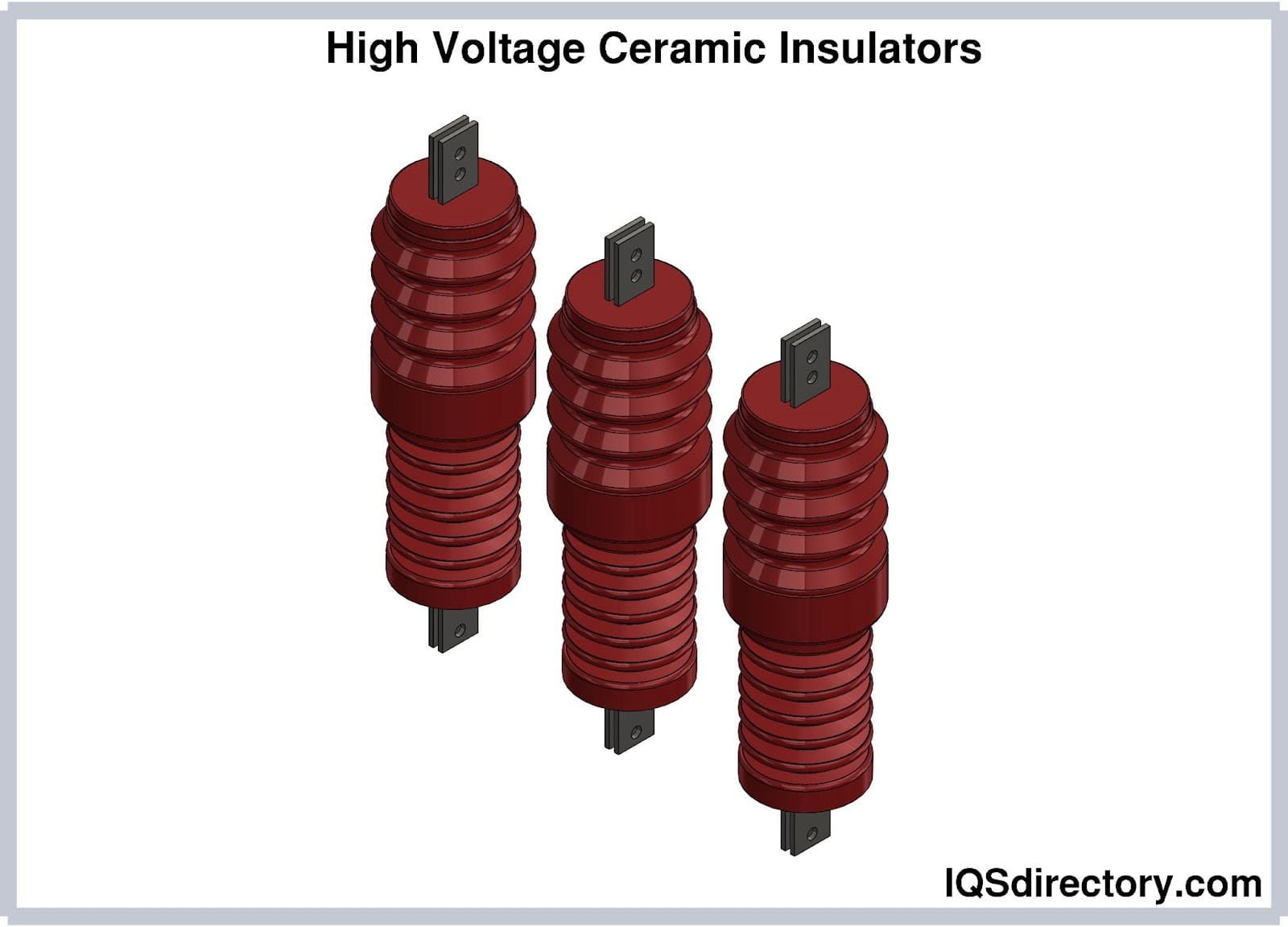
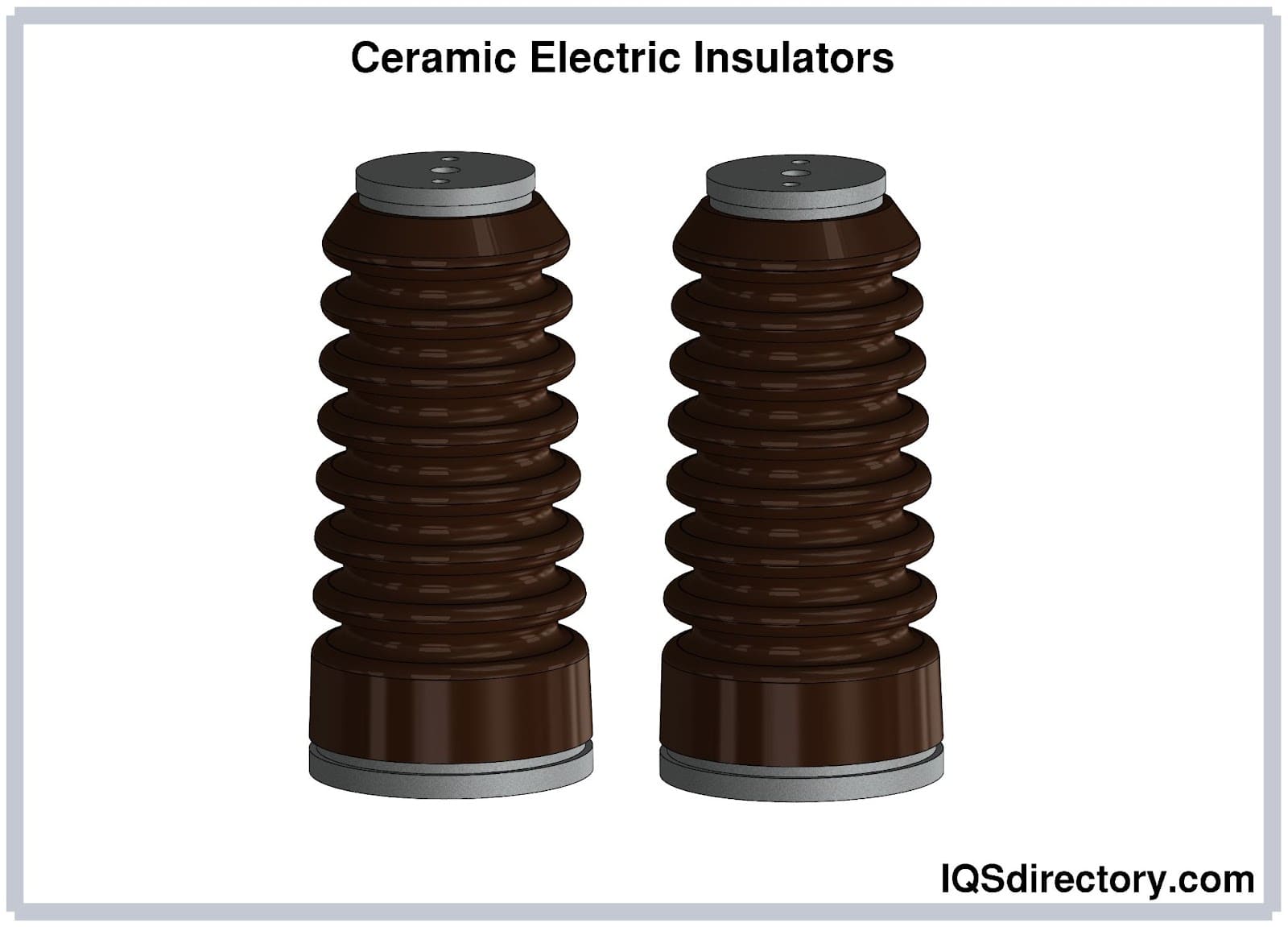
Ceramic Insulator Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for ceramic insulator
In an increasingly interconnected world, sourcing high-quality ceramic insulators presents a significant challenge for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse and dynamic markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Germany and Saudi Arabia. As industries demand greater reliability and efficiency, understanding the complexities of ceramic insulator options becomes critical. This guide will explore various types of ceramic insulators, their applications, and the latest advancements in materials such as alumina, cordierite, and steatite, empowering buyers to make informed decisions.
Navigating the global market for ceramic insulators requires a strategic approach to supplier vetting, pricing, and product specifications. This comprehensive resource will delve into key factors influencing purchasing decisions, including performance characteristics, manufacturing processes, and compliance with international standards. By providing actionable insights into cost considerations and supplier evaluation, this guide aims to equip international B2B buyers with the knowledge they need to secure optimal products that meet their specific operational requirements.
Whether you are looking to enhance electrical insulation in industrial settings or seeking durable components for high-temperature applications, this guide serves as a valuable tool. It will help you navigate the complexities of sourcing ceramic insulators, ultimately leading to enhanced operational efficiency and reduced downtime in your projects.
Understanding ceramic insulator Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina Ceramics | High hardness, excellent electrical resistance, low porosity | Electronics, aerospace, industrial machinery | Pros: High durability, excellent thermal properties. Cons: Higher cost compared to other ceramics. |
| Cordierite | Exceptional thermal shock resistance, low thermal expansion | Electrical heating applications, automotive | Pros: Rapid heating/cooling, cost-effective. Cons: Limited high-temperature performance. |
| Steatite | Good strength, economical, high dielectric strength | General electrical insulation, appliance components | Pros: Cost-effective, decent thermal conductivity. Cons: Lower mechanical strength compared to alumina. |
| Zirconia Ceramics | High toughness, corrosion resistance, low brittleness | Medical devices, high-performance applications | Pros: Superior mechanical properties, long lifespan. Cons: More expensive and less available. |
| ZTA (Zirconia Toughened Alumina) | Enhanced toughness from zirconia addition | Advanced electrical components, high-stress environments | Pros: Combines benefits of alumina and zirconia. Cons: Higher production costs and complexity. |
What Are the Characteristics of Alumina Ceramics for B2B Buyers?
Alumina ceramics are known for their exceptional hardness and strength, making them ideal for applications requiring durability. Their low porosity and excellent electrical resistance at both room and elevated temperatures make them highly suitable for electronics and aerospace industries. B2B buyers should consider the higher cost of alumina ceramics against their long-term benefits, including reduced maintenance and increased product lifespan.
How Does Cordierite Compare for Thermal Applications?
Cordierite is distinguished by its remarkable thermal shock resistance and low thermal expansion, allowing it to perform well in environments that experience rapid temperature changes. This makes it a preferred choice for electrical heating applications and automotive components. Buyers looking for cost-effective solutions should weigh its benefits against the limitations in high-temperature performance, ensuring it aligns with their specific operational needs.
Why Choose Steatite for General Electrical Insulation?
Steatite ceramics offer a balance of good mechanical strength and thermal conductivity at a lower cost compared to higher-end materials like alumina. They are commonly used in general electrical insulation and appliance components. B2B buyers should consider steatite if they require a reliable insulator without the premium price tag. However, it is essential to recognize that it may not withstand extreme mechanical stress as effectively as other options.

Illustrative image related to ceramic insulator
What Advantages Do Zirconia Ceramics Provide?
Zirconia ceramics are known for their high toughness and corrosion resistance, making them suitable for demanding applications such as medical devices and other high-performance environments. B2B buyers benefit from their long lifespan and durability, though they should be prepared for the higher costs associated with zirconia materials. Understanding the specific application requirements can help in making an informed purchasing decision.
How Does ZTA Enhance Performance in Electrical Components?
Zirconia Toughened Alumina (ZTA) combines the strengths of both alumina and zirconia, providing enhanced toughness and durability. This makes ZTA an excellent choice for advanced electrical components subjected to high stress. While it offers superior performance, buyers should be aware of the increased production costs and complexity involved in sourcing ZTA, ensuring it fits within their budget and application specifications.
Key Industrial Applications of ceramic insulator
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Ceramic Insulator | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrical Power Generation | Insulating components in transformers and circuit breakers | Enhanced safety and reliability in high-voltage environments | Material durability, thermal resistance, and compliance with international standards |
| Industrial Heating Equipment | Insulators for heating coils and elements | Improved energy efficiency and reduced heat loss | Temperature tolerance, mechanical strength, and thermal shock resistance |
| Telecommunications | Insulation in RF and microwave applications | Increased signal integrity and reduced interference | Dielectric strength, material purity, and dimensional precision |
| Automotive Manufacturing | Electrical insulators in ignition systems | Enhanced performance and reliability of ignition systems | High-temperature stability, resistance to chemical exposure, and lightweight design |
| Aerospace and Defense | Insulators in avionics and radar systems | Critical reliability in extreme conditions and operational safety | Compliance with stringent aerospace standards and long-term performance under high stress |
In the Electrical Power Generation sector, ceramic insulators are crucial for insulating components in transformers and circuit breakers. These insulators ensure safety and reliability in high-voltage environments, which is vital for preventing electrical failures that could lead to costly downtimes. Buyers must consider the durability of materials, thermal resistance, and compliance with international safety standards when sourcing these products, particularly for regions with varying regulatory frameworks.
In Industrial Heating Equipment, ceramic insulators are utilized for insulating heating coils and elements. This application enhances energy efficiency and minimizes heat loss, making it essential for manufacturers focused on sustainability and cost-effectiveness. Buyers need to prioritize temperature tolerance and mechanical strength to ensure optimal performance under high heat conditions, especially in industries where energy costs are a significant concern.
The Telecommunications industry employs ceramic insulators in RF and microwave applications to maintain signal integrity and reduce interference. High dielectric strength and material purity are critical factors for buyers in this sector, as these properties directly impact the performance of communication systems. Suppliers must provide precise dimensions to meet the stringent requirements of modern telecommunications infrastructure.
In Automotive Manufacturing, ceramic insulators play a vital role in the ignition systems of vehicles. Their ability to withstand high temperatures and resist chemical exposure enhances the performance and reliability of these systems. Sourcing considerations include lightweight design and high-temperature stability, which are essential for modern automotive applications aiming for efficiency and performance.
Finally, in the Aerospace and Defense sector, ceramic insulators are used in avionics and radar systems, where reliability under extreme conditions is paramount. These applications require compliance with stringent aerospace standards and the capability to perform under high stress over long periods. Buyers should focus on sourcing insulators that guarantee long-term performance and safety in critical applications.
Illustrative image related to ceramic insulator
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘ceramic insulator’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Ceramic Insulator Material for Specific Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges in selecting the appropriate type of ceramic insulator for their specific application. With various materials available—such as alumina, steatite, and cordierite—each offering unique properties like thermal conductivity, dielectric strength, and chemical resistance, the decision can become overwhelming. For instance, a manufacturer in the electronics sector may require insulators that can withstand high temperatures while providing excellent electrical insulation, but they might struggle to differentiate between the suitable options.
The Solution: To effectively address this issue, buyers should start by clearly defining their application requirements, including operating temperatures, environmental conditions, and electrical specifications. Engaging with suppliers who offer detailed technical data sheets on their ceramic insulators can also provide clarity. For example, if high thermal conductivity and low expansion are critical, opting for cordierite insulators would be ideal. Buyers should request samples or prototypes to test in their environments, ensuring compatibility before making bulk purchases. Additionally, consulting with manufacturers who specialize in custom solutions can lead to tailored products that meet specific operational needs.
Scenario 2: Issues with Supply Chain and Availability of Ceramic Insulators
The Problem: Many B2B buyers experience delays and uncertainties in their supply chain for ceramic insulators, particularly when sourcing from international suppliers. This is especially prevalent in regions like Africa and South America, where logistical challenges can lead to extended lead times and increased costs. Such delays can halt production lines and impact project timelines, resulting in financial losses and strained client relationships.
The Solution: To mitigate supply chain issues, buyers should diversify their sourcing strategy by establishing relationships with multiple suppliers across different regions. This not only reduces dependency on a single source but also helps in negotiating better terms and prices. Additionally, buyers can benefit from employing local distributors who can maintain an inventory of ceramic insulators, providing quicker access to products when needed. Utilizing technology such as supply chain management software can help track orders, predict delays, and manage inventory effectively, ensuring that operations remain uninterrupted.
Scenario 3: Challenges with Installation and Maintenance of Ceramic Insulators
The Problem: Once ceramic insulators are procured, B2B buyers often encounter difficulties during installation and maintenance. Improper handling or installation can lead to insulator failure, which can compromise safety and performance. For instance, in high-temperature environments, incorrect installation might lead to thermal shock or mechanical failure, posing risks to equipment and personnel.
The Solution: To overcome these challenges, comprehensive training programs should be established for the technical teams responsible for the installation and maintenance of ceramic insulators. Suppliers should provide clear installation guidelines and best practices tailored to specific products. Additionally, investing in high-quality installation tools and protective gear can enhance the safety and efficiency of the process. Regular maintenance checks and prompt replacement of worn insulators will also prolong their lifespan and maintain optimal performance. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement and education regarding ceramic insulator handling, companies can significantly reduce the risk of installation-related issues.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for ceramic insulator
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used for Ceramic Insulators?
When selecting ceramic insulators, understanding the properties of the materials involved is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in specific applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in ceramic insulators: Alumina, Cordierite, Steatite, and Zirconia. Each material has unique characteristics that influence its suitability for various industrial applications.
How Does Alumina Perform as a Ceramic Insulator?
Alumina, or aluminum oxide, is known for its exceptional hardness and strength. It can withstand high temperatures (up to 1800°C) and has excellent electrical insulation properties. Its low porosity (0-0.05%) contributes to its durability and resistance to chemical attacks, making it suitable for harsh environments.
Illustrative image related to ceramic insulator
Pros: High dielectric strength, excellent thermal conductivity, and resistance to corrosion make alumina ideal for high-performance applications.
Cons: The manufacturing process can be complex and costly, which may not be suitable for budget-sensitive projects.
Impact on Application: Alumina is compatible with a wide range of media, making it versatile for electrical and thermal insulation in industries such as power generation and electronics.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential. Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East often prefer materials with established certifications.
What Are the Benefits of Using Cordierite in Ceramic Insulators?
Cordierite is recognized for its excellent thermal shock resistance and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for applications involving rapid temperature changes. It typically operates effectively at temperatures around 1400°C.
Pros: Its ability to withstand thermal cycling without cracking is a significant advantage in environments with fluctuating temperatures.
Cons: While it is less expensive than alumina, cordierite may not offer the same level of electrical insulation performance under extreme conditions.
Impact on Application: Cordierite is particularly suitable for insulating heating elements in appliances and industrial furnaces, where thermal stability is critical.

Illustrative image related to ceramic insulator
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that cordierite products meet relevant industry standards, especially in markets that prioritize energy efficiency and safety, such as Germany.
How Does Steatite Compare as a Material for Ceramic Insulators?
Steatite is a cost-effective option that offers reasonable strength and thermal stability, functioning well at temperatures up to 1100°C. It has a moderate dielectric strength and is often used in applications where high performance is not the primary concern.
Pros: Its affordability and ease of manufacturing make it an attractive choice for less demanding applications.
Cons: Steatite’s lower thermal and electrical performance compared to alumina and cordierite may limit its use in high-stress environments.
Impact on Application: Steatite is commonly used in electrical insulators for low to medium voltage applications, making it suitable for consumer electronics and household appliances.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with local standards, particularly in regions with strict electrical safety regulations.
What Are the Unique Properties of Zirconia for Ceramic Insulators?
Zirconia, or zirconium dioxide, is known for its exceptional toughness and resistance to wear and corrosion. It can withstand high temperatures (up to 2400°C) and is often used in applications requiring high mechanical strength.
Pros: Its durability and high dielectric strength make it suitable for demanding electrical applications.
Cons: The high cost of zirconia can be a barrier for some applications, especially when compared to more economical materials like steatite.
Impact on Application: Zirconia is ideal for high-performance insulators in industries such as aerospace and high-voltage electrical systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the material’s certification and compliance with international standards, especially in sectors where safety and reliability are paramount.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Ceramic Insulators
| Material | Typical Use Case for ceramic insulator | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina | High-performance electrical insulators | Exceptional hardness and strength | High manufacturing complexity | High |
| Cordierite | Insulating heating elements | Excellent thermal shock resistance | Lower electrical performance | Medium |
| Steatite | Low to medium voltage applications | Cost-effective and easy to manufacture | Limited high-stress performance | Low |
| Zirconia | High-voltage electrical systems | High toughness and dielectric strength | High cost | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials used in ceramic insulators, emphasizing the importance of material selection based on application requirements and regional compliance standards. Understanding these factors will aid international B2B buyers in making informed decisions tailored to their specific needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for ceramic insulator
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Ceramic Insulators?
The manufacturing of ceramic insulators is a complex process that involves several critical stages, each contributing to the final product’s performance and reliability. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Ceramic Insulator Production?
Material preparation begins with the selection of high-quality raw materials, such as alumina, cordierite, steatite, or zirconia. Each material has unique properties that influence the insulator’s performance. For instance, alumina is known for its high dielectric strength and thermal conductivity, while cordierite excels in thermal shock resistance. The raw materials are typically milled to a fine powder to ensure uniformity.
Once milled, the powder may undergo a blending process to achieve the desired composition. This blend is crucial for achieving specific electrical and mechanical properties. After blending, additives such as binders or plasticizers might be included to enhance workability during the forming stage.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Ceramic Insulators?
Forming techniques play a pivotal role in shaping the insulator. Common methods include:
-
Injection Molding: This technique is favored for producing complex shapes and high-volume production runs. The prepared ceramic powder is mixed with a binder and injected into molds.
-
Die Pressing: In this method, the powder is compacted in a die under high pressure, creating a dense preform. It is often used for simpler shapes and allows for efficient mass production.
-
Isostatic Pressing: This method applies uniform pressure in all directions, resulting in a dense and uniform product. It is particularly useful for intricate designs.
-
Slip Casting: A slurry of ceramic powder and water is poured into a mold. As water is absorbed, a solid layer forms, which is then removed and dried.
-
Extrusion: This technique is used for creating long, continuous shapes, such as tubes or rods. The ceramic paste is forced through a die, shaping it as it exits.
Each of these methods has distinct advantages and is chosen based on the design requirements and production volume.
How Are Ceramic Insulators Assembled and Finished?
Once formed, the insulators undergo assembly, where multiple components may be joined if the design requires it. This could involve using ceramic adhesives or mechanical fastening methods. Following assembly, the components are dried to remove moisture content, which is essential for preventing defects during firing.
The finishing stage includes sintering, where the formed parts are subjected to high temperatures in a kiln, allowing the particles to fuse and attain their final strength and density. Post-sintering processes such as grinding, polishing, and surface treatment may be performed to achieve the required dimensions and surface finish.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for Ceramic Insulators?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in ensuring that ceramic insulators meet international standards and specific industry requirements. A robust QA system typically aligns with ISO 9001 standards, which emphasize quality management principles such as customer satisfaction, process approach, and continuous improvement.

Illustrative image related to ceramic insulator
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers adhere to relevant international standards. For ceramic insulators, certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) for the European market and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for oil and gas applications are important. These certifications indicate that the products meet safety and performance criteria.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Ceramic Insulator Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are integral to maintaining product integrity throughout the manufacturing process. Common checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials before they enter the production line to ensure they meet specified criteria.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, regular checks are conducted to monitor parameters like temperature and pressure in forming and sintering processes.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, the finished insulators undergo rigorous testing for mechanical strength, dielectric properties, and thermal performance.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Ceramic Insulators?
Several testing methods are employed to verify the quality and performance of ceramic insulators, including:
-
Mechanical Testing: This assesses the tensile strength, compressive strength, and impact resistance of the insulators.
-
Electrical Testing: Dielectric strength tests evaluate how well the insulator can withstand electrical stress without breaking down.
-
Thermal Testing: Thermal shock tests determine the insulator’s ability to withstand rapid temperature changes.
-
Porosity Measurement: This ensures that the insulator has the appropriate density and porosity to function effectively in its application.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards. Conducting regular audits of suppliers is essential. These audits should focus on the entire manufacturing process, from material sourcing to final product testing.
Buyers should also request quality reports, including testing results and certifications. Third-party inspections can provide an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturing process and product quality. This is especially important when dealing with international suppliers, as variations in quality standards may exist.
What Are the Nuances in Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is crucial to understand the specific regulatory and compliance requirements in their respective markets. Different regions may have varying standards for electrical safety, environmental impact, and material specifications.

Illustrative image related to ceramic insulator
Additionally, language barriers and cultural differences can affect communication regarding quality expectations. Establishing clear guidelines and maintaining open lines of communication with suppliers can help bridge these gaps, ensuring that both parties have a mutual understanding of quality requirements.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for ceramic insulators, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that they source reliable and high-quality products for their applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘ceramic insulator’
The following guide provides a structured approach for B2B buyers looking to procure ceramic insulators. It aims to streamline the sourcing process, ensuring that buyers make informed decisions while considering their specific needs and regional market dynamics.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clearly define the technical specifications required for your ceramic insulators. Consider factors such as material type (e.g., alumina, steatite, cordierite), dimensions, dielectric strength, and thermal conductivity. Understanding these specifications will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure that the products meet your application requirements.
Step 2: Identify Reliable Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reputable suppliers of ceramic insulators. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record and positive reviews from previous clients. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online marketplaces to compile a list of potential suppliers. Pay attention to their experience in your specific industry and region, as local expertise can significantly impact product quality and delivery timelines.

Illustrative image related to ceramic insulator
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to any supplier, it’s crucial to vet them thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Consider conducting site visits if possible, as this will provide insight into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. A reliable supplier should also be willing to provide samples for testing before finalizing the order.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your chosen suppliers possess the necessary certifications and compliance standards relevant to your industry. Certifications may include ISO 9001 for quality management or specific electrical safety standards. These credentials are vital as they indicate the supplier’s commitment to maintaining high production standards and adherence to international safety regulations.
Step 5: Assess Pricing and Payment Terms
Once you have narrowed down your supplier options, request detailed quotations that outline pricing, shipping costs, and payment terms. Compare these offers while considering the total cost of ownership, which includes delivery times and potential customs fees. Establish clear payment terms that protect your interests, such as upfront payments for larger orders or milestone payments based on delivery stages.
Step 6: Review Warranty and Support Policies
Understand the warranty and support policies offered by your suppliers. A robust warranty can protect your investment and provide peace of mind regarding product performance. Additionally, inquire about after-sales support and technical assistance, as this can be crucial for troubleshooting and maintenance in the long term.
Step 7: Finalize and Monitor the Order
After selecting a supplier and finalizing the terms, place your order and establish a monitoring process. Stay in regular contact with the supplier to track production progress and ensure timely delivery. Implement a quality assurance protocol upon receipt to verify that the ceramic insulators meet your specified standards before integration into your operations.
This comprehensive checklist will guide you through the sourcing process of ceramic insulators, helping you make informed decisions that align with your business objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for ceramic insulator Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Ceramic Insulator Manufacturing?
When sourcing ceramic insulators, international B2B buyers should understand the various cost components that contribute to the final pricing. The primary elements include:
-
Materials: The type of ceramic material—such as alumina, cordierite, or steatite—significantly influences cost. High-performance materials like zirconia may command higher prices due to their superior properties.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for the precise machining and finishing processes involved in producing ceramic insulators. Labor costs can vary by region, impacting overall pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize overhead.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be high, especially for custom designs. However, these costs are amortized over larger production runs, making high volumes more cost-effective.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that products meet industry standards and certifications. The cost of QC may be built into the pricing structure.
-
Logistics: Transporting ceramic insulators, especially over long distances, incurs significant costs. These can fluctuate based on fuel prices and shipping methods.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their expenses and profit. This can vary widely based on competition and market demand.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Ceramic Insulator Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of ceramic insulators, particularly for international buyers:
Illustrative image related to ceramic insulator
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ) can significantly impact unit prices. Larger orders often yield better per-unit pricing due to economies of scale.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom designs or unique specifications can lead to higher costs due to increased complexity in manufacturing and potential tooling changes.
-
Materials: The choice of materials not only affects performance but also the cost. High-grade materials can enhance durability but increase initial outlay.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet specific industry certifications may be priced higher due to the additional processing and testing required.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, location, and production capacity can all influence pricing. Established suppliers with a history of reliability may charge a premium.
-
Incoterms: The agreed-upon Incoterms affect logistics costs and responsibilities, which can alter the total landed cost for buyers.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Costs in Ceramic Insulator Sourcing?
International buyers can employ several strategies to enhance cost efficiency and maximize value when sourcing ceramic insulators:
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially for larger orders. Building a relationship can lead to better terms and potential discounts.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the initial purchase price. Factors such as durability, maintenance, and energy efficiency can influence long-term costs.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Understand the implications of currency fluctuations and trade tariffs that could affect pricing when sourcing from different regions.
-
Supplier Diversity: Explore multiple suppliers to compare offerings and prices. This can provide leverage during negotiations and help identify the best overall value.
-
Quality Assurance: Invest in quality products to minimize replacements and warranty claims. The upfront cost may be higher, but the long-term savings can be significant.
Conclusion
Understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing influencers is crucial for international B2B buyers of ceramic insulators. By considering these elements and employing strategic sourcing techniques, businesses can optimize their procurement processes and achieve significant savings. It’s essential to note that the prices mentioned here are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier relationships, and specific project requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing ceramic insulator With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Ceramic Insulators
In the realm of electrical insulation, ceramic insulators are a popular choice due to their high durability and excellent electrical resistance. However, various alternatives exist that may better suit specific applications or budgets. Understanding these alternatives is crucial for B2B buyers seeking optimal solutions for their insulation needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Ceramic Insulator | Polymer Insulator | Glass Insulator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High dielectric strength; withstands high temperatures (up to 3000°F) | Good insulation properties; suitable for lower temperatures | Excellent electrical properties; good for high-voltage applications |
| Cost | Moderate ($31.00 for 12 units) | Lower ($15.00 for 10 units) | Higher ($50.00 for 5 units) |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized installation techniques | Easy to install; flexible design | Moderate; requires careful handling |
| Maintenance | Minimal; durable and long-lasting | Moderate; may degrade over time | Low; glass is resistant to environmental factors |
| Best Use Case | High-temperature and high-voltage applications | General electrical applications with moderate voltage | High-voltage overhead lines and outdoor applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Polymer Insulators
Polymer insulators are increasingly being used as an alternative to ceramic insulators, particularly in lower voltage applications. They are lightweight and flexible, which makes them easier to install compared to ceramics. However, while they offer good insulation properties, they may not perform as well in high-temperature environments or under extreme electrical stress. Over time, polymer materials can degrade due to environmental factors, requiring more frequent replacements than ceramic options.
Glass Insulators
Glass insulators are known for their exceptional electrical properties and durability, making them suitable for high-voltage applications. They are often used in overhead power lines and outdoor environments due to their resistance to moisture and UV radiation. However, glass insulators can be heavier and more fragile than ceramic options, which might complicate installation and transportation. Additionally, their cost is generally higher, making them less appealing for budget-conscious projects.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Insulation Solution
Selecting the appropriate insulation solution requires careful consideration of specific project requirements, including environmental conditions, voltage levels, and budget constraints. Ceramic insulators are ideal for high-temperature and high-voltage applications, while polymer insulators offer flexibility and ease of installation for less demanding scenarios. Glass insulators excel in outdoor, high-voltage environments but come at a premium cost. By evaluating these factors and understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each option, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and financial goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for ceramic insulator
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Ceramic Insulators?
Understanding the technical properties of ceramic insulators is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure they select the right products for their applications. Here are some essential specifications:
-
Material Grade
Ceramic insulators are typically made from materials like alumina, cordierite, steatite, or zirconia. Each material has distinct properties; for example, alumina offers high hardness and excellent electrical resistance, making it ideal for high-performance applications. Understanding the material grade helps in selecting insulators that meet specific electrical and thermal requirements. -
Dielectric Strength
This property measures the insulator’s ability to withstand high voltage without conducting electricity. A higher dielectric strength means better insulation performance, which is vital for applications in power generation and electrical components. For instance, materials like steatite may have dielectric strengths suitable for moderate temperature environments, while alumina excels in high-temperature conditions. -
Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity indicates how well a material can conduct heat. In applications involving electrical heating elements, low thermal conductivity is often desirable to prevent heat loss. For instance, cordierite has low thermal conductivity and excellent thermal shock resistance, making it suitable for insulators in heating applications. -
Porosity
Porosity affects the insulator’s strength and durability. Low porosity (0-0.05%) is often preferred as it enhances mechanical strength and reduces moisture absorption, which can compromise insulation properties. This is especially critical in humid environments, where insulators need to maintain performance under varying conditions. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from specified dimensions in manufacturing. Tight tolerances are essential for ensuring that insulators fit precisely in their applications, minimizing the risk of failure. This is particularly important in custom applications where precise specifications are crucial for functionality. -
Temperature Resistance
The ability to withstand high temperatures without degrading is a vital property of ceramic insulators. Materials like zirconia can endure extreme conditions, making them suitable for high-temperature applications, such as in the aerospace or automotive industries.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Ceramic Insulator Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and procurement processes. Here are some key terms to know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify trusted suppliers for specific ceramic insulator needs. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest amount of product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchasing strategy and budget, particularly when sourcing insulators for large-scale projects. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers asking for pricing and terms for specific products. Submitting an RFQ can help buyers compare offers and negotiate better deals, ensuring they secure the best value for ceramic insulators. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, delivery timelines, and risk management. -
Lead Time
This term refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. Understanding lead times is crucial for project planning and ensuring that materials arrive on schedule, particularly for time-sensitive projects. -
Certification
Certifications indicate that products meet specific industry standards or regulations. For ceramic insulators, certifications can assure buyers of quality and safety, making it easier to comply with industry regulations in their respective regions.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing ceramic insulators, ensuring compatibility with their applications and compliance with industry standards.
Illustrative image related to ceramic insulator
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the ceramic insulator Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Ceramic Insulator Sector?
The global ceramic insulator market is experiencing robust growth driven by increasing demand across various industries, including electrical, electronics, and telecommunications. Key trends influencing this market include the adoption of advanced materials like alumina and zirconia ceramics, which offer superior electrical resistance and thermal stability. International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly sourcing high-performance ceramic insulators for applications in high-temperature environments and electrical insulation needs.
Emerging technologies such as additive manufacturing and precision ceramic machining are reshaping sourcing strategies, allowing for customized solutions that enhance efficiency and reduce lead times. Furthermore, the trend towards digitization in supply chain management is facilitating better forecasting and inventory management for B2B buyers, enabling them to respond swiftly to market fluctuations. As industries focus on energy efficiency and sustainability, ceramic insulators that support these objectives are becoming a pivotal consideration in procurement decisions.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the Ceramic Insulator Market?
Environmental impact and ethical sourcing are paramount for B2B buyers in the ceramic insulator sector. The production of ceramic materials often involves significant energy consumption and resource extraction, raising concerns about sustainability. Consequently, international buyers are prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to environmentally friendly practices, such as minimizing waste and reducing carbon footprints in their manufacturing processes.
Additionally, the demand for ‘green’ certifications is on the rise, as companies seek materials that align with their sustainability goals. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and adherence to REACH regulations are becoming critical factors in supplier selection. Buyers are also increasingly interested in sourcing insulators made from recycled materials or those that utilize eco-friendly production methods. This shift not only mitigates environmental impact but also enhances brand reputation and compliance with global sustainability standards.
What Is the Historical Context of the Ceramic Insulator Industry?
The ceramic insulator industry has evolved significantly over the past century, transitioning from basic electrical insulating materials to advanced, high-performance ceramics. Early ceramic insulators were primarily used in telecommunication and electrical applications, but advancements in material science have broadened their applications across various sectors, including automotive and renewable energy.
With the rise of new technologies, such as smart grids and electric vehicles, the demand for innovative ceramic insulators has surged, prompting manufacturers to invest in research and development. Today, the industry is characterized by a focus on enhancing durability, thermal resistance, and electrical performance, catering to the evolving needs of global markets. This historical evolution underscores the importance of staying informed about technological advancements and market dynamics for effective sourcing strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of ceramic insulator
-
How do I choose the right ceramic insulator for my application?
Selecting the right ceramic insulator involves understanding the specific requirements of your application, such as temperature resistance, dielectric strength, and chemical exposure. For high-temperature environments, materials like alumina or cordierite are ideal due to their durability and thermal shock resistance. Evaluate the operating conditions, including voltage and environmental factors, to ensure the insulator can withstand them. Consulting with manufacturers or suppliers can also provide insights into the best material options tailored to your needs. -
What are the key benefits of using ceramic insulators in industrial applications?
Ceramic insulators offer several advantages, including high dielectric strength, excellent thermal resistance, and low thermal conductivity. They are resistant to chemical attacks and environmental degradation, making them suitable for harsh industrial settings. Additionally, ceramics are non-conductive, which helps prevent electrical leakage and enhances safety. Their longevity and low maintenance requirements also contribute to reduced operational costs over time, making them a cost-effective solution for many applications. -
What factors should I consider when vetting ceramic insulator suppliers?
When vetting suppliers, consider their experience in the ceramic insulator market, customer reviews, and certifications (such as ISO 9001). Evaluate their production capabilities and the range of materials they offer, ensuring they align with your specifications. Additionally, inquire about their quality assurance processes, lead times, and flexibility in meeting custom orders. Requesting samples can help assess the quality of their products before making a larger commitment. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for ceramic insulators?
MOQs for ceramic insulators can vary significantly based on the supplier and the type of insulator required. Generally, they can range from a few dozen to several hundred units. Some suppliers may offer flexible MOQs for custom designs, while others may have stricter requirements for standard products. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that work for both parties. -
How do I handle international payments for ceramic insulator purchases?
When dealing with international suppliers, it’s crucial to establish clear payment terms upfront. Common payment methods include wire transfers, letters of credit, or payment platforms like PayPal. Be aware of currency exchange rates and any additional fees that may apply. Ensure that the supplier provides a proforma invoice detailing the costs involved. It’s also wise to consider escrow services for larger transactions to mitigate risks. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from a ceramic insulator supplier?
Reputable suppliers should have rigorous quality assurance protocols in place. This typically includes raw material inspections, in-process quality checks, and final product testing to ensure compliance with industry standards. Request documentation of their testing methods and certifications. It’s also beneficial to ask if they offer warranties or guarantees on their products, which can provide additional peace of mind regarding their quality. -
How can I ensure timely delivery of ceramic insulators to my location?
To ensure timely delivery, communicate clearly with your supplier about your delivery timelines and any specific logistical requirements. Discuss shipping methods and estimated transit times, considering factors such as customs clearance and local regulations. Using reliable freight forwarders can also enhance efficiency. Tracking shipments and maintaining open lines of communication with your supplier can help address any potential delays proactively. -
What customization options are available for ceramic insulators?
Many suppliers offer customization options for ceramic insulators to meet specific application requirements. Customizations can include variations in size, shape, and material composition based on your technical needs. Some suppliers may also provide design services to develop insulators tailored to unique operational environments. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to explore the extent of their customization capabilities and any associated costs.
Top 9 Ceramic Insulator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. AccuGlass – Ceramic Insulator 2 Hole Design
Domain: accuglassproducts.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Ceramic Insulator 2 Hole Design – 0.020″ ID”, “Part Number”: “112292”, “Model Number”: “BC-CER-INS”, “Material”: “Steatite”, “ID”: “0.020””, “AWG”: “24AWG nominal”, “Length”: “1.00””, “Weight”: “0.1 lbs”, “Quantity per Package”: “12”, “Price”: “$31.00”, “Max Bake Temperature”: “450ºC”, “Max Operating Temperature”: “450ºC”, “Min Operating Temperature”: “-200ºC”, “Max Vacuum Level”…
2. eBay – Ceramic Insulator
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Ceramic Insulator for sale on eBay. Related searches include Ceramic Electrical Insulators, Old Ceramic Insulators, White Porcelain Insulator, Plastic Insulator, Glass Insulator, Vintage Electrical Insulators, Rare Glass Insulator, and more. Featured refinements include Ceramic Insulator, Glass Insulator, Porcelain Insulator, and Telephone Insulators. Condition options are New, Used, or Not Specif…
3. IQS Directory – Ceramic Insulators
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Ceramic insulators are insulating materials made from clay, characterized by a porous texture and available in red, brown, or white. They offer outstanding dielectric properties, exceptional resistance to electrical currents, low energy dissipation, and are easy to maintain. They are highly resistant to staining and residue buildup, making them ideal for electrical insulation. Ceramic insulators a…
4. Therm-Coil – Cordierite Ceramic Insulators
Domain: therm-coil.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Ceramic Insulators made from Cordierite for insulating electrical heating coils. Available sizes include:
– 5/8″ O.D. x 19/64″ I.D. x 29/64″ thick
– 3/4″ O.D. x 5/16″ I.D. x 3/8″ thick
– 7/8″ O.D. x 13/32″ I.D. x 7/16″ thick.
Pack sizes range from 25 to 75 quantity packs. Prices range from $62.35 to $115.26 depending on size and quantity.
5. Associated Ceramics – Custom Electrical and Thermal Insulators
Domain: associatedceramics.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Associated Ceramics is a custom manufacturer of electrical ceramic insulators and thermal ceramic insulators for various industries including appliance, power generation, medical, and electronics. Key materials used include: 1. Alumina: High strength and hardness, excellent electrical resistance, high thermal conductivity, high resistance to chemical and corrosion, 0-0.05% porosity, high dielectri…
6. Zareba Systems – Ceramic Insulators
Domain: zarebasystems.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Ceramic Insulators: Made from red, brown, or white porous clay, fired at 2,100° to 2,300° F. Lower price, can chip or break in cold weather, excellent insulation quality, better durability than plastic insulators. Varieties include Multi-Groove with Nails, Multi-Groove (no nails), Single Groove, Large Insulator with Lag Screw, Small Insulator with Lag Screw, Corner Post Insulator, Duralator Self-D…
7. Etsy – Vintage 1950s Large Ceramic Electrical Insulator
Domain: etsy.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Vintage Ceramic Insulators available on Etsy, with over 1,000 items listed. Key products include:
– Vintage 1950s Large Ceramic Electrical High Voltage Insulator with Brown Porcelain Glaze priced at $50.00.
– Vintage Porcelain/Ceramic Telegraph/Telephone Railroad Insulators, originally $59.22, on sale for $35.53 (40% off).
– Vintage Glass Insulator, decorative railroad glass, priced at $35.99 with…
8. Porcelain Insulators – 100 Years of Heritage
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 100 years of porcelain insulators (1892-1992). The collector has retired almost half of these insulators over 17 years in the trade, with the rest being gifted or found on abandoned lines in the southwest. The insulators are noted for their traditional shapes, which serve a functional purpose in preventing moisture from bridging distances between energized conductors and mounting attachments.
9. Asheville Mica – Custom Ceramic Insulation Parts
Domain: ashevillemica.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Custom ceramic insulation parts for braking resistors and industrial applications. Materials include Steatite, Cordierite, Alumina, Teflon, Nomex, Kapton, Nylon, Vulcanized Fiber, and Silicone Rubber. Capabilities to cross-reference to Mil Spec M38527 and M49466. High-pressure laminates available in NEMA Grades G-3, G-5, G-7, G-9, G10, G-11, and GPO3. Typical industries served: Aviation/Aerospace/…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for ceramic insulator
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Procurement of Ceramic Insulators?
In summary, strategic sourcing is pivotal for B2B buyers seeking ceramic insulators, particularly in the diverse markets of Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By leveraging a thorough understanding of material properties—such as the durability of alumina and the thermal resilience of cordierite—buyers can make informed decisions that optimize both performance and cost-efficiency. Establishing strong relationships with suppliers who can provide quality products at competitive prices is essential for long-term success.
Furthermore, as industries increasingly demand sustainable and innovative solutions, sourcing ceramic insulators from manufacturers committed to environmental standards will not only enhance corporate responsibility but also align with global market trends. Buyers should actively seek partnerships that offer custom solutions tailored to specific applications, ensuring that their procurement strategies remain agile and responsive to market needs.
As we look to the future, the ceramic insulator market is poised for growth driven by technological advancements and increased demand across various sectors. International buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers now to capitalize on emerging opportunities and secure a competitive edge in their respective industries.

Illustrative image related to ceramic insulator
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.