A Deep Dive into Industrial Quartz Glass Solution
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for industrial quartz glass
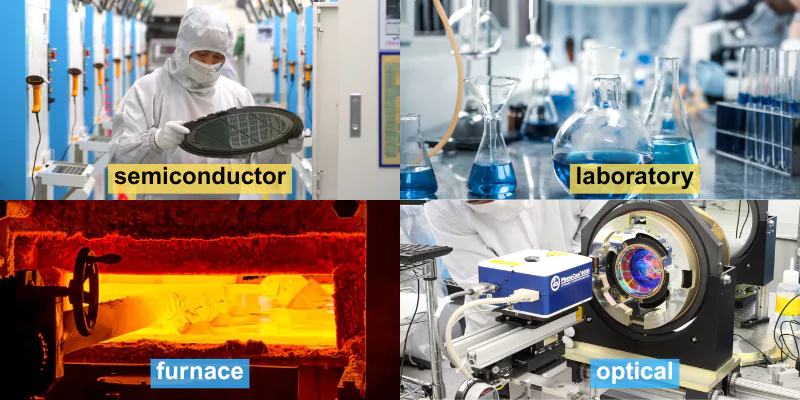
In today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, sourcing high-quality industrial quartz glass can be a daunting task for B2B buyers. With its exceptional thermal stability, optical clarity, and chemical inertness, quartz glass is increasingly sought after across various sectors, from semiconductor manufacturing to laboratory applications. However, navigating the complexities of the global market for this specialized material requires a comprehensive understanding of its types, applications, and sourcing strategies.
This guide serves as an essential resource for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—regions that are witnessing significant growth in industrial and technological advancements. We delve into the diverse types of quartz glass available, including fused quartz, synthetic quartz, and satin quartz, each tailored for specific applications and industries. Additionally, we provide insights on vetting suppliers, understanding cost implications, and ensuring the material meets stringent quality standards.
By equipping buyers with actionable insights and a deep understanding of the market, this guide empowers informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are looking to optimize production processes or enhance laboratory efficiency, mastering the nuances of industrial quartz glass will enable you to leverage its unique properties to your advantage. Embrace this opportunity to elevate your sourcing strategy and secure a competitive edge in your industry.
Understanding industrial quartz glass Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fused Quartz | Made from natural quartz, high thermal resistance, low expansion | Semiconductor fabrication, UV applications | Pros: High purity, excellent light transmission. Cons: Limited availability in thick sizes. |
| Synthetic Quartz | Superior purity and optical properties, custom-made options | Laboratory equipment, optics, precision instruments | Pros: Enhanced performance, tailored specifications. Cons: Longer lead times due to custom production. |
| Fused Silica Satin | Matte finish, not transparent, available in tube form | Sight glasses, high-temperature applications | Pros: Good thermal stability, reduced glare. Cons: Limited applications due to non-transparency. |
| UV-Fused Silica | Low inclusion content, high refractive index homogeneity | UV bonding, photonics, high-tech manufacturing | Pros: Exceptional UV transmission, precise optical properties. Cons: Higher cost due to specialized processing. |
| Industrial Fused Silica | Commercial grade, good balance of properties | General industrial uses, sight glasses | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile applications. Cons: May have lower purity compared to synthetic quartz. |
What are the Characteristics of Fused Quartz?
Fused quartz is derived from natural quartz sand, which is melted at high temperatures. This type boasts remarkable thermal resistance, able to withstand temperatures up to 1600 °C, and exhibits a low coefficient of thermal expansion, making it ideal for applications requiring stability under thermal stress. B2B buyers should consider fused quartz for semiconductor fabrication and UV applications due to its high purity and excellent optical clarity. However, sourcing thicker sizes may be challenging, necessitating advanced planning for procurement.
How Does Synthetic Quartz Enhance Industrial Applications?
Synthetic quartz is engineered to achieve superior purity and optical properties compared to its natural counterpart. This type is often custom-made, allowing for tailored specifications that meet precise industrial needs. Its exceptional light transmission makes it a preferred choice for laboratory equipment and optical devices. B2B buyers should be prepared for potentially longer lead times due to the custom nature of synthetic quartz, but the enhanced performance justifies the wait for many high-tech applications.
What Makes Fused Silica Satin Unique?
Fused silica satin is characterized by its matte finish and is primarily available in tube form. While it lacks the transparency of other quartz types, it offers excellent thermal stability, making it suitable for high-temperature environments where glare reduction is crucial. Industries that rely on sight glasses in extreme conditions often opt for this variant. Buyers should assess whether the non-transparent properties align with their specific needs, as this may limit its versatility compared to clearer quartz options.
Why Choose UV-Fused Silica for Advanced Applications?
UV-fused silica is specifically designed for applications requiring exceptional UV transmission and low inclusion content. Its high refractive index homogeneity makes it suitable for photonics and UV bonding processes. B2B buyers in high-tech manufacturing will appreciate the precision and quality this type offers. However, the specialized nature of UV-fused silica typically comes at a higher cost, making it essential for buyers to evaluate their budget against the performance benefits.
How Does Industrial Fused Silica Serve General Needs?
Industrial fused silica represents a commercial grade of quartz glass that balances performance and cost-effectiveness. It is widely utilized in various industrial applications, including sight glasses and general-purpose glassware. While it may not match the purity levels of synthetic quartz, its versatility and affordability make it an attractive option for many businesses. Buyers should consider their specific application requirements and budget constraints when evaluating this type of quartz glass.
Key Industrial Applications of industrial quartz glass
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of industrial quartz glass | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Semiconductor Manufacturing | Wafer fabrication and processing equipment | Ensures high precision and reduces contamination risks | Need for high-purity quartz and precise dimensional tolerances |
| Laboratory Equipment | Analytical instruments and lab glassware | Provides reliable results due to chemical inertness | Requirement for optical clarity and thermal stability |
| Telecommunications | Fiber optic components | Enhances signal transmission and reduces signal loss | Consideration for UV transparency and thermal resistance |
| Solar Energy | Solar panel production and testing | Improves efficiency of energy conversion | Sourcing quartz glass with high purity for optimal performance |
| Chemical Processing | Reaction vessels and sight glasses | Ensures safety and durability in corrosive environments | Need for chemical stability and resistance to thermal shock |
How is industrial quartz glass utilized in semiconductor manufacturing, and what should buyers consider?
In semiconductor manufacturing, industrial quartz glass is critical for wafer fabrication and processing equipment. Its high purity minimizes contamination, which is vital for achieving the precision required in semiconductor devices. Buyers must consider sourcing quartz glass that meets stringent dimensional tolerances and purity levels to prevent defects during the manufacturing process. The ability to withstand high temperatures also enhances its suitability for various fabrication techniques.
What role does industrial quartz glass play in laboratory equipment, and what are the key requirements for buyers?
Industrial quartz glass is extensively used in analytical instruments and lab glassware due to its exceptional chemical inertness and thermal stability. This material ensures that experiments yield reliable results without interference from the glass itself. For international buyers, particularly from regions with stringent quality standards, sourcing high-purity quartz glass is essential. Buyers should also ensure that the glass meets optical clarity requirements for precise light transmission in spectroscopy and other optical analyses.
How does industrial quartz glass contribute to telecommunications, and what should buyers focus on?
In telecommunications, industrial quartz glass is used in fiber optic components, enhancing signal transmission and reducing losses. The material’s UV transparency and thermal resistance are crucial for maintaining the integrity of optical signals over long distances. Buyers should focus on sourcing quartz glass that meets industry specifications for refractive index and purity to ensure optimal performance in high-speed communication networks.
What advantages does industrial quartz glass offer in solar energy applications, and what considerations should buyers keep in mind?
Industrial quartz glass is vital in the production and testing of solar panels, significantly improving the efficiency of energy conversion. Its high purity ensures that no impurities affect the performance of photovoltaic cells. Buyers in the solar energy sector should prioritize sourcing quartz glass with excellent optical transmission and durability to withstand environmental conditions. Additionally, understanding the supplier’s ability to provide custom dimensions can be beneficial for specific project requirements.
How is industrial quartz glass utilized in chemical processing, and what are the sourcing considerations?
In chemical processing, industrial quartz glass is employed for reaction vessels and sight glasses, offering safety and durability in corrosive environments. Its chemical stability prevents reactions with aggressive substances, thus protecting both the materials and the integrity of the processes. For buyers, especially in regions with diverse chemical applications, it is essential to source quartz glass that can withstand high temperatures and thermal shocks, ensuring reliability and longevity in demanding settings.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘industrial quartz glass’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Ensuring Consistent Quality in High-Temperature Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers in industries like semiconductor manufacturing or high-temperature laboratory settings often face challenges related to the consistency and reliability of quartz glass products. Variability in purity and thermal resistance can lead to equipment failures, impacting production efficiency and product quality. For instance, if the quartz glass used in a UV application has impurities, it can absorb UV light instead of transmitting it, leading to inadequate curing or sterilization.
The Solution: To ensure consistent quality, buyers should prioritize sourcing quartz glass from reputable manufacturers who provide detailed specifications and certifications for their products. When requesting quotes, ask for information on the glass’s purity levels, thermal expansion coefficients, and specific optical transmission rates. Additionally, consider implementing a quality assurance protocol that includes testing samples of quartz glass before full-scale procurement. This proactive approach helps mitigate risks associated with subpar materials and ensures that the quartz glass meets the stringent requirements of high-temperature applications.
Scenario 2: Navigating Complex Sourcing and Customization Needs
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle with sourcing custom quartz glass solutions that fit specific design and functional requirements. Industries such as aerospace and medical device manufacturing often require unique dimensions and properties, which can complicate the procurement process. Buyers may find themselves at the mercy of lead times, unclear pricing, and limited options from suppliers, leading to project delays and increased costs.
The Solution: To effectively navigate these challenges, buyers should establish clear communication with potential suppliers regarding their specific needs. Providing detailed specifications—including dimensions, thickness, and required optical properties—can help suppliers offer tailored solutions more efficiently. Additionally, consider working with manufacturers who have the capability for rapid prototyping and small-batch production. Engaging in discussions about potential design modifications early on can also foster a collaborative relationship, reducing the time and cost associated with sourcing custom quartz glass.

Illustrative image related to industrial quartz glass
Scenario 3: Managing Costs and Long-Term Investment in Quartz Glass
The Problem: B2B buyers often grapple with the high upfront costs associated with purchasing industrial quartz glass, especially synthetic options known for superior performance. While the initial investment may seem steep, the long-term benefits of durability and reduced maintenance can be overlooked. Buyers may hesitate to invest in high-quality quartz glass, fearing it will negatively impact their budgets in the short term.
The Solution: To address these cost concerns, buyers should conduct a total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis when evaluating quartz glass options. This analysis should factor in not only the purchase price but also the potential for fewer replacements, lower maintenance costs, and improved operational efficiency over time. Buyers can also explore financing options or bulk purchasing agreements with suppliers to mitigate upfront costs. Engaging in discussions about the long-term benefits of high-quality quartz glass can help stakeholders understand its value, leading to more informed purchasing decisions that support sustainable operations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for industrial quartz glass
What Are the Key Properties of Fused Quartz in Industrial Applications?
Fused quartz, often referred to as natural quartz glass, is renowned for its exceptional thermal stability and high purity. It can withstand temperatures up to 1600 °C, making it suitable for high-temperature applications such as sight glasses in furnaces and reactors. Its low coefficient of thermal expansion ensures minimal dimensional changes under temperature fluctuations, which is crucial in precision applications.

Illustrative image related to industrial quartz glass
Pros: The primary advantages of fused quartz include its durability, high optical clarity, and chemical resistance. It is ideal for applications requiring high transparency to UV and IR light, such as in UV sterilization processes.
Cons: However, fused quartz can be more expensive than other glass types due to its manufacturing process, which involves melting high-purity quartz sand. Additionally, it cannot be thermally tempered, which limits its use in applications requiring enhanced mechanical strength.
How Does Synthetic Quartz Compare to Natural Quartz?
Synthetic quartz glass is manufactured under controlled conditions, resulting in even higher purity levels than natural fused quartz. This material exhibits superior optical and thermal properties, making it ideal for high-tech applications such as semiconductor manufacturing and laboratory equipment.
Pros: The key advantage of synthetic quartz lies in its enhanced performance characteristics, including better transmission of UV light and lower levels of inclusions. This makes it suitable for applications where precision and reliability are paramount.
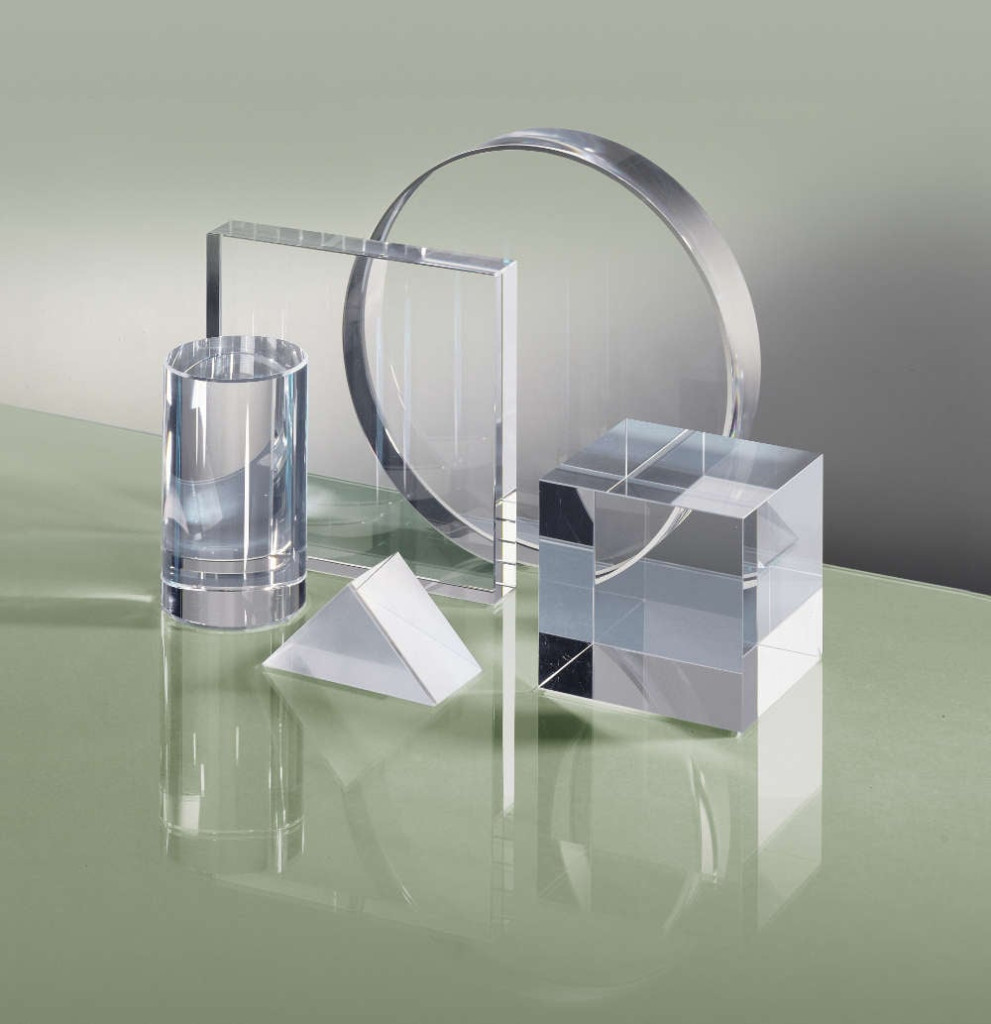

Illustrative image related to industrial quartz glass
Cons: On the downside, synthetic quartz typically comes at a higher cost and longer lead times due to custom manufacturing requirements. International buyers should be prepared for potential delays in procurement.
What Are the Benefits of Fused Silica Satin in Industrial Use?
Fused silica satin, characterized by its matte finish, is primarily used in applications where glare reduction is essential. Its unique surface properties make it suitable for optical applications and as protective covers in harsh environments.
Pros: The main advantage of satin quartz is its ability to diffuse light, which can enhance visibility in certain applications. It also retains the high-temperature resistance and chemical inertness of traditional quartz.
Cons: However, the matte finish may limit its use in applications requiring high optical clarity. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be complex, leading to higher costs compared to standard quartz glass.
What Should International Buyers Consider When Selecting Quartz Glass Materials?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must consider compliance with local and international standards such as ASTM, DIN, and JIS. Understanding regional preferences for material specifications is crucial for ensuring compatibility with existing systems and processes. Additionally, factors such as lead times, shipping logistics, and potential tariffs should be factored into the procurement strategy.
Summary Table of Quartz Glass Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for industrial quartz glass | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fused Quartz | Sight glasses in high-temperature environments | Exceptional thermal stability | Higher cost, cannot be thermally tempered | High |
| Synthetic Quartz | Semiconductor fabrication and laboratory equipment | Superior optical and thermal properties | Higher cost, longer lead times | High |
| Fused Silica Satin | Optical applications requiring glare reduction | Diffuses light effectively | Limited optical clarity | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview for B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions based on the specific needs and applications of industrial quartz glass.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for industrial quartz glass
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Industrial Quartz Glass?
The manufacturing of industrial quartz glass involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets stringent quality standards. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Quartz Glass Production?
The process begins with the selection of high-purity raw materials, primarily silica sand, which must be free from impurities that could affect the glass’s optical and thermal properties. This sand undergoes rigorous processing to eliminate contaminants, including grinding and sieving to achieve the desired granule size. In some cases, synthetic silica is used for its superior purity, which is essential for applications requiring high optical transmission.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Quartz Glass?
Once the materials are prepared, the next step is forming the quartz glass. This typically involves melting the silica in a high-temperature furnace, where temperatures can exceed 1600 °C. The molten glass is then shaped into various forms such as sheets, tubes, or rods. Techniques such as blowing, pressing, or molding may be employed, depending on the desired product specifications. Advanced methods like precision machining are also utilized for creating complex geometries.
How Is Assembly Handled in Quartz Glass Manufacturing?
For products that require multiple components, assembly is an integral part of the manufacturing process. This stage may involve joining different pieces of quartz glass or integrating other materials, such as metals or polymers, to create composite structures. Techniques like adhesive bonding, particularly UV-cured adhesives, are often used due to their compatibility with quartz glass’s properties. Careful handling is crucial at this stage to prevent any micro-cracks or defects that could compromise the integrity of the final product.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Employed?
Finishing is the final stage in the manufacturing process, where the glass undergoes treatments to enhance its optical clarity and surface finish. Common finishing techniques include polishing, sandblasting, and coating. Polishing is essential for applications requiring high transparency, while sandblasting may be used for creating matte surfaces. Quality assurance checks are performed throughout the finishing process to ensure that the glass meets the required specifications.
What International Standards Govern Quality Assurance in Quartz Glass Manufacturing?
Quality assurance in quartz glass manufacturing is critical, especially for B2B buyers who require reliable and consistent products. Many manufacturers adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. Additionally, industry-specific standards like CE marking for European markets and API standards for the oil and gas industry may also apply, depending on the application of the quartz glass.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Established?
Quality control (QC) is an integral part of the manufacturing process, with multiple checkpoints established to monitor quality throughout production. These checkpoints typically include:

Illustrative image related to industrial quartz glass
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected for purity and compliance with specifications before they are used in production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, various parameters are monitored, including temperature control in furnaces and dimensional accuracy of formed glass.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After finishing, the products undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet the specified quality standards. This may include optical testing, thermal shock resistance, and chemical durability tests.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quartz Glass Quality Assurance?
Common testing methods for quartz glass include:
-
Optical Transmission Testing: To measure how much light passes through the glass, ensuring it meets the required specifications for transparency.
-
Thermal Shock Testing: Assessing the material’s ability to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking.
-
Chemical Resistance Testing: Evaluating the glass’s durability against various chemicals, which is crucial for industrial applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers. This can include:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits to assess the manufacturing processes, quality assurance protocols, and overall compliance with international standards.
-
Reviewing Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports that outline testing results and compliance with relevant standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent organizations to conduct audits or inspections can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control measures.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is essential. Different regions may have varying requirements, and certifications that are recognized in one area may not hold the same weight in another. For example, European buyers often look for CE marking, while buyers in the Middle East may prioritize compliance with local regulations. Buyers should ensure that suppliers are familiar with the specific certifications required in their target markets and that they can provide documentation verifying compliance.
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality in Industrial Quartz Glass Manufacturing
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for industrial quartz glass are multifaceted and critical to producing high-quality products. By understanding these processes and establishing robust verification methods, B2B buyers can confidently source quartz glass that meets their specific industrial needs. The emphasis on quality control, adherence to international standards, and the ability to verify supplier compliance are vital components for successful procurement in this specialized market.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘industrial quartz glass’
This guide aims to assist B2B buyers in navigating the complexities of sourcing industrial quartz glass. Given its unique properties and applications across various industries, following a structured approach can ensure you select the right materials and suppliers for your needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is critical in the sourcing process. Determine the required dimensions, thickness, and type of quartz glass you need, such as fused quartz, synthetic quartz, or satin quartz. Consider the specific properties essential for your application, such as thermal resistance, optical clarity, and chemical inertness.
Illustrative image related to industrial quartz glass
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in industrial quartz glass. Look for companies with a strong reputation in your target regions, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online forums to gather a list of potential candidates, ensuring they have a history of reliability and quality.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before engaging a supplier, verify their certifications and compliance with international standards. Look for ISO certifications or other relevant quality assurances that indicate their commitment to quality and safety. Certifications can provide confidence that the supplier adheres to best practices in production and material handling.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request samples of the quartz glass. Testing samples allows you to evaluate the material’s performance against your specifications, particularly in terms of optical clarity and thermal resistance. Ensure that the samples meet the quality benchmarks necessary for your application, especially if you’re working in high-tech industries like semiconductors or laboratory environments.
Step 5: Assess Pricing and Payment Terms
Compare pricing structures among your shortlisted suppliers, but don’t focus solely on cost. Consider the total cost of ownership, which includes shipping, handling, and potential tariffs. Evaluate the payment terms offered, ensuring they align with your cash flow and procurement policies.
Step 6: Review Lead Times and Availability
Understanding lead times is crucial for planning your production schedules. Inquire about the typical delivery times for different types of quartz glass and whether the supplier can meet your deadlines. Confirm their inventory levels to ensure they can fulfill your order promptly, especially if you require custom dimensions or large quantities.

Illustrative image related to industrial quartz glass
Step 7: Establish Communication Channels
Finally, establish clear communication channels with your selected supplier. Define points of contact for technical support, order inquiries, and after-sales service. Effective communication can resolve issues quickly and foster a strong partnership, ensuring a smoother procurement process in the long run.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing industrial quartz glass, ensuring they select the right materials and suppliers to meet their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for industrial quartz glass Sourcing
When sourcing industrial quartz glass, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for B2B buyers. The costs associated with quartz glass encompass various components, including raw materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and the supplier’s profit margin.

Illustrative image related to industrial quartz glass
What Are the Key Cost Components in Industrial Quartz Glass Production?
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in quartz glass sourcing is the raw material itself—high-purity silica sand or synthetic quartz. Natural quartz has varying prices depending on availability and purity levels. Synthetic quartz, while often more expensive due to its manufacturing process, offers superior quality and specifications.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is required for the production and processing of quartz glass. This includes handling, shaping, and finishing the glass, which can significantly impact labor costs, especially in regions with higher wage standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, maintenance of equipment, and facility operations. The energy-intensive nature of glass production means that overhead can be substantial, particularly in areas with high energy prices.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in molds and specialized equipment for manufacturing specific shapes or sizes of quartz glass can be significant. Tooling costs are often amortized over large production runs, making them less impactful for high-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the glass meets strict specifications and standards requires rigorous testing and quality assurance processes. This adds to the overall cost but is critical for maintaining product integrity, especially in high-tech applications.
-
Logistics: Transporting quartz glass can be challenging due to its fragility and weight. Logistics costs can vary widely based on the distance from the supplier to the buyer, shipping methods, and packaging requirements.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins can vary significantly based on market competition and product differentiation. Understanding this component helps buyers gauge the overall pricing landscape.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Quartz Glass Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of industrial quartz glass:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders typically result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs carefully to optimize order sizes.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom dimensions, finishes, or additional processing (e.g., drilling, sandblasting) can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials Quality and Certifications: Higher purity levels and certifications (e.g., ISO standards) often come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the importance of these factors against their application needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but often provide better quality assurance and customer support.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) dictate the responsibilities of buyers and suppliers regarding shipping costs, insurance, and logistics. Understanding these terms is crucial for calculating total landed costs.
What Are the Best Negotiation Strategies for B2B Buyers?
-
Negotiate Based on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Buyers should consider not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with quality, maintenance, and operational efficiency.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: Committing to larger orders can provide leverage for negotiating better pricing. Establishing a long-term partnership with suppliers may yield favorable terms.
-
Evaluate Multiple Suppliers: Obtaining quotes from various suppliers can help identify competitive pricing and better understand market rates.
-
Understand Regional Pricing Nuances: Pricing can vary significantly based on regional factors, such as local demand, transportation costs, and tariffs. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should research these aspects to make informed decisions.
-
Be Prepared for Price Fluctuations: Global market conditions, such as supply chain disruptions or raw material shortages, can lead to price volatility. Buyers should stay informed about market trends to anticipate changes.
Conclusion
While sourcing industrial quartz glass, it is vital for B2B buyers to consider the multifaceted cost structure and the various factors influencing pricing. By understanding these elements and employing effective negotiation strategies, buyers can achieve more favorable outcomes in their procurement processes. As always, it is essential to consult with suppliers for indicative pricing tailored to specific requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing industrial quartz glass With Other Solutions
When exploring the industrial glass market, buyers often encounter a variety of solutions that may meet their needs. Industrial quartz glass is a leading choice due to its unique properties, but understanding its alternatives is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This analysis compares industrial quartz glass with two viable alternatives: borosilicate glass and tempered glass.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Industrial Quartz Glass | Borosilicate Glass | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High thermal resistance, UV transparency, chemical inertness | Good thermal resistance, lower UV transparency | High strength, moderate thermal resistance |
| Cost | Generally higher due to purity and processing | Moderate cost, widely available | Variable cost, higher than standard glass |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized handling and installation | Easily processed and shaped | Standard installation practices |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, durable under extreme conditions | Moderate maintenance, susceptible to scratches | Low maintenance, durable but can shatter if not handled correctly |
| Best Use Case | Semiconductor fabrication, high-precision optics | Laboratory glassware, kitchenware | Architectural applications, safety glass |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Borosilicate Glass
Borosilicate glass is known for its excellent thermal resistance and is often used in laboratory environments. It can withstand temperature fluctuations, making it suitable for glassware and cooking utensils. However, its UV transparency is not as high as that of quartz glass, which limits its use in applications requiring UV light transmission. Additionally, borosilicate glass is generally more affordable and easier to implement compared to quartz glass, but it may not provide the same level of chemical inertness.
Tempered Glass
Tempered glass is manufactured through a process of extreme heating and rapid cooling, resulting in a material that is significantly stronger than standard glass. This makes it ideal for architectural applications where safety and durability are paramount. While tempered glass offers good strength, it has a moderate thermal resistance and can shatter upon impact if not handled properly. Its cost is variable and typically higher than standard glass, but it is less expensive than quartz glass. However, its performance in UV transmission and chemical resistance does not match that of industrial quartz glass.
Conclusion
Choosing the right solution depends heavily on the specific needs of your application. For industries requiring high thermal stability, UV transparency, and chemical purity—such as semiconductor manufacturing—industrial quartz glass is often the best choice despite its higher cost. In contrast, if budget constraints are a concern and the application involves less demanding conditions, borosilicate glass may suffice. For architectural needs where safety is critical, tempered glass provides a reliable alternative. Ultimately, evaluating the performance, cost, and application requirements will guide B2B buyers in selecting the most suitable glass solution for their operations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for industrial quartz glass
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Industrial Quartz Glass?
1. Thermal Stability
Quartz glass exhibits exceptional thermal stability, capable of withstanding temperatures up to 1600 °C without compromising its structural integrity. This property is critical for industries that operate under extreme heat conditions, such as semiconductor manufacturing and high-temperature laboratory processes. The low coefficient of thermal expansion ensures that quartz glass maintains its dimensions even under rapid temperature changes, making it an ideal choice for precision applications.
2. Optical Transparency
One of the standout features of quartz glass is its high optical transparency across a wide spectrum, including ultraviolet (UV), visible, and infrared (IR) light. This property is essential for applications involving UV light, such as UV curing and sterilization processes. The ability to transmit light effectively enhances the performance of instruments used in scientific research and industrial applications, where accurate measurements and observations are paramount.
3. Chemical Inertness
Quartz glass is highly resistant to chemical reactions, making it suitable for handling corrosive substances and extreme pH conditions. This chemical stability is particularly important in laboratory settings and chemical processing industries, where the integrity of samples must be preserved. Using quartz glass minimizes contamination risks, ensuring that experimental results remain valid and reliable.
4. Mechanical Strength
The mechanical strength of quartz glass surpasses that of conventional glass, providing durability and resistance to breakage. This characteristic is vital for applications that require frequent handling or exposure to mechanical stresses. Industries that rely on robust laboratory equipment benefit significantly from using quartz glass, as it reduces the likelihood of damage and the associated costs of replacements.
5. Purity
High-purity quartz glass is manufactured from silica sand that undergoes extensive processing to eliminate impurities. This purity is crucial in high-tech applications, such as the semiconductor and pharmaceutical industries, where even minor contaminants can lead to significant failures. The importance of purity cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts the quality and reliability of the end products.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Industrial Quartz Glass?
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that manufactures products that are used as components in another company’s product. In the quartz glass industry, OEM relationships are crucial for ensuring that the specific glass components meet the unique requirements of different applications. Understanding OEM dynamics helps buyers source the right materials that fit their production needs.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. In the context of industrial quartz glass, MOQs can vary significantly based on material type and customization requirements. Knowing the MOQ is essential for B2B buyers to plan their inventory and budget, especially when dealing with specialized glass products that may require longer lead times.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a quote for specific products or services. For buyers of quartz glass, submitting an RFQ is a critical step in the procurement process, allowing them to compare pricing, terms, and delivery options across different suppliers. A well-prepared RFQ can streamline negotiations and ensure that all necessary specifications are clearly communicated.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is vital for B2B buyers of quartz glass, as they dictate who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and customs duties. Familiarity with Incoterms helps prevent misunderstandings and ensures a smooth transaction process.
5. Fused Quartz vs. Fused Silica
Fused quartz is produced from natural quartz, while fused silica is synthesized from silica precursors. Both materials have high purity and excellent thermal properties, but understanding their differences can guide buyers in selecting the appropriate material for specific applications. Knowing which type to use can significantly impact performance and cost-effectiveness in industrial settings.
By comprehending these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing industrial quartz glass, ensuring they select materials that meet their specific operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the industrial quartz glass Sector
What are the Key Trends Driving the Industrial Quartz Glass Market?
The industrial quartz glass market is experiencing significant growth driven by several global factors. The increasing demand for high-purity materials in sectors such as semiconductor manufacturing, telecommunications, and laboratory equipment is a primary driver. As industries pursue higher efficiency and precision, the unique properties of quartz glass, including its high thermal resistance and excellent optical transmission, make it a preferred choice.
Emerging technologies such as advanced manufacturing processes and automation are reshaping sourcing strategies. B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging digital platforms for procurement, enabling more efficient supplier selection and contract management. This trend is particularly evident in regions such as Europe and South America, where digitalization is enhancing transparency and operational efficiency in sourcing. Additionally, the rise of Industry 4.0 is prompting buyers to seek quartz glass suppliers who can provide tailored solutions that align with their specific production needs.
Moreover, as global supply chains continue to adapt post-pandemic, buyers from Africa and the Middle East are prioritizing local suppliers to mitigate risks associated with international logistics. This shift is leading to increased collaboration between regional manufacturers and international companies, fostering innovation and responsiveness to market demands.
How are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Industrial Quartz Glass Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a critical focus for B2B buyers in the industrial quartz glass sector. The environmental impact of sourcing and manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, pushing companies to adopt more sustainable practices. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint and promoting eco-friendly manufacturing processes.
Illustrative image related to industrial quartz glass
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as companies aim to establish responsible supply chains that prioritize fair labor practices and environmental stewardship. Buyers are encouraged to look for suppliers with green certifications or those utilizing recycled materials in their production processes. Such certifications not only enhance a company’s reputation but also meet the growing consumer demand for transparency and corporate responsibility.
In addition, the adoption of green technologies in the production of quartz glass, such as energy-efficient manufacturing processes and the use of renewable energy sources, is gaining traction. These practices not only reduce environmental impact but also result in cost savings, creating a compelling value proposition for B2B buyers.
How has the Industrial Quartz Glass Market Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the industrial quartz glass market can be traced back to its early applications in scientific laboratories and high-temperature environments. Initially, quartz glass was primarily utilized for its thermal resistance and optical clarity in laboratory glassware. Over the decades, advancements in manufacturing techniques have expanded its applications across various industries, including telecommunications and semiconductor fabrication.
As technology progressed, the demand for higher purity and precision led to the development of synthetic quartz glass, which offers enhanced properties compared to its natural counterpart. This evolution has positioned quartz glass as a vital material in high-tech applications, catering to the increasing needs of modern industries.
Today, the market is characterized by a diverse range of products, including fused quartz, synthetic quartz, and specialized glass forms, such as tubes and rods. The ongoing innovations in material science and manufacturing processes continue to drive the market forward, providing B2B buyers with more options and tailored solutions to meet their specific requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of industrial quartz glass
-
How do I select the right type of industrial quartz glass for my application?
Selecting the right type of industrial quartz glass involves understanding your specific application requirements. Fused quartz is typically favored for high-temperature environments due to its thermal resistance, while synthetic quartz offers superior optical clarity and purity for precision applications like semiconductor manufacturing. Evaluate factors such as temperature tolerance, optical transmission needs, and chemical resistance to make an informed decision. Consulting with your supplier about customization options can also help tailor the glass to your specific needs. -
What are the key properties of quartz glass that make it suitable for industrial applications?
Quartz glass is prized for its exceptional properties, including high thermal stability, excellent optical transparency across UV, visible, and infrared spectrums, and remarkable chemical inertness. It can withstand temperatures exceeding 1600 °C without deforming and exhibits low thermal expansion, making it ideal for applications that require precision and reliability. Additionally, its high mechanical strength ensures durability, reducing the risk of breakage in demanding environments, thus making it an optimal choice for various industrial uses. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for quartz glass products?
Minimum order quantities for quartz glass can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the specific product type. For standard sizes and forms, such as sheets or tubes, the MOQ might be lower, often starting at a few pieces. However, for custom orders or specialized products, suppliers may require larger quantities to justify production costs. It’s advisable to discuss your requirements directly with suppliers to understand their policies and explore potential flexibility in MOQs. -
How can I ensure the quality of quartz glass products from my supplier?
To ensure the quality of quartz glass products, it’s essential to vet potential suppliers thoroughly. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards. Request product samples to evaluate their properties firsthand, and inquire about their quality assurance processes, including testing methods for thermal and optical characteristics. Establishing a clear communication channel and checking customer references can also provide insights into the supplier’s reliability and product quality. -
What are the common payment terms for purchasing quartz glass internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of quartz glass typically include options like advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery, depending on the supplier’s policies and your business relationship. It is common to negotiate terms that suit both parties, with many suppliers requiring a deposit to initiate production and the balance payable upon shipment. Ensure clarity on the payment terms in the purchase agreement to avoid any misunderstandings and establish a secure transaction process. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing quartz glass internationally?
When sourcing quartz glass internationally, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs that may impact delivery times and costs. Collaborate with suppliers who have experience in international shipping and can provide insights into the best practices for packaging and handling fragile materials. It’s also vital to account for lead times, especially for custom orders, and ensure that logistics partners are reliable to minimize disruptions in your supply chain. -
Can I customize quartz glass products to meet my specific requirements?
Yes, most suppliers offer customization options for quartz glass products to meet specific requirements. This may include variations in thickness, dimensions, shapes, and finishes. Additionally, some suppliers can provide services such as drilling, sandblasting, or bending the glass to suit particular applications. Discuss your needs with your supplier to explore available customization options and any associated costs or lead times. -
What industries commonly use quartz glass, and what are their applications?
Quartz glass is utilized across various industries due to its versatile properties. Common applications include semiconductor fabrication, laboratory equipment, optical devices, and high-temperature industrial processes. In the medical field, quartz glass is employed in sterilization equipment, while in telecommunications, it is integral to fiber optic cables. Understanding the specific industry applications can help you identify the best quartz glass solutions for your business needs and enhance operational efficiency.
Top 6 Industrial Quartz Glass Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Miritglas – Quartz Glass Solutions
Domain: miritglas.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Quartz glass is a pure material with excellent transmission properties, capable of withstanding temperatures up to 1600 °C. It has high light transmission from the UV to IR range and is available in plates, tubes, and rods. There are three main types: Fused quartz (natural, >99% quartz sand), Synthetic quartz (superior purity and light transmission), and Fused silica satin (matte finish). Mirit Gl…
2. Swift Glass – Quartz Products
Domain: swiftglass.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Quartz is extremely pure with high working and melting temperatures. It offers high chemical purity, high-temperature resistance, and precise dimensional tolerances. Key properties include high heat resistance, light transparency, chemical stability, and electrical insulation. Quartz and fused silica are ideal for semiconductor fabrication and laboratory equipment. The fused silica features a cros…
3. CS Ceramic – Quartz Glass Solutions
Domain: csceramic.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Quartz is one of the most abundant and widely distributed minerals in nature and is the only stable polymorph of crystalline silica on the Earth’s surface. The chemical formula of quartz is SiO2. Quartz glass is used in the manufacturing of optical devices, lighting systems, refractory materials, and chemical apparatuses. Key products include: 99.99% Transparent Cylindrical Quartz Crucible, Silica…
4. Technical Glass – Fused Silica & UV Quartz Plates
Domain: technicalglass.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Durable Fused Silica Plates & UV Grade Quartz Plates for Precision Applications. Clear fused silica plates and UV grade quartz plates are suitable for various industries due to their exceptional UV transmission and optical clarity. They can withstand high temperatures up to 1200°C, making them ideal for heat-resistant applications such as microscope slides. Custom sizes are available upon request….
5. UQG Optics – Fused Quartz Optical Grade
Domain: uqgoptics.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Fused Quartz optical grade is suitable for general optical windows, substrates, and optical components. Key differences between fused quartz and fused silica include purity and transmission values; fused silica is preferred for transmission below 260nm, while fused quartz is better for above 260nm. Fused quartz fluoresces, whereas fused silica is virtually fluorescent free. It can withstand high t…
6. CG Industrial Glass – Fused Quartz Silica Supplier
Domain: cgindustrialglass.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Fused Quartz Silica Glass Supplier, Fused Quartz Distributor, Fused Silica GE 124®, high temperature tolerance, thermal shock resistance, no additional ingredients required for lower melt temperature, high working and melting temperatures, developed by melting crystalline silica, low OH content, high degree of purity, high chemical resistance, good thermal shock resistance, low thermal expansion c…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for industrial quartz glass
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of industrial quartz glass presents a unique opportunity for businesses across various sectors, particularly those in high-tech industries like semiconductors, laboratory equipment, and optical applications. The exceptional properties of quartz glass—such as its high-temperature resistance, chemical inertness, and superior optical transparency—make it an invaluable material for ensuring product quality and operational efficiency.
As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including Germany and Brazil) navigate their sourcing decisions, it is crucial to prioritize suppliers who can provide not only high-quality materials but also customization options that meet specific industrial needs. Building strong partnerships with trusted manufacturers can lead to long-term advantages, including cost efficiency and innovation in product development.
Looking ahead, the demand for quartz glass is expected to grow, driven by advancements in technology and increasing applications across various industries. Engage with reliable suppliers today to secure your competitive edge in this evolving market. By investing in strategic sourcing now, you position your business for future success and resilience in an increasingly dynamic global landscape.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.