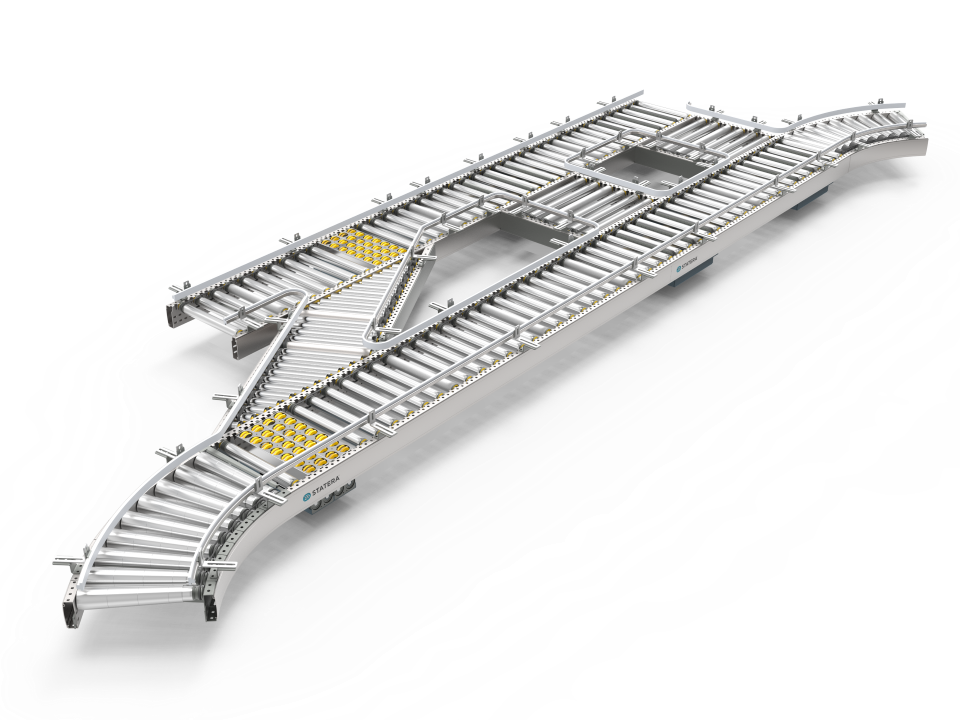
Case Conveyors: The Ultimate 2025 B2B Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for case conveyors
In today’s fast-paced global market, sourcing reliable case conveyors poses a significant challenge for B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As businesses expand and adapt to increasing consumer demands, the need for efficient, high-capacity case handling solutions becomes paramount. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, covering a variety of case conveyor types, their specific applications, and the crucial factors to consider during the supplier vetting process.
From understanding the nuances of different conveyor technologies, such as Motor Driven Roller (MDR) systems and gravity conveyors, to evaluating cost implications and maintenance needs, this guide empowers international B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Our focus extends to practical insights that facilitate seamless integration into existing operations, ensuring optimal performance and scalability.
Whether you are in Vietnam or Germany, navigating the complexities of case conveyor systems can be daunting. This guide is designed to demystify the selection process, equipping you with the knowledge needed to choose the right solutions for your unique operational requirements. By leveraging the expertise and insights presented here, you can enhance your supply chain efficiency and ultimately drive your business’s success in an increasingly competitive landscape.
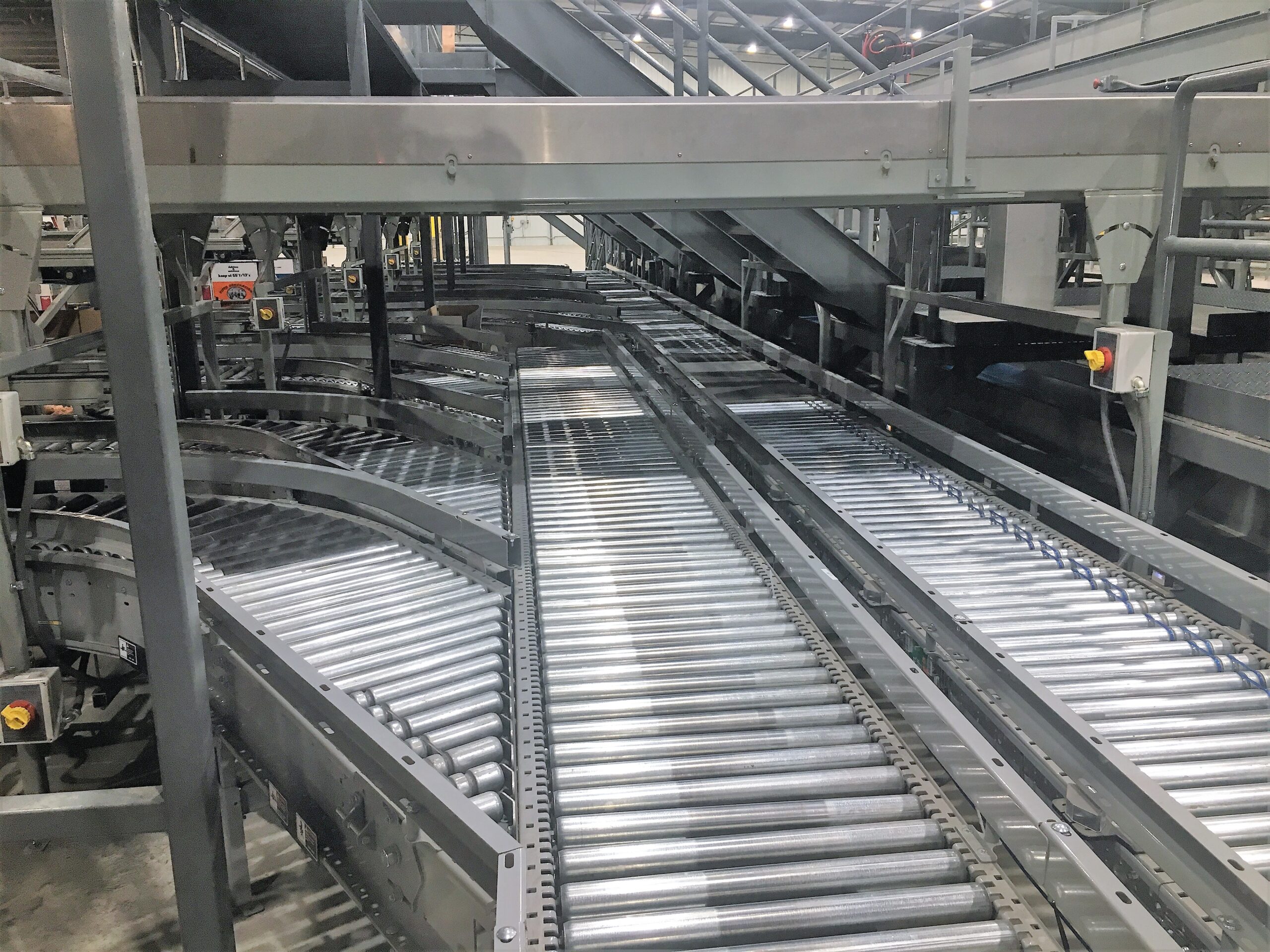
Understanding case conveyors Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Motor Driven Roller (MDR) | Electrically powered, modular design, zero back pressure | High-speed accumulation, case transport | Pros: Low maintenance, flexible; Cons: Higher initial investment |
| Gravity Conveyor | Relies on gravity for movement, low-cost and lightweight | Manual sorting, low-volume transport | Pros: Economical, easy setup; Cons: Limited to downhill transport |
| Extendable Conveyor | Adjustable length, portable for loading/unloading | Loading/unloading from trailers, docks | Pros: Versatile, space-saving; Cons: May require manual operation |
| Belt Conveyor | Continuous belt for case movement, suitable for various products | Bulk handling, packaging lines | Pros: Smooth transport, good for fragile items; Cons: Higher maintenance |
| Chain Driven Live Roller (CDLR) | Chain-driven rollers, robust for heavy loads | Heavy-duty applications, warehousing | Pros: Durable, reliable for heavy cases; Cons: More complex setup |
What Are the Characteristics of Motor Driven Roller (MDR) Conveyors?
Motor Driven Roller (MDR) conveyors are characterized by their modular design and the use of electric motors for movement, allowing for zero back pressure during case handling. This feature is particularly beneficial for high-speed accumulation and transport applications, making them ideal for larger facilities with complex logistics needs. When considering MDR systems, buyers should evaluate their production requirements, as these conveyors offer scalability and low maintenance costs, although they may require a higher initial investment.
How Do Gravity Conveyors Function in B2B Applications?
Gravity conveyors utilize the force of gravity to move products along the conveyor line, making them a cost-effective solution for low-volume transportation and manual sorting applications. Their lightweight construction allows for easy installation and flexibility in layout. However, buyers should note that gravity conveyors are limited to downhill transport and may not be suitable for all environments, especially where powered movement is necessary.
Why Choose Extendable Conveyors for Loading and Unloading?
Extendable conveyors are designed for flexibility and portability, allowing them to be adjusted in length for various loading and unloading tasks. This adaptability makes them particularly useful in shipping and receiving areas, where space is often at a premium. While they provide significant versatility, buyers should consider that extendable conveyors may require manual operation, which could limit efficiency compared to fully automated systems.
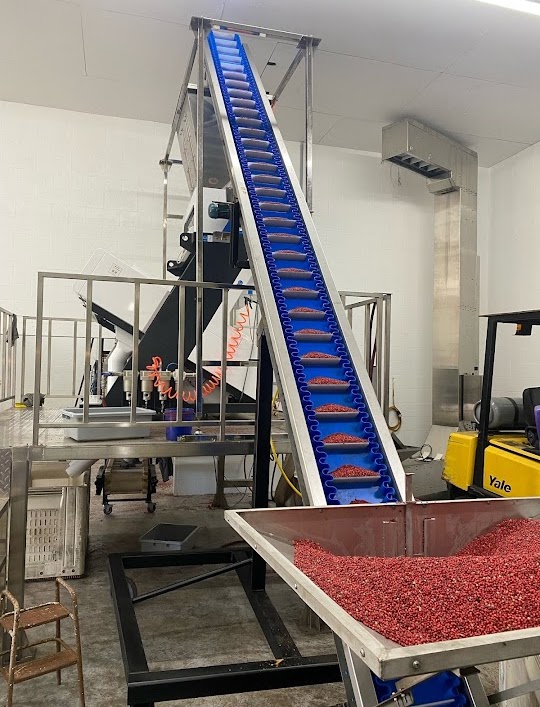
What Advantages Do Belt Conveyors Offer for Case Handling?
Belt conveyors are known for their continuous movement capabilities, which makes them suitable for transporting a wide range of products, including fragile cases. Their smooth operation minimizes the risk of damage during transport, making them a popular choice in packaging lines. However, buyers should be aware that belt conveyors may require more maintenance compared to other systems, especially in environments with heavy use.
How Are Chain Driven Live Roller (CDLR) Conveyors Beneficial for Heavy Loads?
Chain Driven Live Roller (CDLR) conveyors are specifically designed for handling heavy cases, utilizing chain-driven rollers to provide reliable movement. This robustness makes them ideal for warehousing and heavy-duty applications where durability is crucial. While CDLR systems offer significant advantages in terms of reliability and load capacity, potential buyers should also consider the complexity of installation and maintenance associated with these systems.
Key Industrial Applications of case conveyors
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Case Conveyors | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food & Beverage | Transporting packaged food items from production to storage | Increases efficiency and reduces manual handling | Consider hygiene standards, material durability, and ease of cleaning |
| Pharmaceuticals | Moving cases of medicines from packaging to distribution | Ensures safe and compliant handling of sensitive products | Look for systems that offer zero back pressure and customizable zones |
| E-commerce & Retail | Sorting and distributing packaged goods in warehouses | Enhances order fulfillment speed and accuracy | Evaluate modular designs for scalability and integration with existing systems |
| Consumer Goods | Transferring cases of household products from assembly lines to shipping | Streamlines operations, reducing bottlenecks | Assess load capacity and conveyor speed to match production needs |
| Automotive | Handling cases of automotive parts in assembly lines | Improves production flow and reduces downtime | Ensure compatibility with various part sizes and weights, and consider maintenance needs |
How Are Case Conveyors Used in the Food & Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage sector, case conveyors are critical for transporting packaged items from production lines to storage or shipping areas. These conveyors help minimize manual handling, which can reduce the risk of contamination and improve operational efficiency. Buyers in this industry must prioritize hygiene standards, ensuring that the materials used in the conveyor systems are durable and easy to clean to meet regulatory requirements.
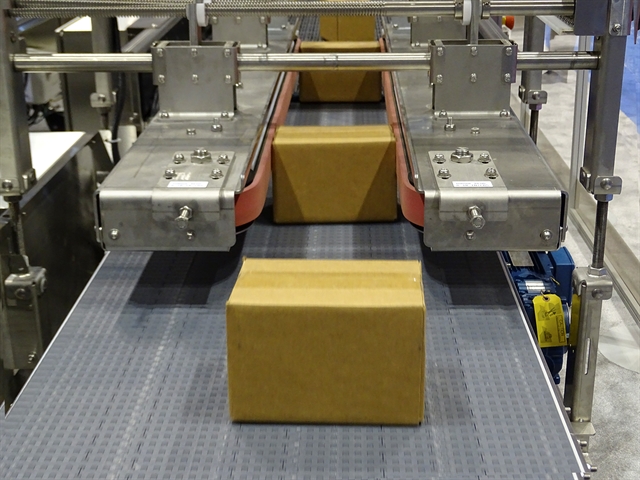

Illustrative image related to case conveyors
What Role Do Case Conveyors Play in Pharmaceuticals?
Pharmaceutical companies utilize case conveyors to move packaged medicines efficiently while maintaining compliance with safety standards. These conveyors are designed to prevent case-to-case contact, ensuring that sensitive products are handled safely. International buyers should focus on sourcing systems that provide zero back pressure and customizable zones to accommodate varying product sizes and ensure smooth operation during high-demand periods.
How Do Case Conveyors Enhance E-commerce and Retail Operations?
In the fast-paced e-commerce and retail sectors, case conveyors facilitate the sorting and distribution of packaged goods within warehouses. This automation significantly boosts order fulfillment speed and accuracy, allowing businesses to meet customer expectations more effectively. When sourcing conveyors for these applications, companies should consider modular designs that allow for easy scalability and integration with existing systems, accommodating future growth.
What Benefits Do Case Conveyors Provide for Consumer Goods?
For the consumer goods industry, case conveyors are essential for moving cases of products from assembly lines to shipping areas. By streamlining operations, these systems help reduce bottlenecks and improve overall productivity. Buyers should assess the load capacity and conveyor speed to ensure the selected systems align with their specific production requirements and operational workflows.
How Are Case Conveyors Used in the Automotive Industry?
In automotive manufacturing, case conveyors are employed to handle cases of parts and components on assembly lines. This use enhances production flow and minimizes downtime, which is crucial in a competitive market. When sourcing case conveyors for automotive applications, businesses should ensure compatibility with various part sizes and weights, as well as consider the maintenance needs to minimize disruptions in production.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘case conveyors’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Managing High Volume with Limited Space
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods face the challenge of transporting high volumes of packaged goods through facilities with limited space. The need to optimize workflow while minimizing physical footprint can lead to inefficient processes, increased labor costs, and potential bottlenecks. For example, a manufacturer might struggle with how to implement an effective case conveyor system that accommodates various case sizes without overwhelming the available floor space.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should consider modular case conveyor systems that allow for flexible configurations. Opting for a Motor Driven Roller (MDR) conveyor can enhance space efficiency due to its low-profile design and ability to be customized for specific workflows. When sourcing these systems, it’s essential to work with suppliers who offer pre-engineered solutions tailored to the unique requirements of your operations. Buyers should also consult with engineering experts who can provide layout simulations, ensuring that the chosen system not only fits spatial constraints but also maximizes throughput and minimizes downtime. By selecting a system that incorporates features like zero back pressure for case handling, companies can further optimize their space while maintaining a streamlined process.
Scenario 2: Downtime and Maintenance Challenges
The Problem: Frequent downtime due to maintenance issues is a major concern for B2B buyers, particularly in industries that rely heavily on continuous operations. Buyers often find themselves dealing with conveyor systems that are difficult to maintain, leading to increased operational costs and loss of productivity. For instance, a distribution center may experience interruptions in their case conveyor system due to mechanical failures or complex maintenance requirements, which can disrupt the entire supply chain.
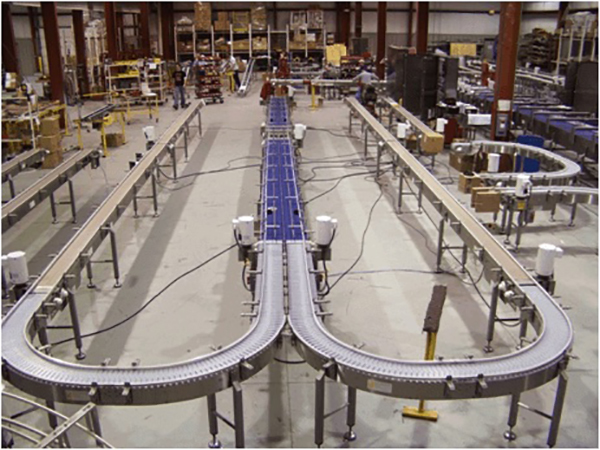

Illustrative image related to case conveyors
The Solution: To mitigate these challenges, businesses should invest in case conveyors that feature sealed-for-life roller bearings and maintenance-free components. These innovations reduce the need for regular maintenance and enhance the reliability of the system. When evaluating options, buyers should prioritize systems with a modular design, allowing for quick replacement of parts without extensive downtime. Additionally, working with suppliers that offer comprehensive maintenance contracts can ensure ongoing support and prompt service when issues arise. Implementing a proactive maintenance schedule, along with training staff on the specific needs of the conveyor system, will significantly reduce unexpected breakdowns and improve overall efficiency.
Scenario 3: Integrating Advanced Technology for Automation
The Problem: Many B2B buyers are looking to integrate advanced technologies into their case conveyor systems to enhance automation and efficiency. However, they often face hurdles in selecting the right technology that aligns with their current operations and scales with future growth. This can lead to poor investment decisions or systems that fail to deliver expected productivity gains. For example, a logistics company may struggle to implement automatic sorting and merging capabilities that enhance workflow without disrupting existing processes.
The Solution: To effectively integrate advanced technology, buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their current operations and future needs. Collaborating with a supplier that offers customizable case conveyor solutions is crucial. These suppliers can provide systems that incorporate advanced features such as automated sorting, indexing, and real-time monitoring. It is beneficial to request demonstrations or simulations of how the proposed systems would function within the existing layout. Additionally, engaging in pilot programs can help identify any operational challenges before full-scale implementation. By choosing suppliers with a strong engineering background and project management capabilities, businesses can ensure a smoother transition to automated systems that genuinely enhance productivity and reduce human error.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for case conveyors
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Case Conveyors?
When selecting materials for case conveyors, several options stand out, each with unique properties that affect performance, durability, and cost. The most common materials include stainless steel, mild steel, aluminum, and plastic. Understanding their properties and suitability for specific applications is crucial for international B2B buyers.
How Does Stainless Steel Compare for Case Conveyors?
Stainless steel is renowned for its exceptional corrosion resistance and strength, making it ideal for environments where hygiene is paramount, such as food and pharmaceuticals. Its temperature tolerance allows it to perform well in both cold and hot applications without compromising structural integrity.
Pros: Stainless steel is highly durable, resistant to rust, and easy to clean, which is essential for maintaining compliance with health standards. Its longevity reduces the need for frequent replacements, which can be a cost-saving factor in the long run.
Cons: The primary drawback is its higher cost compared to other materials. Additionally, manufacturing stainless steel components can be complex, leading to longer lead times.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is suitable for environments that require frequent cleaning and exposure to moisture, making it a preferred choice in industries like food processing and pharmaceuticals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN for food-grade materials, which can affect sourcing decisions.
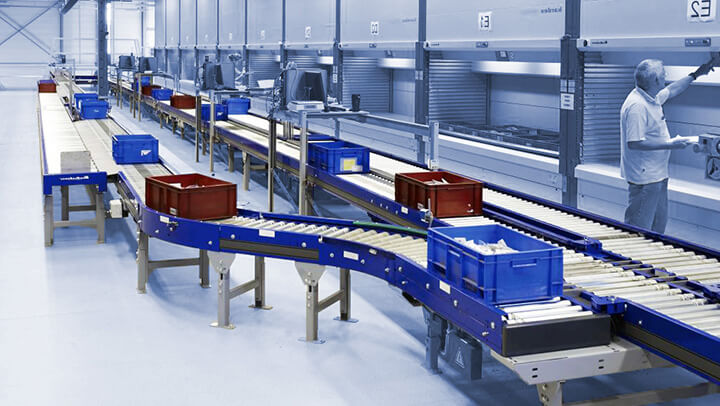

Illustrative image related to case conveyors
What Are the Advantages of Mild Steel for Case Conveyors?
Mild steel is a cost-effective option often used in non-corrosive environments. It offers good strength and is relatively easy to fabricate, making it a popular choice for general-purpose applications.
Pros: Its affordability and ease of manufacturing make mild steel an attractive option for budget-conscious projects. It can be coated or painted to enhance its corrosion resistance.
Cons: Mild steel is susceptible to rust and corrosion if not properly maintained, which can shorten its lifespan in humid or wet conditions.
Impact on Application: This material is best suited for dry environments or applications where cases are not exposed to moisture, such as packaging or warehousing.
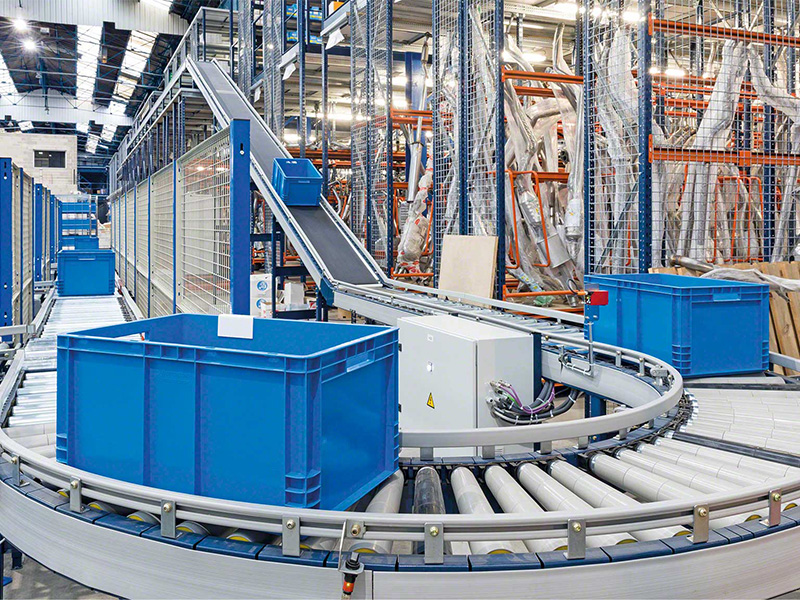

Illustrative image related to case conveyors
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding coatings and treatments, especially in humid climates prevalent in regions like South America and Africa.
How Does Aluminum Perform in Case Conveyor Applications?
Aluminum is lightweight and offers excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for a variety of applications, especially where weight is a concern.
Pros: Its lightweight nature allows for easier installation and reduced energy costs during operation. Aluminum is also highly resistant to corrosion, which extends its service life.
Cons: While durable, aluminum can be less robust than stainless steel and may not withstand heavy loads as effectively. Additionally, it can be more expensive than mild steel.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is ideal for applications requiring frequent mobility or where conveyor systems need to be reconfigured often.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the specific alloy used, as different grades of aluminum have varying strength and corrosion resistance, aligning with local standards such as JIS in Asia.
What Role Does Plastic Play in Case Conveyors?
Plastic is increasingly used in case conveyor systems, particularly in lighter-duty applications. It can be molded into various shapes, allowing for innovative designs.
Pros: Plastic is lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and can be produced in a variety of colors and shapes, enhancing branding opportunities. It is also generally less expensive than metal options.
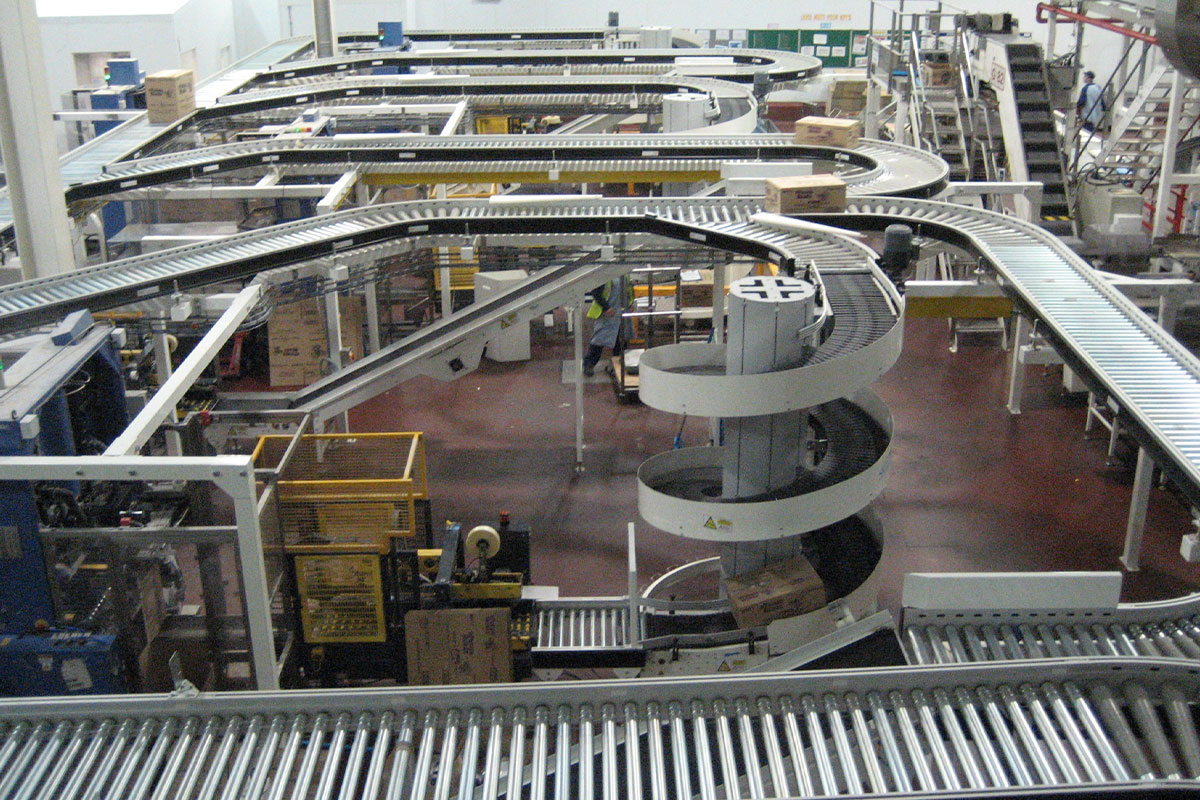

Illustrative image related to case conveyors
Cons: Plastic may not withstand heavy loads or extreme temperatures as well as metal materials. Its lifespan can be shorter in demanding environments.
Impact on Application: Plastic is suitable for light-duty applications, such as transporting lightweight cases or products that do not require high strength.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the plastic used meets local safety and environmental regulations, particularly in regions with strict compliance standards.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Case Conveyors
| Material | Typical Use Case for case conveyors | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | High durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Mild Steel | General-purpose applications | Cost-effective and easy to fabricate | Susceptible to rust without treatment | Low |
| Aluminum | Lightweight and mobile applications | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less robust under heavy loads | Medium |
| Plastic | Light-duty applications | Lightweight and customizable | Shorter lifespan and lower load capacity | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers looking to optimize their case conveyor systems, ensuring they choose the right material for their specific operational needs and compliance requirements.
Illustrative image related to case conveyors
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for case conveyors
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Case Conveyors?
The manufacturing process of case conveyors involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the necessary standards of quality and performance. Each stage contributes to the overall efficiency, durability, and reliability of the conveyor systems.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used?
The first stage in manufacturing case conveyors is material preparation. Manufacturers typically use high-quality materials such as stainless steel, mild steel, and various plastics, depending on the application and environment. Stainless steel is favored for its corrosion resistance, particularly in food and beverage industries, while mild steel is often used in dry environments.
During this phase, raw materials are sourced from reputable suppliers to ensure compliance with international standards. Manufacturers may conduct initial inspections to verify the material’s quality, checking for factors like thickness, finish, and overall integrity.
How Is the Forming Process Executed?
The forming stage involves transforming raw materials into specific shapes and components required for the conveyor system. Techniques such as cutting, bending, welding, and machining are commonly employed.
- Cutting: Precision cutting tools are used to achieve the desired dimensions for various parts, such as frames and conveyor belts.
- Bending and Welding: These processes create the structural components of the conveyor. Advanced welding techniques ensure strong joints, which are crucial for the longevity of the conveyor.
- Machining: This step fine-tunes components to exact specifications, ensuring that they fit together seamlessly.
By utilizing computer numerical control (CNC) machinery, manufacturers can achieve high precision and repeatability, which is essential for mass production.
What Does the Assembly Process Entail?
The assembly stage is where individual components come together to form the complete case conveyor system. This process typically involves the following steps:
- Component Assembly: Individual parts such as rollers, motors, and frames are assembled into a cohesive unit. Modular designs allow for flexibility and easy adjustments.
- Integration of Electrical Components: Electric motors and control systems are integrated to ensure the conveyor operates efficiently. This includes wiring and programming controls for automation.
- Quality Checks: During assembly, manufacturers conduct in-process quality control (IPQC) checks to ensure that each component meets specifications before moving forward.
This stage is crucial for minimizing errors and ensuring that the conveyor system will perform reliably in a production environment.
How Is the Finishing Process Conducted?
The finishing stage involves surface treatments and coatings that enhance the conveyor’s durability and aesthetic appeal. Common finishing techniques include:
- Painting and Coating: A protective layer is applied to prevent corrosion and wear, especially for conveyors used in harsh environments.
- Polishing: For stainless steel conveyors, polishing not only improves appearance but also reduces the potential for contamination in food handling applications.
Final inspections are conducted to ensure that the finish meets both aesthetic and functional requirements before the product is packaged for shipment.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Implemented in Case Conveyor Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process of case conveyors. It ensures that products meet international standards and customer specifications.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Quality Control?
Manufacturers typically adhere to various international standards to ensure quality. ISO 9001 is the most widely recognized quality management standard, focusing on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Compliance with ISO standards demonstrates a commitment to quality and operational excellence.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for European markets and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for oil and gas applications may be required, depending on the application.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This is the first line of defense, where raw materials and components are inspected for quality before they enter the production process.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during the manufacturing stages ensure that all processes comply with specified standards. This includes monitoring assembly and integration.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the conveyor is fully assembled, a final inspection is performed to verify that it meets all specifications and performance requirements.
These checkpoints help identify and rectify any issues before the product reaches the customer.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Assurance?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality assurance practices of their suppliers. Here are several methods:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers allows buyers to assess their compliance with quality standards and practices.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask for detailed quality assurance reports, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC checks.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes.
Buyers from international markets, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must also consider cultural and regulatory differences that may affect quality assurance practices.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers should be aware of specific nuances in quality control that may impact their procurement processes. These include:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have specific regulatory requirements. For example, the European Union has stringent regulations regarding machinery safety, which may not be applicable in other regions.
- Cultural Differences: Understanding the local manufacturing culture and practices can help buyers set realistic expectations regarding quality and delivery.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Variability: The complexity of international shipping may affect product quality due to handling and transportation conditions. Buyers should consider this when negotiating terms and conditions with suppliers.
By understanding these factors, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions and establish fruitful partnerships with case conveyor manufacturers.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘case conveyors’
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing and logistics environments, sourcing the right case conveyor system is crucial for optimizing efficiency and reducing operational costs. This practical checklist serves as a step-by-step guide for B2B buyers to navigate the procurement process effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clearly outline the technical specifications required for your case conveyor. This includes load capacity, conveyor speed, and dimensions. Understanding these specifications ensures you select a conveyor system that meets your operational needs while maximizing efficiency.
- Load Capacity: Consider the weight and volume of the cases to be transported.
- Conveyor Speed: Assess the required throughput to maintain production efficiency.
Step 2: Research Different Types of Case Conveyors
Familiarize yourself with the various types of case conveyors available in the market, such as motor-driven roller (MDR) systems, gravity conveyors, and belt conveyors. Each type has unique benefits and suitability depending on your operational requirements.
- MDR Systems: Known for low maintenance and flexibility, ideal for automated environments.
- Gravity Conveyors: Cost-effective solutions for lighter loads with minimal moving parts.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers to ensure reliability and quality. Request information about their experience, case studies, and references from clients in similar industries or regions.
- Company Profile: Verify their history and expertise in manufacturing case conveyors.
- Customer Testimonials: Look for feedback from existing clients to gauge satisfaction levels.
Step 4: Assess Customization Options
Determine whether the supplier can provide customization based on your specific operational needs. A modular design allows for easy adjustments and scalability as your business grows.
- Design Flexibility: Ensure the supplier can adapt the conveyor to fit unique layouts and product types.
- Modular Components: Check if they offer interchangeable parts for future upgrades.
Step 5: Inquire About Maintenance and Support
Understand the maintenance requirements and support services offered by the supplier. This is critical to minimize downtime and ensure long-term operational efficiency.
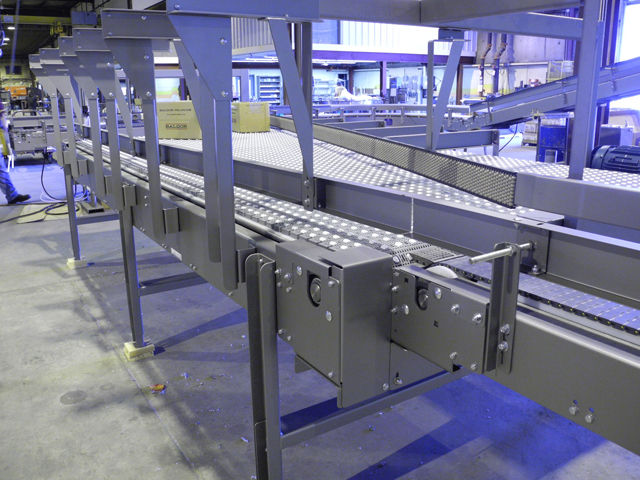

Illustrative image related to case conveyors
- Maintenance Plans: Look for warranties and service agreements that include regular inspections.
- Technical Support: Confirm availability of technical assistance and training for your staff.
Step 6: Request Quotes and Compare Costs
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotes for your desired conveyor systems. Comparing costs will help you understand the market rates and ensure you receive a competitive offer.
- Cost Breakdown: Examine the quotes for transparency on pricing, including installation and shipping.
- Total Cost of Ownership: Consider long-term costs, including maintenance and energy consumption.
Step 7: Finalize the Contract and Review Terms
After selecting a supplier, carefully review the contract terms before finalizing the purchase. Ensure that all agreed-upon specifications, delivery timelines, and warranty details are documented.
- Payment Terms: Clarify payment schedules and any potential penalties for delays.
- Delivery and Installation: Confirm timelines for delivery and installation to align with your operational schedule.
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing case conveyors, ensuring a smooth procurement process that meets their operational requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for case conveyors Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Case Conveyor Sourcing?
When sourcing case conveyors, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and decision-making. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials, such as stainless steel versus painted mild steel, significantly impacts the overall cost. Stainless steel options often come at a premium due to their durability and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for harsh environments.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can be influenced by the complexity of the conveyor system. Skilled labor is necessary for installation, programming, and maintenance, which adds to the overall expense.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, including facility costs, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these costs.
-
Tooling: Specialized tooling may be required for the production of custom components. This initial investment can increase costs but is often necessary for tailored solutions.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the conveyors meet specified standards incurs additional costs. Implementing rigorous QC processes is crucial for maintaining reliability and performance, especially for systems subjected to heavy use.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs vary based on the distance and mode of transport. International buyers should consider potential tariffs, duties, and shipping insurance when calculating total logistics costs.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can fluctuate based on their market position, brand reputation, and the level of customization offered. Understanding these factors can aid buyers in negotiating better prices.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Case Conveyor Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of case conveyors:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher order volumes typically lead to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk purchases, making it advantageous for businesses with significant needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Tailored solutions that meet specific operational requirements often come at a higher price. Buyers should weigh the necessity of customization against potential cost increases.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials directly impacts durability and performance. Additionally, conveyors that meet specific quality certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) may command higher prices due to the assurance of quality.
-
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers with a track record of reliability may charge a premium. However, this can be justified by the reduced risk of operational downtime and maintenance issues.
-
Incoterms: The shipping terms negotiated with suppliers can also affect pricing. Different Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) can lead to variations in the total cost based on who bears the shipping responsibilities.
What Are Effective Negotiation and Cost-Efficiency Strategies for Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiate Terms: Always negotiate not just on price but also on payment terms, delivery schedules, and warranty conditions. Suppliers may be more flexible than initially presented.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also maintenance costs, energy consumption, and potential downtime. This holistic view can lead to better long-term investment decisions.
-
Leverage Local Partnerships: Building relationships with local suppliers or distributors can reduce logistics costs and lead to better service and support. This is particularly relevant in regions where infrastructure may pose challenges.
-
Research Market Rates: Understanding the market rates for case conveyors and having comparative quotes can strengthen your negotiating position. This is crucial for ensuring you receive a fair price.
-
Monitor Pricing Trends: Keep an eye on market trends and emerging technologies that could impact costs. Staying informed allows you to make timely decisions and capitalize on favorable pricing conditions.
Conclusion: What Should Buyers Keep in Mind?
While indicative prices for case conveyors can vary widely based on the factors discussed, it is essential for buyers to conduct thorough research and engage in careful planning. By understanding the cost components, price influencers, and effective negotiation strategies, businesses can optimize their sourcing process and achieve the best value for their investment.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing case conveyors With Other Solutions
When considering the best solution for transporting packaged goods, businesses often evaluate a variety of options. Case conveyors are a popular choice, but it’s essential to explore alternative technologies that may suit specific operational needs. This analysis will compare case conveyors with two viable alternatives: Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and Gravity Conveyors.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Case Conveyors | Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) | Gravity Conveyors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High throughput; suitable for large volumes | Flexible routing; good for varied layouts | Simple, effective for light loads |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; lower total cost of ownership | Higher upfront costs; operational savings over time | Low cost; inexpensive materials |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires planning and installation | Complex setup; may need extensive mapping | Quick to install; minimal training required |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance with modular components | Requires regular battery and software maintenance | Minimal maintenance; simple mechanics |
| Best Use Case | High volume, continuous flow applications | Dynamic environments needing flexibility | Low to moderate volume, short distances |
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)?
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) offer a flexible and adaptive transportation solution. They can navigate through a facility without fixed paths, which allows for easy adjustments to layouts as needs change. AGVs are particularly beneficial in environments that require dynamic routing, such as warehouses with fluctuating inventory levels. However, they come with higher upfront costs and necessitate a more complex setup, including mapping and software integration. Additionally, ongoing maintenance is required to ensure battery performance and software updates, which can add to operational costs.
How Do Gravity Conveyors Compare in Terms of Efficiency and Cost?
Gravity conveyors are a cost-effective solution for transporting lighter loads over short distances. They operate without power, relying on the force of gravity, which minimizes energy costs and simplifies maintenance. These systems are particularly suitable for low to moderate volume applications and are quick to install, making them ideal for temporary setups or businesses with limited space. However, gravity conveyors may not provide the same level of throughput and efficiency as powered systems like case conveyors or AGVs, limiting their effectiveness in high-demand environments.
Illustrative image related to case conveyors
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Business Needs?
Selecting the right transportation solution for your operations depends on various factors, including volume, layout flexibility, and budget constraints. Case conveyors excel in high-volume scenarios where continuous flow is essential, while AGVs provide adaptability in dynamic environments at a higher cost. Gravity conveyors serve as an economical choice for lighter loads and shorter distances but may not meet the demands of larger operations. By carefully assessing these factors and aligning them with your business goals, you can make an informed decision that enhances productivity and efficiency in your supply chain.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for case conveyors
What Are the Critical Technical Properties of Case Conveyors?
When selecting case conveyors, understanding the technical properties is essential for ensuring optimal performance and reliability. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material used in case conveyors often includes stainless steel or mild steel. Stainless steel is preferred for its corrosion resistance, making it ideal for food or chemical handling. Mild steel, while less resistant to corrosion, can be more economical for dry applications. The choice of material affects durability, maintenance needs, and overall lifespan, which are crucial for businesses aiming for long-term efficiency.
2. Load Capacity
This specification indicates the maximum weight a conveyor can handle safely. Knowing the load capacity is vital for ensuring that the conveyor system can support the volume and weight of the cases being transported. Underestimating load capacity can lead to system failures, increased maintenance costs, and reduced operational efficiency.
3. Conveyor Speed
Measured in feet per minute (CFPM), conveyor speed determines how quickly products can be moved from one point to another. This factor is crucial for optimizing throughput in high-volume operations. Selecting the right speed can enhance productivity and reduce bottlenecks in the packaging or distribution process.
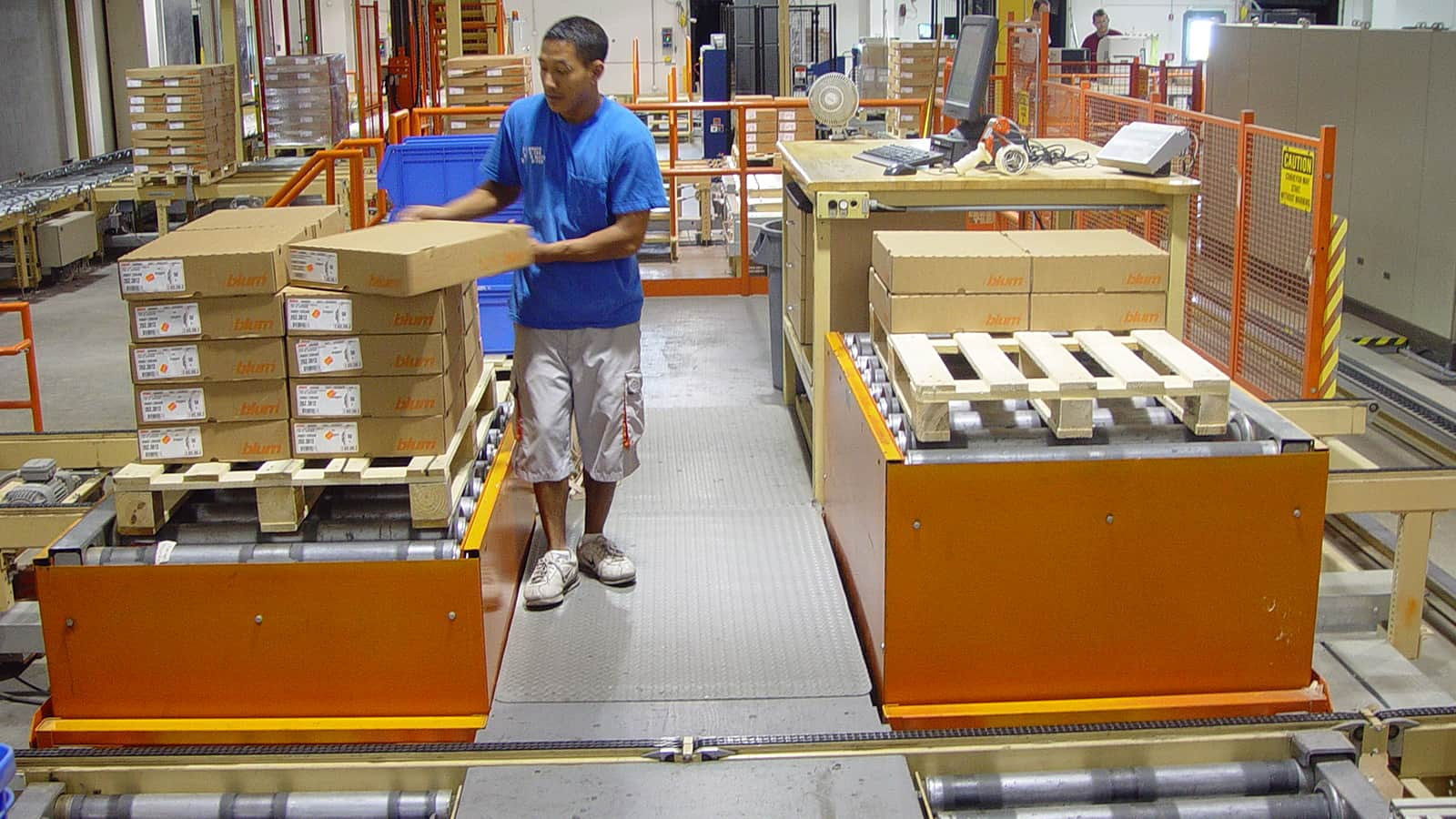

Illustrative image related to case conveyors
4. Accumulation Logic
Accumulation systems are designed to manage the flow of cases without causing back pressure. Understanding the accumulation logic is essential for maintaining workflow efficiency, especially in environments where products need to be queued before processing or shipping. Proper accumulation management can significantly reduce the risk of damage to products.
5. Frame Configuration
The frame configuration refers to the design and structure of the conveyor system. Options include straight, curved, incline, or decline designs. The right frame configuration can optimize space utilization and workflow, ensuring seamless integration into existing operations.
6. Drive Location
This specification refers to the positioning of the conveyor’s drive mechanism. Drives can be located at various points (e.g., end drives, center drives), affecting the overall layout and functionality of the conveyor system. Understanding drive location is critical for effective system design and can impact maintenance and operational efficiency.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Case Conveyor Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B marketplace. Here are some common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces components or systems that are used in another company’s end product. For case conveyors, working with OEMs can ensure that you receive high-quality parts that meet specific performance standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is important for budgeting and inventory management, particularly for smaller businesses that may not require large quantities of conveyors at once.
3. RFQ (Request for Quote)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. Crafting a detailed RFQ can help buyers obtain competitive pricing and better understand the offerings of different suppliers.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping costs, risk transfer, and delivery points. Familiarity with these terms is essential for international buyers to avoid misunderstandings and disputes.
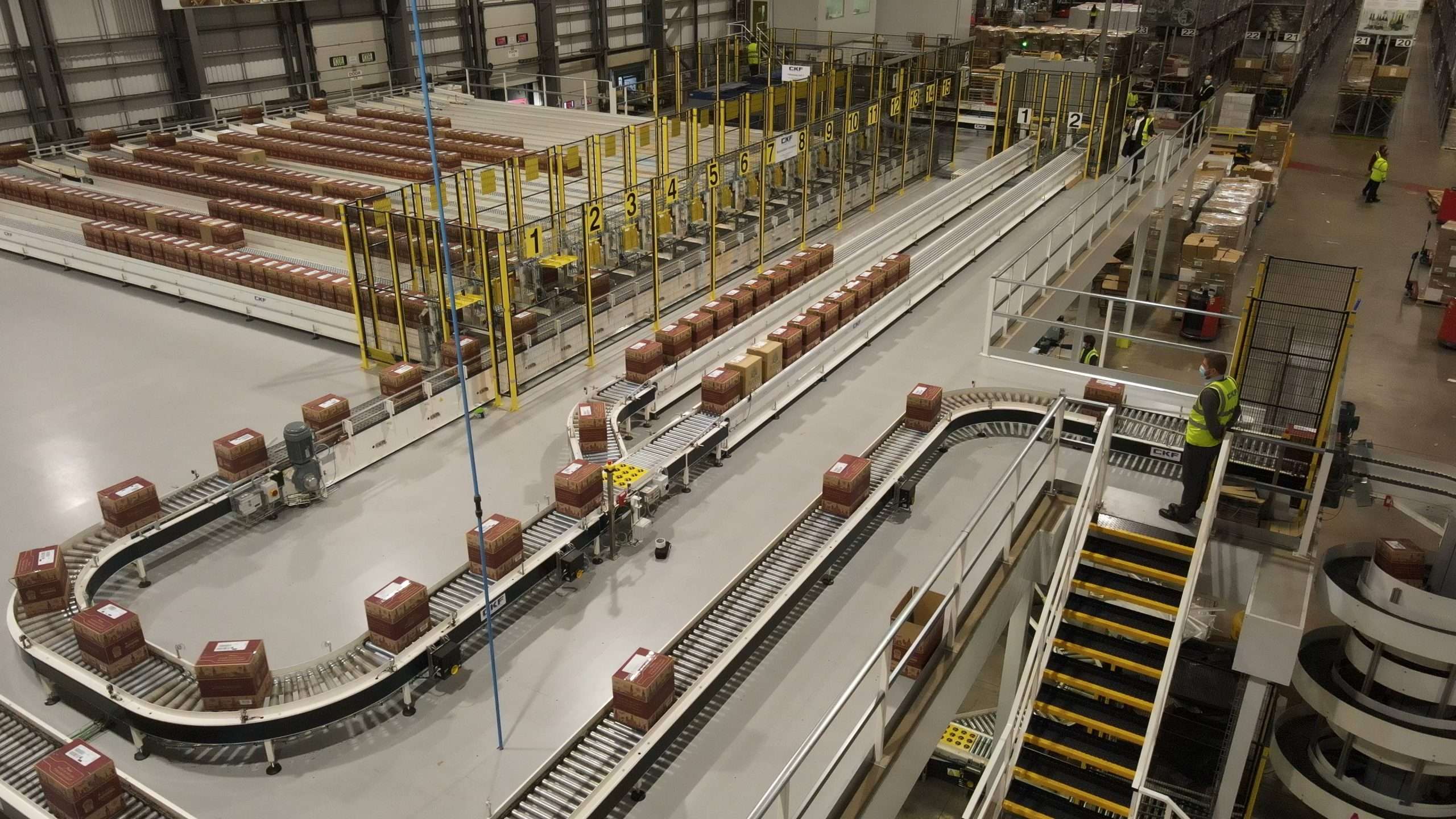

Illustrative image related to case conveyors
5. Throughput
Throughput is a measure of how much product is processed in a given period. This metric is vital for assessing the efficiency of a case conveyor system and can influence decisions about system upgrades or expansions.
6. Zoned Accumulation
This term refers to a system where products are accumulated in designated zones without back pressure. Zoned accumulation is beneficial for maintaining product integrity and optimizing workflow, particularly in high-volume environments.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions regarding case conveyor systems, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the case conveyors Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Case Conveyors Sector?
The global case conveyors market is witnessing significant transformation driven by technological advancements, increased automation, and changing consumer demands. International B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly looking for efficient solutions to enhance their supply chain operations. Key trends include the adoption of Motor Driven Roller (MDR) systems, which offer low maintenance and flexibility to adapt to changing production requirements. Moreover, the integration of IoT and AI technologies is facilitating real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, further optimizing operational efficiency.
Another notable trend is the growing demand for customized solutions tailored to specific industry needs, such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods. This is particularly relevant for buyers in emerging markets, where the emphasis is on cost-effective yet robust systems that can handle diverse product types. As the global logistics landscape continues to evolve, there is a notable shift towards integrating case conveyors with other automated systems, enhancing overall productivity and reducing manual labor.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Trends in the Case Conveyors Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in the sourcing decisions of international B2B buyers. The environmental impact of conveyor systems, particularly in terms of energy consumption and material waste, is prompting companies to seek greener alternatives. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate commitment to sustainability through the use of eco-friendly materials, such as stainless steel and recyclable components.
Moreover, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are now looking for partners who are transparent about their sourcing practices and adhere to fair labor standards. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and LEED for sustainable building are gaining traction, as they provide assurances of a supplier’s dedication to reducing their ecological footprint. By aligning with these sustainability goals, companies not only improve their operational efficiency but also enhance their brand reputation in a competitive marketplace.
How Has the Case Conveyors Sector Evolved Over Time?
The case conveyors sector has evolved significantly since its inception, adapting to the changing demands of the manufacturing and logistics industries. Initially, conveyors were primarily mechanical systems with limited functionality, focusing solely on transportation. However, advancements in technology have transformed case conveyors into sophisticated systems capable of performing various functions, including accumulation, sorting, and inspection.
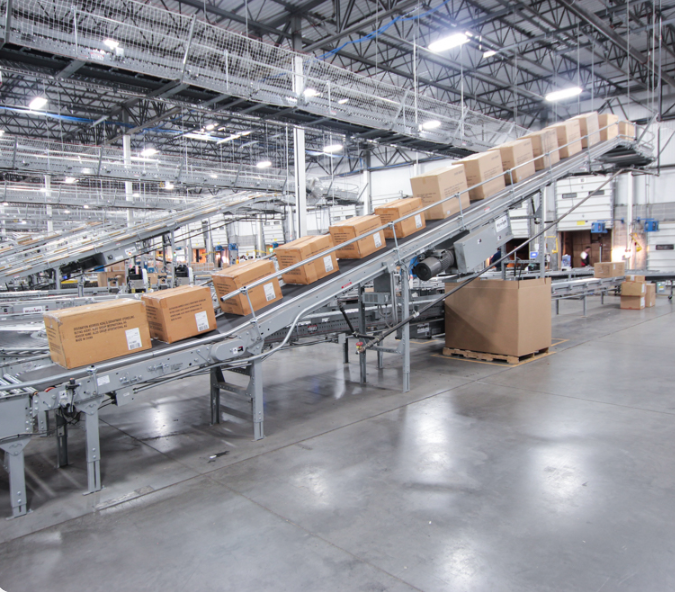

Illustrative image related to case conveyors
The introduction of modular designs has allowed for greater flexibility and scalability, making it easier for businesses to adapt their systems as their needs change. Furthermore, the rise of automation and smart technologies has shifted the focus towards integrated solutions that enhance productivity and reduce labor costs. As international markets continue to expand, the evolution of case conveyors reflects a broader trend towards efficiency, sustainability, and customization in manufacturing processes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of case conveyors
-
How do I select the right case conveyor for my production needs?
Choosing the right case conveyor requires understanding your specific operational requirements. Consider factors such as load capacity, conveyor speed, and the types of products being transported. Evaluate whether you need features like accumulation, sorting, or merging capabilities. Consulting with a supplier’s engineering team can help tailor a solution that meets your production demands while ensuring compatibility with existing systems. -
What are the advantages of using motor-driven roller (MDR) case conveyors?
MDR case conveyors offer numerous benefits, including reduced noise levels and lower maintenance costs due to the absence of pneumatic components. Their modular design allows for flexibility in configurations, making them suitable for various applications. Additionally, MDR systems provide zero back pressure handling, which minimizes product damage and improves operational efficiency by ensuring smooth product flow without bottlenecks. -
What customization options are available for case conveyors?
Most manufacturers offer extensive customization options, including variations in frame materials (such as stainless steel or painted mild steel), lengths, widths, and conveyor bed types (roller, belt, or chain). You can also specify features like incline/decline transitions, end drives, and automated sorting mechanisms. Discussing your unique requirements with the supplier will help ensure the conveyor meets your specific operational needs. -
What is the typical lead time for ordering case conveyors?
Lead times can vary significantly based on the complexity of the project and the manufacturer’s production schedule. Standard models may be available for quicker delivery, often within a few weeks, while customized solutions can take several months. It’s advisable to communicate your timeline with potential suppliers early in the negotiation process to align expectations and avoid operational delays. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for case conveyors?
Minimum order quantities can differ by supplier and are often influenced by the type of conveyor system being purchased. While some manufacturers may allow single-unit orders for standard models, others may require larger quantities for customized solutions. Understanding the MOQ is critical for budget planning and ensuring that your procurement strategy aligns with your operational scale. -
How should I evaluate suppliers for case conveyors?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry experience, reputation, and customer reviews. Request case studies or references from similar projects to gauge their capability. Additionally, assess their engineering expertise and support services, including installation and maintenance. A supplier that offers comprehensive service can significantly enhance the overall value of your investment. -
What payment terms are typically offered for international B2B purchases of case conveyors?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers. Common practices include upfront deposits, payment upon delivery, or payment terms extending up to 30, 60, or 90 days after delivery. Always clarify the payment structure in your contract and consider discussing options like letters of credit for larger transactions to mitigate financial risks during international trade. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) in my case conveyor purchase?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed specifications and certifications related to the materials and components used in the conveyor system. Inquire about the supplier’s QA processes, including testing procedures and compliance with international standards. Consider arranging for factory acceptance testing (FAT) to verify that the equipment meets your requirements before shipment, which can help prevent issues during installation and operation.
Top 5 Case Conveyors Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Norpak – Case Conveyor Systems
Domain: norpak.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Case conveyor systems are designed to move cases of products within facilities, offering an economical solution for high-volume transportation. They come in various sizes, shapes, and configurations, allowing businesses to customize their systems. Key benefits include reduced forklift traffic, decreased manual labor, and the ability to integrate automation features like automatic sorting and mergi…
2. NCCAS – Case Handling Conveyors
Domain: nccas.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Case handling conveyors are specialized systems designed for the efficient and automated movement of unitized products such as boxes and totes. Types of case handling conveyors include belt driven, lineshaft driven, and powered roller systems. The selection of drive style is based on the specific application. Case conveyors can be used for straight transportation and include both non-sanitary and …
3. Intralox – Key Products for Case Package Handling
Domain: intralox.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Key products for case package handling from Intralox include: 1. Modular Plastic Belting: A versatile belting solution that supports various conveyor systems. 2. ThermoDrive Belting: Designed for high-performance applications. 3. AIM Equipment: Active Integrated Motion equipment for gentle product handling, increasing throughput and reducing labor costs. 4. ARB Equipment: Activated Roller Belt tec…
4. Dynamic Conveyor – Case Turning Conveyors
Domain: dynamicconveyor.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Case turning conveyors ensure a complete package or case turn every time, even if stopped and restarted mid-cycle. They come with a 5-year warranty and can be custom designed. Key benefits include precision handling for seamless product orientation, optimized workflow efficiency by rotating cases 90° or 180° on the fly, consistent product orientation minimizing jams, and customizable options like …
5. Scott Automation – Case Conveyors
Domain: scottautomation.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Scott offers a vast range of case conveyors for unit loads designed for horizontal and/or inclined transport. The types of conveyors include belt, slat chain, modular belt, and roller conveyors, tailored to specific product requirements. Key features include:
– Horizontal transport capabilities for long-distance conveying and product accumulation in demanding environments (e.g., freezing, dust).
-…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for case conveyors
Why is Strategic Sourcing Crucial for Case Conveyors?
In the competitive landscape of global supply chains, strategic sourcing of case conveyors is pivotal for optimizing operational efficiency and reducing costs. By leveraging partnerships with reliable manufacturers, international buyers can ensure access to high-quality, customizable solutions tailored to their specific operational needs. The modular design and advanced technology of modern case conveyors offer flexibility and scalability, enabling businesses to adapt quickly to changing market demands.
How Can B2B Buyers Leverage Technological Advancements?
Investing in state-of-the-art case conveyor systems, such as Motor Driven Roller (MDR) technologies, can significantly enhance productivity while minimizing maintenance costs. The shift towards electrification and automation not only streamlines operations but also reduces reliance on manual labor, paving the way for a more efficient workforce. Furthermore, features such as zero back pressure and seamless integration with other technologies can transform logistics and warehousing processes.
Illustrative image related to case conveyors
What’s Next for International Buyers in Emerging Markets?
As the demand for efficient material handling solutions continues to grow in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, B2B buyers are encouraged to explore innovative sourcing strategies. Collaborating with manufacturers who provide comprehensive support—from design to installation—will be essential for achieving long-term success. By proactively seeking out cutting-edge solutions, buyers can position themselves at the forefront of industry advancements, ensuring a competitive edge in the marketplace. Consider initiating discussions with potential suppliers today to explore how modern case conveyor systems can elevate your operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.