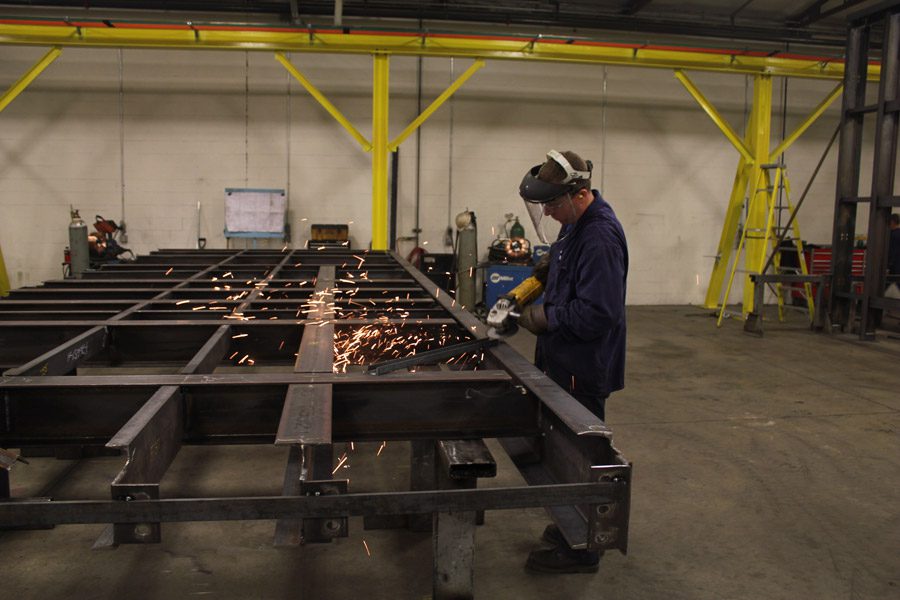
A Deep Dive into What Is A Steel Fabricator Solution
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is a steel fabricator
In the quest for sourcing reliable steel fabricators, international B2B buyers often encounter a myriad of challenges, from quality assurance to logistical complexities. Steel fabricators play a pivotal role in transforming raw steel into essential components for various industries, including construction, automotive, and infrastructure. This comprehensive guide will demystify the steel fabrication process, exploring the different types of fabricators, their applications, and the critical factors to consider when selecting a supplier.
Buyers will gain insights into the latest fabrication technologies, essential techniques such as welding and machining, and the importance of precision in meeting project specifications. We will also delve into effective strategies for vetting suppliers, understanding pricing structures, and assessing the overall value of steel fabrication services.
This guide is specifically tailored for international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Nigeria and Vietnam. By equipping decision-makers with actionable insights and best practices, we empower them to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and budgetary constraints. Whether you are looking to streamline your supply chain or enhance the quality of your projects, this guide serves as a valuable resource in navigating the complexities of the global steel fabrication market.
Understanding what is a steel fabricator Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structural Steel Fabricator | Specializes in large-scale structural components like beams and columns. | Commercial and residential construction projects. | Pros: High strength and durability; Cons: Can be costlier due to material and complexity. |
| Custom Steel Fabricator | Offers tailored solutions for specific client needs and designs. | Specialized industries (e.g., aerospace, automotive). | Pros: Unique designs; Cons: Longer lead times for production. |
| Industrial Steel Fabricator | Focuses on heavy machinery and equipment fabrication for various industries. | Mining, manufacturing, and energy sectors. | Pros: Robust construction; Cons: May require extensive maintenance. |
| Sheet Metal Fabricator | Works with thin sheets of metal for various applications. | HVAC, automotive, and consumer goods. | Pros: Versatile and lightweight; Cons: Less strength compared to structural options. |
| Steel Coating Specialist | Provides protective coatings like galvanization and painting. | Construction, automotive, and infrastructure. | Pros: Increases lifespan of steel; Cons: Additional costs for coating processes. |
What Are the Characteristics of Structural Steel Fabricators?
Structural steel fabricators focus on creating large-scale components essential for the framework of buildings and other structures. They typically work with materials such as beams, columns, and trusses, which are critical for load-bearing applications. When considering a structural steel fabricator, B2B buyers should evaluate the fabricator’s experience with local building codes and regulations, as compliance is crucial. Additionally, the ability to provide comprehensive services, including design assistance and project management, can significantly enhance value.
How Do Custom Steel Fabricators Cater to Specific Needs?
Custom steel fabricators excel in delivering tailored solutions that meet unique project specifications. They often collaborate closely with clients to develop designs that might involve complex geometries or specialized materials. This type of fabrication is particularly relevant for industries like aerospace and automotive, where precision and customization are paramount. Buyers should consider the fabricator’s past projects and capabilities in advanced technologies, such as CNC machining and 3D modeling, to ensure they can meet specific requirements efficiently.
What Are the Key Features of Industrial Steel Fabricators?
Industrial steel fabricators specialize in producing heavy machinery and equipment, primarily serving sectors such as mining, manufacturing, and energy. Their products often require robust construction to withstand harsh operational environments. When selecting an industrial steel fabricator, buyers should assess the company’s ability to handle large-scale projects and their experience with heavy-duty materials. Quality assurance processes and certifications are also essential to ensure that the fabricated products meet industry standards.
What Makes Sheet Metal Fabricators Unique?
Sheet metal fabricators work with thin sheets of metal, which can be easily shaped and formed into various products. This type of fabrication is prevalent in industries like HVAC, automotive, and consumer goods, where lightweight and versatile components are needed. Buyers should look for fabricators with experience in precision cutting and forming techniques, as well as a variety of finishing options. Cost-effectiveness and quick turnaround times are significant advantages, but buyers should also consider the strength limitations of sheet metal compared to heavier structural options.
How Do Steel Coating Specialists Enhance Product Longevity?
Steel coating specialists focus on applying protective coatings, such as galvanization or painting, to enhance the durability and lifespan of steel products. This process is critical in preventing corrosion and maintaining aesthetics in various applications, including construction and automotive. When engaging with a steel coating specialist, B2B buyers should inquire about the types of coatings available, their environmental impact, and the expected lifespan of the coatings. Understanding the balance between cost and the added value of enhanced protection can influence purchasing decisions significantly.
Key Industrial Applications of what is a steel fabricator
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of what is a steel fabricator | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Structural steel framing for buildings | Provides strength and durability to structures, ensuring safety and longevity. | Look for fabricators with experience in local regulations and building codes. |
| Shipbuilding | Fabrication of hulls and structural components | Enhances vessel integrity and performance, critical for safety and efficiency at sea. | Ensure compliance with maritime standards and certifications. |
| Mining | Custom steel supports and machinery components | Improves operational efficiency and safety in harsh environments. | Assess the fabricator’s ability to withstand extreme conditions and provide timely delivery. |
| Automotive Manufacturing | Production of chassis and body components | Reduces weight while maintaining strength, improving vehicle performance and fuel efficiency. | Prioritize fabricators with precision machining capabilities and rapid prototyping options. |
| Civil Infrastructure | Fabrication of bridges and public transport systems | Facilitates efficient transportation and connectivity, crucial for economic growth. | Evaluate the fabricator’s track record in large-scale projects and adherence to safety standards. |
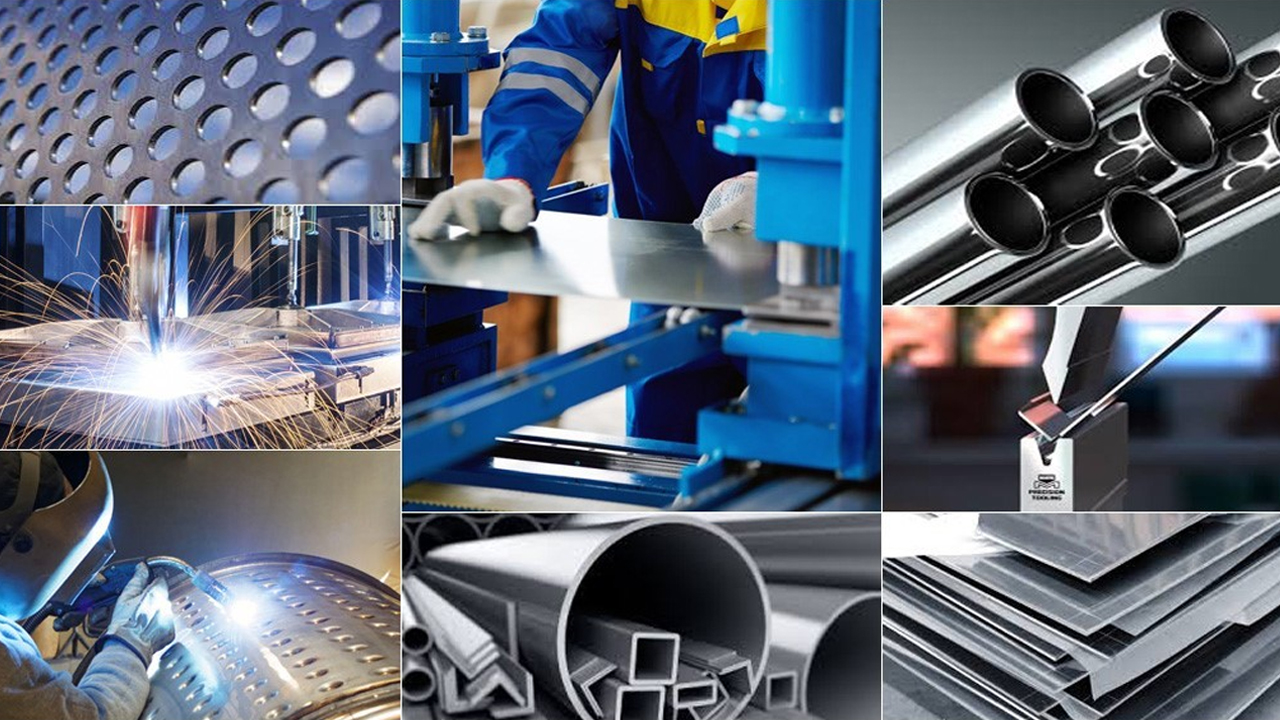
How is Steel Fabrication Used in Construction?
In the construction industry, steel fabricators play a crucial role by providing structural steel framing for buildings. This involves transforming raw steel into beams, columns, and other components that form the skeleton of a structure. The primary benefit of utilizing steel is its strength and durability, which ensure the safety and longevity of buildings. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, it is essential to partner with fabricators who understand local regulations and building codes, ensuring compliance and smooth project execution.

Illustrative image related to what is a steel fabricator
What Role Does Steel Fabrication Play in Shipbuilding?
Steel fabrication is integral to the shipbuilding sector, where it is used to create hulls and various structural components of vessels. These fabricated parts enhance the integrity and performance of ships, making them safer and more efficient in navigating maritime environments. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should seek fabricators who adhere to maritime standards and possess the necessary certifications to guarantee quality and compliance, which is vital in this highly regulated industry.
How is Steel Fabrication Applied in Mining?
In the mining sector, steel fabricators provide custom solutions such as steel supports and machinery components tailored to withstand harsh operating conditions. The primary advantage of these fabricated products is their ability to improve operational efficiency and ensure safety in environments that can be dangerous. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, it is essential to assess a fabricator’s experience in producing robust solutions that can endure extreme conditions while also being able to deliver on time.
What is the Importance of Steel Fabrication in Automotive Manufacturing?
The automotive industry relies heavily on steel fabrication for producing chassis and body components. Fabricated steel parts contribute to reducing vehicle weight while maintaining necessary strength, which ultimately enhances performance and fuel efficiency. Buyers in South America and Europe should prioritize fabricators with advanced precision machining capabilities and rapid prototyping services to ensure that their specifications are met efficiently and accurately.
How Does Steel Fabrication Support Civil Infrastructure Projects?
Steel fabrication is vital in civil infrastructure projects, such as the construction of bridges and public transport systems. These fabricated components facilitate efficient transportation and connectivity, which are essential for economic growth. When sourcing steel fabricators for such large-scale projects, international buyers should evaluate a fabricator’s track record in delivering complex projects on time and their adherence to safety standards, which are critical for public infrastructure development.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is a steel fabricator’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Unclear Specifications Leading to Project Delays
The Problem: A common challenge faced by B2B buyers in the steel fabrication sector is the lack of clarity in project specifications. When architectural designs or engineering plans are ambiguous, it can lead to misunderstandings between buyers and fabricators. For example, a construction company may provide vague drawings, resulting in fabricated steel components that do not fit the intended design. This can cause significant project delays, increased costs due to rework, and frustration for all parties involved.
The Solution: To avoid such issues, it is essential to develop a comprehensive and detailed specification document before engaging with a steel fabricator. Buyers should work closely with architects and engineers to create precise drawings that include dimensions, tolerances, and material specifications. Utilizing 3D modeling tools can help visualize the components and facilitate better communication with fabricators. Additionally, engaging in early discussions with the fabricator about their capabilities and limitations can align expectations and ensure a smoother fabrication process. Establishing a feedback loop during the design phase allows for adjustments before production begins, minimizing the risk of costly errors.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Quality of Fabricated Steel Products
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter inconsistent quality in steel fabrication, which can lead to structural failures and safety hazards. This inconsistency can stem from various factors, including inadequate quality control processes, the use of subpar raw materials, or lack of skilled labor. For instance, a buyer might receive steel beams that vary in thickness or finish, jeopardizing the integrity of the entire project.
The Solution: To mitigate quality concerns, buyers should prioritize sourcing steel fabricators with robust quality assurance protocols. Conducting thorough research and asking potential fabricators about their quality control measures is crucial. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to international quality management standards. Buyers should also request samples of previous work and, if possible, visit the fabrication facility to observe the processes in action. Establishing clear quality expectations in contracts and conducting periodic inspections during the fabrication phase can further ensure that the final products meet the required standards.
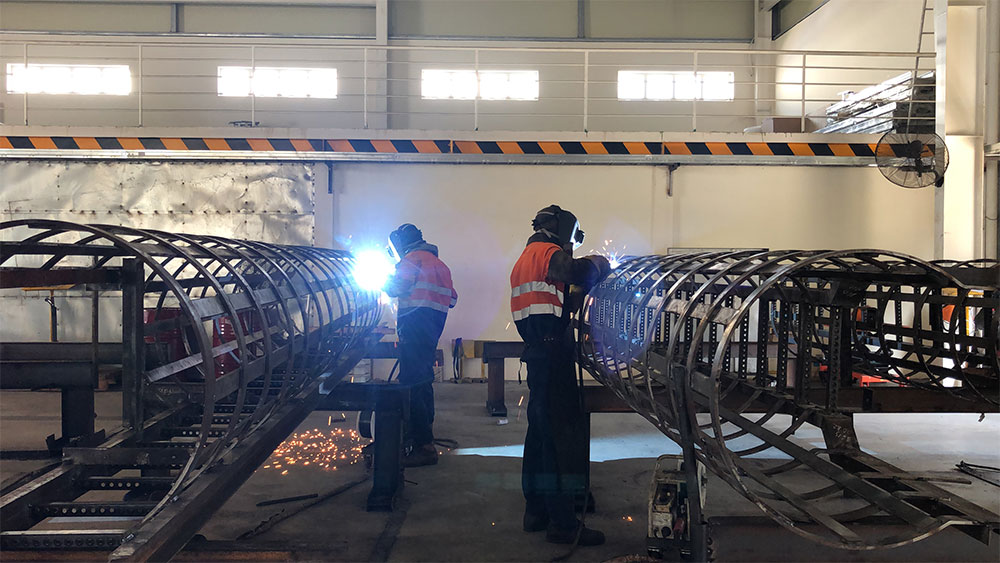
Scenario 3: Long Lead Times Affecting Project Timelines
The Problem: Timely delivery of fabricated steel components is critical for keeping construction projects on schedule. However, B2B buyers often face long lead times due to factors such as high demand, limited production capacity, or inefficient manufacturing processes. For instance, a buyer may find that the fabricator cannot meet the delivery timeline, leading to project delays and increased costs.
The Solution: To address lead time issues, buyers should adopt a proactive approach by clearly communicating their project timelines and requirements upfront. It is beneficial to develop a strong relationship with the steel fabricator, allowing for better negotiation on timelines and prioritization of projects. Additionally, buyers can implement a just-in-time (JIT) inventory strategy, which involves scheduling deliveries of fabricated components to coincide with specific phases of the project. This approach not only minimizes inventory costs but also allows for a more flexible response to any unforeseen delays. Lastly, considering multiple fabricators and maintaining a list of backup suppliers can provide alternative options should lead times become unmanageable.

Illustrative image related to what is a steel fabricator
Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is a steel fabricator
What Are the Key Materials Used by Steel Fabricators?
Steel fabricators rely on a variety of materials, each with unique properties that influence their performance in specific applications. Understanding these materials is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Below, we analyze four common materials used in steel fabrication, focusing on their properties, advantages and disadvantages, application impacts, and considerations for international buyers.
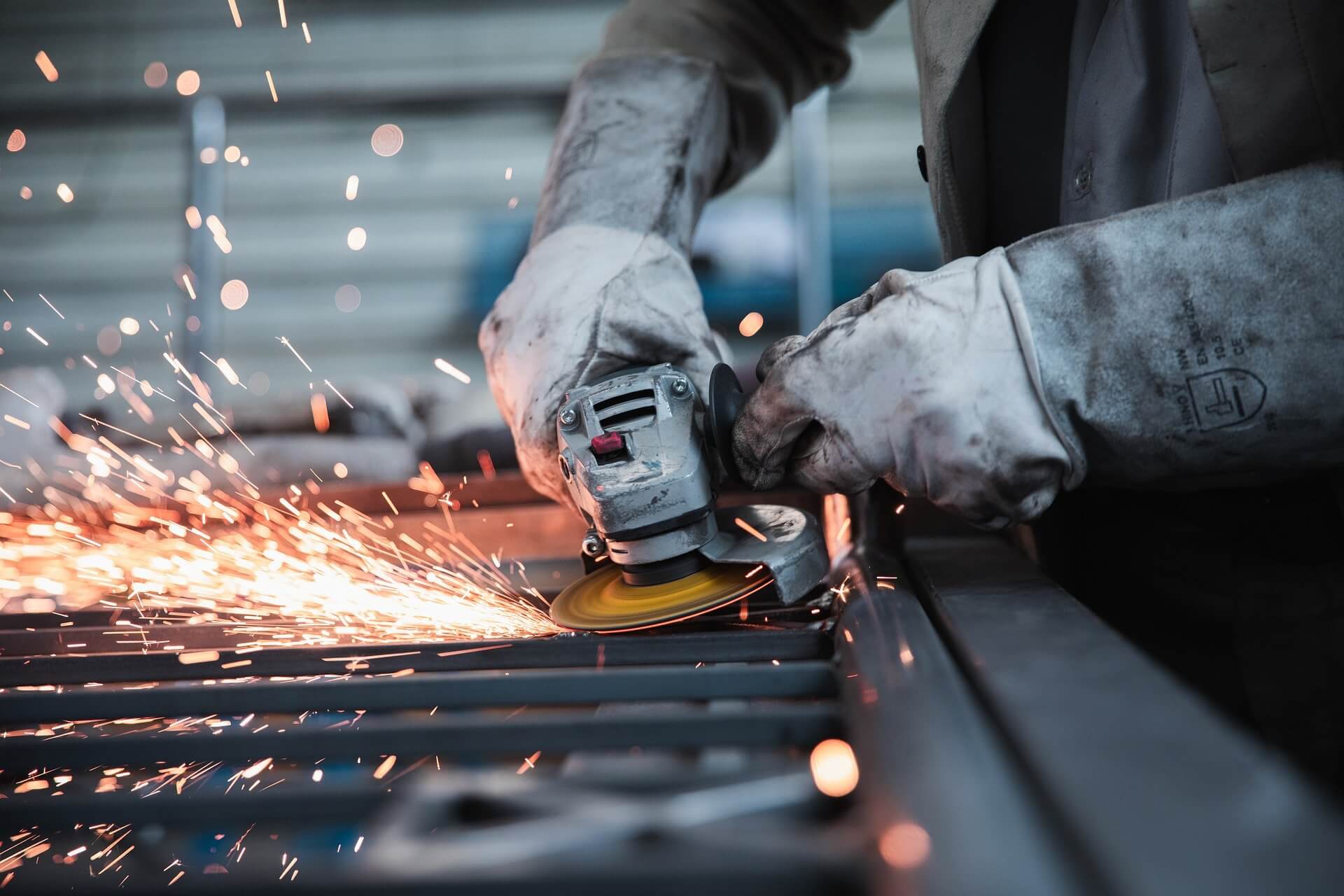
What Are the Key Properties of Mild Steel?
Mild steel, or low-carbon steel, is one of the most commonly used materials in fabrication. Its key properties include good weldability and ductility, making it suitable for various applications. Mild steel typically has a temperature rating of up to 400°C and can withstand moderate pressure.
Pros: Mild steel is cost-effective, easy to work with, and has a high strength-to-weight ratio. It is ideal for structural applications, such as beams and frames.
Cons: However, it has limited corrosion resistance and may require protective coatings in humid or corrosive environments.

Illustrative image related to what is a steel fabricator
Impact on Application: Mild steel is compatible with standard construction practices and is often used in buildings, bridges, and automotive components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM A36 or EN 10025, and consider the availability of protective coatings to enhance durability in specific climates.
How Does Stainless Steel Compare in Terms of Performance?
Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. It typically withstands temperatures up to 800°C and is suitable for high-pressure applications.
Pros: Its durability and resistance to rust make it ideal for applications in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and marine environments.
Cons: The main drawback is its higher cost compared to mild steel, along with increased manufacturing complexity due to its hardness.
Illustrative image related to what is a steel fabricator
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is often used in environments where hygiene and corrosion resistance are critical, such as in kitchen equipment and medical devices.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for compliance with standards like ASTM A240 or EN 10088 and consider the specific grades of stainless steel that meet their application needs.
What Are the Advantages of Using Aluminum in Fabrication?
Aluminum is another material frequently used in steel fabrication, particularly for lightweight applications. It has a temperature rating of up to 600°C and is highly resistant to corrosion.
Pros: Aluminum is lightweight, making it easier to transport and install. It also has excellent thermal and electrical conductivity.
Cons: The primary disadvantage is its lower strength compared to steel, which may limit its use in heavy-load applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is ideal for applications in aerospace, automotive, and architectural designs where weight reduction is essential.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with relevant standards such as ASTM B221 and consider the availability of aluminum alloys that suit their specific requirements.
What Role Does Carbon Steel Play in Steel Fabrication?
Carbon steel is a versatile material that can be tailored for different applications by adjusting its carbon content. It typically has a temperature rating similar to mild steel, up to 400°C, and can handle moderate pressure.
Pros: Carbon steel is strong and can be heat-treated to enhance its mechanical properties, making it suitable for various structural applications.

Illustrative image related to what is a steel fabricator
Cons: It is prone to rusting and requires protective coatings or treatments to enhance its longevity.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is widely used in construction, manufacturing, and automotive industries due to its adaptability.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with standards such as ASTM A992 and consider the environmental conditions of their specific regions when selecting carbon steel.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Steel Fabrication
| Material | Typical Use Case for what is a steel fabricator | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mild Steel | Structural beams and frames | Cost-effective and easy to work with | Limited corrosion resistance | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing and medical devices | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace and architectural designs | Lightweight and easy to transport | Lower strength compared to steel | Medium |
| Carbon Steel | Construction and manufacturing | Strong and adaptable | Prone to rust without coatings | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly utilized in steel fabrication, equipping international B2B buyers with the necessary insights to make informed decisions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is a steel fabricator
What Are the Main Stages of Steel Fabrication Manufacturing Processes?
Steel fabrication is a multi-stage process that transforms raw steel into the components and structures used in various industries. Understanding the stages involved can help B2B buyers assess the capabilities of potential suppliers. The primary stages of the manufacturing process include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Preparation Conducted in Steel Fabrication?
The first stage in the steel fabrication process is material preparation. This involves sourcing raw steel materials, which can come in various forms such as plates, sheets, and sections. The selected materials undergo a thorough inspection to ensure they meet quality standards and specifications. This stage may also involve cutting the steel to manageable sizes using techniques such as flame cutting, plasma cutting, or water jet cutting.
Once the materials are cut, they are often subjected to shot blasting to remove impurities and prepare the surface for further processing. This not only enhances the quality of welds but also ensures that coatings adhere properly during the finishing stage.
What Techniques Are Used for Forming Steel Components?
Forming is the next critical step in the fabrication process. This stage involves shaping the steel into the required forms through various techniques:
- Bending: Steel sections are bent using tools like roll benders or press brakes to achieve specific angles and curves.
- Machining: This process involves removing material to create precise dimensions and shapes. Techniques include milling, drilling, and turning, which are executed using CNC machinery for high precision.
- Welding: As a vital aspect of steel fabrication, welding combines different steel parts into a cohesive structure. Master welders employ various methods, including MIG, TIG, and arc welding, ensuring strong and durable joints.
How Does Assembly Work in Steel Fabrication?
Once the individual components are formed, the assembly stage begins. This involves fitting together various parts to create larger structures. Steel fabricators often work from detailed designs provided by drafters or engineers, ensuring each piece fits perfectly. This stage may include additional welding, bolting, or riveting to secure components together.
Quality assurance is crucial during assembly, as any misalignment can affect the structural integrity of the final product. Fabricators often perform in-process inspections to ensure that all components meet specifications before moving on to the finishing stage.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Used in Steel Fabrication?
The finishing stage adds the final touches to the fabricated steel components. This can include:
- Coating: Steel surfaces are often coated to enhance durability and aesthetics. Common methods include galvanization for corrosion resistance and painting for visual appeal.
- Surface Treatment: Techniques such as sandblasting or polishing may be employed to achieve a desired finish or texture.
Quality checks are essential during this stage to ensure that the coatings are applied uniformly and adhere properly to the steel surface.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Steel Fabricators?
Quality assurance in steel fabrication is governed by various international and industry-specific standards. B2B buyers should be familiar with these standards to ensure that their suppliers maintain high-quality processes.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS) that ensures consistent quality in products and services. Suppliers who are ISO 9001 certified demonstrate their commitment to continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
- ISO 3834: Specifically relevant to welding, this standard provides criteria for quality requirements in fusion welding of metallic materials, ensuring that welding processes are carried out with precision and quality control.
What Industry-Specific Standards Should Be Noted?
- CE Marking: In Europe, CE marking is a declaration by the manufacturer that their product meets EU safety, health, and environmental protection requirements. This is particularly important for construction-related products.
- API Standards: For industries such as oil and gas, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is critical. These standards ensure that materials and products meet rigorous safety and performance criteria.
How Can B2B Buyers Ensure Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should implement several strategies to verify the quality control processes of their steel fabrication suppliers.

Illustrative image related to what is a steel fabricator
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specified standards before they are used in production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the fabrication process, regular inspections are conducted to catch any defects early and ensure compliance with design specifications.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before delivery, a comprehensive inspection is conducted on the finished products to confirm that they meet all quality standards and specifications.
How Can Buyers Verify Supplier QC Practices?
Buyers can verify a supplier’s quality control practices through:
- Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the supplier’s quality management systems and processes firsthand.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can provide insights into the supplier’s performance and adherence to standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspectors to evaluate the fabrication process can offer an unbiased assessment of quality control measures in place.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
When dealing with suppliers from different regions, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers should be aware of specific nuances in quality assurance practices.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have varying regulations regarding steel fabrication. Buyers should ensure that suppliers comply with local and international standards applicable to their market.
- Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural attitudes towards quality can influence how suppliers approach manufacturing and quality assurance. Building strong relationships based on trust can enhance communication and quality outcomes.
- Logistical Considerations: International shipping can introduce challenges related to quality control, such as damage during transit. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have robust packaging and handling protocols to mitigate these risks.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance standards involved in steel fabrication, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and select suppliers that meet their specifications and quality requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is a steel fabricator’
The purpose of this guide is to provide B2B buyers with a comprehensive checklist to effectively source steel fabricators. By following these steps, you can ensure that you select a qualified partner that meets your specific needs for steel fabrication, whether for construction, manufacturing, or other applications.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to potential fabricators, clearly outline your project requirements. This includes the types of steel needed, dimensions, and any specific fabrication techniques (such as welding or cutting) that must be employed. Defining these specifications helps you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensures they can meet your technical needs.

Illustrative image related to what is a steel fabricator
Step 2: Research Potential Fabricators
Conduct thorough research to identify potential steel fabricators in your target regions, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Use industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to compile a list. Pay attention to their experience in your industry and the types of projects they have completed, which can indicate their capability and reliability.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that potential fabricators hold relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 for quality management or specific welding certifications. These certifications are crucial as they demonstrate the fabricator’s commitment to maintaining industry standards and quality assurance processes. Additionally, inquire about their health and safety compliance to ensure a safe working environment.
Step 4: Request Detailed Proposals
Once you have narrowed down your list, request detailed proposals from each fabricator. This should include pricing, timelines, and a breakdown of materials and processes. A comprehensive proposal allows you to compare options effectively and ensures that there are no hidden costs later in the project.
Step 5: Inspect Previous Work and References
Ask for case studies or examples of previous projects similar to yours. Reach out to past clients for references to gain insights into their experiences with the fabricator. Understanding their performance history can help you assess their reliability and the quality of their work.

Illustrative image related to what is a steel fabricator
Step 6: Assess Technological Capabilities
Inquire about the technology and equipment the fabricator uses. Advanced tools like CNC machines, laser cutters, and 3D modeling software can significantly enhance precision and efficiency in fabrication. A fabricator that invests in cutting-edge technology is more likely to deliver high-quality results.
Step 7: Evaluate Communication and Support
Effective communication is vital throughout the fabrication process. Assess how responsive and supportive potential fabricators are during your initial interactions. A supplier that prioritizes communication will be easier to work with and more likely to address any issues that arise during the project.
By following this checklist, you can ensure a thorough evaluation of potential steel fabricators, leading to a successful partnership that meets your project requirements and quality standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is a steel fabricator Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of Steel Fabrication?
Understanding the cost structure of steel fabrication is crucial for international B2B buyers looking to source competitively priced products. The main components influencing the overall cost include:
-
Materials: The type of steel used significantly impacts costs. Options range from mild steel to high-strength alloys, each with varying price points. Additionally, raw materials such as welding wire, fittings, and coatings (e.g., galvanization) also contribute to the total material cost.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential in steel fabrication. Costs can vary based on geographic location and the complexity of the work required. Regions with higher wage standards, such as parts of Europe, may see elevated labor costs compared to other areas, such as South America or Africa.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to running a fabrication facility, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. High overhead can drive up prices, especially in regions where operational costs are significantly elevated.
-
Tooling: The need for specialized tools and machinery (e.g., CNC machines, laser cutters) can also affect pricing. Initial investment in advanced technology can lead to higher upfront costs but may provide efficiencies that reduce long-term expenses.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality involves additional costs, from inspections to certifications. Buyers requiring high-quality standards or specific certifications (e.g., ISO, CE marking) should be prepared for higher pricing.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary widely, especially for international shipments. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties all play a role in the final cost.
-
Margin: Profit margins for steel fabricators can vary based on competition and market demand. Buyers should consider the balance between price and the quality of service provided when evaluating quotes.
What Factors Influence Steel Fabrication Pricing?
Several pricing influencers can affect the final cost of steel fabrication, especially for international buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often attract discounts, making it crucial for buyers to understand the MOQ policies of potential suppliers. Negotiating bulk pricing can lead to significant savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom projects generally incur higher costs due to the additional labor and materials involved. Clear communication regarding specifications can help avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: The level of quality and any required certifications can lead to price fluctuations. Buyers should be aware of the industry standards necessary for their projects to ensure compliance without incurring unnecessary costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more for their products due to their proven track record, but they often provide additional value in terms of quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial for international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers, affecting overall costs related to transportation and liability.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating Steel Fabrication Costs?
For international B2B buyers, effective negotiation strategies can lead to cost-efficiency:
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also the lifetime costs associated with the product, including maintenance, durability, and potential resale value.
-
Leverage Competition: Solicit quotes from multiple suppliers to leverage competitive pricing. Highlighting alternatives can encourage suppliers to offer better terms.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and improved product quality over time.
-
Understand Local Market Dynamics: Buyers from regions such as Africa and South America should be aware of local market conditions and currency fluctuations, which can impact pricing and supplier negotiations.
-
Communicate Clearly: Ensure that all specifications and requirements are clearly communicated to avoid misunderstandings that can lead to increased costs.
Conclusion
While prices for steel fabrication can vary significantly based on numerous factors, understanding the cost components and pricing influencers empowers buyers to make informed decisions. By employing effective negotiation strategies and considering the total cost of ownership, international B2B buyers can optimize their sourcing process, ensuring they receive quality products at competitive prices.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is a steel fabricator With Other Solutions
In the realm of metal processing and construction, the role of a steel fabricator is crucial. However, businesses often seek alternatives that may fulfill their needs in different ways. This analysis will compare steel fabrication with two viable alternatives: modular construction and additive manufacturing (3D printing). Each method offers unique benefits and challenges that can influence a buyer’s decision.
| Comparison Aspect | What Is A Steel Fabricator | Modular Construction | Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and durability for complex structures. | Fast construction, but may lack the same level of customization. | Excellent for intricate designs but limited by material types. |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on project complexity and materials. | Generally lower costs due to reduced labor and time. | Can be high for materials but reduces waste and labor costs. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled labor and equipment setup. | Streamlined processes but may face zoning and permitting challenges. | Requires specialized equipment and knowledge but can be integrated with existing workflows. |
| Maintenance | High-quality finishes reduce long-term maintenance needs. | May require ongoing maintenance based on material used. | Limited maintenance but depends on the durability of the printed materials. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for custom structural projects in construction and manufacturing. | Best for rapid builds like housing or commercial spaces. | Suitable for prototyping and small-scale production of complex geometries. |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Modular Construction?
Modular construction involves prefabricating sections of a building off-site, which are then transported and assembled on-site. This method significantly reduces construction time and labor costs, making it an attractive alternative for projects needing rapid completion. However, modular construction may face challenges with zoning regulations and site-specific adjustments, potentially limiting customization. Its performance may not match that of traditional steel fabrication in terms of structural integrity for complex designs.

Illustrative image related to what is a steel fabricator
What Are the Pros and Cons of Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)?
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, allows for the creation of intricate designs layer by layer, using materials like plastics and metals. This method excels in rapid prototyping, enabling businesses to test and iterate designs quickly. It also minimizes waste, as materials are only used where necessary. However, the range of materials suitable for 3D printing is currently limited compared to traditional steel fabrication, and the initial investment in specialized equipment can be high. Additionally, while 3D printing can produce complex shapes, it may not provide the same structural strength required for large-scale applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting between a steel fabricator and alternative solutions, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including project scope, timeline, budget, and specific performance requirements. For projects demanding high structural integrity and customization, steel fabrication remains a robust option. Conversely, if speed and cost-effectiveness are paramount, modular construction may be preferable. For innovative designs and rapid prototyping, additive manufacturing can offer unique advantages. Understanding these elements will empower buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific operational needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is a steel fabricator
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Steel Fabrication?
Understanding the technical properties associated with steel fabrication is crucial for B2B buyers in making informed decisions. Here are some essential specifications that impact the quality and suitability of fabricated steel products:
-
Material Grade
Material grades refer to the classification of steel based on its chemical composition and mechanical properties. Common grades include ASTM A36, A992, and A572. Selecting the appropriate grade is vital for ensuring structural integrity, as different applications may require different strength levels, corrosion resistance, or weldability. B2B buyers must consider these factors to avoid costly failures in construction or manufacturing. -
Tolerance
Tolerance defines the allowable deviation from specified dimensions during the fabrication process. Tight tolerances are critical in applications where precision is paramount, such as in structural components or machinery parts. Understanding tolerance levels can help buyers ensure that the fabricated items fit seamlessly into their projects, reducing the need for costly rework or adjustments. -
Surface Finish
Surface finish refers to the texture and quality of a steel component’s surface after fabrication. It can include coatings like galvanization or paint, which protect against corrosion and enhance aesthetics. B2B buyers should specify surface finish requirements to ensure that products meet both functional and visual standards, particularly for architectural applications. -
Welding Specifications
Welding specifications encompass the types of welding processes and materials used to join steel components. Common welding methods include MIG (Metal Inert Gas) and TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas). Buyers should be aware of welding requirements to ensure compatibility with their project needs, as improper welding can lead to structural failures or increased maintenance costs. -
Weight Capacity
Weight capacity refers to the maximum load that a fabricated steel component can safely support. It is essential for ensuring that structures can bear the loads they are designed for, especially in construction and heavy machinery applications. Buyers must assess weight capacity specifications to guarantee safety and compliance with industry standards. -
Mechanical Properties
Mechanical properties such as yield strength, tensile strength, and ductility provide insights into how steel behaves under stress. These properties are crucial for assessing the performance of steel in various applications. B2B buyers should consider these factors when selecting steel products to ensure they meet the demands of their specific projects.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Steel Fabrication?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication in steel fabrication. Here are some commonly used trade terms:

Illustrative image related to what is a steel fabricator
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In steel fabrication, OEMs often require custom fabricated components for their products. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers navigate supply chains and ensure quality in the parts they procure. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to produce or sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers to understand, as it impacts purchasing decisions and inventory management. Knowing the MOQ can help buyers strategize their orders to meet project timelines without overcommitting resources. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used by buyers to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. It typically includes detailed specifications, quantities, and delivery timelines. Utilizing RFQs effectively can help buyers compare offers and negotiate better terms with fabricators. -
Incoterms
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) are a set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers engaged in international transactions to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth logistics. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the amount of time required from placing an order to receiving the finished product. Understanding lead times is critical for project planning and can affect timelines significantly. Buyers should inquire about lead times to align production schedules with project deadlines. -
Steel Detailer
A steel detailer is a professional who creates detailed drawings and specifications for steel fabricators. Their work is essential for ensuring accuracy in the fabrication process. Buyers should recognize the importance of collaboration with detailers to achieve precise outcomes in their projects.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when engaging with steel fabricators, ensuring project success and operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is a steel fabricator Sector
What Are the Key Drivers Influencing the Steel Fabrication Market?
The global steel fabrication market is witnessing significant transformation driven by a confluence of technological advancements, economic growth, and changing regulatory landscapes. Key drivers include the increasing demand for steel in construction, automotive, and infrastructure sectors, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, and the Middle East. The rise of urbanization in these regions has led to a surge in construction activities, amplifying the need for reliable steel fabricators.
Moreover, advancements in B2B technology, such as Computer Numerical Control (CNC) and 3D modeling, are enhancing precision and efficiency in fabrication processes. These technologies allow for real-time adjustments and improved design capabilities, making it easier for fabricators to meet the customized needs of clients. As international buyers, particularly from regions like Nigeria and Vietnam, look for suppliers who can deliver high-quality products on time, these technological trends become vital in maintaining competitive advantage.
Furthermore, the market dynamics are influenced by the increasing emphasis on sustainability and ethical sourcing. Fabricators are now expected to adopt greener practices, which is reshaping sourcing strategies. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to reducing environmental impacts and adhering to ethical labor practices, thereby driving a shift towards more sustainable supply chains.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in Steel Fabrication?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of the steel fabrication industry, reflecting a broader shift towards environmental responsibility. The steel industry is a significant contributor to carbon emissions, which necessitates urgent action to mitigate its environmental footprint. For B2B buyers, choosing a steel fabricator that prioritizes sustainability is not just a regulatory requirement but also a strategic decision that aligns with global trends towards greener practices.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as it ensures that the materials used in fabrication are procured responsibly, without compromising labor rights or environmental standards. Many fabricators are now seeking certifications that demonstrate their commitment to sustainable practices, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and various green building certifications.

Illustrative image related to what is a steel fabricator
Additionally, the use of recycled steel and eco-friendly materials is gaining traction. Buyers are increasingly looking for fabricators who can provide sustainable materials that meet their project specifications while minimizing environmental impact. This focus on sustainability and ethical sourcing can enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty, making it a critical factor for B2B partnerships in the steel fabrication sector.
What Is the Historical Context of Steel Fabrication in the B2B Landscape?
The history of steel fabrication dates back centuries, evolving from rudimentary blacksmithing practices to a complex industry driven by technological innovation. Initially, steel was primarily used for tools and weapons, but its application broadened significantly during the Industrial Revolution. The mass production of steel structures began in the 19th century, making it a cornerstone material for railways, bridges, and buildings.
As the 20th century progressed, advancements in welding techniques and the introduction of machinery such as CNC dramatically transformed the fabrication landscape. This evolution has allowed steel fabricators to produce more intricate designs and larger structures with enhanced precision. Today, the integration of digital technologies and a focus on sustainability represent the latest phase in the evolution of steel fabrication, positioning it as a critical component in modern construction and manufacturing processes.

Illustrative image related to what is a steel fabricator
In summary, understanding the dynamics of the steel fabrication market, particularly the importance of sustainability and the historical evolution of the industry, can provide international B2B buyers with valuable insights for making informed sourcing decisions. As global demand continues to rise, aligning with forward-thinking fabricators will be essential for achieving both operational and strategic goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is a steel fabricator
-
How do I choose the right steel fabricator for my project?
Choosing the right steel fabricator involves assessing several critical factors. Start by evaluating their experience and specialization in the specific type of fabrication you need, whether it’s structural steel, custom designs, or specific industries like construction or shipbuilding. Request references and examples of previous work to gauge their capabilities. Additionally, consider their technology and equipment, as advanced machinery like CNC systems can significantly enhance precision and efficiency. Lastly, ensure they have a robust quality assurance process to meet your project’s standards. -
What are the common steel fabrication processes used by fabricators?
Common steel fabrication processes include cutting, bending, welding, and coating. Cutting techniques like plasma or water jet cutting allow for precise shaping of steel sections. Bending is often achieved through rolling or press braking to create specific angles or curves. Welding is essential for joining metal pieces, requiring skilled technicians to ensure strong seams. Finally, coating processes, such as galvanization, protect steel from corrosion and enhance its aesthetic appeal, making it suitable for various applications. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for steel fabrication services?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among steel fabricators, often influenced by the complexity of the project and the materials required. Many fabricators may have a standard MOQ to ensure cost-effectiveness, especially for custom pieces. It’s advisable to discuss your project requirements upfront to determine if the fabricator can accommodate your needs, particularly if you’re a smaller buyer. Some may offer flexibility for trial orders or smaller projects, while others might require larger commitments for specialized work. -
How do I vet a steel fabricator for international trade?
Vetting a steel fabricator for international trade entails thorough research and communication. Start by checking their certifications and compliance with international standards, such as ISO 9001 for quality management. Request documentation of their experience with export processes, including customs regulations relevant to your region. Additionally, consider their financial stability by reviewing credit ratings or requesting financial statements. Engaging with past international clients can provide insights into their reliability and service quality. -
What payment terms should I expect from a steel fabricator?
Payment terms can vary widely among steel fabricators, influenced by factors such as order size and project complexity. Common terms may include deposits ranging from 30% to 50% upfront, with the balance due upon completion or delivery. For larger projects, some fabricators might offer milestone payments tied to specific project phases. Always clarify payment methods accepted, whether bank transfers, letters of credit, or other options, and ensure these terms are documented in the contract to avoid disputes. -
What quality assurance measures should a steel fabricator have in place?
A reputable steel fabricator should implement comprehensive quality assurance measures throughout the fabrication process. This includes inspections at various stages, from raw material sourcing to final product delivery. Look for fabricators that perform non-destructive testing (NDT) methods, such as ultrasonic or magnetic particle testing, to ensure structural integrity. Additionally, inquire about their adherence to industry standards and certifications, which indicate a commitment to maintaining high-quality output and consistency. -
How can I customize steel fabrication for my specific needs?
Customizing steel fabrication begins with clear communication of your project requirements to the fabricator. Provide detailed specifications, including dimensions, material grades, and any unique design elements. Many fabricators utilize advanced software for 3D modeling, allowing you to visualize the final product before production. Be open to discussing potential design modifications that could enhance manufacturability or reduce costs. Collaborating closely with the fabricator during the design phase can lead to innovative solutions tailored to your needs. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when working with a steel fabricator?
Logistics play a crucial role in the successful delivery of fabricated steel products. Discuss shipping options with your fabricator, including whether they handle logistics or if you need to arrange transportation. Understand the estimated lead times for production and delivery, as these can vary based on project complexity and the fabricator’s workload. Additionally, consider customs regulations and import duties for international shipments to avoid unexpected costs. Establishing a clear timeline and communication plan can help ensure timely delivery to your project site.
Top 5 What Is A Steel Fabricator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Aminds – Steel Fabrication Solutions
Domain: aminds.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Steel fabrication is the process of converting steel into structures or spare parts using methods such as cutting, bending, welding, and assembling. Key products include: steel structures, steel components, steel spare parts, steel water tanks, steel silos, stainless steel components, and residential & commercial building products. The company offers custom solutions for various applications acros…
2. Indeed – Metal Fabrication Services
Domain: indeed.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: This company, Indeed – Metal Fabrication Services, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. BeamCut – Advanced CNC Plasma Cutting Technology
Domain: beamcut.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: BeamCut offers advanced CNC plasma cutting technology for structural steel and plate fabrication. Key features include: 1. FANUC Robotics: A six-axis robotic arm capable of 360-degree beveling and processing various shapes, three times stronger and longer-lasting than industry standards. 2. Hypertherm Plasma: High-performance X-Definition plasma for efficient cutting through structural steel and p…
4. Excel Steel – Steel Fabrication Solutions
Domain: excel-steel.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Steel fabrication involves transforming raw steel into usable components for construction, including buildings and bridges. Key processes include welding, shot blasting, coating, and cutting. Essential skills for steel fabricators include precision, technical knowledge, physical strength, problem-solving abilities, and expertise in welding. The coating process protects steel from environmental dam…
5. Buyabeam – Steel Fabrication & Welding Solutions
Domain: buyabeam.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Steel Fabrication and Steel Welding are two distinct processes in the creation of structural steel products. Steel fabrication involves multiple processes such as metal cutting, machining, and bending to transform raw steel into required objects. Fabricators use various cutting machines like mechanical saws, laser cutters, and plasma torches, and may also design items before fabrication. Steel wel…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is a steel fabricator
In the dynamic landscape of global trade, understanding the role of steel fabricators is crucial for businesses seeking to optimize their supply chains. Steel fabricators transform raw materials into essential components used across various industries, including construction, automotive, and infrastructure. By leveraging advanced technologies such as CNC machining and 3D modeling, these professionals ensure precision and quality, which are vital for meeting stringent project requirements.
Strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in connecting international buyers with reliable steel fabricators. This approach allows companies to assess multiple suppliers, evaluate their capabilities, and negotiate favorable terms, ultimately ensuring that projects are completed on time and within budget. As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to grow, the demand for high-quality fabricated steel will only increase.
As you look to enhance your operations, consider forging partnerships with established steel fabricators who can deliver tailored solutions that meet your specific needs. Embrace the opportunities that strategic sourcing presents, and position your business for success in the evolving global marketplace.

Illustrative image related to what is a steel fabricator
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.