Bag Packing Machine: The Ultimate 2025 Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Bag Packing Machines
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing landscape, efficient bag packaging is the linchpin for businesses aiming to scale operations, reduce costs, and meet rising demands for sustainability. For USA and European companies in sectors like food, pharmaceuticals, and e-commerce, investing in the right bag packing machine can transform workflows—boosting throughput by up to 50% while minimizing errors. Yet, with a global market flooded by options from standard tabletop baggers to fully automated systems, how do you choose wisely?
The core challenge lies in navigating this complexity: identifying reliable suppliers amid varying regulations, balancing customization needs with budget constraints, and integrating innovations like biodegradable foils or vision-based quality control. Many buyers face pitfalls such as incompatible machinery, high downtime, or overlooked features like inline printing and robot integration, leading to inefficient processes and inflated costs.
This comprehensive B2B guide demystifies the bag packing machine market, equipping you with actionable insights to make informed decisions. We’ll cover:
- Market Overview: Key trends, including automation and eco-friendly solutions like pre-opened biodegradable bags-on-a-roll.
- Selection Criteria: Evaluating standard vs. customized systems, with focus on footprint, speed, and accessories like Zebra printers.
- Supplier Evaluation: Tips for assessing family-owned specialists vs. big brands, emphasizing service, stock availability, and Europe-wide support.
- Implementation Strategies: Optimizing workflows through analysis, consultation, and integration for cost reduction and quality enhancement.
- Case Studies and Reviews: Real-world examples from satisfied users in diverse industries.
Armed with this knowledge, you’ll streamline procurement and drive operational excellence. (248 words)
Top 10 Bag Packing Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. 19 Bagging Machinery Manufacturers in 2025 – Metoree
Domain: us.metoree.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Newlong Machine Works, Ltd. established in Tokyo, Japan, in 1955, is a manufacturer of packaging machinery, bag-making machinery, industrial sewing ……
2. Automatic bagging machine manufacturers – Concetti
Domain: concetti.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: We manufacture technologically advanced complete lines with high-quality construction for weighing, bagging and palletizing bulk products in bags, and boxes….
3. Need help finding the best bagger and filler machine! – Reddit
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Vevor has good inexpensive options for many packaging chores….
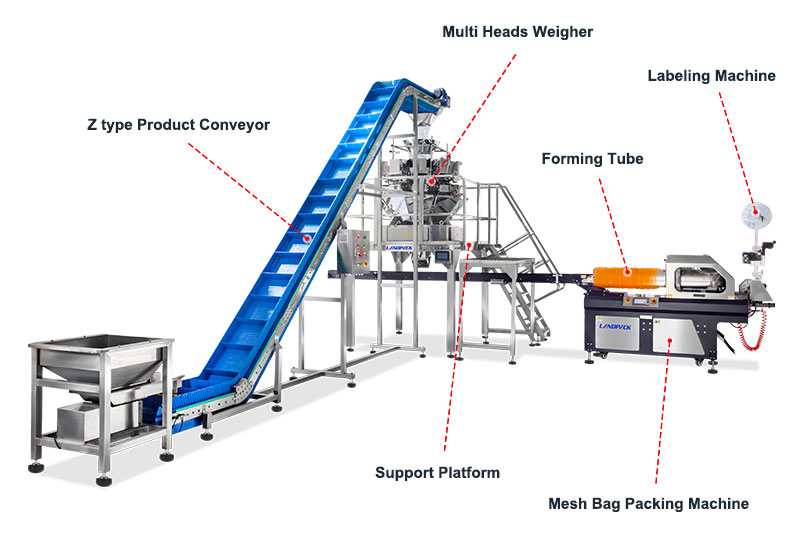
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
4. Premade Pouch Packing Machine Manufacturer & Supplier
Domain: richpacking020.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: RQ company is a professional Stand up Pouch Packing Machine factory,we offer high quality Premade Pouch Packing Machine at the best price….
5. Poly Bag Packing Machine
Domain: packmate-machine.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Buy good quality Poly Bag Packing Machine from Poly Bag Packing Machine manufacturer, We provide low priced Poly Bag Packing Machine from China….
Understanding bag packing machine Types and Variations
Understanding Bag Packing Machine Types and Variations
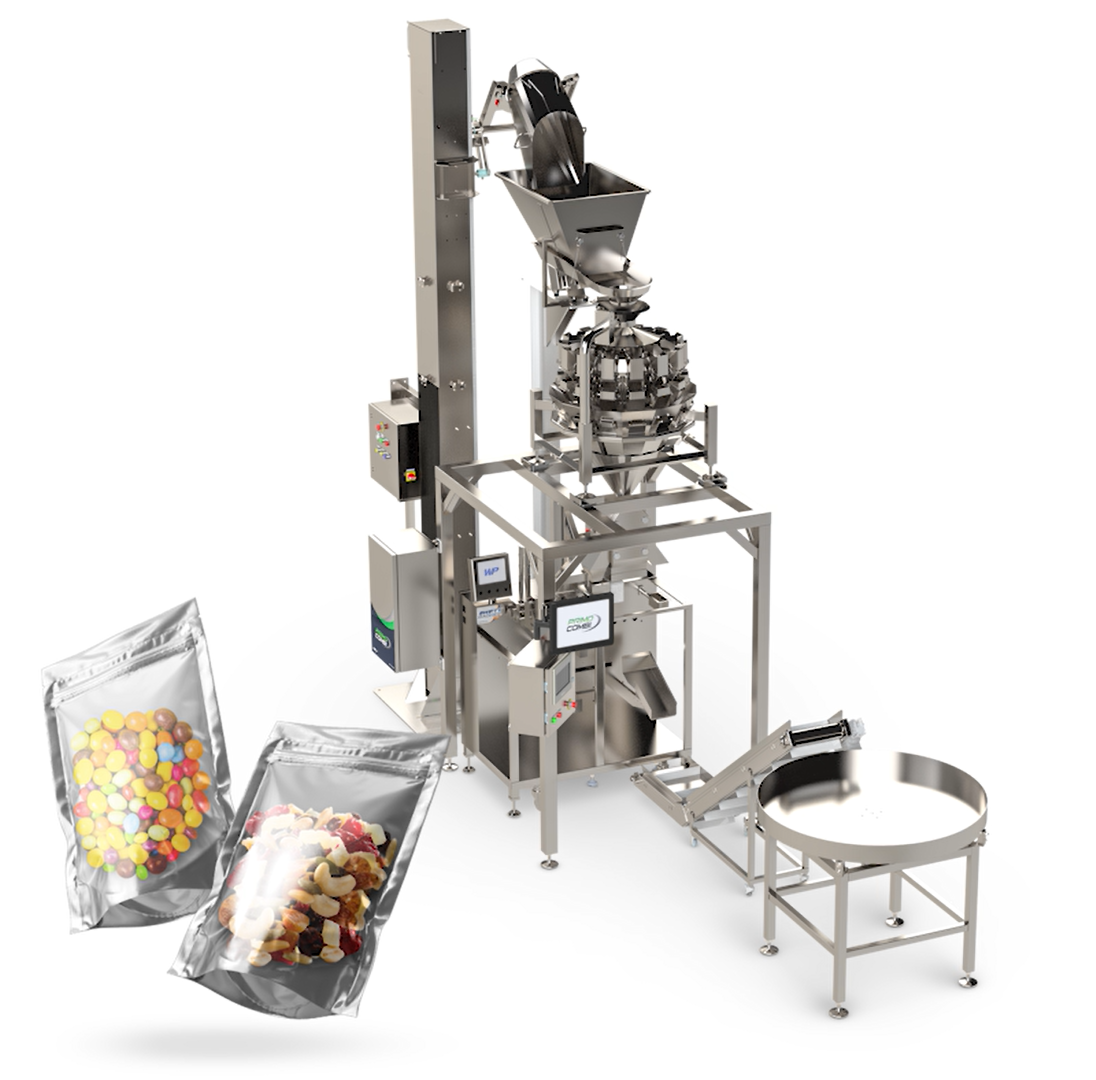
Bag packing machines, also known as baggers, automate the process of filling and sealing bags for various products. Based on industry standards and solutions like those from BagMatic, key types include semi-automatic, fully automatic, table top baggers, and customized systems. These variations cater to different operational scales, from small businesses to high-volume manufacturing. Below is a summary table, followed by detailed descriptions.
| Type | Features | Applications | Pros/Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Semi-Automatic Bag Packing Machines | Operator-assisted loading; automatic sealing and optional printing (e.g., inline Zebra printer); compatible with pre-opened bags-on-a-roll; basic vision systems for quality control. | Small to medium-scale packaging in industries like food, hardware, and electronics; suitable for variable product runs. | Pros: Cost-effective, flexible for manual adjustments, smaller footprint. Cons: Requires operator intervention, lower throughput compared to fully automatic models. |
| Fully Automatic Bag Packing Machines | Automated loading, counting, filling, sealing, and output; integration with robots and advanced vision systems for precise counting (e.g., small parts like seeds); static electricity neutralization; biodegradable bag options. | High-volume production in manufacturing, agriculture, and pharmaceuticals; ideal for consistent, large-scale bagging. | Pros: High efficiency, minimal labor, accurate for small/light items. Cons: Higher initial cost, requires technical setup and maintenance. |
| Table Top Baggers | Compact design for benchtop use; uses pre-opened bags-on-a-roll; semi-automatic operation with optional printing and accessories for product input/output. | Small businesses, labs, or e-commerce fulfillment; packaging small items like parts, samples, or kits. | Pros: Space-saving, easy to operate, quick setup for low-volume tasks. Cons: Limited capacity, not suited for heavy or bulky products. |
| Customized Bagging Solutions | Tailored designs with unique features like robot integration, specialized counting for tiny parts, and full-system automation; includes analysis and consultation for process optimization. | Specialized needs in sectors like automotive, medical devices, or custom manufacturing; for unique workflows requiring high precision. | Pros: Optimized for specific requirements, potential cost savings through efficiency. Cons: Longer lead times, higher customization costs. |
Semi-Automatic Bag Packing Machines
These machines streamline packaging by automating sealing and optional printing while relying on operators for product loading. They are ideal for businesses transitioning from manual processes, offering compatibility with printed or biodegradable bags. Key benefits include reduced labor costs and improved consistency, with applications in diverse sectors requiring moderate output. Maintenance is straightforward, and they integrate well with existing workflows.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Fully Automatic Bag Packing Machines
Designed for end-to-end automation, these systems handle everything from product feeding to sealed bag output without constant human oversight. Features like vision-based quality control and robot integration ensure accuracy, even for challenging items such as lightweight seeds. They excel in high-throughput environments, supporting biodegradable materials and inline labeling for compliance in regulated industries like food and pharma. Investment in these machines often yields long-term ROI through operational efficiency.
Table Top Baggers
Compact and user-friendly, table top baggers are entry-level solutions for automated bagging on a small scale. They use rolls of pre-opened bags and can incorporate printers for on-demand labeling. Best suited for low-volume operations, they minimize workspace requirements and enable quick setup. Businesses in e-commerce or prototyping benefit from their versatility, though scalability is limited for larger production needs.
Customized Bagging Solutions
These are bespoke systems developed through client consultations to address unique packaging challenges. Incorporating advanced elements like static neutralization and specialized counting, they can include full robot automation for hands-free operation. Applications span industries with non-standard requirements, such as precise packaging of micro-components. While initial costs are higher, they deliver tailored efficiency gains, often reducing overall packaging expenses.
Key Industrial Applications of bag packing machine
Key Industrial Applications of Bag Packing Machines
Bag packing machines, such as those offered by BagMatic, provide efficient, automated solutions for bagging products using pre-opened bags-on-a-roll. These systems support standard or customized designs, including biodegradable options, inline printing, vision-based quality control, and robot integration. Below is a table outlining key industries, specific applications, and detailed benefits.
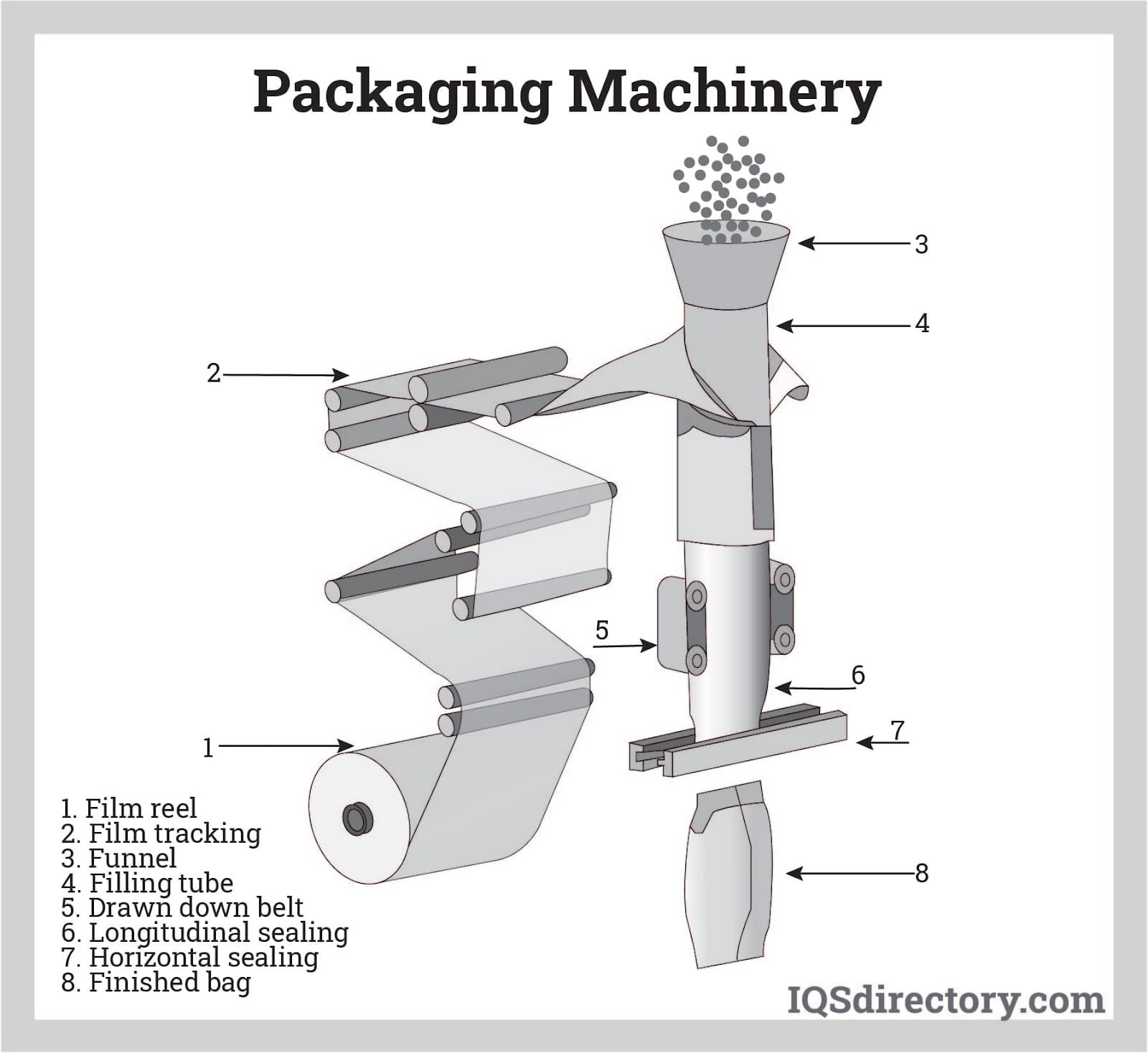
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
| Industry/Application | Detailed Benefits |
|---|---|
| Agriculture (e.g., Seed Packaging) | Enables precise counting and packaging of small, lightweight items like flower seeds using unique vision systems for accurate quality control; neutralizes static electricity to prevent clumping; reduces labor costs through semi- or fully automated processes, ensuring consistent bag sealing and optional inline printing for labeling. |
| Manufacturing (e.g., Small Parts and Hardware) | Integrates with robots for automated parts loading and bagging; offers camera-based registration for error-free counting; minimizes footprint for space-efficient operations; supports customized systems to optimize workflows, lowering costs and improving output speed with accessories for enhanced product input and filled bag handling. |
| E-commerce and Fulfillment (e.g., Product Bagging for Shipping) | Facilitates quick, reliable packaging with pre-opened bags and inline Zebra printing for customized labels; provides semi-automatic options for variable batch sizes; enhances efficiency with biodegradable foils for eco-friendly shipping, reducing manual handling and ensuring high-quality, tamper-evident seals. |
| Pharmaceuticals and Medical (e.g., Small Components Packaging) | Utilizes vision systems for precise counting and quality assurance of lightweight parts; includes static neutralization to maintain product integrity; offers fully automated solutions with robot integration for sterile, high-speed operations; ensures compliance through accurate, printed bag labeling and minimal contamination risks. |
| Electronics (e.g., Component Bagging) | Supports handling of static-sensitive parts with neutralization features; provides robot-integrated systems for precise, high-volume packaging; reduces errors via camera-based counting; delivers cost-effective, space-saving machines with options for biodegradable bags, improving overall process speed and reliability. |
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘bag packing machine’ & Their Solutions
3 Common User Pain Points for Bag Packing Machines & Their Solutions
Pain Point 1: Inefficient Manual Processes Leading to High Labor Costs
- Scenario: A mid-sized manufacturer in the USA relies on manual bag packing for small components, resulting in slow throughput during peak production periods.
- Problem: Manual operations increase labor expenses, introduce human errors, and limit scalability, often leading to overtime costs and delayed order fulfillment.
- Solution: Implement semi-automatic or fully automatic bag packing machines with robot integration for parts loading. These systems optimize workflows, reduce labor needs by up to 50%, and incorporate features like inline printing for customized labeling, ensuring cost-effective scaling.
Pain Point 2: Inaccurate Counting and Quality Control for Small or Lightweight Items
- Scenario: A European distributor of agricultural products, such as seeds, struggles with precise packaging of tiny, lightweight items using outdated equipment.
- Problem: Static electricity and manual counting cause inaccuracies, product loss, and quality issues, resulting in customer complaints and rework expenses.
- Solution: Adopt machines equipped with vision systems for automated counting and quality inspection, plus static neutralization features. This ensures accurate packaging of small parts like seeds, minimizes errors, and supports biodegradable bag options for eco-compliant operations.
Pain Point 3: Lack of Customization for Unique Packaging Needs
- Scenario: A B2B supplier in Europe requires tailored bag printing and handling for variable product sizes but uses rigid, standard machinery.
- Problem: Off-the-shelf solutions fail to adapt to specific requirements, causing inefficiencies, higher material waste, and inability to meet client demands for branded or specialized packaging.
- Solution: Opt for customizable bag packing systems with inline Zebra printers and modular accessories for product input/output. These provide tailored designs, fair pricing on new or reconditioned units, and on-site support to align with individual workflows, enhancing overall efficiency and quality.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for bag packing machine
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Bag Packing Machines
In the context of bag packing machines, strategic material selection focuses on bags and foils that optimize efficiency, cost, and compliance with regional regulations in the USA and Europe. Key considerations include material durability, compatibility with automated systems (e.g., pre-opened bags-on-a-roll), printability for branding or tracking (e.g., via inline Zebra printers), and environmental impact. This guide analyzes common materials, highlighting their properties and applications to support informed B2B decisions.
Key Factors in Material Selection
- Compatibility with Machines: Materials must integrate seamlessly with semi-automatic or fully automatic systems, including features like static neutralization for small parts and robot integration.
- Performance Requirements: Evaluate tensile strength, sealability, and resistance to tearing or static electricity, especially for lightweight items like seeds.
- Regulatory and Sustainability Compliance: In Europe, adhere to EU directives on single-use plastics; in the USA, consider EPA guidelines. Biodegradable options address growing demands for eco-friendly packaging.
- Cost and Efficiency: Balance initial costs with long-term benefits like reduced waste and faster workflows.
- Customization: Opt for materials supporting inline printing and quality control via vision systems for accurate counting and packaging.
Analysis of Common Materials
Bag packing machines typically use thermoplastic films or foils. Below is an analysis of primary types:
- Polyethylene (PE) Bags and Foils:
- Properties: High flexibility, excellent sealability, and moisture resistance. Available as pre-opened rolls for automated feeding.
- Advantages: Cost-effective, durable for heavy loads, and compatible with high-speed bagging. Supports inline printing for labels or barcodes.
- Applications: Ideal for industrial packaging of hardware, electronics, or food items. Suitable for machines with robot integration.
-
Limitations: Non-biodegradable, contributing to plastic waste; may require static neutralization for light parts.
-
Polypropylene (PP) Bags and Foils:
- Properties: Strong tensile strength, clarity for visibility, and heat resistance.
- Advantages: Lightweight and recyclable in many facilities. Enhances product presentation and works well with vision systems for quality control.
- Applications: Best for retail packaging, such as consumer goods or small components. Integrates with semi-automatic tabletop baggers.
-
Limitations: Higher cost than PE; less flexible, potentially leading to jams in high-speed operations.
-
Biodegradable Bags and Foils (e.g., PLA or Starch-Based):
- Properties: Derived from renewable sources, compostable under industrial conditions, and available as pre-opened rolls.
- Advantages: Reduces environmental footprint, aligning with EU Green Deal and USA sustainability initiatives. Maintains sealability and printability similar to traditional plastics.
- Applications: Suitable for eco-conscious sectors like agriculture (e.g., seed packaging) or food. Compatible with customized systems for small, light parts.
-
Limitations: Higher upfront cost; shorter shelf life and sensitivity to humidity, requiring controlled storage.
-
Specialized Foils (e.g., Laminated or Anti-Static):
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Properties: Multi-layer construction for added barrier protection; anti-static variants prevent charge buildup.
- Advantages: Enhances product safety for sensitive items. Supports unique features like camera-based counting.
- Applications: Electronics or pharmaceuticals, where contamination control is critical.
- Limitations: Premium pricing; may require machine modifications for optimal performance.
Selecting the right material involves assessing your specific workflow—e.g., standard machines for quick setups or customized solutions for complex needs. Consulting providers like BagMatic ensures alignment with fair pricing and Europe-wide support.
Material Comparison Table
| Material Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Best Applications | Cost Level (Relative) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene (PE) | Cost-effective, durable, printable | Non-biodegradable, static issues | Industrial hardware, food | Low |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Strong, recyclable, clear | Less flexible, higher cost | Retail goods, small components | Medium |
| Biodegradable (e.g., PLA) | Eco-friendly, compostable | Humidity-sensitive, shorter life | Agriculture, sustainable packaging | High |
| Specialized Foils | Barrier protection, anti-static | Premium price, setup complexity | Electronics, pharmaceuticals | High |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for bag packing machine
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Bag Packing Machines
Bag packing machines, such as those offered by BagMatic, are engineered for efficiency in automated bagging operations. These systems often incorporate advanced features like vision-based quality control, inline Zebra printing, and robot integration for handling small or static-sensitive parts. Below, we outline the key manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, drawing from industry standards to ensure reliability for B2B applications in the USA and Europe.
Manufacturing Processes
The production of bag packing machines follows a structured workflow to meet demands for customization, such as standard tabletop baggers or fully automated systems with biodegradable bag foils. Processes are optimized for precision, scalability, and integration of components like cameras for part registration and static neutralization systems.
Preparation
This initial phase involves material selection and planning to align with client needs, such as efficient workflows for bagging with printed or unprinted bags.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Material Sourcing: High-grade metals (e.g., stainless steel for durability), electronics (e.g., sensors for vision systems), and polymers (e.g., for biodegradable foils) are procured from certified suppliers. Compliance with environmental regulations, including REACH in Europe and EPA standards in the USA, is verified.
- Design and Prototyping: CAD models are developed based on customer requirements, incorporating features like robot integration or inline printing. Prototypes are tested for footprint efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- Component Preparation: Parts are pre-cut, cleaned, and treated (e.g., anti-static coatings) to prevent issues during assembly.
Forming
Shaping raw materials into functional components ensures the machine’s structural integrity and operational precision.
- Machining and Fabrication: CNC milling and laser cutting form frames and housings. For example, enclosures for vision systems are precision-formed to accommodate cameras that register small parts like flower seeds.
- Component Molding: Plastic or composite parts, such as bag holders or feeder mechanisms, are injection-molded for semi-automatic or fully automatic models.
- Surface Treatment: Components undergo processes like powder coating or anodizing to enhance corrosion resistance, especially for machines used in varied industrial environments.
Assembly
Integration of components creates a cohesive system, often customized for specific applications like high-speed bagging with Zebra print solutions.
- Sub-Assembly: Modules like the bagging mechanism, printer integration, and robot arms are built separately. Electrical wiring and software for quality control (e.g., counting accuracy) are installed.
- Final Integration: All sub-assemblies are combined on the production line. Features such as static electricity neutralization are tested in real-time to ensure seamless operation.
- Customization: For bespoke solutions, accessories like automated feeders or output optimizers are added based on client analysis, reducing working costs and improving speed.
Quality Control
Rigorous testing at multiple stages verifies performance and reliability, aligning with BagMatic’s emphasis on unique solutions like vision systems for accurate counting.
- In-Process Inspections: Dimensional checks and functional tests occur during assembly to detect defects early.
- Final Testing: Machines undergo simulated operations, including bag filling with pre-opened rolls, to measure speed, accuracy, and footprint efficiency. Vision systems are calibrated for part registration.
- Certification Checks: Compliance with safety standards (e.g., CE marking in Europe, UL certification in the USA) is confirmed.
Quality Assurance and Standards
Quality assurance in bag packing machine manufacturing adheres to international benchmarks to deliver consistent, high-performance products. BagMatic, as a third-generation family-owned company, emphasizes competencies in semi-automatic and fully automatic systems, supported by Europe-wide on-site service.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- ISO Standards: Production typically follows ISO 9001 for quality management systems, ensuring process optimization and customer satisfaction. For precision components, ISO 13485 may apply if machines are used in regulated sectors like pharmaceuticals.
- Additional Certifications: Machines often meet ISO 14001 for environmental management, particularly with biodegradable bag options. Traceability is maintained through documented audits, covering everything from material sourcing to post-sale support.
- Performance Metrics: Key indicators include defect rates below 1%, uptime exceeding 98%, and customer reviews (e.g., via Proven Experts) validating efficiency and reliability.
| Aspect | Key Standard | Benefit for B2B Users |
|---|---|---|
| Quality Management | ISO 9001 | Consistent production quality and reduced defects |
| Environmental Compliance | ISO 14001 | Sustainable practices, e.g., biodegradable foils |
| Safety and Reliability | CE/UL | Safe operation in industrial settings across USA/Europe |
By adhering to these processes and standards, manufacturers like BagMatic provide cost-effective, customizable solutions that optimize packaging workflows and enhance operational efficiency. For tailored consultations, contact specialists to analyze your specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘bag packing machine’
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for Bag Packing Machines
This checklist provides a structured approach for B2B professionals in the USA and Europe to source bag packing machines, focusing on automatic systems for efficient bagging processes. It draws on key considerations such as customization, automation levels, and support services.
Step 1: Define Your Requirements
- Identify your packaging needs: Determine product types (e.g., small/light parts like seeds or larger items), volume (daily/weekly output), and bag specifications (pre-opened bags-on-a-roll, printed or unprinted, biodegradable options).
- Assess workflow integration: Evaluate needs for features like inline printing (e.g., Zebra printers), vision systems for quality control and counting, static electricity neutralization, or robot integration for automated loading.
- Set budget and timeline: Factor in costs for standard vs. customized machines, including accessories for product input/output optimization.
Step 2: Research Suppliers
- Compile a list of providers: Focus on established brands like BagMatic or Advanced Poly Packaging, prioritizing those offering semi-automatic and fully automatic solutions with EU/USA compliance.
- Review credentials: Check for family-owned expertise, stock availability (new/reconditioned machines), and customer reviews on platforms like Proven Experts.
- Evaluate geographic support: Ensure Europe-wide on-site service and competitive pricing aligned with USA/Europe markets.
Step 3: Evaluate Machine Features and Compatibility
- Compare core functionalities: Look for quick, reliable systems with limited footprints, suitable for standard or individualized designs.
- Assess add-ons: Prioritize unique features like camera-based part registration, accurate counting for small items, and biodegradable bag foils.
- Test compatibility: Verify integration with existing systems, such as automated packaging lines or additional accessories.
Step 4: Request Consultations and Quotes
- Initiate contact: Reach out for analysis and consultation to optimize processes, reduce costs, and improve quality.
- Request demos or trials: Ask for demonstrations of standard machines or customized concepts, including speed enhancements and cost-benefit analyses.
- Obtain detailed quotes: Include full-service packages covering machinery, support, education, and maintenance.
Step 5: Assess Support and Long-Term Value
- Review service offerings: Confirm incomparable customer service, on-site support in Europe, and availability of parts/services in the USA.
- Evaluate sustainability and scalability: Consider biodegradable options and future-proof designs for evolving packaging demands.
- Analyze ROI: Calculate potential reductions in working costs through efficient, automated solutions.
Step 6: Finalize and Procure
- Compare proposals: Use a decision matrix to weigh factors like price, features, and service quality.
- Negotiate terms: Secure fair, competitive pricing and warranties.
- Proceed with purchase: Opt for suppliers offering quick standardized or unique solutions, ensuring seamless implementation.
For tailored advice, contact suppliers like BagMatic for a detailed process analysis.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for bag packing machine Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Bag Packing Machine Sourcing
Sourcing bag packing machines involves evaluating total ownership costs beyond the initial purchase price. This analysis breaks down key components—materials, labor, and logistics—based on industry standards for automatic bagging systems like those from BagMatic, which offer standard, customized, semi-automatic, and fully automatic options. Prices can vary by supplier, customization level, and region (USA or Europe). Expect entry-level tabletop baggers to start at $5,000–$15,000 USD/€4,500–€13,500, while fully automated systems with features like Zebra printing or robot integration range from $20,000–$100,000 USD/€18,000–€90,000 or more.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Cost Breakdown: Materials
Materials encompass the machine, consumables, and accessories. BagMatic emphasizes fair pricing for new and reconditioned units, with options for biodegradable bags to meet sustainability demands in the USA and Europe.
| Component | Description | Estimated Cost Range (USD/EUR) |
|---|---|---|
| Machine Base | Standard tabletop bagger or semi-automatic system; includes features like vision systems for quality control. | $5,000–$50,000 / €4,500–€45,000 |
| Customization | Add-ons like inline Zebra printers, robot integration, or static neutralization for small parts (e.g., seeds). | $2,000–$20,000 / €1,800–€18,000 |
| Consumables | Pre-opened bags-on-a-roll (standard or biodegradable); foils and printing supplies. | $0.01–$0.10 per bag / €0.01–€0.09; bulk rolls $500–$2,000 / €450–€1,800 annually |
| Accessories | Conveyors, counting cameras, or output optimizers. | $1,000–$10,000 / €900–€9,000 |
Cost Breakdown: Labor
Labor costs include setup, operation, and maintenance. BagMatic provides Europe-wide on-site support and training, which can reduce long-term expenses through efficient workflows.
| Component | Description | Estimated Cost Range (USD/EUR) |
|---|---|---|
| Installation and Training | Professional setup and staff education on features like automated counting or printing. | $1,000–$5,000 / €900–€4,500 (one-time) |
| Operation | Daily use; automated systems minimize manual input, saving 20–50% on labor vs. manual packing. | $20–$50 per hour / €18–€45; annual costs depend on volume (e.g., $10,000–$50,000 / €9,000–€45,000 for full-time operator) |
| Maintenance | Routine servicing; BagMatic offers in-house and on-site support for semi- and fully automatic machines. | $500–$2,000 annually / €450–€1,800; reconditioned machines may lower this by 30% |
Cost Breakdown: Logistics
Logistics cover shipping, duties, and delivery. For USA/Europe sourcing, factor in BagMatic’s stock availability for quicker turnaround and reduced freight costs.
| Component | Description | Estimated Cost Range (USD/EUR) |
|---|---|---|
| Shipping and Freight | Domestic (Europe) or international (to USA); compact designs like BagMatic’s limited footprint reduce fees. | $500–$3,000 / €450–€2,700 per unit |
| Import Duties and Taxes | USA tariffs on machinery (around 0–2.5%); EU VAT (up to 27% varying by country). | 0–25% of machine value |
| Warehousing and Delivery | Storage if delayed; on-site delivery with BagMatic’s Europe-wide service. | $200–$1,000 / €180–€900 |
Tips to Save Costs
- Opt for Reconditioned Machines: BagMatic stocks refurbished units at 20–40% below new prices, maintaining quality with warranties.
- Standardize Over Customization: Choose off-the-shelf models to avoid add-on premiums; integrate features like vision systems only if essential for your workflow.
- Bulk Purchase Consumables: Buy biodegradable bags-on-a-roll in volume for discounts up to 15–20%; this also optimizes logistics.
- Leverage Supplier Analysis: Engage providers like BagMatic for free consultations to analyze current processes and recommend cost-reducing solutions, such as automation to cut labor by increasing speed.
- Regional Sourcing: Source from Europe-based suppliers like BagMatic for EU buyers to minimize duties; for USA, consider partners with local stock to reduce shipping.
- Maintenance Contracts: Invest in service plans for predictable costs and downtime reduction, potentially saving 10–25% annually on repairs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing bag packing machine With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Bag Packing Machine With Other Solutions
In this section, we compare BagMatic’s automatic bag packing machines—featuring pre-opened bags-on-a-roll, inline Zebra printing, and options for standard or customized designs—with two common alternatives: manual bag packing and vertical form fill seal (VFFS) machines. This analysis highlights key factors such as efficiency, cost, and scalability for B2B operations in the USA and Europe.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Comparison Table
| Feature | BagMatic Bag Packing Machine | Manual Bag Packing | Vertical Form Fill Seal (VFFS) Machines |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automation Level | Fully or semi-automated, expandable with robotics and vision systems for counting and quality control. | None; relies on human labor. | Fully automated, but focused on forming bags from film rolls. |
| Speed and Efficiency | High throughput (quick and reliable for small to large batches); optimizes workflows and reduces labor costs. | Low; prone to human error and fatigue, limiting output. | High for continuous production, but slower setup for small runs. |
| Customization | Standard or fully customized solutions, including biodegradable bags and inline printing. | Limited; dependent on operator skill. | Moderate; customizable for bag sizes, but less flexible for printing or small parts. |
| Footprint | Compact tabletop design with limited space requirements. | Minimal equipment, but requires more workspace for personnel. | Larger footprint due to vertical design and film handling. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Competitive pricing with low operational costs; fair prices for new or reconditioned units, plus cost savings from efficiency. | Low initial cost, but high long-term labor expenses. | Higher upfront costs; efficient for high-volume, but less so for variable needs. |
| Additional Features | Unique vision system for accurate counting (e.g., small parts like seeds), static neutralization, and Europe-wide on-site service. | None. | Integrated sealing and filling, but lacks advanced counting or printing without add-ons. |
| Sustainability | Supports biodegradable bag foils. | Variable; depends on materials chosen. | Can use eco-friendly films, but generates more waste from film trimming. |
Analysis
BagMatic’s bag packing machines excel in versatility and efficiency for businesses seeking to optimize packaging processes without significant space or cost investments. Compared to manual methods, they offer substantial labor savings and reduced error rates, making them ideal for scaling operations in competitive markets like the USA and Europe. While VFFS machines provide strong performance for high-volume, uniform production, they are less adaptable for customized or small-batch needs, where BagMatic’s inline printing and vision systems provide a clear edge. For companies prioritizing quick ROI, BagMatic solutions deliver superior workflow improvements and support, including robot integration and professional consultation to tailor systems to specific demands. Businesses should evaluate based on production volume, product type (e.g., small/light parts), and sustainability goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for bag packing machine
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Bag Packing Machines
This section outlines the core technical features of bag packing machines and defines key trade terms commonly used in B2B transactions for sourcing, customization, and procurement. These insights are drawn from industry standards for automatic and semi-automatic systems, focusing on efficiency, automation, and quality control.
Key Technical Properties
Bag packing machines, also known as baggers or table top baggers, automate the packaging process using pre-opened bags-on-a-roll. Below are essential properties that define their performance and suitability for industrial applications:
- Automation Level: Available in semi-automatic (requiring manual product loading) or fully automatic configurations (with robot integration for parts loading and handling).
- Bag Types and Materials: Compatible with printed or unprinted bags, including biodegradable foils for eco-friendly options. Supports bags-on-a-roll for continuous operation.
- Printing Integration: Inline printing capabilities (e.g., using Zebra printers) for on-demand labeling during the bagging process.
- Quality Control Systems: Vision systems with cameras for product registration, accurate counting, and defect detection, ideal for small or lightweight items like seeds.
- Static Neutralization: Features to eliminate static electricity on parts before packaging, ensuring smooth handling and preventing clumping.
- Footprint and Scalability: Compact designs with limited space requirements, scalable from standard machines to customized systems with accessories for optimized input/output.
- Speed and Efficiency: High-speed operation for cost reduction, with options for unique solutions like counting very small parts.
- Additional Accessories: Integration with conveyors, feeders, and neutralization units for enhanced workflow in sectors like manufacturing and e-commerce.
| Property | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Vision System | Camera-based monitoring for quality and count accuracy | Reduces errors and ensures compliance with standards |
| Robot Integration | Automated loading and packaging | Increases throughput and minimizes labor costs |
| Biodegradable Compatibility | Support for eco-friendly bag foils | Meets sustainability regulations in USA and Europe |
| Inline Printing | Real-time bag customization | Enables branding and traceability without secondary processes |
Essential Trade Terminology
In B2B dealings for bag packing machines, understanding these terms facilitates negotiations, contracts, and supply chain management. Terms are standardized across USA and European markets.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): The smallest quantity of machines or accessories a supplier will produce or sell in a single order, often to ensure production efficiency (e.g., 1-10 units for custom systems).
- OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): A company that designs and manufactures machines under its own brand, which may be rebranded by buyers (e.g., Advanced Poly Packaging™ as an OEM partner).
- Customization: Tailored machine designs based on client needs, such as individual packaging solutions for specific workflows.
- Lead Time: The duration from order placement to delivery, typically 4-12 weeks for standard machines and longer for customized ones.
- FOB (Free on Board): Shipping term indicating the point at which risk transfers from seller to buyer (e.g., FOB factory for cost-effective European sourcing).
- CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight): Seller covers costs, insurance, and freight to the buyer’s port, common for USA imports from Europe.
- Bags-on-a-Roll: Pre-opened, continuous bag rolls used in automated baggers for seamless feeding.
- Table Top Bagger: Compact, desktop-sized machine for small-scale or semi-automatic packaging.
- Vision System: Integrated camera technology for automated quality inspection and counting.
- Inline Printer: Device embedded in the machine for printing labels or codes during operation.
For procurement, consult suppliers for stock availability (new or reconditioned) and services like on-site support in Europe or USA.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the bag packing machine Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Bag Packing Machine Sector
The bag packing machine sector has evolved significantly, driven by automation demands, efficiency needs, and regulatory pressures in the USA and Europe. This section examines the historical development, key market trends, sustainability considerations, and sourcing strategies to help B2B professionals optimize procurement and operations.
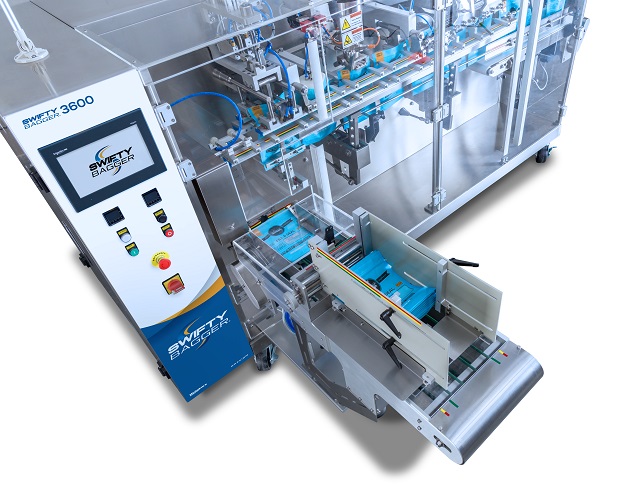
Historical Evolution of Bag Packing Machines
Bag packing machines originated in the mid-20th century as manual and semi-automatic systems to streamline packaging in manufacturing and food industries. Key milestones include:
- 1950s-1970s: Introduction of basic mechanical baggers for bulk goods, focusing on speed and labor reduction.
- 1980s-1990s: Shift to automated systems with electronic controls, enabling integration with production lines and features like inline printing (e.g., Zebra solutions).
- 2000s-Present: Advancement to fully automated, customizable machines with robotics, vision systems for quality control, and static electricity neutralization. Family-owned specialists, now in their third generation, have driven innovations in counting small parts (e.g., seeds) and robot-integrated loading.
This progression reflects a move from labor-intensive processes to high-efficiency, data-driven solutions, reducing costs and improving accuracy.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Current Market Trends
The sector is experiencing robust growth, projected at a CAGR of 5-7% through 2030 in the USA and Europe, fueled by e-commerce, pharmaceuticals, and food packaging demands. Notable trends include:
- Automation and Customization: Demand for semi-automatic and fully automatic machines, with options for standard models or tailored systems. Integration of accessories like robot arms and camera-based counting enhances throughput.
- Inline Printing and Efficiency: Use of technologies like Zebra printers for on-demand bag labeling during bagging, optimizing workflows and reducing inventory needs.
- Compact Footprints and Scalability: Machines designed for limited space, offering quick setup and compatibility with pre-opened bags-on-a-roll, appealing to SMEs and large enterprises.
- Service-Oriented Solutions: Providers emphasize full-service models, including analysis, consultation, and on-site support, with stock availability for new and reconditioned units.
| Trend | Impact on USA/Europe Markets | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Automation Integration | Reduces labor costs by 20-30% | Robot loading for fully automatic systems |
| Digital Printing | Enables variable data on bags | Inline Zebra solutions for branding |
| Compact Designs | Suits space-constrained facilities | Tabletop baggers with small footprints |
These trends prioritize cost reduction, speed, and quality, with providers like BagMatic and Advanced Poly Packaging™ leading in Europe and North America.
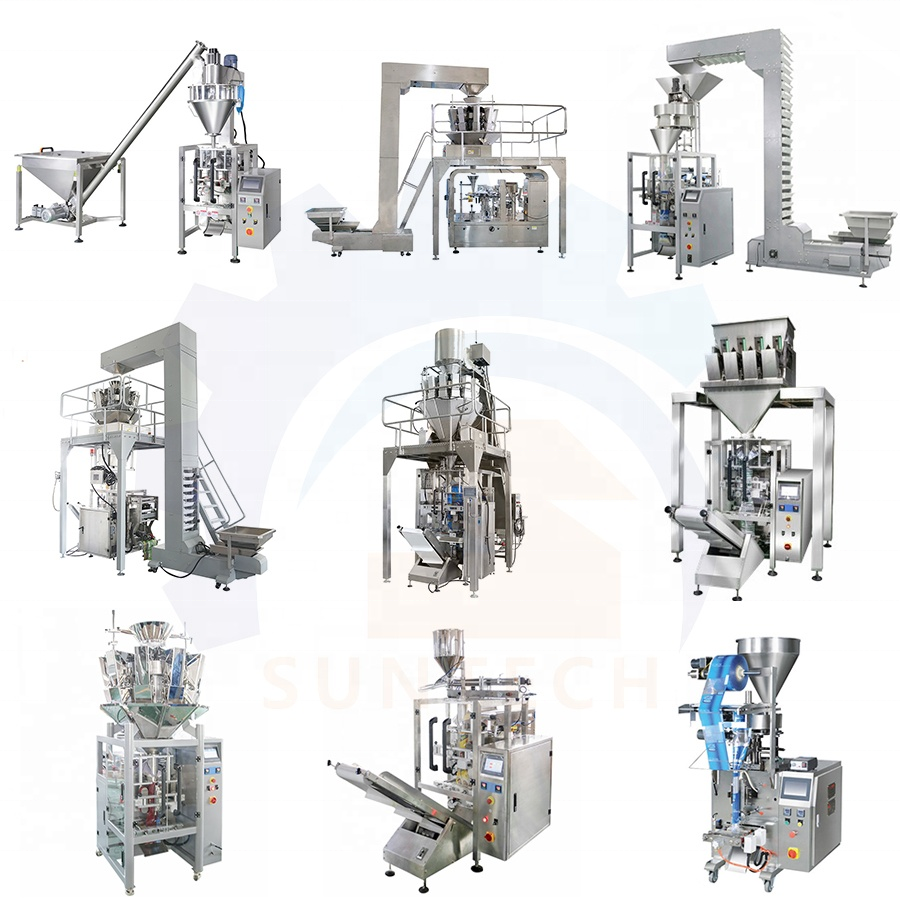
Sustainability Considerations
Sustainability is a core driver, influenced by EU regulations (e.g., Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive) and US initiatives like the EPA’s waste reduction goals. Key aspects include:
- Biodegradable Materials: Shift to eco-friendly bag foils, such as biodegradable pre-opened bags-on-a-roll, reducing plastic waste and aligning with circular economy principles.
- Energy-Efficient Designs: Machines with low-energy consumption and features like static neutralization to minimize material waste.
- Lifecycle Optimization: Providers offer consultations to analyze and refine processes, lowering overall environmental impact through higher efficiency and reduced over-packaging.
Adopting sustainable machines can yield 10-15% cost savings via waste reduction and compliance, with growing demand for certified biodegradable options in food and consumer goods sectors.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Sourcing Strategies
Effective sourcing in the USA and Europe focuses on reliability, customization, and total cost of ownership. Recommended approaches:
- Supplier Evaluation: Prioritize family-owned specialists with proven expertise (e.g., third-generation companies) offering Europe-wide on-site service and competitive pricing.
- Standard vs. Custom: Opt for standard machines for quick deployment or customized solutions for unique needs, such as vision systems for precise counting.
- Brand Partnerships: Source from established brands like Advanced Poly Packaging™ for semi-automated systems, ensuring compatibility with accessories.
- Procurement Tips:
- Conduct detailed process analysis to identify optimization opportunities.
- Seek providers with stock availability and full-service support, including education and maintenance.
- Prioritize fair pricing and reviews (e.g., via Proven Experts) for long-term value.
By aligning sourcing with these trends, businesses can achieve efficient, sustainable bag packing operations tailored to regional market dynamics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of bag packing machine
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Bag Packing Machines
1. What types of bag packing machines are available for B2B applications?
We offer semi-automatic and fully automatic bag packing machines, including tabletop baggers using pre-opened bags-on-a-roll. Options include standard models from brands like Advanced Poly Packaging™ and customized systems tailored to specific workflows, with accessories for product input and output optimization.
2. Can your bag packing machines be customized for unique business needs?
Yes, we provide both standard and fully customized solutions. Through detailed analysis and consultation, we design systems to optimize your packaging processes, including robot integration for automated parts loading and specialized features for counting small or light items like seeds.
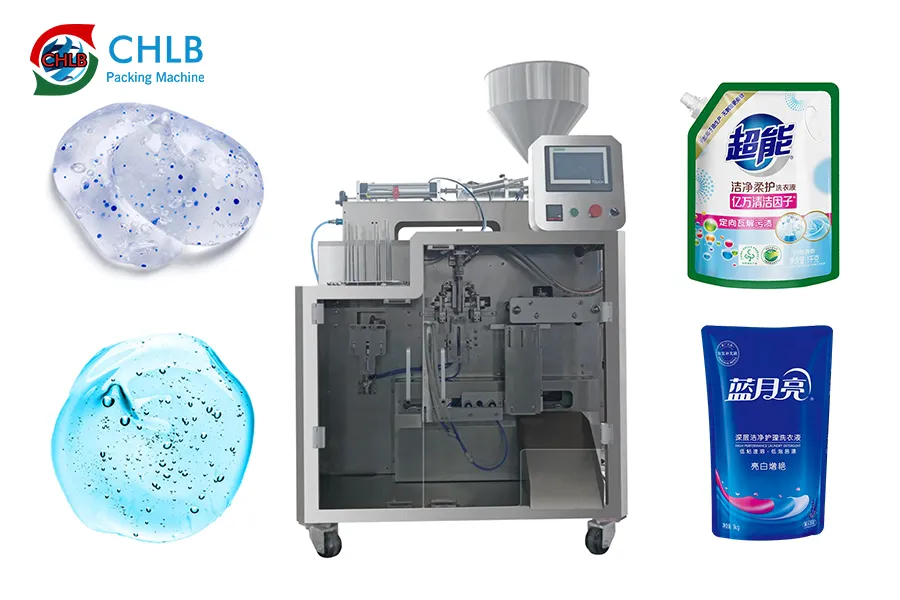
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
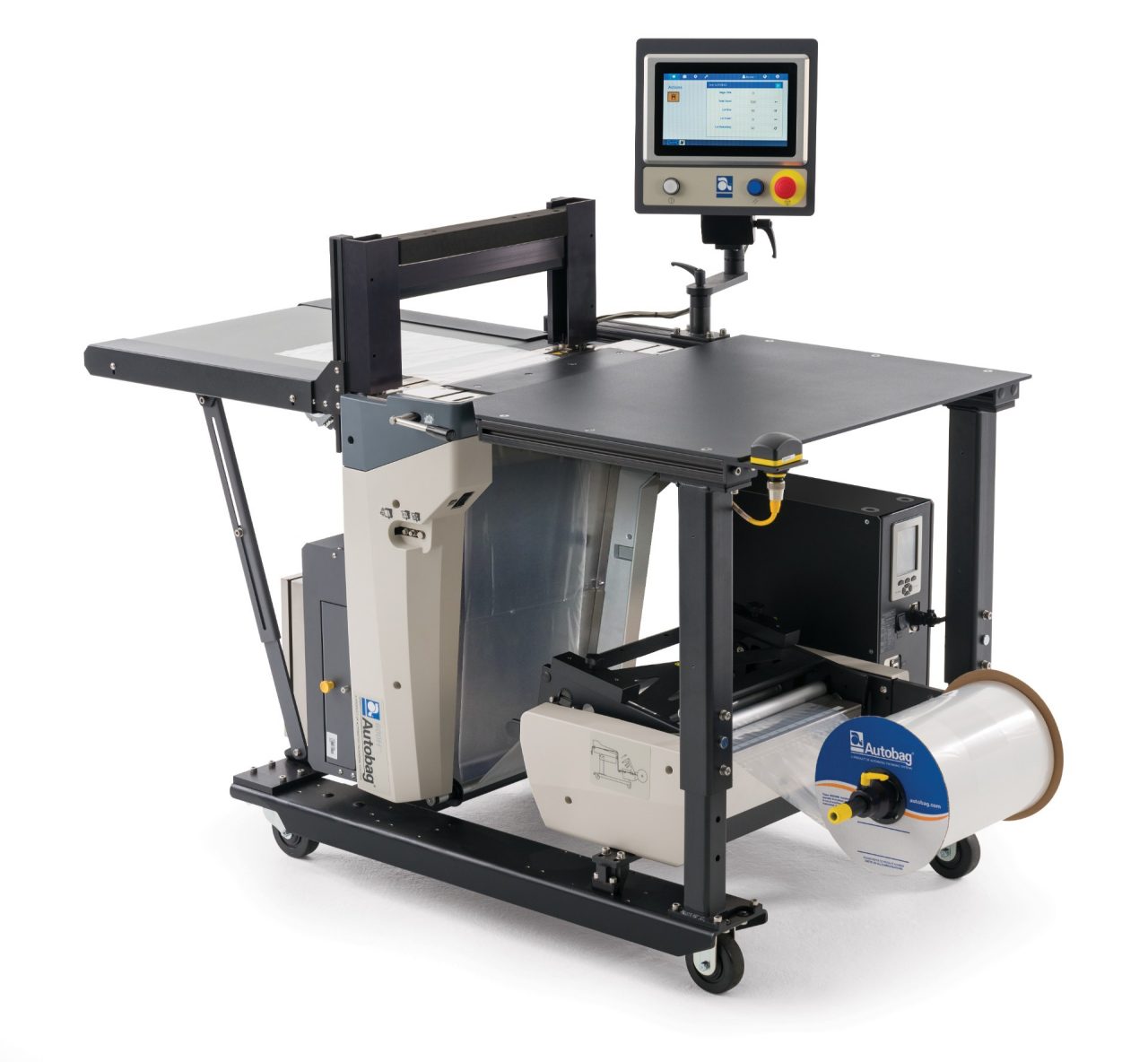
3. What quality control features do your machines include?
Our machines feature a unique vision system with camera technology for accurate product registration, counting, and quality checks before bagging. This ensures precision, especially for small or lightweight parts, and includes static electricity neutralization to prevent issues during packaging.
4. Do you offer biodegradable bag options for sustainable packaging?
Yes, we provide biodegradable pre-opened bags-on-a-roll compatible with our machines. These eco-friendly foils support sustainable operations while maintaining efficiency and compatibility with printing and bagging processes.
5. How does inline printing work on your bag packing machines?
Our systems integrate Zebra printers for inline printing during the bagging process. This allows real-time customization of bags with or without printing, enhancing branding and traceability without interrupting workflow.
6. What kind of customer support and service do you provide?
We offer comprehensive Europe-wide support, including on-site assistance, training, and maintenance for both new and reconditioned machines. As a family-owned company with decades of expertise, we ensure fair pricing and quick response times to minimize downtime.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
7. What are the cost and efficiency benefits of your bag packing solutions?
Our machines reduce working costs by increasing packaging speed and quality, with a compact footprint for space efficiency. B2B clients report high satisfaction due to optimized workflows, competitive pricing, and options for both new and reconditioned units in stock.
8. How do you assist with integrating bag packing machines into existing operations?
We start with an analysis of your current processes, followed by consultation and concept development. This results in tailored solutions that integrate seamlessly, including accessories for better product handling and full automation to boost overall productivity.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for bag packing machine
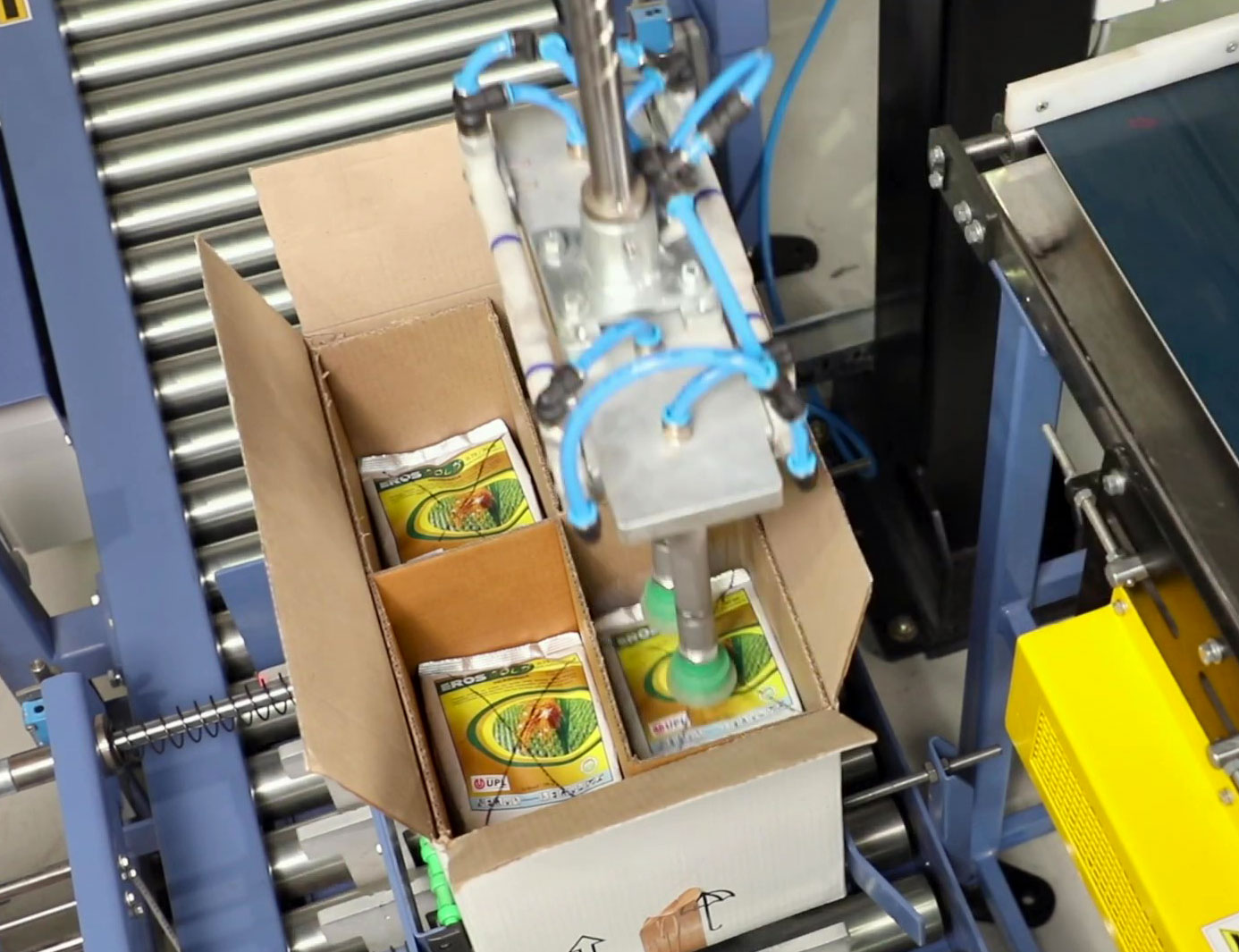
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for Bag Packing Machines
In the competitive landscape of B2B manufacturing, strategic sourcing of bag packing machines delivers substantial value by enhancing operational efficiency, reducing costs, and ensuring scalability. Providers like BagMatic exemplify this through reliable, automated solutions that integrate standard or customized designs, inline printing with Zebra systems, and innovative features such as vision-based quality control and robot integration. These machines optimize workflows for industries handling diverse products, from small parts to biodegradable bag foils, while minimizing footprint and static electricity issues.
Key value propositions include:
– Cost Efficiency: Fair pricing on new and reconditioned units, with rapid ROI through process automation.
– Customization and Flexibility: Tailored systems for semi-automatic or fully automated needs, including unique counting for lightweight items like seeds.
– Sustainability and Innovation: Adoption of biodegradable bags and eco-friendly practices to meet USA and European regulatory demands.
– Service Excellence: Europe-wide on-site support from a family-owned specialist, backed by high customer satisfaction ratings.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Looking ahead, the outlook for bag packing machines is promising, driven by advancements in AI-driven automation, sustainable materials, and integration with Industry 4.0. Businesses sourcing strategically can anticipate 20-30% efficiency gains, positioning them for long-term growth in global markets. Prioritize partners offering comprehensive analysis and consultation to align with evolving demands.
(Word count: 198)
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.