Bearing Parts: The Ultimate 2025 B2B Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for bearing parts
Navigating the global market for bearing parts can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The challenge often lies in sourcing high-quality components that meet specific operational needs while ensuring cost-effectiveness. This guide is designed to alleviate those challenges by providing a comprehensive overview of bearing parts, including various types, applications, and critical factors to consider when selecting suppliers.
Within these pages, you will find detailed insights into the diverse categories of bearings—from ball and roller bearings to specialized options for extreme environments. We delve into their applications across multiple industries, ensuring that buyers can identify the right products for their unique requirements. Furthermore, the guide addresses the essential process of vetting suppliers, empowering you with the knowledge to make informed decisions and avoid common pitfalls associated with international procurement.
By understanding the intricacies of bearing parts and the global market landscape, B2B buyers will be better equipped to navigate their purchasing strategies. This guide not only facilitates smarter buying choices but also enhances operational efficiency, ultimately leading to more successful business outcomes. Whether you’re in Saudi Arabia, Vietnam, or beyond, the insights contained herein will serve as a valuable resource in your sourcing endeavors.
Understanding bearing parts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ball Bearings | Spherical rolling elements, low friction, versatile design. | Automotive, machinery, appliances. | Pros: High speed, low noise. Cons: Limited load capacity. |
| Roller Bearings | Cylindrical rolling elements, higher load capacity than balls. | Heavy machinery, construction equipment. | Pros: Better load distribution. Cons: Higher friction than ball bearings. |
| Needle Bearings | Slim cylindrical rollers, compact design for space constraints. | Automotive, aerospace, industrial tools. | Pros: Excellent for tight spaces. Cons: Less durable under shock loads. |
| Tapered Roller Bearings | Conical shape allows for axial and radial load handling. | Trucks, trailers, heavy machinery. | Pros: High load capacity and stability. Cons: Complex installation and alignment. |
| Thrust Bearings | Designed to support axial loads, featuring flat surfaces. | Gearboxes, automotive applications. | Pros: Efficient axial load handling. Cons: Limited radial load capacity. |
What Are the Characteristics of Ball Bearings and Their Suitability for B2B Buyers?
Ball bearings are among the most common types of bearings, featuring spherical rolling elements that reduce friction and enable smooth rotation. Their versatile design makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, including automotive, machinery, and household appliances. B2B buyers should consider their operational speed and noise levels, as ball bearings excel in high-speed applications but have a limited load capacity compared to other types. When selecting ball bearings, ensure compatibility with the intended application to optimize performance.
How Do Roller Bearings Differ and What Are Their Key Applications?
Roller bearings utilize cylindrical rolling elements, which provide a larger contact area than ball bearings, allowing them to handle higher loads. This makes them particularly useful in heavy machinery and construction equipment. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of improved load distribution against the increased friction, which may affect efficiency. When sourcing roller bearings, consider the specific load requirements and operating conditions to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Why Are Needle Bearings Ideal for Space-Constrained Applications?
Needle bearings are characterized by their slim cylindrical rollers, making them ideal for applications with limited space, such as in automotive and aerospace components. Their design allows for a compact configuration while maintaining functionality. However, B2B buyers must be cautious about their durability under shock loads, as needle bearings can be more susceptible to wear in high-impact situations. It’s essential to evaluate the environmental conditions and load characteristics before selecting needle bearings for specific applications.
What Are the Advantages of Tapered Roller Bearings for Heavy Loads?
Tapered roller bearings feature conical rolling elements that enable them to handle both axial and radial loads effectively. This dual capacity makes them a preferred choice for trucks, trailers, and heavy machinery. Buyers should appreciate the high load capacity and stability offered by tapered roller bearings, but they must also consider the complexities involved in installation and alignment. Proper installation is critical for maximizing their performance, so sourcing from reputable manufacturers is advisable.
How Do Thrust Bearings Function and What Should Buyers Consider?
Thrust bearings are specifically designed to support axial loads, featuring flat surfaces that facilitate efficient load handling. They are commonly used in gearboxes and various automotive applications. While thrust bearings excel in managing axial loads, they are not suitable for radial loads, which is a critical consideration for B2B buyers. When selecting thrust bearings, it’s important to understand the load dynamics of the application to avoid premature failure and ensure operational efficiency.
Key Industrial Applications of bearing parts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of bearing parts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Wheel hubs and transmission systems | Enhances vehicle performance and safety | Ensure compatibility with various vehicle models; focus on durability and heat resistance. |
| Agricultural Machinery | Agricultural equipment like tractors and harvesters | Improves efficiency and reduces maintenance costs | Look for bearings designed for high loads and harsh conditions; verify supplier reliability. |
| Industrial Equipment | Conveyor systems and manufacturing machinery | Increases productivity and reduces downtime | Source bearings that offer high precision and low friction; consider local regulations on imports. |
| Mining and Construction | Heavy-duty machinery and equipment | Supports heavy loads and enhances operational safety | Focus on high-load capacity and corrosion resistance; evaluate lead times for critical projects. |
| Renewable Energy | Wind turbine components | Maximizes energy output and reduces operational costs | Look for specialized bearings that withstand extreme conditions; assess supplier certifications and warranties. |
How Are Bearing Parts Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, bearing parts are integral to wheel hubs and transmission systems, facilitating smooth rotation and reducing friction. This is crucial for enhancing vehicle performance and safety, as faulty bearings can lead to significant mechanical failures. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, should prioritize sourcing high-quality bearings that offer durability and heat resistance, ensuring compatibility with various vehicle models.
What Role Do Bearing Parts Play in Agricultural Machinery?
Bearing parts are essential in agricultural machinery, such as tractors and harvesters, where they support rotating shafts and wheels. By improving efficiency and reducing maintenance costs, high-quality bearings enable these machines to operate at optimal levels, especially during peak seasons. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should seek bearings designed for high loads and harsh conditions, ensuring reliable performance in demanding agricultural environments.

Illustrative image related to bearing parts
How Are Bearing Parts Utilized in Industrial Equipment?
In industrial equipment, bearing parts are critical for conveyor systems and various manufacturing machinery, where they enhance productivity by minimizing friction. This reduction in friction translates to less energy consumption and lower operational costs, making it vital for businesses aiming to improve their bottom line. B2B buyers must focus on sourcing bearings that offer high precision and low friction characteristics, while also considering local regulations that may affect import processes.
Why Are Bearing Parts Important in Mining and Construction?
In the mining and construction industries, bearing parts are crucial for the operation of heavy-duty machinery and equipment that must support substantial loads. These bearings enhance operational safety and efficiency, preventing breakdowns that could halt project timelines. Buyers should prioritize high-load capacity and corrosion-resistant bearings, and evaluate lead times from suppliers to ensure timely delivery for critical projects in challenging environments.
How Do Bearing Parts Contribute to Renewable Energy Solutions?
In renewable energy, particularly in wind turbine components, bearing parts are vital for maximizing energy output and reducing operational costs. They enable the smooth rotation of turbine blades, which is essential for efficient energy generation. Buyers should look for specialized bearings that can withstand extreme environmental conditions, and assess supplier certifications to ensure they meet industry standards for quality and reliability.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘bearing parts’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing Quality Bearing Parts in Diverse Markets
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges when sourcing high-quality bearing parts, especially in regions like Africa and South America, where there may be a limited supply of reliable manufacturers. This can lead to difficulties in ensuring product quality, compliance with international standards, and timely delivery. Buyers may find themselves dealing with counterfeit or substandard products that fail to meet the required specifications, resulting in increased downtime, maintenance costs, and operational inefficiencies.
The Solution: To effectively source quality bearing parts, buyers should establish relationships with reputable suppliers who have a proven track record in the industry. It’s essential to conduct thorough due diligence by reviewing supplier certifications, product testing results, and customer testimonials. Additionally, leveraging global platforms that specialize in bearings can help identify trustworthy manufacturers. Buyers should also consider implementing a quality assurance process that includes testing samples before making large purchases. Utilizing third-party inspection services can further ensure that the products meet required standards and specifications.

Illustrative image related to bearing parts
Scenario 2: Understanding Bearing Specifications for Optimal Performance
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle with understanding the technical specifications of bearing parts, which can lead to incorrect purchases. This is particularly prevalent in sectors such as automotive and industrial machinery, where the wrong type or size of bearing can cause equipment failures, leading to costly repairs and production delays. Buyers may feel overwhelmed by the complexity of bearing types, load ratings, and material choices, which complicates their decision-making process.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should invest time in training and education on bearing specifications. This can involve attending workshops, webinars, or industry conferences focused on bearing technology. Additionally, creating a specification checklist that includes essential parameters—such as load capacity, dimensions, speed ratings, and environmental conditions—can help streamline the selection process. Collaborating with engineering teams or bearing specialists to assess the specific application needs can also provide valuable insights, ensuring that the right bearing is selected for optimal performance.
Scenario 3: Managing Bearing Maintenance and Replacement
The Problem: Proper maintenance of bearing parts is crucial for the longevity and efficiency of machinery. However, many B2B buyers overlook this aspect, leading to unexpected failures and costly downtime. This issue is often exacerbated in industries with limited access to technical support or maintenance training, where staff may lack the knowledge to perform regular inspections or identify early signs of wear and tear.
The Solution: To manage bearing maintenance effectively, buyers should implement a proactive maintenance program that includes regular inspections and condition monitoring. This could involve using vibration analysis tools to detect anomalies in bearing performance and scheduling routine maintenance checks based on operational hours. Training staff on the importance of bearing care and replacement protocols is also essential. Providing access to detailed maintenance manuals and creating a schedule for preventive maintenance can help ensure that bearings are monitored and replaced before they fail, ultimately saving costs and reducing downtime.

Illustrative image related to bearing parts
Strategic Material Selection Guide for bearing parts
When selecting materials for bearing parts, international B2B buyers must consider several factors that impact performance, durability, and cost. Here, we analyze four common materials used in bearing manufacturing: steel, stainless steel, polymer, and ceramic. Each material has unique properties and implications for various applications.
What are the Key Properties of Steel in Bearing Parts?
Steel is the most widely used material for bearing components due to its excellent mechanical properties. It typically offers high strength, good wear resistance, and the ability to withstand high loads and pressures. Standard carbon steels can operate at temperatures up to 120°C, while alloy steels can endure even higher temperatures. However, steel is prone to corrosion unless adequately treated or coated.
Pros: Steel bearings are durable, cost-effective, and straightforward to manufacture. They are suitable for a wide range of applications, from automotive to industrial machinery.

Illustrative image related to bearing parts
Cons: The susceptibility to corrosion limits their use in harsh environments without protective coatings. Additionally, the weight of steel may be a disadvantage in applications where weight reduction is critical.
How Does Stainless Steel Enhance Bearing Performance?
Stainless steel is an alloy known for its corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications exposed to moisture or aggressive chemicals. It maintains strength at elevated temperatures and can operate effectively in environments ranging from -50°C to 300°C.
Pros: The primary advantage of stainless steel bearings is their resistance to rust and corrosion, which extends their lifespan in challenging conditions. They also provide good mechanical properties similar to carbon steel.
Cons: Stainless steel is generally more expensive than carbon steel, and the manufacturing process can be more complex, potentially leading to higher production costs.
What Role Do Polymers Play in Bearing Applications?
Polymer bearings are increasingly popular in specific applications due to their lightweight nature and excellent resistance to corrosion and chemicals. They can operate effectively in temperatures ranging from -40°C to 120°C, depending on the type of polymer used.
Pros: The key advantage of polymer bearings is their low friction coefficient, which can enhance efficiency in applications such as food processing or pharmaceuticals, where contamination must be minimized.
Cons: While polymer bearings are resistant to corrosion, they typically have lower load-bearing capacity compared to metal options. They may also wear out faster under high loads or extreme temperatures.
Why Choose Ceramic Bearings for Specialized Applications?
Ceramic materials, such as silicon nitride, are known for their exceptional hardness and wear resistance. They can operate in extreme temperatures (up to 800°C) and are non-magnetic and non-corrosive.
Pros: The primary advantage of ceramic bearings is their ability to withstand high speeds and loads, making them suitable for applications in aerospace and high-performance motorsports.
Cons: However, ceramic bearings are significantly more expensive than metal counterparts and can be brittle, which may lead to failure under shock loads.
Summary of Material Selection for Bearing Parts
| Material | Typical Use Case for bearing parts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | General industrial applications | High strength and durability | Prone to corrosion without treatment | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, marine environments | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | Medium |
| Polymer | Medical devices, light machinery | Lightweight and low friction | Lower load capacity and wear over time | Medium |
| Ceramic | Aerospace, high-performance motors | High speed and temperature resistance | High cost and brittleness under shock loads | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on performance requirements, environmental conditions, and cost considerations. Understanding these materials’ properties and limitations is crucial for ensuring the reliability and efficiency of bearing applications across diverse industries.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for bearing parts
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Bearing Parts?
The manufacturing of bearing parts involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the required performance specifications. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Bearing Parts?
The manufacturing process begins with the selection of high-quality raw materials, typically high-carbon steel or other specialized alloys. The material is subjected to heat treatment to improve hardness and durability. This stage often involves processes such as annealing to relieve stress and ensure uniform microstructure, which is vital for the bearing’s performance.
What Techniques Are Used for Forming Bearing Parts?
Forming is the next stage and can involve various methods, including forging, machining, and grinding.
- Forging: This technique shapes the material using compressive forces, creating a dense and strong component.
- Machining: Precision machining is essential for creating the inner and outer races of the bearing. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are commonly used to achieve high tolerances.
- Grinding: This process is used to achieve the required surface finish and dimensional accuracy. The inner and outer surfaces must be smooth to reduce friction during operation.
Each forming technique contributes to the overall integrity and functionality of the bearing, ensuring it can withstand the operational loads and speeds expected in various applications.
How Are Bearing Parts Assembled?
The assembly process involves the careful fitting of various components, such as the inner and outer races, rolling elements, and cages. It is crucial that these parts are assembled in a clean environment to prevent contamination.

Illustrative image related to bearing parts
Automated assembly lines often utilize specialized equipment to ensure precise alignment and fitting of components. This stage may also include lubrication application, which is essential for reducing friction and wear during operation.
What Finishing Processes Are Involved in Bearing Manufacturing?
Finishing processes are critical for enhancing the performance and longevity of bearing parts. These may include:
- Surface Treatment: Techniques such as hardening, coating, or polishing to improve wear resistance and reduce friction.
- Inspection: A thorough inspection is conducted to verify dimensions and surface quality before packaging.
These finishing touches not only enhance the performance of the bearing but also contribute to its aesthetic appeal, which can be a consideration for some buyers.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for Bearing Parts?
Quality assurance (QA) in bearing manufacturing is paramount to ensure that products meet international and industry-specific standards. The following QA practices are commonly implemented:
Which International Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
For B2B buyers, understanding relevant international standards is crucial. The ISO 9001 standard for quality management systems is widely recognized and ensures that manufacturers follow consistent quality processes. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for European markets and API standards for the oil and gas industry may also apply.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials before production to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): This checkpoint monitors production processes, ensuring they adhere to established protocols and specifications.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of the finished product is conducted to verify it meets all performance and safety standards.
These checkpoints help identify potential issues early in the manufacturing process, reducing the risk of defects in the final product.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Bearing Quality Assurance?
To ensure reliability and performance, various testing methods are employed:
- Dimensional Inspection: This involves using precision measuring tools to verify that bearing dimensions comply with specifications.
- Material Testing: Hardness tests and tensile strength assessments ensure that the materials used can withstand operational demands.
- Performance Testing: Bearings may be subjected to dynamic testing to evaluate their performance under load and speed conditions.
These testing methods provide B2B buyers with confidence in the durability and performance of the bearing parts they procure.

Illustrative image related to bearing parts
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is essential. Here are several strategies:
What Steps Can Buyers Take to Conduct Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is a proactive approach to assess a manufacturer’s quality control processes. Buyers can request documentation of QA procedures, inspection reports, and certifications. Audits can be performed in-person or via third-party services that specialize in manufacturing assessments.
How Can Buyers Utilize Reports and Third-Party Inspections?
Buyers should also seek transparency in the form of detailed quality reports from suppliers. These reports should outline testing results and any corrective actions taken for past defects. Additionally, engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s adherence to quality standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
Understanding the nuances of QC in different regions is vital for international buyers. Variations in standards and practices can affect product quality. For instance, European markets may have stricter regulations regarding environmental impact and material sourcing compared to other regions.
B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and industry standards relevant to their specific market. This knowledge not only aids in supplier selection but also ensures compliance with local laws, potentially reducing the risk of penalties or product recalls.
Conclusion
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for bearing parts are intricate and multifaceted. By understanding the key stages of manufacturing, the importance of quality assurance, and the various methods for verifying supplier standards, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their supply chain efficiency and product reliability. Engaging with suppliers who prioritize quality at every stage of production will ultimately lead to better performance and satisfaction in their applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘bearing parts’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure bearing parts effectively. The procurement process can be complex, especially when sourcing from international suppliers. By following these steps, buyers can ensure they select the right components that meet their operational needs while minimizing risks associated with quality and supplier reliability.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for the bearing parts you need. This includes dimensions, load capacity, speed ratings, and material specifications. Precise specifications help prevent costly errors and ensure compatibility with existing machinery.
- Consider application needs: Identify whether the bearings will be used in high-speed, high-load, or corrosive environments.
- Document tolerances: Specify tolerances for dimensions and operational conditions to avoid compatibility issues.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research
Investigate the market to identify potential suppliers and products. Understanding the competitive landscape can provide insights into pricing, availability, and emerging technologies.
- Explore regional suppliers: Focus on suppliers from your target regions, such as Africa, South America, or Europe, to reduce shipping times and costs.
- Use industry directories: Leverage online platforms and trade shows to discover reputable suppliers and manufacturers.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. This step is crucial for ensuring that your chosen supplier can meet your quality and delivery requirements.
- Request documentation: Ask for company profiles, certifications (e.g., ISO), and references from similar industries.
- Assess production capabilities: Inquire about their manufacturing processes, technology, and quality control measures.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that the suppliers possess the necessary certifications that demonstrate their compliance with industry standards. This is vital for ensuring product quality and reliability.
- Look for international standards: Certifications like ISO 9001 or industry-specific standards indicate adherence to quality management systems.
- Check for product-specific certifications: Certain applications may require additional certifications, such as those for food safety or aerospace standards.
Step 5: Request Samples or Prototypes
Before placing a bulk order, request samples or prototypes of the bearing parts. This allows you to assess the quality and performance of the products firsthand.
- Conduct performance tests: Evaluate the samples under conditions that mimic actual operating environments.
- Examine quality: Check for any visible defects and ensure that the specifications match your requirements.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have identified a suitable supplier and evaluated the samples, enter into negotiations regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules.
- Discuss bulk purchase discounts: Inquire about volume discounts or loyalty programs for long-term partnerships.
- Clarify payment terms: Ensure that terms are mutually beneficial and consider using secure payment methods to mitigate risks.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Create a clear communication strategy for ongoing interactions with your supplier. This will facilitate smoother transactions and address any potential issues promptly.
- Define points of contact: Assign dedicated personnel for managing communications to ensure consistency.
- Set expectations for updates: Agree on regular updates regarding order status, shipping, and any potential delays.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can streamline the procurement of bearing parts, ensuring they secure quality products that meet their operational needs while fostering reliable supplier relationships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for bearing parts Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Bearing Parts Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure for bearing parts is essential for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly affects the overall cost. High-quality steel, ceramic, or specialty materials for bearings can lead to variations in pricing. For instance, bearings made from stainless steel may command a premium due to their corrosion resistance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and manufacturing process. Countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but this can sometimes compromise quality. It’s crucial to assess the labor skill level, as skilled labor can lead to better manufacturing outcomes.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility operations, utilities, and administrative costs. Efficient manufacturers often have lower overhead, allowing them to pass savings onto buyers.
-
Tooling: The cost of tooling can be significant, especially for custom or specialized bearings. Buyers should consider whether the supplier has the necessary equipment to produce the desired specifications without incurring excessive tooling costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in quality control processes can add to costs but is essential for ensuring product reliability. Certifications and testing may lead to higher prices but are critical for maintaining standards, especially in industries where safety is paramount.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely based on the origin of the bearings and the destination. Incoterms can influence these costs, affecting who bears the risk and responsibility during transit.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary based on market conditions, competition, and the perceived value of the product. Understanding the market can help buyers negotiate better terms.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Bearing Parts Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of bearing parts, including:
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Suppliers may offer discounts for larger orders, making it advantageous for buyers to consolidate their purchases.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom bearings tailored to specific applications can significantly increase costs. Standardized products typically come at a lower price point. Buyers should evaluate whether customization is necessary.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts price. Advanced materials that enhance performance may lead to higher costs but can provide long-term benefits.
-
Quality/Certifications: Bearings that meet international quality standards or possess certifications can command higher prices. Buyers should weigh the benefits of these certifications against their costs.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and service quality can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The agreed-upon Incoterms dictate responsibilities regarding shipping and insurance, which can affect the final cost. Buyers should clarify these terms to avoid unexpected expenses.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Bearing Parts Sourcing?
To optimize costs when sourcing bearing parts, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate: Don’t hesitate to negotiate prices, especially for larger orders. Leverage competitive quotes from multiple suppliers to secure better terms.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Consider factors like maintenance costs, lifespan, and performance when assessing the overall value of the bearings.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Purchases: Currency fluctuations, import duties, and local taxes can impact the final price. Buyers should factor these elements into their budget.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing a good relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and access to new products or innovations.
-
Research Market Trends: Stay informed about market dynamics and material costs. This knowledge can empower buyers during negotiations and help them anticipate price changes.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
The prices for bearing parts can vary significantly based on the aforementioned factors, and the figures presented in this guide are indicative. Buyers should conduct thorough market research and obtain specific quotes tailored to their needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing bearing parts With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Bearing Parts: A Comparative Analysis
In the realm of mechanical engineering and industrial applications, bearing parts are essential for reducing friction and facilitating smooth movement. However, there are alternative technologies and methods that can achieve similar objectives. This section explores viable alternatives, comparing them against traditional bearing parts to aid B2B buyers in making informed decisions.

Illustrative image related to bearing parts
| Comparison Aspect | Bearing Parts | Magnetic Bearings | Plain Bearings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency in load-bearing and motion transfer. | Excellent for high-speed applications with low friction. | Adequate for light loads but less efficient than bearings. |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on type and brand. | High initial investment with potential long-term savings. | Low cost, but may require frequent replacements. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires precise installation and alignment. | Complex setup needing specialized knowledge. | Simple installation, widely understood. |
| Maintenance | Regular lubrication and inspection required. | Minimal maintenance; self-lubricating options available. | Frequent lubrication and replacement can be necessary. |
| Best Use Case | Heavy machinery, automotive, and industrial equipment. | High-speed motors, aerospace applications, and sensitive environments. | Low-load applications like simple rotary mechanisms. |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
What Are Magnetic Bearings and Their Benefits?
Magnetic bearings utilize magnetic fields to support moving components without direct contact. This technology offers superior performance in high-speed applications, significantly reducing friction and wear. The primary advantage is their minimal maintenance needs due to self-lubricating properties. However, the complexity of installation and high initial costs can deter some users. They are ideal for aerospace and precision machinery where performance and reliability are critical.
How Do Plain Bearings Compare?
Plain bearings, also known as bushings, are the simplest form of bearing technology, consisting of a smooth surface allowing for sliding motion. They are cost-effective and easy to install, making them suitable for low-load applications such as household appliances or light machinery. However, their performance under heavy loads is inferior to that of bearing parts, leading to quicker wear and the need for more frequent replacements. For companies with budget constraints and lower operational demands, plain bearings can be a practical choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Needs
When selecting between bearing parts and their alternatives, B2B buyers must consider specific application requirements, including load capacity, speed, maintenance needs, and budget constraints. Bearing parts offer robust performance for demanding environments, while magnetic bearings excel in specialized applications with stringent requirements for efficiency and maintenance. On the other hand, plain bearings can provide a cost-effective solution for less demanding applications. By carefully assessing these factors, buyers can choose the most suitable solution that aligns with their operational goals and financial considerations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for bearing parts
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Bearing Parts That B2B Buyers Should Consider?
When sourcing bearing parts for industrial applications, understanding their essential technical properties is crucial. Here are some critical specifications:
1. Material Grade
The material used in bearing parts significantly affects their performance, durability, and suitability for specific applications. Common materials include chrome steel, stainless steel, and ceramic. Each material has unique properties, such as corrosion resistance and load-bearing capacity, which influence the bearing’s lifespan and maintenance requirements. Selecting the appropriate material grade can lead to reduced downtime and lower replacement costs, making it vital for B2B buyers to assess their operational environment.
Illustrative image related to bearing parts
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit or limits of variation in a physical dimension, such as diameter or thickness. High-precision bearings often require tighter tolerances to ensure proper fit and function within machinery. Understanding tolerance levels helps buyers ensure compatibility with existing systems and reduces the likelihood of premature failure due to misalignment. Accurate tolerances are essential for maintaining operational efficiency, particularly in high-speed or high-load applications.
3. Load Rating
Load rating indicates the maximum load a bearing can handle while maintaining optimal performance. This specification is critical when selecting bearings for heavy machinery or equipment. Bearings are typically rated for dynamic and static loads, and exceeding these ratings can lead to premature wear or catastrophic failure. For B2B buyers, understanding load ratings can help in selecting the right bearing for their specific application, ensuring safety and reliability.
4. Speed Rating
Speed rating defines the maximum operational speed of a bearing under specific conditions. Bearings designed for high-speed applications, such as in turbines or motors, must be capable of withstanding centrifugal forces without compromising performance. Buyers should consider speed ratings to prevent overheating and ensure the longevity of the bearing in high-velocity applications.
5. Lubrication Type
The type of lubrication used in bearings affects their performance and maintenance needs. Common lubricants include grease and oil, each with its own advantages depending on the application. Proper lubrication minimizes friction, reduces wear, and extends the bearing’s life. Understanding the lubrication requirements can help B2B buyers choose bearings that align with their maintenance capabilities and operational demands.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Bearing Industry?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are some common trade terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the bearing industry, understanding whether a supplier is an OEM can indicate the quality and reliability of the products being offered. OEM parts often meet specific standards and specifications required by manufacturers, making them a preferred choice for many B2B buyers.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ represents the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is particularly important for B2B buyers to understand, as it can affect inventory management and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their purchases and ensure they are making cost-effective decisions.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where a buyer requests price quotes from multiple suppliers for specific products or services. This process allows B2B buyers to compare prices, terms, and conditions before making purchasing decisions. Understanding how to craft an effective RFQ can streamline the procurement process and lead to better pricing negotiations.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. These terms clarify who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and risk during transportation. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers engaged in global sourcing, as it ensures clarity and reduces potential disputes.

Illustrative image related to bearing parts
5. Bearing Clearance
Bearing clearance refers to the space between the rolling elements and the bearing races. It is crucial for ensuring proper lubrication and thermal expansion. Understanding bearing clearance helps buyers select the right bearing for their application, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
In summary, a solid grasp of technical properties and industry terminology empowers B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing bearing parts, ultimately leading to more efficient operations and cost savings.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the bearing parts Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Affecting the Bearing Parts Sector?
The bearing parts sector is experiencing significant shifts driven by globalization, technological advancements, and changing consumer demands. Emerging markets in Africa, South America, and the Middle East are witnessing increased industrialization, leading to heightened demand for high-quality bearing components across various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. Notably, advancements in B2B e-commerce platforms are transforming how international buyers engage with suppliers, enabling seamless transactions and fostering competitiveness.
Furthermore, the rise of Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT) are reshaping sourcing strategies. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that utilize smart technologies for predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring of bearing performance. This trend enhances operational efficiency and reduces downtime, critical factors for industries relying heavily on machinery.
Additionally, buyers are becoming more discerning regarding product quality and supplier reliability. As a result, the market is witnessing a surge in demand for suppliers that can demonstrate quality certifications and robust supply chain management practices. This shift emphasizes the importance of building long-term relationships with trusted suppliers who can navigate the complexities of international trade.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Changing the Bearing Parts Market?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are no longer optional considerations for B2B buyers in the bearing parts sector; they are essential to maintaining competitive advantage. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly in terms of waste generation and carbon emissions, has prompted companies to adopt more sustainable practices. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that utilize eco-friendly materials and processes, which can lead to improved brand reputation and customer loyalty.
Incorporating ‘green’ certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management, is becoming a critical criterion for many buyers. These certifications not only demonstrate a commitment to sustainability but also ensure compliance with increasingly stringent regulations in many regions, particularly in Europe and North America.
Moreover, ethical supply chains that emphasize fair labor practices and transparency are gaining traction. Buyers are looking for suppliers who can provide traceability of materials and evidence of responsible sourcing practices. This trend is especially pronounced in regions where ethical considerations are paramount, such as in South America and Africa, where societal impacts can be significant.

Illustrative image related to bearing parts
What Is the Historical Context of Bearing Parts in the B2B Landscape?
The evolution of bearing parts dates back to ancient civilizations, where rudimentary forms of bearings were used to facilitate the movement of heavy objects. The modern bearing, as we know it, began to take shape in the 19th century, with innovations like the ball bearing developed by Philip Vaughan in 1794 and further advancements by notable figures such as Leonardo da Vinci.
Over the decades, the bearing industry has evolved significantly, driven by technological advancements and the increasing complexity of machinery. The introduction of new materials and manufacturing techniques has enhanced the performance and longevity of bearing components, making them indispensable in contemporary industrial applications.
Today, the bearing parts sector is characterized by continuous innovation, with a strong focus on improving efficiency, reducing friction, and ensuring reliability. This historical context underscores the importance of understanding both the technical evolution and the market dynamics that influence sourcing strategies for international B2B buyers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of bearing parts
-
How do I choose the right bearing for my application?
Selecting the right bearing involves understanding the specific requirements of your application, such as load capacity, speed, and environmental conditions. Consider the type of load (radial or axial) and the bearing configuration (e.g., ball or roller). It’s also essential to evaluate the operating temperature, potential exposure to contaminants, and the required lifespan. Consulting with a supplier who can provide technical support and detailed specifications will help ensure you select the most suitable bearing for your needs. -
What is the best type of bearing for high-speed applications?
For high-speed applications, ball bearings are generally preferred due to their lower friction and ability to handle higher RPMs. Specifically, look for precision ball bearings that are designed for high-speed rotation and have a robust lubrication system. Additionally, consider bearings made from materials with high fatigue strength, such as stainless steel or ceramic, to enhance performance and longevity under high-speed conditions. -
How can I verify the credibility of a bearing supplier?
To vet a bearing supplier, start by checking their certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicates quality management standards. Review customer testimonials and case studies to gauge their reliability and product quality. Additionally, request references from other international buyers and assess their response times and customer service. Conducting a site visit, if possible, can also provide valuable insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. -
What are the common payment terms in international bearing transactions?
Payment terms in international transactions often vary, but common options include advance payment, letter of credit, and payment upon delivery. Advance payment offers security for the supplier, while letters of credit provide a balance of risk for both parties. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that protect your interests and ensure a smooth transaction. Always clarify any additional fees, currency exchange rates, and payment methods accepted by the supplier. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for bearing parts?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between suppliers and may depend on the type of bearing and customization options. Typically, MOQs range from a few units to several hundred. It’s essential to discuss your specific needs with the supplier to determine if they can accommodate smaller orders, especially if you are testing a new product or entering a new market. Some suppliers may also offer flexible terms for long-term partnerships. -
How do I handle shipping and logistics for international bearing purchases?
When purchasing bearings internationally, consider working with a logistics provider experienced in handling industrial components. Discuss shipping methods (air, sea, or land) that align with your budget and timeline. Ensure that the supplier provides proper documentation, including invoices and shipping labels, to facilitate customs clearance. It’s also advisable to check the import regulations in your country to avoid delays or additional costs upon arrival. -
What quality assurance processes should I expect from my bearing supplier?
A reputable bearing supplier should have stringent quality assurance processes in place, including material inspections, dimensional checks, and performance testing. Ask about their testing protocols, such as fatigue testing and noise measurement, to ensure the bearings meet industry standards. Additionally, inquire if they offer warranties or guarantees on their products, as this can indicate confidence in their quality. -
Can I customize bearing parts for specific applications?
Many suppliers offer customization options for bearing parts, such as modifying dimensions, materials, or lubrication types to meet specific application requirements. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and performance expectations to the supplier. Be aware that custom orders may require longer lead times and higher MOQs, so plan accordingly. Collaborating closely with the supplier during the design phase can ensure the final product meets your operational needs.
Top 8 Bearing Parts Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Bearings.parts – Key Product Categories
Domain: bearings.parts
Introduction: Key product categories include: 2-Bolt Flange Bearings, 3-Bolt Flange Bearings, 4-Bolt Flange Bearings, Angular Contact Ball Bearings, Bearing Housings, CSK-Series One Way Clutch Bearings, Cylindrical Roller Bearings, Disc Harrow Bearings, Insert Bearings, Lawn Mower Bearings, Motor Sports Bearings, OEM Replacement Bearings, Pillow Block Bearings, Radial Ball Bearings, Self-Aligning Ball Bearings,…
2. Koyo – Bearings Structure Components
Domain: koyo.jtekt.co.jp
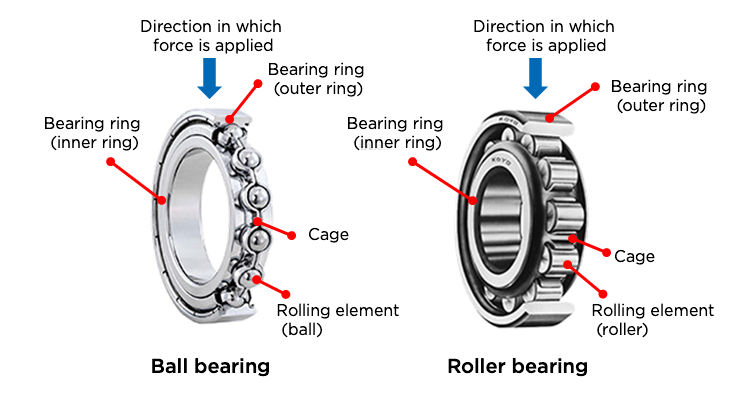
Introduction: The structure of bearings includes the following components: 1. Bearing rings (races) – ring-shaped components. 2. Rolling elements – components that roll between the bearing rings, which can be either balls or rollers. 3. Cage – maintains a fixed gap so the rolling elements do not contact each other. Bearings can be categorized into radial bearings (supporting forces applied perpendicularly to th…
3. Motorcar Parts – Hub Assemblies and Bearings
Domain: motorcarparts.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Hub Assemblies and Bearings from Motorcar Parts of America (MPA) are designed, manufactured, and tested to exceed quality and performance standards. Key features include:
– Segment leading coverage on light vehicle applications.
– Products tested on computerized testers in state-of-the-art facilities.
– Stringent standards verification processes for form, fit, and function.
– Free tech support…
4. Motion – Industrial Supplies & Solutions
Domain: motion.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: Industrial Supplies, Bearings, Mechanical Power Transmission, Chemicals, Lubricants and Equipment, Electrical, Facility Maintenance, Hose and Fittings, Hydraulics, Linear Motion, Material Handling, Pneumatics, Safety, Seals and Gaskets.
5. The Big Bearing Store – Bearings & Power Transmission Specialists
Domain: thebigbearingstore.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Bearings, Power Transmission Specialists, ATV Bearings, ATV Brake Pads, ATV Differential Kits, ATV Wheel Bearing Kits, Specialty Bearings, Pillow Block Bearings, UCP200 Series, GYAP200, Timken Series, UCPX00 Series, HCAK200 Series, UEP200 Series, SBSP200 Series, SSUCP200 Series, SSUCP200-TP Series, Type E Series, E1000 Series, M2000 Series, SAF Series, BLP200 Series, ALP200 Series, UCPH200 Series,…
6. NTN – Bearing Finder
Domain: bearingfinder.ntnamericas.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: NTN Bearing Finder offers an online catalog and interchange tool for various bearing products. Key product categories include: Ball Bearings, Constant Velocity Joints, Cylindrical Roller Bearings, Differential Kits, Flanged Discs, High Precision Bearings, Installation & Removal Tools, Linear Motion, Mounted Units & Pillow Blocks, Needle Roller Bearings, Single Point Lubricators, Spherical Roller B…
7. NSK – Bearings and Roller Solutions
Domain: nsk.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: NSK offers a wide range of products including:
– Ball Bearings:
– Deep Groove Ball Bearings
– Angular Contact Ball Bearings
– Self-Aligning Ball Bearings
– Thrust Ball Bearings
– N Series Thin-Section Ball Bearings
– Roller Bearings:
– Spherical Roller Bearings
– Cylindrical Roller Bearings
– Tapered Roller Bearings
– Thrust Roller Bearings
– Needle Roll…
8. McMaster – Bearings Selection
Domain: mcmaster.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, McMaster – Bearings Selection, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for bearing parts
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Bearing Parts Procurement?
In the evolving landscape of bearing parts procurement, strategic sourcing stands as a cornerstone for B2B buyers aiming to optimize their supply chains. By leveraging data-driven insights and supplier relationships, businesses can achieve not only cost efficiencies but also enhanced quality and reliability in their bearing components. It is crucial for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to prioritize suppliers who offer transparency, robust logistics, and responsiveness to market demands.
Investing in strategic sourcing allows companies to mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions and fluctuating prices. As the global market continues to adapt to technological advancements and sustainability initiatives, buyers should seek partnerships that align with their long-term objectives.
Looking ahead, the potential for growth in the bearing parts sector remains significant. By embracing a proactive approach to sourcing and fostering collaborative relationships with manufacturers, international buyers can position themselves for success. Engage with your suppliers today to explore innovative solutions that meet your operational needs and drive your business forward.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.