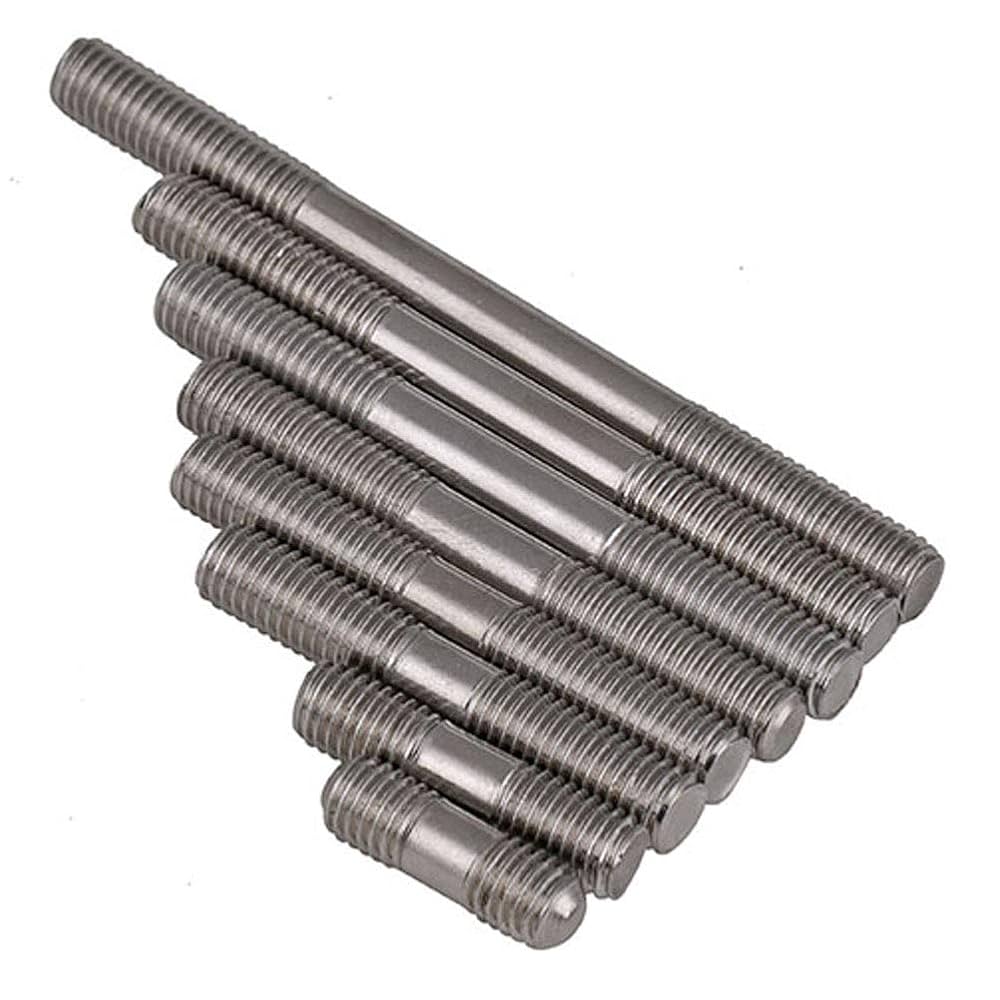
Bolt With Threads On Both Ends: The Ultimate B2B Sourcing Guide for Global Buyer
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for bolt with threads on both ends
In the ever-evolving landscape of global manufacturing and construction, sourcing reliable bolts with threads on both ends presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. These specialized fasteners, known for their strength and versatility, play a crucial role in various applications, from heavy machinery to structural engineering. However, the complexity of selecting the right type, understanding material specifications, and navigating supplier options can be daunting, especially for businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including regions like Saudi Arabia and Brazil.
This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the intricacies of sourcing double-threaded bolts, offering valuable insights into the different types available, their applications across industries, and essential criteria for vetting suppliers. We will explore the nuances of cost considerations, quality standards, and the importance of material selection to ensure that you make informed purchasing decisions. By equipping international buyers with the knowledge needed to navigate this specialized market, this guide empowers you to enhance operational efficiency and drive project success. Whether you are looking to procure standard sizes or custom-manufactured solutions, understanding the global market dynamics will be key to your sourcing strategy.
Understanding bolt with threads on both ends Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fully Threaded Stud | Threaded from end to end, no head, high tensile strength | Flange bolting, structural reinforcement | Pros: High strength, versatile; Cons: Requires two nuts, may be overkill for lighter applications. |
| Tap-End Stud | Short thread on one end for tapping, longer thread on other end | Machinery assembly, HVAC installations | Pros: Easy installation; Cons: Limited to specific applications, not suitable for all structures. |
| Double-End Stud | Equal or unequal length threads on both ends, chamfered points | Flange bolting, pipe connections | Pros: Versatile for various applications; Cons: May require precise measurements for effective use. |
| Hanger Bolt | One end threaded for wood, other end for metal | Furniture assembly, construction projects | Pros: Dual functionality; Cons: Limited load-bearing capacity compared to other types. |
| Double-Ended Bolt | Fully threaded with a smooth section between threads | Heavy machinery, automotive applications | Pros: Strong and reliable; Cons: Can be more expensive due to manufacturing complexity. |
What are the characteristics and suitability of fully threaded studs for B2B buyers?
Fully threaded studs are characterized by their continuous threading from one end to the other, offering no head. This design allows for a higher tensile strength compared to standard bolts, making them ideal for applications requiring significant load-bearing capabilities. They are predominantly used in flange bolting and structural reinforcement across various industries, including manufacturing and construction. When considering these studs, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific load requirements and installation conditions, as they typically necessitate the use of two nuts.
How do tap-end studs differ and what are their primary applications?
Tap-end studs feature a short thread on one end, designed for insertion into a tapped hole, while the other end is longer and fully threaded. This design makes them particularly suitable for machinery assembly and HVAC installations where precise fitting is essential. Buyers should consider the compatibility of tap-end studs with their existing components and the ease of installation, as these studs simplify the connection process but may not be suitable for all applications.
In what scenarios are double-end studs most effective for B2B applications?
Double-end studs have threads on both ends, which can be of equal or unequal length, and typically come with chamfered points. They are commonly used in flange bolting and pipe connections, providing versatility in various assembly contexts. B2B buyers should assess the specific requirements of their projects, including the need for precise length and thread specifications, to ensure optimal performance and reliability in their applications.
What advantages do hanger bolts offer for construction projects?
Hanger bolts have one end designed for wood applications, while the other end is threaded for metal. This dual functionality makes them particularly valuable in furniture assembly and construction projects where different materials must be connected. However, buyers should be aware of their limited load-bearing capacity compared to other bolt types, making them suitable primarily for lighter applications.
Why consider double-ended bolts for heavy machinery and automotive uses?
Double-ended bolts are fully threaded with a smooth section in the middle, providing a robust fastening solution for heavy machinery and automotive applications. Their strength and reliability make them a preferred choice in demanding environments. Buyers should consider the potential higher costs associated with these bolts due to their complex manufacturing process, balanced against their performance benefits in critical applications.
Key Industrial Applications of bolt with threads on both ends
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of bolt with threads on both ends | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Used in machinery assembly for securing parts together | Enhances structural integrity and reduces maintenance costs | Ensure compliance with industry standards and specifications |
| Construction | Employed in structural frameworks and scaffolding systems | Provides reliable support and safety for construction sites | Look for corrosion-resistant materials suitable for outdoor use |
| Oil and Gas | Utilized in flanged connections for pipelines and valves | Ensures leak-proof connections in high-pressure environments | Consider high-temperature and high-pressure ratings |
| Automotive | Applied in engine and chassis assembly | Increases durability and performance of vehicles | Verify compatibility with specific vehicle models and materials |
| Plumbing | Used in piping systems to connect various plumbing fixtures | Guarantees tight seals and prevents leaks | Source materials that meet plumbing codes and standards |
How Are Bolts with Threads on Both Ends Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, bolts with threads on both ends are critical for assembling complex machinery. These bolts provide a robust connection between components, enhancing the structural integrity of machines. By using threaded bolts, manufacturers can reduce downtime caused by maintenance and repairs, as these fasteners are designed to withstand significant stress. For international buyers, sourcing bolts that comply with specific industry standards is essential to ensure quality and performance, particularly in regions with varying regulations.
What Role Do Double-Ended Bolts Play in Construction?
In construction, double-ended bolts are frequently used to secure structural frameworks and scaffolding systems. Their design allows for easy installation and removal, making them ideal for temporary and permanent structures alike. The ability to withstand heavy loads while providing a secure hold is crucial for safety on construction sites. Buyers should prioritize corrosion-resistant materials, especially in regions with harsh environmental conditions, to maintain the longevity and safety of their constructions.

Illustrative image related to bolt with threads on both ends
Why Are These Bolts Essential in the Oil and Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas sector, bolts with threads on both ends are essential for creating flanged connections in pipelines and valves. They ensure leak-proof seals under high pressure, which is critical for operational safety and environmental protection. Buyers in this industry must consider the specific requirements for high-temperature and high-pressure applications, ensuring that the sourced bolts meet the necessary ASTM standards for reliability and performance.
How Are Double-Ended Bolts Used in Automotive Applications?
In the automotive industry, double-ended bolts are widely used in engine and chassis assembly. Their ability to provide a strong, durable connection contributes to the overall performance and longevity of vehicles. For B2B buyers in this sector, it’s vital to verify compatibility with specific vehicle models and to select materials that can withstand the rigors of automotive environments, including exposure to heat and chemicals.
What Are the Benefits of Using These Bolts in Plumbing Systems?
In plumbing applications, bolts with threads on both ends are used to connect various fixtures, ensuring tight seals that prevent leaks. This is particularly important in residential and commercial plumbing systems, where water integrity is paramount. Buyers should focus on sourcing materials that comply with local plumbing codes and standards to guarantee safety and reliability, especially in regions where water quality and pressure vary significantly.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘bolt with threads on both ends’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing Quality Double-Ended Bolts for Critical Applications
The Problem: In industries like manufacturing and construction, the integrity of fasteners is paramount. B2B buyers often struggle with sourcing double-ended bolts that meet specific material and strength requirements for critical applications. Subpar quality can lead to structural failures, safety hazards, and costly project delays. Furthermore, different regions have varying standards and regulations, complicating the procurement process. Buyers may find themselves overwhelmed by inconsistent product specifications, leading to the risk of choosing the wrong fasteners.
The Solution: To ensure the procurement of high-quality double-ended bolts, buyers should first identify their specific needs, including load requirements, environmental conditions, and applicable standards (like ASTM A193 for high-pressure applications). Engaging with reputable suppliers who specialize in fasteners is crucial. These suppliers often provide detailed product specifications, including material grades and tensile strength ratings. Buyers should request samples or prototypes to test for compatibility with their applications before placing bulk orders. Additionally, establishing long-term partnerships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and customized solutions tailored to unique project requirements.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Proper Installation of Double-Ended Studs
The Problem: Even when the right double-ended bolts are sourced, improper installation can lead to performance issues or failures. B2B buyers often face challenges during the installation phase, particularly if their teams lack the necessary training or if installation guidelines are unclear. Misalignment, over-tightening, or inadequate securing can compromise the effectiveness of the fastener, leading to costly rework and potential safety risks.
The Solution: To address installation challenges, organizations should invest in comprehensive training for their technical teams. This includes understanding the specific requirements for double-ended bolts, such as the correct torque specifications and the appropriate use of nuts and washers. Providing clear, visual installation guides or manuals can also help mitigate errors. Additionally, incorporating technology such as torque wrenches with digital readouts can assist in achieving the precise tightness needed for each application. Regular audits of installation practices can further ensure that teams adhere to best practices and maintain safety standards.
Scenario 3: Managing Inventory and Lead Times for Double-Ended Bolts
The Problem: Fluctuating demand and varying project timelines can make inventory management a significant pain point for B2B buyers of double-ended bolts. Maintaining an optimal stock level is essential to avoid delays in production while also minimizing excess inventory costs. Buyers may experience long lead times from suppliers, which can disrupt project schedules, especially if they require custom sizes or materials.
The Solution: To enhance inventory management, buyers should implement a just-in-time (JIT) inventory system that aligns stock levels with project schedules. Collaborating closely with suppliers to establish reliable lead times is critical; this may include negotiating terms for expedited shipping or setting up consignment inventory agreements where suppliers manage stock on-site. Additionally, utilizing inventory management software can help track usage patterns and predict future needs based on historical data, allowing for proactive ordering. Maintaining an ongoing dialogue with suppliers about upcoming projects can also help ensure that they are prepared to meet demand without excessive lead times.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for bolt with threads on both ends
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials for Bolts with Threads on Both Ends?
When selecting materials for bolts with threads on both ends, it is crucial to consider their mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and temperature/pressure ratings. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of these fasteners.

Illustrative image related to bolt with threads on both ends
1. Carbon Steel
Key Properties:
Carbon steel bolts are known for their high tensile strength and hardness. They can withstand high pressure and are suitable for applications involving significant mechanical stress. However, they are less resistant to corrosion unless treated.
Pros & Cons:
Carbon steel is relatively inexpensive and widely available, making it a cost-effective choice for many applications. However, its susceptibility to rust and corrosion can limit its use in environments exposed to moisture or corrosive substances.
Impact on Application:
Carbon steel bolts are ideal for construction and manufacturing environments where strength is paramount, but they may not be suitable for marine or chemical applications without protective coatings.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A307 for carbon steel bolts. In regions with high humidity, like parts of South America and the Middle East, protective coatings or alternative materials may be necessary.
2. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel bolts offer excellent corrosion resistance due to their chromium content, which forms a protective oxide layer. They can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for a variety of applications.
Pros & Cons:
While stainless steel is more expensive than carbon steel, its durability and resistance to corrosion justify the higher cost for many applications. However, it is more challenging to machine and may require specialized tools for manufacturing.
Impact on Application:
These bolts are particularly well-suited for applications in the food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries, where hygiene and resistance to corrosion are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with standards such as ASTM A193 for high-pressure applications is crucial. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East should also consider the specific grades of stainless steel, such as 304 or 316, based on their environmental conditions.
3. Alloy Steel
Key Properties:
Alloy steel bolts are engineered for enhanced mechanical properties, including increased tensile strength and toughness. They can be treated to improve hardness and wear resistance, making them suitable for demanding applications.
Pros & Cons:
These bolts can handle extreme conditions and are often used in heavy machinery and automotive applications. However, they tend to be more expensive and may require complex manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application:
Alloy steel bolts are ideal for high-stress applications, such as in the oil and gas industry, where both strength and resistance to wear are essential.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should verify compliance with standards like ASTM A325 for structural applications. In regions with varying quality control standards, such as Africa and South America, sourcing from reputable manufacturers is essential.
4. Titanium
Key Properties:
Titanium bolts are known for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and outstanding corrosion resistance, even in harsh environments. They can withstand high temperatures and are non-magnetic.
Pros & Cons:
While titanium bolts are lightweight and highly durable, they are significantly more expensive than other materials. Their manufacturing processes are also more complex, which can lead to longer lead times.
Impact on Application:
These bolts are ideal for aerospace and marine applications, where weight savings and corrosion resistance are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with aerospace standards, such as ASTM B348, is vital for buyers in the aerospace sector. In regions like the Middle East, where high-performance materials are often required, titanium bolts can be a preferred choice despite their cost.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Bolts with Threads on Both Ends
| Material | Typical Use Case for bolt with threads on both ends | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Construction, manufacturing | Cost-effective, high tensile strength | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food, pharmaceutical, chemical industries | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, complex machining | High |
| Alloy Steel | Oil and gas, heavy machinery | Enhanced strength and toughness | More expensive, complex manufacturing | Med |
| Titanium | Aerospace, marine applications | Lightweight, outstanding corrosion resistance | Very high cost, complex manufacturing | High |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for bolt with threads on both ends
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Double-Threaded Bolts?
The manufacturing of double-threaded bolts involves several critical stages to ensure high quality and performance. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Double-Threaded Bolts?
The process begins with the selection of high-quality raw materials, typically steel or alloy steel, which are chosen for their tensile strength and durability. The material is often subjected to heat treatment to enhance its mechanical properties. This preparation stage includes cutting the raw material into lengths suitable for the desired bolt specifications.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Double-Threaded Bolts?
Forming is a pivotal stage where the prepared material is shaped into the desired bolt configuration. Techniques such as forging, machining, and rolling are commonly employed.
-
Forging: This process involves shaping the metal while it is hot, allowing for greater strength and a refined grain structure, which results in a more durable bolt.
-
Machining: After forging, the bolts undergo precision machining to create the threads. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are often used to ensure accuracy and consistency in thread dimensions.
-
Rolling: Thread rolling is a cold-forming process that creates threads without removing material, enhancing the bolt’s surface integrity and fatigue resistance.
What Assembly Processes Are Involved in Manufacturing Double-Threaded Bolts?
Once the threads are formed, the assembly process begins. This stage may involve additional treatments, such as applying coatings for corrosion resistance. Depending on the application, bolts may be fitted with nuts or other hardware to ensure secure fastening.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Used for Double-Threaded Bolts?
Finishing is essential for enhancing the appearance and performance of double-threaded bolts. Common techniques include:
- Plating: A layer of material, such as zinc or nickel, is applied to prevent corrosion.
- Anodizing: This electrochemical process increases corrosion resistance and surface hardness.
- Passivation: A treatment that enhances the natural oxide layer on stainless steel, improving corrosion resistance.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into the Manufacturing Process?
Quality assurance (QA) is crucial in the manufacturing of double-threaded bolts to ensure that they meet international standards and customer expectations. A robust QA process typically includes various checkpoints and testing methods.

Illustrative image related to bolt with threads on both ends
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
For double-threaded bolts, compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 is critical. This standard ensures that manufacturers maintain quality management systems that consistently produce quality products. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking (for European markets) and API specifications (for the oil and gas industry) may also apply, depending on the application.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) involves systematic checks at various stages of production:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage assesses the quality of raw materials before production begins. Suppliers should provide certification for material properties to ensure compliance with specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, various checks are performed to monitor critical parameters, such as thread dimensions and mechanical properties. This step often includes real-time monitoring using advanced measurement tools.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, the finished bolts undergo a final inspection. This may involve dimensional checks, surface quality assessments, and mechanical testing to ensure that the products meet all specified requirements.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Assurance for Double-Threaded Bolts?
Several testing methods are employed to verify the integrity and performance of double-threaded bolts:
- Tensile Testing: This measures the maximum load a bolt can withstand before failure, assessing its strength.
- Hardness Testing: This evaluates the material’s resistance to deformation, providing insights into its durability.
- Torque Testing: This method examines the bolt’s performance under load, ensuring it can withstand the required torque without failure.
- Dimensional Inspection: Using tools like calipers and micrometers, manufacturers check the bolt dimensions against specified tolerances.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential for risk management.
-
Supplier Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can reveal their adherence to quality standards and manufacturing practices. Buyers should assess both the facility and the processes in place.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports and certifications can provide insight into the supplier’s compliance with international standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies can offer an unbiased assessment of the product quality and the manufacturing process.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International Buyers?
International buyers should be aware of specific nuances related to quality control. For instance, different regions may have varying regulatory requirements and standards that must be adhered to. Understanding these differences is crucial for ensuring compliance and avoiding potential delays or rejections upon import.
Additionally, language barriers and cultural differences can impact the interpretation of quality standards. Hence, establishing clear communication channels with suppliers is vital for successful collaboration.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for double-threaded bolts is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can ensure they procure high-quality products that meet their specific needs and comply with international standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘bolt with threads on both ends’
Introduction
This sourcing guide provides a practical checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure bolts with threads on both ends, also known as double-end studs. These fasteners play a crucial role in various applications, including manufacturing, construction, and plumbing, where strength and reliability are paramount. Following this checklist will help you make informed decisions, ensuring that you select the right product and supplier to meet your operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding the specific requirements for your application is essential. Consider factors such as diameter, length, thread type (right-hand or left-hand), and material (e.g., stainless steel, carbon steel). Clearly defining these specifications will streamline the sourcing process and help avoid miscommunication with suppliers.

Illustrative image related to bolt with threads on both ends
Step 2: Identify Industry Standards and Compliance
Familiarize yourself with relevant industry standards for double-end studs, such as ASTM specifications (e.g., ASTM A193 for high-temperature applications). Ensuring compliance with these standards is crucial for product performance and safety, particularly in high-stress environments. Look for suppliers that provide documentation proving their products meet these standards.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers before making a commitment. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Assess their production capabilities, including material sourcing and manufacturing processes, to ensure they can meet your specific requirements.
- Check for certifications such as ISO 9001 or other relevant quality management systems.
- Inquire about their experience in your industry to gauge their understanding of your needs.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before placing a bulk order, request samples of the bolts to evaluate their quality and compatibility with your application. Testing samples allows you to assess the strength, durability, and finish of the product. This step is critical to avoid costly errors and ensure that the fasteners will perform as expected under operational conditions.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you’ve identified a suitable supplier and verified product quality, engage in price negotiations. Consider not only the unit price but also the terms of payment, lead times, and shipping options. Establishing clear terms upfront can help prevent disputes later and ensure a smooth procurement process.
- Ask about bulk discounts if you plan to order large quantities.
- Clarify return policies and warranties to safeguard your investment.
Step 6: Ensure After-Sales Support and Communication
Select a supplier that offers robust after-sales support and maintains open lines of communication. This is vital for addressing any issues that may arise post-purchase, such as product defects or order discrepancies. A reliable supplier will also provide technical support and guidance on product usage.
Step 7: Document Your Procurement Process
Finally, maintain thorough documentation of your procurement process, including specifications, supplier communications, and contracts. This record will serve as a valuable reference for future orders and can help streamline subsequent procurement efforts. Proper documentation also aids in compliance audits and quality assurance processes.
Following this checklist will empower you to make informed decisions when sourcing double-end studs, ensuring that you secure high-quality products that meet your specific operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for bolt with threads on both ends Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Double-Ended Bolts?
When sourcing bolts with threads on both ends, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type of steel used (low carbon, medium carbon, stainless) significantly influences pricing. Higher-grade materials, such as ASTM A193 B7, are more expensive due to their strength and suitability for high-stress applications.
-
Labor: Manufacturing labor costs vary by region and complexity of the bolt design. Skilled labor is often required for custom threading and machining, which can add to the overall cost.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to the facilities, utilities, and administrative expenses associated with production. Overhead can vary widely based on the manufacturer’s location and operational efficiency.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be necessary for specialized bolt designs or dimensions, which can increase initial costs but may reduce per-unit costs in larger production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that the bolts meet industry standards, particularly for high-stress applications. The cost of testing and certification can be significant, especially for international buyers needing compliance with local regulations.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can fluctuate based on the distance, mode of transport, and any duties or tariffs applicable to international trade. Efficient logistics planning can mitigate some of these costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a profit margin based on their operational costs and market demand, typically ranging from 10% to 30%.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Double-Ended Bolts?
Several factors influence the pricing of double-ended bolts, which buyers should consider:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk orders, so it’s beneficial to negotiate MOQs based on your projected needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can increase costs. If standard sizes and threads suffice, opting for these can significantly reduce expenses.
-
Materials: The choice of material directly impacts pricing. For instance, stainless steel bolts will cost more than those made from carbon steel. Custom finishes, such as galvanization, can also add to the overall price.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet specific industry standards (like ISO or ASTM) may carry a premium. Buyers should weigh the importance of certifications against the added costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better quality assurance and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is essential for pricing clarity. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) dictate who is responsible for shipping costs and risks, impacting the total cost.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Sourcing Double-Ended Bolts Internationally?
Navigating the international sourcing landscape for double-ended bolts requires strategic planning:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Leverage your understanding of the cost components and price influencers to negotiate better terms. Consider long-term partnerships for more favorable pricing.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, shipping, handling, and potential downtime costs due to quality issues. A lower upfront cost may not always be the most economical choice in the long run.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Familiarize yourself with the specific needs of your region. For example, tariffs on imported goods may affect pricing in Africa or South America, while European buyers might prioritize certifications more heavily.
-
Plan for Logistics: Account for shipping times and costs in your procurement process. Consider local suppliers when feasible to reduce logistical complexities.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Keeping abreast of market conditions, such as material costs and demand fluctuations, can help you make informed buying decisions and anticipate price changes.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for double-ended bolts can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. Always consult with suppliers for the most accurate and current pricing tailored to your specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing bolt with threads on both ends With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Bolts with Threads on Both Ends
In the world of fasteners, bolts with threads on both ends offer unique advantages, particularly in applications requiring secure and adjustable connections. However, various alternatives exist that can meet similar needs. This analysis compares bolts with threads on both ends against other viable fastening solutions, providing B2B buyers with insights into performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.

Illustrative image related to bolt with threads on both ends
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Bolt With Threads On Both Ends | Alternative 1: Fully Threaded Studs | Alternative 2: Standard Bolts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High tensile strength, versatile | Higher tensile strength, fully threaded for maximum grip | Sufficient for standard applications, lower tensile strength |
| Cost | Moderate cost, variable by material | Typically lower cost, depending on size and material | Generally lower cost, widely available |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires precise alignment and nut fastening | Easier to install with two nuts for secure fastening | Simple installation, often requires a wrench |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, durable | Similar durability, but may require periodic checks | Moderate maintenance, subject to wear |
| Best Use Case | High-stress applications, flanged connections | Heavy-duty applications, machinery assembly | General construction, non-critical fastening |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Fully Threaded Studs
Fully threaded studs are bolts that feature continuous threading along their entire length. This design allows for maximum grip and load distribution, making them ideal for high-stress applications such as flange bolting in industrial settings. The primary advantage of fully threaded studs is their ability to accommodate varying thicknesses of materials, offering flexibility in assembly. However, they may require more precise installation techniques to ensure proper tension and alignment.
Standard Bolts
Standard bolts are the most commonly used fasteners in various industries. They consist of a head and a threaded shank, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. While they are generally less robust than double-ended bolts or fully threaded studs, they are often more cost-effective and easier to install. Standard bolts are ideal for general construction and non-critical applications. However, their limited grip in high-stress situations can lead to loosening over time, necessitating regular inspections and maintenance.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Fastening Solution
When selecting the appropriate fastening solution for your B2B needs, it’s crucial to consider the specific requirements of your application. For high-stress environments requiring adjustable connections, bolts with threads on both ends or fully threaded studs may be the best choice. Conversely, for general construction projects where cost and ease of installation are priorities, standard bolts can suffice. Assessing the performance, cost, and maintenance needs of each option will help ensure that you choose the right fastener to meet your operational demands while optimizing efficiency and safety.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for bolt with threads on both ends
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Bolts with Threads on Both Ends?
Understanding the technical specifications of bolts with threads on both ends is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when ensuring compatibility and performance in various applications. Here are some essential properties:
1. Material Grade
The material grade of a bolt determines its strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. Common materials include low carbon steel, medium carbon steel, and stainless steel (e.g., A193 B7). For example, A193 B7 is a high-strength steel used for high-temperature and high-pressure applications, making it suitable for industries like oil and gas. Choosing the right material ensures that the bolt can withstand environmental conditions and operational stresses.
2. Thread Type
Bolts can feature different thread types, including coarse and fine threads. Coarse threads are easier to assemble and disassemble, while fine threads provide better tension and resistance to loosening. Understanding the thread type is essential for ensuring compatibility with nuts and other fasteners, particularly in applications requiring precise tensioning.
3. Tensile Strength
Tensile strength measures the maximum load a bolt can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. This property is critical for applications involving high stress and load-bearing. For instance, bolts with a tensile strength of 120,000 psi are commonly used in heavy machinery. Selecting bolts with appropriate tensile strength helps prevent failures and enhances safety.
4. Length and Diameter
The length and diameter of bolts with threads on both ends are vital for their application. Standard sizes vary, and custom lengths may be required depending on the project specifications. Typically, diameters range from ¼ inch to several inches, with lengths up to 20 feet available. Ensuring the correct dimensions aligns with design requirements and load distribution.
5. Finish and Coating
The finish of a bolt affects its corrosion resistance and aesthetic quality. Options include plain, galvanized, and coated finishes like black oxide or zinc. A proper finish can significantly extend the life of the bolt, particularly in harsh environments. Buyers should consider the operational environment when selecting the appropriate finish to prevent premature failure.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Bolts with Threads on Both Ends?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and enhance procurement processes. Here are several essential terms to know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM specifications ensures that buyers are sourcing components that meet the quality and performance standards required for their applications.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers manage inventory levels and budget constraints. Suppliers often set MOQs based on production costs, and negotiating these terms can lead to cost savings for bulk purchases.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for a specific quantity of goods. This process is crucial for procurement, allowing buyers to compare offers and negotiate better terms. A well-prepared RFQ can lead to significant cost efficiencies.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules defining the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms helps clarify obligations in international transactions, reducing the risk of disputes and ensuring smooth logistics.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to delivery. This metric is essential for project planning, as it affects inventory management and project timelines. Buyers should communicate lead time expectations clearly to avoid delays in project execution.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring the successful procurement and application of bolts with threads on both ends.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the bolt with threads on both ends Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers for Bolt with Threads on Both Ends?
The global market for bolts with threads on both ends is influenced by several factors, including industrial growth, infrastructure development, and technological advancements. Emerging economies in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are experiencing rapid industrialization, driving demand for robust fastening solutions in construction, manufacturing, and energy sectors. The rise of automation and precision engineering further necessitates high-quality, reliable fasteners capable of withstanding extreme conditions, thus favoring double-threaded bolts.
Technological innovations such as digital sourcing platforms and advanced manufacturing processes are reshaping procurement strategies. International B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging e-commerce platforms for efficiency in sourcing, allowing them to compare suppliers, access a broader range of products, and streamline their procurement processes. Additionally, the trend towards customization has gained momentum, with manufacturers offering tailored solutions to meet specific project requirements.
Furthermore, the demand for high-strength materials is accelerating, especially in applications like flange bolting and structural reinforcement. This trend is particularly pertinent in regions such as Saudi Arabia and Brazil, where large-scale infrastructure projects are on the rise. Buyers should remain attentive to these market dynamics and technology trends to optimize their sourcing strategies effectively.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Bolt Industry?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the fastener industry, including bolts with threads on both ends. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and raw material sourcing is under scrutiny, prompting businesses to prioritize ethical supply chains. The use of recycled materials and sustainable manufacturing practices can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with fastener production.
Buyers should seek suppliers that offer green certifications and utilize eco-friendly materials, such as low-carbon steel or stainless steel with minimal environmental impact. Additionally, companies that adhere to ethical labor practices and have transparent supply chains are increasingly favored in the market. This not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with global sustainability goals.
Incorporating sustainability into procurement strategies can also lead to cost savings in the long run, as efficient use of materials and energy can reduce operational costs. As international regulations around sustainability tighten, companies that proactively adopt green practices will likely gain a competitive edge in the marketplace.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Bolt with Threads on Both Ends?
The evolution of bolts with threads on both ends can be traced back to the early days of industrialization when the need for more secure fastening solutions became apparent. Initially, standard bolts were used, but their limitations in strength and application versatility led to the development of double-threaded bolts. These fasteners offered enhanced stability and load-bearing capabilities, making them ideal for critical applications in construction and manufacturing.
Over the decades, advancements in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques have refined the production of threaded bolts. Today, they are often made from high-strength materials that comply with international standards, ensuring reliability across various sectors. The introduction of advanced coating techniques has also improved corrosion resistance, extending the service life of these fasteners in demanding environments.
As industries continue to evolve, the design and functionality of bolts with threads on both ends are expected to adapt further, driven by technological advancements and the increasing demand for customized solutions. B2B buyers must stay informed about these developments to leverage the latest innovations for their specific applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of bolt with threads on both ends
-
How do I select the right double-ended stud bolts for my application?
Choosing the right double-ended stud bolts involves considering the specific application requirements, including load capacity, material compatibility, and environmental conditions. Assess the tensile strength required and select a bolt that meets or exceeds this requirement. Additionally, ensure that the bolt’s diameter and thread pitch match your existing components. Consulting with a supplier or engineer can provide valuable insights, especially for custom applications or unique environmental challenges, such as corrosion resistance in harsh climates. -
What types of materials are commonly used for double-ended stud bolts?
Double-ended stud bolts are typically made from materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel (grades 304 and 316), and alloy steel. The choice of material depends on the application requirements, including strength, corrosion resistance, and temperature tolerance. For instance, stainless steel is ideal for marine environments, while carbon steel is often used in construction. It’s essential to evaluate the environmental factors and mechanical stresses to select a suitable material that ensures longevity and performance. -
What customization options are available for double-ended stud bolts?
Most suppliers offer customization for double-ended stud bolts, including variations in length, diameter, thread pitch, and material finishes. You can also request specific thread types (such as right-hand or left-hand threads) and coatings (like zinc plating or hot-dip galvanizing) to enhance corrosion resistance. Discussing your requirements with the manufacturer allows for tailored solutions that meet your precise specifications, enhancing performance in your application. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for double-ended stud bolts?
Minimum order quantities for double-ended stud bolts can vary significantly by supplier and product specifications. Typically, MOQs range from 50 to several hundred units, depending on the size, material, and customization required. For bulk orders, suppliers may offer discounts or reduced MOQs, especially if you are establishing a long-term relationship. It’s advisable to communicate your needs clearly to the supplier to negotiate the best terms. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing double-ended stud bolts internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of double-ended stud bolts can vary by supplier and region. Common arrangements include upfront payment, partial payment with the balance upon delivery, or letters of credit for larger orders. It’s crucial to clarify these terms before placing an order and to ensure they align with your cash flow management. Building a relationship with your supplier may also provide flexibility in payment options over time. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for double-ended stud bolts?
To ensure quality assurance, choose suppliers who provide certifications such as ISO 9001 or relevant industry standards. Request documentation for material properties, tensile strength tests, and any applicable third-party testing. Establishing a clear quality control process, including inspections upon delivery, can help mitigate risks. Additionally, consider suppliers who offer warranties or guarantees on their products to safeguard your investment. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing double-ended stud bolts?
When importing double-ended stud bolts, consider shipping methods, lead times, and customs clearance processes. Selecting a reliable logistics partner who understands international trade regulations can streamline the import process. Additionally, be aware of tariffs, duties, and any documentation required for customs. Planning for potential delays and ensuring proper packaging to prevent damage during transit are also essential steps. -
What industries commonly utilize double-ended stud bolts, and why?
Double-ended stud bolts are widely used across various industries, including construction, manufacturing, and plumbing. They are favored for their strength and versatility, as they can securely fasten multiple components without the need for a head. In construction, they are often used in flanged connections and structural applications due to their high tensile strength. Understanding the specific needs of your industry can help you select the right type of stud bolts for your projects.
Top 6 Bolt With Threads On Both Ends Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. AFT Fasteners – Threaded Studs
Domain: aftfasteners.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Threaded Studs – Double Threaded Bolts
2. McMaster – Double-End Bolts
Domain: mcmaster.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, McMaster – Double-End Bolts, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Threadline Products – Double Ended Anchor Bolt
Domain: threadlineproducts.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Double Ended Anchor Bolt is threaded on both ends and is a heavy-duty fastener used to connect objects to concrete. It consists of a round steel bar, nuts, flat washers, and plate steel. Available materials include A36, F1554-GR36, F1554-GR55(S1), F1554-GR105, 1018, 4140, 4130 (B7), A193 (B12), COIL ROD, 304SS, and 316SS. Standard sizes include diameters of 1/4-inch, 3/8-inch, 1/2-inch, 5/8-inch, …
4. Reddit – Hanger Bolt
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Double-sided bolt with different ends, commonly referred to as a “hanger bolt” or “collar stud”. One end features HiLo tapping threads, while the other end has a machine screw. Often used in automotive applications for securing door panels and dashboards.
5. Bolt Depot – Fasteners
Domain: boltdepot.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Fastener Categories: Wood Screws (WS), Machine Screws (MS), Thread Cutting Machine Screws, Sheet Metal Screws (SMS), Self Drilling SMS, Hex Bolts (HHMB or HXBT), Carriage Bolts, Lag Bolts, Flange Bolts, Socket Screws, Eye Bolts, Eye Lags, U-Bolts, J-Bolts, Shoulder Bolts, Elevator Bolts, Sex Bolts, Mating Screws, Hanger Bolts, Set Screws. Head Styles: Flat (FH), Oval (OH or OV), Pan (PN), Truss, R…
6. MISUMI – Fully Threaded Bolts & Studs
Domain: us.misumi-ec.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Fully Threaded Bolts & Studs – Hex Socket, Both Ends Right-Hand Screws, Length Configurable. Part Number: Please configure to get your Part Number. Shape: Fully Threaded (Both Ends). Application: Standard. Mounting Hole Shape: Hex Socket. Additional Shape: Standard. Caution: For M16 or M20, if overall length L is specified as between 20 and 25, the pilot hole of the hex socket may go through. Opti…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for bolt with threads on both ends
What Are the Key Benefits of Strategic Sourcing for Double-Ended Bolts?
In the competitive landscape of fasteners, particularly double-ended bolts, strategic sourcing is pivotal for international buyers. By leveraging supplier relationships and market intelligence, businesses can secure high-quality products that meet stringent specifications while optimizing costs. Understanding the unique attributes of double-ended bolts—such as their increased strength and versatility across industries like manufacturing and construction—enables buyers to make informed procurement decisions.
How Can International Buyers Capitalize on Market Trends?
As demand for reliable and efficient fastening solutions grows in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, international buyers should focus on sourcing from manufacturers that offer customization and a range of materials and finishes. This adaptability not only enhances operational efficiency but also aligns with local compliance and project requirements. Engaging with suppliers that provide value-added services, such as technical support and rapid prototyping, can further streamline the procurement process.
What Should Be the Next Steps for B2B Buyers?
Looking ahead, international buyers are encouraged to prioritize strategic partnerships with reputable suppliers who understand the complexities of the global fastener market. By embracing a proactive sourcing approach, businesses can ensure they remain at the forefront of innovation and quality. Take the initiative today—evaluate your current sourcing strategies and explore new opportunities to enhance your supply chain resilience and competitiveness in the fastener market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.