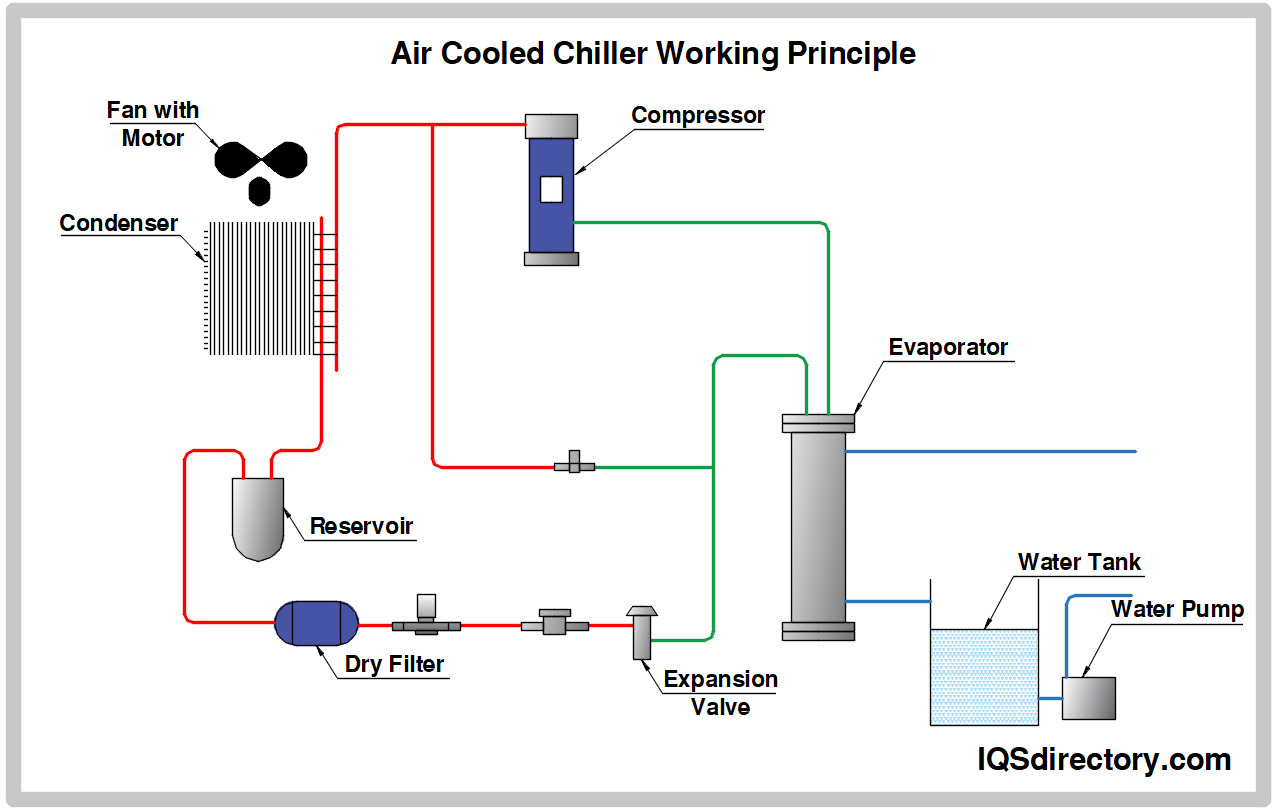
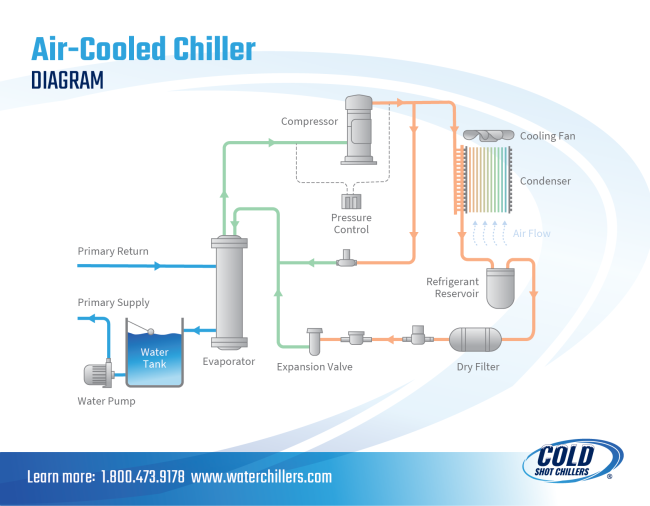
Air Cooled Chiller Diagram: The Ultimate B2B Sourcing Guide for Global Buyer
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for air cooled chiller diagram
Navigating the complexities of sourcing an air-cooled chiller diagram can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As businesses expand and modernize, the need for efficient cooling systems becomes critical to maintain operational efficacy and protect valuable equipment. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of air-cooled chillers, detailing their types, applications, and the key components illustrated in their diagrams.
In this resource, we delve into the nuances of air-cooled chiller systems, highlighting their advantages over water-cooled alternatives, particularly in environments where water scarcity is a concern. We also provide insights into supplier vetting processes, ensuring that buyers can identify reliable manufacturers and distributors. Furthermore, we outline cost considerations that can influence purchasing decisions, empowering stakeholders to make informed choices that align with their budget and operational needs.
This guide serves as an essential tool for B2B buyers looking to optimize their cooling solutions. With actionable insights tailored to the specific challenges faced by industries in diverse regions, readers will gain the knowledge necessary to navigate the global market effectively. Whether you are in Germany, Nigeria, or any other key market, understanding the intricacies of air-cooled chillers will enable you to enhance your business’s efficiency and sustainability.
Understanding air cooled chiller diagram Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Air-Cooled Chiller | Direct heat rejection to ambient air, multiple sizes | Commercial buildings, HVAC systems | Pros: Lower initial cost; Cons: Less efficient in high ambient temperatures. |
| Modular Air-Cooled Chiller | Scalable design, multiple units linked together | Industrial applications, data centers | Pros: Flexible capacity; Cons: Higher upfront investment. |
| Low-Noise Air-Cooled Chiller | Sound-dampening features for noise-sensitive areas | Hospitals, educational facilities | Pros: Quiet operation; Cons: Potentially higher maintenance costs. |
| Heat Recovery Air-Cooled Chiller | Recovers waste heat for reuse in other processes | Manufacturing, food processing | Pros: Energy savings; Cons: Complex installation. |
| Variable Speed Air-Cooled Chiller | Adjusts compressor speed based on demand | Large commercial spaces, process cooling | Pros: Energy efficiency; Cons: Higher initial cost. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Standard Air-Cooled Chillers?
Standard air-cooled chillers are designed for straightforward operation, rejecting heat directly to the surrounding air. Typically available in a range of capacities, they are ideal for commercial buildings and HVAC systems. B2B buyers should consider their lower initial costs, making them accessible for smaller projects. However, their efficiency can decline in high ambient temperatures, which may affect performance in hotter climates.
How Do Modular Air-Cooled Chillers Enhance Scalability?
Modular air-cooled chillers consist of multiple interconnected units, allowing for scalable capacity adjustments. This design is particularly beneficial for industrial applications and data centers that may experience fluctuating cooling demands. Buyers appreciate the flexibility of adding or removing modules as needed, though this scalability often comes with a higher upfront investment compared to standard units.
Why Choose Low-Noise Air-Cooled Chillers?
Low-noise air-cooled chillers are specifically engineered with sound-dampening features, making them suitable for noise-sensitive environments such as hospitals and educational facilities. Their quiet operation is a significant advantage for B2B buyers concerned about noise pollution. However, these units may incur higher maintenance costs due to their specialized components.
What Are the Benefits of Heat Recovery Air-Cooled Chillers?
Heat recovery air-cooled chillers capture waste heat generated during the cooling process and repurpose it for other applications, such as heating water or space heating. This feature is particularly advantageous in manufacturing and food processing industries, where energy efficiency is paramount. While these systems can lead to significant energy savings, the complexity of installation may deter some buyers.
How Do Variable Speed Air-Cooled Chillers Improve Efficiency?
Variable speed air-cooled chillers utilize advanced technology to adjust compressor speeds based on real-time cooling demands. This adaptability makes them ideal for large commercial spaces and process cooling applications where energy efficiency is critical. Although they represent a higher initial investment, the long-term savings on energy costs can justify the expense for many B2B buyers.
Key Industrial Applications of air cooled chiller diagram
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of air cooled chiller diagram | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Chilling in food processing plants | Ensures product safety and quality by maintaining optimal temperatures during production. | Energy efficiency, capacity sizing, and compliance with local regulations. |
| Pharmaceuticals | Cooling in drug manufacturing and storage | Maintains strict temperature control for sensitive products, ensuring efficacy and safety. | Reliability, precision control, and compatibility with existing systems. |
| Plastics and Polymers | Cooling during injection molding processes | Enhances production efficiency and product quality by preventing overheating. | Robustness, maintenance support, and integration with molding machines. |
| HVAC Systems | Chillers in commercial building cooling applications | Provides reliable climate control, improving occupant comfort and energy savings. | System compatibility, energy efficiency ratings, and scalability. |
| Data Centers | Cooling systems for server rooms | Prevents overheating of critical IT infrastructure, ensuring uptime and reliability. | Redundancy features, energy efficiency, and compatibility with existing cooling solutions. |
How is the Air-Cooled Chiller Diagram Applied in the Food and Beverage Industry?
In food processing plants, air-cooled chillers play a critical role in maintaining the required temperatures during production and storage. The air-cooled chiller diagram illustrates how the refrigerant absorbs heat from the process fluids, ensuring products remain safe for consumption. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, considerations include energy efficiency to reduce operational costs and compliance with local health regulations to ensure product safety.
What is the Role of Air-Cooled Chillers in the Pharmaceutical Sector?
Pharmaceutical manufacturers utilize air-cooled chillers to maintain stringent temperature controls essential for drug efficacy and safety. The chiller diagram provides insights into the refrigerant flow and system operation, ensuring that sensitive products are stored and processed at optimal temperatures. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe must prioritize reliability and precision control, alongside compatibility with existing equipment to ensure seamless operations.
How Do Air-Cooled Chillers Enhance Efficiency in Plastics and Polymers Manufacturing?
In the plastics industry, air-cooled chillers are integral to cooling processes during injection molding. The chiller diagram helps manufacturers understand how to optimize cooling cycles, thereby enhancing production efficiency and product quality. For B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets, sourcing considerations include the robustness of the chiller to withstand demanding production environments and the availability of maintenance support to minimize downtime.
Why are Air-Cooled Chillers Important for HVAC Systems?
In commercial buildings, air-cooled chillers are essential for effective HVAC systems, providing reliable climate control. The diagram illustrates the system’s components and flow, highlighting how it contributes to occupant comfort and energy savings. Buyers in Europe and Africa should consider system compatibility, energy efficiency ratings, and scalability to meet future demands.
How Do Data Centers Benefit from Air-Cooled Chillers?
Data centers rely heavily on air-cooled chillers to prevent overheating of critical IT infrastructure. The chiller diagram showcases the cooling process necessary for maintaining optimal operating conditions. For international B2B buyers, key considerations include redundancy features to ensure continuous operation, energy efficiency to manage costs, and compatibility with existing cooling solutions to enhance overall system performance.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘air cooled chiller diagram’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Understanding Chiller System Components
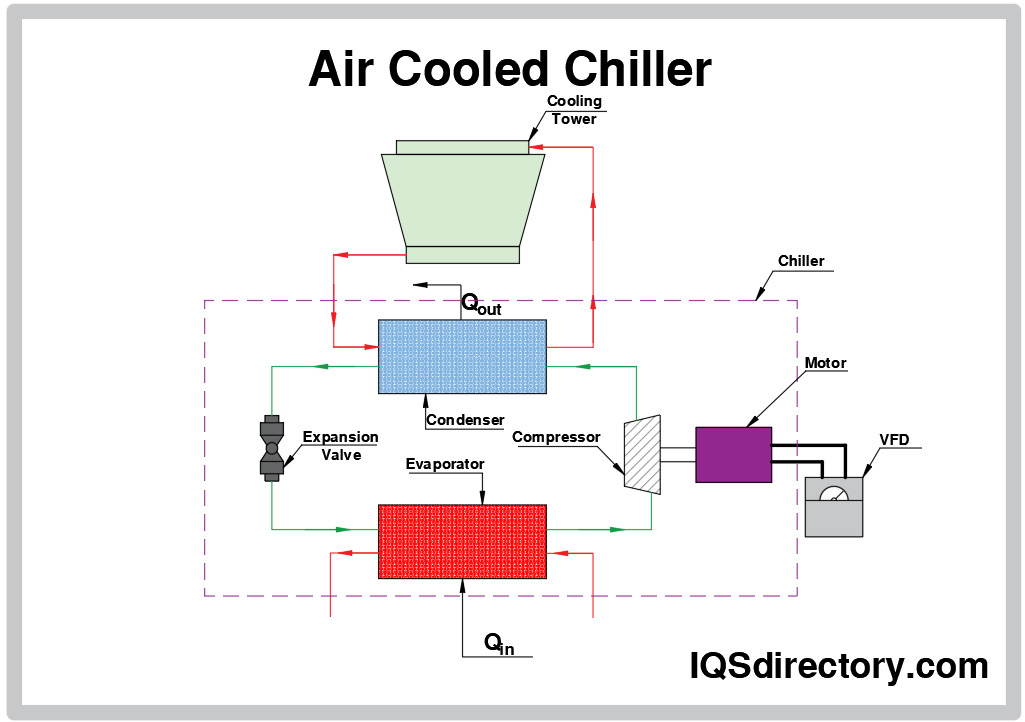
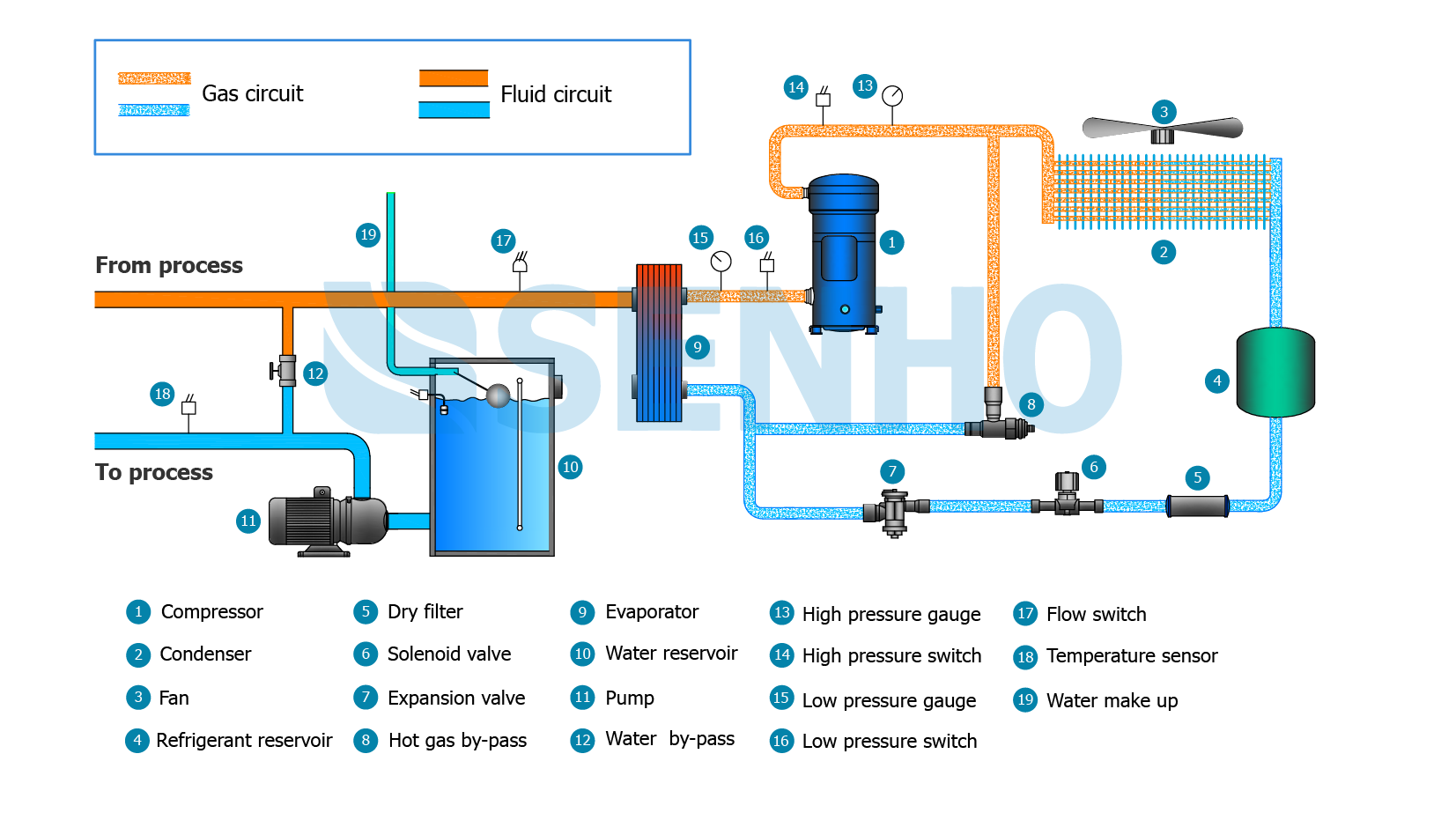
The Problem: B2B buyers, especially those new to industrial cooling systems, often find it challenging to decipher the various components depicted in air-cooled chiller diagrams. For instance, terms like “evaporator,” “compressor,” and “expansion valve” may not be familiar, leading to confusion about how each part contributes to the overall operation. This lack of understanding can hinder effective decision-making when selecting or troubleshooting chiller systems, potentially resulting in costly mistakes or downtime.
Illustrative image related to air cooled chiller diagram
The Solution: To overcome this knowledge gap, buyers should invest time in comprehensive training or resources that break down the chiller system components in detail. Engaging with manufacturers that provide educational materials, such as videos or interactive diagrams, can facilitate a clearer understanding of each component’s role. Additionally, prospective buyers can request tailored training sessions from suppliers or consultants who specialize in air-cooled chillers. By familiarizing themselves with the terminology and functions of each part, buyers will be better equipped to make informed purchasing decisions and effectively communicate their needs with suppliers.
Scenario 2: Inaccurate Sizing and Specifications
The Problem: Sizing an air-cooled chiller appropriately for a specific application is crucial, yet many buyers struggle with this task. Inaccurate sizing can lead to inefficient operation, increased energy costs, or even system failure. For instance, choosing a chiller that is too small may not meet cooling demands, while an oversized unit can lead to unnecessary energy consumption and wear on the system.
The Solution: To ensure accurate sizing and specifications, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of their cooling requirements, considering factors such as process heat loads, ambient conditions, and future scalability. Utilizing software tools or consulting with experienced engineers can provide insights into the precise cooling capacity needed. When reviewing air-cooled chiller diagrams, look for guidelines that indicate recommended capacities based on the application type. Collaborating with reputable suppliers who offer expert advice on sizing based on real-world applications can also mitigate the risk of selecting an inappropriate unit, ultimately leading to more efficient and cost-effective operations.
Scenario 3: Maintenance and Troubleshooting Challenges
The Problem: Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of air-cooled chillers, yet many B2B buyers face challenges in identifying maintenance needs and troubleshooting issues as they arise. Without a clear understanding of the chiller diagram, pinpointing problems like refrigerant leaks or compressor malfunctions can be daunting, leading to extended downtimes and increased operational costs.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize acquiring detailed maintenance manuals and guidelines that align with the specific air-cooled chiller model in use. These resources should include diagrams that highlight critical components and their functions, making it easier to recognize potential issues. Furthermore, establishing a proactive maintenance schedule with a qualified technician who understands the system’s intricacies will facilitate timely interventions. For complex troubleshooting, utilizing digital monitoring systems that provide real-time data on operational parameters can help identify anomalies before they escalate into significant issues. Leveraging the expertise of service providers who can interpret the chiller diagram during maintenance checks will ensure that systems remain in optimal condition and reduce the risk of unexpected failures.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for air cooled chiller diagram
What Are the Best Materials for Air-Cooled Chiller Components?
When selecting materials for the components of air-cooled chillers, several factors must be considered, including thermal properties, pressure ratings, corrosion resistance, and overall compatibility with the refrigerants and process fluids involved. Here, we analyze four common materials used in air-cooled chiller diagrams: copper, aluminum, stainless steel, and plastic composites.
How Does Copper Perform in Air-Cooled Chiller Applications?
Copper is widely recognized for its excellent thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance, making it a preferred choice for heat exchangers and piping in air-cooled chillers. It can withstand high pressures and temperatures, which is crucial in maintaining efficient cooling cycles.
Pros: Copper’s durability and resistance to corrosion enhance its lifespan, while its thermal properties facilitate effective heat exchange, leading to improved energy efficiency.
Cons: The primary drawbacks of copper are its higher cost and susceptibility to pitting corrosion in certain environments, which can lead to leaks.
Impact on Application: Copper is compatible with most refrigerants, but international buyers must consider local regulations regarding copper use, especially in regions with aggressive environmental conditions.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Air-Cooled Chillers?
Aluminum is another common material, particularly for condenser coils and evaporators. Its lightweight nature and good thermal conductivity make it an attractive option for manufacturers looking to reduce overall system weight.
Pros: Aluminum is generally less expensive than copper and offers good resistance to corrosion, especially when anodized.
Cons: While aluminum is lightweight, it is not as strong as copper and may require thicker sections to handle similar pressures, potentially increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s compatibility with various refrigerants and its lighter weight make it suitable for portable or modular chiller designs. However, buyers should ensure compliance with local standards, as aluminum may not be suitable in all industrial applications.
Why Choose Stainless Steel for Air-Cooled Chiller Components?
Stainless steel is often used in air-cooled chillers for components that require high strength and corrosion resistance, such as frames and structural supports. It can handle high pressures and is less likely to corrode than other metals.
Pros: The durability and strength of stainless steel make it ideal for long-term applications, especially in harsh environments. Its resistance to corrosion and staining is also a significant advantage.
Cons: Stainless steel is heavier and more expensive than both copper and aluminum, which may impact installation costs and logistics.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of refrigerants and process fluids, making it versatile for various applications. International buyers should consider the material’s compliance with standards like ASTM and DIN.
How Do Plastic Composites Fit into Air-Cooled Chiller Design?
Plastic composites are increasingly being used in air-cooled chillers for components such as reservoirs and housings. These materials are lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making them appealing for specific applications.
Pros: The low weight and cost of plastic composites can lead to significant savings in manufacturing and transportation. They also provide excellent resistance to chemical corrosion.
Cons: Plastic composites may not withstand high temperatures and pressures as effectively as metals, which can limit their use in critical areas of the chiller.
Impact on Application: Plastic composites are often used in non-structural components, but buyers must ensure that they meet local regulations regarding material safety and environmental impact.
Illustrative image related to air cooled chiller diagram
Summary of Material Selection for Air-Cooled Chillers
| Material | Typical Use Case for air cooled chiller diagram | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Heat exchangers and piping | Excellent thermal conductivity | Higher cost and pitting corrosion risk | High |
| Aluminum | Condenser coils and evaporators | Lightweight and cost-effective | Less strength; potential for manufacturing complexity | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Structural supports and frames | High strength and corrosion resistance | Heavier and more expensive | High |
| Plastic Composites | Reservoirs and non-structural components | Lightweight and resistant to corrosion | Limited pressure/temperature tolerance | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers looking to optimize their air-cooled chiller designs. By understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material, decision-makers can make informed choices that align with their operational requirements and compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for air cooled chiller diagram
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Air-Cooled Chillers?
The manufacturing process of air-cooled chillers is intricate, involving several key stages that ensure the final product meets the required performance and quality standards. This process typically includes material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Air-Cooled Chiller Production?
Material preparation is the first step in manufacturing air-cooled chillers. It involves sourcing high-quality materials such as aluminum, copper, and steel, which are essential for the chiller’s construction. Suppliers must ensure that these materials meet specific standards, such as ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) specifications for metals. The materials are then subjected to quality checks to confirm their integrity and suitability for use in high-pressure environments.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Air-Cooled Chiller Components?
The forming stage involves various techniques to shape the raw materials into specific components of the chiller. Key methods include:
- Sheet Metal Fabrication: Used for creating the chassis and structural components of the chiller. This process may include cutting, bending, and welding.
- Machining: Precise machining processes are employed to manufacture components such as compressor housings and fittings, ensuring tight tolerances and high-quality finishes.
- Extrusion: Aluminum components, such as heat exchanger fins, are often produced through extrusion, allowing for efficient heat transfer and structural integrity.
These techniques require skilled labor and advanced machinery to ensure consistency and precision in every part produced.
How Is the Assembly Process Conducted for Air-Cooled Chillers?
Once individual components are formed, they are brought together in the assembly stage. This process typically follows a systematic approach:
- Sub-Assembly: Smaller components, such as the compressor and evaporator, are assembled separately before being integrated into the main unit.
- Main Assembly: The sub-assemblies are combined, incorporating refrigerant lines, electrical wiring, and control systems. This step often involves rigorous checks to ensure that all components fit together correctly and function as intended.
- Final Assembly and Integration: The completed unit undergoes final integration, where additional systems like pumps and fans are installed. This stage also includes the installation of safety features, such as pressure relief valves and temperature sensors.
Each assembly stage is critical, as errors can lead to performance issues or safety hazards.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Air-Cooled Chillers?
Finishing processes enhance the durability and aesthetic appeal of air-cooled chillers. Key techniques include:
- Surface Treatment: Components may undergo processes such as anodizing or powder coating to protect against corrosion and improve appearance.
- Testing and Calibration: Before leaving the factory, units are rigorously tested for performance, efficiency, and safety compliance. This includes pressure testing and functional checks of electrical systems.
Proper finishing ensures that the chillers can withstand operational stresses and environmental conditions, particularly in diverse climates such as those found in Africa and the Middle East.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Air-Cooled Chiller Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of air-cooled chillers, ensuring that products meet both international standards and customer expectations. Various international and industry-specific standards guide these QA processes.
What International Standards Apply to Air-Cooled Chiller Manufacturing?
Manufacturers often adhere to several international quality standards, including:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system, focusing on meeting customer needs and enhancing satisfaction.
- CE Marking: Essential for products sold in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For manufacturers involved in oil and gas applications, following American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is crucial for quality assurance.
These standards not only enhance product quality but also facilitate market access for international buyers.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically integrated throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials and components are inspected upon arrival to verify that they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, various checks are conducted at each stage of assembly to ensure components are correctly fabricated and assembled.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the finished product undergoes comprehensive testing to assess performance against specifications and safety standards.
These checkpoints are vital for maintaining high-quality outputs and minimizing the risk of failures in the field.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Air-Cooled Chillers?
Testing methods for air-cooled chillers are diverse and tailored to assess various performance metrics:
- Pressure Testing: Ensures that the refrigerant circuit can withstand operational pressures without leaking.
- Thermal Performance Testing: Evaluates the chiller’s ability to maintain desired temperatures under load conditions.
- Electrical Testing: Checks the functionality of electrical components and ensures safety compliance.
B2B buyers should inquire about these testing protocols to understand the reliability of the chillers they are considering.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, verifying supplier quality control practices is crucial for ensuring product reliability and compliance with standards. Here are some strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can help verify adherence to quality standards and manufacturing processes. This includes reviewing documentation and witnessing QC processes firsthand.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports from suppliers can provide insights into their QA processes and any issues encountered during production.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the manufacturing practices and product quality, ensuring compliance with international standards.
These strategies are particularly important for buyers from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, and Europe, where local regulations and market expectations may vary significantly.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must navigate unique challenges regarding quality control in different markets. For example:
Illustrative image related to air cooled chiller diagram
- Cultural Differences: Understanding local practices and standards can help buyers communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure alignment on quality expectations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Buyers should familiarize themselves with the specific regulations governing air-cooled chillers in their target markets, as compliance can differ significantly between regions.
- Logistical Considerations: Factors such as shipping, customs, and local climate can impact the performance and reliability of chillers, necessitating thorough supplier evaluations.
By addressing these nuances, B2B buyers can better mitigate risks and ensure they are sourcing high-quality air-cooled chillers tailored to their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘air cooled chiller diagram’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide provides B2B buyers with a comprehensive checklist for procuring an air-cooled chiller diagram. Understanding the components and functions of an air-cooled chiller is essential for effective cooling solutions in various industries, especially for buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This guide will help streamline the procurement process, ensuring that you select the right equipment for your needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, clearly outline your technical requirements. Identify the cooling capacity, application type, and environmental conditions the chiller will operate under. This will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure that they can meet your specific needs.
- Considerations: Cooling load calculations, ambient temperature ranges, and desired energy efficiency ratings.
Step 2: Research Available Models
Familiarize yourself with different models of air-cooled chillers on the market. Understanding the variations in design, efficiency, and application will allow you to make informed decisions.
- Key Features to Compare: Energy efficiency ratings (EER, SEER), noise levels, and size dimensions.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, thoroughly vet their capabilities and reputation. Look for companies with a proven track record in providing air-cooled chillers that meet your specifications.
Illustrative image related to air cooled chiller diagram
- What to Request: Company profiles, customer references, and case studies that demonstrate successful installations in similar applications.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your potential suppliers have the necessary certifications and compliance with local and international standards. This is crucial for guaranteeing safety and reliability in the operation of the chillers.
- Important Certifications to Look For: ISO 9001 for quality management, CE marking for compliance with European standards, and local environmental compliance certifications.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty
Investigate the level of after-sales support and warranty terms offered by your suppliers. Strong support can prevent costly downtimes and ensure that you receive assistance when needed.
- Key Aspects to Consider: Availability of spare parts, maintenance services, and the length and terms of the warranty.
Step 6: Request Detailed Quotations
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request detailed quotations that break down costs. Look for transparency in pricing, including equipment costs, installation fees, and ongoing maintenance expenses.
- What to Examine: Hidden costs, payment terms, and delivery timelines.
Step 7: Conduct a Final Evaluation
Before making a final decision, compare all gathered information and assess which supplier aligns best with your needs. Consider not only the price but also the quality of the product, service, and overall supplier reliability.
- Decision-Making Criteria: Total cost of ownership, supplier reputation, and alignment with your technical specifications.
By following this checklist, you can streamline the procurement of an air-cooled chiller diagram, ensuring that you select a solution that meets your operational requirements and budget constraints.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for air cooled chiller diagram Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Air Cooled Chiller Diagrams?
Understanding the cost structure of air-cooled chiller diagrams is critical for B2B buyers seeking to make informed purchasing decisions. The major cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
Materials represent a significant portion of the cost. High-quality components such as compressors, condensers, and evaporators are essential for optimal performance and longevity. Buyers should expect variations in material costs based on specifications and certifications.
Labor costs encompass the workforce involved in the design and assembly of the chillers. Skilled labor is necessary for ensuring the precision required in manufacturing and installation.
Manufacturing overhead includes expenses related to the facility, equipment, and utilities used in production. This can vary significantly depending on the geographic location of the manufacturer, affecting overall pricing.
Tooling costs refer to the expenses incurred in creating the tools and molds required for production. Custom designs may incur higher tooling costs, which can influence pricing.
Quality Control is crucial in ensuring that all components meet industry standards. Rigorous QC processes may add to the overall cost but are essential for reliability and performance.
Logistics costs involve transporting the finished chillers to the buyer’s location, which can fluctuate based on distance, shipping methods, and international trade regulations.
Illustrative image related to air cooled chiller diagram
Margins are determined by the manufacturer’s pricing strategy and can vary widely based on brand reputation, market demand, and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Air Cooled Chiller Diagram Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of air-cooled chiller diagrams, which are vital for B2B buyers to consider.
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) often dictate pricing structures. Larger orders typically lead to discounts, whereas smaller orders might incur higher per-unit costs.
Specifications and Customization can significantly affect price. Custom features or designs tailored to specific applications may increase costs due to additional engineering and manufacturing efforts.
Material Choices are another critical factor. Opting for premium materials that offer enhanced performance and durability will elevate costs but may provide better long-term value.
Quality and Certifications can also influence pricing. Products that meet stringent industry standards or possess certifications may command higher prices but offer added reliability.
Supplier Factors, such as the supplier’s reputation, experience, and production capabilities, can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their track record of quality and service.
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs and risk. Understanding these terms is crucial for international buyers to accurately assess the total landed cost of their purchases.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Navigate the Air Cooled Chiller Diagram Market?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance purchasing effectiveness.
Negotiation is key. Buyers should engage in discussions to explore discounts, especially for larger orders. Cultivating a strong relationship with suppliers can lead to better terms and pricing.
Cost Efficiency can be maximized by considering the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO). Beyond the initial purchase price, factors such as maintenance, energy consumption, and operational efficiency should be evaluated to determine the best value.
Buyers should also be aware of pricing nuances specific to their regions. Currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local market conditions can significantly affect costs.
Lastly, conducting thorough market research can provide insights into competitive pricing and available alternatives, empowering buyers to make well-informed decisions.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
Prices for air-cooled chiller diagrams can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. This analysis provides a general overview and should not be taken as definitive pricing. Buyers are encouraged to obtain specific quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing tailored to their unique needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing air cooled chiller diagram With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Cooling Solutions for Industrial Applications
In the realm of industrial cooling, air-cooled chillers play a vital role in managing thermal loads effectively. However, several alternative solutions exist that cater to varying operational needs, budgets, and environmental conditions. This section delves into a comparative analysis of air-cooled chillers against two notable alternatives: water-cooled chillers and evaporative cooling systems. Each option presents unique advantages and challenges, allowing B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Air Cooled Chiller Diagram | Water-Cooled Chiller | Evaporative Cooling System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Moderate efficiency, suitable for smaller loads | High efficiency for larger loads | Highly efficient in dry conditions |
| Cost | Lower initial costs, no water usage | Higher initial costs, ongoing water costs | Moderate initial costs, lower operational costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple installation, minimal infrastructure | Complex setup with cooling towers and pumps | Easy installation, requires water source |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance requirements | Higher maintenance due to water treatment | Regular maintenance needed to prevent scaling |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for small to medium facilities | Best for large industrial operations | Suitable for dry, hot climates |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Water-Cooled Chillers?
Water-cooled chillers operate on a different principle, using water to reject heat from the refrigerant. They generally offer higher efficiency, particularly in larger installations, as they can effectively manage heat loads with less energy consumption. However, the initial costs can be significant due to the need for additional infrastructure, including cooling towers and pumps. Maintenance is another critical factor, as these systems require regular water treatment and monitoring to prevent scaling and corrosion. They are best suited for large industrial operations where cooling loads are substantial and consistent.
How Do Evaporative Cooling Systems Compare?
Evaporative cooling systems utilize the natural process of evaporation to cool air. These systems are highly efficient, especially in hot and dry climates, as they can provide significant temperature drops at lower energy costs. The initial setup is relatively straightforward, requiring only a water source. However, they do necessitate regular maintenance to avoid issues such as scaling and potential water quality problems. Evaporative cooling is an excellent choice for facilities located in arid regions, where humidity levels are low, allowing for optimal performance.
Illustrative image related to air cooled chiller diagram
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Cooling Solution?
Selecting the appropriate cooling solution requires a thorough understanding of specific operational needs and environmental conditions. Buyers should consider the size of their facility, the thermal loads they need to manage, and the local climate. Budget constraints also play a crucial role; while air-cooled chillers may offer lower initial costs, water-cooled systems might provide long-term savings in energy efficiency. Evaporative cooling may present a viable option for those operating in hot, dry areas. By analyzing these factors and understanding the unique characteristics of each system, B2B buyers can make strategic decisions that align with their cooling requirements and business goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for air cooled chiller diagram
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Air-Cooled Chiller Diagrams?
When evaluating air-cooled chillers, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some of the critical specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
-
Cooling Capacity
This is measured in tons or kilowatts and indicates how much heat the chiller can remove from a process. A higher cooling capacity is essential for larger applications or facilities with significant thermal loads. Buyers should align their needs with the chiller’s capacity to ensure efficient operation and avoid over or under-sizing, which can lead to increased energy costs and inadequate cooling. -
Refrigerant Type
The type of refrigerant used in an air-cooled chiller significantly impacts its efficiency and environmental footprint. Common refrigerants include R-410A and R-134A, with newer options like R-32 being more environmentally friendly. Buyers must consider regional regulations on refrigerants, as certain types may be restricted or phased out in specific markets. -
Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER)
EER is a measure of the chiller’s cooling output divided by its energy consumption, expressed in BTU/Watt. A higher EER indicates better energy efficiency, which is crucial for reducing operational costs. In markets like Europe, where energy efficiency is heavily regulated, opting for higher EER units can result in significant savings and compliance with local standards. -
Operating Temperature Range
This specification indicates the ambient temperatures within which the chiller can operate effectively. Understanding the range is vital for applications in regions with extreme weather conditions, ensuring that the chiller performs reliably throughout the year. -
Noise Level
Measured in decibels (dB), the noise level of an air-cooled chiller is an important consideration for installations near residential areas or noise-sensitive environments. Selecting a chiller with a lower noise output can help maintain compliance with local noise ordinances and enhance user comfort. -
Control System
Modern chillers often feature advanced control systems that allow for real-time monitoring and automation of operations. Understanding the capabilities of the control system can help buyers optimize performance, reduce downtime, and enhance energy savings.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Air-Cooled Chillers?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some key terms that decision-makers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces components that are used in another company’s end product. In the context of air-cooled chillers, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers assess the quality and reliability of the components used in the systems they are purchasing. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
This term refers to the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is critical for budgeting and inventory management, as it can affect the total cost of ownership and the ability to scale operations. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to solicit price bids from suppliers. It outlines the specifications and requirements for the chiller systems needed. Crafting a well-defined RFQ can lead to better pricing and clearer understanding of supplier capabilities. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for understanding shipping, insurance, and delivery responsibilities, which can impact overall costs and logistics. -
Lead Time
This term refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. Knowing the lead time is essential for project planning and ensuring that the chiller systems arrive when needed to avoid operational delays. -
Warranty Period
The warranty period indicates how long the manufacturer will cover repairs or replacements for defects. Understanding warranty terms is important for assessing long-term value and risk associated with the purchase.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions regarding air-cooled chillers, ultimately leading to more successful procurement outcomes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the air cooled chiller diagram Sector
What Are the Global Drivers Influencing the Air-Cooled Chiller Diagram Market?
The air-cooled chiller market is significantly influenced by several global drivers, including the increasing demand for energy-efficient cooling solutions and the growing industrial sector across regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East. As industries expand, the need for reliable and efficient cooling systems becomes paramount, particularly in sectors such as manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and data centers. Furthermore, advancements in technology, such as the integration of IoT for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, are revolutionizing how businesses approach cooling solutions.
Emerging trends indicate a shift towards modular and compact chiller systems that are easier to install and maintain, particularly in urban settings where space is limited. International B2B buyers are increasingly looking for systems that not only meet their cooling needs but also align with their operational efficiency goals. In Europe, regulations aimed at reducing carbon emissions are driving the adoption of air-cooled chillers as a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional water-cooled systems. Consequently, suppliers must adapt to these dynamics by offering innovative, energy-efficient products that comply with local regulations while meeting the diverse needs of international markets.
How Do Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Air-Cooled Chiller Diagram Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a critical concern for B2B buyers in the air-cooled chiller sector, as companies increasingly recognize the environmental impact of their operations. The production and operation of chillers can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption, prompting businesses to seek solutions that minimize these effects. Buyers are now prioritizing suppliers that offer ‘green’ certifications, such as Energy Star or LEED, which indicate adherence to environmentally responsible practices.
Moreover, ethical sourcing is gaining traction, with buyers interested in the entire supply chain—from raw materials to manufacturing processes. Companies that can demonstrate transparency and sustainability in their supply chains are more likely to gain the trust of international buyers. The use of eco-friendly refrigerants and materials, along with efficient energy use, not only helps in meeting regulatory compliance but also enhances brand reputation. In regions like Europe and parts of Africa, where sustainability regulations are stringent, suppliers that focus on these aspects can position themselves as leaders in the market.
How Has the Air-Cooled Chiller Market Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the air-cooled chiller market reflects broader technological advancements and changing industrial needs. Initially, chillers were bulky, energy-intensive systems primarily used in large industrial setups. However, the introduction of more compact designs and high-efficiency models has made air-cooled chillers suitable for a wider range of applications, including commercial buildings and small enterprises.
Over the years, the focus has shifted from merely cooling capabilities to incorporating energy efficiency and sustainability. The advent of advanced control systems and smart technologies has further transformed the landscape, enabling predictive maintenance and real-time performance monitoring. Today, air-cooled chillers are not only essential for temperature control but also play a critical role in energy management strategies for businesses across various sectors. As the market continues to evolve, international buyers must stay informed about the latest innovations to make educated sourcing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of air cooled chiller diagram
-
How do I choose the right air-cooled chiller diagram for my application?
Selecting the appropriate air-cooled chiller diagram involves understanding the specific cooling needs of your process. Consider factors such as the required cooling capacity, the temperature range, and the operational environment. Reviewing the schematic will help identify components like compressors, condensers, and expansion valves that align with your system’s requirements. Collaborating with suppliers can also provide insights into the most efficient designs for your application, ensuring optimal performance and energy efficiency. -
What are the key components to look for in an air-cooled chiller diagram?
Essential components to examine in an air-cooled chiller diagram include the compressor, evaporator, condenser, and expansion valve. The compressor is critical for circulating refrigerant, while the evaporator absorbs heat from the process fluid. The condenser releases this heat to the atmosphere, and the expansion valve regulates refrigerant flow. Additionally, components like filters, gauges, and pumps play vital roles in ensuring system efficiency and reliability, making it important to assess their specifications in the diagram. -
How can I verify the quality and reliability of an air-cooled chiller supplier?
To ensure supplier reliability, conduct thorough research on their reputation, including reviews and testimonials from previous clients. Verify their certifications and industry standards compliance, such as ISO certifications. Request references and case studies showcasing their experience with similar projects. Additionally, consider visiting their facilities if possible, or ask for product samples to assess the quality firsthand. Engaging in direct discussions about your specific needs can also provide insights into their customer service and technical support capabilities. -
What customization options are available for air-cooled chillers?
Many suppliers offer customization options for air-cooled chillers to meet specific operational requirements. Customizations can include variations in cooling capacity, design modifications for space constraints, or additional features like sound insulation and energy-efficient components. It’s advisable to discuss your unique needs with potential suppliers early in the sourcing process to understand the scope of available customizations and any implications for lead time and cost. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for air-cooled chillers?
Minimum order quantities for air-cooled chillers can vary significantly among suppliers. Factors influencing MOQ include production capabilities, inventory levels, and the complexity of the chiller design. For larger manufacturers, the MOQ might be higher due to economies of scale, while smaller suppliers may accommodate lower quantities. It’s important to clarify MOQ with suppliers during negotiations, especially if you’re sourcing for a pilot project or smaller facility. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing air-cooled chillers?
Payment terms for air-cooled chillers typically vary based on the supplier and the size of the order. Common terms may include upfront payments, partial payments during production, and final payments upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer financing options or flexible payment plans for larger orders. Always negotiate clear payment terms before finalizing contracts to ensure both parties have aligned expectations and to avoid potential cash flow issues. -
How do I ensure efficient logistics for importing air-cooled chillers?
Efficient logistics for importing air-cooled chillers involve planning for shipping, customs clearance, and local delivery. Collaborate with suppliers to understand their shipping options and timelines. Engage a reliable freight forwarder who specializes in industrial equipment to navigate customs regulations in your region. Additionally, consider local transportation arrangements to ensure timely delivery to your facility. Proper logistics management can minimize delays and reduce overall costs. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from my air-cooled chiller supplier?
Quality assurance measures from suppliers of air-cooled chillers should include rigorous testing protocols, adherence to international standards, and detailed documentation. Look for suppliers who provide certifications, such as ISO or ASME, and conduct performance testing on their chillers before shipping. Additionally, inquire about warranty terms and post-sale support, as these can indicate the supplier’s commitment to quality and customer satisfaction. Regular maintenance and service agreements can also be beneficial in ensuring long-term reliability.
Top 2 Air Cooled Chiller Diagram Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Facebook – Valves Overview
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Facebook – Valves Overview, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. Alpine Intel – Chillers
Domain: alpineintel.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Chillers are complex cooling systems that transfer heat away from spaces requiring climate control using water or a water solution. There are two main types of chillers: water-cooled and air-cooled. Water-cooled chillers are more efficient and have a longer lifespan, commonly used in medium to large facilities like airports, hospitals, and commercial buildings. Air-cooled chillers are typically us…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for air cooled chiller diagram
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Air-Cooled Chiller Procurement?
In conclusion, understanding the intricacies of the air-cooled chiller diagram is essential for international B2B buyers seeking efficient cooling solutions. Key components such as the compressor, evaporator, and condenser play pivotal roles in the cooling process, and recognizing their functions can lead to informed purchasing decisions.
Strategic sourcing offers significant advantages, including cost savings, improved supplier relationships, and enhanced operational efficiency. By partnering with reputable manufacturers and distributors, buyers can ensure they acquire high-quality chillers tailored to their specific needs, ultimately driving down long-term operational costs.
As the global demand for energy-efficient cooling systems continues to rise, now is the time for businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including Germany and Nigeria, to invest in innovative air-cooled chiller technology. Embrace the opportunity to optimize your cooling processes and position your business for future growth. Engage with trusted suppliers today to explore the latest advancements in air-cooled chillers and ensure your operations remain competitive and sustainable.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.