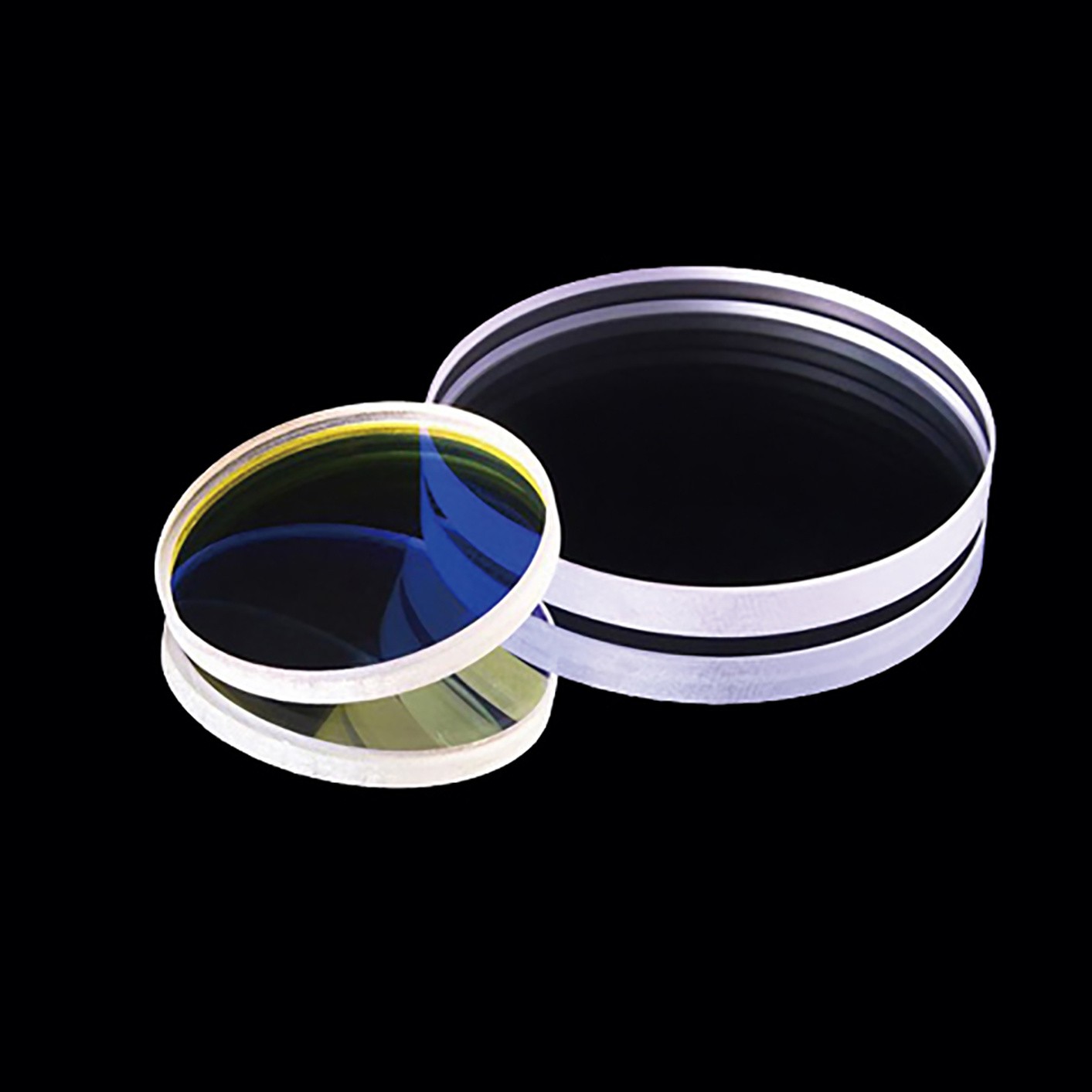
A Deep Dive into Quartz Lens Solution
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for quartz lens
In today’s competitive landscape, international B2B buyers face the challenge of sourcing high-quality quartz lenses that meet specific application requirements while navigating varying standards and suppliers across different regions. Whether you’re based in Nigeria, Germany, or any other part of the world, understanding the nuances of quartz lens specifications and applications is crucial. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the global market for quartz lenses, covering essential topics such as types of lenses available, their diverse applications in industries ranging from optics to manufacturing, and strategies for vetting suppliers effectively.
As you explore the intricacies of quartz lenses, you’ll gain insights into critical factors like performance tolerances, material specifications, and cost considerations. This guide empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions by providing actionable tips on identifying reliable manufacturers and understanding market trends. By equipping yourself with this knowledge, you can enhance your procurement strategy, ensuring that your organization benefits from superior optical solutions tailored to your operational needs.
From understanding the differences between plano-convex and plano-concave lenses to recognizing the significance of surface quality and thickness tolerances, this guide is designed to be your go-to resource. As you navigate the complexities of sourcing quartz lenses, you’ll be better positioned to leverage high-quality products that drive efficiency and innovation in your projects.
Understanding quartz lens Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plano-Convex Lens | One flat and one spherical surface, positive focal length | Imaging systems, laser applications | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile; Cons: Limited for high-precision tasks. |
| Plano-Concave Lens | One flat and one concave surface, negative focal length | Beam expansion, diverging light applications | Pros: Useful for light spreading; Cons: Not suitable for focusing tasks. |
| Bi-Convex Lens | Two outwardly curved surfaces, positive focal length | High-precision imaging, optical instruments | Pros: Excellent for focusing; Cons: More expensive than simpler lenses. |
| Quartz with Inclusions | Unique mineral inclusions, varying optical properties | Energy work, meditation tools | Pros: Enhanced energy properties; Cons: Limited industrial applications. |
| Laser Safety Glasses | Specialized coatings for laser protection | Industrial safety, laser operation | Pros: Essential for safety; Cons: Specific to laser applications only. |
What Are the Characteristics of Plano-Convex Lenses?
Plano-convex lenses feature one flat surface and one convex surface, resulting in a positive focal length. These lenses are ideal for applications requiring light focusing, such as in imaging systems and laser applications. Their cost-effectiveness and versatility make them a popular choice among B2B buyers. However, they may not be suitable for high-precision tasks where more complex lens designs are required.
How Do Plano-Concave Lenses Function?
Plano-concave lenses have one flat and one concave surface, creating a negative focal length. They are primarily used in applications that require light divergence, such as beam expanders and certain optical setups. While these lenses are beneficial for spreading light, buyers should be cautious as they are not designed for focusing light, limiting their use in specific applications.
Why Choose Bi-Convex Lenses for Precision Imaging?
Bi-convex lenses possess two outwardly curved surfaces, giving them a positive focal length. They are often used in high-precision imaging applications and optical instruments due to their ability to focus light effectively. Although they provide excellent performance, their higher cost compared to simpler lens types may be a consideration for budget-conscious buyers.
What Are the Advantages of Quartz with Inclusions Lenses?
Quartz with inclusions lenses are unique due to their embedded minerals, which can enhance their optical properties. While they are primarily used in energy work and meditation tools, their industrial applications are limited. Buyers should note the unique characteristics of these lenses, as they offer added energy properties but may not fit standard optical needs.
How Do Laser Safety Glasses Protect Users?
Laser safety glasses are designed with specialized coatings that protect users from harmful laser exposure. They are essential in environments where lasers are used, such as manufacturing and research facilities. While they are crucial for safety, their application is specific to laser operations, which may limit their broader usability in other optical contexts.
Key Industrial Applications of quartz lens
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of quartz lens | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Optical Manufacturing | Production of high-precision optical instruments | Enhanced product quality and accuracy | Tolerance specifications, surface quality, and custom designs |
| Telecommunications | Fiber optic systems and signal transmission | Improved signal clarity and reduced loss | Compatibility with existing systems and performance metrics |
| Medical Devices | Laser surgery and diagnostic equipment | Precision in surgical procedures and diagnostics | Compliance with safety standards and material certifications |
| Aerospace and Defense | Surveillance and targeting systems | Reliability in critical missions | ITAR compliance and durability under extreme conditions |
| Research and Development | Laboratory experiments and optical testing | Accurate data collection and analysis | Customization options and lead times for delivery |
How is Quartz Lens Utilized in Optical Manufacturing?
In the optical manufacturing sector, quartz lenses are integral in the production of high-precision instruments such as microscopes and telescopes. Their ability to maintain clarity and reduce distortion makes them ideal for applications that require exceptional optical performance. For international buyers, especially from regions like Europe and South America, sourcing quartz lenses involves ensuring that the specifications meet stringent quality standards, including tolerance levels and surface quality. Reliable suppliers will provide detailed product specifications to guarantee optimal performance.
What Role Does Quartz Lens Play in Telecommunications?
Quartz lenses are crucial in telecommunications for enhancing fiber optic systems. They facilitate effective signal transmission by minimizing light loss and ensuring clarity, which is vital for high-speed internet and communication technologies. Businesses in Africa and the Middle East looking to improve their telecommunication infrastructure should consider the compatibility of quartz lenses with existing systems and the performance metrics that define signal strength and quality. Suppliers should be able to provide data on the optical properties of the lenses to ensure they meet the necessary standards.
How Are Quartz Lenses Used in Medical Devices?
In the medical device industry, quartz lenses are employed in laser surgery and diagnostic equipment. Their precision allows for accurate targeting during surgical procedures, which is critical for patient safety and successful outcomes. Buyers in this sector must prioritize suppliers who comply with medical device regulations and safety standards. Additionally, the sourcing of quartz lenses should consider the specific requirements for biocompatibility and durability in sterile environments, ensuring that the lenses can withstand rigorous cleaning and maintenance protocols.
Why Are Quartz Lenses Important for Aerospace and Defense?
The aerospace and defense sectors utilize quartz lenses in surveillance and targeting systems, where reliability and performance are paramount. These lenses must withstand extreme environmental conditions while providing clear imagery for critical missions. International buyers from the defense industry must ensure that their suppliers adhere to ITAR regulations and can provide products that meet the durability and performance standards required for military applications. Understanding the sourcing considerations for high-stakes environments is essential for maintaining operational integrity.
How Do Quartz Lenses Contribute to Research and Development?
In research and development, quartz lenses are vital for laboratory experiments and optical testing, facilitating accurate data collection and analysis. Their optical properties are crucial for experiments requiring precise measurements and observations. Companies in this sector should seek suppliers who offer customization options to cater to specific experimental setups and can guarantee timely delivery. This is particularly important for international buyers who may face longer lead times due to shipping and customs regulations, making it essential to establish reliable sourcing relationships.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘quartz lens’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Quality Across Suppliers
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of inconsistent quality when sourcing quartz lenses from various suppliers. This inconsistency can lead to significant operational disruptions, as the lenses may not meet specific application standards such as focal length tolerance or surface quality. When suppliers provide products that vary in performance, it can result in increased rejection rates, project delays, and ultimately impact client satisfaction.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should establish a rigorous vetting process for suppliers. This includes requesting detailed specifications, such as focal length tolerance (+/- 3%) and surface quality (e.g., 60-40 scratch-dig), to ensure they meet required standards. Furthermore, consider building long-term relationships with a select few trusted suppliers who have a proven track record of delivering high-quality products consistently. Regular audits and quality checks can help maintain the expected quality levels. Additionally, buyers should ask for sample products before placing bulk orders to verify quality firsthand.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Meeting Custom Specifications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter difficulties when they need quartz lenses that meet specific custom specifications for unique applications. Whether it’s a particular diameter, thickness, or design wavelength, the inability to find suppliers who can accommodate these requests can stall projects and lead to lost business opportunities.
The Solution: To address this pain point, buyers should proactively communicate their precise requirements to potential suppliers early in the sourcing process. Engaging with manufacturers that offer custom optical lens work is crucial. Before reaching out, compile a detailed list of specifications, including tolerances for diameter and thickness, as well as any particular design wavelengths needed. This thorough preparation will enable suppliers to provide accurate quotes and timelines, ensuring the custom lenses are produced to meet the exact needs of your project. Additionally, consider utilizing CAD software to visualize your lens design, which can help suppliers better understand your requirements.
Scenario 3: Limited Knowledge on Application Suitability
The Problem: Many B2B buyers may lack the technical knowledge required to select the right quartz lens for specific applications, leading to suboptimal performance in their end products. For instance, using a plano-convex lens in a scenario that requires an achromatic lens could lead to poor imaging quality and customer dissatisfaction.
The Solution: To navigate this challenge, buyers should invest time in understanding the different types of quartz lenses and their applications. It is beneficial to collaborate with experts or opticians who can provide insights into the best lens types for various applications. Create a comprehensive reference guide that includes details on lens types, their optical properties, and suitable applications. Additionally, suppliers often have technical support teams that can assist in recommending the right products based on specific use cases. Engaging in training sessions or workshops can also enhance your team’s knowledge and ensure informed purchasing decisions.
By addressing these common pain points through careful supplier selection, clear communication of specifications, and enhancing product knowledge, B2B buyers can improve their operational efficiency and product quality when sourcing quartz lenses.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for quartz lens
What are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used for Quartz Lenses?
When selecting materials for quartz lenses, it is essential to consider the specific properties that influence performance in various applications. The most common materials include fused quartz, optical glass, and specialized coatings. Each material has unique characteristics that can significantly impact the lens’s functionality, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
Fused Quartz: What Makes It a Preferred Choice?
Fused quartz is a high-purity glass made from silica, known for its excellent thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion. It can withstand high temperatures (up to 1,200°C) and is highly transparent to UV light, making it ideal for applications in optics and laser technology.
Pros: Fused quartz offers superior durability and low thermal expansion, which is crucial for precision optics. Its high transmission rates for UV light make it suitable for photolithography and other UV applications.
Cons: The manufacturing process can be complex and costly, which may deter some buyers. Additionally, while it is robust, it can be more brittle than other materials, requiring careful handling.
Impact on Application: Fused quartz is compatible with various media, including aggressive chemicals, making it suitable for laboratory and industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards like ASTM and DIN is vital. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure that suppliers provide certifications that meet local regulations.
Optical Glass: How Does It Compare?
Optical glass, often used in traditional lens manufacturing, provides excellent optical clarity and is available in various grades. It is often less expensive than fused quartz and easier to work with, making it a popular choice for mass production.

Illustrative image related to quartz lens
Pros: Optical glass is versatile and can be manufactured in different shapes and sizes. It typically has good optical properties and is suitable for a wide range of applications.
Cons: While it is less costly, optical glass may not withstand high temperatures or harsh chemical environments as well as fused quartz. Its thermal expansion can lead to distortion under temperature fluctuations.
Impact on Application: Optical glass is often used in consumer electronics and imaging systems, where high optical quality is necessary but extreme environmental conditions are not a concern.

Illustrative image related to quartz lens
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the varying quality standards across regions. For instance, European buyers may prefer lenses that meet DIN standards, while those in the Middle East may focus on compliance with local specifications.
Specialized Coatings: What Benefits Do They Offer?
Specialized coatings can be applied to both fused quartz and optical glass lenses to enhance their performance. These coatings can provide anti-reflective properties, increase durability, and improve resistance to scratches and environmental factors.
Pros: Coatings can significantly enhance the functionality of a lens, improving transmission rates and reducing glare. They also protect the underlying material from wear and tear.
Cons: The application of coatings can add to the manufacturing complexity and cost. Additionally, not all coatings are suitable for every application, requiring careful selection.

Illustrative image related to quartz lens
Impact on Application: Coated lenses are particularly beneficial in high-performance applications, such as in scientific instruments and high-end imaging systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that coatings meet relevant standards and are compatible with their specific applications, especially in regions with stringent quality requirements.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Quartz Lenses
| Material | Typical Use Case for quartz lens | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fused Quartz | High-precision optics and laser systems | Excellent thermal stability | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
| Optical Glass | Consumer electronics and imaging systems | Versatile and cost-effective | Limited thermal and chemical resistance | Medium |
| Specialized Coatings | High-performance scientific instruments | Enhanced functionality and durability | Increased manufacturing complexity | Medium to High |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of various materials used for quartz lenses. Understanding these factors will facilitate informed purchasing decisions tailored to specific applications and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for quartz lens
What Are the Main Stages of Quartz Lens Manufacturing?
The manufacturing of quartz lenses involves several critical stages that ensure precision and quality. These stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: The process begins with the selection of high-grade quartz, often in the form of fused silica or G1 commercial grade quartz. This material is chosen for its excellent optical properties and durability. The raw quartz is then cleaned and processed to remove any impurities that could affect the lens quality.
Forming: Once prepared, the quartz is subjected to a forming process, which may involve techniques such as grinding and polishing. For plano-convex lenses, one side is shaped to a spherical contour while the other remains flat. This shaping is crucial for achieving the desired focal length and optical performance. Advanced CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are often used in this stage for precision shaping.
Assembly: In some cases, multiple lens elements may need to be assembled to create a compound lens system. This involves aligning each lens accurately to ensure that light passes through as intended, maintaining the optical integrity required for various applications.
Finishing: The final stage includes polishing to achieve a smooth surface that minimizes scattering and maximizes light transmission. Finishing processes may also involve applying anti-reflective coatings or protective layers to enhance performance and durability. Quality checks are performed at each step to ensure adherence to specifications.
Which Key Techniques Are Used in Quartz Lens Production?
Several techniques play a pivotal role in the production of quartz lenses, each contributing to the final product’s performance and quality.
Grinding and Polishing: The grinding process shapes the lens, while polishing enhances the surface quality. High-precision grinding wheels and diamond polishing pads are utilized to achieve the required surface roughness and clarity.
Coating Applications: Anti-reflective and protective coatings are frequently applied to quartz lenses to improve transmission rates and protect against environmental factors. These coatings are typically deposited using vacuum deposition techniques, ensuring uniformity and adherence.
Inspection Technologies: Optical inspection systems are employed to detect surface flaws and measure critical parameters such as diameter, thickness, and focal length. Automated systems can quickly identify defects, ensuring that only lenses meeting quality standards proceed to the next stage.

Illustrative image related to quartz lens
What International Standards Guide Quartz Lens Quality Assurance?
Quality assurance in quartz lens manufacturing is guided by several international standards that ensure consistency and reliability.
ISO 9001: This is a widely recognized quality management standard that outlines criteria for an effective quality management system. Compliance with ISO 9001 assures B2B buyers that the manufacturer has established processes to consistently deliver quality products.
CE Marking: For products sold within the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. This is particularly relevant for B2B buyers in Europe who require assurance of product safety and efficacy.
API Standards: In industries such as oil and gas, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is crucial. These standards ensure that optical components used in sensitive environments meet rigorous performance criteria.

Illustrative image related to quartz lens
What Quality Control Checkpoints Are Essential in Quartz Lens Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are integral to maintaining the integrity of quartz lens production. These checkpoints typically include Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), and Final Quality Control (FQC).
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specified standards. Tests may include visual inspections and material property assessments to confirm that only quality quartz is used in manufacturing.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, continuous monitoring is essential. IPQC involves checking critical parameters at various stages, such as dimensional accuracy and surface quality. This proactive approach helps identify and rectify issues before they escalate.
Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection assesses the completed lenses against all specifications. Common testing methods at this stage may include optical performance testing, scratch-dig tests, and dimensional checks. Only products that pass these rigorous evaluations are cleared for shipment.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control measures is crucial for ensuring product reliability.

Illustrative image related to quartz lens
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess a supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control systems firsthand. This can provide insights into their commitment to quality and adherence to international standards.
Quality Control Reports: Requesting detailed QC reports can offer transparency into the supplier’s testing procedures and outcomes. These reports should cover the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC to provide a comprehensive view of the quality assurance process.
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies can further validate the supplier’s quality claims. These organizations can conduct thorough evaluations of both the manufacturing facility and the products, offering an unbiased assessment of quality.

Illustrative image related to quartz lens
What Are the Specific QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
International B2B buyers face unique challenges when it comes to quality control and certification of quartz lenses.
Understanding Regional Standards: Buyers must be aware of the specific quality standards and certifications required in their respective markets. For instance, products sold in Europe must comply with CE marking, while those in the U.S. may need to meet FDA regulations depending on their application.
Documentation and Compliance: Clear documentation of compliance with international standards is essential. Suppliers should provide certificates that validate their adherence to ISO 9001, CE, or other relevant standards. This documentation is crucial for customs clearance and regulatory compliance.
Cultural and Legal Considerations: Different regions may have varying expectations regarding quality and compliance. Buyers must navigate these nuances by engaging with local experts or legal advisors to ensure that they are meeting all requirements when importing quartz lenses.
Illustrative image related to quartz lens
By understanding the intricacies of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for quartz lenses, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they procure reliable products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘quartz lens’
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure quartz lenses. Sourcing high-quality optical components is essential to ensure optimal performance in various applications. By following these steps, buyers can navigate the procurement process effectively, minimizing risks and ensuring they receive the best products for their needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, it is vital to outline your specific requirements for quartz lenses. Key specifications include focal length, diameter, thickness, and surface quality. Clearly defining these parameters helps streamline the selection process and ensures that suppliers can meet your technical needs without ambiguity.
- Focal Length Tolerance: Specify the acceptable deviation in focal length for your application.
- Surface Quality: Determine the scratch-dig specifications that are acceptable for your project.
Step 2: Research and Identify Reputable Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in quartz optics. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in delivering high-quality products. Checking online directories, industry trade shows, and recommendations from peers can help you compile a list of reputable suppliers.
- Supplier Reviews: Look for testimonials or case studies from previous clients.
- Industry Certifications: Ensure suppliers adhere to relevant standards, such as ISO or ITAR compliance for sensitive applications.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. This step helps ascertain the supplier’s reliability and capability to meet your specific requirements.
- Quality Assurance Processes: Inquire about their manufacturing processes and quality control measures.
- Delivery and Support: Assess their ability to provide timely delivery and post-purchase support.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request samples of the quartz lenses for testing. Evaluating samples allows you to assess the optical quality and ensure that the product meets your specifications before placing a larger order.
- Testing Criteria: Check for performance under your specific conditions, such as wavelength and environmental factors.
- Comparison: Use samples from different suppliers to compare quality and performance.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you are satisfied with the quality of the samples, proceed to negotiate pricing and terms. Be clear about your budget and discuss volume discounts if you plan to order in bulk. It’s also essential to clarify payment terms and delivery schedules to avoid any surprises later.
- Contractual Agreements: Ensure all agreements are documented, including warranties and return policies.
- Shipping Costs: Factor in shipping and handling charges in your overall budget.
Step 6: Verify Compliance with Industry Regulations
Ensure that the quartz lenses you are sourcing comply with relevant industry regulations, especially if they will be used in sensitive applications such as medical or military. This compliance can significantly affect the longevity and performance of the lenses in their intended applications.
- Documentation: Request certifications that prove compliance with applicable regulations.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluate potential risks associated with non-compliance and how they could affect your operations.
Step 7: Establish a Long-term Relationship
After a successful procurement process, focus on establishing a long-term relationship with your chosen supplier. Ongoing collaboration can lead to better pricing, priority service, and access to new products.
- Regular Communication: Schedule periodic check-ins to discuss product performance and any emerging needs.
- Feedback Loop: Provide feedback on product performance, which can help suppliers improve their offerings and services.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can ensure a more efficient and effective sourcing process for quartz lenses, leading to better product performance and enhanced operational success.

Illustrative image related to quartz lens
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for quartz lens Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Quartz Lens Manufacturing?
When sourcing quartz lenses, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type and grade of quartz significantly impact costs. For example, G1 Commercial Grade Fused Quartz is often more affordable than specialized grades used in high-precision applications. Additional materials like coatings or treatments can also raise costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for manufacturing optical components. Labor costs can vary based on the region, with labor-intensive processes like polishing and quality checks affecting overall pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs. Suppliers in regions with higher operational costs may reflect these in their pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in molds and production tools can be substantial. Custom designs or specialized tooling will further increase costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that lenses meet specific standards requires rigorous QC processes, which can add to the overall manufacturing cost.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary significantly depending on the shipping method, distance, and the Incoterms agreed upon. International shipping can also introduce additional fees such as customs duties and tariffs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will factor in their desired profit margins, which can differ based on market conditions and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Quartz Lens Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of quartz lenses, which are essential for B2B buyers to consider:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk orders typically lead to lower per-unit costs. Establishing a minimum order quantity (MOQ) can help negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom lenses with specific dimensions, coatings, or other attributes will command a premium price compared to standard products.
-
Materials: The choice of quartz and any additional materials for coatings or treatments can affect costs. Higher-quality materials generally lead to higher prices.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that comply with international quality standards or have certifications (like ITAR compliance) often come at a higher price due to the added costs of compliance and assurance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and operational efficiency of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to perceived quality, while newer entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The agreed terms for shipping and delivery can significantly affect costs. Understanding terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) is crucial for budgeting.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing Quartz Lenses?
For B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are some actionable tips:
-
Negotiate: Don’t hesitate to negotiate pricing, especially for large orders. Suppliers often have some flexibility in their pricing structures.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price, but also logistics, potential import duties, and the long-term reliability of the lenses. A lower upfront cost may lead to higher maintenance or replacement costs.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. For instance, suppliers in Germany may have higher quality standards and prices than those in other regions, but this could result in lower failure rates and better long-term value.
-
Research Suppliers: Assess potential suppliers based on their production capabilities, quality assurance practices, and customer reviews. This can help you avoid costly mistakes.
-
Plan for Long-Term Relationships: Building relationships with reliable suppliers can lead to better terms over time. Consider long-term contracts for consistent pricing and supply stability.
Disclaimer on Pricing
The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. Always consult with multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing and terms tailored to your needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing quartz lens With Other Solutions
In the realm of optical solutions, businesses often seek alternatives to quartz lenses for various applications. Understanding these options can aid international B2B buyers in making informed decisions that align with their specific operational needs. Below, we compare quartz lenses to two viable alternatives: optical glass lenses and plastic (polycarbonate) lenses.
| Comparison Aspect | Quartz Lens | Optical Glass Lens | Plastic (Polycarbonate) Lens |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High optical clarity, low thermal expansion | Excellent clarity, scratch-resistant | Moderate clarity, impact-resistant |
| Cost | Moderate ($39 for commercial grade) | Higher cost ($50-$100 depending on specifications) | Lower cost ($10-$30) |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires precision in installation | Similar installation process | Easy to implement, lightweight |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, durable | Requires care to avoid scratches | Low maintenance, but can scratch easily |
| Best Use Case | High-end optical applications, UV applications | Imaging systems, scientific instruments | General-purpose applications, safety gear |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Optical Glass Lenses Compared to Quartz Lenses?
Optical glass lenses offer a higher level of scratch resistance and durability compared to quartz lenses. They are often used in high-precision applications, such as imaging systems and scientific instruments, due to their excellent optical clarity. However, they come at a higher price point, which might not be suitable for all budgets. Additionally, they are heavier than quartz lenses, potentially complicating installation in certain applications.
How Do Plastic (Polycarbonate) Lenses Stack Up Against Quartz Lenses?
Plastic (polycarbonate) lenses are significantly lighter and more impact-resistant than quartz lenses, making them an ideal choice for general-purpose applications and safety gear. Their lower cost can be appealing for businesses operating on tight budgets. However, they do not match the optical clarity of quartz or glass lenses and can be prone to scratching. Thus, while they may serve well in less critical applications, they may not be suitable for high-precision uses where clarity is paramount.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Optical Solution?
When selecting the right optical solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific application requirements, including performance, budget constraints, and environmental factors. Quartz lenses are ideal for high-precision tasks, especially those involving UV applications, while optical glass lenses serve well in scientific and imaging contexts. Conversely, for more general and cost-sensitive applications, polycarbonate lenses may offer a suitable balance of functionality and affordability. By evaluating these factors, businesses can make informed decisions that optimize their operational efficiency and product quality.
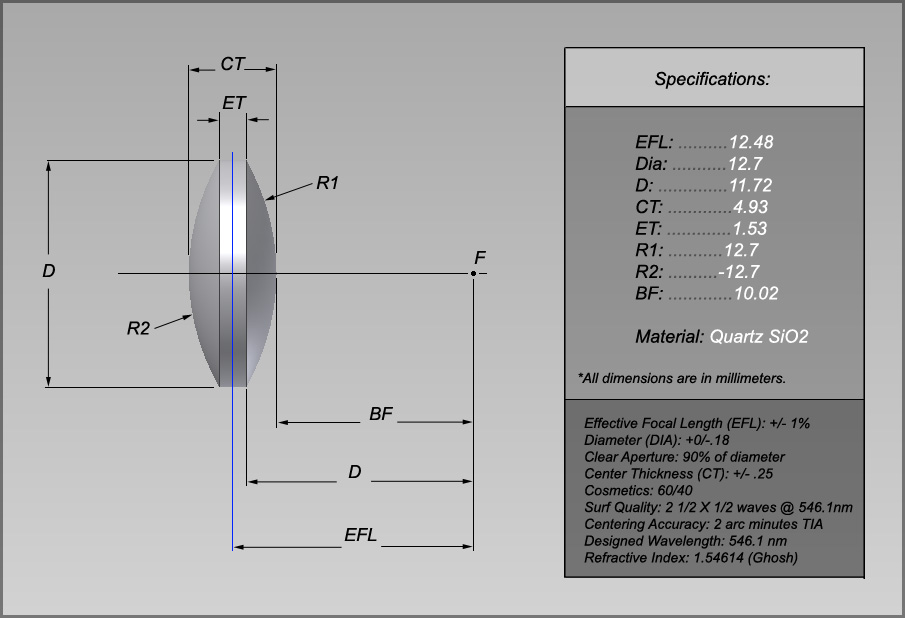
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for quartz lens
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Quartz Lenses Important for B2B Buyers?
Understanding the technical specifications of quartz lenses is crucial for B2B buyers, especially in industries like optics, telecommunications, and manufacturing. Here are several essential properties to consider:

Illustrative image related to quartz lens
-
Material Grade
Quartz lenses are typically made from fused quartz, a high-purity glass that offers excellent thermal stability and optical clarity. The grade of quartz affects not only the performance of the lens but also its cost. For example, G1 commercial grade quartz is suitable for general applications, while higher grades may be necessary for precision optical systems. Buyers should assess their application needs to select the appropriate grade, as it can impact the longevity and effectiveness of the lenses. -
Focal Length Tolerance
This specification indicates the permissible deviation in the focal length of the lens, often expressed as a percentage. A typical tolerance might be ±3%. This is crucial for applications requiring precise focusing, such as in imaging systems. Buyers must ensure that the focal length tolerance aligns with their application to avoid issues in performance, especially in critical optical setups. -
Diameter and Thickness Tolerances
Tolerances for diameter (e.g., ±0.125 mm) and thickness (e.g., ±0.5 mm) are vital for ensuring that lenses fit properly within optical systems. These specifications influence how light interacts with the lens and can affect the overall imaging quality. In B2B scenarios, precise tolerances can reduce the need for costly adjustments or replacements during integration. -
Surface Quality
Surface quality is typically defined by a scratch-dig specification, such as 60-40, which refers to the allowable number of surface imperfections. This is critical for maintaining optical performance and clarity. Higher surface quality ratings lead to better light transmission and reduced distortion. B2B buyers need to ensure that the surface quality meets their operational standards, especially for high-performance applications. -
Centration
Centration refers to the alignment of the lens surfaces and is measured in arc minutes (e.g., <3′). Proper centration is essential for minimizing aberrations in imaging systems. Buyers should prioritize centration specifications to ensure that the lenses will function optimally in their applications.
What Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Know When Purchasing Quartz Lenses?
Familiarity with industry jargon can enhance communication and streamline the purchasing process. Here are several key terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the quartz lens market, understanding whether a supplier is an OEM can help buyers gauge the quality and reliability of the products they are sourcing. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for buyers who may be looking to purchase smaller quantities for testing or initial projects. Knowing the MOQ can help in budget planning and inventory management. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a standard business process where buyers request pricing and terms from suppliers. This document should detail the specifications of the quartz lenses required. A well-prepared RFQ can lead to better pricing and terms, making it a vital tool for B2B buyers. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are international rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. Familiarity with terms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) is essential for understanding shipping costs and responsibilities, particularly for international buyers. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the amount of time it takes for a supplier to fulfill an order after it has been placed. Understanding lead times is crucial for project planning and inventory management, ensuring that production schedules are met without delays. -
Custom Optics
This term refers to lenses that are specifically designed and manufactured to meet unique customer specifications. B2B buyers should be aware that custom optics can often involve longer lead times and higher costs, but they can provide significant advantages for specialized applications.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their procurement processes and optimize their optical systems.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the quartz lens Sector
Global drivers in the quartz lens market are significantly influenced by advancements in technology and increasing demand for high-precision optical components. Sectors such as telecommunications, defense, and healthcare are driving the need for specialized quartz lenses, as these industries require high-quality optics for applications ranging from imaging systems to laser technologies. In particular, the rise of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) applications has spurred innovation and increased demand for custom lens solutions.
Emerging trends in sourcing for quartz lenses include a shift towards integrated supply chains that prioritize speed and efficiency. International B2B buyers are increasingly seeking manufacturers that can provide rapid prototyping and customization options to meet specific project needs. Moreover, digital sourcing platforms are gaining traction, allowing buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to connect directly with suppliers, enhancing transparency and reducing procurement times. The focus on cost-effectiveness is also growing, prompting buyers to explore options such as G1 commercial-grade fused quartz lenses, which offer a balance between quality and affordability.
How is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Quartz Lens Market?
The environmental impact of quartz lens manufacturing is a critical concern for international buyers. The extraction and processing of quartz can lead to significant ecological disruption if not managed responsibly. Consequently, ethical sourcing practices are becoming a priority. B2B buyers are increasingly inclined to partner with suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials or adopting energy-efficient manufacturing techniques.
Certifications like ISO 14001, which focuses on effective environmental management systems, can serve as a valuable indicator for buyers assessing potential suppliers. Additionally, the use of ‘green’ materials is gaining prominence, with manufacturers exploring alternatives that minimize environmental footprints while maintaining high-quality standards. Buyers are advised to inquire about the sustainability credentials of their suppliers to ensure alignment with their corporate social responsibility goals.
What is the Historical Context of Quartz Lens Development?
The evolution of quartz lens technology has been marked by significant milestones that have shaped its current landscape. Historically, quartz lenses were primarily used in scientific and industrial applications due to their superior optical properties. With the advent of laser technology in the late 20th century, the demand for high-quality quartz lenses surged, leading to innovations in manufacturing processes and design.
As industries evolved, so did the applications for quartz lenses, ranging from telecommunications to consumer electronics. Today, the focus has shifted towards customization and integration, with suppliers investing in advanced fabrication technologies to meet the diverse needs of international buyers. This historical context not only informs current market dynamics but also highlights the importance of adaptability and innovation in sourcing strategies.
By staying attuned to these market trends, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of the quartz lens sector more effectively, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational and ethical standards.

Illustrative image related to quartz lens
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of quartz lens
1. How do I select the right quartz lens for my application?
Choosing the right quartz lens requires a thorough understanding of your specific application needs. Consider factors such as focal length, diameter, and thickness tolerance, which impact how the lens will perform. Additionally, evaluate the design wavelength relevant to your light source and the required surface quality. If your application is non-critical, commercial grade options may suffice, while precision applications might necessitate custom solutions. Consulting with suppliers about your requirements can also provide insights into the most suitable products available.
2. What is the best quartz lens material for high-temperature applications?
For high-temperature applications, fused quartz is the preferred material due to its excellent thermal stability and low thermal expansion coefficient. It can withstand temperatures up to 1,200°C without deforming or losing optical properties. When selecting a quartz lens for such environments, ensure that the specifications align with your operational temperature range and consider the lens’s surface quality, as impurities can affect performance. Always discuss your specific needs with suppliers to confirm compatibility with your application.
3. What are the typical lead times for ordering quartz lenses internationally?
Lead times for international orders of quartz lenses can vary significantly based on factors such as production capacity, customization requirements, and shipping logistics. Generally, standard products may take 2-4 weeks, while custom lenses could require 6-8 weeks or more. It’s crucial to communicate your timelines with suppliers upfront and confirm their ability to meet your deadlines. Additionally, consider potential delays in customs clearance when planning your order.

Illustrative image related to quartz lens
4. How do I vet suppliers for quartz lenses?
When vetting suppliers for quartz lenses, prioritize their industry experience, product quality certifications, and customer reviews. Request samples to evaluate product quality firsthand. Additionally, inquire about their manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols to ensure they meet international standards. It’s also beneficial to check if the supplier is compliant with relevant regulations, such as ITAR for military applications. Establishing a relationship with a supplier who understands your market can also enhance collaboration.
5. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for quartz lenses?
Minimum order quantities for quartz lenses can vary by supplier and depend on the type of lens and customization required. Some suppliers may offer low MOQs for standard products, while custom lenses may have higher MOQs due to production costs. It’s advisable to discuss your needs with potential suppliers and negotiate MOQs that align with your project requirements. Additionally, consider the impact of bulk ordering on cost savings and inventory management.
6. What payment terms are commonly accepted for international purchases of quartz lenses?
Payment terms for international purchases of quartz lenses often include options such as wire transfers, letters of credit, and payment upon delivery. Suppliers may require a deposit for custom orders, with the balance due before shipment. It’s essential to clarify payment terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings. Additionally, consider using escrow services for high-value transactions to ensure secure payments and protect both parties involved.
7. How do I ensure quality assurance for quartz lenses?
To ensure quality assurance for quartz lenses, select suppliers who implement stringent quality control measures throughout the manufacturing process. Request detailed specifications and certifications for the lenses, including surface quality and tolerance levels. It may also be beneficial to establish a quality assurance agreement outlining testing protocols and acceptance criteria. Regular communication with the supplier regarding quality expectations can help maintain standards and address any issues promptly.
8. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing quartz lenses?
When importing quartz lenses, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Evaluate whether air or sea freight is more suitable based on urgency and cost. Ensure that the supplier provides accurate documentation to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Additionally, engage with a reliable freight forwarder familiar with international trade regulations to navigate the complexities of importing goods, especially in regions with stringent customs requirements.
Top 7 Quartz Lens Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Esco Optics – Plano-Convex Lenses
Domain: escooptics.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: {‘product_name’: ‘Plano-Convex Lenses, G1 Commercial Grade Fused Quartz’, ‘manufacturer’: ‘Esco Optics, Inc.’, ‘focal_length_tolerance’: ‘+/- 3%’, ‘diameter_tolerance’: ‘+/- 0.125 mm’, ‘thickness_tolerance’: ‘+/- 0.5 mm’, ‘design_wavelength’: ‘546 nm’, ‘centration’: “<3′”, ‘surface_quality’: ’60-40 scratch-dig’, ‘edges’: ‘Fine ground and beveled’, ‘pricing’: [{‘size’: ‘12.7 / 25.4’, ‘price’: ‘$39….
2. Tydex Optics – Fused Quartz & Fused Silica
Domain: tydexoptics.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Fused Quartz and Fused Silica are types of Quartz Glass containing primarily silica in amorphous form. Fused Quartz is made by melting high purity naturally occurring quartz crystals at around 2000°C using electrically heated or gas/oxygen-fuelled furnaces. It is normally transparent. Fused Silica is produced from high purity silica sand and is typically translucent or opaque due to small air bubb…
3. Phillips Safety – Quartz Working Glasses
Domain: phillips-safety.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Quartz Working Glasses designed for quartz working professionals. Categories include: 1. Quartz Split Lens: Features a split lens design with the top 1/3 or 1/2 clear or equipped with Phillips 202 lenses, and the bottom 2/3 or 1/2 shaded with green welding shades (4 to 8). 2. Quartz Green IR Lenses: Shaded between 4 and 10, providing standard IR and UV protection without sodium flare absorption, a…
4. Ray-Beamm – Quartz Super Wide Panoramic AF Lens 0.42X
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Quartz lenses available in various types including macro, super wide, and zoom lenses. Notable products include: 1. Ray-Beamm Quartz Super Wide Panoramic AF Lens 0.42X – Macro, suitable for Canon, priced at $34.99. 2. Crystal Quartz Super Wide AF Lens Macro 0.42X with leather case, priced at $28.99. 3. Meteor-8M 9-38mm f/1.8 zoom lens for 8mm Quarz 1x8S film cameras, priced at $30.00. 4. Crystal A…
5. MicQuartz – Quartz Lenses for Laser Technology
Domain: micquartz.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Quartz lenses are significant optical components in laser technology, known for their high light transmission, thermal stability, and mechanical strength. They are used in various applications including:
1. Optical reflection and transmission in laser systems, utilizing high reflectors and half lenses.
2. Laser interferometers for accurate reflection and refraction of laser beams, ensuring stabili…
6. DPreview – Quartz Lens Applications
Domain: dpreview.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: This company, DPreview – Quartz Lens Applications, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
7. QD Europe – High-Quality Glass and Quartz Lenses
Domain: qd-europe.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: We provide high-quality glass and quartz lenses made from B270, BK7, and Suprasil II. Our product range includes plano and biconvex lenses, as well as plano concave and biconcave lenses, with a variety of focal lengths and diameters ranging from 6.35 to 101.6 mm.
– **Plano Convex Lenses**: Basic optical elements with positive focal lengths, ideal for use as collimating condensers and focusing le…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for quartz lens
As the demand for quartz lenses continues to rise across various industries, strategic sourcing has become essential for international B2B buyers seeking quality, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Key takeaways highlight the importance of understanding product specifications, such as focal length tolerance and surface quality, which directly impact performance in applications ranging from imaging to laser safety. Sourcing from reputable suppliers, especially those compliant with international standards, ensures that businesses can maintain quality while meeting regulatory requirements.
For buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, establishing relationships with trusted manufacturers and understanding regional supply chain dynamics can lead to better pricing and availability. As markets evolve, leveraging technology for procurement can enhance transparency and streamline the sourcing process.
Looking ahead, it is vital for businesses to stay informed about innovations in quartz lens technology and emerging market trends. By prioritizing strategic sourcing now, companies can position themselves competitively for future growth. Engage with suppliers today to explore tailored solutions that meet your specific needs and to ensure your business remains at the forefront of optical advancements.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.