A Deep Dive into What Is Blind Broaching Solution
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is blind broaching
In the complex landscape of manufacturing, sourcing effective solutions for precision machining can be a daunting task. One such solution is blind broaching, a process that allows for the creation of internal shapes, such as keyways, without the need for a through hole. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource for international B2B buyers seeking to understand the nuances of blind broaching. It covers various types of broaching methods, applications across different industries, and best practices for supplier vetting and cost considerations.
As businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia, increasingly rely on advanced manufacturing techniques, understanding blind broaching becomes essential. This guide empowers buyers to make informed purchasing decisions by providing insights into the technical requirements, potential challenges, and solutions associated with blind broaching. Additionally, it highlights the importance of chip management, tooling options, and relief areas necessary for successful broaching operations.
By leveraging the information contained within this guide, B2B buyers can enhance their operational efficiency and product quality while navigating the global market for blind broaching solutions. With a focus on actionable insights, this resource aims to demystify the process and facilitate strategic sourcing decisions that align with the unique needs of diverse manufacturing environments.
Understanding what is blind broaching Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blind Keyway Broaching | Keyway stops in the middle of the material; requires relief area | Electric motors, automotive components | Pros: High precision; Cons: Requires careful setup |
| Rotary Broaching | Utilizes wobble technique; allows for various shapes in blind holes | Socket cap screws, custom fasteners | Pros: Fast and efficient; Cons: Limited to specific forms |
| Blind Spline Broaching | Similar to keyway but designed for spline profiles; depth control | Gear manufacturing, coupling components | Pros: Versatile for different spline types; Cons: Complexity in setup |
| Blind Hole Broaching | Can create hex, square, and torx forms; typically requires pre-drilling | Tooling, fixtures, custom parts | Pros: Flexible shape options; Cons: Requires precision alignment |
| Blind Slot Broaching | Creates slots in blind holes; often used in conjunction with other forms | Mechanical assemblies, housing components | Pros: Effective for tight spaces; Cons: Chip management challenges |
What Are the Characteristics of Blind Keyway Broaching?
Blind keyway broaching is a specialized process where a keyway is machined into a workpiece that does not extend through the entire material. This method requires the creation of a relief area to prevent damage to the tool during retraction. It is ideal for applications in electric motors and automotive components where precision is crucial. Buyers should consider the need for adequate relief space and the ability of their machines to handle such operations.
How Does Rotary Broaching Work for Blind Holes?
Rotary broaching, or wobble broaching, is a fast and efficient method for machining various polygonal shapes, such as hex, square, and torx forms, into blind holes. This technique is particularly advantageous for socket cap screws and custom fasteners. It allows for quick machining on lathes and mills without requiring a through hole. Buyers should evaluate their machining capabilities and the specific forms they need, as this method may be limited to certain geometries.
What Are the Applications of Blind Spline Broaching?
Blind spline broaching is tailored for creating spline profiles within a blind hole, making it suitable for gear manufacturing and coupling components. This method shares similarities with keyway broaching but requires more precise depth control. Buyers should assess the complexity of their designs and the necessary tooling, as the setup can be intricate but offers high versatility for various spline configurations.
Why Is Blind Hole Broaching Important for Custom Tooling?
Blind hole broaching allows for the creation of various shapes, including hex, square, and custom forms, making it essential for tooling and fixture applications. This method often requires pre-drilling to facilitate chip removal, ensuring a smooth machining process. Buyers must prioritize precision alignment and the capability of their machines to handle the required forms, as misalignment can lead to costly errors.
What Are the Benefits of Blind Slot Broaching?
Blind slot broaching is effective for creating slots in blind holes, often used alongside other broaching forms. This method is beneficial for mechanical assemblies and housing components where space is limited. Buyers should be aware of the challenges related to chip management during the broaching process, as effective chip evacuation is critical for maintaining tool integrity and achieving desired tolerances.
Key Industrial Applications of what is blind broaching
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of what is blind broaching | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Manufacturing of keyways for transmission components | Enhanced precision and reliability in power transmission | Need for high-quality broaching tools that maintain tolerances |
| Aerospace | Creation of blind keyways in engine components | Improved performance and safety through exact specifications | Certification of tools to meet stringent industry standards |
| Electrical Equipment | Broaching keyways in electric motor shafts | Increased efficiency and reduced production downtime | Access to specialized broaching machines for complex shapes |
| Heavy Machinery | Fabrication of keyways in hydraulic systems | Enhanced operational efficiency and reduced wear on parts | Availability of durable broaching tools for tough materials |
| Construction Machinery | Producing blind keyways in gear assemblies | Improved strength and durability in high-stress applications | Sourcing from reliable suppliers with experience in heavy-duty applications |
How is Blind Broaching Applied in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, blind broaching is essential for creating precise keyways used in transmission components. This process allows manufacturers to achieve tight tolerances that are critical for the effective transfer of power. The primary challenge is ensuring that the broaching tools used can handle the high volume of production while maintaining accuracy. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, should consider sourcing tools that are known for their durability and reliability, which can lead to reduced maintenance costs and improved production efficiency.
What Role Does Blind Broaching Play in Aerospace Applications?
In aerospace, blind broaching is utilized for machining keyways in critical engine components. The precision required in this industry is paramount, as even minor deviations can lead to catastrophic failures. Buyers in this sector must ensure that the broaching tools are certified to meet rigorous aerospace standards. Additionally, sourcing from reputable manufacturers with a track record in aerospace applications is crucial for ensuring safety and compliance, particularly for buyers from the Middle East and Europe.
How is Blind Broaching Used in Electrical Equipment Manufacturing?
For electrical equipment, blind broaching is commonly employed to create keyways in electric motor shafts. This application enhances the efficiency of motors by ensuring that components fit together seamlessly. The challenge lies in selecting tools that can handle diverse materials and complex shapes. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who offer a variety of broaching tools tailored for different applications, ensuring compatibility with their specific machinery and production processes.
Why is Blind Broaching Important for Heavy Machinery?
In the heavy machinery industry, blind broaching is critical for fabricating keyways in hydraulic systems. This process ensures that hydraulic components work efficiently under high pressure, reducing the risk of failure. Buyers must focus on sourcing robust broaching tools capable of machining tough materials, which is essential for the longevity and performance of machinery. International buyers should also consider suppliers who can offer technical support and guidance on best practices for broaching in heavy-duty applications.
How Does Blind Broaching Benefit Construction Machinery?
Blind broaching is widely used in the construction machinery sector for producing keyways in gear assemblies. The strength and durability of these assemblies are vital for the machinery’s overall performance. Buyers should seek out suppliers who specialize in broaching tools for construction applications, as these tools need to withstand harsh operating conditions. Additionally, ensuring that the tools are designed for ease of use and maintenance can help reduce downtime and improve productivity in construction operations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is blind broaching’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Achieving Accurate Blind Keyway Depth
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with achieving the precise depth for blind keyways during machining operations. The challenge arises because a blind keyway must end accurately within the material without breaking through, which can lead to increased setup times and potential product defects. In regions with varying machining capabilities, such as Africa or South America, access to advanced machinery may be limited, compounding the issue for manufacturers who are trying to maintain quality while minimizing costs.
The Solution: To address this challenge, buyers should invest in CNC broaching tools that are specifically designed for blind keyway applications. Utilizing broaches with inserts allows for greater precision and adaptability across different machines. It’s crucial to ensure that the tooling selected includes features for depth control, such as adjustable stops or programmable depth settings. Additionally, implementing a pre-drilling process can help create a deeper cavity for chip accumulation, thus preventing tool damage and ensuring a cleaner cut. Training operators on the importance of chip evacuation techniques, such as using coolant to help flush away debris, can also improve results significantly. By sourcing high-quality tools and investing in operator training, manufacturers can enhance their machining accuracy and reduce the risk of costly errors.
Scenario 2: Chip Accumulation Leading to Tool Damage
The Problem: One of the most common pain points faced by manufacturers using blind broaching is chip accumulation at the bottom of the blind hole. This often leads to tool damage, as the chips can exert pressure on the cutting edge when the tool is retracted, particularly in processes that require a flat-bottomed blind hole. This is especially concerning for companies in the Middle East and Europe where high production volumes demand consistent tool performance and minimal downtime.
The Solution: Implementing a strategy that involves deeper pre-drilling can significantly mitigate chip accumulation issues. Buyers should consider using rotary broaching methods, which allow for effective machining of polygon forms without the need for complete through-holes. If deeper drilling is not feasible, incorporating an undercut in the blind hole design allows chips to break away more freely. Additionally, using an alignment tool to maintain consistent broach positioning can facilitate better chip evacuation during machining. Regular maintenance and inspection of broaching tools will also ensure that they are in optimal condition to withstand the operational stresses. By addressing chip management proactively, companies can prolong tool life and enhance operational efficiency.
Scenario 3: Inconsistent Results from Manual Broaching Techniques
The Problem: Many manufacturers still rely on manual broaching techniques, which can lead to inconsistent results and increased variability in product quality. This inconsistency is particularly problematic for businesses in competitive markets, such as Europe, where precision and reliability are paramount. Manual broaching can result in variations in keyway dimensions, leading to costly rework and diminished customer satisfaction.
The Solution: Transitioning to automated broaching solutions, such as CNC broaching machines, can greatly enhance consistency and quality control. These machines can be programmed to execute precise broaching operations that minimize human error. B2B buyers should look for systems that offer advanced features like real-time monitoring and feedback to detect inconsistencies during the process. Furthermore, investing in high-quality broaching tools that are specifically engineered for blind applications will ensure that the finished dimensions meet required specifications consistently. Regular calibration of machines and tools, alongside training programs for operators, will help maintain the quality of broaching operations. By leveraging technology and standardizing processes, manufacturers can achieve the reliability needed to compete in the global market.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is blind broaching
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Blind Broaching?
When selecting materials for blind broaching applications, it’s essential to consider properties such as strength, machinability, and resistance to wear and corrosion. Here, we analyze four common materials used in blind broaching, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Steel Perform in Blind Broaching Applications?
Key Properties: Steel, particularly alloy steels like 4140, is known for its high tensile strength and toughness. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for demanding applications. Additionally, steel can be treated for enhanced corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons: The durability of steel is a significant advantage, as it can handle repeated stress without deforming. However, it can be more expensive than other materials, depending on the alloying elements. Machining steel requires specialized tools and techniques, which may increase manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Steel’s compatibility with various media, including oils and chemicals, makes it a versatile choice for many industries. However, the specific grade of steel must be selected based on the intended environment to ensure optimal performance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial for international procurement. Countries like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia often have specific requirements for material certifications, which should be verified before purchase.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Blind Broaching?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, has good corrosion resistance, and offers excellent machinability. Its thermal and electrical conductivity also make it suitable for specific applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which can reduce overall product weight and improve efficiency in applications like automotive and aerospace. However, it is generally less durable than steel, making it less suitable for high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with a variety of media but may not perform well in high-temperature environments. It is often used in applications where weight savings are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific aluminum grades and their properties. Compliance with JIS standards is common in Asian markets, while European buyers may prioritize EN standards.

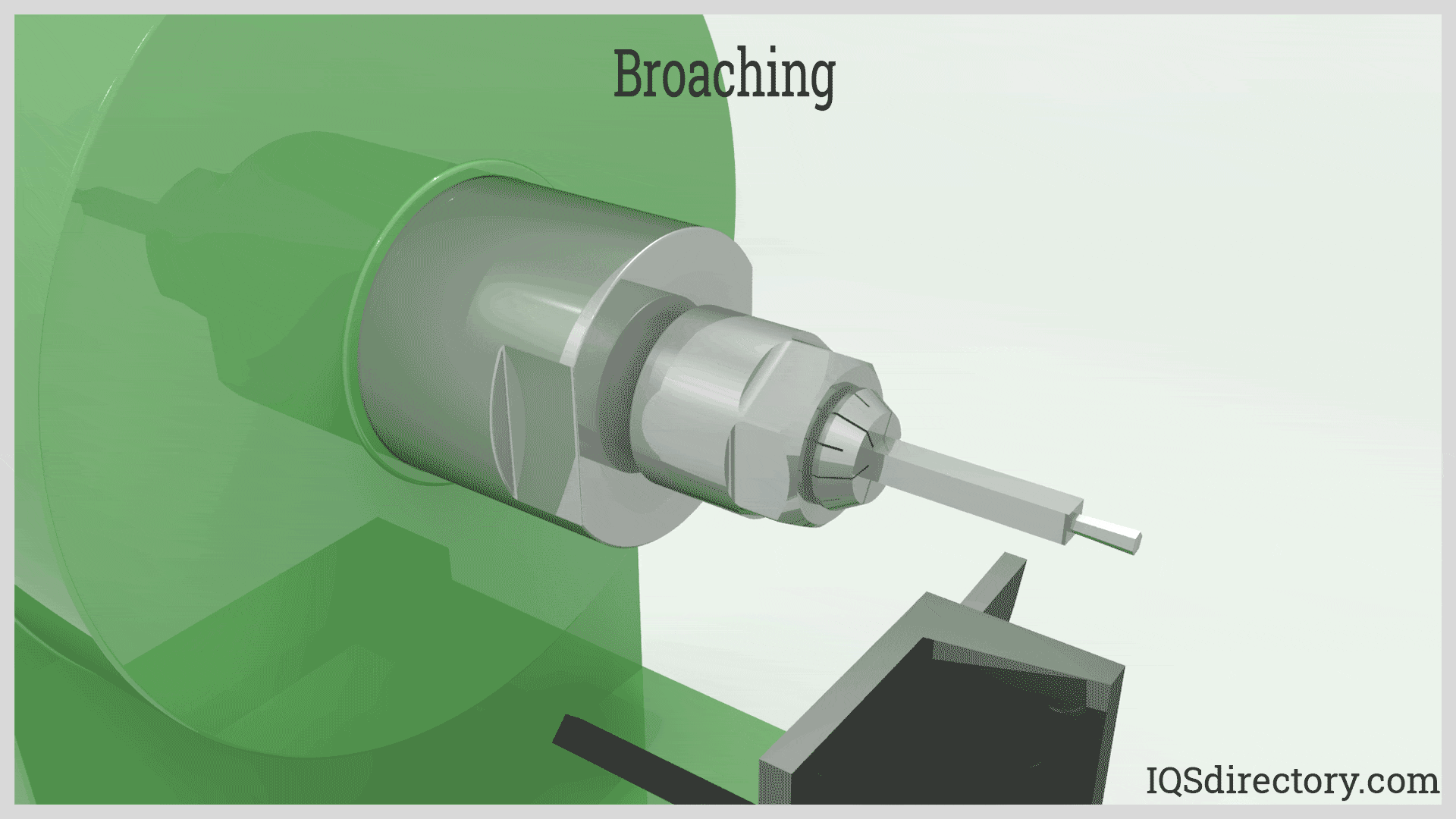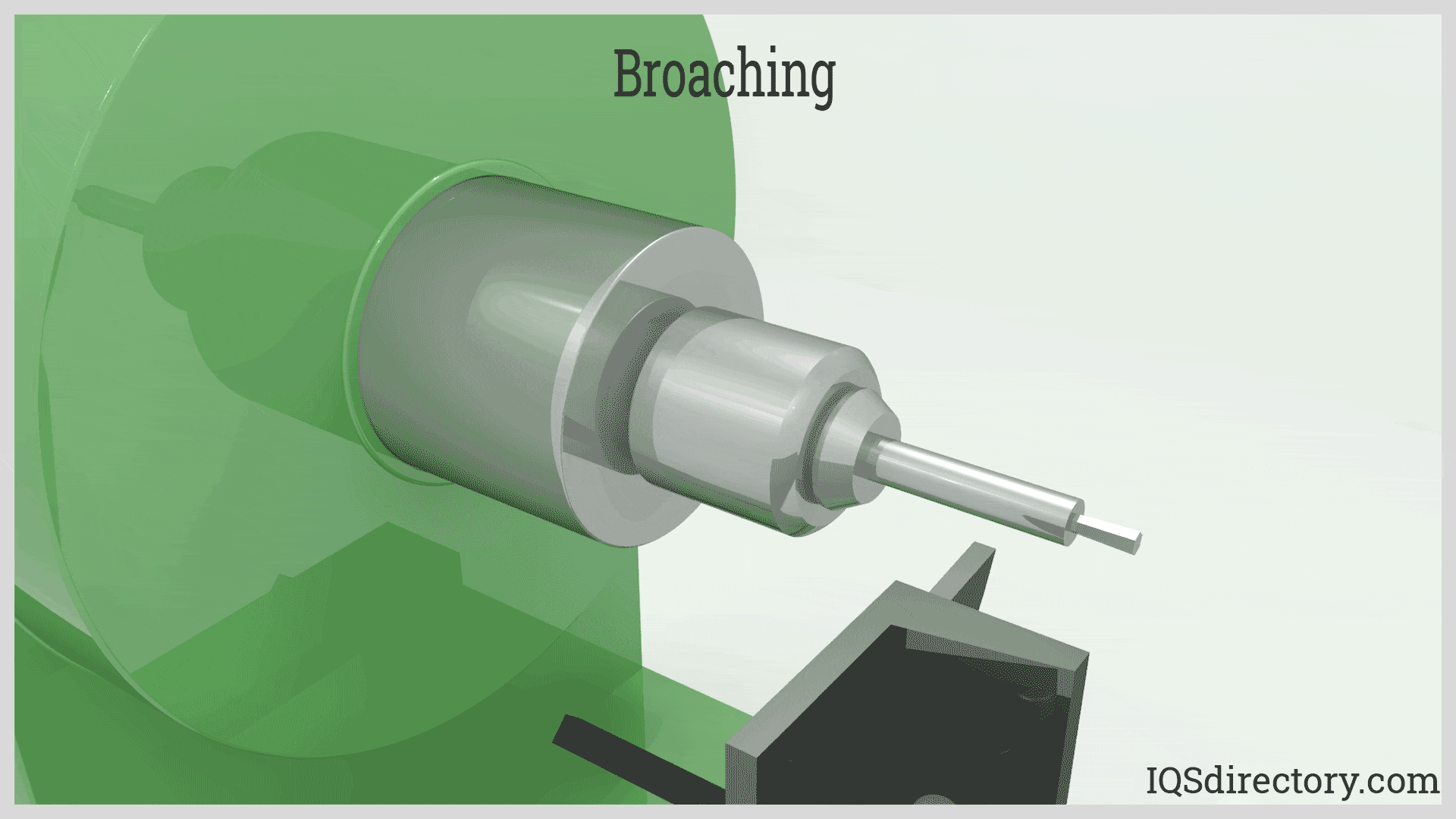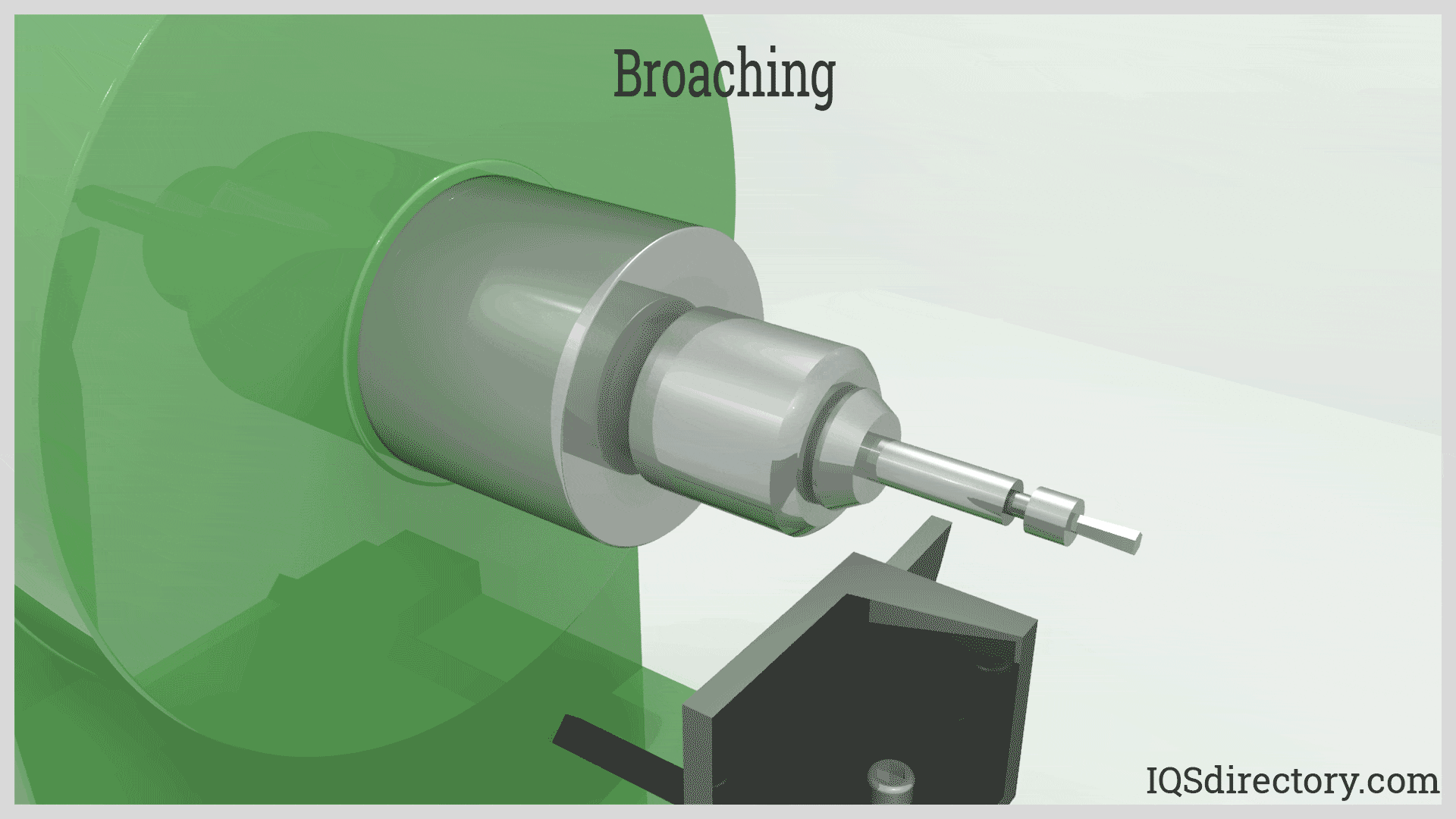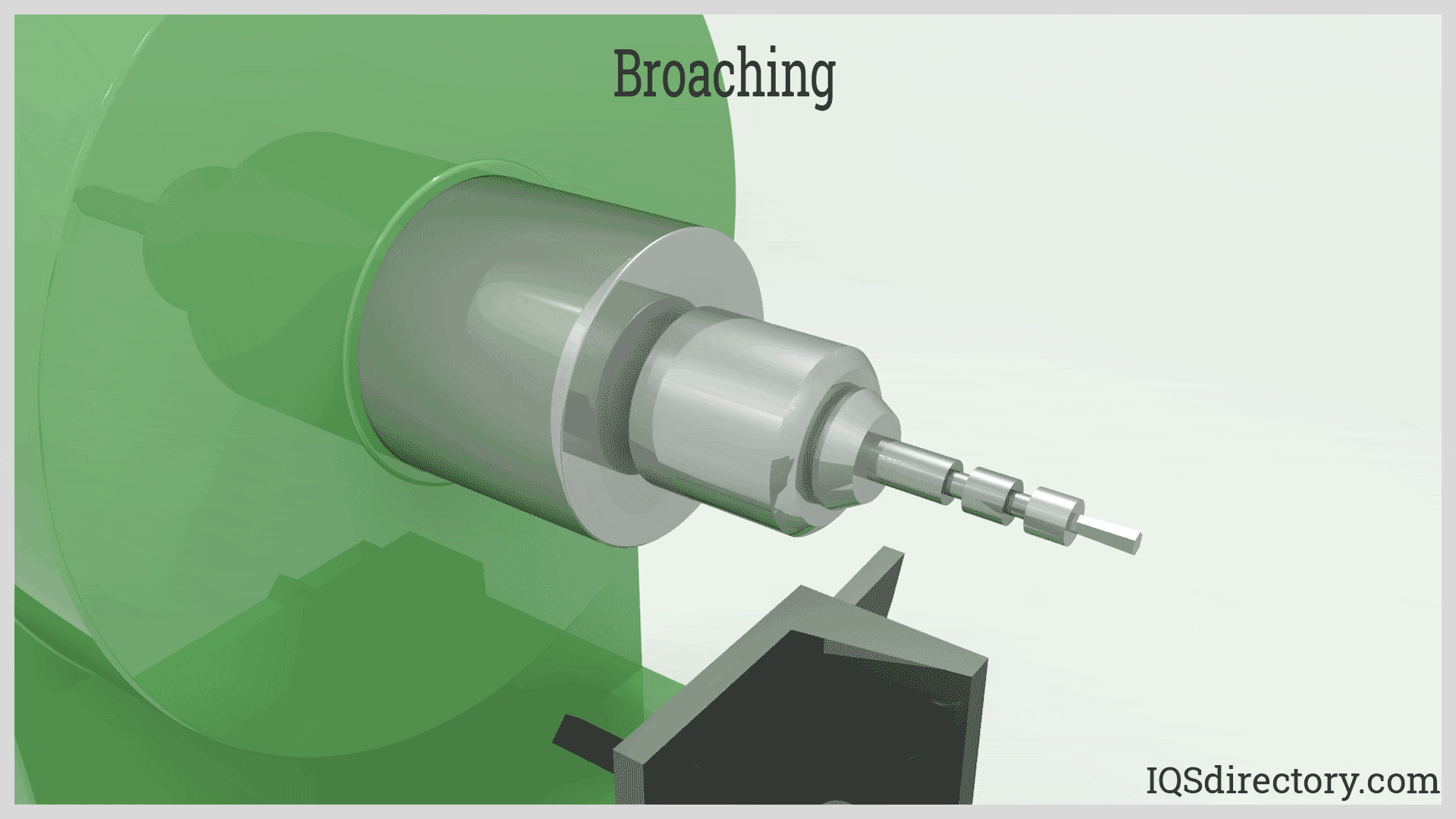
Illustrative image related to what is blind broaching
Why Is Brass Used in Blind Broaching?
Key Properties: Brass is known for its excellent machinability and good corrosion resistance. It also has a low friction coefficient, making it ideal for applications requiring smooth movement.
Pros & Cons: The ease of machining brass allows for complex shapes and designs, which can be beneficial in precision applications. However, brass can be more expensive than steel and may not be suitable for high-stress environments.
Impact on Application: Brass is compatible with various fluids, making it a popular choice in plumbing and electrical applications. Its aesthetic appeal also makes it suitable for decorative components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Brass alloys must comply with specific standards, such as ASTM B36 for copper-zinc alloys. Buyers should ensure that the material meets local regulations and standards in their respective regions.
How Does Plastic Compare in Blind Broaching?
Key Properties: Engineering plastics, such as nylon or acetal, offer good chemical resistance and are lightweight. They can also be molded into complex shapes, which is beneficial for certain applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of plastics is their low weight and resistance to corrosion. However, they may not withstand high temperatures or heavy loads as effectively as metals, limiting their use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Plastics are often used in applications where electrical insulation is required. Their compatibility with various chemicals makes them suitable for use in the food and pharmaceutical industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the specific type of plastic and its properties, ensuring compliance with relevant standards such as FDA regulations for food applications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Blind Broaching
| Material | Typical Use Case for what is blind broaching | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | High-stress applications, automotive parts | High durability and strength | Higher cost and machining complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight components, automotive, aerospace | Low weight and good machinability | Less durable than steel | Medium |
| Brass | Plumbing fittings, electrical components | Excellent machinability and corrosion resistance | More expensive and less stress-resistant | Medium |
| Plastic | Electrical insulation, food industry applications | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Limited temperature and load capacity | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers across various international markets, helping them make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance considerations.
Illustrative image related to what is blind broaching
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is blind broaching
What Are the Main Stages of the Manufacturing Process for Blind Broaching?
Blind broaching is a specialized machining process used to create internal features such as keyways, hex shapes, or splines in a workpiece. The process is particularly useful for producing shapes that are not accessible from the end of a workpiece, hence the term “blind.” Understanding the manufacturing process involves several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Blind Broaching?
The initial stage in the blind broaching process is material preparation. This involves selecting the appropriate raw material, typically metal, such as steel or aluminum, based on the required strength and durability of the final product. The material is often cut into manageable sizes, followed by a machining operation to ensure it meets specific dimensions and tolerances required for broaching.
Once the material is sized, it may undergo surface treatments to enhance its machinability and reduce wear during the broaching process. This is particularly important when working with harder materials, as they can cause excessive tool wear if not adequately prepared.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of Blind Broaching?
The forming stage is where the actual broaching takes place. This process can utilize either rotary or linear broaching techniques, depending on the application and the type of broach being used.
-
Rotary Broaching: This technique allows for creating polygonal shapes in blind holes quickly and efficiently. The broach is rotated and pressed into the material, enabling the machining of shapes like hex, square, or torx forms without needing a through hole.
-
Linear Broaching: In cases where the application requires a linear motion, the broach is pulled or pushed through the workpiece, cutting the desired shape as it moves. This method is commonly used for producing keyways and splines.
During this stage, it’s crucial to have effective chip removal strategies in place, particularly with blind holes. Techniques such as pre-drilling deeper than the broach depth or using an undercut can help manage chip accumulation and ensure a smooth broaching process.
What Are the Finishing Steps in Blind Broaching Manufacturing?
After forming, the workpieces typically undergo finishing processes to achieve the desired surface quality and dimensions. This may involve secondary machining operations like grinding or polishing to enhance surface finish, particularly in applications where aesthetic quality or smooth operation is critical.
Finishing also includes inspection and verification to ensure that the produced parts meet the specified tolerances. This may involve using precision measuring tools and techniques such as coordinate measuring machines (CMM) to assess dimensions and geometries.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Blind Broaching?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the blind broaching manufacturing process. It ensures that the final product meets international standards and customer specifications. For B2B buyers, understanding the QA process is essential for making informed procurement decisions.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
For manufacturers engaged in blind broaching, compliance with international quality standards such as ISO 9001 is vital. This standard outlines a framework for consistent quality management systems, ensuring that products meet customer and regulatory requirements.

Illustrative image related to what is blind broaching
Additionally, industry-specific certifications may be relevant, such as CE marking for products sold in the European Economic Area or API standards for oil and gas applications. Buyers should inquire about these certifications when evaluating potential suppliers.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Blind Broaching?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established at various stages of the manufacturing process to monitor and ensure product quality. The key checkpoints typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting raw materials upon arrival to confirm they meet specified requirements.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring the manufacturing process to ensure that it adheres to established standards and tolerances. This may involve regular measurements and tests during broaching.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducting thorough inspections of finished products before they are shipped. This step often includes dimensional checks, surface quality assessments, and functional testing.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control measures is critical to ensuring product reliability and performance. Here are several strategies:
-
Audits: Conducting supplier audits can provide insights into their manufacturing processes, quality control systems, and adherence to industry standards. This can be done either through on-site visits or remote assessments.
-
Documentation and Reports: Requesting quality control documentation, including inspection reports and certifications, can help validate the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an independent assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices and the products being manufactured.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing products globally, B2B buyers must be aware of the nuances related to quality control and certification. Each region may have specific regulatory requirements and standards that need to be considered.
For example, buyers from Africa and South America may encounter different compliance challenges than those in Europe or the Middle East. It is essential for buyers to understand these regional differences and ensure that suppliers can meet the necessary certifications and quality standards for their target markets.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for blind broaching play a crucial role in delivering reliable and high-quality components. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and ensure they partner with suppliers that meet their quality expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is blind broaching’
To assist B2B buyers in understanding and procuring blind broaching services, this practical sourcing guide outlines essential steps to ensure a successful procurement process. Blind broaching is a specialized machining method that creates keyways and other forms in blind holes, and selecting the right supplier can significantly impact production efficiency and product quality.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establish clear technical specifications for your blind broaching needs. This includes dimensions, tolerances, and the type of material being processed. Precise specifications help suppliers understand your requirements and ensure that the finished product meets your operational standards.
- Consider the type of keyway or form: Identify whether you need blind keyways, hex forms, or other custom shapes.
- Specify material characteristics: Consider the properties of the material being machined, such as hardness and ductility.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in blind broaching services. Look for companies with a proven track record in your industry and positive reviews from past clients.
- Utilize industry directories: Websites and platforms that focus on manufacturing and machining can provide valuable insights into potential suppliers.
- Seek recommendations: Network with industry peers or join relevant forums to gather insights on reliable suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before making a commitment, verify the certifications and quality management systems of potential suppliers. This ensures they adhere to industry standards and best practices.
- Check for ISO certifications: Suppliers with ISO 9001 or similar certifications demonstrate a commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
- Assess safety and environmental compliance: Ensure that the supplier meets relevant safety and environmental regulations.
Step 4: Request Samples and Case Studies
Request samples of previous work and case studies that demonstrate the supplier’s capability in blind broaching. This will provide a clearer understanding of their expertise and the quality of their output.
- Analyze sample quality: Evaluate the precision and finish of the samples to ensure they meet your specifications.
- Review case studies: Look for projects similar to yours to gauge their experience in handling specific challenges.
Step 5: Understand the Broaching Process
Gain insight into the broaching process employed by potential suppliers. Understanding their techniques can help you assess their capability to meet your requirements effectively.
- Inquire about the tools used: Different broaching tools, such as inserted broaches or rotary broaches, may yield different results.
- Discuss chip management strategies: Effective chip removal is crucial in blind broaching to avoid tool damage and ensure precision.
Step 6: Assess Communication and Support
Evaluate the communication channels and customer support offered by the supplier. Strong communication is vital for addressing any issues that may arise during the machining process.
- Look for responsiveness: A supplier that promptly answers queries and provides updates shows a commitment to customer service.
- Evaluate technical support: Ensure that they can offer assistance throughout the project, from initial design to final delivery.
Step 7: Compare Pricing and Terms
Finally, compare pricing structures and payment terms among shortlisted suppliers. While cost is important, ensure that it does not compromise quality.
- Request detailed quotes: Ensure that quotes include all costs related to the broaching process, including setup and tooling.
- Negotiate terms: Discuss payment terms and delivery schedules to find a mutually beneficial agreement.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the procurement process for blind broaching services, ensuring they select the right supplier to meet their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is blind broaching Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing for blind broaching is crucial for international B2B buyers looking to optimize their sourcing strategies. This section delves into the various components influencing costs, the factors affecting pricing, and practical tips for buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Blind Broaching?
The cost structure for blind broaching can be broken down into several essential components:
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly impacts costs. Common materials include steel alloys like 4140, which are durable and suitable for broaching. The price of these materials fluctuates based on market demand and supplier location.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is necessary for broaching operations. Labor costs vary widely depending on the region, local wage standards, and the complexity of the broaching process. In regions with a skilled workforce, such as Europe, labor costs may be higher compared to Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility operations, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing practices can help reduce overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Investment in quality tooling, such as broaches and inserts, is critical. Tooling costs can be substantial, especially for customized solutions, which may require specialized designs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that broached components meet required specifications is essential. Implementing robust QC processes incurs additional costs but is necessary to avoid expensive reworks or product failures.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing costs are significant, especially for international shipments. Factors such as distance, shipping mode, and customs duties affect overall logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a profit margin to cover their operating costs and ensure profitability. This margin can vary based on the competitive landscape and supplier relationships.
What Influences Pricing in Blind Broaching?
Several factors can influence the pricing of blind broaching services:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Higher order volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk orders, making it economically beneficial for buyers.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized solutions that require specific tooling or unique designs will generally incur higher costs. Clearly defining specifications upfront can help manage expectations and costs.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Using high-quality materials and ensuring compliance with industry certifications can increase costs but also enhance product reliability and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, location, and capabilities of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers with advanced technologies may charge more but offer better quality and faster turnaround times.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects logistics costs and responsibilities. Understanding the implications of terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) is vital for budgeting.
What Tips Can Buyers Use to Negotiate Better Prices?
Buyers can adopt several strategies to enhance cost-efficiency and negotiate better pricing:
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but all associated costs, including logistics, maintenance, and potential downtime. This holistic view can inform better purchasing decisions.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: Consolidate orders or collaborate with other buyers to achieve higher order quantities, thereby negotiating better rates.
-
Be Clear on Specifications: Provide detailed specifications and requirements to avoid misunderstandings that could lead to costly changes during production.
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Conduct thorough market research to identify potential suppliers. Comparing multiple quotes can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: For buyers in regions like Africa or South America, sourcing from local suppliers can reduce logistics costs and lead times, enhancing overall value.
Conclusion
Navigating the cost structure and pricing nuances of blind broaching requires diligence and strategic planning. By understanding the various cost components and pricing influencers, international buyers can make informed decisions that drive efficiency and value in their sourcing processes. While prices may vary based on the factors discussed, it’s essential to engage with suppliers openly and collaboratively to achieve the best possible outcomes.

Illustrative image related to what is blind broaching
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is blind broaching With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Blind Broaching
In the manufacturing landscape, especially for B2B buyers, understanding the various methods available for creating keyways and other internal shapes is crucial. Blind broaching is a specialized technique for machining internal features in blind holes, but it is essential to evaluate its effectiveness against alternative solutions. This analysis will compare blind broaching with rotary broaching and milling operations, highlighting their respective advantages and drawbacks.
| Comparison Aspect | What Is Blind Broaching | Rotary Broaching | Milling Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision for blind keyways | Quick and efficient for various shapes | Versatile but may require multiple setups |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment | Lower tooling costs, faster cycle times | Varies widely based on machine type and tooling |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific tooling and setup | Easy to implement on existing lathes or mills | Commonly used but may need extensive programming |
| Maintenance | Requires maintenance of broaching tools | Minimal maintenance, easy tool replacement | Regular maintenance needed for milling machines |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for high-volume production | Best for low to medium volume with diverse shapes | Suitable for complex parts but may not be efficient for simple forms |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Each Alternative?
Rotary Broaching: What Are Its Advantages and Disadvantages?
Rotary broaching is a method that allows for the machining of various polygonal shapes in a blind hole using a wobbling motion. One of its key advantages is speed; it can efficiently create hex, square, and torx forms in a matter of seconds. This method is particularly beneficial for B2B applications where quick turnaround times are essential, such as in fastener production. However, rotary broaching may not achieve the same level of precision as blind broaching when dealing with intricate keyways, limiting its applicability for high-precision requirements.
Milling Operations: What Are Their Strengths and Weaknesses?
Milling operations are widely used in manufacturing for their versatility in creating complex geometries. They can be adapted to produce blind keyways and other internal features but may require additional programming and setup time. The cost of milling can vary significantly based on the equipment used and the complexity of the part. While milling can handle a wide array of materials and designs, it may not be the most efficient for high-volume production of simple shapes, where blind broaching excels.
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the appropriate method for machining internal features, B2B buyers must consider several factors, including production volume, required precision, and existing equipment capabilities. For high-volume applications where precision in blind keyways is paramount, blind broaching remains a top choice. Conversely, if speed and versatility are critical, rotary broaching might offer a better solution. For complex parts requiring diverse operations, milling could be the most suitable approach, despite potentially higher costs and longer setup times. Ultimately, understanding the specific needs of the project and the strengths of each method will guide buyers in making an informed decision.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is blind broaching
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Blind Broaching?
When considering blind broaching as a manufacturing solution, understanding its critical specifications is essential for ensuring efficiency and quality in production. Below are some of the vital properties relevant to this process:
1. Material Grade
The choice of material for broaching tools significantly impacts their performance. Common materials include high-speed steel (HSS) and carbide. HSS offers good toughness and wear resistance, making it suitable for less demanding applications, while carbide provides superior hardness and longevity for high-volume production. For B2B buyers, selecting the right material affects tool life and machining efficiency, leading to reduced operational costs.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. In blind broaching, achieving tight tolerances is crucial for the precision fit of components, especially in applications like automotive or aerospace where safety and performance are paramount. Understanding the required tolerances helps manufacturers ensure parts fit correctly, minimizing the need for rework and enhancing overall product quality.
3. Depth of Cut
The depth of cut in blind broaching determines how much material is removed in a single pass. This specification affects tool wear and the quality of the final surface finish. A deeper cut can increase productivity but may also lead to excessive tool wear or damage if not managed correctly. For B2B decision-makers, optimizing the depth of cut can balance efficiency and cost-effectiveness in production.
4. Chip Evacuation
Effective chip evacuation is critical in blind broaching to prevent chip accumulation, which can lead to tool damage or poor surface finish. This property is particularly important when broaching blind keyways, as chips can easily obstruct further cutting operations. Ensuring proper chip management strategies can enhance tool performance and reduce downtime, making it a vital consideration for manufacturers.
5. Broaching Speed
The speed at which broaching occurs affects both the quality of the cut and the lifespan of the broaching tool. Higher speeds can lead to faster production times but may also increase the risk of tool failure if not appropriately managed. For B2B buyers, understanding the relationship between speed and tool life is essential for optimizing production processes and maintaining cost efficiency.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Associated with Blind Broaching?
Navigating the terminology of blind broaching can streamline communication and decision-making processes. Here are some essential trade terms to be familiar with:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of blind broaching, OEMs often require precise broaching services to ensure their components meet industry standards. Understanding OEM relationships helps B2B buyers identify reliable suppliers for their manufacturing needs.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of products that a supplier is willing to sell. In blind broaching, knowing the MOQ helps buyers manage inventory and production planning effectively. It is crucial for maintaining cost efficiency, especially for businesses that may not require large quantities.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a standard business process used to invite suppliers to bid on specific products or services. For companies involved in blind broaching, submitting RFQs allows them to compare pricing, quality, and lead times from various suppliers, facilitating informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to understand shipping costs, risks, and delivery responsibilities when sourcing broaching services or tools globally.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the total time it takes from placing an order to receiving the finished product. In the context of blind broaching, understanding lead times helps businesses plan their production schedules effectively and avoid delays in their supply chain, which is critical for maintaining customer satisfaction.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and improve their overall manufacturing processes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is blind broaching Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics Impacting Blind Broaching?
The global market for blind broaching is significantly influenced by several key drivers, including technological advancements, increasing demand for precision manufacturing, and the growing need for efficient machining processes. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery are increasingly integrating blind broaching into their operations due to its ability to produce complex internal shapes quickly and accurately. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where manufacturing sectors are rapidly evolving.
Emerging technologies, such as CNC machining and advanced broaching tools, are reshaping the sourcing landscape. Manufacturers are adopting insertable broach systems that can be utilized in standard CNC machines, thus eliminating the need for dedicated broaching machines and streamlining operations. This shift not only enhances efficiency but also reduces costs, making it an attractive option for international buyers looking to optimize their production lines.
In addition, the demand for customized broaching solutions is on the rise, as companies seek to differentiate their products in competitive markets. This customization trend presents opportunities for suppliers who can offer tailored broaching tools and services that meet specific industry requirements, such as varying keyway widths or intricate spline designs.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Blind Broaching Sector?
As the manufacturing industry increasingly focuses on sustainability, ethical sourcing in the blind broaching sector has gained prominence. Environmental impacts associated with machining processes, such as waste generation and energy consumption, have prompted companies to seek greener alternatives. Manufacturers are now prioritizing sourcing materials that are recyclable or derived from sustainable practices.
In this context, the use of ‘green’ certifications and materials is becoming essential. Suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with environmental standards and offer eco-friendly machining solutions are likely to gain a competitive edge. For instance, using high-quality, durable materials that minimize waste can not only reduce the ecological footprint but also enhance the longevity and performance of broaching tools.
Moreover, ethical supply chains are critical for international buyers, particularly in regions where labor practices and environmental regulations may vary. By ensuring that their suppliers adhere to ethical sourcing practices, companies can mitigate risks associated with reputational damage and regulatory compliance. This alignment with sustainability goals not only meets consumer expectations but also positions businesses favorably in a market that increasingly values corporate responsibility.
What Is the Historical Evolution of Blind Broaching?
The evolution of blind broaching can be traced back to the early 20th century when broaching was first introduced as a method for machining complex shapes. Initially, the process required a through-hole, limiting its application. However, advancements in tooling technology led to the development of blind hole broaching techniques, enabling manufacturers to create internal shapes without the need for a through hole.
Over the decades, the integration of CNC technology revolutionized the blind broaching process, allowing for greater precision and efficiency. The introduction of rotary broaching further expanded the capabilities of manufacturers, enabling them to broach various shapes quickly and effectively. Today, with the increasing demand for customization and efficiency in manufacturing, blind broaching continues to evolve, driven by innovations in tooling and machining technologies that cater to diverse industrial needs.
This historical context underscores the ongoing importance of adapting to technological advancements and market demands, providing valuable insights for international B2B buyers looking to invest in blind broaching solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is blind broaching
-
How do I solve issues with chip accumulation when broaching a blind keyway?
To address chip accumulation during blind keyway broaching, it is crucial to ensure that the blind hole is drilled deeper than the keyway form. This additional depth allows chips to accumulate without clogging the cutting area. If drilling deeper is not feasible, consider using an undercut at the bottom of the blind hole to facilitate chip removal. Additionally, incorporating a cross-hole relief can enhance chip evacuation, especially when using CNC mills, as it allows coolant to flush out debris effectively. -
What is the best method for broaching a blind keyway in a CNC lathe?
Using a broach that accepts inserts is often the most effective method for broaching blind keyways in CNC lathes. This approach allows for flexibility in producing various keyway widths while maintaining precision. Ensure that the machine is robust to support the broaching process effectively. Implementing a programmed retraction technique can help manage chip buildup, preventing damage to the cutting tool and ensuring a clean cut. -
What are the key considerations when sourcing blind broaching services internationally?
When sourcing blind broaching services, consider the supplier’s experience and expertise in your specific industry. Evaluate their quality assurance processes to ensure they meet international standards. Additionally, assess their capabilities for customization to suit your unique requirements, including material specifications and design complexities. It’s also beneficial to check their logistics capabilities to ensure timely delivery to your region, whether it’s Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe. -
How can I vet suppliers for blind broaching services?
To vet suppliers effectively, start by reviewing their credentials, certifications, and industry experience. Request samples of their previous work to assess the quality of their broaching services. Additionally, consider reaching out to their existing clients for testimonials. Visiting the facility, if possible, can also provide insight into their operational capabilities and quality control measures. Lastly, ensure they have a clear communication protocol to handle your inquiries promptly. -
What customization options should I look for in blind broaching services?
Customization options can include variations in broach design, keyway dimensions, and material types. Some suppliers may also offer specialized broaching forms such as hex, square, or torx shapes, tailored to your specific application needs. Ensure that the supplier can accommodate your project requirements, including batch sizes and specific tolerances. Discuss your customization needs upfront to confirm that they can deliver according to your specifications. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for blind broaching services?
Minimum order quantities for blind broaching services can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the broaching project. Generally, MOQs may range from a few hundred units for simple designs to several thousand for more intricate or customized broaching tasks. Discuss your needs with the supplier to determine if they can accommodate smaller batch sizes, especially for prototyping or initial runs. -
What payment terms are common for international B2B transactions in blind broaching?
Payment terms can differ based on the supplier’s policies and the nature of your agreement. Common arrangements include upfront deposits, payment upon delivery, or net terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60 days). It’s advisable to clarify payment expectations early in negotiations to avoid misunderstandings. Consider utilizing secure payment methods, such as letters of credit or escrow services, especially for larger transactions or new supplier relationships. -
How can I ensure quality assurance in blind broaching processes?
To ensure quality assurance, inquire about the supplier’s quality control protocols, including inspections and testing methods used throughout the broaching process. Request documentation of their certifications, such as ISO standards, which indicate adherence to international quality benchmarks. Establish clear specifications and tolerances in your purchase agreement to facilitate consistent quality. Regular communication with the supplier during the production phase can also help address any potential quality issues proactively.
Top 6 What Is Blind Broaching Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. CNC Broach Tools – Blind Keyway Broaching
Domain: cncbroachtools.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Blind Keyway Broaching tools are designed for CNC lathes and mills. They are inserted keyway broach tools sold directly to end users without distributors. Keyway broaching requires adequate relief areas, such as cross holes or grooves, to prevent crashes during machining. Recommendations include ensuring the relief area is larger than the keyway and programming the insert cutting edge to stop appr…
2. Polygon Solutions – Blind Hole Broaching
Domain: polygonsolutions.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Blind Hole Broaching for hex, square, torx, and keyway forms. Fast and easy process for broaching internal shapes in blind holes using a lathe or mill. Requires pre-drilling slightly deeper than the form to allow for chip accumulation. Offers orientation brake for consistent broach positioning. Suitable for machining hex forms into socket cap screws. Available forms include hex, square, torx, keyw…
3. duMONT – Minute Man Broaching System
Domain: ctemag.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: The duMONT Minute Man broaching system allows for broaching blind keyways on CNC lathes and machining centers. It accepts keyway inserts, slotting, and special inserts, with widths ranging from 3/32″ to ¾” and 2mm to 25mm. The system promotes continuous tool movement to prevent chip buildup, and users can ramp the tool out at a 45° angle to maintain insert integrity. CNC Broach Tool offers indexab…
4. National Machine Tool Co. – Broaching Tool
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: 1. Tool from National Machine Tool Co. for broaching keyways in blind holes, costing approximately $500-600. 2. Cutter sizes available: 5/8 inch bore for 3/16 x 3/32 keyway and 1 inch cutter for 1/4 x 1/8 keyway. 3. Contact information: Phone – 1-800-528-6682, Email – [email protected], Website – www.keyseaters.com. 4. Alternative methods suggested include using a lathe with a boring bar, Bridg…
5. Rev – Broaching Tool
Domain: revtool.eu
Introduction: Product Name: Rev Broaching Tool – Blind Internal Keyway Without Relief
Description: The Rev Broaching Tool allows for the execution of a keyway inside a workpiece without the need for a relief groove, significantly reducing processing times. This method is beneficial when creating relief grooves is difficult or could weaken the structure of the workpiece.
Programming Examples: Specific programs a…
6. Gisstec – Keyway Broaching Tools
Domain: gisstec.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Keyway Broaching Tools for CNC Lathes: 1. Live Driven Broaching Tool for Lathes 2. Square Broaching Tools 3. Hexagon Broaching Tools 4. Spline Broaching Tools 5. Angle Heads: GA Series (90º Angle Head), GS Series (90° Slim Angle Head), GT Series (Tilting Head), GD Series (Double Angle Head), GA-F Series (Angle Head with Flange Connection) 6. Spindle Speeders 7. Multispindle Heads 8. Toolholders
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is blind broaching
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, understanding the intricacies of blind broaching is essential for international B2B buyers. This technique enables the precise machining of blind keyways and various internal forms, enhancing product performance and reliability. Key takeaways include the importance of proper chip evacuation strategies, such as using cross-hole or groove reliefs, and the advantages of integrating broaching processes within CNC operations to optimize setup and accuracy.
Illustrative image related to what is blind broaching
Strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in ensuring that your manufacturing processes are both efficient and cost-effective. By partnering with suppliers who understand the nuances of blind broaching, businesses can leverage superior tooling solutions and innovative techniques tailored to their specific needs.
Looking ahead, it is crucial for buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to engage with knowledgeable suppliers who can provide insights into the latest advancements in broaching technology. Embrace the opportunity to elevate your production capabilities and establish robust supply chains that enhance your competitive edge. Start exploring strategic partnerships today to drive innovation and growth in your manufacturing processes.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.