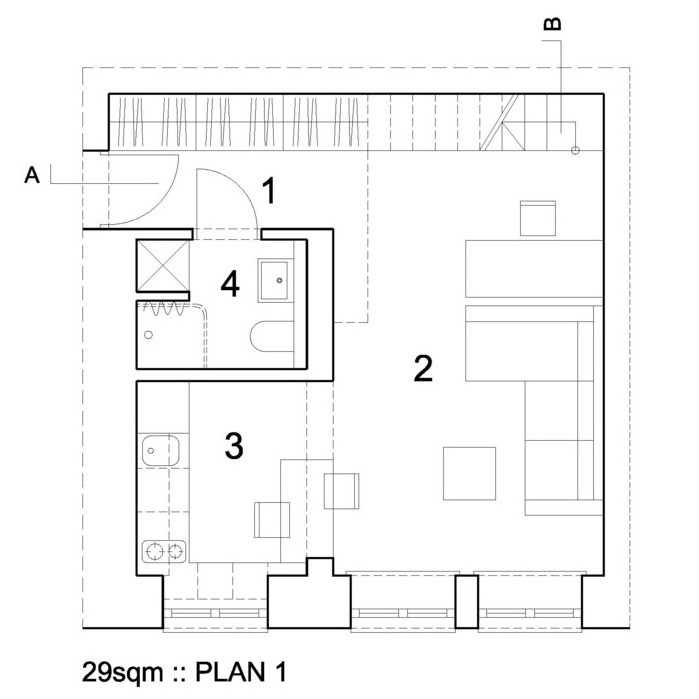
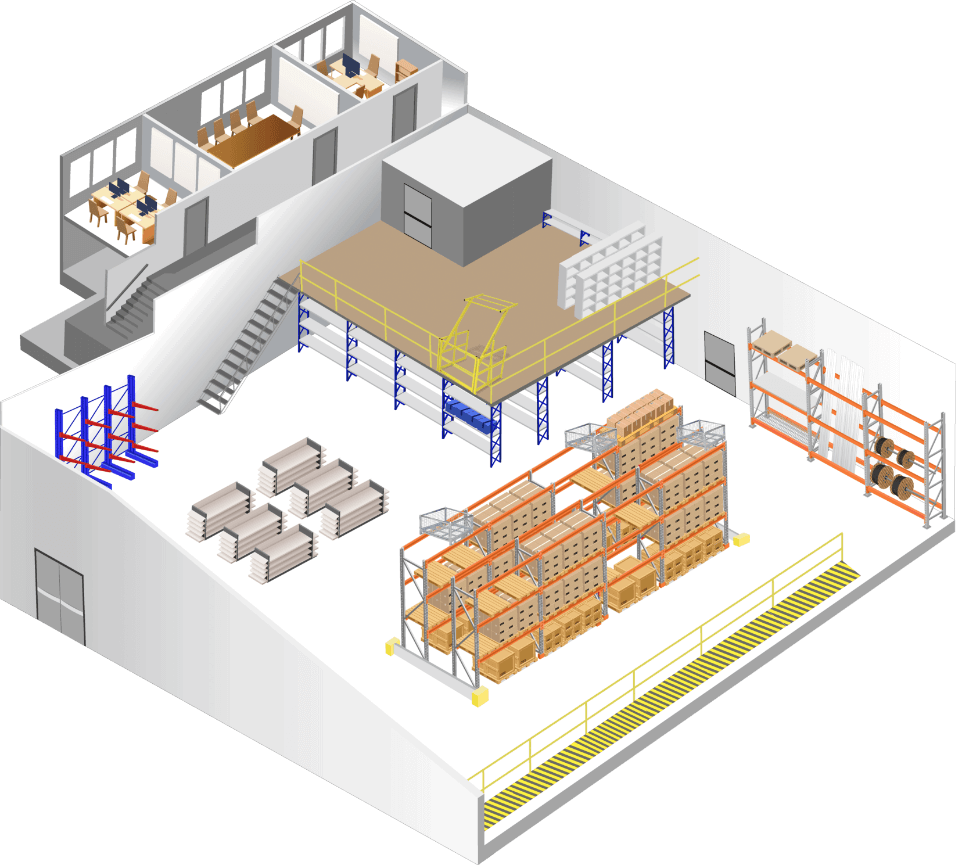
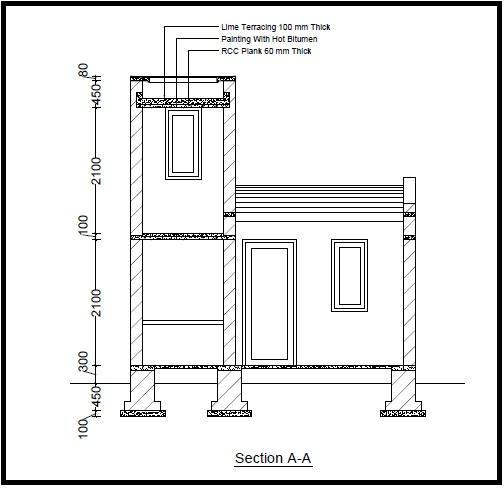
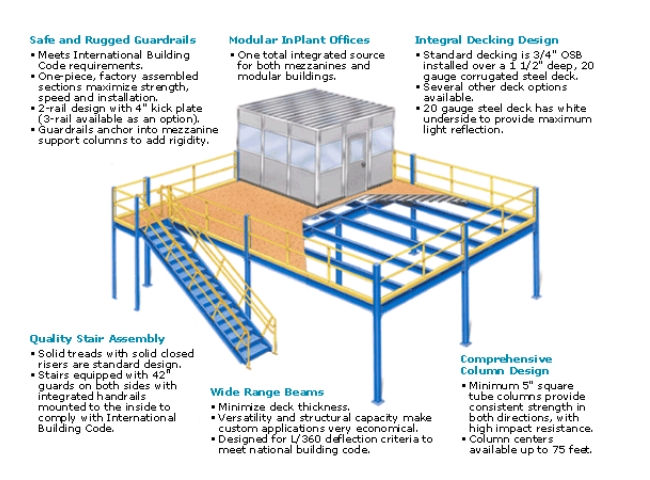
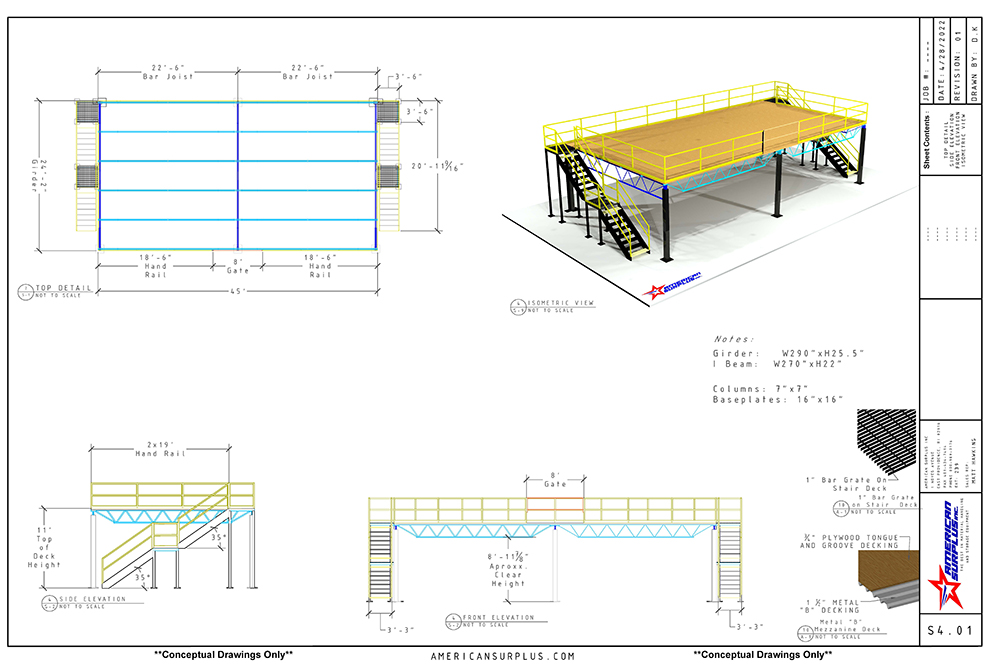
A Deep Dive into Mezzanine Plan Solution
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for mezzanine plan
In today’s fast-paced global economy, businesses face the challenge of optimizing space utilization while maintaining operational efficiency. Sourcing a mezzanine plan that meets specific needs can significantly enhance storage capabilities or office layouts, offering a strategic advantage in competitive markets. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Saudi Arabia and Brazil.
Within this guide, we will explore various types of mezzanine designs, their applications across different industries, and the critical factors to consider when evaluating suppliers. From understanding local regulations and compliance standards to assessing the cost implications of mezzanine installations, our insights will help you navigate the complexities of this investment.
By empowering you with actionable strategies and expert recommendations, this guide aims to facilitate informed purchasing decisions, ensuring that your mezzanine solution aligns with your business goals. Whether you are seeking to enhance operational efficiency, expand storage capacity, or create collaborative workspaces, this resource will equip you with the knowledge needed to make confident and strategic choices in the global market for mezzanine plans.
Understanding mezzanine plan Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Storage Mezzanine | Optimized for heavy loads, often open-plan design | Warehouses, distribution centers | Pros: Maximizes vertical space, cost-effective. Cons: Requires careful load planning. |
| Office Mezzanine | Designed for office environments, includes partitions | Corporate offices, coworking spaces | Pros: Enhances workspace efficiency, improves aesthetics. Cons: May require additional HVAC solutions. |
| Retail Mezzanine | Integrated into retail spaces, often open to below | Shopping malls, boutiques | Pros: Increases sales floor area, attracts customers. Cons: Can complicate customer flow. |
| Industrial Mezzanine | Heavy-duty construction, often with equipment access | Factories, manufacturing plants | Pros: Supports heavy machinery, durable. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Custom Mezzanine | Tailored design based on specific needs | Various industries | Pros: Fully adaptable to business needs. Cons: Potentially longer lead times and higher costs. |
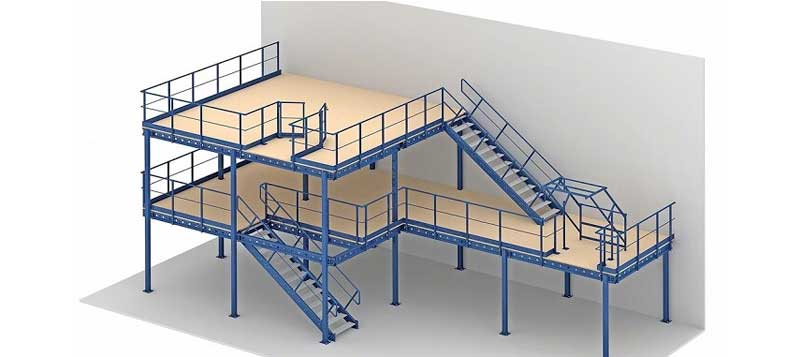
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Storage Mezzanines?
Storage mezzanines are primarily designed to accommodate heavy loads and maximize vertical space in warehouses and distribution centers. They typically feature an open-plan design, allowing for easy access to stored items. When considering a storage mezzanine, B2B buyers should assess the load-bearing capacity and the layout to ensure efficient operations. These mezzanines are ideal for businesses looking to optimize storage without expanding their footprint, making them a cost-effective solution for inventory management.
How Do Office Mezzanines Enhance Workspace Efficiency?
Office mezzanines are tailored for corporate environments, often incorporating partitions and ergonomic designs. They are ideal for businesses that require additional office space without relocating. Buyers should consider factors such as HVAC integration and compliance with local building codes when planning an office mezzanine. The primary advantage of this type is the enhancement of workspace efficiency and aesthetics, which can lead to increased employee satisfaction and productivity.
Illustrative image related to mezzanine plan
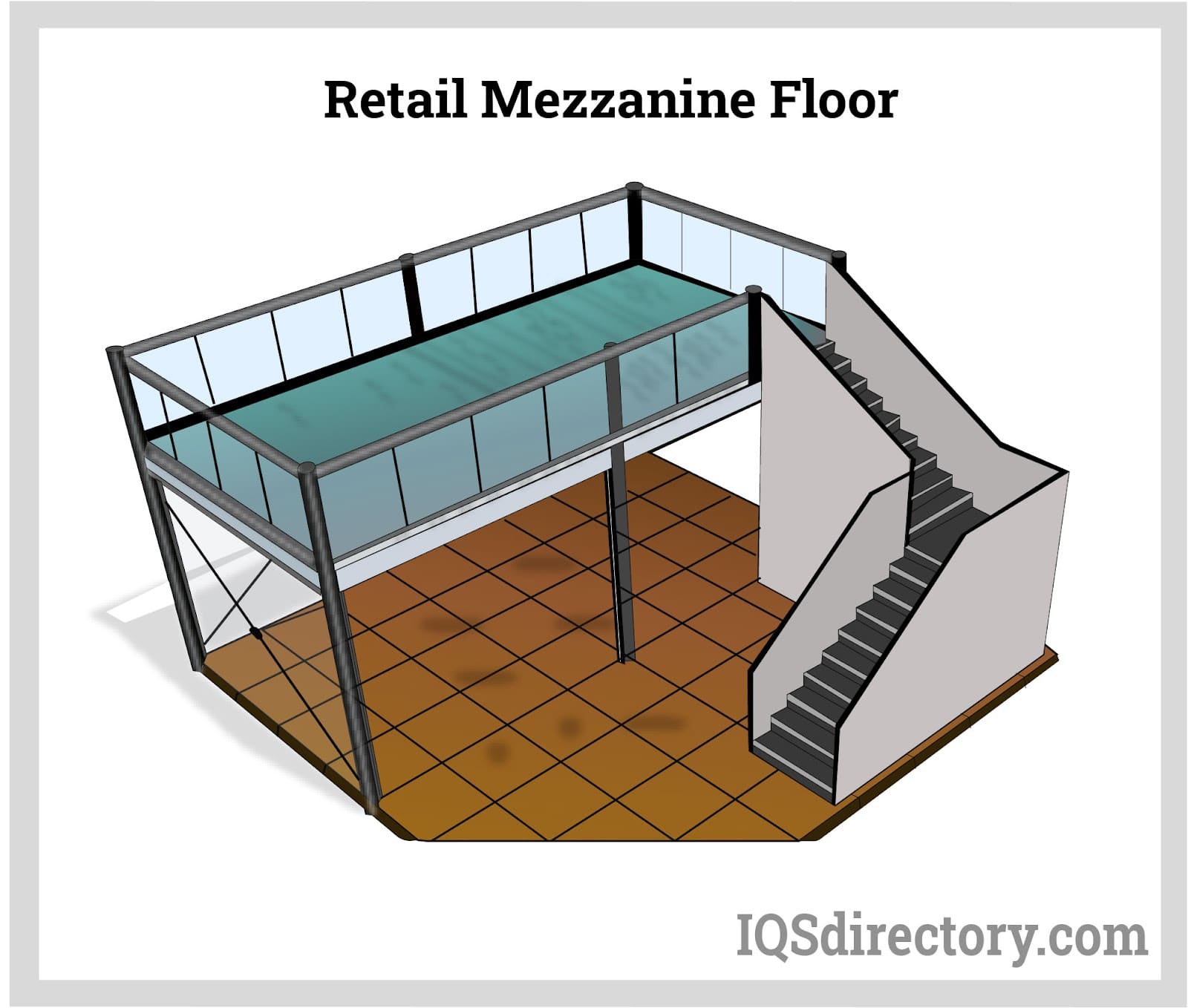
What Advantages Do Retail Mezzanines Offer to Businesses?
Retail mezzanines are strategically integrated into retail spaces, providing additional sales floor area while maintaining an open feel. They are particularly beneficial in shopping malls and boutiques, where attracting customers is crucial. B2B buyers should evaluate how a retail mezzanine can enhance customer flow and visibility. While they can significantly increase sales potential, careful planning is required to avoid complicating customer navigation through the space.
Why Choose Industrial Mezzanines for Heavy-Duty Applications?
Industrial mezzanines are constructed to support heavy machinery and equipment, making them suitable for factories and manufacturing plants. They are designed with durability and load-bearing capacity in mind. When purchasing an industrial mezzanine, businesses should assess their specific machinery requirements and the structural integrity of the existing building. While these mezzanines come with a higher initial investment, their long-term durability and functionality can lead to significant operational efficiencies.
What are the Benefits of Custom Mezzanines for Diverse Industries?
Custom mezzanines are tailored to meet the specific needs of various industries, providing a unique solution for businesses with specialized requirements. They can be designed for storage, office use, or even retail applications. B2B buyers should be prepared for potentially longer lead times and higher costs associated with custom designs. However, the flexibility and adaptability of custom mezzanines can provide significant competitive advantages, allowing businesses to optimize their space efficiently.

Illustrative image related to mezzanine plan
Key Industrial Applications of mezzanine plan
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of mezzanine plan | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Warehousing and Logistics | Additional storage space for inventory management | Maximizes vertical space, reducing the footprint needed for storage | Load capacity, safety compliance, and ease of access |
| Manufacturing | Elevated workstations for assembly lines | Improves workflow efficiency and safety for workers | Structural integrity, material selection, and space planning |
| Retail | Customer engagement areas above sales floors | Enhances shopping experience and can increase sales volume | Design aesthetics, accessibility, and compliance with regulations |
| Food and Beverage | Storage for equipment and ingredients | Optimizes operational efficiency and space utilization | Hygiene standards, load-bearing requirements, and ease of cleaning |
| Construction | Temporary office spaces for project management | Provides flexible and scalable workspace solutions | Compliance with safety standards, mobility, and design adaptability |
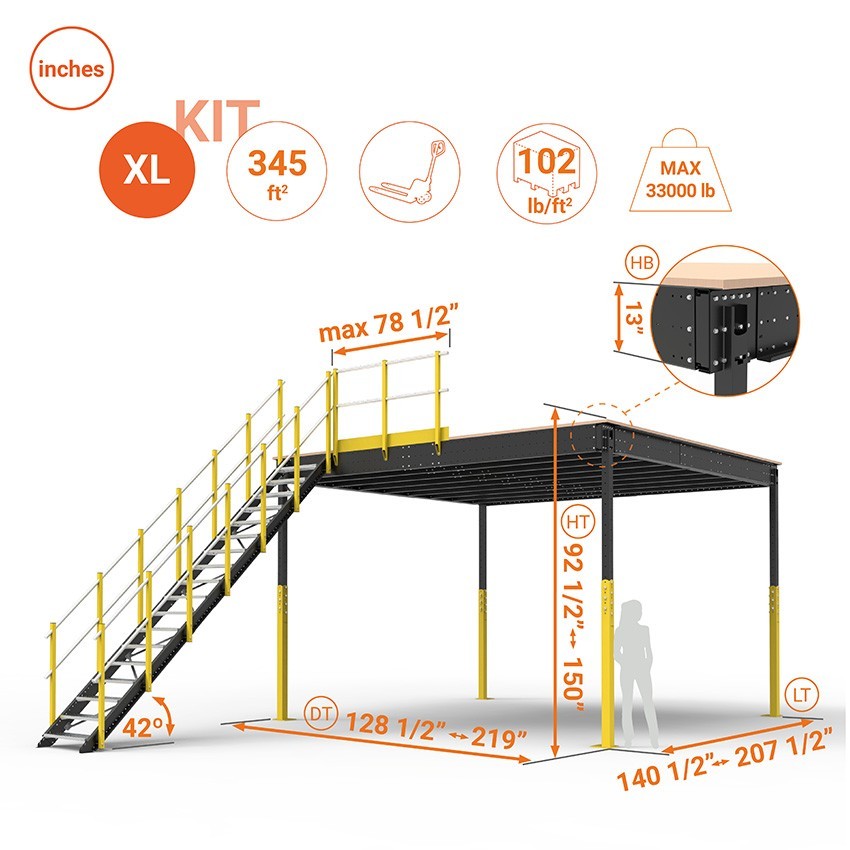
How Can a Mezzanine Plan Enhance Warehousing and Logistics?
In the warehousing and logistics sector, mezzanine plans are primarily utilized to create additional storage space without expanding the building’s footprint. This is crucial for businesses that experience fluctuating inventory levels. By maximizing vertical space, companies can store more products, thereby reducing the need for costly expansion. Buyers in this sector should focus on load capacity and safety compliance, ensuring the mezzanine can support the intended weight while providing easy access for personnel and equipment.
What Role Does a Mezzanine Plan Play in Manufacturing?
In manufacturing, mezzanine floors serve as elevated workstations that facilitate assembly line operations. These structures help streamline workflows by reducing the distance workers need to travel between tasks. Moreover, they can enhance safety by keeping heavy machinery and tools at a designated height, minimizing hazards. Buyers should prioritize structural integrity and material selection to ensure the mezzanine can withstand the operational demands of the manufacturing environment.
How Does a Mezzanine Plan Improve Retail Spaces?
Retail environments benefit from mezzanine plans by creating engaging customer areas above sales floors. This design not only adds aesthetic value but also increases sales potential by providing additional space for product displays or relaxation zones. International buyers should consider design aesthetics and accessibility features to ensure the mezzanine complements the overall shopping experience while adhering to local regulations.

Illustrative image related to mezzanine plan
What Are the Benefits of a Mezzanine Plan in Food and Beverage Industries?
In the food and beverage sector, mezzanine floors are often used to store equipment and ingredients, optimizing the use of space in often crowded facilities. This allows businesses to keep their operations efficient and organized, which is essential for maintaining hygiene standards. Buyers need to focus on load-bearing requirements and ease of cleaning when sourcing mezzanine solutions, ensuring compliance with health regulations.
How Can a Mezzanine Plan Support Construction Projects?
For construction firms, mezzanine plans can provide temporary office spaces for project management teams, facilitating better communication and oversight on-site. This flexibility allows companies to adapt to changing project needs without significant investment in permanent structures. Buyers should ensure compliance with safety standards and consider mobility features, allowing the mezzanine to be relocated as project demands shift.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘mezzanine plan’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Complex Regulations for Mezzanine Plans
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter challenges when trying to comply with local building codes and regulations for mezzanine installations. Different regions, especially in diverse markets like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, have varying requirements regarding height, load capacity, and safety features. This can lead to significant delays, increased costs, and even project cancellations if regulations are not adequately addressed from the outset.
The Solution: To effectively navigate these complexities, buyers should begin by thoroughly researching local building codes specific to mezzanine structures in their region. Collaborating with local architects or structural engineers who understand these regulations can provide invaluable insight. When sourcing a mezzanine plan, ensure it includes detailed compliance information and structural specifications that align with local requirements. Additionally, consider engaging a consultant who specializes in mezzanine designs to conduct an initial assessment of your site. This proactive approach will help avoid costly modifications later and ensure that your mezzanine installation is both safe and compliant.
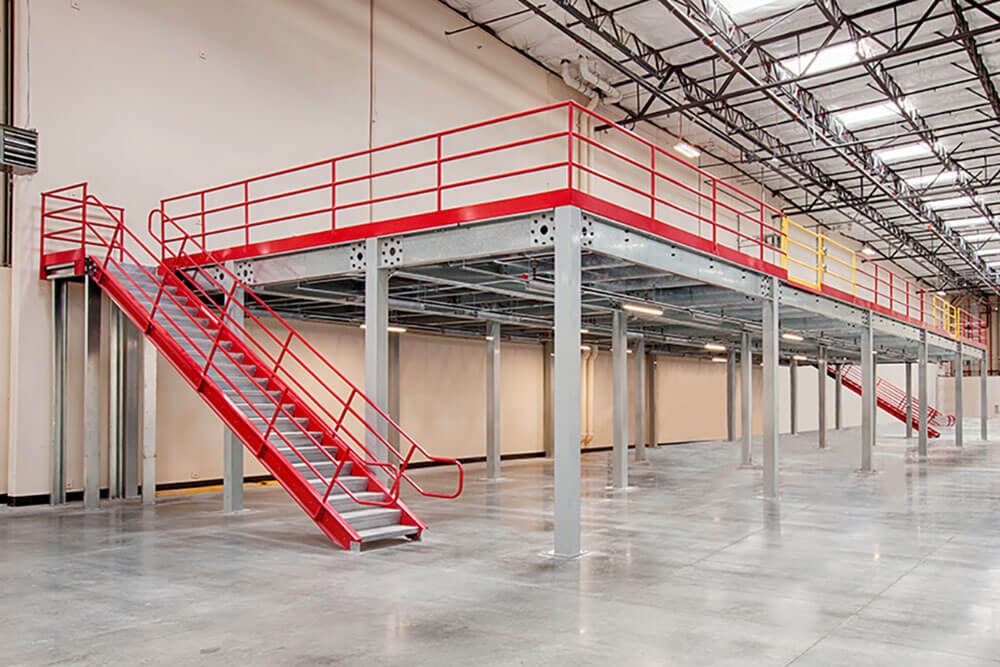
Scenario 2: Maximizing Space Utilization While Maintaining Safety
The Problem: Many businesses face difficulties in optimizing their available space when planning a mezzanine. The challenge lies not only in maximizing storage or office areas but also in ensuring that the design adheres to safety standards. Poorly designed mezzanines can lead to overcrowding, inadequate access, and even safety hazards, particularly in industrial settings where heavy equipment is used.

Illustrative image related to mezzanine plan
The Solution: To address this, buyers should first define the primary purpose of the mezzanine—whether for storage, office space, or both. This clarity will guide the design process. Implementing a robust layout that includes spacious staircases and clear access points is crucial for safety and functionality. When selecting a mezzanine plan, prioritize designs that include safety features such as load-bearing calculations, guardrails, and emergency exits. Engaging a professional to perform a load assessment can further ensure that the mezzanine can safely accommodate the intended use. Conducting regular safety audits post-installation will also help maintain compliance and ensure the safety of all personnel using the space.
Scenario 3: Choosing the Right Materials for Longevity and Cost-Efficiency
The Problem: Selecting the appropriate materials for a mezzanine plan can be a daunting task for B2B buyers, especially when balancing cost, durability, and aesthetic appeal. In regions with varying climates, the chosen materials must withstand local environmental conditions while also adhering to budget constraints. This decision can significantly impact the overall success and lifespan of the mezzanine.
The Solution: To make informed material choices, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of the specific environmental factors that will affect the mezzanine. For example, in humid regions, opting for corrosion-resistant materials like galvanized steel may be more cost-effective in the long run, despite higher upfront costs. Engage suppliers who can provide samples and technical specifications, ensuring that the materials chosen meet both structural and aesthetic requirements. Additionally, consider the long-term maintenance costs associated with different materials, as some may require more frequent upkeep than others. By prioritizing high-quality, durable materials that align with the intended use and environmental factors, buyers can ensure a cost-efficient and long-lasting mezzanine solution.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for mezzanine plan
What Are the Key Materials for Mezzanine Plans?
When planning a mezzanine floor, selecting the appropriate materials is crucial for ensuring structural integrity, safety, and functionality. Below, we analyze four common materials used in mezzanine construction, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
Illustrative image related to mezzanine plan
Steel: The Backbone of Mezzanine Structures
Key Properties: Steel is renowned for its high strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for load-bearing applications. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 500°F (260°C) and exhibits excellent corrosion resistance when treated with protective coatings.
Pros & Cons: The durability of steel is unmatched, ensuring longevity and minimal maintenance. However, the initial cost can be high, and the manufacturing process may be complex, requiring specialized equipment. Steel is suitable for heavy-duty applications, but its weight can complicate installation.
Impact on Application: Steel mezzanines are particularly effective in environments where heavy loads are anticipated, such as warehouses and manufacturing facilities. They can support various media, including machinery and storage systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local standards such as ASTM in the U.S. or EN standards in Europe is essential. Buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East should also consider the availability of local suppliers and the potential for corrosion due to humidity.
Concrete: A Solid Choice for Stability
Key Properties: Concrete offers excellent compressive strength and can withstand high temperatures. It is also resistant to fire and moisture, making it suitable for various environments.
Illustrative image related to mezzanine plan
Pros & Cons: While concrete is highly durable and provides a solid foundation, it is also heavy and can be costly to transport and install. The complexity of forming and curing can extend project timelines.
Impact on Application: Concrete is ideal for mezzanines that require stability and durability, particularly in industrial settings. Its compatibility with heavy loads makes it a go-to choice for storage and operational areas.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local building codes and standards, such as DIN in Germany or JIS in Japan. In developing regions, the availability of skilled labor for installation may also be a concern.
Illustrative image related to mezzanine plan
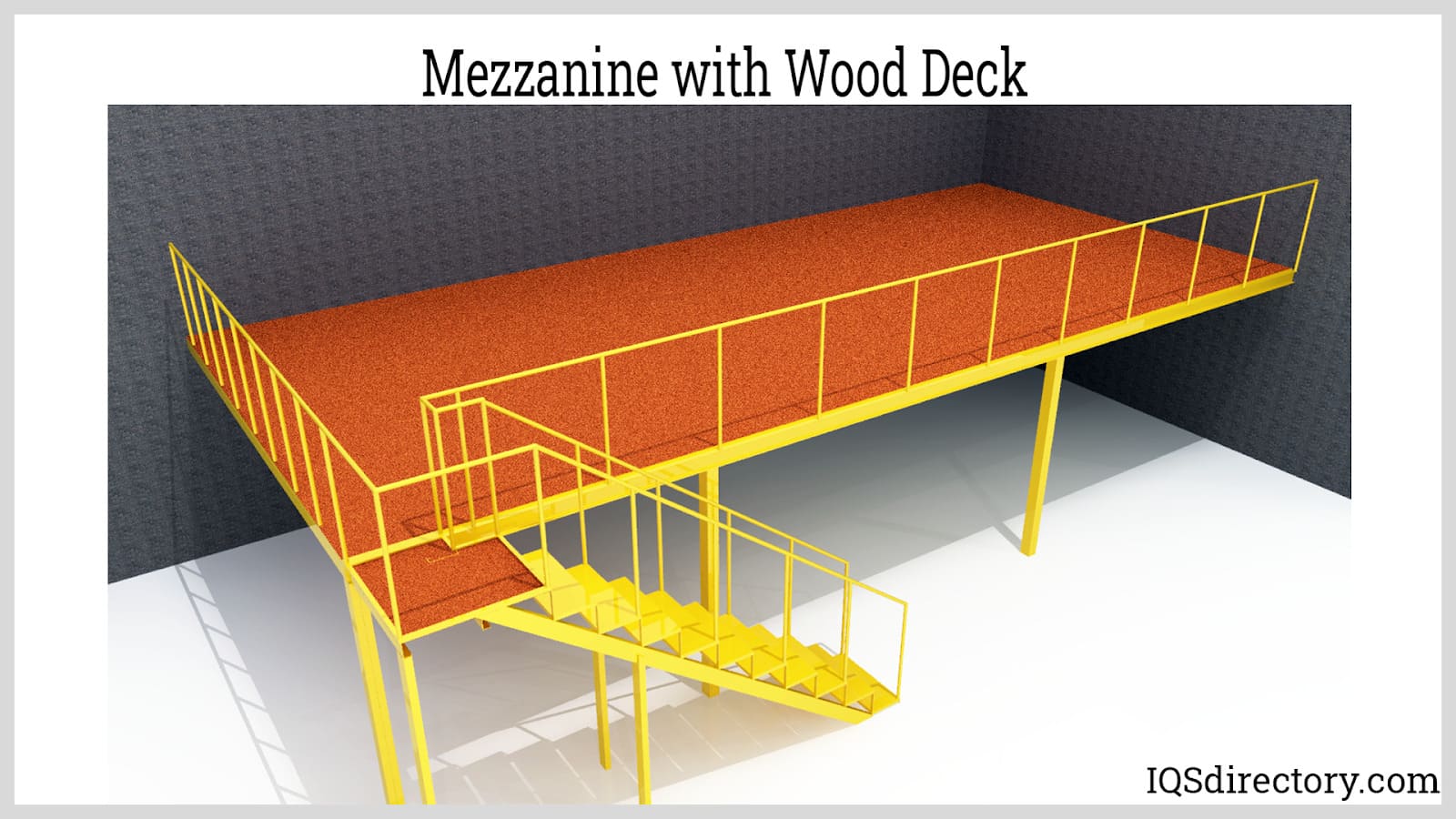
Wood: A Versatile and Aesthetic Option
Key Properties: Wood is lightweight and offers good insulation properties. Its load-bearing capacity varies depending on the type of wood used, with engineered wood products like LVL (Laminated Veneer Lumber) providing enhanced strength.
Pros & Cons: Wood is often more cost-effective than steel or concrete and offers aesthetic appeal. However, it is less durable in high-moisture environments and may require regular maintenance to prevent rot and pest damage.
Impact on Application: Wood mezzanines are suitable for office spaces, retail environments, or areas where aesthetics are important. They can support lighter loads, making them less ideal for heavy industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local fire safety codes is crucial, particularly in regions with stringent regulations. Buyers should also consider the sustainability of wood sources, especially in markets sensitive to environmental issues.
Aluminum: Lightweight and Corrosion-Resistant
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has a high strength-to-weight ratio. It can withstand temperatures up to 400°F (204°C) without significant degradation.
Pros & Cons: Aluminum is easy to work with and can be fabricated into various shapes, making it suitable for custom designs. However, it is generally more expensive than steel and may not support as heavy a load.
Impact on Application: Aluminum mezzanines are ideal for environments where corrosion is a concern, such as in chemical plants or coastal areas. They are also suitable for temporary structures due to their lightweight nature.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards like ASTM and ISO is important. Buyers in regions with high humidity should ensure that the aluminum is adequately treated to prevent oxidation.
Illustrative image related to mezzanine plan
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for mezzanine plan | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty industrial applications | High strength-to-weight ratio | High initial cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Concrete | Industrial storage and operational areas | Excellent durability and fire resistance | Heavy and costly to transport/install | Medium |
| Wood | Office spaces and retail environments | Cost-effective and aesthetically pleasing | Less durable in high-moisture environments | Low |
| Aluminum | Corrosion-prone environments | Lightweight and easy to fabricate | Generally more expensive than steel | High |
Selecting the right material for a mezzanine plan is essential for meeting specific operational needs while ensuring compliance with local regulations. By understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their project requirements.
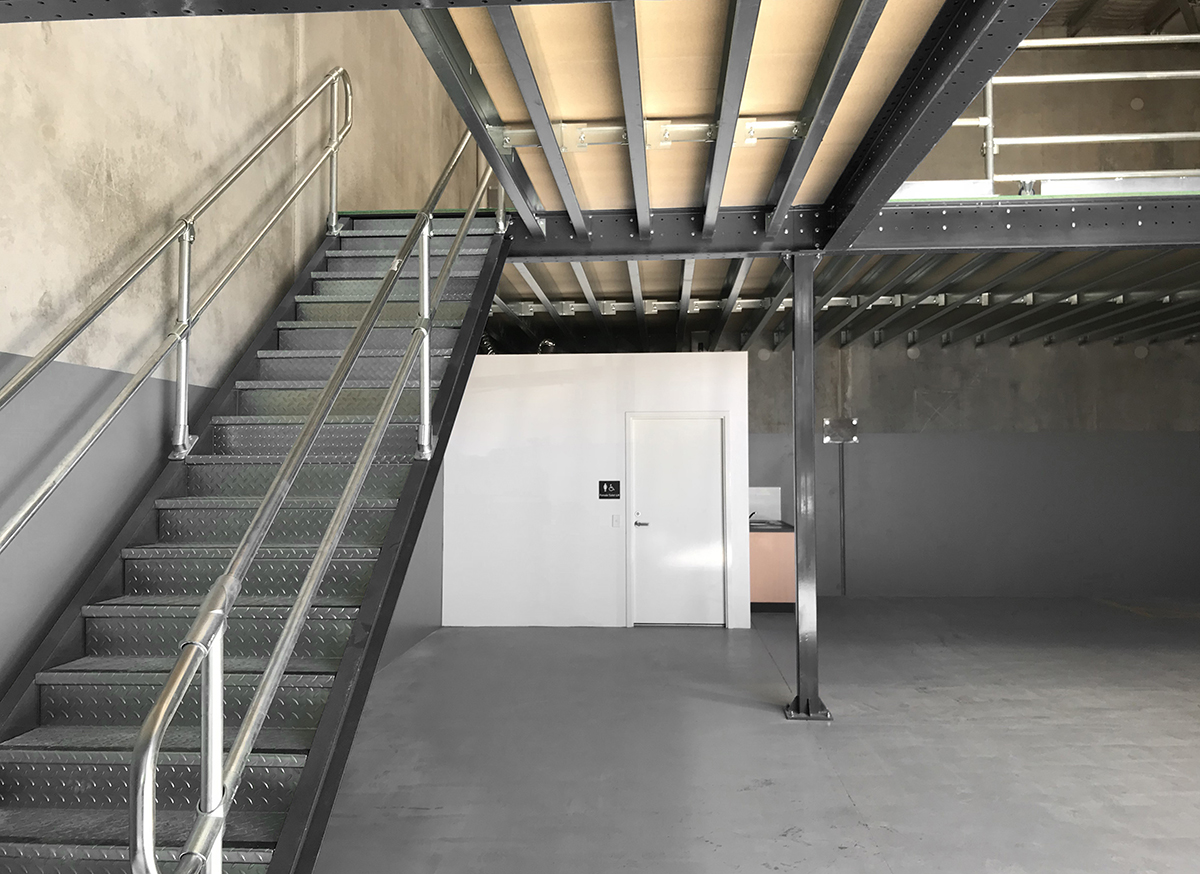
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for mezzanine plan
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Mezzanine Plans?
The manufacturing process for mezzanine plans involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets quality and performance standards. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Mezzanine Construction?
Material preparation is the initial step in the manufacturing process, where raw materials are selected based on the specific requirements of the mezzanine plan. Common materials include steel, aluminum, and timber. Each material undergoes inspection to ensure compliance with specifications. For steel structures, this may involve checking for impurities or structural integrity through non-destructive testing methods.
Once the materials are verified, they are cut and shaped to the required dimensions. This step often employs precision cutting techniques, such as laser cutting or plasma cutting, to ensure accuracy. For timber, preparation might include drying and treating the wood to enhance durability and resistance to pests and moisture.
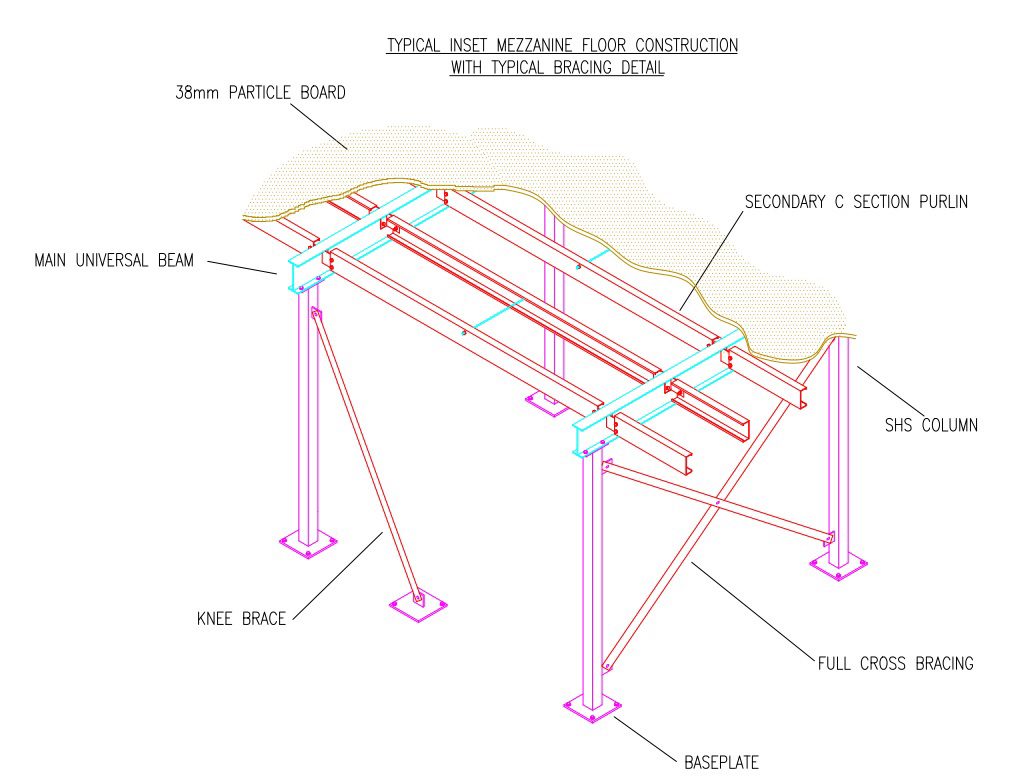
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Mezzanine Structures?
Forming is the next stage, where the prepared materials are transformed into the structural components of the mezzanine. Techniques such as welding, bending, and machining are commonly used, particularly for steel mezzanines. Advanced welding technologies, including MIG and TIG welding, ensure strong joints that can support heavy loads.
Illustrative image related to mezzanine plan
For timber mezzanines, forming may include joinery techniques, such as mortise and tenon or dovetail joints, which enhance structural integrity. Additionally, computer numerical control (CNC) machines are often employed to achieve precise cuts and shapes, ensuring uniformity across all components.
How Is Assembly Conducted in Mezzanine Manufacturing?
The assembly stage is where the formed components come together to create the mezzanine structure. Skilled labor is essential here, as workers must follow detailed assembly plans to ensure the structure’s stability and safety. This stage often includes the installation of load-bearing elements, such as beams and columns, which must be aligned accurately to distribute weight evenly.
During assembly, quality checkpoints are crucial. Companies typically conduct inspections at various stages to verify that components fit as intended and meet design specifications. These inspections are often documented to provide a traceable quality history.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied to Mezzanine Structures?
Finishing is the final stage in the manufacturing process, where the mezzanine is prepared for delivery and installation. This may involve surface treatments such as painting, powder coating, or galvanizing to protect against corrosion and wear. Finishing not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the mezzanine but also ensures longevity, particularly in environments subject to humidity or chemical exposure.
Quality control during finishing includes visual inspections to check for uniformity and adherence to specified finishes. Companies may also perform adhesion tests for coatings to ensure they will withstand environmental conditions.
What Are the Quality Assurance Standards Relevant to Mezzanine Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in mezzanine manufacturing, ensuring that products meet both international and industry-specific standards. International standards such as ISO 9001 are commonly implemented, focusing on quality management systems that enhance customer satisfaction through effective process management.
Which Industry-Specific Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
In addition to ISO 9001, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking (for European markets) and API standards (for petroleum and natural gas industries) may apply. These certifications signify compliance with safety and performance requirements, which is essential for B2B buyers looking to ensure reliability in their investments.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) encompasses several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process, typically categorized into Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), and Final Quality Control (FQC).
How Does Incoming Quality Control (IQC) Function?
IQC involves inspecting raw materials upon delivery to ensure they meet predefined specifications. This can include physical inspections, material tests, and verification of certification documents. For B2B buyers, understanding the IQC processes of suppliers can provide insights into the reliability of the materials used in mezzanine construction.
What Is In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)?
IPQC occurs during the manufacturing process and includes regular inspections at various stages of production. This ensures that any deviations from the design or quality standards are caught early, minimizing waste and rework. B2B buyers should inquire about the frequency and methods of IPQC used by their suppliers to gauge their commitment to maintaining quality throughout production.
How Is Final Quality Control (FQC) Conducted?
FQC is conducted after assembly and finishing, ensuring the final product meets all specifications and quality standards. This may involve load testing, dimensional checks, and surface quality assessments. For international buyers, understanding FQC procedures can help ensure the products meet their specific requirements before shipment.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control measures implemented by their suppliers. This can include:
-
Conducting Supplier Audits: Regular audits can help assess the effectiveness of a supplier’s quality management system. Buyers should focus on the supplier’s compliance with international standards and their internal QC processes.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their QC processes, including inspection reports and certifications. This transparency can build trust and ensure that buyers are informed about the quality of the products they are purchasing.
-
Engaging Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality practices. These inspectors can conduct thorough assessments and generate reports that highlight any areas of concern.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is crucial to understand the nuances of quality control in international trade. Differences in regulatory requirements, cultural expectations, and logistical challenges can impact the quality assurance process.
Illustrative image related to mezzanine plan
How Do Regulatory Differences Affect Quality Assurance?
Regulatory standards can vary significantly across regions. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations regarding construction and safety to ensure compliance. This may involve understanding specific codes that govern mezzanine installations in their respective countries.
What Cultural Considerations Should Be Accounted For?
Cultural differences can influence communication and expectations around quality. Establishing clear lines of communication and understanding the local business culture can help foster better relationships with suppliers, leading to improved quality outcomes.
By prioritizing a robust understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with mezzanine plans, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and quality standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘mezzanine plan’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of a mezzanine plan requires careful consideration and strategic planning. This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist to assist B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse international markets, in sourcing effective mezzanine solutions tailored to their specific needs. By following these steps, you can ensure that your investment leads to a functional and compliant space that maximizes your operational efficiency.

Illustrative image related to mezzanine plan
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before you begin sourcing, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of your requirements. Determine the purpose of the mezzanine—whether for storage, office space, or another function—as this will influence the design and structural needs.
- Consider load-bearing requirements: Identify the weight capacity necessary for your intended use, ensuring the structure can support both personnel and equipment.
- Assess height and clearance: Establish the required dimensions to comply with local regulations while ensuring usability.
Step 2: Research and Shortlist Potential Suppliers
With your specifications defined, start researching suppliers who specialize in mezzanine solutions. Look for companies with a strong track record in your industry and region.
- Seek industry-specific experience: Suppliers familiar with the unique challenges of your sector can offer tailored solutions.
- Check online reviews and testimonials: Investigate feedback from previous clients to gauge reliability and service quality.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region.
- Assess previous projects: Look for examples of completed mezzanine installations that align with your vision.
- Verify financial stability: Ensure that the supplier is financially sound, which can be crucial for project continuity.
Step 4: Request Detailed Proposals
Once you’ve narrowed down your options, ask for detailed proposals from your shortlisted suppliers. This should include design plans, material specifications, and timelines.
Illustrative image related to mezzanine plan
- Compare costs and offerings: Ensure that proposals are comprehensive, allowing for side-by-side comparisons.
- Evaluate design flexibility: Assess whether suppliers can adapt their designs to meet your evolving needs.
Step 5: Verify Compliance with Local Regulations
Compliance with local building codes and safety regulations is non-negotiable. Ensure that any proposed mezzanine plans adhere to these standards.
- Request proof of compliance: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation that demonstrates their understanding of local requirements.
- Consider the need for permits: Discuss the process of obtaining necessary permits and whether the supplier assists in this area.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Before finalizing any agreement, negotiate the terms and conditions to protect your interests. This includes delivery timelines, payment schedules, and warranties.
- Clarify after-sales support: Understand what support and maintenance services are included post-installation.
- Address potential delays: Establish a clear plan for managing any unforeseen issues that may arise during the project.
Step 7: Finalize Contracts and Monitor Progress
Once you’ve agreed on terms, finalize contracts with your chosen supplier. Ensure all details are clearly outlined and agreed upon.
- Establish a communication plan: Regular updates and open lines of communication will help manage expectations and resolve issues promptly.
- Monitor the project closely: Regularly check the progress against the timeline to ensure the project remains on track.
By following these steps, you can confidently procure a mezzanine plan that meets your operational needs while ensuring compliance and efficiency.
Illustrative image related to mezzanine plan
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for mezzanine plan Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics for sourcing mezzanine plans is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This section delves into the various cost components, pricing influencers, and offers strategic buyer tips to help you navigate the procurement process effectively.
What Are the Key Cost Components Involved in Mezzanine Plans?
When sourcing mezzanine plans, several cost components come into play:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. Steel and concrete are common for heavy-duty mezzanines, while lighter options such as timber might be used for smaller installations. Prices can vary based on local availability and market conditions.
-
Labor: Labor costs can fluctuate based on geographical location and the complexity of the mezzanine installation. Regions with higher labor rates may see increased costs, so it’s vital to account for this in your budget.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, equipment depreciation, and facility maintenance. Understanding these costs helps in evaluating the total price offered by suppliers.
-
Tooling: If your mezzanine plan requires custom features or specific tooling, this can add to the overall cost. Investing in specialized tools may be necessary for unique designs, impacting your budget.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the mezzanine meets safety and quality standards incurs additional costs. Engaging third-party inspection services can add to the price but is crucial for compliance, especially for international buyers.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs vary based on the origin of materials and the destination. Factors like shipping methods, distances, and local tariffs play a significant role in determining logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding typical margins in your industry can help you assess whether a quote is reasonable.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Mezzanine Plan Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of mezzanine plans:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Purchasing in larger quantities often leads to price discounts. If your business can commit to higher volumes, negotiate for better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific features can lead to higher costs. Clearly defining your requirements can help avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (such as ISO standards) may increase costs but can enhance durability and safety. Consider the long-term benefits of investing in quality.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, experience, and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their services, but they often provide better support and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of sale (Incoterms) is vital for determining who bears the costs and risks during transport. This knowledge can prevent unexpected expenses from arising during delivery.
What Are Some Effective Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Mezzanine Sourcing?
To maximize cost-efficiency in your mezzanine sourcing, consider the following tips:
-
Negotiation: Always be prepared to negotiate terms and pricing with suppliers. Building a relationship can lead to better offers and terms over time.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO rather than just the upfront price. Consider maintenance, operational costs, and potential resale value when making decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local market conditions that can affect pricing. Collaborating with local experts can provide insights into these dynamics.
-
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices: Prices can vary significantly based on market conditions, local regulations, and supplier terms. Always request updated quotes and verify details before proceeding with orders.
By comprehensively understanding the cost components, pricing influencers, and employing strategic negotiation techniques, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing mezzanine plans, ensuring that they achieve both cost-effectiveness and quality in their investments.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing mezzanine plan With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Mezzanine Plans
In the quest for maximizing space efficiency in commercial and industrial settings, a mezzanine plan is often a popular choice. However, it’s essential for B2B buyers to consider various alternatives that could meet their operational needs more effectively or economically. This section provides a comparative analysis of mezzanine plans against other viable solutions, helping businesses make informed decisions based on performance, cost, implementation ease, maintenance, and best use cases.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Mezzanine Plan | Modular Storage Systems | Vertical Lift Modules |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High load capacity and flexible design for various uses | Moderate load capacity, customizable configurations | High efficiency in vertical transport of goods |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; potential for high ROI | Variable costs based on size and configuration | Higher initial costs due to technology integration |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires structural assessment and permits | Quick installation with minimal disruption | Requires specialized installation and training |
| Maintenance | Low to moderate; periodic inspections necessary | Low; generally requires little upkeep | Moderate; requires occasional servicing |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for creating additional office or storage space | Suitable for dynamic storage needs in constrained spaces | Best for high-density storage and retrieval in warehouses |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Modular Storage Systems
Modular storage systems are flexible and adaptable solutions that can be customized to fit specific storage needs. These systems allow businesses to maximize vertical space and can be reconfigured as requirements change. The ease of installation is a significant advantage, as they can often be set up quickly without extensive downtime. However, their load capacity may not be as high as that of mezzanine floors, making them less suitable for heavy-duty applications.

Illustrative image related to mezzanine plan
Vertical Lift Modules (VLMs)
Vertical lift modules offer a high-tech solution for storage and retrieval, utilizing an automated system to transport items vertically. This technology optimizes space by minimizing the footprint required for storage. VLMs excel in environments where quick access to inventory is crucial, such as distribution centers. However, the upfront costs can be substantial, and the need for specialized installation and training may deter some businesses. The maintenance of VLMs can also be more complex, requiring regular servicing to ensure operational efficiency.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
Selecting the right solution for space optimization hinges on specific operational needs, budget constraints, and long-term goals. Mezzanine plans offer a blend of flexibility and load capacity, making them ideal for many businesses looking to expand their facilities without significant structural changes. Alternatively, modular storage systems provide a quick and adaptable solution for dynamic storage needs, while vertical lift modules cater to high-density environments where speed and efficiency are paramount. B2B buyers should carefully assess their unique requirements and consider the pros and cons of each option to make an informed decision that aligns with their operational strategy.
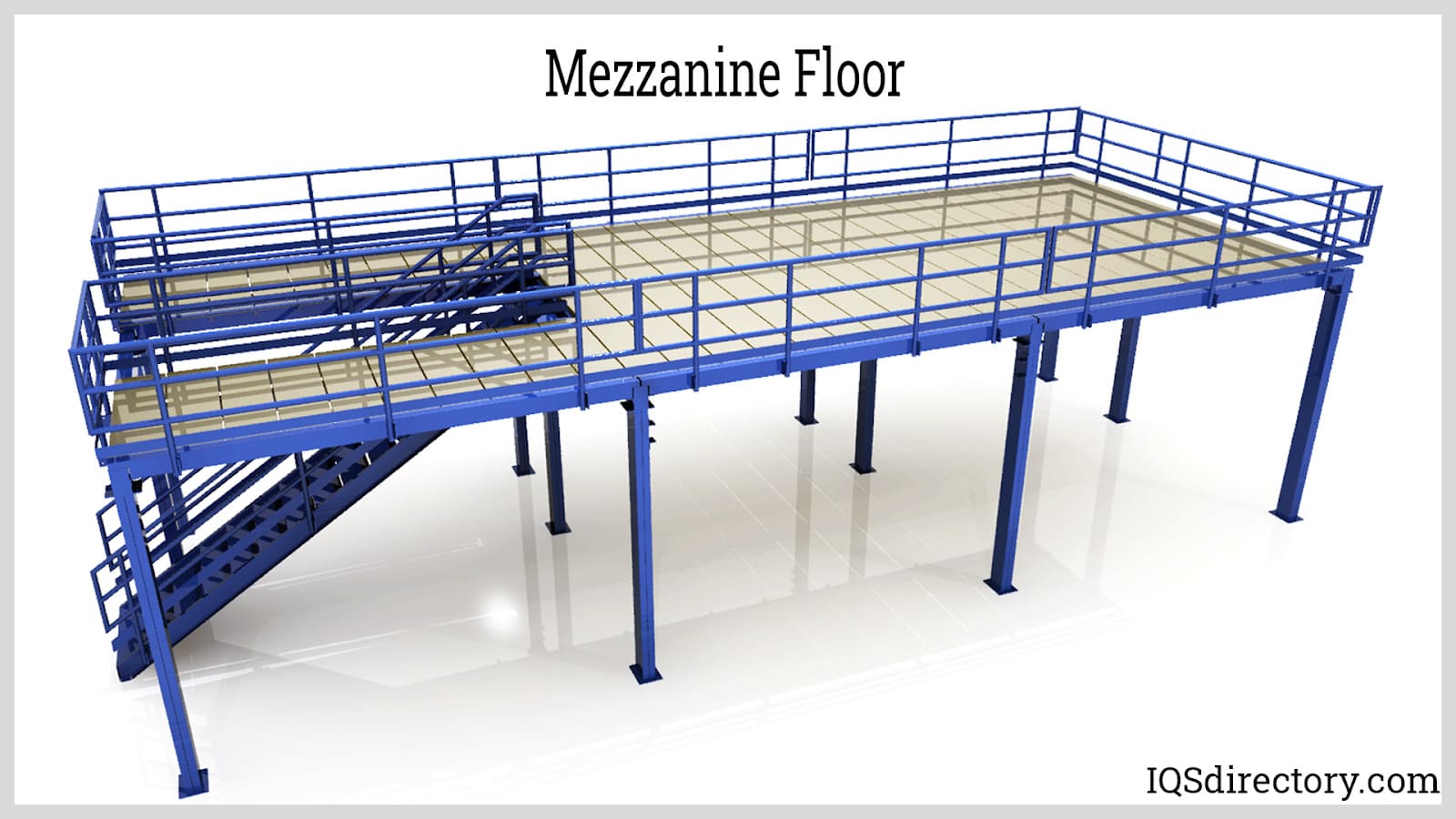
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for mezzanine plan
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Mezzanine Plan?
When considering a mezzanine plan, several technical properties are critical to ensuring the structure’s safety, functionality, and compliance with local regulations. Understanding these specifications is vital for B2B buyers, particularly in sectors where space optimization is paramount.

Illustrative image related to mezzanine plan
-
Load-Bearing Capacity
This refers to the maximum weight a mezzanine can safely support, including the weight of the structure itself and any equipment or personnel. Load-bearing capacity is crucial for determining the type of materials and design needed for the mezzanine, ensuring it meets safety standards and operational needs. For B2B buyers, understanding this specification helps in selecting appropriate designs that align with their operational requirements. -
Material Grade
The grade of materials used (e.g., steel, concrete, wood) significantly impacts the durability and longevity of the mezzanine. Higher-grade materials may offer better resistance to wear and tear, making them suitable for environments with heavy usage. Buyers must consider material grades as they directly influence long-term costs and maintenance requirements. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the permissible limits of variation in physical dimensions of the mezzanine components. It is essential for ensuring that all parts fit together correctly during assembly. Inaccurate tolerances can lead to structural weaknesses or installation issues. For international buyers, understanding tolerance levels helps in avoiding costly modifications or delays. -
Height Clearance
Adequate height clearance is necessary for both safety and functionality. A minimum clearance of 2.5 to 3 meters is generally recommended beneath the mezzanine to ensure comfortable movement and avoid accidents. Buyers should ensure that their mezzanine plans comply with local building codes regarding height clearance to avoid legal complications. -
Fire Rating
This property indicates how long a structure can withstand exposure to fire without losing its structural integrity. A higher fire rating is often required in commercial settings, particularly in warehouses storing flammable materials. Understanding fire ratings is essential for B2B buyers to ensure compliance with safety regulations and protect their investments.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Mezzanine Plans?
Familiarity with industry jargon can significantly streamline the procurement process for B2B buyers. Here are several common terms related to mezzanine plans.
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of mezzanine floors, OEMs can provide specialized components that meet specific requirements, ensuring quality and compatibility. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For buyers, understanding MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, particularly when planning large-scale installations of mezzanine systems. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. This is a critical step in the purchasing process, allowing B2B buyers to compare costs and terms before making decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, outlining the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers engaged in cross-border procurement of mezzanine components, as they dictate shipping responsibilities, risks, and costs. -
BIM (Building Information Modeling)
BIM refers to the digital representation of physical and functional characteristics of a facility. It is increasingly used in mezzanine planning to enhance visualization, coordination, and decision-making throughout the design and construction process.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when planning and purchasing mezzanine solutions, ensuring they meet their business needs efficiently and effectively.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the mezzanine plan Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Mezzanine Plan Sector?
The global mezzanine plan market is experiencing notable growth, driven by several factors, including the increasing demand for efficient space utilization in commercial and industrial sectors. As businesses worldwide face space constraints, particularly in urban areas, the integration of mezzanine floors offers a practical solution for maximizing vertical space without the need for extensive renovations. Emerging technologies are also reshaping the landscape, with advancements in warehouse automation and structural engineering enabling the design of more versatile and safer mezzanine solutions.
In particular, international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are witnessing a surge in sourcing opportunities. Countries like Saudi Arabia and Brazil are investing in infrastructure development, creating a robust demand for mezzanine systems in warehouses, retail spaces, and manufacturing plants. Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce has accelerated the need for efficient logistics and storage solutions, further propelling the market for mezzanine plans. Collaborative platforms and digital marketplaces are also emerging, facilitating easier connections between suppliers and buyers, while providing real-time insights into product availability and pricing trends.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Mezzanine Plan Sector?
As sustainability becomes a core consideration in business operations, the mezzanine plan sector is not left behind. The environmental impact of construction materials and processes is gaining attention, prompting B2B buyers to prioritize suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices. Ethical sourcing is increasingly significant, as companies seek to minimize their carbon footprint and ensure that materials are obtained responsibly.
Illustrative image related to mezzanine plan
Buyers should look for suppliers that offer green certifications for materials, such as recycled steel or sustainably sourced wood, which can significantly reduce environmental impact. Additionally, incorporating energy-efficient designs and construction practices not only supports sustainability goals but can also lead to long-term cost savings through reduced energy consumption. By choosing suppliers committed to ethical practices, businesses can enhance their brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
How Has the Mezzanine Plan Sector Evolved Over Time?
The mezzanine plan sector has evolved significantly from its early days, where these structures were primarily viewed as basic storage solutions. Initially popular in industrial settings, the design and application of mezzanines have expanded to accommodate various sectors, including retail and office spaces. Today, mezzanine floors are recognized for their versatility, enabling businesses to create multi-functional environments that enhance operational efficiency.
Advancements in materials and engineering have allowed for more innovative designs, increasing the safety and aesthetic appeal of mezzanine structures. As global markets continue to evolve, the emphasis on maximizing space utilization and integrating sustainable practices will further shape the future of mezzanine plans, making them a crucial component of modern architectural solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of mezzanine plan
-
How do I choose the right mezzanine plan for my business needs?
Selecting the right mezzanine plan involves assessing your specific requirements, such as the intended use (storage, office space, etc.), available height, and load-bearing needs. Begin by measuring your space and understanding the local building codes that may affect your design. Additionally, consider consulting with architects or structural engineers to ensure that the plan aligns with your operational objectives and safety regulations. Evaluating different designs can help you find the most effective solution for maximizing your space. -
What are the essential features to look for in a mezzanine plan?
When evaluating mezzanine plans, prioritize features like structural integrity, accessibility, and compliance with local regulations. Ensure the design includes adequate load-bearing capacity for your intended use, whether it’s for storage or office work. Additionally, consider safety features such as stair access, balustrades, and fire exits. A well-designed plan should also allow for flexibility in layout, enabling future modifications to meet changing business needs. -
What customization options are available for mezzanine plans?
Most mezzanine plans offer a range of customization options to suit your specific requirements. You can modify dimensions, materials, and layout to enhance functionality. Some suppliers provide bespoke designs that incorporate unique features like integrated shelving or specialized access points. It’s essential to communicate your needs clearly with the supplier to ensure the final design meets your expectations and complies with local building codes. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for mezzanine plans?
Minimum order quantities for mezzanine plans can vary widely depending on the supplier and the complexity of the design. Some manufacturers may have a MOQ of one custom plan, while others might require bulk orders for prefabricated designs. When sourcing internationally, it’s crucial to clarify these terms upfront to avoid any misunderstandings. Additionally, consider the potential for volume discounts if you plan to order multiple units. -
How can I ensure the quality of the mezzanine plan I am purchasing?
To ensure quality, start by vetting potential suppliers thoroughly. Look for reviews, case studies, and certifications that validate their expertise in mezzanine design and construction. Request samples of previous work and ask about their quality assurance processes. Additionally, consider engaging a local structural engineer to review the proposed plan for compliance with regional standards, ensuring that your investment meets both safety and performance criteria. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing mezzanine plans internationally?
Payment terms can vary significantly by supplier and region, but common practices include a deposit upfront (often 30-50%) with the balance due upon completion or delivery. Be sure to discuss and negotiate terms that suit your cash flow and project timeline. Additionally, inquire about payment methods accepted, as options may include wire transfers, credit cards, or payment through escrow services to protect both parties during the transaction. -
How do logistics work for shipping mezzanine plans internationally?
Logistics for shipping mezzanine plans depend on the supplier’s location and your own. Typically, suppliers will provide shipping options, which may include air freight for faster delivery or sea freight for cost-effective transport. It’s essential to discuss packaging and handling to prevent damage during transit. Additionally, ensure you understand customs regulations and any import duties that may apply in your country, which can impact overall project costs. -
What are the common challenges faced when implementing a mezzanine plan, and how can I mitigate them?
Common challenges include compliance with local building codes, integration with existing structures, and ensuring adequate load-bearing capacity. To mitigate these issues, engage professionals early in the design process, including architects and engineers, to navigate regulatory requirements effectively. Conduct thorough site assessments to identify potential obstacles and ensure that your design accommodates any unique site conditions. Clear communication with all stakeholders throughout the project will also help address issues promptly.
Top 2 Mezzanine Plan Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Pinterest – Innovative Home Design Ideas
Domain: pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Mezzanine floor plan, small home interior designs under 40 square metres, neutral decor with sparing colour accents, dynamic storage systems, clever layouts, container home floor plans, shipping container housing solutions, floating walls house design, two-storey farmhouse with mezzanine, free CAD drawings, fully editable Autocad DWG files, contemporary loft space, apartment with mezzanine in Podi…
2. Drummond House Plans – Cottage with Mezzanine
Domain: drummondhouseplans.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Cottage with Mezzanine, designed by Drummond House Plans, features a cozy and functional layout suitable for various lifestyles. The design includes a mezzanine level, providing additional living space. The house is characterized by its charming aesthetic, making it ideal for both permanent residence and vacation use. Key features include open living areas, multiple bedrooms, and a well-appointed …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for mezzanine plan
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers Considering Mezzanine Plans?
Incorporating a mezzanine floor can significantly enhance operational efficiency and maximize space utilization, making it an attractive option for businesses across diverse industries. For international B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing of mezzanine solutions is essential to ensure compliance with local regulations and to address specific operational needs. Understanding the structural requirements, load-bearing capabilities, and aesthetic considerations of mezzanine designs will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their business objectives.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Mezzanine Projects?
Strategic sourcing not only streamlines procurement processes but also fosters partnerships with reliable suppliers who can provide high-quality materials and expertise. Engaging with local architects and structural engineers can further enhance the design and implementation phases, ensuring that the mezzanine meets safety standards and operational requirements.
What’s Next for International Buyers?
As you consider adding a mezzanine to your facilities, view this as an investment in your business’s future. By focusing on strategic sourcing, you can optimize your space while enhancing productivity. Now is the time to act—connect with industry professionals, explore innovative designs, and leverage the benefits of a well-planned mezzanine to propel your business forward.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
Illustrative image related to mezzanine plan
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.