Ceramic Magnets: The Ultimate B2B Sourcing Guide for Global Buyer
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for ceramic magnets
Navigating the complexities of sourcing ceramic magnets can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With their low cost, lightweight properties, and impressive resistance to corrosion, ceramic magnets have become an essential component in numerous applications ranging from industrial machinery to consumer electronics. However, understanding the variations in types, applications, and supplier capabilities is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide aims to equip B2B buyers with the knowledge necessary to navigate the global market for ceramic magnets. We will explore the different types of ceramic magnets, including discs, blocks, and rings, and their specific applications across various industries. Additionally, we will provide insights into effective supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and quality standards to ensure that you partner with the right manufacturers.
By addressing these key aspects, this guide empowers international buyers to confidently source ceramic magnets that meet their unique needs. Whether you are in Nigeria, Vietnam, or any other global market, understanding the intricacies of ceramic magnets will enable you to make strategic purchasing decisions that enhance your operational efficiency and product offerings.
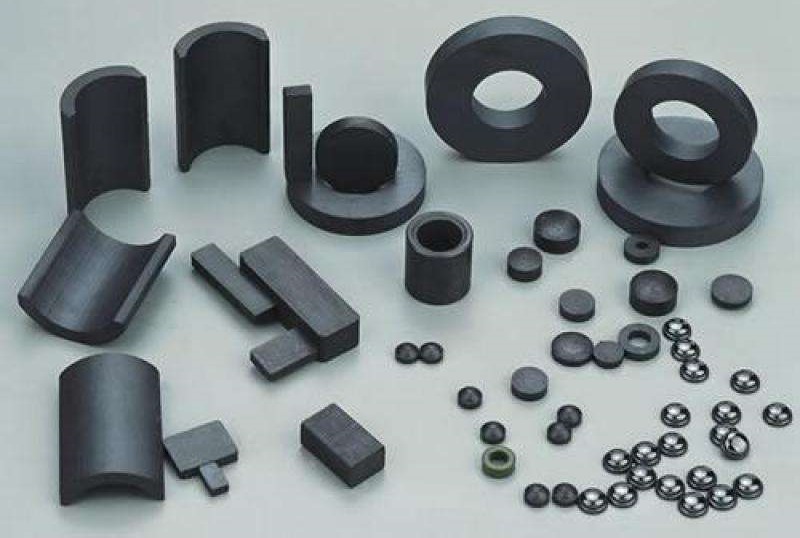
Understanding ceramic magnets Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ceramic Disc Magnets | Round shape, varying diameters and thicknesses | Electronics, crafting, and educational projects | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile. Cons: Limited strength compared to other types. |
| Ceramic Block Magnets | Rectangular or square shape, high holding power | Industrial machinery, automotive applications | Pros: High stability, easy to mount. Cons: Brittle; can chip if mishandled. |
| Ceramic Ring Magnets | Central hole for mounting, good for rotating parts | Motors, generators, and sensors | Pros: Efficient for dynamic applications. Cons: Requires precise installation. |
| Ceramic Pot Magnets | Cup-shaped with strong holding capacity | Lifting applications, tool holders | Pros: Excellent for vertical applications. Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
| Ceramic Channel Magnets | Long, narrow shape, often with grooves for fitting | Signage, display fixtures, and retail applications | Pros: Customizable, good for tight spaces. Cons: May require additional mounting hardware. |
What Are the Characteristics of Ceramic Disc Magnets?
Ceramic disc magnets are widely used due to their circular shape, which allows for easy integration into various applications. They come in multiple sizes and thicknesses, making them suitable for electronics, crafting, and educational projects. Buyers should consider their magnetic strength relative to size, as while they are cost-effective, they may not provide the same holding power as other magnet types. Their affordability and versatility make them a popular choice for many businesses.
How Do Ceramic Block Magnets Stand Out?
Ceramic block magnets are characterized by their rectangular or square shapes, which provide high holding power and stability. They are commonly employed in industrial machinery and automotive applications due to their robustness. However, buyers must be cautious about their brittle nature, as improper handling can lead to chipping. The ease of mounting and the ability to withstand high temperatures are significant advantages for businesses looking for reliable magnetic solutions.
Why Choose Ceramic Ring Magnets for Dynamic Applications?
Ceramic ring magnets feature a central hole, making them ideal for use in motors, generators, and sensors where rotation is essential. Their design allows for efficient magnetic flux, which is crucial for performance in dynamic applications. However, the installation process requires precision to ensure optimal function. Buyers should assess their specific needs, as the benefits of efficiency must be weighed against the installation complexity.

Illustrative image related to ceramic magnets
What Are the Benefits of Ceramic Pot Magnets?
Ceramic pot magnets, with their cup-shaped design, are known for their strong holding capacity, making them particularly effective in lifting applications and tool holders. Their ability to maintain a firm grip in vertical settings is a significant advantage for industrial use. However, businesses should note that their application range can be limited, and they may not be suitable for all situations. The strength of these magnets can enhance operational efficiency, making them a valuable asset in many workplaces.
How Do Ceramic Channel Magnets Fit into Business Needs?
Ceramic channel magnets are long and narrow, often equipped with grooves for easy fitting into signage and display fixtures. Their customizable nature allows businesses to adapt them for various retail applications. While they offer versatility in design, buyers should consider the potential need for additional mounting hardware, which may increase overall costs. Their effectiveness in tight spaces makes them an attractive option for businesses focused on maximizing display visibility.
Key Industrial Applications of ceramic magnets
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of ceramic magnets | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | DC Motors and Sensors | High reliability and cost-effectiveness for mass production | Ensure compliance with automotive standards and specifications |
| Consumer Electronics | Loudspeakers and Microphones | Enhanced sound quality with lightweight components | Focus on size and strength specifications for optimal performance |
| Industrial Machinery | Eddy Current Separators | Efficient separation of materials, reducing waste | Assess operational temperature limits and corrosion resistance |
| Medical Devices | Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) systems | Critical for accurate imaging and patient safety | Verify compatibility with medical regulations and certifications |
| Crafting and DIY Projects | Crafting tools and home decor | Versatile and cost-effective solutions for various applications | Consider customization options for specific project needs |
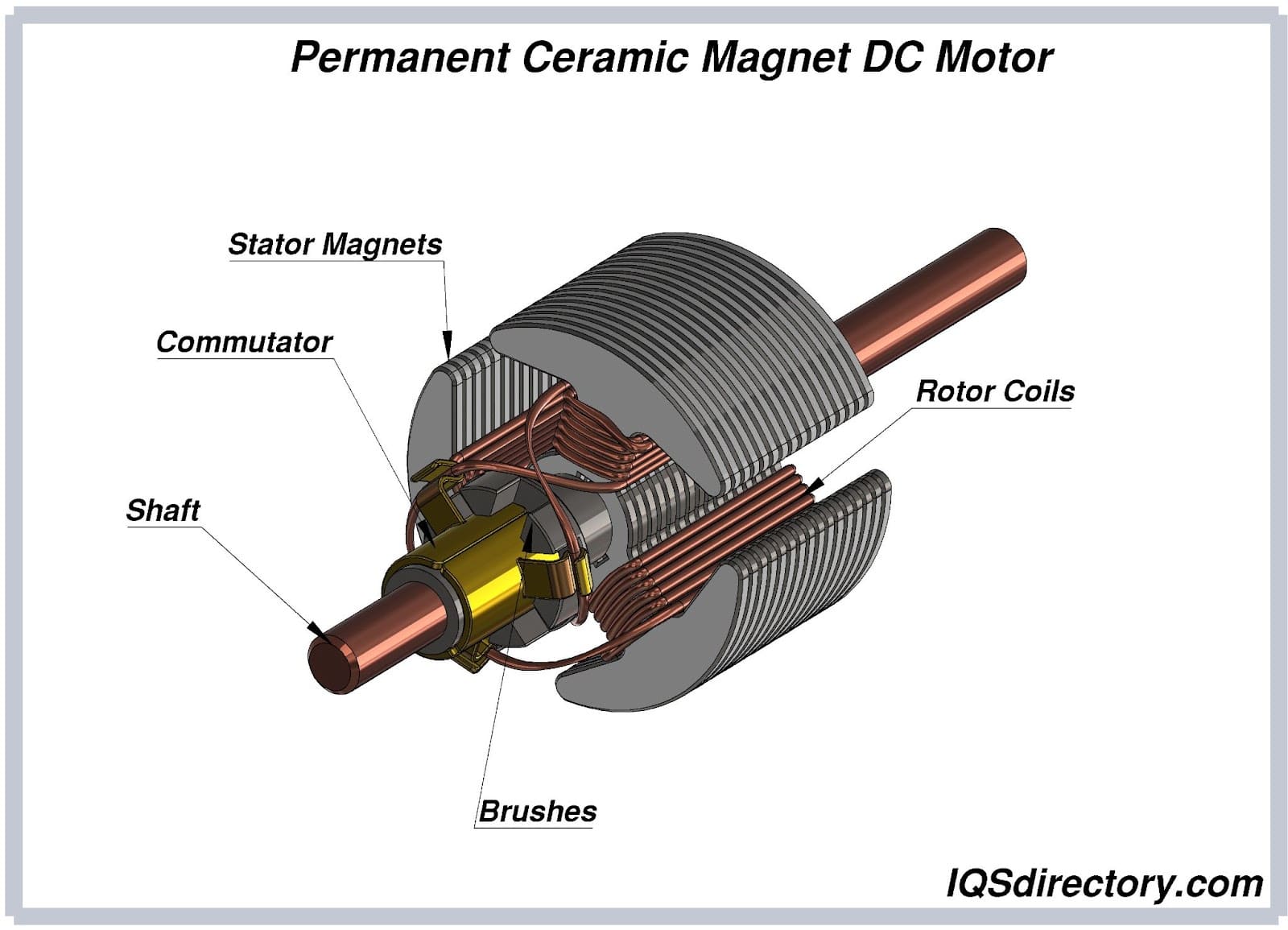
How Are Ceramic Magnets Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, ceramic magnets are integral to the functionality of DC motors and sensors. These magnets provide reliable performance and are cost-effective, making them ideal for large-scale production. They help in improving efficiency and durability in applications such as window lifts, wipers, and fuel pumps. Buyers should ensure that the ceramic magnets sourced comply with automotive industry standards and can withstand high operational temperatures, especially in regions with varying climates like Africa and South America.
What Role Do Ceramic Magnets Play in Consumer Electronics?
Ceramic magnets are widely used in loudspeakers and microphones, where they enhance sound quality while maintaining a lightweight design. This is particularly beneficial for manufacturers looking to create portable and efficient audio devices. The challenge for buyers is to ensure that the magnets meet specific size and strength requirements for optimal acoustic performance. Sourcing from reputable suppliers who can provide consistent quality is crucial for maintaining product integrity in competitive markets like Europe and the Middle East.
How Are Ceramic Magnets Applied in Industrial Machinery?
In industrial settings, ceramic magnets are utilized in eddy current separators, which efficiently separate non-ferrous metals from waste materials. This application is essential for recycling operations and material recovery, contributing to sustainability efforts. Buyers need to consider the operational temperature limits and the magnets’ corrosion resistance, especially in harsh environments. Sourcing magnets that meet these specifications can enhance productivity and reduce operational costs.
Why Are Ceramic Magnets Important in Medical Devices?
Ceramic magnets are critical in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) systems, where they contribute to high-quality imaging and patient safety. The reliability of these magnets is vital for accurate diagnostics, making them a preferred choice in the medical field. Buyers in this sector must verify that the magnets comply with medical regulations and certifications, ensuring safety and efficacy in sensitive applications. This is particularly important for suppliers looking to enter or expand in the healthcare markets of Africa and the Middle East.
How Can Ceramic Magnets Benefit Crafting and DIY Projects?
For crafting and DIY enthusiasts, ceramic magnets offer versatile and cost-effective solutions for various applications, such as tool holders, fridge magnets, and decorative items. Their lightweight nature and ease of customization make them appealing for small-scale projects. Buyers should consider the specific needs of their projects, such as size and magnetic strength, and seek suppliers that provide customization options. This is especially valuable for artisans in regions like South America and Europe, where unique designs can cater to local tastes.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘ceramic magnets’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing Quality Ceramic Magnets for Diverse Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with sourcing ceramic magnets that meet specific application requirements. With varying grades, shapes, and strengths available, making an informed decision can be overwhelming. In many cases, buyers may inadvertently select a magnet that does not fit the operational demands of their machinery or product design, leading to performance issues or costly returns. Additionally, fluctuations in material availability can impact lead times, further complicating the procurement process.
The Solution: To effectively source ceramic magnets, B2B buyers should start by clearly defining the specifications required for their application. This includes understanding the necessary magnetic strength (measured in Gauss), the operating temperature range, and the specific shape needed for integration into their products. Engaging with suppliers who offer detailed technical data on their magnets can provide critical insights. Additionally, buyers should consider requesting samples before making bulk purchases to assess performance in real-world applications. Building a relationship with a reliable manufacturer that can offer custom solutions will also ensure that buyers can adapt to changing project demands without unnecessary delays.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Demagnetization in High-Temperature Environments
The Problem: One common issue faced by manufacturers using ceramic magnets is the risk of demagnetization in high-temperature environments. Many applications, such as motors or sensors, may expose magnets to temperatures exceeding their rated limits, resulting in a loss of magnetic strength. This can lead to malfunctions in the final product, affecting operational efficiency and causing unexpected downtime.
The Solution: To mitigate the risk of demagnetization, B2B buyers should carefully assess the temperature ratings of ceramic magnets and select those designed to withstand higher operational temperatures. For example, opting for higher-grade ceramic magnets, which can retain their magnetic properties at temperatures up to 300°C (592°F), is crucial for demanding applications. Moreover, implementing thermal management solutions, such as heat sinks or insulating materials, can help maintain optimal temperatures around the magnets. Providing suppliers with detailed operational conditions can also enable them to recommend the most suitable ceramic magnets for the specific use case, ensuring reliability and performance longevity.
Scenario 3: Managing Breakage and Handling Issues with Ceramic Magnets
The Problem: Ceramic magnets, known for their hard and brittle nature, are prone to chipping or breaking during handling and installation. This characteristic poses significant challenges for B2B buyers, particularly in industries where magnets are assembled into larger systems or products. Breakage not only leads to increased costs due to wasted materials but can also delay production schedules and negatively impact client satisfaction.
The Solution: To address the handling challenges associated with ceramic magnets, B2B buyers should implement strict handling protocols and training for employees. Educating staff about the brittle nature of these magnets will encourage careful handling and reduce the risk of breakage. Additionally, utilizing protective packaging and storage solutions can prevent accidental damage during transport. When integrating ceramic magnets into final products, employing strategic design modifications—such as using softer materials as buffers or protective casings—can also help absorb shocks and minimize the risk of breakage. Lastly, fostering a partnership with suppliers who can provide guidance on best practices for handling and installation will further enhance the longevity and reliability of ceramic magnets in various applications.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for ceramic magnets
What Are the Key Materials Used in Ceramic Magnets?
Ceramic magnets, also known as ferrite magnets, are primarily composed of iron oxide and strontium carbonate. However, the selection of materials can vary based on specific applications and performance requirements. Below, we analyze several common materials used in the production of ceramic magnets from a B2B perspective, focusing on their properties, advantages, limitations, and considerations for international buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Iron Oxide in Ceramic Magnets?
Iron oxide is the fundamental component of ceramic magnets, contributing significantly to their magnetic properties.
-
Key Properties: Iron oxide provides medium magnetic strength and is capable of withstanding high temperatures, with a maximum operating temperature of around 300°C (572°F). It also exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for various environmental conditions.
-
Pros & Cons: The low cost and availability of iron oxide make it an attractive option for manufacturers. However, its brittleness can lead to chipping or cracking during handling or machining.
-
Impact on Application: Iron oxide’s compatibility with various media makes it suitable for applications in motors, generators, and magnetic separators.
-
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure that the iron oxide used complies with local standards, such as ASTM or DIN, particularly in industries like automotive and electronics.
How Does Strontium Carbonate Enhance Ceramic Magnet Performance?
Strontium carbonate complements iron oxide in ceramic magnets, enhancing their overall properties.
-
Key Properties: This material contributes to the magnet’s ability to maintain its magnetic properties under high temperatures, with a Curie temperature around 450°C (842°F).
-
Pros & Cons: Strontium carbonate is relatively inexpensive and readily available. However, its processing can be complex, requiring specialized techniques to achieve the desired magnetic properties.
-
Impact on Application: The high-temperature stability provided by strontium carbonate is crucial for applications in automotive sensors and industrial machinery.
-
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must consider the sourcing of strontium carbonate, ensuring compliance with international quality standards to avoid supply chain disruptions.
What Role Does Manufacturing Process Play in Ceramic Magnet Quality?
The manufacturing process of ceramic magnets significantly influences their performance and applicability.
-
Key Properties: The powder metallurgy process used in producing ceramic magnets allows for precise control over the magnetic properties and shapes.
-
Pros & Cons: While this method offers flexibility in design and performance, it requires advanced machinery and skilled labor, which can increase production costs.
-
Impact on Application: The ability to customize shapes and sizes makes ceramic magnets versatile for various applications, from consumer electronics to industrial equipment.
-
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should assess manufacturers’ capabilities to ensure they can meet specific design requirements and quality standards, particularly in regions with stringent regulations.
How Do Environmental Factors Affect the Selection of Ceramic Magnet Materials?
Environmental factors, including temperature and humidity, can impact the performance of ceramic magnets.
-
Key Properties: Ceramic magnets are designed to resist oxidation and maintain their magnetic properties in various conditions, making them suitable for outdoor and industrial applications.
-
Pros & Cons: Their durability and resistance to environmental factors are significant advantages. However, their brittleness can be a drawback in high-impact applications.
-
Impact on Application: The environmental resistance makes ceramic magnets ideal for applications in construction and outdoor equipment.
-
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should evaluate the environmental conditions in their regions, ensuring that the selected ceramic magnets will perform reliably in their specific applications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Ceramic Magnets
| Material | Typical Use Case for ceramic magnets | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iron Oxide | Motors, generators, magnetic separators | Low cost and high availability | Brittle, prone to chipping | Low |
| Strontium Carbonate | Automotive sensors, industrial machinery | High-temperature stability | Complex processing requirements | Low |
| Manufacturing Process | Custom applications in electronics | Flexibility in design and performance | Higher production costs | Medium |
| Environmental Factors | Outdoor and industrial equipment | Excellent resistance to oxidation | Brittleness in high-impact scenarios | Medium |
By understanding these materials and their implications, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.

Illustrative image related to ceramic magnets
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for ceramic magnets
Ceramic magnets, also known as ferrite magnets, are integral components in various industries due to their cost-effectiveness and versatility. Understanding their manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to source these materials efficiently.
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Ceramic Magnets?
The manufacturing of ceramic magnets involves several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a vital role in ensuring the final product meets industry standards and customer specifications.
How Is Material Prepared for Ceramic Magnet Production?
The primary raw materials for ceramic magnets are iron oxide and strontium carbonate. These materials are carefully sourced to ensure quality. Initially, they are mixed in precise ratios and subjected to high-temperature processing, reaching up to 2000°F. This process transforms the raw materials into a ferrite compound through a chemical reaction, which is essential for the magnetic properties of the final product.

Illustrative image related to ceramic magnets
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Ceramic Magnets?
Once the ferrite is prepared, it undergoes forming techniques that shape the material into the desired configurations. This can be done using two primary methods: dry pressing and wet pressing.
- Dry Pressing: In this method, the ferrite powder is compacted in a die under high pressure without any added moisture.
- Wet Pressing: This involves mixing the ferrite powder with water to create a slurry, which is then compacted in the presence of a magnetic field. This alignment enhances the magnetic properties of the material.
After forming, the magnets are sintered at high temperatures to enhance density and durability. This step is critical as it solidifies the magnetic structure.
How Is Assembly and Finishing Conducted for Ceramic Magnets?
After sintering, the magnets often require finishing processes to achieve the desired dimensions and surface quality. This typically involves grinding using diamond wheels, as the material is hard and brittle. Additional treatments, such as coating or polishing, can be applied depending on the application requirements. For instance, while ceramic magnets are generally resistant to corrosion, a protective coating may be considered for specific environments.
Illustrative image related to ceramic magnets
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for Ceramic Magnets?
Quality assurance in the manufacturing of ceramic magnets is paramount, particularly for international B2B transactions. Buyers must ensure that suppliers adhere to strict quality standards to minimize risks associated with product failure.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Look For?
International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems across various industries, including magnet manufacturing. Compliance with these standards indicates that the supplier has established processes for quality control and continual improvement.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for products sold in Europe and API standards for oil and gas applications, may be relevant depending on the intended use of the magnets. B2B buyers should inquire about these certifications as part of their due diligence.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process are essential for ensuring product integrity. These typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to confirm they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, regular checks are performed to monitor parameters such as temperature, pressure, and dimensions to ensure consistency.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once production is complete, finished magnets undergo rigorous testing to assess their magnetic properties, dimensional accuracy, and surface quality.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Ceramic Magnets?
Several testing methods are employed to verify the quality of ceramic magnets:
- Magnetic Testing: This includes measuring residual induction and coercive force to assess the magnet’s strength.
- Dimensional Testing: Using precision tools, manufacturers confirm that the magnets meet specified dimensions and tolerances.
- Thermal Testing: Evaluating how the magnets perform at elevated temperatures ensures they meet application requirements.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
To ensure that suppliers maintain high standards of quality, B2B buyers should implement thorough verification processes. This includes:
- Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can help assess their compliance with quality standards and operational practices.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask for detailed quality reports that outline testing results and compliance with relevant standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturing process and product quality.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is crucial. Different regions may have varying expectations regarding quality standards and certifications. Buyers should be proactive in communicating their requirements and ensuring that suppliers are aware of any specific regulations applicable to their markets.
Additionally, language barriers and cultural differences can affect the clarity of quality expectations. Therefore, establishing clear communication channels and possibly involving local representatives can facilitate smoother transactions and enhance mutual understanding.
In conclusion, ceramic magnets are a vital component in numerous applications, and a thorough understanding of their manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on these areas, buyers can make informed decisions and establish reliable partnerships with manufacturers, ultimately ensuring the success of their projects.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘ceramic magnets’
Ceramic magnets, known for their affordability and versatility, play a crucial role in various applications across multiple industries. This guide aims to assist B2B buyers in navigating the procurement process for ceramic magnets by providing a clear, actionable checklist.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing precise technical specifications is essential for ensuring that the ceramic magnets meet your application requirements. Consider factors such as size, shape, strength, and operating temperature. Be specific about the grade and type of ceramic magnet needed, as these attributes will significantly affect performance.
Step 2: Research Supplier Options
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers of ceramic magnets. Look for manufacturers with a strong reputation in the industry and experience in producing the type of magnets you require. Utilize online directories, trade shows, and industry publications to gather information about reputable suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Look for suppliers that demonstrate reliability and have a track record of timely delivery and quality assurance.
- Check for Certifications: Ensure that the suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001, which can indicate a commitment to quality management.
- Assess Manufacturing Capabilities: Understand the supplier’s manufacturing processes and whether they can handle custom orders if necessary.
Step 4: Request Samples
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request samples of the ceramic magnets. Testing samples allows you to evaluate their quality and performance firsthand. Pay attention to key attributes such as magnetic strength, resistance to demagnetization, and durability under operational conditions.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Terms
Gather quotes from multiple suppliers and compare them not only based on price but also on the terms of sale. Look for hidden costs, such as shipping fees or minimum order quantities, that may affect your overall budget. A comprehensive comparison will help you identify the best value for your investment.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve selected a supplier, engage in negotiations to finalize the terms of purchase. Discuss payment terms, delivery schedules, and warranty conditions. Clear communication about expectations can help avoid misunderstandings and build a strong supplier relationship.
Step 7: Establish a Quality Control Plan
Develop a quality control plan to monitor the ceramic magnets received. Outline the criteria for acceptance and the procedures for handling defective products. Implementing a quality control process will ensure that the magnets meet your specifications and maintain performance over time.
By following this practical checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for ceramic magnets, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for ceramic magnets Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Ceramic Magnets?
Understanding the cost structure for ceramic magnets is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to make informed purchasing decisions. The primary components that contribute to the overall cost include:

Illustrative image related to ceramic magnets
-
Materials: Ceramic magnets are primarily composed of iron oxide and strontium carbonate. These materials are generally low-cost and readily available, which contributes to the competitive pricing of ceramic magnets. However, fluctuations in raw material prices can impact overall costs, so it’s essential to monitor market trends.
-
Labor: Manufacturing ceramic magnets involves skilled labor for processes such as mixing, pressing, sintering, and grinding. Labor costs can vary significantly based on geographic location and local wage standards. For instance, sourcing from regions with lower labor costs may offer significant savings.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to the maintenance of machinery, utilities, and factory space. Efficient production processes can help minimize overhead costs, making it beneficial for buyers to choose suppliers with optimized operations.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific magnet shapes or sizes can add to initial costs. While standard shapes may be cheaper, custom orders often require investment in specialized molds or dies, which can be amortized over larger production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous quality control processes are necessary to ensure that the magnets meet specified performance criteria. This may involve additional testing and inspection costs, which should be factored into the total price.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary greatly depending on the distance from the supplier, the chosen shipping method, and the complexity of the order. Incoterms also play a significant role in determining who bears the costs and risks associated with transportation.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. Understanding the margin expectations can help buyers negotiate better terms.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Ceramic Magnets?
Several factors can influence the pricing of ceramic magnets, making it essential for buyers to consider the following:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to bulk discounts, reducing the unit price. Buyers should evaluate their needs carefully and consider consolidating orders to benefit from economies of scale.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications, such as unique sizes or magnetic strengths, can significantly impact pricing. Buyers must balance their requirements with cost implications, as more specialized products often come with a higher price tag.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials or those that meet specific industry certifications can lead to increased costs. Buyers should assess whether the additional investment in quality aligns with their application requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and production capabilities of suppliers can affect pricing. Working with established suppliers with a track record of quality can sometimes justify higher costs due to reduced risk and improved service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of trade (such as FOB, CIF) is crucial for calculating the total landed cost. This impacts not only the price but also the responsibility for logistics and insurance.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Sourcing Ceramic Magnets?
B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing strategies by considering these actionable tips:
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate pricing, especially for larger orders or long-term contracts. Suppliers may have flexibility on margins, particularly if they see potential for ongoing business.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, not just the purchase price. Consider factors like durability, performance, and potential for failure, which can lead to additional costs over time.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, and the Middle East should be aware of potential tariffs, import duties, and currency exchange fluctuations that could affect overall costs. It’s advisable to work with suppliers familiar with international trade to navigate these challenges effectively.
-
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices: Always verify that pricing is indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, material availability, and supplier capacity. Request updated quotes regularly to avoid unexpected costs.
By keeping these insights in mind, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing ceramic magnets and make more informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing ceramic magnets With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Ceramic Magnets in Industrial Applications
In the quest for effective magnetic solutions, businesses often weigh the benefits and drawbacks of ceramic magnets against other alternatives. Understanding these alternatives is crucial for B2B buyers who aim to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. Below, we present a comparative analysis of ceramic magnets alongside two viable alternatives: Neodymium Magnets and Alnico Magnets.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Ceramic Magnets | Neodymium Magnets | Alnico Magnets |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Medium strength, good temperature resistance (up to 480°F) | High strength, retains magnetism well at high temperatures | Moderate strength, excellent temperature stability |
| Cost | Low cost; economical for bulk applications | Higher cost; premium pricing due to production complexity | Moderate cost; more expensive than ceramic but cheaper than neodymium |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to source and implement, widely available | Requires careful handling and installation | Requires special mounting due to brittleness |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; corrosion-resistant | Low maintenance but sensitive to demagnetization | Moderate maintenance; can corrode if not coated |
| Best Use Case | Consumer products, motors, and general applications | High-performance applications like electric vehicles and industrial machinery | High-temperature environments, sensors, and musical instruments |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Neodymium Magnets
Neodymium magnets, part of the rare-earth magnet family, are known for their exceptional magnetic strength. They are ideal for applications requiring compact, powerful magnets, such as electric motors, generators, and high-performance speakers. However, their higher cost and sensitivity to demagnetization can be significant drawbacks. Neodymium magnets can be easily damaged if subjected to high temperatures or physical impact, necessitating careful handling and protective measures during installation.

Illustrative image related to ceramic magnets
Alnico Magnets
Alnico magnets, composed primarily of aluminum, nickel, and cobalt, offer moderate magnetic strength and are renowned for their ability to maintain magnetism even at elevated temperatures. This makes them suitable for specialized applications like sensors and precision instruments. However, they are more brittle than ceramic magnets and require careful mounting to prevent chipping. While their cost is moderate, they can still be more expensive than ceramic options, particularly for high-grade varieties.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Magnetic Solution for Your Needs
For B2B buyers evaluating magnetic solutions, the choice between ceramic, neodymium, and alnico magnets ultimately hinges on specific application requirements, budget constraints, and performance expectations. Ceramic magnets are a cost-effective choice for general applications where high strength is not critical. In contrast, neodymium magnets excel in high-performance scenarios but come at a premium, while alnico magnets serve well in high-temperature environments but may require more careful handling and installation. By thoroughly assessing these factors, businesses can select the most suitable magnetic solution to meet their operational demands efficiently.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for ceramic magnets
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Ceramic Magnets for B2B Buyers?
Understanding the technical properties of ceramic magnets is crucial for international B2B buyers who are looking to optimize their procurement processes and ensure compatibility with their applications. Here are several essential specifications to consider:
1. Material Composition
Ceramic magnets, also known as ferrite magnets, are primarily composed of iron oxide and strontium carbonate. This combination not only makes them cost-effective but also contributes to their corrosion resistance and durability. For B2B buyers, the material composition is vital for assessing performance in specific applications, especially in environments prone to moisture or other corrosive elements.
2. Magnetic Strength (Br)
Magnetic strength, measured in Gauss, indicates the magnet’s capability to exert a magnetic force. Ceramic magnets typically have a residual induction (Br) value ranging from 3,500 to 4,500 Gauss. Buyers should prioritize the magnetic strength needed for their applications, as this can significantly impact the effectiveness of the magnet in tasks such as holding or lifting.
3. Maximum Operating Temperature
Ceramic magnets can operate at temperatures up to 300°C (approximately 572°F). However, their magnetic properties can degrade at elevated temperatures, with about 75% of their strength retained at 175°C (350°F). Understanding the maximum operating temperature is essential for buyers to ensure that the magnets will perform adequately in their intended applications, particularly in industries such as automotive or manufacturing.
4. Coercive Force (Hc)
Coercive force, measured in Oersteds, represents the resistance of a magnet to demagnetization. Ceramic magnets generally have a coercive force between 1,500 and 2,500 Oersteds. A higher coercive force is particularly important for applications that involve fluctuating magnetic fields, ensuring that the magnet retains its properties over time.
Illustrative image related to ceramic magnets
5. Density
The density of ceramic magnets is typically around 4.9 g/cm³. This property affects the weight and overall performance of the magnet in practical applications. Buyers should consider the density when evaluating how the magnet will fit within their product designs, especially in lightweight applications.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Ceramic Magnet Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some commonly used terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding this term helps buyers identify potential suppliers who can provide custom ceramic magnets tailored to specific product requirements.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For ceramic magnets, MOQs can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and type of magnet. Knowing the MOQ is essential for buyers to plan their inventory and budget effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quote)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing and terms for specific products. For ceramic magnets, submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare prices and specifications from multiple suppliers, aiding in informed decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for buyers to clarify shipping, insurance, and risk responsibilities associated with ceramic magnets.
5. Custom Manufacturing
This term refers to the process of creating products tailored to specific requirements. Many suppliers of ceramic magnets offer custom manufacturing services, allowing buyers to specify dimensions, shapes, and magnetic properties to meet their unique application needs.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring that they procure ceramic magnets that align with their operational requirements and market needs.
Illustrative image related to ceramic magnets
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the ceramic magnets Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing Ceramic Magnets?
The ceramic magnets market is witnessing a robust growth trajectory, driven by increasing demand in diverse applications such as automotive, consumer electronics, and industrial machinery. As a low-cost alternative to metallic magnets, ceramic magnets are particularly appealing to international B2B buyers from emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Countries like Nigeria and Vietnam are experiencing rapid industrialization, leading to heightened demand for reliable and cost-effective magnetic solutions.
Key trends include the integration of advanced manufacturing technologies, such as automation and robotics, which streamline production processes and enhance product quality. Additionally, digital sourcing platforms are gaining traction, enabling buyers to efficiently compare suppliers, negotiate prices, and manage logistics from multiple regions. The rise of e-commerce in B2B transactions is further transforming how buyers approach sourcing ceramic magnets, allowing for greater flexibility and access to global markets.
Moreover, the growing emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainability is shaping purchasing decisions. Buyers are increasingly considering the lifecycle impact of materials, prompting suppliers to adapt by optimizing their manufacturing processes and reducing waste. This trend not only reflects environmental consciousness but also aligns with the regulatory frameworks in many regions that prioritize sustainable practices.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Ceramic Magnets Supply Chain?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount in the ceramic magnets sector, particularly as global awareness of environmental issues rises. The production of ceramic magnets typically involves materials like iron oxide and strontium carbonate, which, while abundant, necessitate responsible extraction and processing methods to minimize environmental degradation. International B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, including waste reduction, energy efficiency, and responsible sourcing of raw materials.

Illustrative image related to ceramic magnets
The significance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers who engage with suppliers that adhere to ethical standards not only mitigate risks associated with non-compliance but also enhance their brand reputation. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management or adherence to the Responsible Minerals Initiative can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Furthermore, the demand for “green” materials is influencing the ceramic magnets market. Buyers can look for magnets that incorporate environmentally friendly manufacturing processes or materials. This trend not only addresses consumer preferences but also aligns with evolving regulatory requirements aimed at promoting sustainability in manufacturing.
What Is the Historical Context of Ceramic Magnets Relevant to Today’s B2B Landscape?
Ceramic magnets, also known as ferrite magnets, emerged in the 1960s as an economical alternative to metallic magnets. Their development marked a significant advancement in magnetic technology, allowing for the mass production of low-cost, reliable magnets that have since become integral to various applications, including motors, sensors, and consumer electronics.
Initially, the focus was on maximizing magnetic strength while minimizing production costs, which has shaped the industry’s landscape. Over the decades, the manufacturing processes have evolved from simple sintering techniques to more sophisticated methods, allowing for greater precision and customization. As a result, ceramic magnets now account for over 75% of global magnet consumption by weight, emphasizing their importance in both industrial and consumer markets.
Understanding the historical context of ceramic magnets provides valuable insights into current market dynamics. It highlights the ongoing innovation and adaptation within the industry, underscoring the need for B2B buyers to stay informed about technological advancements that can enhance product quality and operational efficiency. As the market continues to evolve, recognizing these historical trends will be crucial for making informed sourcing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of ceramic magnets
-
How do I determine the right type of ceramic magnet for my application?
Choosing the right ceramic magnet depends on several factors, including the required magnetic strength, temperature tolerance, shape, and size. Start by assessing the specific needs of your application, such as whether the magnet will be used in a high-temperature environment or needs to withstand corrosion. Consult with suppliers for technical specifications and consider custom solutions if standard options do not meet your requirements. It’s also beneficial to review case studies or applications similar to yours to see what types of ceramic magnets have been successful. -
What are the common applications for ceramic magnets in various industries?
Ceramic magnets are widely used in industries such as automotive, electronics, and consumer goods. Common applications include motors, generators, magnetic separators, loudspeakers, and even craft projects. Their low cost and good performance at high temperatures make them a preferred choice for many applications. Understanding the typical uses in your industry can help you identify the best magnet options for your specific needs. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for ceramic magnets?
MOQs for ceramic magnets can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on the type and customization of the magnets. Generally, standard ceramic magnets may have a lower MOQ, often starting from 100 to 500 units, while custom designs might require higher quantities. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies and negotiate terms that suit your business. -
How can I vet suppliers when sourcing ceramic magnets internationally?
To vet suppliers, start by researching their reputation through online reviews and industry forums. Request references from previous clients and verify their business credentials. It’s also crucial to assess their production capabilities, quality control processes, and adherence to international standards. Consider visiting the supplier’s facility if possible or engaging in a virtual audit. Establishing clear communication and understanding their logistical capabilities will also help ensure you select a reliable partner. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing ceramic magnets?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier and the size of your order. Common practices include a deposit upon order confirmation, with the balance due before shipment. Some suppliers may offer more flexible terms, such as payment on delivery or net payment terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60). It’s important to discuss and agree on payment terms upfront to avoid any misunderstandings and to ensure secure transactions. -
What quality assurance measures should I consider for ceramic magnets?
When sourcing ceramic magnets, inquire about the supplier’s quality assurance (QA) protocols. This includes their testing methods for magnetic strength, dimensional accuracy, and resistance to environmental factors like humidity and temperature. Ask for certifications that demonstrate compliance with international quality standards, such as ISO 9001. Establishing clear QA expectations in your contract can help ensure you receive products that meet your specifications. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing ceramic magnets?
Logistics play a crucial role in the successful importation of ceramic magnets. Consider factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations in your country. Work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping and can provide necessary documentation for customs clearance. It’s also wise to discuss insurance options for your shipment to protect against loss or damage during transit. -
Can ceramic magnets be customized to fit specific project needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for ceramic magnets, including variations in size, shape, strength, and coating. When requesting custom magnets, provide detailed specifications and application requirements to ensure the final product meets your expectations. Engaging in a collaborative design process can help suppliers better understand your needs and provide tailored solutions that enhance your project outcomes.
Top 4 Ceramic Magnets Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Applied Magnets – Strong Ceramic Ferrite & Disc Magnets
Domain: appliedmagnets.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Strong Ceramic Ferrite & Disc Magnets from Applied Magnets include Ceramic Bar Magnets & Blocks, Ceramic Disc Magnets & Cylinders, Strontium Ferrite Ceramic Magnet Rings, and Cup Magnets – Ceramic Magnet Cups.
2. MagnetShop – Ceramic Ferrite Magnets
Domain: magnetshop.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Ceramic Magnets (Ferrite) are permanent magnets made from strontium carbonate and iron oxide. They are low-cost, medium-strength magnets suitable for high temperatures, corrosion-resistant, and easy to magnetize. Available shapes include discs, blocks (rectangular & square), rings, and round cups. Custom manufacturing is offered. Technical specifications include: Grade 5, Br: 3,950 Gauss, BHmax: 3…
3. Hobby Lobby – Round Ceramic Magnets
Domain: hobbylobby.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Round Ceramic Magnets – 3/4”, “SKU”: “381913”, “Original Price”: “$3.79”, “Diameter”: “3/4 inch”, “Thickness”: “3/16 inch”, “Gauss Rating”: “1,000”, “Package Contains”: “50 magnets”}
4. IQS Directory – Ceramic Magnets
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Ceramic magnets, also known as ferrite magnets, are permanent magnets made by combining iron oxide with strontium carbonate. They are produced by heating the mixture to temperatures exceeding 2000°F, resulting in a ferrite substance with a magnetic field. Key features include:
– Cost-effective alternative to natural magnets
– Excellent corrosion resistance
– Widely used in consumer goods and in…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for ceramic magnets
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers of Ceramic Magnets?
In conclusion, ceramic magnets represent a compelling choice for international B2B buyers seeking cost-effective, reliable solutions across various applications. Their low manufacturing costs, high-temperature resistance, and corrosion durability make them suitable for diverse sectors, from automotive to consumer electronics. Strategic sourcing of ceramic magnets not only enhances operational efficiency but also enables businesses to leverage the competitive pricing and availability of raw materials such as iron oxide and strontium carbonate.
How Can Buyers Optimize Their Sourcing Strategy?
As you navigate the sourcing landscape, consider establishing relationships with manufacturers that offer custom solutions tailored to your specific needs. Engaging with suppliers who prioritize quality and sustainability can provide an edge in maintaining product integrity while optimizing costs.
What’s Next for the Ceramic Magnet Market?
Looking ahead, the demand for ceramic magnets is poised to grow, driven by advancements in technology and increasing applications in emerging markets. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, now is the time to act. By investing in strategic sourcing practices today, you can secure a reliable supply chain that meets both current and future demands. Embrace this opportunity to enhance your competitive advantage in the evolving global market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.