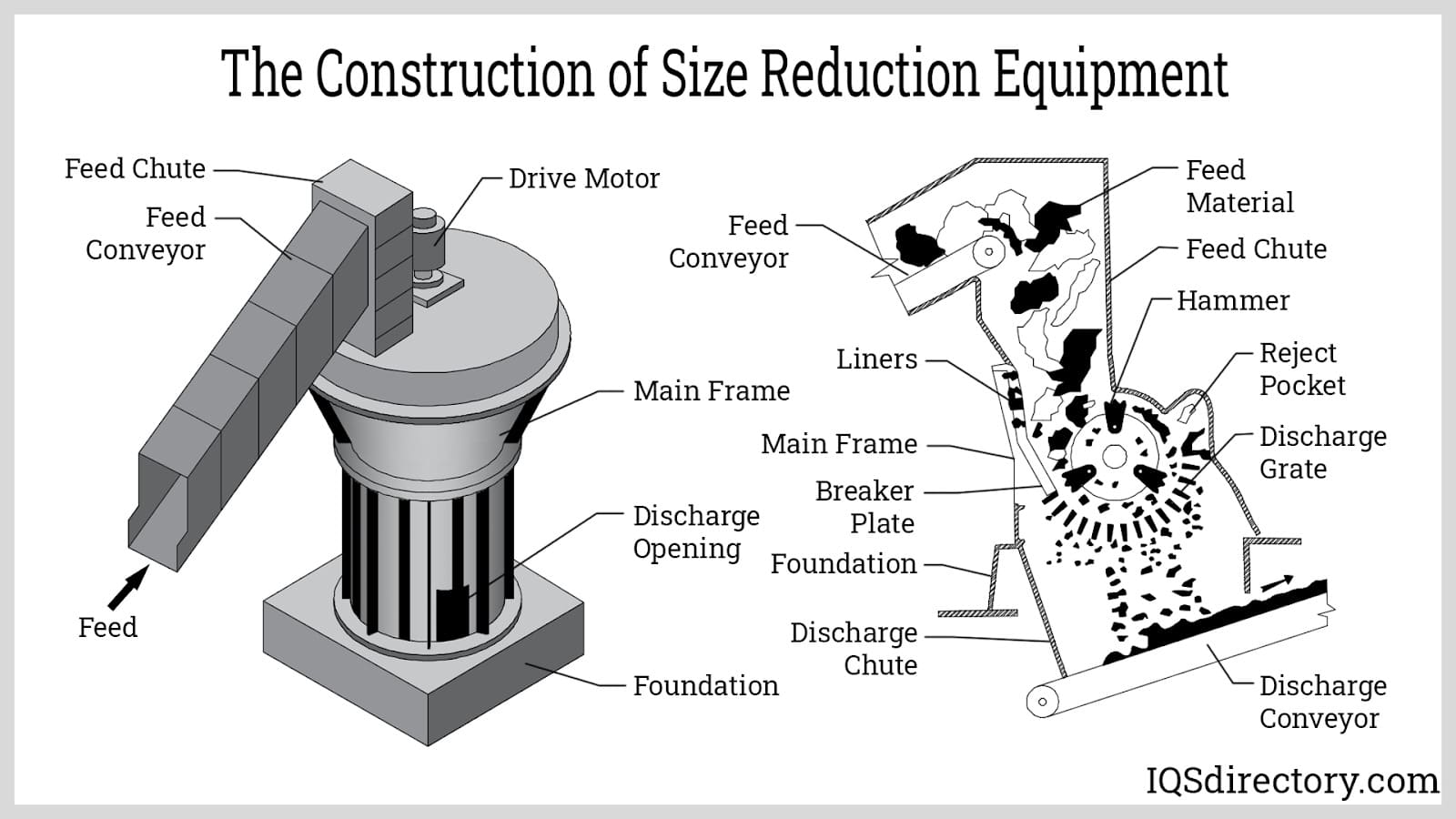
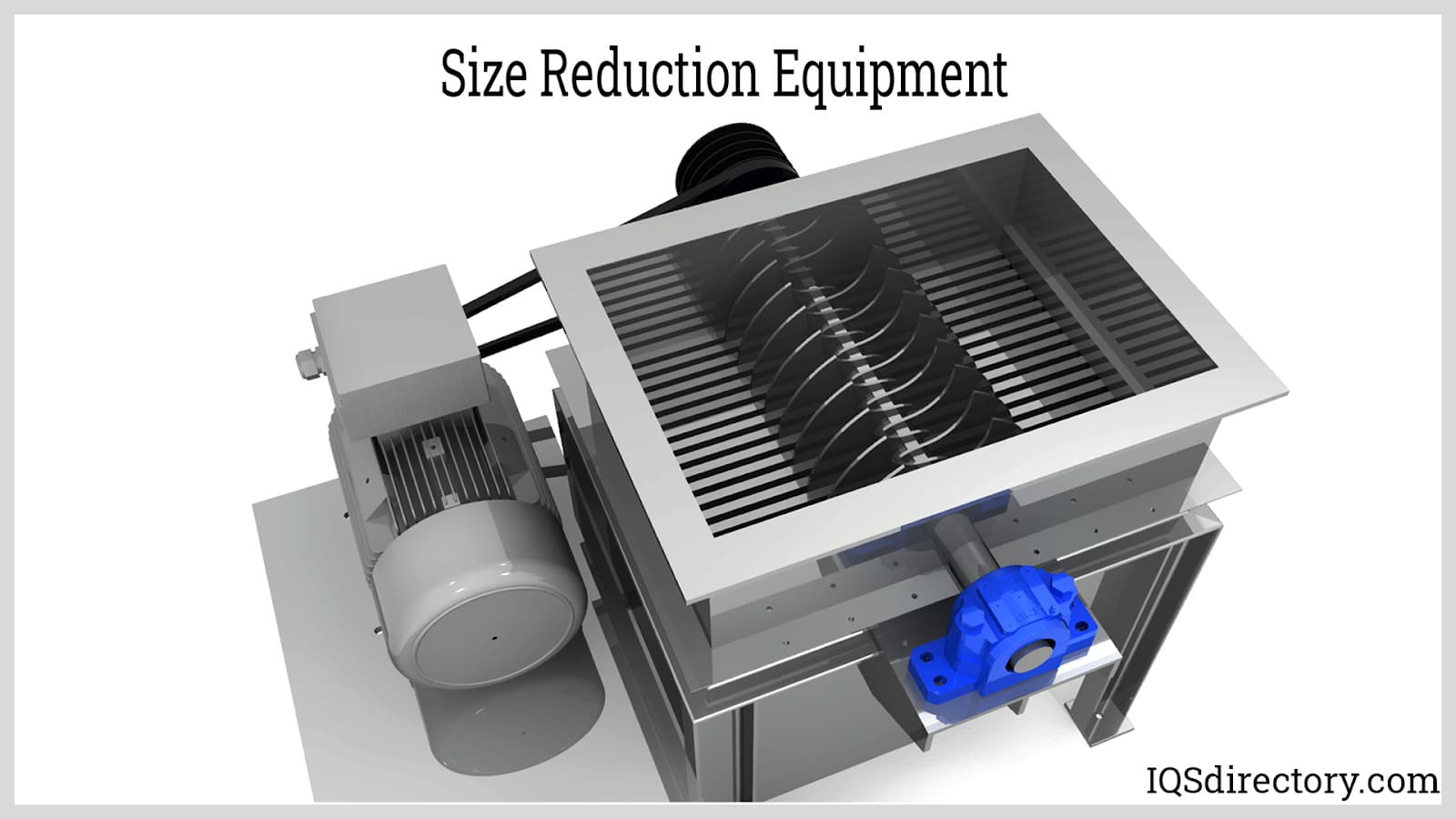
A Deep Dive into Size Reduction Equipment Solution
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for size reduction equipment
In the dynamic landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing the right size reduction equipment can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers. Whether in the mining sector of South America or the food processing industries in Europe, businesses face the critical task of selecting machinery that not only meets their specific operational needs but also aligns with budgetary constraints and local regulations. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the complexities surrounding size reduction equipment by exploring various types, applications, and the nuances of supplier vetting.
From crushers and grinders to shredders and pulverizers, understanding the diverse functionalities of each equipment type is essential for optimizing production processes. Furthermore, this guide delves into the cost considerations, ensuring that international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can make informed purchasing decisions that enhance operational efficiency and product quality.
By providing actionable insights and a framework for evaluating potential suppliers, this guide empowers B2B buyers to navigate the intricacies of the global market confidently. As industries continue to evolve, staying informed about the latest advancements and best practices in size reduction technology is vital for maintaining a competitive edge.
Understanding size reduction equipment Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crushers | Heavy-duty machines that break large materials into smaller pieces. | Mining, recycling, construction | Pros: Efficient for large volumes; Cons: High energy consumption. |
| Grinders | Reduce materials to finer sizes than crushers; includes various types. | Food processing, pharmaceuticals, manufacturing | Pros: Versatile for different materials; Cons: May require multiple passes for very fine sizes. |
| Pulverizers | Achieve very fine particle sizes; essential for specific industries. | Pharmaceuticals, food processing, chemicals | Pros: Produces high-quality powders; Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Industrial Shredders | Designed for shredding dense materials; often used for recycling. | Waste management, recycling, manufacturing | Pros: Environmentally friendly; Cons: Maintenance can be intensive. |
| High Shear Mixers | Used for emulsifying and homogenizing materials; precise control. | Food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals | Pros: Ensures uniformity; Cons: Complexity in operation and maintenance. |
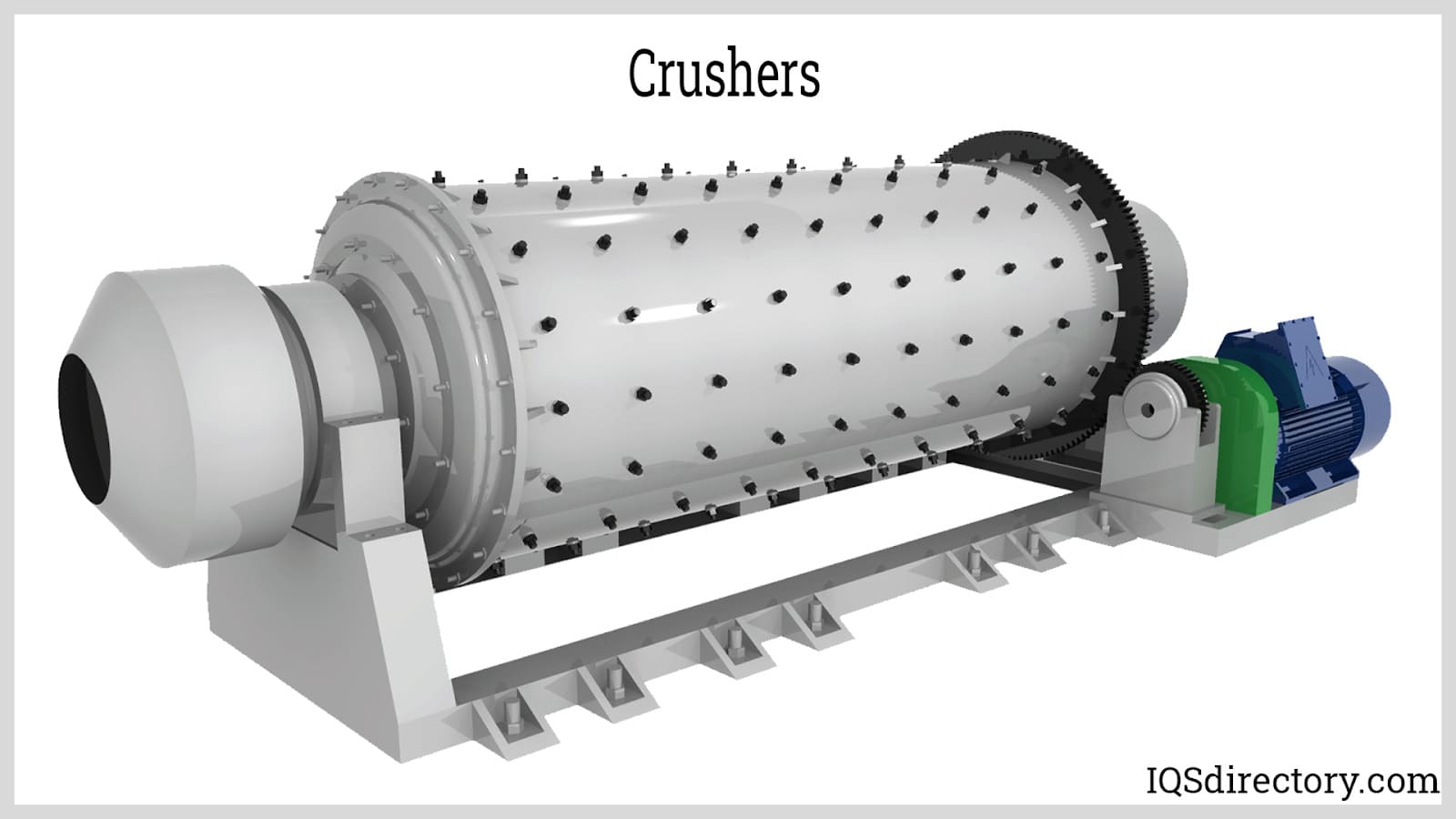
What Are Crushers and Their Suitability for B2B Buyers?
Crushers are robust machines designed to reduce large solid materials into smaller fragments, often serving as the first step in the size reduction process. They are essential in industries like mining and construction, where they facilitate the handling of bulky materials. When selecting a crusher, buyers should consider the material’s hardness, moisture content, and desired output size. While crushers are efficient for large volumes, their high energy consumption can lead to increased operational costs.
How Do Grinders Differ in Functionality for Various Industries?
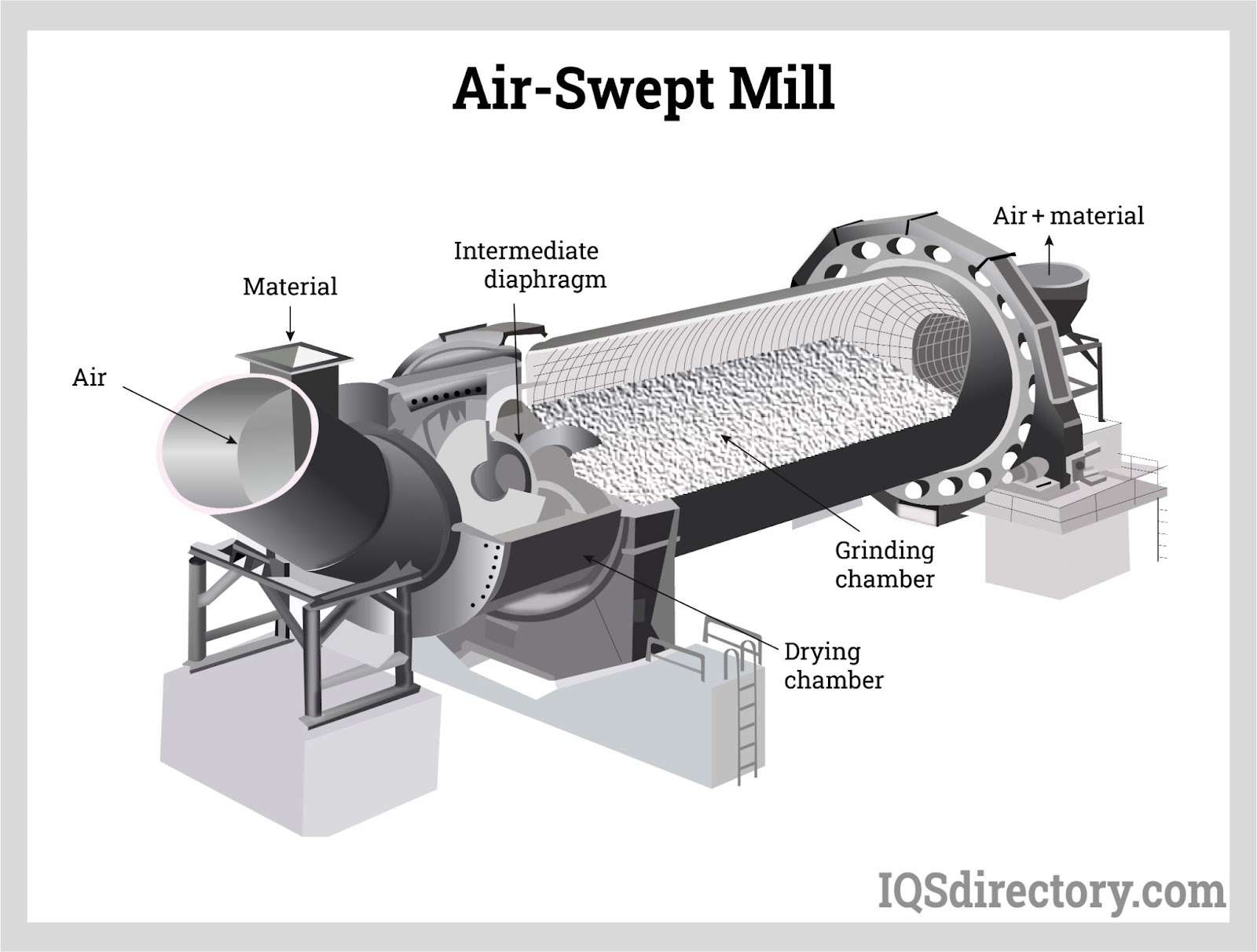
Grinders are versatile machines that reduce materials to finer sizes than crushers and are commonly used in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing. They encompass various types, including ball mills and hammer mills, tailored to specific applications. B2B buyers should evaluate the material characteristics, desired particle size, and production volume when choosing a grinder. Although grinders offer flexibility, achieving very fine particles may require multiple processing stages, potentially increasing processing time and costs.
Why Are Pulverizers Critical in Certain Industries?
Pulverizers are specialized machines that create very fine particle sizes, crucial in industries like pharmaceuticals and food processing. They employ mechanisms such as disc and vibratory mills to achieve the desired fineness. Buyers must assess the specific requirements of their application, including the type of material and necessary particle size. While pulverizers ensure high-quality powder production, they often come with a higher initial investment, making cost analysis essential for potential buyers.

Illustrative image related to size reduction equipment
What Role Do Industrial Shredders Play in Waste Management?
Industrial shredders are designed to shred dense materials, making them vital in waste management and recycling sectors. They effectively reduce the size of various materials, facilitating easier handling and processing. B2B buyers should consider factors such as material type, shredding capacity, and maintenance requirements. While shredders promote environmental sustainability through recycling, they may require intensive maintenance, which can affect operational efficiency.
How Do High Shear Mixers Enhance Product Consistency?
High shear mixers are advanced machines used for emulsifying and homogenizing materials, ensuring a consistent product. They are particularly valuable in food, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical industries, where uniformity is critical. When selecting a high shear mixer, buyers should consider the specific mixing requirements, batch size, and operational complexity. Although these mixers provide high-quality results, their complexity can lead to increased maintenance needs and operational challenges.
Key Industrial Applications of size reduction equipment
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Size Reduction Equipment | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mining | Crushing and grinding of ores | Improved extraction efficiency and reduced processing costs | Material hardness, required particle size, and energy consumption of equipment |
| Food Processing | Milling grains and grinding spices | Enhanced product consistency and quality | Compliance with food safety standards and material compatibility |
| Pharmaceuticals | Pulverizing active ingredients | Precise dosing and improved bioavailability | GMP compliance, material properties, and particle size uniformity |
| Recycling | Shredding plastics and metals | Increased material recovery rates and reduced transport costs | Equipment durability, throughput capacity, and maintenance requirements |
| Chemical Manufacturing | Grinding raw materials for chemical reactions | Enhanced reaction rates and product quality | Material compatibility, desired particle size, and production volume requirements |
How is Size Reduction Equipment Used in Mining?
In the mining sector, size reduction equipment, such as crushers and grinders, is crucial for processing ores. These machines break down large rock formations into manageable sizes, facilitating easier extraction of valuable minerals. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, understanding the hardness and abrasiveness of local ores is essential. Buyers should consider energy efficiency and equipment durability, as these factors significantly impact operational costs and productivity.
What Role Does Size Reduction Equipment Play in Food Processing?
In food processing, size reduction equipment is used for milling grains, grinding spices, and producing uniform ingredient sizes. This ensures consistency in product quality, which is vital for consumer satisfaction. B2B buyers in Europe and the Middle East must prioritize compliance with food safety regulations and select machines that are easy to clean and maintain. Additionally, material compatibility is crucial to avoid contamination and ensure product integrity.
Why is Size Reduction Important in Pharmaceuticals?
Pharmaceutical companies utilize size reduction equipment to pulverize active ingredients into fine powders, enhancing their solubility and bioavailability. This is critical for ensuring accurate dosing and effective drug delivery. For buyers in the Middle East and Europe, adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) is non-negotiable. Buyers should focus on the properties of the materials being processed, as well as the need for uniform particle sizes to achieve consistent product performance.
Illustrative image related to size reduction equipment
How Does Size Reduction Equipment Benefit Recycling Efforts?
In the recycling industry, shredders and grinders are employed to process waste materials like plastics and metals. This not only increases recovery rates but also reduces transportation costs by minimizing material volume. For international buyers, particularly in South America and Africa, sourcing equipment that can handle diverse materials and withstand harsh operating conditions is vital. Considerations such as equipment durability and maintenance support can significantly influence operational efficiency.
What is the Impact of Size Reduction in Chemical Manufacturing?
Chemical manufacturing often requires the grinding of raw materials to achieve specific particle sizes that enhance reaction rates. Size reduction equipment plays a pivotal role in ensuring that materials meet the necessary specifications for optimal production. For buyers in Europe and the Middle East, it’s important to evaluate the compatibility of equipment with various chemicals and the scale of production needed. Additionally, understanding the desired final particle size is essential for achieving high-quality outputs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘size reduction equipment’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Achieving Desired Particle Size for Specific Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in industries such as pharmaceuticals or food processing struggle to achieve a specific particle size during the size reduction process. For example, a company may require a powder with a particle size of less than 100 micrometers for effective dissolution and bioavailability in drugs. If the machinery fails to produce this fineness, it can lead to increased production costs, longer processing times, and potential quality control issues. Buyers often find themselves navigating a complex landscape of equipment types and specifications, which can be overwhelming and lead to costly mistakes.
The Solution: To effectively meet particle size requirements, it’s critical to first conduct a thorough analysis of the material properties, including hardness, moisture content, and desired end-use. Buyers should collaborate closely with equipment manufacturers to select machinery specifically designed for their material’s characteristics. For instance, using a combination of crushers for initial size reduction followed by high shear mixers or fine grinders can optimize the process. Additionally, investing in equipment that allows for adjustable parameters such as speed and pressure can provide the flexibility needed to fine-tune particle size. Regular testing of the output using techniques like laser diffraction can ensure that the desired specifications are met consistently.
Scenario 2: High Operational Costs Due to Inefficient Equipment
The Problem: Many companies face escalating operational costs because their existing size reduction equipment is inefficient. This inefficiency can stem from outdated machinery, inadequate maintenance, or improper selection for the materials being processed. For instance, a mining company might find that their crushers are not effectively reducing ore to the desired size, leading to increased energy consumption and wear on the equipment, ultimately resulting in higher operational costs and reduced profitability.
The Solution: To combat high operational costs, it is essential to conduct an equipment audit to assess the performance of current machinery. Buyers should look for modern, energy-efficient models that offer advanced features such as automation and real-time monitoring. Investing in equipment with better energy ratings or multi-functional capabilities can reduce energy consumption and maintenance needs. Additionally, implementing a regular maintenance schedule ensures that equipment remains in optimal condition, which can help extend its lifespan and improve efficiency. Forming partnerships with manufacturers who offer ongoing support and training can also enhance operational effectiveness and reduce costs over time.
Scenario 3: Challenges with Material Handling and Transportation
The Problem: In many industrial settings, the handling and transportation of materials before and after size reduction can be a significant pain point. For example, a recycling company might struggle with efficiently transporting shredded materials from one processing station to another, leading to bottlenecks in production. This can result in delayed processing times, increased labor costs, and potential safety hazards due to cluttered workspaces.
The Solution: To address material handling challenges, companies should consider integrating a comprehensive conveyor system tailored to their specific operations. Options include pneumatic conveying for lightweight materials or roller conveyors for heavier items, which can streamline the movement of materials throughout the facility. Automation of these systems can further enhance efficiency, reducing manual handling and the risk of injury. Additionally, implementing a well-designed layout that minimizes the distance materials need to travel can significantly reduce bottlenecks and optimize workflow. Investing in training for staff on the efficient use of these systems can also lead to smoother operations and improved safety standards.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for size reduction equipment
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Size Reduction Equipment?
When selecting materials for size reduction equipment, it is crucial to understand the properties of the materials being processed. Different materials exhibit unique characteristics that affect their performance in size reduction applications. Below are analyses of four common materials: metals, plastics, rubber, and food products.
Metals: What Are Their Key Properties and Considerations?
Metals, such as steel and aluminum, are frequently processed in size reduction equipment. They typically have high hardness and tensile strength, which allows them to withstand substantial mechanical stress. However, they may also exhibit brittleness at low temperatures, impacting their performance during size reduction.
Illustrative image related to size reduction equipment
Pros: Metals are durable and can handle high-pressure applications, making them suitable for heavy-duty size reduction tasks. Their recyclability also adds to their appeal.
Cons: The cost of metal components can be high, and their manufacturing complexity often requires specialized equipment. Additionally, certain metals may corrode if not adequately protected.
Impact on Application: Metals are compatible with a variety of processing media but require consideration of corrosion resistance, especially in humid environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM for metals is essential. Buyers in regions like Brazil and Saudi Arabia should also consider local regulations regarding metal recycling and waste management.
Plastics: How Do They Perform in Size Reduction Equipment?
Plastics, including polyethylene and polypropylene, are widely used due to their lightweight and versatile nature. They generally have lower hardness compared to metals, which affects their size reduction process.
Pros: Plastics are cost-effective and can be processed at lower temperatures, reducing energy consumption. They also offer good chemical resistance.
Cons: Plastics can be less durable than metals and may deform under high pressure or temperature. Their recyclability can also vary widely based on the type of plastic.
Impact on Application: Specific plastics may be incompatible with certain solvents or chemicals, necessitating careful selection based on the intended application.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with standards like DIN for plastics. In regions like South America, where plastic waste management is a growing concern, selecting recyclable materials can be advantageous.
Rubber: What Are the Key Properties and Challenges?
Rubber materials, such as natural rubber and synthetic elastomers, are commonly processed in size reduction equipment, especially in the recycling and manufacturing sectors. They exhibit excellent elasticity and resilience.
Pros: Rubber materials are highly durable and can absorb shocks, making them suitable for applications requiring flexibility.
Cons: Their performance can degrade at high temperatures, and they may require specific machinery for effective size reduction. Additionally, rubber can be more expensive than other materials.
Impact on Application: Rubber’s compatibility with various media is generally good, but care should be taken to avoid high-temperature environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with JIS standards for rubber is essential, especially in the Middle East, where specific regulations may govern material use in manufacturing.
Food Products: What Are the Unique Considerations?
Food products, including grains and vegetables, require specialized size reduction equipment to ensure safety and hygiene. These materials often have moisture content that affects their processing.
Pros: Food products are generally easy to process and can be reduced to fine particles, enhancing flavor and texture.
Cons: Their organic nature can lead to spoilage, and they may require strict adherence to food safety standards.
Illustrative image related to size reduction equipment
Impact on Application: The moisture content in food products can significantly influence the choice of size reduction equipment, necessitating machines that can handle wet materials.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with food safety standards, such as HACCP, is critical for buyers in Europe and Africa, where food regulations are stringent.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Size Reduction Equipment
| Material | Typical Use Case for size reduction equipment | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metals | Heavy-duty crushing and grinding | High durability and strength | High cost and potential corrosion | High |
| Plastics | Recycling and manufacturing | Cost-effective and lightweight | Less durable under high pressure | Medium |
| Rubber | Shock absorption in recycling applications | Excellent elasticity and resilience | Performance degradation at high temps | Medium |
| Food Products | Grinding grains and vegetables | Enhances flavor and texture | Spoilage risk and hygiene concerns | Low |
This guide provides actionable insights for international B2B buyers, emphasizing the importance of material properties, application impacts, and compliance considerations in selecting the right size reduction equipment.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for size reduction equipment
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Size Reduction Equipment?
The manufacturing of size reduction equipment is a multifaceted process that incorporates various stages, each critical to ensuring the final product meets industry standards and customer specifications.
-
Material Preparation: This initial phase involves selecting high-quality raw materials, often metals such as stainless steel or carbon steel, depending on the application requirements. The materials undergo rigorous testing for hardness, tensile strength, and corrosion resistance to ensure they can withstand the operational demands of size reduction processes.
-
Forming: The forming stage includes processes such as cutting, bending, and machining. Advanced techniques like laser cutting and CNC machining are frequently employed to achieve precise dimensions and complex geometries. This stage is pivotal as it lays the foundation for the equipment’s performance and durability.
-
Assembly: During assembly, components such as motors, blades, and housing are brought together. This step often utilizes automated assembly lines to enhance efficiency and consistency. Skilled technicians oversee the assembly to ensure that all parts fit seamlessly, and any alignment issues are rectified immediately.
-
Finishing: The finishing process may involve surface treatments such as powder coating, anodizing, or polishing to enhance the equipment’s appearance and protect it from wear and corrosion. Quality checks are conducted to ensure that surface finishes meet the required specifications, which is especially crucial for equipment used in food and pharmaceutical applications.
What Key Techniques Are Used in Manufacturing Size Reduction Equipment?
The manufacturing of size reduction equipment utilizes several key techniques that enhance the effectiveness and reliability of the machines:
-
Precision Machining: CNC machines are often employed to manufacture components with high precision, ensuring that tolerances are maintained throughout the production process.
-
Heat Treatment: Components are frequently subjected to heat treatment processes to improve their hardness and wear resistance. This step is essential, particularly for parts that will encounter high-stress conditions during operation.
-
Welding and Fabrication: Advanced welding techniques, such as TIG and MIG welding, are used to assemble structural components. The quality of welding directly impacts the structural integrity and longevity of the equipment.
-
Dynamic Balancing: For rotating components, dynamic balancing is performed to minimize vibrations during operation, ensuring smoother performance and reducing wear on bearings and other components.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in the Manufacturing of Size Reduction Equipment?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process of size reduction equipment, ensuring that each unit meets both domestic and international standards.
-
International Standards: Compliance with ISO 9001 is common in the manufacturing sector, establishing a framework for quality management systems. This certification emphasizes continuous improvement, customer satisfaction, and process optimization. Additionally, equipment intended for the European market must comply with CE marking requirements, ensuring conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
-
Industry-Specific Standards: In sectors such as pharmaceuticals and food processing, adherence to standards like API (American Petroleum Institute) and FDA regulations is crucial. These standards dictate specific requirements for equipment used in processing sensitive materials.
-
Quality Control Checkpoints: Various checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified quality criteria.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process allows for immediate identification and correction of defects.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of the finished product is conducted to ensure it meets all technical specifications and performance standards.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Quality?
Testing methods play a crucial role in validating the quality and performance of size reduction equipment. Some common testing techniques include:

Illustrative image related to size reduction equipment
-
Performance Testing: Equipment is subjected to operational tests that simulate actual working conditions. This testing measures efficiency, throughput, and particle size distribution.
-
Material Testing: Hardness tests (e.g., Rockwell or Brinell) and tensile tests ensure that materials used can withstand operational stresses.
-
Safety Testing: Electrical and mechanical safety tests ensure that the equipment complies with safety regulations to prevent accidents and injuries during operation.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Assurance?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality assurance is critical. Here are some strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess manufacturing processes, quality control systems, and overall compliance with industry standards.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should request comprehensive quality reports that detail the results of various tests performed on the equipment, including certifications and compliance with relevant standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the equipment’s quality and adherence to specifications before shipment.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers should be aware of specific nuances when it comes to quality control and certification:
-
Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Different regions may have varying standards and expectations for quality. Understanding local regulations and practices is essential for compliance and successful business operations.
-
Documentation Requirements: Ensure that all documentation, such as certificates of compliance, test reports, and quality management system certifications, are in order and meet the specific requirements of the importing country.
-
Language Barriers: When dealing with suppliers from different countries, language barriers can pose challenges in understanding quality standards and specifications. It is advisable to have clear communication protocols in place to mitigate misunderstandings.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices associated with size reduction equipment, B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and quality expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘size reduction equipment’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in effectively procuring size reduction equipment. Whether you’re in mining, food processing, or pharmaceuticals, making informed decisions is crucial for optimizing production processes and achieving desired outcomes. Follow this checklist to ensure you select the right equipment that meets your specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes the type of materials you’ll be processing, desired particle size, and throughput capacity. Knowing these specifications will help you identify the most suitable equipment, ensuring it aligns with your operational goals.
Step 2: Research Different Types of Size Reduction Equipment
Familiarize yourself with various types of size reduction equipment such as crushers, grinders, and pulverizers. Each type serves distinct purposes and operates differently:
– Crushers are ideal for breaking down large materials.
– Grinders are used for intermediate and fine grinding.
– Pulverizers provide very fine particle sizes, essential for industries like pharmaceuticals.
Understanding these options will enable you to select equipment tailored to your specific application.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they have a solid reputation and relevant experience. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Pay attention to their after-sales support and service capabilities, as these can significantly impact your equipment’s operational efficiency.
Step 4: Assess Compliance and Safety Standards
Check that the equipment complies with international safety and quality standards. This is particularly important for sectors like food processing and pharmaceuticals, where regulatory compliance is critical. Look for certifications such as ISO or CE markings to ensure the equipment meets industry standards.

Illustrative image related to size reduction equipment
Step 5: Request Demonstrations and Trials
Whenever possible, request product demonstrations or trial periods. This hands-on experience allows you to assess the equipment’s performance and suitability for your specific applications. Pay attention to ease of use, maintenance requirements, and the equipment’s ability to achieve your desired particle size.
Step 6: Compare Pricing and Total Cost of Ownership
Once you have shortlisted equipment options, compare their pricing alongside the total cost of ownership (TCO). TCO includes not just the initial purchase price, but also maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime costs. A lower initial price may not always equate to a better deal if ongoing costs are higher.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Finalize the Purchase
After selecting the right equipment and supplier, negotiate terms of the purchase, including payment options, delivery timelines, and warranties. Ensure you understand the terms of service and support offered, as this will be critical to your long-term satisfaction and equipment performance.
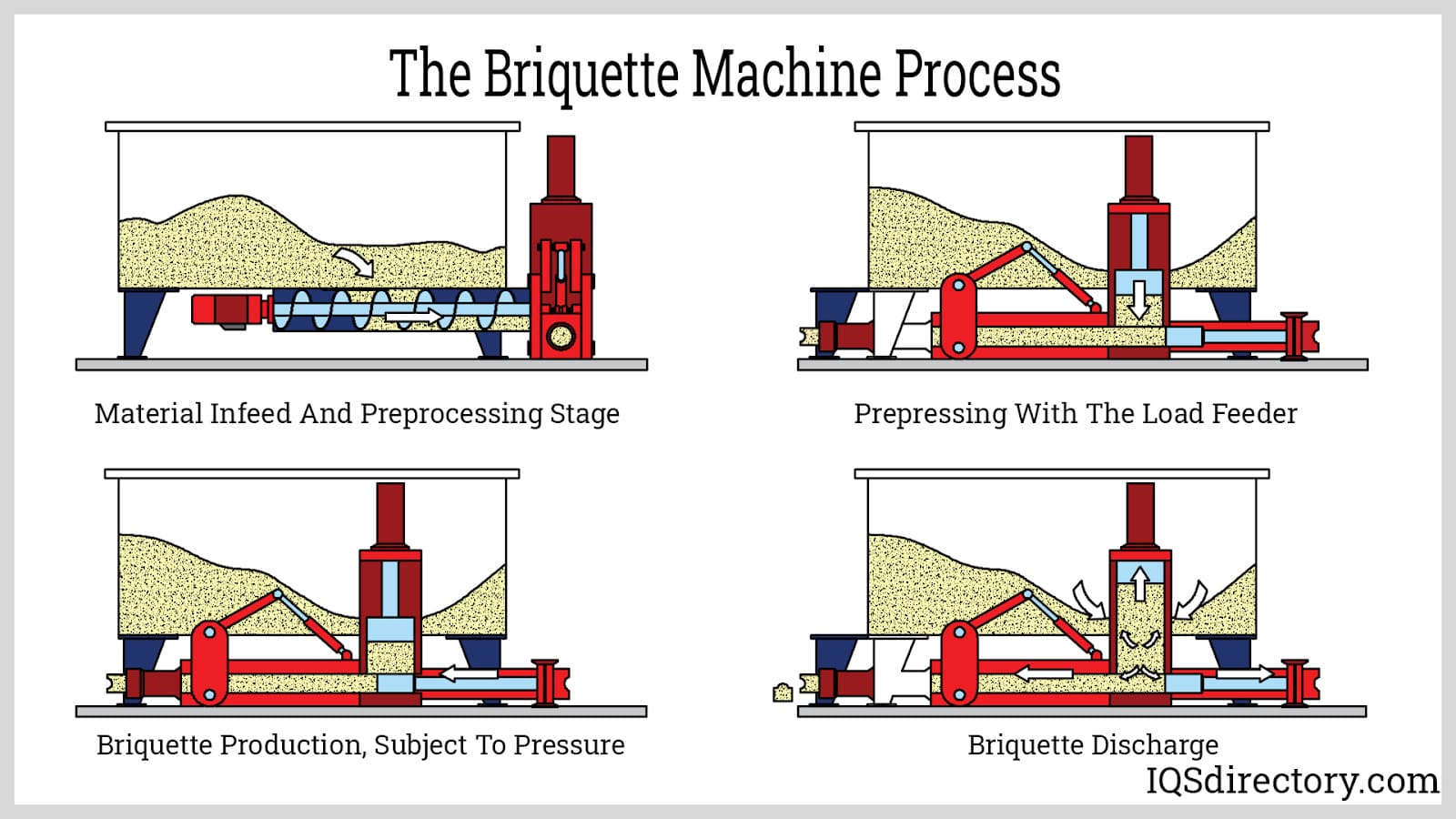
Illustrative image related to size reduction equipment
By following these steps, you can make a well-informed decision when sourcing size reduction equipment, ultimately leading to improved efficiency and productivity in your operations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for size reduction equipment Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of size reduction equipment is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The following analysis outlines key cost components, price influencers, and practical buyer tips that can enhance your procurement strategy.
What Are the Key Cost Components for Size Reduction Equipment?
The cost structure for size reduction equipment encompasses several critical components:
-
Materials: The type and quality of materials used in manufacturing play a significant role in overall costs. High-grade steel, for instance, increases durability but also elevates the price.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for the assembly and quality control of size reduction equipment. Labor costs can vary significantly based on the region and the complexity of the machinery.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these overheads.
-
Tooling: Specialized tooling for production can add to costs, particularly for custom or complex equipment. Tooling costs must be factored in for both initial manufacturing and any future modifications.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the machinery meets industry standards necessitates rigorous QC processes, which can add to the overall expense but is vital for maintaining product integrity.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs for moving equipment from the manufacturer to the buyer can vary based on distance, shipping methods, and local regulations. This is particularly important for international buyers who must consider customs and import tariffs.
-
Margin: Suppliers often add a margin to cover their operational costs and desired profit. This margin can vary widely based on competition and market demand.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Size Reduction Equipment Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of size reduction equipment:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically lead to discounted prices. Buyers should negotiate volume pricing to lower per-unit costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom equipment tailored to specific needs may incur additional costs. Buyers should evaluate whether customization is necessary or if standard models suffice.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Equipment made from premium materials or those that meet specific certifications (e.g., ISO) may command higher prices but can offer better performance and longevity.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, production capacity, and location can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their reliability and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the chosen Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) is crucial as they dictate shipping responsibilities and costs, impacting the total price.
What Practical Tips Can Buyers Utilize for Cost-Efficient Sourcing?
To optimize your purchasing strategy for size reduction equipment, consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Engage in discussions about pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Suppliers may be willing to offer discounts for prompt payment or bulk orders.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. TCO includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. Equipment that is slightly more expensive upfront may offer significant savings over time.
-
Understand Regional Pricing Nuances: Prices can vary based on regional market conditions. For instance, equipment sourced from Europe may have different pricing dynamics compared to South American suppliers. Conduct thorough market research to understand these variances.
-
Stay Informed on Currency Fluctuations: For international transactions, currency rates can significantly affect costs. Consider hedging strategies or negotiating prices in stable currencies to mitigate risks.
-
Assess After-Sales Support: Reliable after-sales service can save costs related to repairs and maintenance. Ensure that the supplier provides adequate support and parts availability.
Conclusion
Navigating the cost structure and pricing nuances of size reduction equipment requires a strategic approach. By understanding the key cost components, recognizing price influencers, and employing effective negotiation tactics, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. Always remember that pricing can fluctuate, so obtaining indicative prices and understanding market trends is essential for successful sourcing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing size reduction equipment With Other Solutions
When considering size reduction solutions, businesses must evaluate various methods that can achieve similar objectives. Size reduction equipment, such as crushers and mills, is a common choice, but alternatives exist that may better suit specific operational needs or constraints. This section compares size reduction equipment with two viable alternatives: mechanical shredders and chemical processes.
| Comparison Aspect | Size Reduction Equipment | Mechanical Shredders | Chemical Processes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and efficiency for various materials; tailored designs for specific tasks. | Effective for bulk materials but may produce inconsistent particle sizes. | Capable of breaking down materials at the molecular level, ensuring uniformity. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment and operating costs, but potential for long-term savings through efficiency. | Generally lower upfront costs; however, maintenance can add to overall expenses. | Variable costs depending on the chemicals used and regulatory compliance. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific installation and training; complex systems can take time to set up. | Easier to implement with minimal setup required; often plug-and-play solutions. | Implementation can be complex due to safety and regulatory requirements. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed to ensure optimal performance; can be costly over time. | Lower maintenance needs; however, blades may require frequent replacements. | Requires careful monitoring and compliance checks, which can be resource-intensive. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for industries needing precise particle sizes, such as pharmaceuticals and food processing. | Best suited for recycling and waste management applications where uniformity is less critical. | Effective for applications requiring complete material breakdown, such as in chemical manufacturing. |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Mechanical Shredders as an Alternative to Size Reduction Equipment?
Mechanical shredders are designed to break down bulk materials into smaller pieces, often used in recycling processes. Their primary advantage is lower initial costs and simpler operation compared to traditional size reduction equipment. However, they may not achieve the precise particle sizes required for certain applications, which can limit their effectiveness in industries that demand high standards, such as pharmaceuticals. Additionally, while they require less maintenance, the blades do wear down quickly, necessitating regular replacements.
How Do Chemical Processes Compare to Size Reduction Equipment?
Chemical processes utilize reactive agents to break down materials at a molecular level, offering the benefit of achieving uniformity in particle size. This method can be highly effective in industries where thorough material breakdown is crucial, such as chemical manufacturing. However, the costs associated with chemicals and the need for stringent safety protocols can make this option expensive and complex to implement. Furthermore, regulatory compliance can add layers of complication, making it less appealing for some businesses compared to mechanical or size reduction equipment.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting between size reduction equipment and its alternatives, B2B buyers should thoroughly assess their specific operational requirements. Factors such as the type of material being processed, the desired particle size, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities are critical in making an informed decision. Buyers should also consider long-term operational efficiency and potential savings against initial costs. Consulting with industry experts and conducting a cost-benefit analysis can further aid in identifying the most suitable solution for their unique business context.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for size reduction equipment
What are the Key Technical Properties of Size Reduction Equipment?
Understanding the technical specifications of size reduction equipment is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure optimal performance and suitability for specific applications. Here are some essential properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material grade of the equipment components (e.g., stainless steel, carbon steel) influences durability and resistance to corrosion or wear. Selecting the appropriate material is vital for industries dealing with abrasive or corrosive substances, as it impacts the longevity and maintenance costs of the machinery. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in dimensions and performance specifications. High tolerance levels are critical in applications requiring precise particle sizes, such as pharmaceuticals and food processing. Inadequate tolerances can lead to inconsistent product quality and inefficiencies in production processes. -
Power Requirements
This specification indicates the energy consumption needed to operate the equipment effectively. Understanding power requirements helps in assessing operational costs and ensuring compatibility with existing electrical systems. Equipment that demands less energy can lead to significant cost savings in large-scale operations. -
Throughput Capacity
Throughput capacity denotes the volume of material that can be processed over a specific time frame. This property is essential for determining whether the equipment meets production demands. A mismatch between capacity and operational needs can lead to bottlenecks and decreased efficiency. -
Particle Size Distribution
This property describes the range of particle sizes produced by the equipment. Different industries have specific requirements for particle size distributions, affecting subsequent processing steps. Understanding how the equipment achieves desired particle sizes ensures that the final product meets quality standards. -
Operational Noise Levels
This specification refers to the sound produced during the operation of the equipment. In many industrial settings, excessive noise can lead to safety concerns and regulatory compliance issues. Choosing equipment with lower noise levels can enhance workplace safety and employee comfort.
What are Common Trade Terms Related to Size Reduction Equipment?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B space. Here are some common terms used in the size reduction equipment sector:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding the OEM relationship is vital for buyers seeking quality assurance and compatibility with existing machinery. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest amount of product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is important for B2B buyers to ensure that they are making purchases that align with their production needs without overcommitting resources. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific equipment or services. It is a crucial step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare options and negotiate favorable terms. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, defining the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Knowing Incoterms helps in understanding shipping costs, risks, and delivery obligations. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the duration from placing an order until its delivery. This term is crucial for planning and inventory management, allowing businesses to align their production schedules with equipment availability. -
Technical Data Sheet (TDS)
A TDS provides detailed information about the equipment, including specifications, performance data, and operational guidelines. Reviewing a TDS helps buyers make informed decisions regarding compatibility and functionality for their specific applications.
Understanding these technical properties and industry terms equips B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions in the size reduction equipment sector. This knowledge can lead to more efficient operations and better alignment with business objectives.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the size reduction equipment Sector
What Are the Global Drivers and Key Trends Influencing the Size Reduction Equipment Market?
The size reduction equipment market is currently witnessing significant growth driven by several global factors. Increased industrialization and urbanization in emerging markets, particularly in Africa and South America, are propelling demand for efficient processing machinery across sectors such as mining, food processing, and pharmaceuticals. Additionally, technological advancements, including automation and the integration of IoT in manufacturing processes, are reshaping sourcing strategies. These innovations enhance operational efficiency, reduce downtime, and improve product quality, making them attractive to international B2B buyers.

Illustrative image related to size reduction equipment
Moreover, the rising focus on sustainability is influencing purchasing decisions. Companies are increasingly seeking equipment that not only meets performance requirements but also minimizes environmental impact. This trend is evident in the growing demand for energy-efficient machines and those capable of processing recyclable materials. Furthermore, the market is witnessing a shift towards modular and flexible equipment designs, enabling businesses to adapt quickly to changing production needs. For buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East, this adaptability is critical for maintaining competitiveness in fluctuating markets.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Size Reduction Equipment Sector?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of purchasing strategies in the size reduction equipment sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, prompting companies to evaluate the lifecycle of their equipment. This includes considering energy consumption during operation, the recyclability of materials used, and the overall carbon footprint of the equipment. International B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction, with businesses seeking suppliers that adhere to social responsibility standards. This includes fair labor practices, transparency in supply chains, and adherence to local and international regulations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are becoming essential for vendors looking to establish credibility in the market. For buyers in regions like Brazil and Saudi Arabia, partnering with ethically responsible suppliers not only aligns with corporate values but also enhances brand reputation and customer loyalty.
What Is the Historical Context of Size Reduction Equipment Development?
The evolution of size reduction equipment has been marked by significant technological advancements and changing industry demands. Initially, size reduction processes were rudimentary, relying on manual labor and simple tools. However, the Industrial Revolution catalyzed the development of mechanical devices, leading to the creation of various crushers and mills designed to enhance efficiency and precision.
In the latter half of the 20th century, innovations such as high shear mixers and advanced grinding technologies emerged, significantly improving the capabilities of size reduction equipment. These advancements not only allowed for finer particle sizes but also enabled the processing of a broader range of materials, catering to diverse industries. Today, the focus is on integrating smart technologies and sustainability into equipment design, reflecting the changing priorities of B2B buyers globally. This historical context underscores the continuous evolution of size reduction equipment, aligning with market demands and technological progress.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of size reduction equipment
-
1. How do I select the right size reduction equipment for my material?
Choosing the right size reduction equipment involves understanding the properties of your material, such as hardness, moisture content, and desired particle size. For instance, crushers are suitable for larger chunks, while grinders and pulverizers are better for finer sizes. Evaluate the specific requirements of your application, including the type of processing involved and the final product’s quality. Consult with suppliers who can provide insights based on their equipment’s capabilities and your material characteristics. -
2. What is the best equipment for reducing tough materials?
For tough materials, heavy-duty crushers like jaw or gyratory crushers are often the most effective initial choice, as they can handle large pieces and tough compositions. After initial crushing, a grinder or pulverizer can be used for finer reductions. It’s essential to consider the material’s behavior during size reduction—hard, brittle materials may require impact crushing, while softer materials might need shearing or cutting methods. Engage with manufacturers to determine the most suitable machinery for your specific needs. -
3. How can I ensure the quality of the size reduction equipment I purchase?
To ensure quality, start by vetting potential suppliers through their certifications, customer reviews, and industry reputation. Request product demonstrations or visit existing installations to see the equipment in action. It’s also beneficial to ask for case studies or references from similar industries to gauge performance. Additionally, ensure that the equipment adheres to international standards for safety and efficiency, and consider suppliers who offer warranties and after-sales support. -
4. What are the common payment terms in international B2B transactions for equipment?
Payment terms can vary significantly by supplier and region, but common practices include partial upfront payments (often 30% to 50%) with the balance due upon shipment or installation. For larger orders, consider options like letters of credit or escrow services to protect both parties. Always clarify payment terms before finalizing contracts to avoid misunderstandings. It’s advisable to work with suppliers who have transparent billing practices and can accommodate your preferred payment methods. -
5. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for size reduction equipment?
MOQs for size reduction equipment can vary by manufacturer and the complexity of the machinery. Smaller equipment or components might have lower MOQs, while custom-built or specialized machinery may require larger orders to justify production costs. Always inquire about MOQs during your supplier discussions, and consider negotiating terms that suit your business needs, particularly if you are a smaller buyer or new to the industry. -
6. How does logistics impact the procurement of size reduction equipment?
Logistics plays a crucial role in the procurement process, especially for international buyers. Consider factors like shipping costs, delivery times, and customs regulations in your target market. Collaborate with suppliers who can provide insights into the best shipping methods and any potential delays. It’s also wise to factor in installation and setup logistics, as complex machinery may require specialized handling and expertise during transport and assembly. -
7. Can size reduction equipment be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options to meet specific application needs. Customization may involve altering equipment dimensions, components, or features to enhance efficiency or accommodate unique material properties. When discussing your requirements with suppliers, be clear about your application and performance goals. This dialogue can lead to tailored solutions that provide better productivity and cost-efficiency in your operations. -
8. What are the key factors to consider when vetting suppliers for size reduction equipment?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry experience, technological capabilities, and customer support services. Assess their production capabilities and whether they can meet your volume requirements and timelines. Additionally, examine their track record for quality assurance and compliance with international standards. Establishing a good rapport and clear communication with potential suppliers is crucial for long-term partnerships, so prioritize those who demonstrate responsiveness and reliability.
Top 4 Size Reduction Equipment Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. IQS Directory – Size Reduction Equipment
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Size Reduction Equipment: Devices engineered to crush and grind materials, effectively reducing their size. Types include pulverizers, crushers, and grinding media. Applications span various industries such as mining, mineral processing, chemical production, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and waste recycling. Key materials handled include coal, shale, brick, concrete, wood, limestone, and pla…
2. Fitzpatrick – Particle Processing Solutions
Domain: fitzpatrick-mpt.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Fitzpatrick offers a range of particle processing and size reduction technologies, including: 1. Hammer Mills: M5A & D6A, DASO6 & DKASO12 2. Scalable Lab System (SLS) 3. SDx™ Series Roller Compaction: High Containment Contained System, Lab Compaction System. The company specializes in dry granulation and precision particle size reduction, serving industries such as pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals,…
3. Conair – Size Reduction Equipment
Domain: conairgroup.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Conair offers a range of size reduction equipment for plastics processing, including:
1. **Beside-the-Press Granulators**:
– 12 Series Viper Granulators
– 6 Series Viper Granulators
– 8 Series Viper Granulators
– S Series Granulators
2. **Central Granulators**:
– 17 Series Viper Granulators
– 23 Series Viper Granulators
– 32 and 35 Series Viper Granulators
3. **Thermoformin…
4. Kason Corporation – MARION Lump Breakers & Cone Mills
Domain: kason.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Kason Corporation supplies and manufactures size reduction screening equipment for various applications, providing high-capacity grinding and milling while minimizing noise, dust, and heat generation. Key products include MARION Lump Breakers and Cone Mills, designed to reduce agglomerates into tiny particles and process heat-sensitive materials at high rates, respectively. The equipment is availa…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for size reduction equipment
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Investment in Size Reduction Equipment?
In the competitive landscape of industrial processing, the strategic sourcing of size reduction equipment is essential for optimizing operations. By understanding the diverse types of machinery—such as crushers, grinders, and pulverizers—businesses can select equipment that aligns with their specific material characteristics and processing requirements. This tailored approach not only enhances efficiency but also improves product quality and reduces operational costs.
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must prioritize partnerships with reliable suppliers that offer robust after-sales support and customization options. Establishing these relationships can lead to long-term savings and improved production outcomes.
Looking ahead, the demand for advanced size reduction solutions will continue to grow as industries seek to enhance sustainability and efficiency. As a proactive buyer, take the initiative to explore innovative technologies and equipment that meet evolving market needs. Engage with suppliers to discuss your unique challenges and explore tailored solutions. By investing wisely in size reduction equipment now, you position your business for success in the future.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.