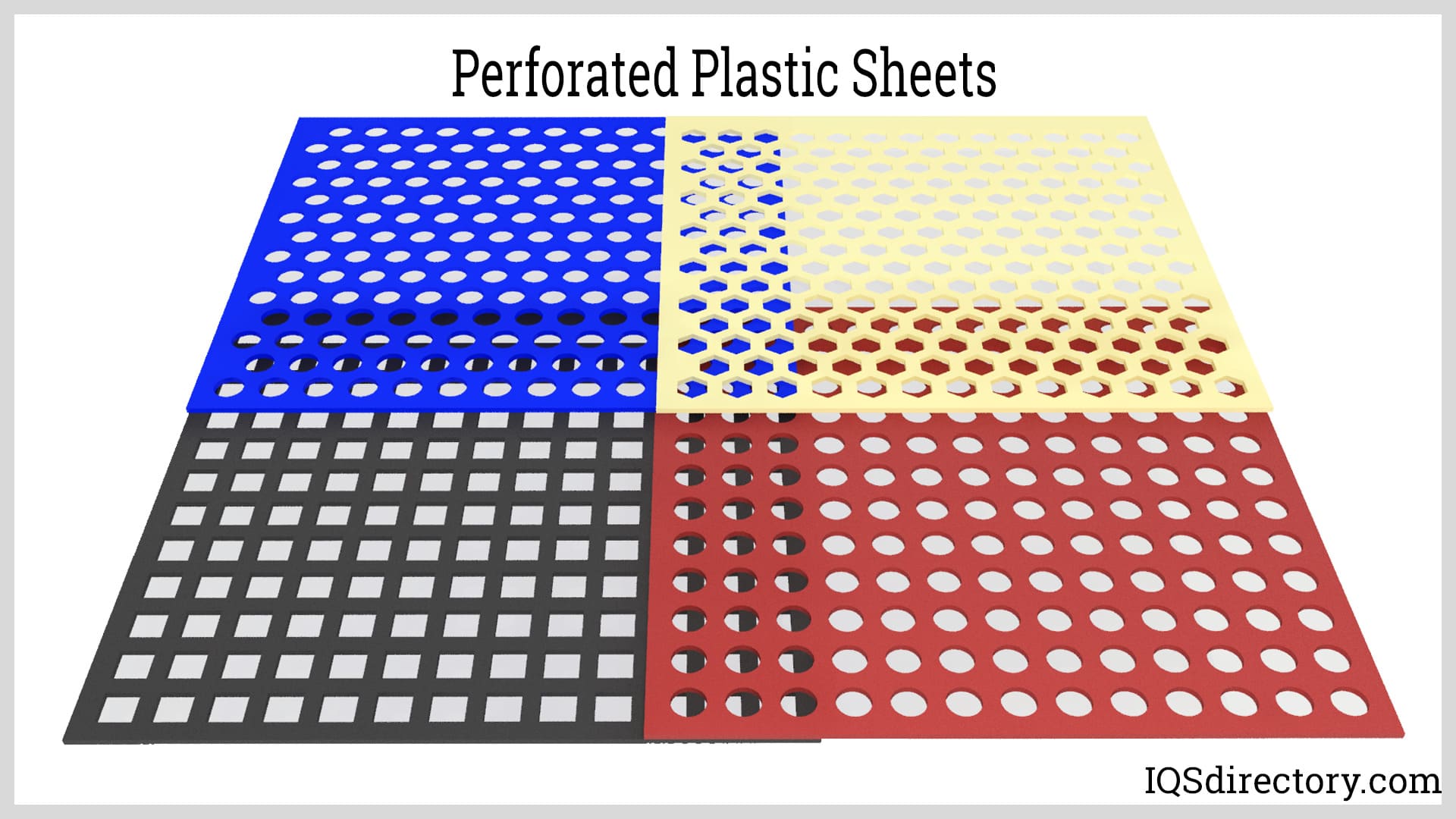
A Deep Dive into Perforated Plastic Solution
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for perforated plastic
In the ever-evolving global market, sourcing high-quality perforated plastic can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers. The challenge lies not only in understanding the diverse types of perforated plastics available but also in identifying the most suitable applications for specific industrial needs. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, offering insights into the various types of perforated plastic, their applications across industries, and the nuances of supplier vetting.
From food processing to construction and automotive sectors, perforated plastics are integral for enhancing functionality and efficiency. This guide empowers buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia—by providing a structured approach to making informed purchasing decisions.
By exploring material options, understanding cost implications, and learning best practices for supplier engagement, readers will be equipped to navigate the complexities of sourcing perforated plastics. With an emphasis on quality, durability, and performance, this guide aims to streamline the procurement process, ensuring that businesses can leverage the full potential of perforated plastics in their operations. Whether you are looking to enhance product performance or meet regulatory requirements, this resource will be your go-to reference for successful sourcing strategies.
Understanding perforated plastic Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Round Hole Perforated Plastic | Features circular holes arranged in various patterns. | Ventilation panels, filters, sound insulation | Pros: Aesthetic appeal, lightweight, good airflow. Cons: Limited structural support compared to other types. |
| Square Hole Perforated Plastic | Square-shaped holes that provide a unique appearance. | Architectural applications, furniture design | Pros: Enhanced strength and rigidity, customizable patterns. Cons: May not allow for as much airflow as round holes. |
| Custom Perforated Plastic | Tailored hole sizes and patterns based on specific needs. | Specialized industrial applications, custom machinery parts | Pros: Highly versatile, meets specific project requirements. Cons: Potentially higher cost and longer lead times. |
| Slotted Perforated Plastic | Features elongated holes for improved drainage and airflow. | Agricultural applications, drainage systems | Pros: Efficient liquid and air flow, suitable for diverse environments. Cons: May require more material for equivalent strength. |
| Multi-layer Perforated Plastic | Composed of multiple layers with varying perforation styles. | High-performance filters, sound barriers | Pros: Enhanced durability and functionality, unique applications. Cons: More complex manufacturing process, potentially higher costs. |
What Are the Characteristics of Round Hole Perforated Plastic?
Round hole perforated plastic is characterized by its circular openings, which can be arranged in various patterns such as staggered or straight lines. This type is particularly popular for applications requiring airflow, such as ventilation panels and sound insulation. When considering B2B purchases, buyers should note the aesthetic benefits and lightweight nature, which make it easier to handle. However, its structural limitations may not suit all applications, especially where load-bearing is critical.

Illustrative image related to perforated plastic
How Does Square Hole Perforated Plastic Stand Out?
Square hole perforated plastic offers a distinct look with its square-shaped openings, providing enhanced strength and rigidity. This type is often utilized in architectural applications and furniture design, where visual appeal and durability are paramount. For B2B buyers, the customizable patterns available can meet specific project needs. However, while it offers good strength, it may not facilitate airflow as effectively as round holes, making it less suitable for ventilation-focused applications.
Why Opt for Custom Perforated Plastic Solutions?
Custom perforated plastic allows for tailored hole sizes and patterns, making it ideal for specialized industrial applications and custom machinery parts. This type is particularly beneficial for businesses that require unique solutions to specific challenges. B2B buyers should consider the versatility and adaptability of this option, although it may come at a higher cost and longer lead times compared to standard products.
What Are the Benefits of Slotted Perforated Plastic?
Slotted perforated plastic features elongated holes that enhance drainage and airflow, making it a popular choice in agricultural applications and drainage systems. Its design allows for efficient liquid and air flow, which is crucial in various environments. For B2B buyers, the practicality of this type is clear, but they should also consider that it may require more material to achieve equivalent strength compared to other perforated types.
Illustrative image related to perforated plastic
How Does Multi-layer Perforated Plastic Enhance Performance?
Multi-layer perforated plastic consists of several layers, each potentially featuring different perforation styles. This complexity enhances durability and functionality, making it suitable for high-performance filters and sound barriers. B2B buyers looking for innovative solutions will find this type advantageous, though they should be aware of the more complex manufacturing process and potentially higher costs involved.
Key Industrial Applications of perforated plastic
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Perforated Plastic | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Processing | Perforated sheets for seafood processing | Enhances hygiene and prevents contamination | Material certifications, compliance with food safety standards |
| Agriculture | Ventilation panels for greenhouses | Improves airflow and temperature control | UV resistance, durability in harsh weather conditions |
| Chemical Industry | Filters for liquid separation | Efficient filtration of harmful substances | Chemical resistance, custom perforation patterns |
| Automotive | Lightweight components for vehicle interiors | Reduces overall vehicle weight, improving fuel efficiency | Material strength, aesthetic options |
| Construction | Sound insulation panels | Enhances acoustic comfort in buildings | Fire resistance, structural integrity |
How is Perforated Plastic Used in Food Processing?
In the food processing industry, perforated plastic sheets are extensively used for applications such as seafood processing. These sheets allow for optimal drainage and airflow, which are critical for maintaining hygiene and preventing contamination. When sourcing perforated plastic for this application, international buyers must ensure that the materials meet stringent food safety regulations and certifications. Additionally, the choice of material should resist corrosion and be easy to clean, ensuring longevity and compliance in environments with frequent exposure to moisture and cleaning agents.
What Role Does Perforated Plastic Play in Agriculture?
In agriculture, perforated plastic is primarily utilized in ventilation panels for greenhouses. These panels facilitate essential airflow, promoting healthy plant growth while managing internal temperatures. For buyers in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing durable, UV-resistant perforated plastic is vital due to the intense sunlight and varying weather conditions. Selecting materials that can withstand environmental stresses while providing the necessary ventilation will enhance crop yields and operational efficiency.
How is Perforated Plastic Beneficial in the Chemical Industry?
Perforated plastic plays a critical role in the chemical industry, particularly in the development of filters for liquid separation processes. These filters enable efficient removal of particulates and impurities from chemicals, ensuring product quality and safety. Buyers must consider sourcing materials that exhibit high chemical resistance and can be customized with specific perforation patterns for optimal filtration performance. Understanding local regulations regarding chemical handling is also essential for compliance and safety.

Illustrative image related to perforated plastic
In What Ways is Perforated Plastic Used in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, perforated plastic is increasingly used for lightweight components in vehicle interiors. This application not only contributes to reduced overall vehicle weight, enhancing fuel efficiency, but also allows for design flexibility and aesthetic appeal. When sourcing perforated plastic for automotive applications, buyers should prioritize materials that offer high strength-to-weight ratios and comply with automotive standards for safety and durability. The ability to customize perforation patterns can also provide unique design elements.
How Does Perforated Plastic Enhance Construction Projects?
Perforated plastic is utilized in construction for sound insulation panels, contributing to improved acoustic comfort within buildings. These panels help to minimize noise pollution, creating more pleasant living and working environments. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should focus on sourcing perforated plastics that meet fire safety regulations and provide the necessary structural integrity. Material selection is critical, as it should balance acoustic performance with durability to withstand environmental conditions.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘perforated plastic’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Quality Assurance in Perforated Plastic Sourcing
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with ensuring the quality and durability of perforated plastic materials. In industries like food processing and chemical manufacturing, the integrity of the material is crucial. Buyers may find themselves facing issues such as material degradation, inconsistent perforation patterns, or inadequate chemical resistance, leading to operational disruptions and safety concerns. Without proper quality assurance, these buyers risk costly downtime and potential damage to their reputations.
The Solution: To overcome these challenges, it is essential for buyers to establish a robust supplier evaluation process. Begin by requesting samples of perforated plastic from multiple manufacturers, focusing on their specifications for chemical resistance, mechanical stability, and UV stability. Conduct thorough testing in your specific application environments to assess performance under real-world conditions. Additionally, consider suppliers that offer certifications or compliance with industry standards, as this can provide an extra layer of confidence in the material’s quality. Regular communication with your supplier about your specific requirements and performance feedback can also foster a more reliable partnership.
Illustrative image related to perforated plastic
Scenario 2: Customization Challenges in Perforated Plastic Designs
The Problem: Many B2B buyers find themselves needing highly customized perforated plastic solutions to meet unique application requirements. However, the challenge often lies in the limited options available from standard suppliers. This can lead to delays in project timelines, increased costs due to rework, and a mismatch between the product and the intended use, which can ultimately impact operational efficiency.
The Solution: To address customization challenges, buyers should engage directly with manufacturers that specialize in bespoke perforated plastic products. Initiate discussions early in the design phase, providing detailed specifications regarding hole sizes, patterns, and material types that align with your application needs. Leverage CAD drawings or prototypes to visualize the final product. Some manufacturers offer advanced design software that can help in visualizing different perforation patterns and their effects on functionality. By collaborating closely with the manufacturer, buyers can ensure that the final product meets all operational requirements, thus streamlining the production process and minimizing delays.
Scenario 3: Cost Management and Efficiency in Perforated Plastic Procurement
The Problem: B2B buyers often face financial pressures when procuring perforated plastic, particularly when balancing quality and cost. The challenge arises when attempting to source high-quality materials without exceeding budget constraints. Buyers may find themselves compromising on quality to save costs, which can lead to increased maintenance expenses and product failures down the line.
The Solution: To effectively manage costs while ensuring quality, buyers should consider adopting a strategic sourcing approach. Start by analyzing your current usage of perforated plastic to identify potential bulk purchasing opportunities. Engaging in long-term contracts with manufacturers can often yield better pricing and ensure a consistent supply of materials. Additionally, explore different material options that provide the necessary properties at a lower cost. For instance, lightweight thermoplastics may offer a more economical solution compared to traditional materials without sacrificing performance. Implementing a total cost of ownership analysis can also help in understanding the long-term value of quality materials, guiding better purchasing decisions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for perforated plastic
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used for Perforated Plastic?
When selecting materials for perforated plastic, understanding their properties is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in specific applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the production of perforated plastic sheets: Polypropylene, Polyethylene, Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS).
How Does Polypropylene Perform as a Perforated Plastic Material?
Polypropylene is known for its lightweight and high chemical resistance, making it ideal for applications in the food processing and chemical industries. It can withstand temperatures up to 100°C (212°F) and is resistant to moisture, which prevents rot and delamination.
Pros: Polypropylene is economical and easy to fabricate, allowing for various perforation patterns. Its flexibility and impact resistance make it suitable for applications requiring durability.
Cons: While it is strong, polypropylene may not be suitable for high-temperature applications beyond its rated limit. Additionally, it can become brittle over time when exposed to UV light unless treated.

Illustrative image related to perforated plastic
Impact on Application: Polypropylene is compatible with food products, making it an excellent choice for perforated sheets used in food processing and packaging.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with food safety standards, such as those set by ASTM or local regulations regarding food contact materials.
What Are the Advantages of Using Polyethylene for Perforated Plastic Sheets?
Polyethylene is another widely used thermoplastic known for its excellent impact resistance and low moisture absorption. It typically operates effectively at temperatures up to 80°C (176°F) and is resistant to a variety of chemicals.
Pros: Polyethylene is lightweight and cost-effective, making it an attractive option for various applications, including drainage systems and ventilation panels.
Cons: Its lower temperature tolerance may limit its use in high-heat environments. Additionally, it can be less rigid than other materials, affecting structural applications.
Illustrative image related to perforated plastic
Impact on Application: Polyethylene is suitable for applications involving water and other liquids due to its excellent moisture resistance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that the polyethylene used meets regional standards for environmental impact, particularly in South America, where regulations may vary significantly.
How Does PVC Compare in Terms of Performance for Perforated Plastic?
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is a versatile plastic that offers high strength and rigidity. It can withstand temperatures up to 60°C (140°F) and is highly resistant to chemicals and corrosion.
Pros: PVC is durable and can be produced in various colors and finishes, making it aesthetically appealing for architectural applications. It is also cost-effective for large-scale projects.

Illustrative image related to perforated plastic
Cons: The rigidity of PVC can be a limitation in applications requiring flexibility. Additionally, it may not perform well in high-temperature environments.
Impact on Application: PVC is commonly used in construction for ventilation and filtration applications, where durability and chemical resistance are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with building codes and environmental regulations is critical, especially in Europe, where standards are stringent.
What Makes Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) a Preferred Choice for Certain Applications?
ABS is known for its high impact resistance and toughness, making it suitable for demanding applications. It operates effectively at temperatures up to 80°C (176°F) and has good chemical resistance.
Pros: ABS is easy to machine and fabricate, allowing for intricate designs and custom perforation patterns. Its aesthetic appeal makes it suitable for consumer products.
Cons: ABS can be more expensive than other thermoplastics and may not be as UV resistant, which can limit its outdoor applications.

Illustrative image related to perforated plastic
Impact on Application: ABS is often used in the automotive and consumer goods industries, where durability and appearance are essential.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of ABS in their region and ensure compliance with industry standards, especially in the automotive sector.
Summary of Material Properties for Perforated Plastic
| Material | Typical Use Case for perforated plastic | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polypropylene | Food processing, chemical applications | Lightweight and chemical resistant | Limited high-temperature performance | Medium |
| Polyethylene | Drainage systems, ventilation panels | Cost-effective and impact resistant | Lower rigidity and temperature tolerance | Low |
| PVC | Construction, filtration | Durable and aesthetically versatile | Rigid, limited flexibility | Medium |
| ABS | Automotive, consumer products | High impact resistance and machinability | Higher cost and UV sensitivity | High |
This guide serves as a strategic resource for international B2B buyers, helping them navigate material selection for perforated plastic applications while considering regional compliance and performance requirements.

Illustrative image related to perforated plastic
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for perforated plastic
What Are the Main Stages of the Manufacturing Process for Perforated Plastic?
The manufacturing of perforated plastic involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the specifications required for various applications. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation
The process begins with the selection of appropriate plastic materials. Common options include polypropylene, polycarbonate, and PVC, chosen for their lightweight, chemical resistance, and durability. Material preparation involves cutting the plastic sheets to size, which can be customized according to customer specifications regarding dimensions, thickness, and perforation patterns. This step is crucial as the quality of the raw materials directly impacts the performance of the final product.
Forming Techniques
The heart of the manufacturing process is the perforating stage, where holes are punched into the plastic sheets using specialized dies. Techniques such as rotary perforating and mechanical punching are employed to create various hole shapes and sizes. The choice of technique depends on the material type and the desired hole configuration, whether round, square, or custom shapes. This step not only defines the functionality of the perforated sheets but also affects their aesthetic appeal.
Assembly
In cases where perforated plastic is part of a larger assembly, components may be joined through methods such as welding or adhesive bonding. This stage is essential for applications requiring complex structures, such as ventilation panels or filters. Precise alignment and secure attachment are vital to ensure structural integrity and operational efficiency.
Finishing Processes
The final stage in manufacturing involves surface finishing, which may include polishing, coating, or texturing the sheets. This enhances the product’s durability, aesthetic qualities, and performance characteristics. For example, a textured surface can improve grip and reduce glare, making it suitable for specific applications in architecture or automotive industries.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in the Production of Perforated Plastic?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital aspect of the manufacturing process for perforated plastic, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations. The QA process typically involves several key checkpoints and compliance with relevant standards.
International Standards and Compliance
Manufacturers often adhere to ISO 9001 standards, which outline the requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with these standards helps ensure that processes are consistently controlled and products are reliable. Industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for European markets or API standards for oil and gas applications may also be applicable, depending on the end-use of the perforated plastic.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) procedures are integrated throughout the manufacturing process. Common checkpoints include:

Illustrative image related to perforated plastic
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon delivery to ensure they meet specified requirements before processing begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, random samples are taken to monitor the perforating process, checking for accuracy in hole size, spacing, and overall quality.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once production is complete, finished products undergo rigorous testing for dimensional accuracy, surface quality, and physical properties such as tensile strength and impact resistance.
Testing Methods for Quality Assurance
To verify product performance, various testing methods are employed, including tensile tests, impact resistance tests, and chemical resistance evaluations. These tests help confirm that the perforated plastic can withstand the conditions it will encounter in its intended application.
What Should B2B Buyers Know About Verifying Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, ensuring the quality of perforated plastic products is paramount. Here are essential considerations for verifying supplier quality control:
Supplier Audits and Evaluations
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to assess a manufacturer’s quality control systems. Buyers can request to review the supplier’s quality management certifications, inspection records, and compliance with international standards. On-site visits can provide valuable insights into manufacturing practices and adherence to QA protocols.
Requesting Quality Reports and Documentation
Buyers should request detailed quality reports, including IQC, IPQC, and FQC results. This documentation serves as evidence of the supplier’s commitment to quality and helps buyers make informed decisions. Additionally, third-party inspection reports can further validate a supplier’s claims regarding product quality.
Illustrative image related to perforated plastic
Understanding Regional Certification Nuances
Different regions may have specific requirements for quality certifications. For instance, products exported to the European Union may need CE marking, while those entering certain Middle Eastern markets may require compliance with local standards. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these regional nuances to ensure their suppliers meet the necessary requirements.
How Do Material Selection and Testing Impact the Quality of Perforated Plastic?
The choice of materials significantly impacts the performance and durability of perforated plastic products. High-quality thermoplastics not only offer lighter weight compared to metals but also provide advantages like corrosion resistance and longevity.
Material Properties and Their Relevance
Different plastics come with distinct properties, such as temperature resistance and moisture absorption. For instance, polypropylene is known for its chemical resistance, making it suitable for harsh environments, while polycarbonate is preferred for applications requiring high impact resistance. Understanding these properties allows buyers to select materials that best fit their specific application needs.
Importance of Testing for Material Integrity
Testing the integrity of the materials used in perforated plastic is crucial for ensuring the final product performs well under expected conditions. Buyers should ensure that suppliers conduct rigorous testing, including checks for UV resistance, mechanical stability, and sterilizability, especially for applications in food processing or medical settings.

Illustrative image related to perforated plastic
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for perforated plastic is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material selection, rigorous QA protocols, and supplier verification, buyers can ensure they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘perforated plastic’
To assist B2B buyers in effectively sourcing perforated plastic, this guide outlines a systematic checklist to ensure you make informed and strategic procurement decisions. Each step is designed to help you understand the intricacies involved in selecting the right perforated plastic for your specific application and to identify reliable suppliers.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly outlining your technical requirements for the perforated plastic. This includes dimensions, thickness, hole size, and patterns that suit your application. Understanding these specifications is crucial to ensure that the product meets your operational needs and integrates seamlessly into your existing processes.
- Key Considerations:
- Identify whether you need round, square, or custom-shaped perforations.
- Determine the required thickness (typically between 2-8 mm) based on application stresses.
Step 2: Assess Material Requirements
Perforated plastics come in various materials, each with unique properties. Evaluate whether you need standard plastics or high-performance thermoplastics based on factors such as temperature resistance, chemical exposure, and mechanical strength.
- Material Types:
- Common choices include polypropylene and polycarbonate, known for their lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties.
- Consider the environmental conditions the plastic will be exposed to, such as moisture and UV radiation.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before finalizing any agreements, it’s essential to vet potential suppliers. A reliable supplier not only provides quality products but also offers support in terms of customization and after-sales service.
- Supplier Verification:
- Request company profiles, including their manufacturing capabilities and industry experience.
- Seek references or case studies from other clients in your sector to gauge their reliability and quality.
Step 4: Request Samples
Once you have narrowed down your list of suppliers, request samples of the perforated plastic sheets. This step allows you to physically assess the quality, finish, and suitability of the materials for your applications.
- Sample Evaluation:
- Check for uniformity in perforation size and distribution.
- Assess the overall finish, ensuring it meets your aesthetic and functional standards.
Step 5: Confirm Compliance and Certifications
Ensure that the suppliers you consider comply with relevant international standards and certifications, especially if you operate in regulated industries such as food processing or pharmaceuticals.
- Certification Checks:
- Look for certifications related to quality management (ISO 9001) and material safety (FDA compliance for food-grade applications).
- Verify if the supplier adheres to environmental regulations, particularly in sustainable practices.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have selected a supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, delivery timelines, and payment terms. A clear understanding of these factors can save costs and avoid delays in your supply chain.

Illustrative image related to perforated plastic
- Negotiation Tips:
- Be transparent about your budget while also considering the value of quality materials.
- Discuss bulk order discounts or long-term partnership agreements for better pricing.
Step 7: Establish a Quality Assurance Process
After finalizing your order, set up a quality assurance process for incoming materials. This will ensure that the perforated plastic sheets meet your specifications and prevent issues in production.
- Quality Control Steps:
- Develop inspection criteria based on your initial specifications.
- Plan for periodic reviews of supplier performance to maintain quality over time.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing process for perforated plastic, ensuring they select the right materials and suppliers for their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for perforated plastic Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Perforated Plastic Sourcing?
When sourcing perforated plastic, understanding the cost structure is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of plastic significantly influences pricing. Common materials like polypropylene and polycarbonate vary in cost based on availability and regional market conditions. Specialty plastics with enhanced properties (e.g., UV resistance, high-temperature performance) will incur higher costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs can differ widely based on the region and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Automated processes may reduce labor costs, while custom or intricate designs often require skilled labor, impacting overall pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the costs associated with the manufacturing facility, machinery maintenance, utilities, and administrative expenses. Suppliers with modern facilities may offer competitive pricing due to increased efficiency.
-
Tooling: Custom perforation patterns require specialized tooling, which can be a significant upfront investment for manufacturers. This cost is typically amortized over the production run, influencing pricing based on order volume.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that the perforated plastic meets industry standards and specifications. The extent of QC measures can affect pricing, with higher quality assurance leading to increased costs.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary significantly based on the distance, shipping method, and the weight of the products. Buyers should consider logistics when evaluating overall costs, especially for international shipments.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on their market positioning and the competitive landscape.
What Influences Pricing for Perforated Plastic?
Several factors can influence the pricing of perforated plastic products:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Understanding the supplier’s MOQ can help in negotiating better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized perforation patterns, sizes, and colors increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., FDA-approved for food applications) can increase costs. Buyers in regulated industries must balance quality with budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, experience, and operational efficiency can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for reliability and service.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterm affects cost responsibility for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Buyers should clarify these terms to avoid miscalculations in total costs.
How Can Buyers Negotiate for Better Pricing?
Effective negotiation strategies can lead to more favorable terms and pricing:
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond initial costs, consider long-term expenses such as maintenance, durability, and replacement frequency. A higher upfront cost may lead to lower TCO if the product lasts longer or requires less maintenance.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If your business can commit to larger orders, negotiate for volume discounts. Suppliers are often willing to offer better rates for guaranteed business.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Obtain quotes from various suppliers to understand the market rate and leverage this information during negotiations.
-
Be Clear on Requirements: Clearly outline your specifications to avoid additional costs later in the process. Ambiguity can lead to changes that increase pricing.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: For international buyers, sourcing from local suppliers can reduce logistics costs and lead times. This is particularly relevant in regions like Africa and South America, where local manufacturing capabilities may be growing.
What Should International Buyers Keep in Mind?
For international buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa and the Middle East, there are unique considerations:
-
Currency Fluctuations: Be aware of exchange rate risks when pricing in different currencies. This can significantly affect the final cost.
-
Tariffs and Import Duties: Understand the implications of tariffs and duties on imported goods, which can add to the overall cost.
-
Cultural Factors: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service. Understanding local business practices is essential for successful negotiations.
In conclusion, sourcing perforated plastic involves careful consideration of various cost components and pricing influencers. By understanding these factors and employing strategic negotiation tactics, international B2B buyers can achieve more favorable outcomes. Always remember that indicative prices can vary based on market conditions, supplier capabilities, and specific project requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing perforated plastic With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Perforated Plastic
In the quest for effective solutions, businesses often encounter a range of materials and technologies that can serve similar purposes to perforated plastic. Understanding these alternatives is essential for making informed decisions that align with specific operational needs, budget constraints, and performance expectations. This analysis will compare perforated plastic to two viable alternatives: perforated metal and expanded metal. Each option offers unique attributes that may suit different applications across various industries.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Perforated Plastic | Perforated Metal | Expanded Metal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | High strength-to-weight ratio | Excellent airflow and light passage |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher initial investment | Moderate cost, depends on gauge |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to fabricate and install | Requires more specialized tools | Simple to install, but may need cutting |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, resistant to rot | Requires regular maintenance to prevent rust | Minimal maintenance needed |
| Best Use Case | Food processing, interior architecture | Industrial applications, security enclosures | Ventilation, screening applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Perforated Metal?
Perforated metal is a robust alternative known for its high strength and durability, making it suitable for demanding industrial applications. It offers a superior strength-to-weight ratio, allowing for structural integrity in heavy-duty environments. However, the initial cost is significantly higher than perforated plastic, and its weight can be a disadvantage in applications where lightweight materials are preferred. Additionally, perforated metal requires more specialized tools for installation and maintenance to prevent rust and corrosion, especially in harsh environments.

Illustrative image related to perforated plastic
How Does Expanded Metal Compare to Perforated Plastic?
Expanded metal is another viable option that excels in applications requiring excellent airflow and light passage. Its unique design allows for a high percentage of open area, making it suitable for ventilation and screening applications. The cost is generally moderate, but the material can be heavier and may require cutting for custom applications. While expanded metal has minimal maintenance needs, its rigidity can limit its use in applications where flexibility is crucial, such as in certain architectural designs.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Business Needs
When selecting between perforated plastic and its alternatives, B2B buyers should carefully consider the specific requirements of their applications, including performance needs, budget, and ease of installation. Perforated plastic is often the go-to choice for industries requiring lightweight, corrosion-resistant materials, particularly in food processing and architecture. In contrast, perforated metal may be better suited for heavy-duty applications, while expanded metal shines in ventilation and screening scenarios. By assessing these factors, businesses can choose the most appropriate solution that meets their operational demands and enhances their overall efficiency.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for perforated plastic
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Perforated Plastic That B2B Buyers Should Know?
Understanding the essential technical properties of perforated plastic is crucial for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications:
-
Material Grade
The material grade of perforated plastic determines its performance characteristics. Common materials include polypropylene, polycarbonate, and PVC, each offering varying levels of strength, chemical resistance, and temperature tolerance. Selecting the right grade is vital for applications in harsh environments, such as chemical processing or food production, where durability and safety are paramount. -
Thickness
The thickness of perforated plastic sheets typically ranges from 2 mm to 8 mm. Thickness impacts not only the strength and rigidity of the material but also its weight and ease of handling. For instance, thinner sheets may be ideal for lightweight applications, while thicker sheets are better suited for structural uses, such as in construction or automotive parts. -
Perforation Pattern and Size
The pattern and size of the perforations—round, square, or custom shapes—affect airflow, light transmission, and aesthetic appeal. Buyers should consider how these factors align with their specific needs, such as ventilation in machinery or decorative elements in architecture. Custom patterns may also be available to meet unique specifications. -
Open Area Percentage
This refers to the proportion of the sheet’s surface area that is perforated. A higher open area percentage allows for better airflow and visibility but may reduce structural integrity. B2B buyers need to balance these factors based on the intended application, such as sound insulation or filtration. -
Chemical Resistance
Depending on the material used, perforated plastics can exhibit varying degrees of resistance to chemicals, UV light, and weathering. This property is especially critical for applications in industries like agriculture, automotive, and chemical processing, where exposure to harsh conditions is common. -
Weight and Density
Perforated plastics are generally lighter than traditional materials like steel, with a density often around 0.92 g/cm³. This lightweight nature not only reduces shipping costs but also simplifies handling and installation, making it a favorable choice for many industries.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Perforated Plastic?
Being familiar with industry jargon can enhance communication and facilitate smoother transactions. Here are some essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
In the context of perforated plastic, an OEM refers to a company that produces components or products using perforated plastic sheets. Understanding this term helps buyers identify potential manufacturers for their specific applications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. This is crucial for buyers to know, as it can affect budgeting and inventory management. Some suppliers may offer flexibility, while others may have strict MOQs based on production capabilities. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products, such as perforated plastic sheets. Buyers should provide detailed specifications in their RFQ to ensure accurate and competitive quotes. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms is essential for understanding shipping costs, insurance, and delivery responsibilities, which can significantly impact the total cost of procurement. -
Lead Time
This term refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is critical for project planning and inventory management, especially in industries with tight deadlines. -
Customization
Customization refers to the ability to modify perforated plastic sheets to meet specific requirements. This may include changes in perforation patterns, dimensions, or material properties. Knowing the extent of customization options can help buyers tailor solutions to their unique needs.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the perforated plastic market more effectively, ensuring they select the right products for their applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the perforated plastic Sector
What are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Influencing Perforated Plastic Sourcing?
The global market for perforated plastic is being shaped by several key drivers. The increasing demand for lightweight and corrosion-resistant materials across various industries—including food processing, automotive, and construction—positions perforated plastic as a favorable alternative to traditional materials like metal. Moreover, rapid urbanization and infrastructural development in emerging markets such as Nigeria and Saudi Arabia are propelling the need for versatile materials that can meet diverse applications, from ventilation systems to architectural designs.
Emerging technologies, including advanced manufacturing techniques like 3D printing and automation, are enhancing the customization capabilities of perforated plastic products. This allows suppliers to offer tailored solutions that meet specific client needs, which is particularly appealing to B2B buyers looking for unique applications. The trend towards digitization in procurement processes is also gaining traction, with platforms for online sourcing and B2B marketplaces facilitating easier access to suppliers and products globally.
Another significant trend is the focus on supply chain resilience. Disruptions caused by geopolitical tensions and the pandemic have prompted businesses to reassess their sourcing strategies. Buyers are increasingly looking for reliable suppliers with robust logistics capabilities to ensure uninterrupted supply chains, particularly in regions like South America and Europe where market volatility can impact availability.

Illustrative image related to perforated plastic
How is Sustainability Shaping the Perforated Plastic Sector in B2B Transactions?
Sustainability has become a focal point for many B2B buyers in the perforated plastic sector. The environmental impact of plastic production and waste management is prompting companies to seek materials that are not only effective but also eco-friendly. Perforated plastics can be manufactured from recycled materials, and many suppliers are now focusing on sustainability certifications and compliance with environmental regulations.
Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to ethical sourcing and sustainable practices. This includes the use of green materials that minimize environmental harm and the implementation of processes that reduce carbon footprints. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and other eco-labels can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainable practices.
Moreover, there is a growing market for biodegradable and compostable perforated plastics, particularly in regions with stringent environmental regulations. This is especially relevant in Europe, where consumers and businesses alike are pushing for greener alternatives. By adopting sustainable sourcing practices, B2B buyers not only meet regulatory requirements but also enhance their brand reputation, ultimately leading to increased customer loyalty.
What is the Historical Context of Perforated Plastic in B2B Markets?
The evolution of perforated plastic can be traced back to the mid-20th century when advances in polymer science led to the development of various plastic types suitable for perforation. Initially, perforated plastics were primarily used in niche applications, but their versatility and benefits soon gained recognition. By the 1980s, as industries expanded and the need for lightweight, durable materials grew, perforated plastics began to see broader application across sectors such as agriculture, construction, and automotive.
The technological advancements in manufacturing processes, such as CNC machining and laser cutting, have further refined the ability to produce customized perforated designs. This shift has enabled manufacturers to cater to the specific needs of B2B buyers, leading to a more dynamic market where customization and quick turnarounds are possible. As we move into the future, the integration of sustainable practices and innovative technologies will continue to shape the trajectory of the perforated plastic market, making it a key area of interest for international B2B buyers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of perforated plastic
-
How do I choose the right perforated plastic for my application?
Selecting the right perforated plastic involves considering several factors including the specific application, environmental conditions, and desired performance characteristics. Assess the material options, such as polypropylene or polycarbonate, based on their chemical resistance, impact strength, and temperature tolerance. Additionally, consider the perforation pattern and size, as these can affect airflow, light passage, and aesthetic appeal. Consulting with suppliers can provide valuable insights tailored to your needs and ensure optimal functionality. -
What customization options are available for perforated plastic sheets?
Most suppliers offer extensive customization options for perforated plastic sheets, including various hole sizes, shapes, and arrangements to suit specific applications. You can also select dimensions, thicknesses, and colors, allowing for a tailored solution that meets your design and functional requirements. Some manufacturers allow for the combination of different perforation styles on a single sheet, enhancing versatility. Be sure to communicate your exact specifications when placing an order to ensure that the final product aligns with your project needs. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for perforated plastic?
Minimum order quantities for perforated plastic sheets can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on factors such as material type and customization requirements. Generally, MOQs can range from a few sheets to several hundred, particularly for specialized products. It is advisable to inquire directly with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies and whether they offer flexibility for smaller orders, especially for testing or prototype purposes. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing perforated plastic?
Payment terms for B2B purchases of perforated plastic typically vary by supplier and can include options such as upfront payment, payment on delivery, or credit terms extending to 30, 60, or even 90 days. It’s essential to clarify these terms before finalizing any agreements to avoid misunderstandings. Some suppliers may also require a deposit for custom orders. Ensure that you have a clear agreement regarding payment schedules, methods, and any potential penalties for late payments. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when sourcing perforated plastic?
To ensure quality assurance, select suppliers that adhere to recognized industry standards and certifications. Request samples prior to placing large orders to evaluate the material’s performance and suitability for your applications. Additionally, inquire about the supplier’s quality control processes, including testing for durability, chemical resistance, and dimensional accuracy. Establishing a clear communication channel for ongoing quality assessments can also help maintain standards throughout the production process. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing perforated plastic?
When importing perforated plastic, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations in your country. Choose a reliable freight forwarder who understands the specific requirements for transporting plastics, including any potential tariffs or trade restrictions. It’s also vital to coordinate with your supplier to ensure that packaging is suitable for the journey and that all necessary documentation is in order to prevent delays during customs clearance. -
What industries commonly use perforated plastic, and for what applications?
Perforated plastic is utilized across various industries, including food processing, agriculture, automotive, and construction. Common applications include ventilation panels, strainers, filters, and decorative elements in architecture. Its lightweight, corrosion-resistant properties make it ideal for environments where traditional materials may fail. Understanding the diverse applications can help you identify how perforated plastic can enhance your products or operations. -
How do I vet suppliers for perforated plastic products?
To vet suppliers effectively, start by researching their reputation in the industry, including customer reviews and testimonials. Evaluate their experience in producing perforated plastic and their capacity to meet your specific needs. Request references and verify their compliance with industry standards. Engaging in direct communication can also help gauge their responsiveness and willingness to address your concerns. Consider requesting a small trial order to assess product quality and service before committing to larger purchases.
Top 8 Perforated Plastic Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. US Plastic – Polypropylene Perforated Sheeting
Domain: usplastic.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Product Name: Polypropylene Perforated Sheeting
Material: Polypropylene
Color: Natural
Features:
– Rigid with fair impact resistance
– Very good abrasion resistance
– Not UV stabilized
– Excellent corrosion resistance to a wide range of items
Forming Temperature: 310°F to 325°F
Temperature Range: 40°F to 210°F
Standards: Meets FDA standards
Cut Tolerance: ±1/4″
Hole Tolerance: ±0.005″ (1/16″ thic…
2. McMaster – Perforated Plastic Sheets
Domain: mcmaster.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, McMaster – Perforated Plastic Sheets, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. 1800 Ceiling – Plastic & Perforated Tiles
Domain: 1800ceiling.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Plastic tiles and perforated tiles for ceilings, available in various styles and designs, suitable for commercial and residential applications. Features include lightweight construction, easy installation, and sound absorption properties. Ideal for enhancing aesthetics and functionality in spaces such as offices, schools, and retail environments.
4. Roechling – Custom Perforated Plastic Sheets
Domain: roechling.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Perforated plastic sheets custom-tailored for various applications with different perforations, shapes, dimensions, and free surfaces. Form options include square and round shapes. Lengths up to 4 m, widths up to 2,500 mm, and thicknesses from 2 to 8 mm. Standard colors are grey and natural, with other colors available upon request. Surface options include smooth on both sides or one-sided grained…
5. Ametco – Perforated Plastic Solutions
Domain: ametco.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Perforated plastic is available in stock sheets or can be custom perforated. It comes in polypropylene (variety of colors) and PVC (dark grey, type 1 – class 1). It is lighter and more corrosive-resistant than perforated steel, suitable for various applications including acoustical wall and ceiling projects, railing systems, sun shades, and decorative design elements. The perforated patterns and o…
6. US Packaging – Perforated All Purpose Plastic Wrap
Domain: uspackagingandwrapping.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Perforated All Purpose Plastic Wrap
Price Range: $23.03 – $51.77
Shipping: Ships Within 24 Hours
Discounts: Available for 5 or More Rolls
Thickness: 35 gauge
Applications: Suitable for kitchens, delis, bakeries, hair salons, printers, and more.
Product Sizes and Details:
– SKU: WP-301, Size: 6″x5″, Sheets/Roll: 3000, Weight: 1.6 LBS, Price: $23.03, Sale Price: $19.50
– SKU: WP-304, Size: 8″x8″, Sh…
7. Direct Metals – Perforated Plastic
Domain: directmetals.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Perforated plastic is a sheet of plastic that contains holes punched by a die. Key features include: economical, lightweight with corrosive resistant properties, versatile, chemical resistant properties, aesthetically appealing, allows for passage of air, light, sound, and gases, easy to fabricate, impact resistant (will not dent like metal), and flexible. Available in a variety of gauges, hole si…
8. Reddit – Perforated Plastic Canvas
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Perforated plastic canvas is available in various counts (ct) such as 7ct, 10ct, and 14ct. It can be found in different colors including white, clear, black, and several others (light blue, blue, orange, brown, yellow, magenta, light pink, purple, green). Prices range from $1.50 to $3 per sheet depending on the color and site. Amazon, Michaels, JoAnn’s, and Aliexpress are suggested sources for pur…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for perforated plastic
In summary, perforated plastic offers a multitude of advantages for diverse industries, including lightweight construction, corrosion resistance, and ease of customization. These features make perforated plastic an attractive alternative to traditional materials like metal, especially for applications in food processing, automotive, and construction. Strategic sourcing of perforated plastic is essential for international B2B buyers to ensure access to high-quality materials tailored to specific needs.
As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to evolve, the demand for versatile and cost-effective solutions will only grow. Buyers should prioritize establishing relationships with suppliers who can provide customized solutions, from varying thicknesses to unique perforation patterns.
Looking ahead, the potential for innovation in perforated plastic applications is vast. Embrace these opportunities by collaborating with manufacturers who understand your local market dynamics and can deliver cutting-edge solutions. Take the first step towards enhancing your operational efficiency and product quality by exploring the vast offerings in perforated plastic today.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to perforated plastic
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.