you plan to integrate into your systems.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s essential to thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. This diligence helps in assessing the supplier’s reputation, reliability, and ability to meet your specific requirements.
- Supplier Experience: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in manufacturing 4-way solenoid valves.
- Customer Feedback: Seek testimonials or reviews from previous clients to gauge satisfaction levels.
Step 4: Request Product Samples
Whenever possible, request samples of the 4-way solenoid valves you are considering. Testing samples allows you to evaluate their quality, performance, and compatibility with your systems. It is a practical way to ensure the product meets your operational needs before making a larger investment.
Step 5: Assess Pricing and Payment Terms
Compare pricing structures among various suppliers while also considering the total cost of ownership. This includes not just the initial purchase price but also shipping, handling, and potential maintenance costs. Additionally, negotiate payment terms that align with your budget cycles to improve cash flow management.
Step 6: Inquire About After-Sales Support and Warranty
Inquire about the after-sales support and warranty offered by the supplier. A robust warranty and responsive customer service can significantly impact the long-term satisfaction and operational efficiency of your purchase. Ensure that the supplier is willing to provide technical support and assistance when needed.
Step 7: Finalize the Order and Confirm Delivery Times
Once you have selected a supplier, finalize the order and confirm the delivery times. Clear communication about delivery expectations is essential to avoid disruptions in your operations. Ensure that all agreements are documented to facilitate a smooth transaction and to hold the supplier accountable.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the procurement process for 4-way solenoid valves effectively, ensuring that they make informed decisions that support their business objectives.

Illustrative image related to 4 way solenoid valve
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for 4 way solenoid valve Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in 4-Way Solenoid Valve Sourcing?
When sourcing 4-way solenoid valves, understanding the cost structure is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. Common materials like brass, stainless steel, and various plastics come with differing price points. For instance, stainless steel valves are generally more expensive due to their durability and corrosion resistance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Skilled labor is often required for precision assembly and quality control, which can drive up costs in countries with higher wage standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, and administrative costs that manufacturers incur. Efficient manufacturing processes and economies of scale can help lower these overhead costs.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for production can be substantial, especially for custom or specialized valves. This cost is typically spread over the production run, making it essential to consider the volume of orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous testing and quality assurance procedures are necessary to ensure that solenoid valves meet industry standards. Enhanced QC processes can increase costs but are vital for maintaining product reliability.
-
Logistics: Shipping, handling, and storage costs can significantly affect the final price, especially for international transactions. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and local tariffs should be factored in.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. This margin can vary widely based on the supplier’s market position and the perceived value of the product.
How Do Price Influencers Impact 4-Way Solenoid Valve Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of 4-way solenoid valves in the B2B marketplace:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often qualify for bulk pricing discounts. Understanding the supplier’s MOQ can help buyers negotiate better rates.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized valves tailored to specific applications can incur higher costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (such as ISO or CE) can raise prices. Buyers should weigh the benefits of quality against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and service capabilities can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium but can offer better support and warranty options.
-
Incoterms: The agreed terms of shipment (e.g., FOB, CIF) can affect the overall cost. Understanding these terms is essential for calculating total landed costs, especially in international transactions.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Negotiating 4-Way Solenoid Valve Prices?
To maximize value when sourcing 4-way solenoid valves, consider these buyer tips:
-
Negotiation: Don’t hesitate to negotiate prices. Suppliers often have flexibility, especially for larger orders. Presenting a well-researched case can help in securing better terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Focus on the total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just the initial purchase price. Factors such as energy efficiency, maintenance requirements, and longevity can impact overall costs significantly.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of potential fluctuations in currency exchange rates and local tariffs. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can also lead to more favorable pricing over time.
-
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices: Always approach indicative prices with caution. Prices can fluctuate due to raw material costs and market demand, so it’s essential to obtain quotes before making purchasing decisions.
By understanding these cost components and price influencers, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing 4-way solenoid valves, ultimately leading to better procurement outcomes.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing 4 way solenoid valve With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to the 4 Way Solenoid Valve
When evaluating industrial automation solutions, it’s crucial to consider various technologies that can fulfill similar functions as the 4-way solenoid valve. This analysis will compare the 4-way solenoid valve with two viable alternatives: the 5/2-way pneumatic valve and manual control valves. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each option, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
| Comparison Aspect | 4 Way Solenoid Valve | 5/2-Way Pneumatic Valve | Manual Control Valve |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Efficient for controlling double-acting cylinders; provides precise control. | Versatile, allowing independent exhaust paths; suitable for complex systems. | Basic control; manual operation may lead to slower response times. |
| Cost | Moderate pricing; cost-effective for automated systems. | Generally lower cost; good for budget-conscious applications. | Low initial investment, but can lead to higher labor costs. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires electrical setup; straightforward for automation systems. | Simple pneumatic connections; easy to integrate with existing systems. | Requires training for operators; installation can be complex. |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic electrical checks and cleaning; reliable with proper care. | Minimal maintenance; mostly requires checking pneumatic lines. | Frequent maintenance required due to wear and tear. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for automated machinery requiring precise actuation. | Best for applications needing flexible exhaust options and pneumatic control. | Suitable for manual operations or low-frequency applications. |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of the 5/2-Way Pneumatic Valve?
The 5/2-way pneumatic valve is a strong alternative to the 4-way solenoid valve, particularly in systems that require more control over exhaust paths. Its five ports allow for better management of air flow and exhaust, making it ideal for complex pneumatic setups. However, while it offers flexibility, it may not be as precise as the 4-way solenoid valve in applications requiring exact positioning. Additionally, while the initial cost is generally lower, the complexity of the system can lead to higher costs in the long run if not managed properly.

Illustrative image related to 4 way solenoid valve
How Does the Manual Control Valve Compare?
Manual control valves offer a straightforward, low-cost solution for applications where automation is not critical. They are easy to install and maintain but require human intervention for operation, which can slow down processes and lead to inconsistencies. This type of valve is suitable for simpler tasks or environments where automation isn’t feasible. However, for industries aiming for efficiency and precision, manual control valves can become a bottleneck, ultimately hindering productivity.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
Selecting the right valve solution hinges on understanding the specific requirements of your application. If your operations demand precise control and automation, the 4-way solenoid valve stands out as a superior choice. For applications that prioritize flexibility and cost, the 5/2-way pneumatic valve may be ideal. Conversely, if budget constraints are significant and automation is less critical, manual control valves could suffice, albeit with potential trade-offs in efficiency. Analyzing these factors will empower B2B buyers to choose the most suitable solution for their operational context, ensuring that they achieve the desired balance between performance, cost, and ease of use.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for 4 way solenoid valve
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of a 4-Way Solenoid Valve?
When selecting a 4-way solenoid valve, understanding its technical properties is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and compatibility with your systems. Below are several key specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
1. Material Grade
The material of the solenoid valve affects its durability, resistance to corrosion, and suitability for specific applications. Common materials include brass, stainless steel, and aluminum. For instance, brass is often used in general applications, while stainless steel is preferred for corrosive environments. Choosing the right material is essential for longevity and maintaining operational efficiency.
2. Operating Pressure
Operating pressure is a critical parameter that defines the maximum pressure the valve can handle during operation. It is usually measured in bar or psi. A valve rated for high pressure can be used in more demanding applications, making it vital for buyers to match this specification with their system requirements to prevent failure or leaks.

Illustrative image related to 4 way solenoid valve
3. Flow Rate
Flow rate, measured in liters per minute (L/min) or gallons per minute (GPM), indicates how much fluid can pass through the valve at a given pressure. This specification is essential for ensuring that the valve can meet the demands of the application, particularly in systems requiring precise control over fluid delivery.
4. Electrical Specifications
These include voltage ratings (e.g., 24V, 110V), power consumption, and coil resistance. Understanding the electrical specifications is critical for ensuring compatibility with the existing electrical infrastructure. Additionally, knowing the power requirements helps in planning energy consumption and operational costs.
5. Temperature Range
The temperature range indicates the limits within which the valve can operate effectively. Valves designed for high-temperature applications are often made from specialized materials or treated to withstand extreme conditions. Selecting a valve with an appropriate temperature rating is crucial for maintaining performance and safety in various environments.
6. Actuation Type
4-way solenoid valves can be direct-acting or pilot-operated. Direct-acting valves are activated directly by the solenoid, while pilot-operated valves use pressure to control the spool. Understanding the actuation type is essential for application suitability and determining the speed and responsiveness of the valve.
What Are Common Trade Terms Associated with 4-Way Solenoid Valves?
Familiarity with industry-specific jargon can streamline the purchasing process and enhance communication between buyers and suppliers. Here are several common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of solenoid valves, buyers often seek OEMs for reliable and tested products that ensure compatibility and quality.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for B2B buyers, particularly when budgeting for purchases and determining inventory levels.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal request from a buyer to a supplier to provide pricing and terms for specific products. This term is vital for initiating negotiations and obtaining competitive pricing for bulk orders of solenoid valves.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure clarity on shipping, costs, and risks associated with the delivery of solenoid valves.
5. Actuator Type
In the context of solenoid valves, actuator type refers to the mechanism that operates the valve. Familiarity with actuator types, such as electric or pneumatic, helps buyers choose the right valve for their specific applications.

Illustrative image related to 4 way solenoid valve
6. Service Life
Service life refers to the expected duration a valve can operate effectively before failure. Knowing the service life is essential for planning maintenance schedules and ensuring operational continuity in industrial applications.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions when procuring 4-way solenoid valves, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and cost savings.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the 4 way solenoid valve Sector
What Are the Key Drivers and Trends Shaping the 4-Way Solenoid Valve Market?
The global 4-way solenoid valve market is witnessing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for automation across various industries, including manufacturing, oil and gas, and automotive. As businesses strive for enhanced operational efficiency, the adoption of advanced pneumatic control systems, such as 4-way solenoid valves, has become essential. These valves are pivotal for controlling double-acting cylinders, thereby facilitating precise movement in automated machinery.
Emerging technologies, such as IoT and Industry 4.0, are transforming sourcing trends, making it imperative for international B2B buyers to focus on suppliers that offer smart, connected solutions. In regions like Africa and South America, where industrialization is accelerating, the demand for cost-effective and efficient pneumatic systems is on the rise. Buyers should be aware of local market dynamics, including potential supply chain disruptions, which can be mitigated through strategic partnerships and diversified sourcing.
Moreover, sustainability is increasingly influencing purchasing decisions. B2B buyers in the Middle East and Europe are actively seeking suppliers that prioritize eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes. The focus on reducing carbon footprints is not just a trend but a necessity, as companies navigate regulatory pressures and changing consumer expectations. As such, understanding these market dynamics is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the B2B Market for 4-Way Solenoid Valves?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are not merely trends; they are integral to the business strategies of many organizations. The production of 4-way solenoid valves can have environmental implications, particularly regarding energy consumption and waste generation during manufacturing. International B2B buyers are increasingly aware of these impacts and are seeking suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices.
Implementing ethical supply chains enhances brand reputation and fosters customer loyalty. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that demonstrate transparency in their sourcing processes and offer certifications for environmentally friendly materials. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and RoHS compliance for hazardous substances can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Furthermore, the integration of ‘green’ materials in the production of 4-way solenoid valves can significantly reduce environmental impacts. For example, using recyclable metals and eco-friendly packaging materials can appeal to environmentally conscious buyers, particularly in regions like Europe, where sustainability standards are stringent. By aligning sourcing strategies with sustainability goals, businesses can not only meet regulatory requirements but also enhance their competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market.
What Is the Historical Context of 4-Way Solenoid Valves in the B2B Sector?
The evolution of 4-way solenoid valves can be traced back to the early developments in pneumatic technology. Initially, these valves were designed for simple on-off control applications. However, as industrial processes became more complex, the need for more sophisticated control mechanisms grew. The introduction of 4-way solenoid valves allowed for enhanced functionality, enabling the control of double-acting actuators with greater precision.
Over the decades, advancements in materials and manufacturing techniques have led to the development of more durable and efficient solenoid valves. The integration of electronic controls and smart technology has further revolutionized their application in various industries. Today, 4-way solenoid valves are not only crucial components in automation systems but also play a vital role in the drive towards sustainability and efficiency in industrial operations. Understanding this historical context helps B2B buyers appreciate the value and functionality of these essential components in modern industrial applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of 4 way solenoid valve
-
How do I choose the right 4-way solenoid valve for my application?
Selecting the appropriate 4-way solenoid valve involves understanding your specific application requirements, including the type of actuator (e.g., double-acting cylinder) and the required flow rate. Consider the valve’s pressure rating, operating temperature, and the medium it will control (air, water, etc.). Additionally, assess the valve’s configuration—whether you need a 4/2 or 4/3 position valve—and the electrical specifications, such as voltage and coil type. Consulting with suppliers or technical experts can provide tailored recommendations based on your operational conditions. -
What are the key differences between 4/2-way and 4/3-way solenoid valves?
The primary distinction lies in their functionality. A 4/2-way solenoid valve has four ports and two switching positions, suitable for applications requiring simple on/off control of a double-acting cylinder. In contrast, a 4/3-way valve offers an additional position, allowing for more complex control of the flow path, which can be beneficial in applications needing simultaneous actuation or precise directional control. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right valve for your specific pneumatic control needs. -
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for 4-way solenoid valves?
When evaluating suppliers, consider their industry experience, product quality certifications (such as ISO), and their ability to provide technical support. Investigate their track record for timely delivery and customer service responsiveness. Additionally, assess their production capacity, especially if you require large quantities or customization. Requesting samples and checking customer reviews can also help gauge supplier reliability and product performance. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for 4-way solenoid valves?
MOQs can vary significantly by supplier and region. Generally, manufacturers may set an MOQ ranging from 50 to 100 units for standard models. However, this can be lower for stock items or higher for customized valves. Always discuss your specific needs with the supplier to understand their MOQ policies and explore options that may accommodate smaller orders, especially for new or trial projects. -
What payment terms are commonly offered for international orders of 4-way solenoid valves?
Payment terms can differ based on supplier policies and your relationship with them. Common arrangements include payment in advance, a letter of credit, or net 30 to 60 days after delivery. For large orders or ongoing partnerships, negotiating favorable terms may be possible. Always clarify payment expectations upfront to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth transactions. -
How can I ensure the quality of the 4-way solenoid valves I order?
To ensure quality, look for suppliers that adhere to recognized industry standards and certifications. Request detailed product specifications, including material data sheets and performance testing results. Consider asking for samples before placing a bulk order to assess the valve’s fit and functionality in your application. Additionally, inquire about the supplier’s quality assurance processes and any warranty or return policies they offer. -
What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing 4-way solenoid valves internationally?
Logistics play a crucial role in international sourcing. Consider shipping costs, delivery timelines, and the reliability of the chosen shipping method. It’s essential to understand customs regulations and duties applicable to your region to avoid unexpected delays or charges. Working with suppliers experienced in international shipping can streamline the process, and using a freight forwarder may help manage logistics more effectively. -
Can I customize a 4-way solenoid valve for specific applications?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for 4-way solenoid valves, including modifications to size, material, port configurations, and electrical specifications. When discussing customization with a supplier, provide detailed requirements and any specific performance criteria your application demands. Custom solutions can enhance compatibility and performance, but be aware that they may also affect lead times and pricing.
Top 7 4 Way Solenoid Valve Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. McMaster – Four-Way Solenoid Valves
Domain: mcmaster.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, McMaster – Four-Way Solenoid Valves, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. Emerson – ASCO Solenoid Valves
Domain: emerson.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: This company, Emerson – ASCO Solenoid Valves, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Electric Solenoid Valves – 4V210-08 4 Way, 5 Ports, 2 Position
Domain: electricsolenoidvalves.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: {“SKU”:”4V210-08″,”Valve Type”:”4 Way, 5 Ports, 2 Position”,”Suitable Media”:”Clean Air (40 Micron Filter)”,”Operation Type”:”Single Solenoid, Air Return”,”Port Size”:”1/4″ Female NPT”,”Flow Rate”:”CV=0.89″,”Response Time”:”Less than 0.05 Seconds”,”Body Material”:”Aluminum Alloy”,”Seal Material”:”NBR O-Ring”,”Power”:”AC: 4.0VA / DC: 3.0 Watts”,”Insolation Class”:”Class F”,”Enclosure Rating”:”IP65 …
4. Dwyer – Brass and AL Solenoid Valves
Domain: dwyeromega.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: 3 and 4-Way, NC and Universal, Brass and AL Solenoid Valves
– Models: SV240-Thru-SV270-Series
– Price: From $315.88
– Duty Cycle: 100%
– Enclosure Ratings: IP65, NEMA Type 4
– Mounting: Pipe mounting, any direction
– Operating Temperature: Max 50 °C, Min -9 °C
– Process Connection Type: NPT Male
– Static Pressure: 5 times max psid
– Applications: Mobile Equipment, Gas Sampling, Compressors, Ball …
5. Anderson Bolds – Multi-Port Valves
Domain: anderson-bolds.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: This company, Anderson Bolds – Multi-Port Valves, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
6. Tameson – Pneumatic Solenoid Valves
Domain: tameson.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: 5/2-way pneumatic solenoid valve: 5 ports, 2 switching positions; directs compressed air to pneumatic devices, allows separate exhaust paths. 4/2-way pneumatic solenoid valve: 4 ports, 2 switching positions; uses the same exhaust path for both ports. Circuit functions: 5/2 State 1 connects supply port to outlet port 2, exhausts through port 5; State 2 connects supply to outlet port 4, exhausts thr…
7. Instrument Basics – 4-Way Solenoid Valve
Domain: instrumentbasics.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: 4-Way Solenoid Valve: Designed for pneumatic actuators requiring air pressure on two different ports for movement. Features four ports: one for air supply (P), one for exhaust (E), and two for cylinder ports (A and B). Utilizes a spool-type design for directional hydraulic controls, providing pressure balance on the moving part. Can be spring-centered with solenoid coils for actuation in two direc…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for 4 way solenoid valve
What Are the Key Benefits of Strategic Sourcing for 4-Way Solenoid Valves?
In summary, strategic sourcing of 4-way solenoid valves presents significant advantages for businesses in diverse sectors, including manufacturing, automation, and fluid control. By prioritizing supplier relationships and leveraging global market insights, companies can optimize procurement processes, enhance supply chain resilience, and ensure access to high-quality products. The importance of understanding valve specifications—such as port configurations and operating principles—cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts operational efficiency and performance.
How Can International Buyers Prepare for Future Market Trends?
Looking ahead, international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should remain vigilant in monitoring technological advancements and evolving industry standards. The increasing demand for automation and energy-efficient solutions will drive innovation in solenoid valve design and functionality. Engaging with reliable suppliers who offer not only competitive pricing but also robust technical support will be crucial for maintaining a competitive edge.
What Steps Should You Take Next?
As you navigate the complexities of sourcing 4-way solenoid valves, consider adopting a proactive approach to supplier evaluation and market research. This will empower your business to make informed decisions that align with your operational goals. Embrace the future of procurement by building strategic partnerships that support your long-term success in an increasingly interconnected global marketplace.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.