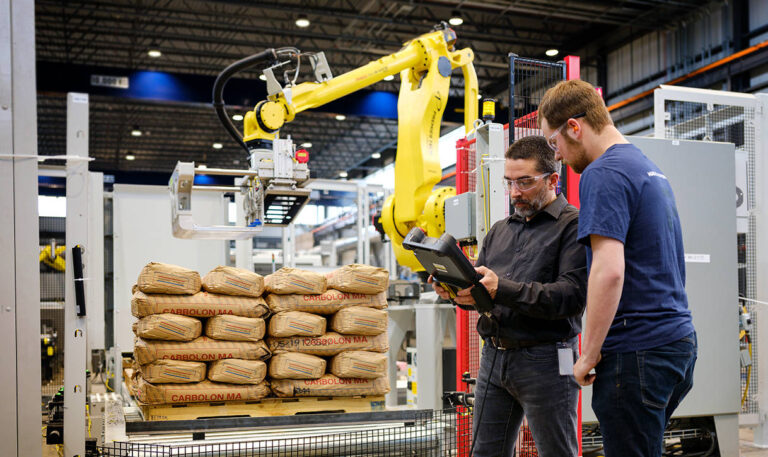
Bolt Heading Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for bolt heading
Navigating the intricate landscape of bolt heading can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The decision-making process often hinges on selecting the right manufacturing method—be it hot or cold heading—while ensuring compliance with local standards and maximizing cost efficiency. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of bolt heading, addressing key aspects such as the various types of heading processes, their applications across industries, and crucial factors for supplier vetting.
With the global market continuously evolving, understanding the nuances of bolt heading is essential for informed purchasing decisions. Buyers will gain insights into the advantages and limitations of hot and cold heading, helping them assess which method aligns best with their production needs and budget constraints. The guide also delves into cost considerations, enabling businesses to strike a balance between quality and affordability.
By empowering B2B buyers with actionable knowledge and strategic insights, this guide aims to streamline the sourcing process, reduce procurement risks, and enhance overall supply chain efficiency. Whether you’re operating in Germany, Nigeria, or elsewhere, navigating the global bolt heading market effectively can lead to significant operational advantages and competitive edge.
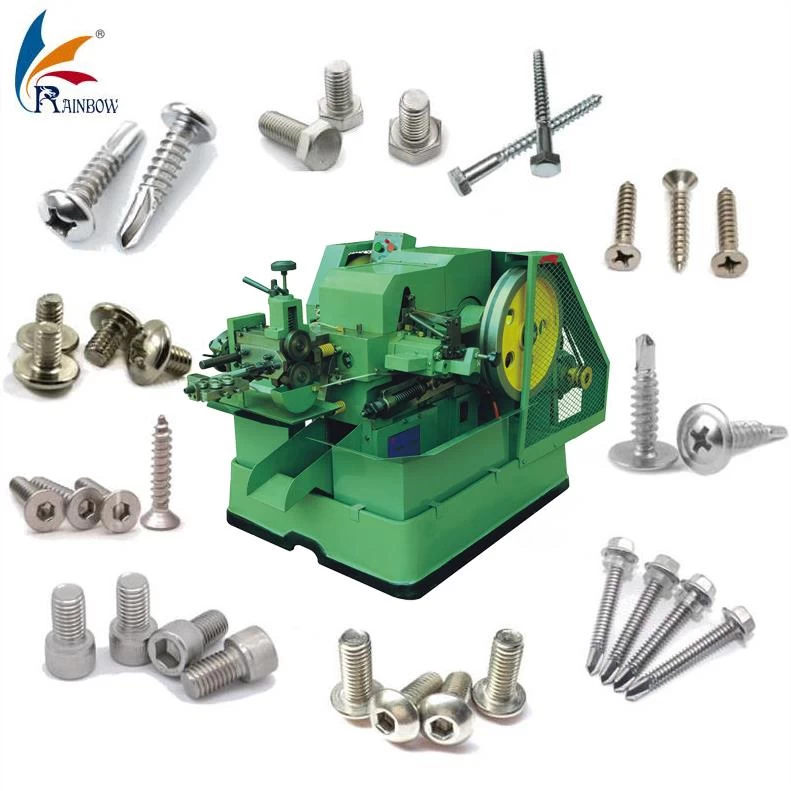
Understanding bolt heading Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot Heading | Involves heating the material before forming; suitable for larger diameters (3/8” to 2”). | Low to medium volume applications; specialty fasteners. | Pros: Lower tooling costs; better formability. Cons: Slower production; higher costs for small quantities. |
| Cold Heading | Forms metal at room temperature; ideal for high-volume production (½” to 1 1/8” diameters). | Aerospace, automotive, construction. | Pros: High precision; faster production; minimal waste. Cons: Higher initial tooling costs; limited to smaller sizes. |
| Upset Heading | Uses a plunger to compress heated metal; capable of producing large diameter bolts (up to 2.5”). | Heavy machinery, structural applications. | Pros: Versatile for different head styles; no length limitations. Cons: More complex setup; potentially longer lead times. |
| Custom Heading | Tailored designs for specific applications; can incorporate logos or unique shapes. | Niche markets, promotional items, custom machinery. | Pros: Meets specific client needs; enhances brand visibility. Cons: Higher costs; longer production times for custom tooling. |
| Structural Heading | Focuses on creating bolts with specific strength and marking standards; often used in construction. | Infrastructure projects, bridges, buildings. | Pros: Meets stringent safety standards; reliable performance. Cons: Limited design flexibility; potentially higher prices due to quality control. |
What Are the Characteristics and Suitability of Hot Heading?
Hot heading involves heating the round bar material to a high temperature before shaping it into the bolt head. This process is particularly suitable for larger diameter bolts, typically ranging from 3/8” to 2”. B2B buyers looking for low to medium volume applications or specialty fasteners may find hot heading advantageous due to its lower tooling costs and enhanced formability. However, the slower production speed and higher costs for smaller quantities could be drawbacks, necessitating careful consideration of order size and urgency.
How Does Cold Heading Benefit High-Volume Production?
Cold heading is a high-speed manufacturing process that shapes metal at room temperature, making it ideal for producing fasteners in high volumes, typically between ½” and 1 1/8” in diameter. This method is favored in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and construction, where precision and efficiency are paramount. The significant reduction in waste and faster production times are major benefits for B2B buyers, although the higher initial tooling costs and limitations on size may require a strategic approach to purchasing.
What Makes Upset Heading Unique for Large Diameter Bolts?
Upset heading employs a plunger to compress heated metal, allowing for the creation of large diameter bolts, up to 2.5”. This versatility makes it suitable for heavy machinery and structural applications. B2B buyers may appreciate the ability to produce various head styles without length restrictions, but the complexity of the setup and potential for longer lead times are factors to consider when placing orders.
Why Choose Custom Heading for Specialized Applications?
Custom heading allows for the production of uniquely designed bolts tailored to specific client requirements, including the incorporation of logos or specialized shapes. This approach is particularly beneficial for niche markets and promotional items. While it offers the advantage of meeting distinct needs and enhancing brand visibility, buyers should be mindful of the higher costs and longer production times associated with custom tooling.
What Are the Key Considerations for Structural Heading?
Structural heading focuses on producing bolts that meet specific strength and marking standards, crucial for construction and infrastructure projects. B2B buyers engaged in these sectors will value the reliability and compliance with stringent safety standards that structural heading provides. However, the limited design flexibility and potentially higher prices due to rigorous quality control should be factored into procurement decisions.
Key Industrial Applications of bolt heading
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of bolt heading | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Manufacturing of engine components | Enhanced durability and performance of critical parts | Material grades, precision tolerances, and volume requirements |
| Construction | Structural connections and framework assembly | Increased structural integrity and safety in construction | Compliance with local standards, custom head designs |
| Aerospace | Fasteners for aircraft assembly | Lightweight and high-strength components for safety | Certification requirements, material traceability |
| Renewable Energy | Wind turbine assembly and maintenance | Reliability and longevity in challenging environments | Corrosion resistance, specialized coatings |
| Heavy Machinery | Assembly of heavy equipment | Robust connections that withstand high stress and fatigue | Customization options, lead times, and bulk pricing |
How is Bolt Heading Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, bolt heading is critical for manufacturing engine components, where precision and durability are paramount. Fasteners produced through bolt heading techniques provide the necessary strength to withstand the high stresses encountered during operation. Buyers in this industry must consider material grades that meet stringent automotive standards, as well as the ability to produce high volumes with tight tolerances to ensure compatibility with assembly lines.
What Role Does Bolt Heading Play in Construction?
In construction, bolt heading is extensively utilized for structural connections and framework assembly. The bolts created through this process enhance the structural integrity and safety of buildings and infrastructure. International buyers, especially in regions like Africa and the Middle East, should prioritize suppliers who can provide custom head designs and comply with local construction standards. Ensuring that fasteners are tested for load-bearing capabilities is also essential for meeting safety regulations.

Illustrative image related to bolt heading
Why is Bolt Heading Important for Aerospace Applications?
Aerospace applications require fasteners that are lightweight yet strong, making bolt heading an ideal manufacturing process. Fasteners used in aircraft assembly must adhere to strict safety and performance standards, with a focus on material traceability and certification. Buyers need to ensure that their suppliers can provide documentation proving compliance with aerospace regulations, as well as the ability to produce specialized fasteners that meet unique design requirements.
How Does Bolt Heading Benefit the Renewable Energy Sector?
In the renewable energy sector, particularly in wind turbine assembly and maintenance, bolt heading provides reliable and long-lasting fasteners that can withstand harsh environmental conditions. The durability of these fasteners ensures that wind turbines operate efficiently over extended periods. Buyers should consider sourcing fasteners with corrosion-resistant coatings and evaluate the supplier’s experience in producing components suitable for renewable energy applications.
What are the Advantages of Bolt Heading in Heavy Machinery Manufacturing?
In the heavy machinery industry, bolt heading is essential for the assembly of robust equipment that must endure high stress and fatigue. The strength and reliability of bolt-headed fasteners directly impact the performance and longevity of machinery. B2B buyers should focus on suppliers who offer customization options to meet specific machinery requirements and can provide competitive pricing for bulk orders, ensuring that their operations remain efficient and cost-effective.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘bolt heading’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating the Complexities of Hot vs. Cold Heading for Custom Orders
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle to decide between hot heading and cold heading when placing custom orders for bolts. This decision is critical because it impacts both cost and lead time. For instance, a buyer in Nigeria may require a large volume of bolts for a construction project but is unsure whether to opt for hot heading, which is slower but can accommodate larger diameters, or cold heading, which is faster but best suited for smaller sizes. This indecision can lead to project delays and increased costs if the wrong method is chosen.
The Solution: To navigate this complexity, buyers should first assess their specific project requirements, including the size and volume of bolts needed, as well as the material specifications. Engaging with suppliers who offer both hot and cold heading processes can provide insights tailored to the project. For example, if the order exceeds 1 1/8” diameter and is not overly large in volume, hot heading may be the better choice due to its cost-effectiveness for such sizes. On the other hand, for high-volume orders of smaller bolts, cold heading is likely to be the optimal method. Buyers should also request detailed quotes that outline the costs associated with both methods, enabling informed decision-making.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Consistency in Bolt Specifications Across International Orders
The Problem: When sourcing bolts from suppliers across different regions, B2B buyers often face challenges in maintaining consistent specifications. For example, a buyer from Europe sourcing bolts for a renewable energy project may find discrepancies in dimensions or material grades when ordering from suppliers in South America. Such inconsistencies can lead to compatibility issues in assemblies, ultimately affecting the safety and integrity of the final product.
The Solution: To ensure consistency, buyers should establish clear and comprehensive specifications before engaging suppliers. This includes detailed drawings, material grades (e.g., stainless steel vs. carbon steel), and tolerance levels. It’s also advisable to request samples from suppliers before placing large orders. Additionally, maintaining open lines of communication with suppliers and conducting periodic audits can help ensure adherence to specifications. Buyers may also benefit from using standardized international codes such as ASTM or ISO to specify bolt requirements, which can further mitigate discrepancies.
Scenario 3: Managing Lead Times and Supply Chain Disruptions in Bolt Heading
The Problem: In today’s global market, B2B buyers are increasingly confronted with lead times and supply chain disruptions, particularly in the manufacturing of bolts. A buyer in the Middle East may experience delays due to global shipping issues or production bottlenecks at the supplier’s facility. Such disruptions can jeopardize project timelines and incur additional costs, which is particularly concerning for industries like construction or aerospace that rely on timely deliveries.

Illustrative image related to bolt heading
The Solution: To effectively manage lead times, buyers should diversify their supplier base and establish relationships with multiple manufacturers. This approach allows for flexibility and quick adjustments in case one supplier faces disruptions. It’s also crucial to implement a robust inventory management system that anticipates demand and allows for safety stock. Buyers should communicate their project timelines clearly with suppliers to prioritize urgent orders. Additionally, leveraging technology for real-time tracking of orders can provide transparency and allow buyers to proactively address potential delays. Regularly reviewing and adjusting supply chain strategies in light of changing market conditions will also help mitigate risks associated with lead time disruptions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for bolt heading
What Are the Key Materials Used in Bolt Heading?
When selecting materials for bolt heading, it’s crucial to consider the properties, advantages, and limitations of each option. The right material can significantly impact the performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness of the final product. Below, we analyze four common materials used in bolt heading: carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, and brass.
How Does Carbon Steel Perform in Bolt Heading Applications?
Carbon steel is one of the most widely used materials for bolt heading due to its excellent mechanical properties and cost-effectiveness. It offers good tensile strength and is suitable for various applications, including construction and automotive sectors. Carbon steel bolts can withstand moderate temperatures and pressures, making them versatile.
Pros: Carbon steel is relatively inexpensive and easy to manufacture, which makes it a popular choice for high-volume production. Its durability is commendable, particularly in non-corrosive environments.
Cons: However, carbon steel has limited corrosion resistance, which can lead to rust and degradation when exposed to moisture or harsh chemicals. This limitation necessitates protective coatings or treatments, which can increase overall costs.

Illustrative image related to bolt heading
Impact on Application: Carbon steel bolts are ideal for applications where environmental conditions are controlled, but they may not be suitable for marine or chemical processing environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM A307 or DIN 933 is essential. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider local climatic conditions that may affect the longevity of carbon steel products.
What Advantages Does Stainless Steel Offer for Bolt Heading?
Stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, making it a prime choice for applications exposed to moisture or harsh environments. It maintains its strength at elevated temperatures, which is critical for high-performance applications.
Pros: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its resistance to corrosion and staining, making it suitable for marine, chemical, and food processing industries. Additionally, it requires minimal maintenance over its lifespan.
Cons: On the downside, stainless steel is generally more expensive than carbon steel and can be more challenging to manufacture due to its toughness. This can lead to higher production costs.

Illustrative image related to bolt heading
Impact on Application: Stainless steel bolts are ideal for applications where exposure to corrosive media is a concern, such as in coastal regions or chemical plants.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM A193 or DIN 1.4401. In Europe, preferences may lean towards specific grades like A2 or A4 stainless steel.
How Does Alloy Steel Enhance Bolt Performance?
Alloy steel is a blend of carbon steel with other elements like chromium, molybdenum, or nickel, enhancing its mechanical properties. This material is often used in high-stress applications, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries.
Pros: The key advantage of alloy steel is its superior strength and toughness, which allows for the production of bolts that can withstand extreme conditions. It can also be heat-treated to improve performance further.
Cons: However, alloy steel can be more expensive and complex to manufacture. The need for heat treatment can also extend production time.
Impact on Application: Alloy steel bolts are suitable for applications requiring high tensile strength and resistance to wear, such as in heavy machinery and automotive components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM A325 or DIN 931 is critical. Buyers should also consider local availability and sourcing options, especially in regions like the Middle East where specific alloys may be preferred.
What Role Does Brass Play in Bolt Heading?
Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, is less common for structural bolts but is often used in applications requiring electrical conductivity or resistance to corrosion. It is particularly useful in plumbing and electrical applications.
Pros: Brass offers excellent corrosion resistance and is easy to machine, making it suitable for intricate designs. It is also aesthetically pleasing, which can be an advantage in visible applications.
Cons: The primary limitation of brass is its lower tensile strength compared to steel, making it unsuitable for high-stress applications. It is also more expensive than carbon steel.
Impact on Application: Brass bolts are ideal for applications in plumbing, electrical fittings, and decorative hardware where corrosion resistance is essential.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM B16 or JIS H3250. In regions like Europe, preferences may vary based on specific applications, such as plumbing or electrical standards.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Bolt Heading
| Material | Typical Use Case for bolt heading | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | General construction and automotive | Cost-effective, durable | Limited corrosion resistance | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Marine and chemical applications | Corrosion resistant | Higher manufacturing cost | High |
| Alloy Steel | Heavy machinery and aerospace | Superior strength | Complex manufacturing process | Medium |
| Brass | Plumbing and electrical fittings | Excellent corrosion resistance | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials used in bolt heading, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for bolt heading
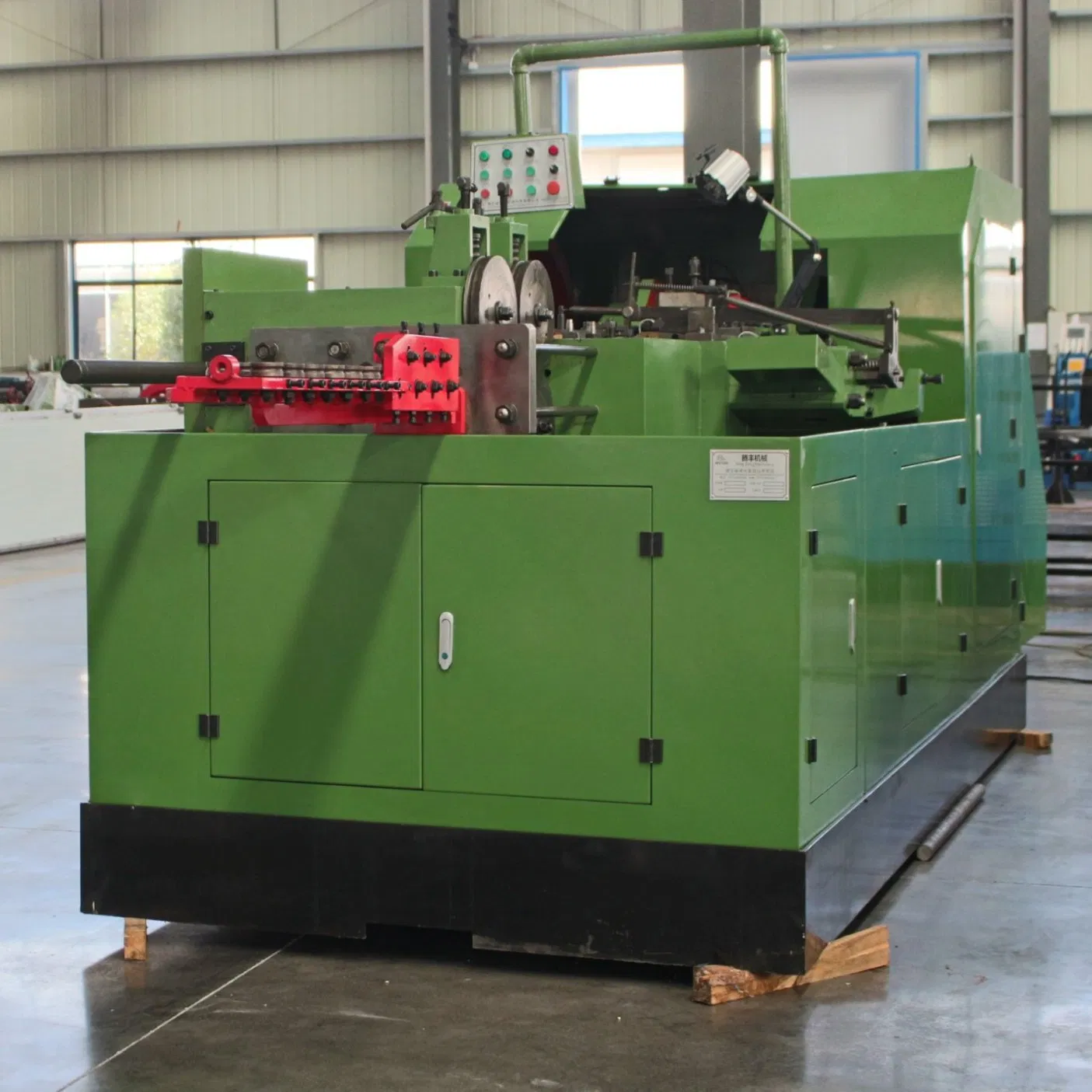
What Are the Main Stages of Bolt Heading Manufacturing?
The manufacturing of bolts through heading involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets the required specifications and quality standards.

Illustrative image related to bolt heading
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used for Bolt Heading?
The process begins with the selection of appropriate raw materials, typically steel or alloys such as stainless steel, low carbon, or medium carbon. These materials are often sourced based on specific requirements, including strength, corrosion resistance, and intended application. Before heading, the round bars are cut to length and may undergo surface treatments to remove any contaminants. This preparation ensures optimal performance during the heading process.
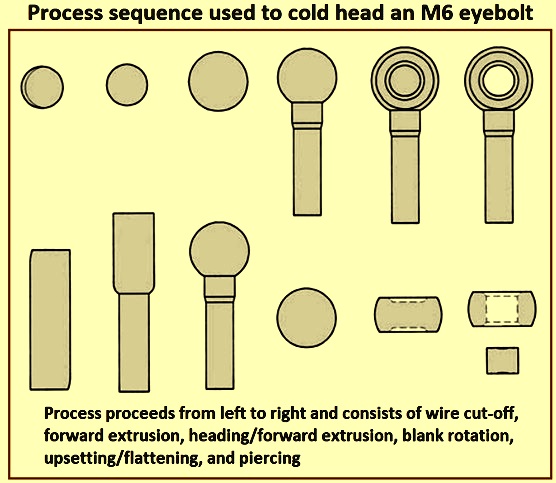
How Are Bolts Formed in the Heading Process?
The core of bolt manufacturing lies in the forming stage, which can utilize either hot or cold heading techniques.
-
Hot Heading involves heating the round bar to a high temperature before forming the head. This method is suitable for larger diameters (generally above 1 1/8 inches) and allows for complex shapes with fewer die impacts. The heated material is placed in a header where it is compressed to create the desired head shape.
-
Cold Heading, on the other hand, shapes the material at room temperature, using high-speed hammers and dies. This method is particularly effective for smaller diameters (typically up to 1 1/8 inches) and is favored for its efficiency, reduced waste, and ability to produce parts with tight tolerances.
Both methods result in a high-quality bolt with distinct characteristics suited for various applications.

Illustrative image related to bolt heading
What Are the Assembly and Finishing Processes in Bolt Manufacturing?
After heading, the bolts may undergo additional processes such as threading, which can occur either before or after the heading stage, depending on the design and functional requirements.
Finishing processes include surface treatments such as galvanizing, plating, or coating to enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. These treatments are crucial for ensuring longevity, especially in demanding environments like construction or automotive applications.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Implemented in Bolt Heading?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in bolt manufacturing, ensuring that the products meet international and industry-specific standards.

Illustrative image related to bolt heading
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Bolt Quality Assurance?
Adherence to international standards such as ISO 9001 is essential for manufacturers aiming to deliver consistent quality. ISO 9001 outlines requirements for a quality management system, emphasizing customer satisfaction and continuous improvement.
Additionally, industry-specific standards, such as the CE marking for European markets and API standards for the oil and gas sector, are vital. These certifications not only demonstrate compliance with safety and performance benchmarks but also enhance the credibility of suppliers in the eyes of B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Bolt Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to identify and address potential issues early on:
Illustrative image related to bolt heading
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials for compliance with specified standards. It ensures that only high-quality materials enter the production process.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during manufacturing helps catch defects early. This includes checks during forming, threading, and finishing stages to ensure that each step meets quality standards.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, the finished bolts undergo rigorous testing to confirm they meet all specifications. This stage often includes dimensional inspections, strength testing, and surface finish evaluations.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Bolt Quality Control?
Several testing methods are commonly employed to ensure the quality of bolts:
-
Tensile Testing: Measures the strength of the bolt by applying force until failure occurs. This test is crucial for determining the load-bearing capacity.
-
Hardness Testing: Evaluates the hardness of the material, which is indicative of its strength and durability.
-
Dimensional Inspection: Uses gauges and measurement tools to verify that the bolts conform to specified dimensions and tolerances.
-
Surface Inspection: Checks for surface defects such as cracks, pits, or inconsistencies that could compromise the bolt’s performance.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, especially from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is critical. Here are some actionable steps to ensure your supplier adheres to high-quality standards:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits of the manufacturing facility can provide insights into the supplier’s processes, equipment, and adherence to quality standards. This on-site assessment can reveal potential risks and confirm compliance with required certifications.
-
Request Quality Control Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their quality control processes, including test results, inspection reports, and certifications. This transparency is crucial for establishing trust.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspection Services: Utilizing independent inspection agencies can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control measures. These agencies can perform random inspections and testing to ensure compliance with international standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing bolts globally, especially from manufacturers in diverse regions, several nuances must be considered:
-
Understanding Regional Standards: Different regions may have varying quality standards and certifications. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal issues.
-
Cultural and Communication Considerations: Building strong relationships with suppliers can facilitate better communication regarding quality expectations. Understanding cultural differences can enhance collaboration and improve quality outcomes.
-
Logistical Challenges: International shipping can introduce variables that affect product quality, such as temperature fluctuations or handling issues. Buyers should consider these factors and discuss them with suppliers to mitigate risks.
Conclusion
The bolt heading manufacturing process is complex, requiring careful attention to each stage from material preparation to quality assurance. By understanding these processes and implementing rigorous quality control measures, B2B buyers can ensure they are sourcing high-quality products that meet their specific needs. Engaging in thorough verification practices with suppliers is essential for maintaining quality standards in international transactions, ultimately leading to successful partnerships and enhanced operational efficiency.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘bolt heading’
Introduction
Sourcing bolt heading services effectively is vital for businesses seeking reliable fasteners for their projects. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to help international B2B buyers navigate the complexities of procuring bolt heading services, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their technical specifications and business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, it’s essential to clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes specifying the diameter, material grade, and head style of the bolts you need.
- Considerations: Identify whether you require hot heading or cold heading based on your volume needs and product specifications. Hot heading is preferable for larger diameters, while cold heading excels in high-volume, precision applications.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in bolt heading. Look for companies that have a strong reputation in the industry, particularly those with experience serving markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
- Key Actions: Utilize online directories, industry associations, and trade shows to gather a list of suppliers. Pay attention to their production capabilities and any client testimonials that speak to their reliability and quality.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that your shortlisted suppliers hold relevant industry certifications that demonstrate their commitment to quality standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 can be indicators of a supplier’s quality management system.
- Why It Matters: Certifications ensure that the supplier adheres to recognized quality benchmarks, which can significantly reduce the risk of defects and non-compliance in your orders.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Once you have narrowed down your options, request samples or prototypes of the bolt heading products. This step allows you to assess the quality of the materials and the precision of the manufacturing process.
- What to Look For: Evaluate the samples for dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and overall durability. This hands-on assessment is crucial in determining if the supplier meets your specifications before placing a larger order.
Step 5: Analyze Cost Structures
Discuss pricing with potential suppliers and analyze their cost structures. Understand the pricing models for both hot and cold heading processes, and consider the total cost of ownership, including shipping and potential tariffs.
- Cost Factors: Remember that while cold heading may offer lower prices for high volumes, hot heading could be more cost-effective for specialized or low-quantity orders. Ensure you factor in all costs to avoid surprises later.
Step 6: Assess Lead Times and Production Capacity
Inquire about the lead times for production and the supplier’s capacity to meet your demands. Understanding these factors is crucial for planning your project timelines effectively.
- Production Flexibility: Ensure the supplier can accommodate fluctuations in order size, as this flexibility can be invaluable for managing inventory and project schedules.
Step 7: Establish Communication and Support Channels
Effective communication is key to a successful supplier relationship. Ensure that the supplier provides robust support and has a clear line of communication for addressing any issues that may arise.
- Support Services: Look for suppliers that offer technical support, after-sales service, and a responsive customer service team. This support can be critical for troubleshooting and ensuring that your specifications are met throughout the production process.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the sourcing process for bolt heading with confidence, ensuring they select the right supplier for their needs.
Illustrative image related to bolt heading
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for bolt heading Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Bolt Heading Sourcing?
When sourcing bolt heading, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and price negotiation. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control, logistics, and supplier margin.
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly impacts the overall cost. Common materials for bolt heading include low carbon, medium carbon, stainless steel, and alloys. Premium materials may incur higher costs but can enhance durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the complexity of the heading process—hot heading typically requires more skilled labor due to its intricate nature compared to cold heading, which is often more automated.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can minimize these overheads, contributing to lower overall costs.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can be substantial, particularly for cold heading where specialized dies are required. Custom tooling for unique specifications may lead to increased initial investment but can yield significant savings in large production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing robust QC processes ensures that the products meet the required standards, which can prevent costly reworks or returns. This is particularly critical for international buyers who need to comply with various certifications.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are critical, especially for international transactions. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and Incoterms can significantly influence logistics costs.
-
Margin: Supplier margin is the profit margin added by manufacturers or distributors. This varies based on market competition, brand reputation, and the complexity of the products.
How Do Volume and Customization Affect Pricing in Bolt Heading?
Pricing in bolt heading is heavily influenced by volume and customization.
-
Volume/MOQ: Generally, larger orders lead to lower per-unit prices due to economies of scale. Suppliers are often willing to negotiate better terms for high-volume commitments, making it beneficial for buyers to assess their needs carefully.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications, such as unique head shapes or specific material grades, can increase costs due to additional tooling and manufacturing complexity. Buyers should balance their need for customization with potential cost implications.
What External Factors Should International Buyers Consider When Sourcing Bolt Heading?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of several external factors that can influence pricing:
-
Quality Certifications: Compliance with international standards (e.g., ISO, ASTM) can affect costs. Suppliers offering certified products may charge a premium but provide assurance of quality.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers play a significant role in pricing. Established suppliers may offer better quality assurance but at a higher cost.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions, as they define responsibilities and costs between buyers and sellers. Incoterms can affect overall pricing, including shipping and insurance costs.
What Are the Best Negotiation Strategies for Buyers in Bolt Heading Sourcing?
To achieve cost efficiency in sourcing bolt heading, buyers should adopt strategic negotiation tactics:

Illustrative image related to bolt heading
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO, which includes not only the purchase price but also logistics, quality assurance, and potential downtime costs. This broader perspective can lead to more informed purchasing decisions.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can result in better pricing and terms. Regular communication and collaboration can enhance trust and lead to long-term partnerships.
-
Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to understand prevailing prices and terms. Being informed about market conditions empowers buyers during negotiations.
Are There Pricing Nuances International Buyers Should Be Aware Of?
International buyers should be aware that currency fluctuations, tariffs, and trade policies can introduce pricing complexities. Always consider these factors when budgeting for bolt heading purchases, as they can significantly impact the final cost.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for bolt heading can vary widely based on numerous factors, including market conditions and specific buyer requirements. It is advisable to consult with suppliers directly for the most accurate and current pricing information tailored to your needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing bolt heading With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Bolt Heading
When considering bolt production methods, understanding alternatives to bolt heading is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to optimize manufacturing processes. Each method offers distinct advantages and limitations depending on specific project requirements, production volumes, and material characteristics. This analysis will explore bolt heading alongside two viable alternatives: cold heading and screw machining, providing insights into their performance, cost-effectiveness, ease of implementation, maintenance needs, and ideal use cases.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Bolt Heading | Cold Heading | Screw Machining |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength, versatile shapes; good for larger diameters | Superior precision and strength; ideal for high volume | Excellent for complex shapes; precision is high but can be slower |
| Cost | Higher tooling costs; more economical for lower volumes | Lower material waste; cost-effective for high volumes | Generally higher material waste; tooling costs can be significant |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate; requires specialized equipment and setup | High; streamlined production process | Moderate; setup can be complex and time-consuming |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed for tooling | Lower maintenance; fewer moving parts | Higher maintenance due to complexity of machinery |
| Best Use Case | Low to medium volume; larger diameter bolts | High-volume production; tight tolerances | Custom parts requiring intricate shapes and details |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Cold Heading
Cold heading is a high-speed metal forming process conducted at room temperature, allowing for the production of strong and precise components with minimal material waste. The process is particularly advantageous for high-volume manufacturing, making it suitable for industries such as automotive and aerospace. Cold heading excels in producing fasteners like bolts and screws with tight dimensional tolerances, enhancing overall product quality. However, the high tooling costs can be a barrier for lower volume projects, and the process may not accommodate larger diameters as effectively as bolt heading.
Screw Machining
Screw machining involves cutting metal to form parts, resulting in high precision and the ability to create complex geometries. This method is ideal for producing custom components with intricate designs, making it a preferred choice for specialized applications in various industries. However, screw machining is often associated with high material waste, as cutting processes can leave up to 70% of raw materials as scrap. Moreover, the setup time and cost can be significant, which may deter its use for larger production runs unless the complexity of the part justifies the expense.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the optimal production method for bolts or similar fasteners hinges on several factors, including project volume, material requirements, and design complexity. For B2B buyers, it is essential to weigh the advantages of each method against their specific needs. Bolt heading may be more suitable for projects requiring larger diameters or lower volumes, while cold heading offers efficiency for high-volume orders with tight tolerances. Meanwhile, screw machining stands out for its capability to create complex parts but may involve higher costs and waste. By carefully assessing these aspects, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budgetary constraints.

Illustrative image related to bolt heading
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for bolt heading
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Bolt Heading?
When selecting bolts for various applications, understanding the technical properties is essential for ensuring product performance and meeting project requirements. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of the metal used in bolt manufacturing, which directly influences strength, corrosion resistance, and overall performance. Common material grades include low carbon steel, medium carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade is crucial for ensuring that the bolts can withstand specific environmental conditions, loads, and stress factors, thereby minimizing failure risks.
Tolerance
Tolerance defines the permissible limit of variation in a bolt’s dimensions, including diameter and length. It ensures that bolts fit precisely within their intended assemblies. Tighter tolerances often result in higher manufacturing costs, but they are essential for applications requiring precision, such as in the aerospace or automotive industries. For buyers, understanding tolerance requirements helps prevent assembly issues and enhances the reliability of the final product.

Illustrative image related to bolt heading
Diameter
The diameter of a bolt is critical for determining its load-bearing capacity and compatibility with nuts and pre-drilled holes. Bolt diameters typically range from 1/2 inch to 2-1/2 inches, depending on the heading process employed (hot or cold heading). B2B buyers should assess the specific requirements of their applications to ensure that the selected bolt diameter aligns with load requirements and structural integrity.
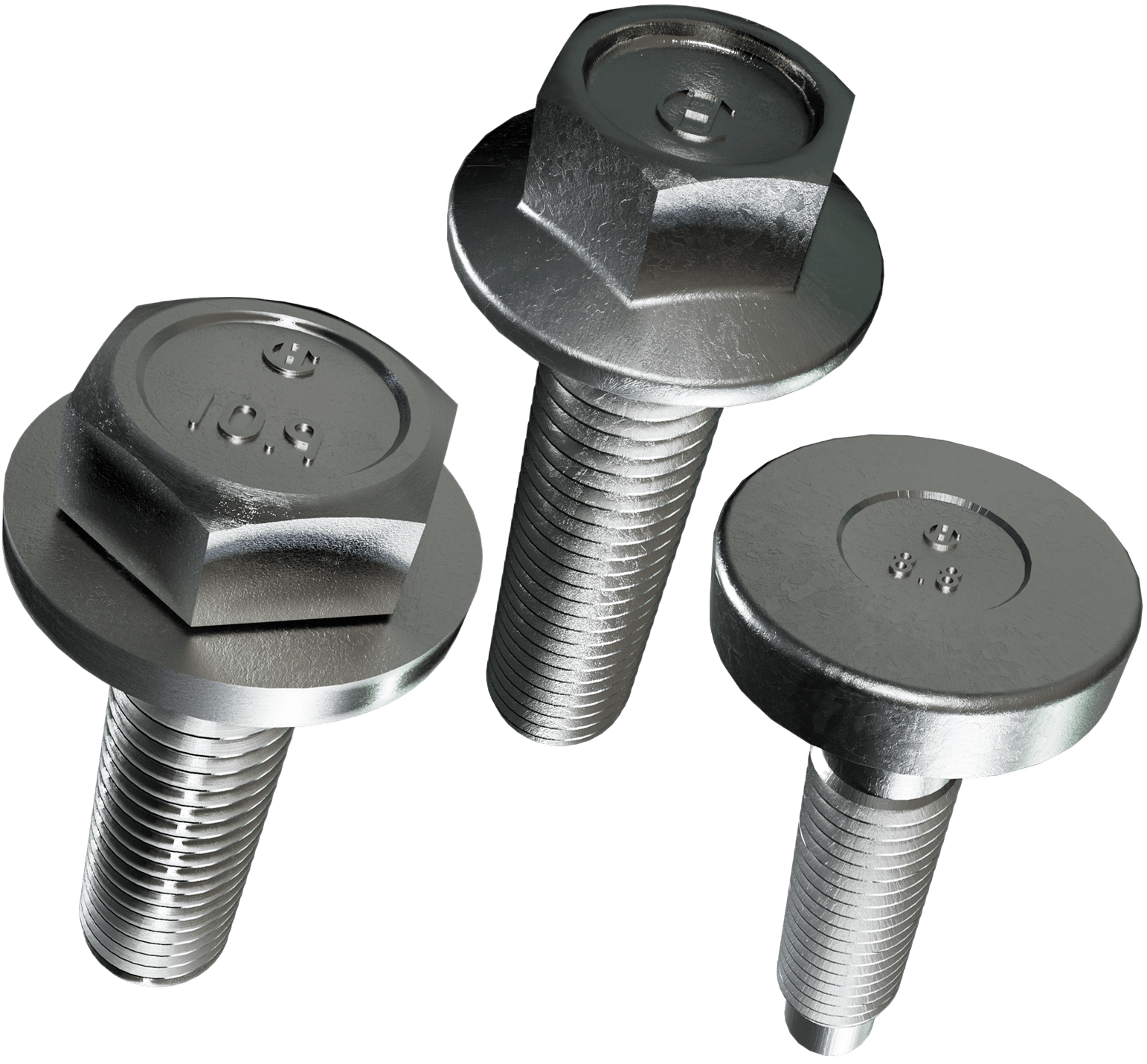
Head Style
The head style of a bolt (e.g., hex, square, or countersunk) affects its installation and the type of tool required for fastening. Different head styles offer various advantages, such as enhanced grip or aesthetic considerations. Buyers should consider the head style that best suits their assembly methods and design preferences to ensure efficient installation and optimal performance.
Strength
The strength of a bolt is determined by its material composition and manufacturing process. Strength ratings, such as ASTM grades, provide a standardized way to assess a bolt’s ability to withstand tensile and shear loads. For B2B buyers, understanding strength ratings is vital for selecting bolts that meet safety and performance standards in their specific applications.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Bolt Heading Industry?
Navigating the bolt heading industry requires familiarity with specific jargon. Here are some common trade terms that B2B buyers should understand:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that are used in another company’s end products. In the context of bolts, OEMs may require custom bolt specifications to meet the unique needs of their applications. Understanding OEM requirements is essential for suppliers to provide tailored solutions and maintain competitive advantage.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the minimum quantity of products that a supplier is willing to sell per order. This term is particularly important for B2B buyers as it influences purchasing decisions and inventory management. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their orders effectively, especially when managing budgets and storage capacities.
Illustrative image related to bolt heading
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. It typically includes detailed specifications, quantities, and delivery requirements. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ ensures that they receive competitive pricing and can compare different suppliers based on their offers.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. They specify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers engaged in cross-border transactions, as it clarifies the logistics and cost responsibilities associated with purchasing bolts.
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. In the fast-paced B2B environment, understanding lead times is essential for managing project timelines and ensuring that materials are available when needed. Buyers should communicate their lead time expectations clearly to suppliers to avoid delays.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing bolts, ensuring that they select the right products for their specific needs while fostering efficient supplier relationships.

Illustrative image related to bolt heading
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the bolt heading Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers Influencing the Bolt Heading Sector?
The global bolt heading market is experiencing significant shifts driven by various factors. Increased demand from construction, automotive, and aerospace industries is propelling growth, particularly in developing regions such as Africa and South America. The rise in infrastructure projects and manufacturing capabilities in these areas is leading to a heightened need for high-quality fasteners. Additionally, advancements in technology, such as automation and digitalization, are streamlining production processes and enhancing supply chain efficiencies. For international B2B buyers, understanding these dynamics is crucial for sourcing decisions.
Emerging trends in sourcing are also reshaping the landscape. The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, including IoT and AI, is enabling manufacturers to optimize production schedules and inventory management. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers seeking reliable suppliers who can offer just-in-time delivery and customized solutions. Moreover, the shift towards e-commerce platforms for procurement is making it easier for buyers in various regions to access a broader range of products and suppliers.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Bolt Heading Supply Chain?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the bolt heading sector. Environmental impacts associated with manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and material waste, are under scrutiny. Companies are increasingly prioritizing ethical sourcing and sustainability as part of their procurement strategies. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the environmental footprint of their suppliers is essential for aligning with global sustainability goals.
The demand for ‘green’ certifications and materials is on the rise. Suppliers who implement eco-friendly practices, such as using recycled materials or adopting energy-efficient production techniques, are gaining a competitive edge. This trend is particularly prominent in Europe, where regulations and consumer preferences are pushing for greater transparency and accountability in supply chains. Buyers are encouraged to seek out suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, ensuring that their sourcing decisions not only meet operational needs but also contribute to broader environmental objectives.
What Is the Historical Context of Bolt Heading in B2B Markets?
The bolt heading process has evolved significantly over the decades, adapting to changing industry needs and technological advancements. Initially, bolt heading was a labor-intensive process, primarily performed manually. However, with the advent of mechanization and later automation, the efficiency and precision of bolt manufacturing have dramatically improved. The introduction of hot and cold heading techniques has allowed manufacturers to cater to a wider range of specifications and applications.
Today, the industry continues to innovate, with a focus on enhancing production capabilities and reducing environmental impacts. Understanding this evolution provides B2B buyers with insights into the reliability and quality of products offered by different suppliers. As the market continues to evolve, maintaining awareness of historical trends can help buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and sustainability commitments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of bolt heading
-
How do I select the right bolt heading process for my project?
When choosing between hot heading and cold heading, consider the specific requirements of your project. Hot heading is ideal for larger diameters (over 1 1/8”) and lower volume orders, offering better formability with less die impact. Conversely, cold heading is more efficient for high-volume production, providing tighter tolerances and reduced waste. Evaluate factors such as the required dimensions, material type, and production volume to determine the best process for your needs. -
What are the advantages of using cold heading for bolt production?
Cold heading offers several benefits, particularly for high-volume manufacturing. It enhances the strength of components through work hardening, reduces material waste by reshaping rather than cutting, and allows for faster production cycles without the need for heating or cooling. This method also minimizes secondary operations, ensuring a cost-effective solution while achieving high precision. These advantages make cold heading a preferred choice for many industries, including automotive and construction. -
What customization options are available for bolt heads?
Most manufacturers offer extensive customization options for bolt heads, including different shapes (e.g., hex, square, or custom designs) and sizes. You can often request specific branding elements, such as your company name or logo, to be forged into the bolt head. Discuss your unique requirements with potential suppliers to understand their capabilities and ensure that they can meet your specifications. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for bolt heading?
The MOQ for bolt heading can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific manufacturing process used. Cold heading typically requires larger quantities due to the higher tooling costs, while hot heading may accommodate smaller orders. It’s essential to communicate your needs with suppliers early in the negotiation process to determine their MOQ and any potential flexibility they may offer. -
How can I vet suppliers for bolt heading?
When sourcing suppliers for bolt heading, assess their experience, manufacturing capabilities, and quality assurance processes. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicate adherence to quality management standards. Additionally, request samples of their work to evaluate the quality of their products. Engaging in direct communication with potential suppliers can also provide insights into their reliability and customer service. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing bolts internationally?
Payment terms in international transactions can vary widely. Common options include upfront payments, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Always clarify payment terms with your supplier before finalizing the order. Consider discussing flexible options, such as staggered payments based on production milestones, to mitigate financial risk and foster a trusting supplier relationship. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from bolt manufacturers?
Reputable bolt manufacturers typically implement rigorous quality assurance protocols, including material testing, dimensional inspections, and adherence to industry standards. Look for suppliers who provide detailed documentation of their QA processes and can demonstrate compliance with relevant certifications such as ASTM standards. Regular audits and feedback mechanisms are also crucial to maintaining product quality throughout the production process. -
How can I ensure timely logistics and delivery for my bolt orders?
To ensure timely logistics and delivery, discuss shipping methods and timelines with your supplier upfront. Factors such as production lead times, customs clearance, and local logistics capabilities can affect delivery schedules. Establish clear communication channels and consider using logistics partners familiar with international shipping to streamline the process. Additionally, building a buffer into your order timeline can help accommodate unforeseen delays.
Top 9 Bolt Heading Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Portland Bolt – Fasteners
Domain: portlandbolt.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Portland Bolt manufactures a wide range of fasteners including headed bolts, hex bolts, heavy hex bolts, structural bolts, square head bolts, timber bolts, headed anchor bolts, hex lag screws, square lag screws, carriage bolts, timber spikes, machine bolts, washer head bolts, round head bolts, countersunk bolts, step bolts, custom heading, guardrail bolts, rods, anchor rods, all thread rods, tie r…
2. TFG USA – Cold Heading Fasteners
Domain: tfgusa.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Cold heading is a high-speed metal forming process that shapes parts at room temperature without the need for heat. It is primarily used for forming the heads on fasteners like bolts, screws, rivets, and nails. Key advantages include minimal waste, faster production, stronger parts, reduced costs, and support for sustainable manufacturing. Cold heading is ideal for high-volume manufacturing, parti…
3. Autobolt USA – Cold Forming Fasteners
Domain: autoboltusa.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Cold Forming Capabilities: Threaded and Non-Threaded parts; Diameter range: 5/16-inch (M8) to 1 1/8-inch (M27); Lengths up to 12 inches (300 millimeters); Materials: low and medium carbon, boron, alloys, 300 and 400 series stainless steel, brass, aluminum, silicon bronze; High-speed bolt making process delivers parts that are headed, pointed, threaded, and ready for heat treat; Streamlined product…
4. Clark Engineering – Cold Heading Fasteners
Domain: clarkengineering.net
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Cold heading is a manufacturing process used to create bolts and fasteners from metal without wasting or removing material. It minimizes raw material waste and produces net-shaped parts with consistent designs. The process involves using specific machines tailored to the material and desired fastener type. Key products include slugs, which are cut from coil material, and the process is efficient, …
5. Tanner Bolt – BUTTON Height Fasteners
Domain: tannerbolt.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Tanner Bolt – BUTTON Height Fasteners, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
6. Fit Fastener – Hot and Cold Heading Manufacturing
Domain: fitfastener.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Hot and Cold Heading Manufacturing at Fastener Innovation Technology, Inc. includes:
1. **Hot Heading**:
– Available in a wide range of diameters.
– Suitable for various material grades, including Inconel 718.
– Advantages: Fewer die blows, better formability on certain head styles, lower tooling costs.
– Recommended for smaller lot runs or larger sizes; less cost-effective for small…
7. FastCo Industries – Custom Cold Headed Bolts and Screws
Domain: fastcoindustries.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Cold Headed Bolts and Screws Manufacturer, Custom, Made in the USA. Specializes in cold heading manufacturing since 1970. Types of fasteners include: Custom Bolts and Screws, Weld Bolts and Screws, Indented Hex Bolts and Screws, Shoulder Bolts and Screws, Collar Bolts and Screws, Isolator Bolts and Screws, Valve Cover Bolts and Screws. Size ranges: M3 to M18, lengths from 10mm to 225mm. Materials:…
8. Level 1 Fasteners – Cold Heading Fasteners
Domain: level1fasteners.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Cold heading process forming shapes without heat; fasteners sizes #2-56 to .875 DIA up to 7″ in length; manufacturing rods, headed bolts, and screws; heading styles: hex head, double hex head, button cap, socket cap, flat socket cap; commonly used materials: K500, 400 Monel, 304, 316, 4140, 8740; benefits: large quantity production, tight tolerances, reduced material waste, lower costs compared to…
9. B&D Cold Headed Products – High Strength Fasteners
Domain: bdcoldheadedproducts.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: B&D Cold Headed Products is a U.S. manufacturer of high strength cold-formed bolts, studs, pins, and other metal fasteners. Key product categories include:
– Threaded Bolts & Screws: Wheel Bolts, Hex Bolts & Screws, Square Head Bolts & Screws, Hex Flange Bolts, Plow Bolts, Shoulder Bolts, Carriage & Timber Bolts, Other Bolts & Screws.
– Threaded Studs: Double End Studs, Hex Studs, Continuous Thr…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for bolt heading
As the global demand for high-quality fasteners continues to rise, understanding the nuances of bolt heading processes—namely hot and cold heading—becomes essential for international buyers. Hot heading offers advantages in producing larger diameter bolts with lower tooling costs, making it ideal for specialized, low-volume orders. Conversely, cold heading is a cost-effective solution for high-volume production, yielding stronger and more precise components while minimizing waste.
Strategic sourcing in bolt heading not only enhances product quality but also optimizes supply chain efficiency, ensuring that businesses can meet their operational demands without compromising on performance. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers who can demonstrate expertise in both hot and cold heading processes. This ensures access to a diverse range of fasteners tailored to specific industry needs.
Looking ahead, as sustainability becomes a focal point in manufacturing, embracing efficient processes like cold heading can significantly reduce environmental impact. We encourage B2B buyers to leverage these insights and collaborate with trusted suppliers to secure a competitive edge in their markets. The future of bolt heading is bright, and the right strategic partnerships will pave the way for innovation and growth.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.