Best Acid For Etching Steel Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for best acid for etching steel
Navigating the intricate landscape of acid sourcing for etching steel poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. As industries increasingly rely on precise metal etching for applications ranging from automotive to electronics, understanding the best acid for etching steel becomes crucial. This comprehensive guide delves into the types of acids available, their specific applications, and the benefits they bring to diverse manufacturing processes. By offering insights into supplier vetting, cost considerations, and regional availability, this resource equips businesses with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions.
For buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Vietnam and Nigeria, the importance of sourcing reliable chemical suppliers cannot be overstated. This guide not only highlights the technical aspects of various etching acids—such as Ferric Chloride and Phosphoric Acid—but also addresses market trends and regulatory compliance, ensuring that your procurement strategy aligns with global standards.
By empowering B2B buyers with actionable insights and practical strategies, this guide serves as a vital tool for optimizing your supply chain and enhancing your competitive edge in the global market. Whether you are a seasoned manufacturer or a newcomer to the industry, our aim is to provide the clarity and confidence needed to navigate the complexities of acid procurement effectively.
Understanding best acid for etching steel Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ferric Chloride | Commonly used, safe to handle with proper precautions | PCB etching, custom markings on tools | Pros: Non-toxic, easy to use; Cons: Slower etching speed. |
| Nitric Acid | Strong oxidizing agent, fast etching capabilities | Industrial applications, metal artwork | Pros: Quick results; Cons: Highly corrosive, requires safety measures. |
| Phosphoric Acid | Good for surface preparation, less aggressive | Rust removal, surface treatment | Pros: Effective for cleaning; Cons: Slower etching process. |
| Hydrochloric Acid | Aggressive etching, effective on various metals | Heavy-duty industrial applications | Pros: Fast and powerful; Cons: Highly dangerous, requires special handling. |
| Citric Acid | Eco-friendly option, less hazardous | Food industry, decorative etching | Pros: Safe and biodegradable; Cons: Slower etching, less effective on hard metals. |
What Are the Characteristics of Ferric Chloride for Etching Steel?
Ferric chloride is a widely recognized acid for etching steel, particularly favored for its balance of effectiveness and safety. It is often used in PCB etching and can create custom markings on tools and components. Its ease of handling makes it accessible for small to medium-sized businesses. However, buyers should note that while it is non-toxic, the etching process can be slower compared to more aggressive acids, which may impact production timelines.
How Does Nitric Acid Compare for Industrial Applications?
Nitric acid is known for its rapid etching capabilities, making it suitable for industrial applications where time is of the essence, such as in metal artwork or high-volume manufacturing. Its strong oxidizing properties allow for quick results, but it is essential for buyers to consider the safety implications, as nitric acid is highly corrosive and requires stringent safety measures during handling. Companies must invest in proper protective equipment and training to mitigate risks.
What Role Does Phosphoric Acid Play in Surface Preparation?
Phosphoric acid is primarily used for surface preparation and rust removal. While it is less aggressive than other acids, it serves an essential function in cleaning metal surfaces before further processing or coating. This acid is particularly suitable for businesses focused on maintenance and restoration. However, its slower etching process may not meet the needs of companies requiring rapid production, making it crucial for buyers to evaluate their specific application requirements.

Illustrative image related to best acid for etching steel
Why Choose Hydrochloric Acid for Heavy-Duty Applications?
Hydrochloric acid is an aggressive etching agent that provides fast and effective results on various metals. It is commonly employed in heavy-duty industrial applications where quick turnaround times are critical. However, its highly dangerous nature necessitates careful handling and proper safety protocols. B2B buyers must weigh the benefits of speed against the safety risks and potential costs associated with protective measures and compliance.
Is Citric Acid a Viable Eco-Friendly Option for Etching?
Citric acid stands out as an eco-friendly alternative for etching steel, particularly appealing to businesses in the food industry and those focused on sustainability. While it is safe and biodegradable, its effectiveness may be limited on harder metals, and the etching process can be slower compared to other acids. Buyers looking for a safer option should consider citric acid, but they must also evaluate whether its slower performance aligns with their production needs.
Key Industrial Applications of best acid for etching steel
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of best acid for etching steel | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision components etching for aircraft parts | Enhances accuracy and reduces weight, improving fuel efficiency | Regulatory compliance, material compatibility, delivery timelines |
| Electronics | PCB manufacturing and custom metal parts for devices | Enables intricate designs and high-performance electronics | Quality certifications, sourcing of eco-friendly acids |
| Automotive | Decorative etching on automotive trim and parts | Adds aesthetic value and brand differentiation | Durability of etch, resistance to corrosion, environmental regulations |
| Medical Devices | Custom etching for surgical instruments and implants | Ensures precision and safety in critical applications | Biocompatibility, sterilization processes, supply chain reliability |
| Art and Design | Artistic etching for sculptures and bespoke items | Offers unique, personalized products that enhance market appeal | Customization options, turnaround time, material handling safety |
In the aerospace industry, best acids for etching steel are crucial for producing precision components used in aircraft. The ability to create intricate designs while minimizing weight is essential for enhancing fuel efficiency and overall performance. Buyers in this sector must consider regulatory compliance and the compatibility of the acid with various steel grades to ensure high-quality outcomes.
In electronics, acid etching is employed in the manufacturing of printed circuit boards (PCBs) and custom metal parts for devices. This process allows for the creation of intricate designs that are essential for high-performance electronics. International buyers need to prioritize suppliers who can provide quality certifications and eco-friendly acids to meet stringent environmental standards.
The automotive sector utilizes acid etching for decorative purposes on trim and components. This not only enhances the aesthetic appeal but also contributes to brand differentiation in a competitive market. Buyers should focus on the durability of the etching, its resistance to corrosion, and compliance with environmental regulations to ensure long-lasting results.

Illustrative image related to best acid for etching steel
In the field of medical devices, acid etching is vital for customizing surgical instruments and implants. Precision in etching guarantees safety and effectiveness in critical medical applications. Buyers must ensure that the acids used are biocompatible and suitable for sterilization processes, while also considering the reliability of supply chains to avoid disruptions.
Finally, in art and design, artists and manufacturers leverage acid etching to create unique sculptures and bespoke items. This technique allows for personalization, which can significantly enhance market appeal. Buyers in this industry should consider customization options, turnaround times, and material handling safety when sourcing acids for etching purposes.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘best acid for etching steel’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Etching Results Leading to Rework
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter issues with inconsistent etching results when using acids for steel etching. This inconsistency can stem from various factors, including improper acid concentration, inadequate surface preparation, or variations in etching time. Such variability not only leads to wasted materials and labor but also results in subpar products that require costly rework or replacement. In industries where precision is critical—such as aerospace or automotive manufacturing—these inconsistencies can have far-reaching implications, affecting timelines and customer satisfaction.
The Solution: To achieve consistent etching results, it’s essential to standardize your process. Begin by carefully measuring the acid-to-water ratio, adhering to recommended guidelines—typically a 50/50 mix for Ferric Chloride. This ensures a uniform etching strength. Surface preparation is equally critical; ensure that the steel is thoroughly cleaned with acetone to remove oils and contaminants that could affect adhesion. Document each etching batch, including time, concentration, and environmental conditions, to identify optimal parameters. Consider investing in a controlled environment for etching processes to minimize variations due to temperature or humidity. Regular training for your team on these best practices can further enhance consistency.

Illustrative image related to best acid for etching steel
Scenario 2: Health and Safety Risks During Etching Processes
The Problem: The use of acids for etching steel poses significant health and safety risks, particularly in regions with less stringent regulatory frameworks. Buyers often face challenges in ensuring that their teams are adequately trained and equipped to handle hazardous materials safely. Exposure to acid fumes can lead to respiratory issues, while improper handling can result in chemical burns or environmental contamination. This not only jeopardizes employee safety but also exposes the company to potential legal liabilities and financial losses.
The Solution: Implementing a robust health and safety protocol is vital. Begin by conducting a comprehensive risk assessment of your etching processes and providing detailed training to employees on the proper handling of acids. Ensure that personal protective equipment (PPE)—including gloves, goggles, and respirators—is readily available and mandatory during etching operations. Establish clear procedures for acid mixing and disposal to mitigate environmental impacts. Furthermore, consider collaborating with suppliers who can provide safer alternative etching solutions, such as less hazardous acid formulations or even non-acid-based methods. Regularly review and update safety protocols to align with international standards, fostering a culture of safety within your organization.
Scenario 3: Difficulty Sourcing Quality Acid for Steel Etching
The Problem: Sourcing high-quality acids for etching steel can be a significant hurdle for B2B buyers, especially in regions where access to reliable suppliers is limited. Many buyers struggle with inconsistent product quality, which can lead to unpredictable etching results. Additionally, regulatory restrictions may complicate the importation and handling of certain acids, further limiting options for buyers. This issue is particularly pressing for manufacturers in emerging markets, where local suppliers may not meet international quality standards.
The Solution: To overcome sourcing challenges, establish strong relationships with reputable suppliers who specialize in etching chemicals. Conduct thorough research and consider suppliers with a proven track record in quality and reliability. Look for suppliers that provide certifications and detailed product specifications to ensure compliance with industry standards. Additionally, consider forming partnerships with suppliers who can offer technical support and guidance on proper usage and handling. Explore bulk purchasing options to secure better pricing and ensure a consistent supply chain. If local sourcing is limited, investigate international suppliers with reliable shipping practices. Finally, consider diversifying your supplier base to mitigate risks associated with single-source dependence, ensuring that you have backup options in case of supply chain disruptions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for best acid for etching steel
When selecting the best acid for etching steel, it’s essential to consider various materials that can effectively achieve desired results while aligning with specific business needs. Below, we analyze four common acids used in the etching process, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
What are the Key Properties of Ferric Chloride for Etching Steel?
Ferric Chloride is a widely used acid in the etching of steel due to its effective corrosion properties. It operates well at room temperature and can be diluted with water, which enhances its versatility. The corrosion resistance of Ferric Chloride is particularly notable, as it can etch through various steel grades without excessive damage to the material itself.
Pros: Ferric Chloride is relatively inexpensive and readily available, making it an attractive option for businesses. It is also less hazardous than other acids, which simplifies handling and storage.
Cons: One limitation is that Ferric Chloride can lead to uneven etching if not applied correctly, requiring careful monitoring during the process. Additionally, it may not be suitable for high-precision applications due to its aggressive nature.
Illustrative image related to best acid for etching steel
How Does Nitric Acid Compare in Terms of Performance?
Nitric Acid is another popular choice for etching steel, known for its strong oxidizing properties. It can effectively etch a variety of metals and is particularly effective at creating fine details in the etching process. Nitric Acid operates well at elevated temperatures, which can enhance its etching speed and efficiency.
Pros: The primary advantage of Nitric Acid is its ability to produce clean and precise etches. It is also effective in removing oxides and other contaminants from the metal surface, which can improve the quality of the final product.
Cons: However, Nitric Acid is more hazardous than Ferric Chloride, requiring strict safety protocols during handling. It is also more expensive and may not be as readily available in certain regions, which could pose challenges for international buyers.

Illustrative image related to best acid for etching steel
What are the Benefits and Limitations of Hydrochloric Acid for Etching?
Hydrochloric Acid is known for its effectiveness in removing rust and scale from steel surfaces, making it a suitable option for etching. It operates effectively at ambient temperatures and is often used in combination with other acids to enhance etching performance.
Pros: The key advantage of Hydrochloric Acid is its rapid action, which can significantly reduce processing time. It is also relatively inexpensive and widely available, making it a practical choice for many businesses.
Cons: On the downside, Hydrochloric Acid can be highly corrosive, which poses risks to both equipment and personnel. It can also produce harmful fumes, necessitating adequate ventilation and protective measures.
Why is Phosphoric Acid a Viable Option for Steel Etching?
Phosphoric Acid is often used in the etching process for its ability to produce a milder etch compared to the other acids discussed. It is particularly effective for preparing surfaces for further processing, such as painting or coating.

Illustrative image related to best acid for etching steel
Pros: The main advantage of Phosphoric Acid is its lower corrosiveness, which makes it safer to handle. It is also effective at creating a uniform etch, which is essential for applications requiring consistent surface preparation.
Cons: However, Phosphoric Acid may not be as effective in deeply etching steel as other stronger acids. Its slower action can also lead to longer processing times, which might not be suitable for high-volume production environments.
Summary Table of Acid Materials for Etching Steel
| Material | Typical Use Case for best acid for etching steel | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ferric Chloride | General metal etching and PCB applications | Cost-effective and widely available | Can cause uneven etching | Low |
| Nitric Acid | High-precision etching for detailed designs | Produces clean, precise etches | More hazardous and expensive | High |
| Hydrochloric Acid | Rust removal and surface preparation | Rapid action reduces processing time | Highly corrosive and produces harmful fumes | Low |
| Phosphoric Acid | Surface preparation for coatings | Lower corrosiveness and safer handling | Slower etching process | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview of the acids used for etching steel, offering valuable insights for international B2B buyers. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each acid can help businesses make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for best acid for etching steel
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Producing Acid for Etching Steel?
The manufacturing of acids used for etching steel involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the quality and effectiveness of the final product. Understanding these processes allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
How Is Material Prepared for Acid Production?
The initial stage in the manufacturing process is material preparation, which involves sourcing high-purity raw materials. For acids like Ferric Chloride or Hydrochloric Acid, the quality of the raw materials is paramount. Suppliers typically perform rigorous checks on incoming materials, ensuring they meet chemical purity standards necessary for etching applications.

Illustrative image related to best acid for etching steel
Once the materials are verified, they undergo processing in controlled environments to prevent contamination. This may include grinding solid materials into fine powders or mixing liquids in precise ratios. Advanced techniques like spectrometry may be employed to analyze the composition, guaranteeing that the materials are suitable for acid production.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Acid Manufacturing?
Following material preparation, the next phase is forming, where raw materials are transformed into the desired acid formulations. This process can involve chemical reactions that require specific temperature and pressure controls. For instance, in the production of Ferric Chloride, iron oxide reacts with hydrochloric acid, necessitating precise control over reaction conditions to achieve the correct concentration.
Additionally, manufacturers may use automated systems to ensure consistency in the mixing and blending of ingredients. This automation reduces human error and enhances the repeatability of the production process, which is crucial for maintaining product quality.
How Is Assembly and Packaging Handled in Acid Production?
The assembly stage in acid production primarily concerns the packaging of the finished product. Proper packaging is essential to preserve the integrity and safety of the acids during storage and transportation. Typically, acids are stored in high-density polyethylene (HDPE) containers or glass bottles, which are resistant to corrosion.
Quality checks are performed at this stage to ensure that packaging meets international safety standards. Labels must clearly indicate hazard warnings and handling instructions, complying with regulations such as the Globally Harmonized System (GHS) for chemical labeling.

Illustrative image related to best acid for etching steel
What Finishing Processes Are Involved in Acid Production?
The finishing stage includes final quality assessments and adjustments to ensure that the acid formulations meet the specified criteria for etching. This may involve diluting concentrated acids to achieve the desired strength or adding stabilizers to enhance shelf life.
After formulation, the acids undergo filtration to remove any impurities or particulates that could affect performance. Advanced testing techniques, such as titration and pH measurement, are employed to confirm the final product’s chemical properties.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Acid Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is crucial in the acid manufacturing process, ensuring that each batch meets international and industry-specific standards. B2B buyers must be aware of these QA measures to verify the reliability of their suppliers.
What International Standards Are Relevant for Acid Manufacturing?
ISO 9001 is the primary international standard for quality management systems, applicable across various industries, including chemical manufacturing. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a manufacturer has established a systematic approach to quality management, including continuous improvement.
In addition to ISO 9001, other standards such as CE marking for European markets and API specifications for petroleum-related acids play a significant role in ensuring product safety and efficacy. These certifications provide assurance that the acids produced are safe for their intended applications.

Illustrative image related to best acid for etching steel
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Acid Production?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are implemented throughout the manufacturing process to maintain high standards. These typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are tested for purity and compliance with specifications before entering production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, samples are taken at various stages to monitor parameters such as pH, concentration, and reaction temperatures.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The finished products undergo comprehensive testing to ensure they meet the required specifications for acid concentration and purity before being released for distribution.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Acid Quality Control?
Common testing methods in acid quality control include:
- Titration: This method measures the concentration of acids by reacting them with a base of known concentration.
- pH Testing: Essential for assessing the acidity level, pH testing ensures that the product is within the specified range for etching applications.
- Spectrophotometry: This technique analyzes the absorption of light by the acid solution, providing insight into its concentration and purity.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Measures?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control measures of their suppliers to ensure they receive high-quality acids. Here are several strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols. This includes reviewing documentation, inspecting facilities, and assessing compliance with international standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can help buyers understand the QC processes employed by suppliers. These reports should include data on testing results, compliance with standards, and any corrective actions taken.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. These organizations often have expertise in specific industries and can offer valuable insights into supplier performance.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is essential. Differences in regulatory requirements can affect how products are manufactured and tested.
Buyers should be aware of regional certifications and standards that may apply to their specific markets. For example, compliance with local regulations in African countries may differ significantly from those in Europe. It’s crucial to establish clear communication with suppliers to ensure that all necessary certifications are obtained and that products are compliant with both local and international standards.

Illustrative image related to best acid for etching steel
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for acids used in etching steel is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on supplier verification, international standards, and quality control checkpoints, buyers can ensure they procure high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘best acid for etching steel’
Acid etching is a widely used method for creating intricate designs and patterns on steel surfaces. For international B2B buyers seeking to procure the best acid for etching steel, understanding the sourcing process is crucial. This guide provides a systematic checklist to streamline your procurement efforts.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the specific requirements for the acid you need for etching steel. Consider factors such as the type of steel, desired etching depth, and the intricacy of designs. This step ensures that you communicate effectively with suppliers and select a product that meets your exact needs.
Step 2: Research Suitable Acid Options
Investigate different types of acids suitable for etching steel, such as Ferric Chloride and Nitric Acid. Each acid has unique properties and applications; for instance, Ferric Chloride is popular for its effectiveness and availability. Understanding these differences allows you to make informed decisions based on your specific etching requirements.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, vet suppliers thoroughly to ensure reliability and quality. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from other buyers in similar industries or regions. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in delivering quality acids and support services.
- Check Certifications: Ensure that suppliers have relevant certifications, such as ISO or local chemical safety regulations, to guarantee the quality and safety of their products.
- Assess Customer Support: Reliable customer service can be crucial for resolving issues that may arise post-purchase.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples of the acids you are considering. Testing these samples on your specific steel types will help you evaluate performance and compatibility. This step minimizes the risk of investing in a product that does not meet your expectations.
Step 5: Understand Pricing Structures
Analyze the pricing models offered by potential suppliers. Consider factors such as bulk discounts, shipping costs, and payment terms. Understanding the total cost of ownership, including potential import duties for international shipping, will help you budget effectively.
Step 6: Review Safety and Handling Guidelines
Ensure that the suppliers provide comprehensive safety and handling instructions for the acids. This information is critical for maintaining a safe work environment and complying with local regulations. Look for suppliers who prioritize safety and can offer technical support if needed.
- Packaging Standards: Verify that the acid is packaged appropriately to prevent leaks and ensure safe transport.
- Disposal Guidelines: Suppliers should also provide guidance on the environmentally responsible disposal of any waste materials.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase Agreement
Once you have selected a supplier, finalize the purchase agreement. Ensure that all terms, including delivery timelines, payment terms, and return policies, are clearly outlined. This step protects your interests and establishes a clear understanding between both parties.

Illustrative image related to best acid for etching steel
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can efficiently navigate the procurement process for the best acid for etching steel, ensuring high-quality results and compliance with safety standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for best acid for etching steel Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Acid for Etching Steel?
When sourcing acids for etching steel, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The type of acid selected—such as Ferric Chloride, hydrochloric acid, or sulfuric acid—directly impacts the base material cost. High-purity chemicals typically command higher prices due to their quality and effectiveness.
-
Labor: The labor costs encompass both the workforce involved in the manufacturing process and the technical expertise required to ensure proper handling and application of the acids.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead, impacting the overall price.
-
Tooling: Depending on the scale of production, specialized tooling may be required to handle the acids safely. This can add to the initial investment but may lead to long-term savings through increased efficiency.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring that the acids meet industry standards and certifications is crucial. Costs associated with QC processes can vary significantly, depending on the regulations in the buyer’s region.
-
Logistics: Shipping acids internationally involves compliance with various regulations, which can influence logistics costs. These costs may include packaging, insurance, and customs duties.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and risks. This margin can vary based on market demand and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Acid Pricing for Etching Steel?
Several factors influence pricing in the B2B acid market, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often qualify for bulk pricing, reducing the per-unit cost. Buyers should assess their needs carefully to negotiate favorable terms.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom formulations or specific concentrations may increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Premium products that come with quality certifications can demand higher prices. Buyers should weigh the benefits of quality against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: Reputation, reliability, and service levels of suppliers play a crucial role in pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but can offer better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital for pricing negotiations. They dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, impacting the total landed cost.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Negotiating Acid Prices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are some strategic tips:

Illustrative image related to best acid for etching steel
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate on price, especially when ordering in bulk. Suppliers may have flexibility in pricing that can lead to significant savings.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the total cost of ownership, including shipping, handling, and potential waste. A slightly higher upfront cost may result in lower overall expenses.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations and economic conditions in both the supplier’s and buyer’s countries. These factors can affect pricing and should be considered in negotiations.
-
Local Regulations: Familiarize yourself with local regulations regarding the importation of chemicals. Compliance costs can vary significantly and impact the total cost.
-
Supplier Relationships: Building long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Regular communication and feedback can foster trust and collaboration.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for acids used in etching steel can vary widely based on the factors discussed. The information provided serves as a guideline, and buyers should conduct thorough market research and obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure they are getting the best value for their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing best acid for etching steel With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Acid for Etching Steel
In the manufacturing and metalworking industries, etching steel is a common practice for creating intricate designs, enhancing aesthetics, or preparing surfaces for further processing. While acids, such as ferric chloride, are widely recognized as effective solutions for this purpose, there are several alternative methods available. This analysis will compare the best acid for etching steel against other viable solutions, allowing B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs.
| Comparison Aspect | Best Acid For Etching Steel | Laser Cutting | Water Jet Cutting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and detail | Excellent for intricate cuts | Versatile across materials |
| Cost | Moderate cost | High initial investment | Moderate to high cost |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires safety precautions | Requires skilled operators | Requires specialized equipment |
| Maintenance | Regular handling of chemicals | Low maintenance | Moderate maintenance |
| Best Use Case | Detailed etching | Cutting complex shapes | Thick materials and hard metals |
What Are the Benefits of Using Laser Cutting as an Alternative?
Laser cutting is a non-contact method that utilizes a focused beam of light to cut through steel and other materials. Its primary advantage lies in its ability to produce intricate shapes with exceptional precision, making it suitable for applications that require fine details, such as custom components or artistic designs. However, the initial investment in laser cutting equipment can be substantial, and skilled operators are necessary to ensure optimal results. Additionally, while laser cutting can achieve clean edges, it may not provide the same depth of etching as acid methods.
How Does Water Jet Cutting Compare to Acid Etching?
Water jet cutting employs high-pressure streams of water, often mixed with abrasives, to cut through various materials, including steel. One of its key benefits is versatility; it can process a wide range of materials without altering their intrinsic properties. Water jet cutting is particularly effective for thick materials and can achieve smooth finishes without the heat-affected zones associated with laser cutting. However, like laser cutting, the equipment costs can be significant, and the process may involve higher maintenance compared to traditional acid etching methods.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Etching Solution for Your Needs
When considering the best approach for etching steel, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific requirements, including the intricacy of designs, material thickness, budget constraints, and available expertise. While acids such as ferric chloride remain a popular choice for their affordability and effectiveness in detailed etching, alternatives like laser and water jet cutting offer unique advantages. By weighing the pros and cons of each method, businesses can select the most suitable solution that aligns with their operational needs and enhances their production capabilities.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for best acid for etching steel
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Acids for Etching Steel?
When selecting the best acid for etching steel, understanding critical technical properties is essential. Here are several specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
1. Concentration Level
The concentration of the acid is crucial for effective etching. For example, Ferric Chloride is commonly used at a concentration of 30-40%. A higher concentration can lead to faster etching but may also increase the risk of over-etching or damaging the substrate. Buyers should assess the optimal concentration based on their specific applications and desired outcomes, ensuring a balance between efficiency and quality.
2. pH Level
The pH level indicates the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. Most etching acids are acidic, with pH levels typically below 7. Maintaining the appropriate pH is vital for achieving consistent etching results. A pH that is too low can lead to excessive etching or corrosion of the metal, while a higher pH might result in inadequate material removal. Understanding the pH can help buyers tailor the etching process to meet their requirements.
3. Viscosity
Viscosity affects how the acid interacts with the metal surface during etching. A more viscous solution may adhere better to the metal, allowing for a more uniform etch. Conversely, lower viscosity allows for better penetration into intricate designs. Buyers should consider the viscosity of the etching acid in relation to the complexity of the components they are processing.
4. Temperature Stability
The effectiveness of etching acids can change with temperature fluctuations. Many acids perform optimally within a specific temperature range. Buyers must ensure that their processes can maintain these temperatures to achieve consistent etching results. Understanding temperature stability also aids in the safe handling and storage of acids.
5. Material Compatibility
Different acids interact uniquely with various types of steel and coatings. For instance, certain acids may be suitable for stainless steel but could damage other alloys or coatings. Buyers should conduct compatibility tests with their specific materials to prevent unexpected reactions and ensure high-quality etching.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Acids for Etching Steel?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B sector. Here are some common terms relevant to the procurement of etching acids:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products based on the specifications provided by another company. In the context of etching acids, buyers may work with OEMs to develop custom formulations tailored to specific applications. Understanding OEM relationships can enhance collaboration and product development.
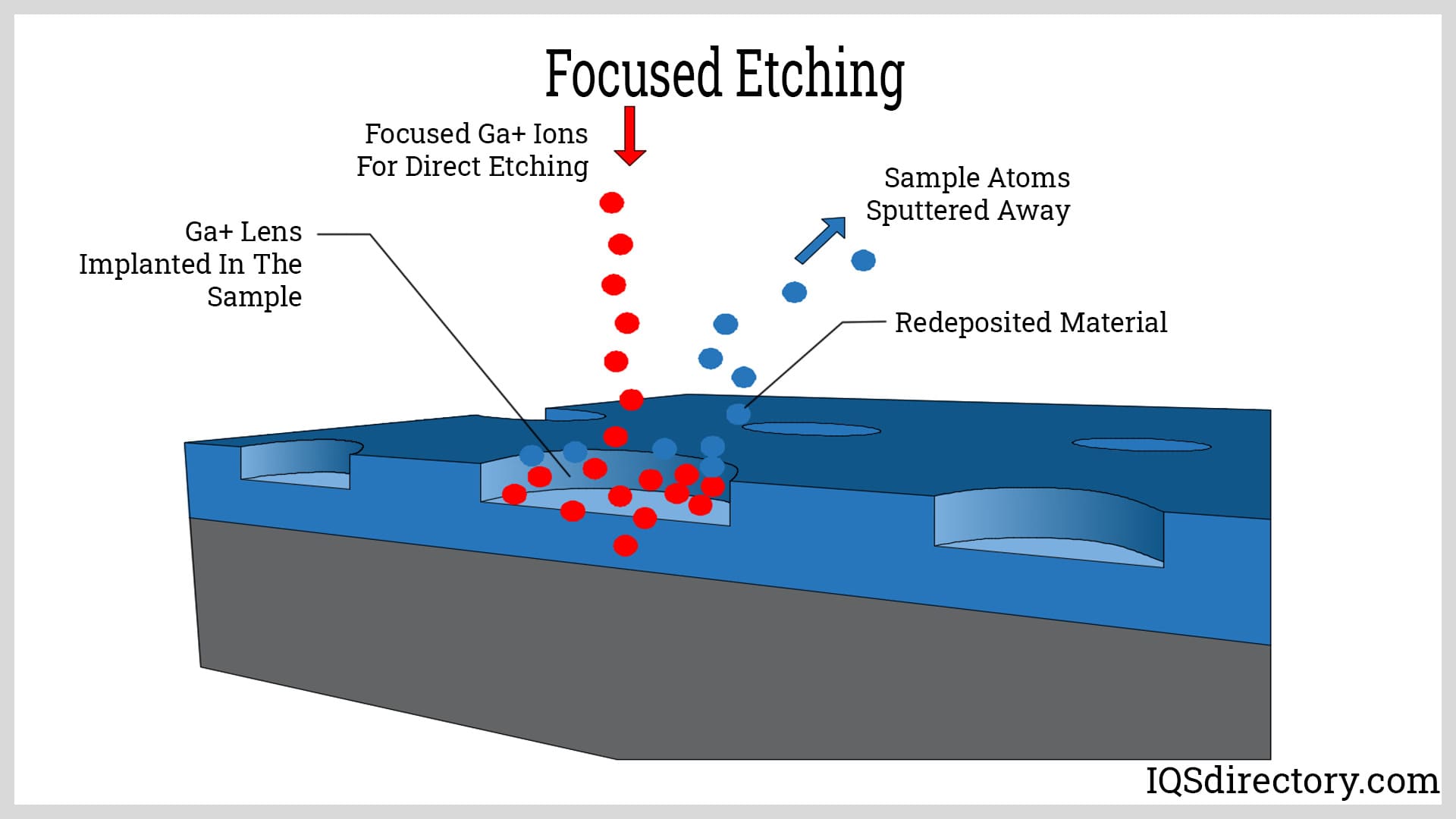
Illustrative image related to best acid for etching steel
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ denotes the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For acids used in etching, MOQs can vary significantly between suppliers and may affect procurement strategies. Buyers should clarify MOQs to optimize inventory management and cost-effectiveness.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal request sent to suppliers to obtain pricing and terms for specific products. When sourcing etching acids, submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare options and negotiate better deals. Including detailed specifications in RFQs can result in more accurate quotes and streamlined procurement.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade transactions. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B buyers importing etching acids, as they clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms can mitigate risks and ensure smoother logistics.

Illustrative image related to best acid for etching steel
5. Batch Number
The batch number is a unique identifier assigned to a specific production run of a product, including etching acids. This information is essential for traceability, quality control, and compliance with safety regulations. Buyers should request batch numbers to ensure they receive consistent and reliable products.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding the selection and procurement of acids for etching steel, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and product quality.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the best acid for etching steel Sector
What Are the Global Drivers Shaping the Market for Acid Used in Steel Etching?
The demand for acids used in steel etching is primarily driven by advancements in manufacturing technologies and the increasing need for precision in metalworking. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics are pushing the boundaries of manufacturing, requiring more intricate designs and higher quality finishes. As global competition intensifies, manufacturers are investing in acid etching processes that enhance product aesthetics and performance. Additionally, the rise of custom fabrication services has led to a surge in demand for specialized etching techniques, contributing to market growth.
Emerging technologies, such as photochemical etching and laser cutting, are transforming traditional practices, offering more efficient and environmentally friendly alternatives. Moreover, the growing trend of Industry 4.0, with its emphasis on automation and data integration, is reshaping sourcing strategies. Buyers are now looking for suppliers that can provide not just high-quality acids, but also advanced delivery systems and real-time inventory management.
In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, international buyers must navigate a complex landscape of regulations and market dynamics. Factors such as currency fluctuations, trade tariffs, and geopolitical tensions can influence sourcing decisions. Understanding local market conditions and establishing strong relationships with suppliers is crucial for securing competitive pricing and reliable supply chains.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Acid Etching Market?
Environmental sustainability is becoming increasingly important in the acid etching sector, as buyers are more inclined to partner with suppliers that prioritize eco-friendly practices. The use of acids like Ferric Chloride, while effective, poses potential environmental hazards if not managed properly. Buyers are advised to seek suppliers who adhere to stringent safety and environmental regulations to mitigate risks.
The trend towards ethical sourcing is also gaining traction, with businesses striving to ensure that their supply chains are free from harmful practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainable practices. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that can demonstrate transparency in their sourcing processes and provide documentation regarding the environmental impact of their products.
The emergence of ‘green’ acids—those made from biodegradable materials or that can be neutralized without harmful byproducts—offers a promising alternative for environmentally conscious businesses. By investing in these sustainable options, companies can not only reduce their ecological footprint but also enhance their brand reputation among increasingly eco-aware consumers.
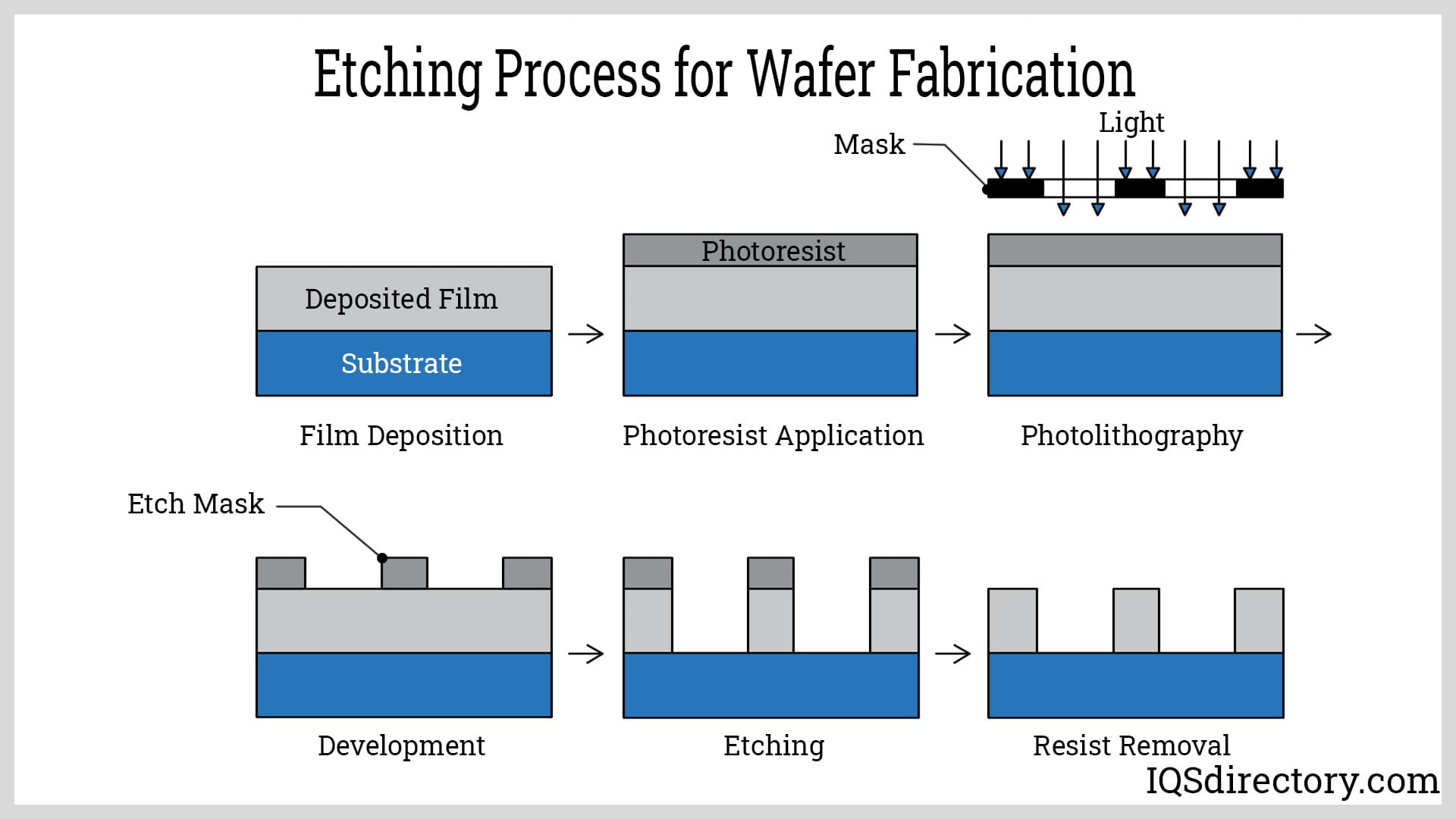
Illustrative image related to best acid for etching steel
What Is the Historical Context of Acid Use in Steel Etching?
The practice of acid etching dates back centuries, with early applications seen in the creation of decorative metalwork and intricate designs. Initially, acids were primarily used for artistic purposes, but as industrial processes evolved, so did the applications of acid etching in manufacturing. The introduction of more sophisticated chemical milling techniques in the mid-20th century marked a significant turning point, allowing for greater precision and efficiency.
As industries began to adopt more complex designs and materials, the demand for effective etching agents grew. Today, acids such as Ferric Chloride and Hydrochloric Acid are widely used not only for their effectiveness but also for their relative ease of handling compared to earlier methods. This evolution reflects the broader trends in manufacturing towards precision, customization, and sustainability, underscoring the importance of acid etching in modern industrial applications.
In conclusion, as international B2B buyers navigate the acid etching landscape, a clear understanding of market dynamics, sustainability considerations, and the historical evolution of these practices will empower them to make informed sourcing decisions.

Illustrative image related to best acid for etching steel
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of best acid for etching steel
-
How do I choose the right acid for etching steel?
Choosing the right acid for etching steel largely depends on the desired outcome and the specific type of steel you are working with. Ferric chloride is commonly used due to its effectiveness and availability, especially in PCB applications. However, other acids like nitric acid and hydrochloric acid can also be considered depending on the intricacy of the design and the etching depth required. Always review the manufacturer’s specifications and conduct small-scale tests to ensure compatibility and desired results. -
What is the best acid for etching steel?
Ferric chloride is widely regarded as one of the best acids for etching steel due to its balanced etching speed and ease of use. It produces clean lines and is less hazardous compared to stronger acids. For more aggressive etching, hydrochloric acid can be used, but it requires more safety precautions. It’s essential to evaluate the specific requirements of your project, including the type of steel, complexity of designs, and safety considerations. -
What safety precautions should I take when using etching acids?
Safety is paramount when working with etching acids. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, goggles, and protective clothing. Work in a well-ventilated area or use fume hoods to prevent inhalation of harmful vapors. Ensure that you have neutralizing agents like baking soda on hand for spills and understand proper disposal methods for used chemicals to avoid environmental hazards. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for etching acids?
Minimum order quantities for etching acids can vary significantly among suppliers. Generally, manufacturers may require an MOQ ranging from 5 to 100 liters, depending on the type of acid and the scale of your business. It’s advisable to communicate your specific needs and negotiate terms directly with suppliers to find a mutually beneficial arrangement. -
How can I vet suppliers of etching acids?
Vetting suppliers is crucial for ensuring product quality and reliability. Start by checking for certifications, such as ISO standards, which indicate adherence to quality management systems. Request samples to assess product quality and evaluate customer reviews or testimonials. Furthermore, consider suppliers’ production capabilities, delivery times, and their willingness to provide technical support for your etching processes. -
What payment terms are typical for international purchases of etching acids?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier and the nature of the transaction. Common terms include upfront payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. For large orders, suppliers may offer flexible terms, including partial payments. Always clarify payment methods, currency, and any potential fees associated with international transactions to avoid misunderstandings. -
How does logistics work for shipping etching acids internationally?
Shipping etching acids internationally requires compliance with various regulations regarding hazardous materials. Ensure that your supplier is experienced in handling such logistics and can provide proper documentation, including safety data sheets (SDS). Discuss shipping methods, insurance options, and estimated delivery times. Additionally, be aware of customs regulations in your country to avoid delays or fines. -
What quality assurance measures should I consider when sourcing etching acids?
Quality assurance is critical when sourcing etching acids to ensure consistency and safety. Inquire about the supplier’s quality control processes, including batch testing and certifications. Request samples for testing before making large purchases and consider third-party testing if necessary. Establishing a clear agreement on quality standards and expectations can help mitigate risks associated with product defects.
Top 9 Best Acid For Etching Steel Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Instructables – Acid Etching Supplies
Domain: instructables.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Supplies needed for acid etching: Ferric Chloride (PCB etch), plastic container, distilled water, etch resist/stencil (nail polish, stickers, vinyl, electrical tape, Sharpie marker), acetone, cotton swabs/Q-tips, paperclip/dental floss, rubber gloves, high grit wet/dry sandpaper or steel wool. Safety precautions include wearing rubber gloves and working in a well-ventilated area.
2. Online Metals – DIY Acid Etching Supplies
Domain: onlinemetals.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: DIY Acid Etching is an art style that allows users to create images on metal by using acid to selectively burn away parts of the material. Popular items for etching include printing plates, decorative plates, jewelry, and knife blades. The process involves coating the metal with an acid-resistant substance called Resist, which protects the underlying metal from being etched. Common metals for etch…
3. iForge Iron – Steel Etching Acids
Domain: iforgeiron.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Acids mentioned for etching steel include: Ferric Chloride, Nital, HCL, and traditional Zag. Users have reported good results with mild steel and Ferric Chloride, but noted that it may not affect high carbon steels. The discussion also highlights the importance of the acid concentration and soak time for effective etching. Wootz steel etching is mentioned, with a focus on the role of carbides and …
4. Bladesmiths Forum – Recommended Etching Acids
Domain: bladesmithsforum.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: 1. Recommended Acids for Etching:
– Nitric Acid: Best for etching wrought iron, quicker on slag than iron.
– Ferric Chloride: Recommended for copper and steel; dilute 1:4 with distilled water for steel.
– Hydrochloric Acid (HCl): Can be used for removing scale but not recommended for pattern welding due to even etching.
2. Availability:
– Ferric Chloride is available at elec…
5. Craftsuprint – Etching Steel Solutions
Domain: craftsuprint.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Type of Steel: Mild steel, stainless steel, high-carbon steel. Etching Acids: Muriatic (hydrochloric) acid (HCl), nitric acid (HNO3), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), ferric chloride (FeCl3), copper sulfate (CuSO4). Preparation Tools: Chlorine cleanser, abrasive sponge, wire brush, fine steel wool, wet number 600 emery paper, corundum paper, turpentine, acetone, alcohol, methyl hydrate. Safety Equipment: Ru…
6. ResearchGate – Stainless Steel Etching Solutions
Domain: researchgate.net
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: 1. **Nital**: Not effective for 316 stainless steel.
2. **HCl + Nitric Acid**: 119ml HCl + 12ml Nitric acid + 119ml distilled water – works well for 316L.
3. **Oxalic Acid**: Saturated solution diluted by 10%vol in deionized water; electrolytic etching recommended at 2V-5V for 10-30 seconds.
4. **Villela Reagent**: 1g picric acid, 5cm3 HCl, 100cm3 ethanol.
5. **Ferric Chloride Solution**: Atta…
7. Practical Machinist – Ferric Chloride Etchant
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Ferric Chloride (PCB etchant) is used for etching metals, particularly effective for blackwashing blades and etching brass for name plates. It is noted for its rapid loss of effectiveness when reacting with copper, creating sludge that coats the etching surface. Users recommend starting with fresh ferric chloride for optimal results. Mixing citric acid into ferric chloride can enhance its cutting …
8. WikiHow – Acid Etching Steel Guide
Domain: wikihow.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Acid etching steel involves using various types of steel such as mild steel, stainless steel, or high-carbon steel. The process requires specific acids or chemicals for etching, including muriatic (hydrochloric) acid, nitric acid, sulfuric acid, ferric chloride, and copper sulfate. Preparation steps include choosing the type of steel, removing burrs, scrubbing the surface, rinsing, and cleaning wi…
9. ACE – Acid Etching Solutions
Domain: ace-uk.net
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Acid Etching is a process used to cut hard surfaces, such as metal, using specially formulated acids to create designs. ACE manufactures millions of acid etched components annually, applying the process to over 2000 different metals in thicknesses from 5 microns to 2.5mm. The process involves several steps: cleaning the metal, applying a photosensitive resist, transferring designs, developing, etc…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for best acid for etching steel
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers on Acid Sourcing for Steel Etching?
In conclusion, selecting the right acid for etching steel involves understanding the specific needs of your application, whether for intricate designs or robust industrial processes. Ferric chloride remains a popular choice due to its effectiveness and ease of handling, but alternatives such as hydrochloric acid and phosphoric acid may also be viable depending on your operational requirements. Strategic sourcing is paramount; establishing relationships with reliable suppliers can ensure consistent quality and supply chain resilience, especially for international buyers from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Operations?
By prioritizing strategic sourcing, businesses can not only optimize costs but also enhance product quality and compliance with safety regulations. Engaging with suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices will also position your company favorably in a competitive market.
What’s Next for International B2B Buyers in Acid Sourcing?
As you consider your sourcing strategies, keep an eye on emerging trends and innovations in chemical etching processes. The future of metal etching will likely integrate more eco-friendly practices, which could further enhance your brand’s reputation. Take proactive steps today by reaching out to potential suppliers, exploring new partnerships, and investing in technology that aligns with your operational goals. Embrace the journey of strategic sourcing to ensure your business remains at the forefront of the industry.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to best acid for etching steel
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.