A Deep Dive into Homogenizer Machine Solution
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for homogenizer machine
In the ever-evolving landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing the right homogenizer machine poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. Whether you are operating in the food and beverage, pharmaceutical, or cosmetic industries, the need for efficient homogenization processes—crucial for product consistency and quality—cannot be overstated. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of homogenizers available, including high-pressure, ultrasonic, and mechanical options, providing insights into their specific applications and advantages.
Navigating the complexities of supplier vetting, pricing strategies, and technical specifications can be daunting, especially for businesses in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries such as Nigeria and Saudi Arabia. This guide is designed to empower you with actionable insights and expert recommendations to facilitate informed purchasing decisions. By understanding the nuances of homogenizer technology, you can optimize your production processes, enhance product quality, and ultimately gain a competitive edge in your market.
Additionally, we will explore key factors to consider when selecting a supplier, including reliability, customization options, and after-sales support, ensuring that your investment in a homogenizer machine aligns with your operational goals and industry standards. With this knowledge, you can confidently navigate the global market and select the right homogenizer to meet your unique business needs.
Understanding homogenizer machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| High Pressure Homogenizers | Utilizes high pressure to force liquids through narrow valves, creating shear and cavitation. | Dairy, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics | Pros: Effective for emulsions and cell disruption. Cons: High initial cost and maintenance requirements. |
| High Shear Mixers | Incorporates an impeller with sharp blades in a perforated housing to chop and mix products. | Food and beverage, chemical processing | Pros: Fast mixing and effective for viscous materials. Cons: Limited to certain viscosity ranges. |
| Ultrasonic Homogenizers | Uses ultrasonic sound waves to agitate and break apart particles. | Pharmaceuticals, biotechnology | Pros: Precise control and suitable for small sample sizes. Cons: May require specialized training for optimal use. |
| Mechanical Homogenizers | Available in handheld and benchtop models for grinding and lysing samples. | Laboratory research, food testing | Pros: Versatile and easy to use. Cons: Limited capacity for large-scale operations. |
| Bead Mill Homogenizers | Employs beads to disrupt cells and homogenize samples through agitation. | Biotechnology, food industry | Pros: Effective for tough-to-homogenize samples. Cons: Potential for contamination from beads. |
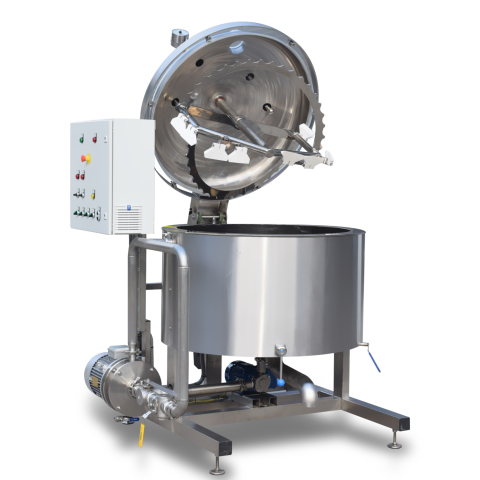
What are High Pressure Homogenizers and Their Applications?
High pressure homogenizers are essential in industries requiring the emulsification of liquids or the disruption of cells. They work by forcing liquids through narrow openings at high pressures, resulting in shear forces that break down fat globules and other particles. This type of homogenizer is particularly suitable for dairy processing, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetic formulations. When considering a high pressure homogenizer, buyers should evaluate the machine’s capacity, maintenance needs, and the cost of operation, as these machines can be expensive to purchase and maintain.
How Do High Shear Mixers Work and Where Are They Used?
High shear mixers utilize an impeller with sharp blades that create high shear forces to mix and emulsify products. They are predominantly used in food and beverage industries, as well as in chemical processing, where rapid and effective mixing of viscous materials is required. Buyers should consider the viscosity of their products and the desired mixing speed when selecting a high shear mixer, as this type of homogenizer may have limitations depending on the material characteristics.
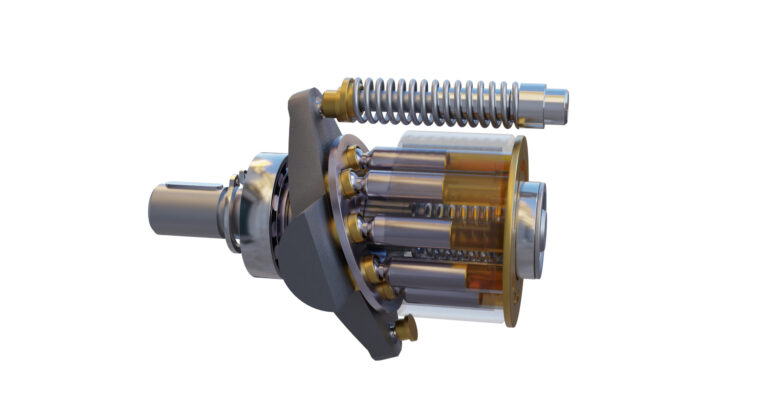
What are the Advantages of Ultrasonic Homogenizers?
Ultrasonic homogenizers leverage sound waves to create high-frequency agitation, breaking down particles with precision. They are widely used in pharmaceuticals and biotechnology for applications requiring delicate handling of samples. The key advantages include their ability to process small volumes with high accuracy and minimal heat generation. However, potential buyers should be aware that optimal operation may require specialized training and understanding of the technology.
What Makes Mechanical Homogenizers Suitable for Laboratories?
Mechanical homogenizers come in various forms, including handheld and benchtop models, making them highly versatile for laboratory settings. They are ideal for grinding, lysing, and homogenizing biological samples before molecular extraction. While they are user-friendly and adaptable to different applications, their capacity may be limited for larger-scale operations, making them more suitable for research and development rather than mass production.
What are Bead Mill Homogenizers and Their Key Considerations?
Bead mill homogenizers utilize small beads to disrupt cells and homogenize samples through mechanical agitation. This method is particularly effective for tough-to-homogenize materials, making it popular in the biotechnology and food industries. When considering a bead mill homogenizer, buyers should assess the potential for contamination from the beads and the machine’s cleaning requirements, as well as its efficiency in processing various sample types.
Key Industrial Applications of homogenizer machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of homogenizer machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food & Beverage | Milk homogenization | Improved product consistency and shelf life | Compliance with food safety standards, energy efficiency |
| Pharmaceuticals | Drug formulation and emulsification | Enhanced bioavailability and efficacy of medications | Regulatory compliance, customization for specific formulations |
| Cosmetics | Cream and lotion production | Improved texture and stability of products | Material compatibility, scalability for production |
| Chemical Manufacturing | Mixing and dispersing chemicals | Better product uniformity and performance | Material compatibility, maintenance requirements |
| Biotechnology | Cell lysis for molecular extraction | Increased yield of target biomolecules | Precision in particle size reduction, adaptability to various samples |
How is the Homogenizer Machine Used in the Food & Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage sector, homogenizers play a crucial role in the homogenization of milk and other dairy products. By breaking down fat globules, these machines ensure a uniform texture and prevent cream separation, thereby extending shelf life. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing homogenizers that comply with local food safety regulations is essential. Energy efficiency is also a key consideration to reduce operational costs in high-volume production environments.
What Role Does Homogenization Play in Pharmaceuticals?
In the pharmaceutical industry, homogenizers are vital for drug formulation, particularly in creating emulsions and suspensions that enhance the bioavailability of active ingredients. By reducing particle size, these machines help in achieving a consistent and effective product. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should focus on suppliers that offer customizable homogenizers tailored to specific drug formulations, along with robust compliance with health regulations to ensure product safety and efficacy.
How Are Homogenizers Utilized in Cosmetics Production?
Cosmetic manufacturers rely on homogenizers to produce creams, lotions, and emulsions with a smooth texture and stable formulation. The ability to mix oils and water-based ingredients efficiently is critical for product quality. Buyers in regions like Africa and Europe should consider sourcing homogenizers that are compatible with various cosmetic formulations and are capable of handling small to large batch sizes, ensuring scalability and flexibility in production.
Why Are Homogenizers Important in Chemical Manufacturing?
In the chemical manufacturing sector, homogenizers are used to mix and disperse various chemicals to ensure uniformity and enhance product performance. This is particularly important in producing paints, coatings, and adhesives. For international buyers, understanding the material compatibility and maintenance requirements of homogenizers is crucial to avoid production downtime and ensure the longevity of the equipment.
How Do Homogenizers Aid in Biotechnology Applications?
In biotechnology, homogenizers are essential for cell lysis, which is necessary for extracting biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. By efficiently breaking down cell walls, these machines increase the yield of target biomolecules, which is critical for research and development. Buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing homogenizers that offer precision in particle size reduction and adaptability to various sample types, ensuring they meet the diverse needs of biotechnological applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘homogenizer machine’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Product Quality in Food and Beverage Production
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in the food and beverage industry face the challenge of maintaining consistent product quality, especially when it comes to emulsions and suspensions. Variability in particle size can lead to separation, poor texture, and an undesirable mouthfeel, impacting customer satisfaction and brand reputation. For example, dairy producers may find that their milk products separate or do not maintain a consistent flavor profile, leading to increased waste and customer complaints.
The Solution: To address this issue, it is crucial to invest in high-pressure homogenizers that are specifically designed for food applications. These machines can effectively reduce particle size and create stable emulsions, ensuring that products remain uniform throughout their shelf life. When sourcing a homogenizer, consider models that offer customizable settings for pressure and flow rate, allowing for adjustments based on the specific product being processed. Regular maintenance and calibration of the equipment also play a vital role in sustaining performance and preventing fluctuations in product quality. Training staff on the correct operation of the homogenizer can further enhance product consistency and reduce the risk of errors.
Scenario 2: High Operational Costs and Energy Consumption
The Problem: B2B buyers often grapple with high operational costs associated with running homogenizer machines, especially in regions with fluctuating energy prices. Machines that are not energy-efficient can lead to significantly increased utility bills, impacting the bottom line. Additionally, older homogenization technology may require frequent repairs and replacements, further exacerbating costs.
The Solution: When evaluating homogenizer machines, prioritize energy-efficient models that are designed to minimize power consumption without sacrificing performance. Look for machines that incorporate advanced technology such as variable frequency drives (VFD) that adjust motor speed according to the processing requirements. This not only reduces energy usage but also extends the lifespan of the machine. Additionally, consider investing in a homogenizer that offers predictive maintenance features, which can alert operators to potential issues before they result in costly downtime or repairs. Collaborating with suppliers who provide comprehensive service agreements can also help manage costs and ensure that the equipment is running optimally.
Scenario 3: Limited Flexibility in Processing Diverse Materials
The Problem: Many businesses encounter difficulties when trying to process a wide range of materials with a single homogenizer. For example, a manufacturer might need to switch between different types of emulsions, creams, or even solid-liquid mixtures, which can lead to inefficiencies and potential contamination issues if the machine is not appropriately configured for each application.
The Solution: To tackle this challenge, B2B buyers should seek versatile homogenizers that can handle multiple applications without compromising quality. Look for machines with interchangeable components or adjustable settings that allow for easy transition between different processing tasks. Investing in a homogenizer with a modular design can also provide the flexibility needed to accommodate future product lines or changes in formulations. Additionally, ensure that the supplier offers comprehensive training and technical support to assist in adapting the machine to new materials and processes. This proactive approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also allows for innovation in product offerings.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for homogenizer machine
What Are the Key Materials Used in Homogenizer Machines?
When selecting materials for homogenizer machines, it’s crucial to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. The choice of material directly impacts the machine’s performance, durability, and suitability for specific applications. Here, we analyze four common materials used in homogenizer machines: stainless steel, ceramic, plastic, and titanium.
How Does Stainless Steel Impact Homogenizer Performance?
Stainless steel is the most widely used material in homogenizer construction due to its excellent mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. It can withstand high pressures and temperatures, making it suitable for various applications, including food processing and pharmaceuticals. The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to wear, which leads to longer machine life and lower maintenance costs.
However, stainless steel can be relatively expensive compared to other materials. Additionally, while it is resistant to many chemicals, it may not be suitable for highly corrosive substances, which could lead to degradation over time. For international buyers, compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential, particularly in industries like food and pharmaceuticals, where hygiene and safety regulations are stringent.
What Are the Benefits of Using Ceramic in Homogenizers?
Ceramic materials are known for their exceptional hardness and wear resistance, making them ideal for applications requiring high precision and durability. They are particularly effective in high-shear homogenizers where fine particle size reduction is critical. Ceramics also exhibit excellent chemical resistance, which is beneficial when processing aggressive substances.
On the downside, ceramics can be brittle and may fracture under impact or stress, limiting their use in certain applications. They are also more expensive to manufacture, which can increase the overall cost of the homogenizer. For buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where cost sensitivity is higher, the price of ceramic components may be a significant consideration.
Why Choose Plastic for Homogenizer Components?
Plastics, particularly high-performance polymers, are increasingly used in homogenizer machines due to their lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion. They are often used in applications where chemical compatibility is a concern, such as in the cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries. Plastics can also be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs that enhance machine efficiency.
However, the durability of plastics is generally lower than that of metals or ceramics, which may lead to more frequent replacements. Additionally, plastics may have lower temperature and pressure ratings, limiting their use in high-demand applications. International buyers should ensure that the plastic materials meet local compliance standards, as regulations can vary significantly across regions.
What Advantages Does Titanium Offer in Homogenizer Design?
Titanium is a premium material known for its strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional corrosion resistance, making it suitable for high-performance homogenizers. It is particularly advantageous in applications involving aggressive chemicals or extreme environments. The longevity of titanium components can lead to lower total cost of ownership over time.
The main drawback of titanium is its high cost and the complexity of manufacturing processes involved. This can make titanium homogenizers less accessible for small to medium-sized enterprises, particularly in developing regions. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should consider the long-term benefits versus the initial investment when evaluating titanium options.
Summary of Material Selection for Homogenizer Machines
| Material | Typical Use Case for homogenizer machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Excellent durability and corrosion resistance | Expensive, may corrode with aggressive chemicals | High |
| Ceramic | High-shear applications | Exceptional hardness and chemical resistance | Brittle, high manufacturing costs | High |
| Plastic | Cosmetics, pharmaceuticals | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Lower durability, limited high-temperature use | Medium |
| Titanium | Aggressive chemical applications | Superior strength and corrosion resistance | High cost, complex manufacturing | High |
In conclusion, the selection of materials for homogenizer machines is critical to ensuring optimal performance and longevity. By understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific application needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for homogenizer machine
What are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Homogenizer Machines?
The manufacturing process of homogenizer machines involves several critical stages, each contributing to the machine’s performance and reliability. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation
The first step is the selection and preparation of materials. Homogenizers are typically constructed from high-quality stainless steel to ensure durability and resistance to corrosion, especially in food and pharmaceutical applications. The materials undergo rigorous inspections to verify their compliance with international standards such as ASTM or ISO specifications. This stage may also involve surface treatments to enhance the material’s properties, such as increasing resistance to wear and tear.
Forming Techniques
Once the materials are prepared, various forming techniques are employed. Common methods include machining, casting, and forging. Machining is particularly prevalent for creating precision components like valves and pumps, where tolerances are critical. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are often used to ensure accuracy and repeatability. Casting may be utilized for larger components, while forging can enhance the mechanical properties of certain parts, making them more resilient under high pressure.
Assembly Process
The assembly stage is where the manufactured components come together to create the final product. Skilled technicians follow detailed assembly protocols to ensure that all parts fit correctly and function as intended. This stage often includes the installation of seals, gaskets, and other components that are essential for maintaining pressure and preventing leaks. Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the assembly process to catch any potential issues early.
Finishing Techniques
The finishing stage involves surface treatments and quality assurance measures that enhance the machine’s performance and aesthetic appeal. Techniques such as polishing, coating, and passivation are used to improve surface smoothness and prevent contamination. This stage is crucial for homogenizers used in sensitive applications like food processing or pharmaceuticals, where cleanliness is paramount.
What Quality Assurance Standards are Relevant for Homogenizer Machines?
Quality assurance in the manufacturing of homogenizer machines is critical to ensure safety, efficiency, and compliance with international regulations. Various standards govern the quality assurance process, including ISO 9001, CE marking, and industry-specific certifications such as API (American Petroleum Institute).
International Standards
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized standard that outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Companies manufacturing homogenizers often seek ISO 9001 certification to demonstrate their commitment to quality and continuous improvement. This certification process includes regular audits and assessments to ensure adherence to the established QMS.
Industry-Specific Certifications
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications are essential. For example, CE marking is required for equipment sold in the European market, indicating compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection legislation. For pharmaceutical applications, adherence to API standards ensures that the equipment meets the stringent requirements for safety and efficacy.

Illustrative image related to homogenizer machine
What are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is an integral part of the manufacturing process, involving several checkpoints to ensure that each homogenizer machine meets the required specifications.
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
The IQC phase involves inspecting raw materials and components as they arrive at the manufacturing facility. This step is crucial for identifying defects or non-conformance before production begins. Suppliers are often required to provide certificates of compliance or test reports to verify that materials meet specified standards.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
During the manufacturing process, IPQC measures are implemented to monitor production. This includes regular checks on machining accuracy, assembly integrity, and adherence to process parameters. Statistical process control (SPC) techniques may be used to track variations and ensure that the manufacturing process remains within acceptable limits.
Final Quality Control (FQC)
The FQC stage occurs once the homogenizer is fully assembled. This comprehensive inspection includes functional testing, pressure testing, and performance evaluation against predetermined specifications. Any deviations are documented, and corrective actions are taken to resolve issues before the product is shipped.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers adhere to stringent quality control measures. Here are several methods to verify supplier QC:
Conducting Supplier Audits
One of the most effective ways to assess a supplier’s quality control processes is through on-site audits. These audits allow buyers to evaluate the manufacturing environment, review documentation, and observe quality control practices firsthand. Auditors can verify compliance with international standards and assess the supplier’s commitment to quality.
Requesting Quality Reports
Buyers should request detailed quality reports that outline the QC measures implemented during production. These reports may include information on IQC, IPQC, and FQC results, providing insights into the supplier’s quality management practices. Regular quality metrics, such as defect rates and corrective action reports, can also offer valuable information.
Engaging Third-Party Inspection Services
Utilizing third-party inspection services is another effective strategy for verifying supplier quality. Independent inspectors can conduct thorough evaluations of manufacturing processes and product quality, providing an unbiased assessment. This step is particularly important for international buyers who may not have the resources to conduct audits themselves.
What are the Quality Control Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate several unique quality control considerations.
Understanding Regional Standards
Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements and quality standards. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these standards to ensure compliance. For example, equipment sold in the European Union must meet CE marking requirements, while buyers in the Middle East may need to adhere to local regulations.
Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Quality control does not end with the manufacturing process; it extends to logistics and supply chain management. Buyers should consider the impact of transportation and storage conditions on product quality. For instance, homogenizers must be handled with care to avoid damage during transit, which could affect their performance.
Language and Cultural Barriers
Language and cultural differences can pose challenges in communication between buyers and suppliers. Clear communication regarding quality expectations and standards is essential for successful transactions. B2B buyers should ensure that all specifications are documented clearly and that there is mutual understanding between parties.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for homogenizer machines are crucial for ensuring that these machines meet the high standards required in various industries. B2B buyers should be diligent in their evaluation of suppliers, leveraging audits, quality reports, and third-party inspections to ensure compliance with international standards and regional regulations. By doing so, they can secure reliable equipment that meets their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘homogenizer machine’
When sourcing a homogenizer machine, it is essential to have a structured approach to ensure you select the right equipment for your needs. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to streamline your procurement process, allowing you to make informed decisions that align with your operational requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by outlining the specific technical requirements of your homogenization process. Consider factors such as the viscosity of the materials, desired particle size, and the type of homogenization needed (e.g., high pressure, high shear, or ultrasonic).
- Key Considerations:
- Material Compatibility: Ensure the homogenizer is suitable for the substances you plan to process.
- Capacity Requirements: Determine the volume of material you will be handling to select a machine with adequate processing capabilities.
Step 2: Research Various Types of Homogenizers
Familiarize yourself with the different types of homogenizers available in the market. High-pressure homogenizers are ideal for emulsifying and processing larger volumes, while high-shear mixers are suitable for breaking down solids.
- Types to Consider:
- High-Pressure Homogenizers: Best for dairy and emulsions.
- Ultrasonic Homogenizers: Effective for smaller batches and sensitive materials.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers. A reliable supplier will have a solid reputation, proven track record, and the ability to meet your specific needs.
- Action Items:
- Request References: Ask for case studies or references from similar industries.
- Check Certifications: Ensure they have relevant industry certifications and compliance with international standards.
Step 4: Assess Customization Options
Consider whether you need a standard model or a customized homogenizer. Many suppliers offer tailored solutions that can enhance performance based on your unique requirements.
- Customization Benefits:
- Adaptability: Customized machines can accommodate specific flow rates, pressures, or materials.
- Efficiency: Tailored solutions may improve processing times and reduce operational costs.
Step 5: Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotes. Compare pricing not only based on initial costs but also on the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and operational expenses.
- Comparison Factors:
- Warranty and Support: Look for suppliers that offer comprehensive support and warranty packages.
- Long-term Value: Consider the durability and efficiency of the homogenizer to gauge long-term savings.
Step 6: Conduct Site Visits or Virtual Demonstrations
If possible, visit the supplier’s facility or request a virtual demonstration of the homogenizer in operation. This will provide insights into the machine’s performance and ease of use.
- Evaluation Criteria:
- Performance Assessment: Observe how the machine handles various materials.
- User Experience: Assess the operator interface and ease of maintenance.
Step 7: Finalize the Purchase Agreement
Once you have selected a supplier, ensure that all terms are clearly outlined in a purchase agreement. This should include delivery timelines, payment terms, and after-sales support.
- Key Elements to Include:
- Delivery Schedule: Confirm lead times for production and shipping.
- Service Agreements: Clarify the terms for maintenance and support post-purchase.
By following this checklist, you can navigate the complexities of sourcing a homogenizer machine with confidence, ensuring that your investment aligns with your operational goals and industry standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for homogenizer machine Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Homogenizer Machines?
When sourcing homogenizer machines, understanding the cost structure is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:

Illustrative image related to homogenizer machine
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used in manufacturing homogenizers significantly influence the overall cost. High-grade stainless steel, specialized alloys, and advanced components for high-pressure systems tend to drive up costs but provide enhanced durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both direct and indirect expenses associated with the manufacturing process. Skilled labor, particularly in regions with higher wage standards, can increase costs. Additionally, labor costs may vary based on the complexity of the homogenizer’s design and the required assembly processes.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, rent, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. Overhead can vary greatly depending on the manufacturer’s location and operational efficiency.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling is often necessary for specialized homogenizer designs. This upfront investment can be significant but is essential for ensuring precision and quality in the final product.
-
Quality Control (QC): Robust QC processes are vital for ensuring that homogenizers meet industry standards and specifications. The costs associated with testing and certification can add to the overall price but are crucial for maintaining product integrity.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs, including shipping, customs duties, and insurance, are significant, especially for international buyers. The choice of shipping method and the distance from the supplier can greatly affect logistics costs.
-
Margin: The supplier’s profit margin will also impact the final price. Margins can vary based on market demand, competition, and the supplier’s brand reputation.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Homogenizer Machine Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of homogenizer machines, which are critical for buyers to consider:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Purchasing in larger volumes often leads to discounts. Suppliers may offer better pricing tiers for bulk orders, making it essential for buyers to evaluate their needs carefully.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customization options, such as specific sizes, flow rates, or specialized materials, can significantly affect pricing. Buyers should clearly communicate their requirements to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Homogenizers built with high-quality materials and certified to industry standards typically come at a higher price. Certifications can assure buyers of the equipment’s reliability and safety, which is particularly important in sectors like food and pharmaceuticals.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, experience, and customer service capabilities can influence price. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record and comprehensive support services.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping and delivery (Incoterms) can also impact the final price. Understanding who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and duties can help buyers avoid unexpected expenses.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Homogenizer Machine Sourcing?
For B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the following tips can enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Engage in negotiations with suppliers. Understanding the cost structure can help buyers identify areas where they can negotiate better terms, whether it’s price, payment terms, or delivery schedules.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Assess the long-term costs associated with maintenance, energy consumption, and operational efficiency. A slightly higher upfront cost may lead to savings over time through lower operational costs.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: Currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local regulations can affect total costs. Buyers should work with suppliers who understand these factors and can provide guidance.
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Conduct thorough research on various suppliers to compare prices, quality, and service. Utilizing platforms that aggregate supplier information can save time and lead to better sourcing decisions.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for homogenizer machines can vary significantly based on the factors mentioned above. The figures provided in various sources may serve as a guideline, but potential buyers should conduct their own research and obtain quotes tailored to their specific needs and circumstances.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing homogenizer machine With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Homogenizer Machines
When evaluating equipment for mixing, emulsifying, or breaking down particles, it’s essential to consider various alternatives to homogenizer machines. Each solution offers unique advantages and potential drawbacks depending on the specific application, material characteristics, and operational requirements. Below, we compare homogenizer machines with two viable alternatives: high shear mixers and ultrasonic homogenizers.
| Comparison Aspect | Homogenizer Machine | High Shear Mixer | Ultrasonic Homogenizer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent for emulsions and cell lysis; achieves micrometer to nanometer particle size. | Effective for mixing and emulsifying; may not achieve as fine a particle size as homogenizers. | Very effective for breaking down particles at the molecular level; ideal for small volumes. |
| Cost | Generally ranges from $21,000 to $50,000+ depending on features and capacity. | Typically less expensive, ranging from $5,000 to $30,000. | Price varies widely; high-end models can exceed $50,000, but basic units start lower. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operation and setup; can be complex. | Generally easier to operate with simpler setup; often more user-friendly. | Requires specialized knowledge for optimal settings; may need calibration. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed to ensure longevity and efficiency; parts can be costly. | Lower maintenance requirements; parts are often less expensive. | Requires periodic maintenance, especially for ultrasonic probes. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for dairy, pharmaceutical, and high-viscosity products; high volume applications. | Best for food processing and cosmetics where particle size is less critical. | Suitable for laboratories and applications requiring precise control over particle size in small batches. |
In-Depth Look at Alternative Solutions
High Shear Mixers
High shear mixers utilize an impeller with sharpened blades to create intense mixing and emulsification. They are often more affordable and user-friendly compared to homogenizer machines. However, while they excel at blending liquids and creating emulsions, they may not achieve the same fine particle sizes as homogenizers, which can be a disadvantage in industries where precise particle size is critical, such as pharmaceuticals and high-end food products.
Ultrasonic Homogenizers
Ultrasonic homogenizers employ sound energy to disrupt particles and achieve fine emulsions or suspensions. They are particularly effective for small-scale applications and can produce very fine particle sizes. Although these machines can be more expensive than high shear mixers, they are often considered for specialized applications like drug formulation or advanced material processing. The main drawback is that they require technical expertise to operate effectively and may not be suitable for high-volume production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Needs
When selecting a homogenization solution, B2B buyers must consider their specific requirements, such as production volume, material characteristics, and the desired particle size. Homogenizer machines are ideal for high-volume applications requiring consistent particle size and emulsification, while high shear mixers offer cost-effective, user-friendly alternatives for less demanding tasks. Ultrasonic homogenizers are best suited for specialized applications in research or small-scale production. By aligning the choice of equipment with operational needs, businesses can enhance efficiency and product quality while optimizing costs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for homogenizer machine
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Homogenizer Machines?
When evaluating homogenizer machines, several critical specifications are pivotal for ensuring optimal performance in various industrial applications. Understanding these properties can guide B2B buyers in making informed purchasing decisions.
1. Pressure Rating
The pressure rating indicates the maximum pressure the homogenizer can handle, typically measured in bar or psi. High-pressure homogenizers are essential for applications such as dairy processing, where milk is subjected to pressures between 1000 to 3000 psi to break down fat globules. For buyers, selecting a machine with the appropriate pressure rating ensures efficient emulsification and reduces the risk of equipment failure.
2. Flow Rate
Flow rate, measured in liters per hour (L/h) or milliliters per minute (mL/min), reflects the volume of material the homogenizer can process over a specific time. This specification is crucial for production planning; a higher flow rate means increased throughput, making it vital for large-scale operations in food and beverage or pharmaceutical industries.
3. Material Grade
The construction material of the homogenizer is critical for durability and compliance with industry standards. Stainless steel is commonly used due to its corrosion resistance and ease of cleaning, which is essential in food and pharmaceutical applications. Buyers should prioritize machines made from high-grade materials to ensure longevity and hygiene.

Illustrative image related to homogenizer machine
4. Temperature Control
Temperature control capabilities are important for processes sensitive to heat, such as those involving proteins or emulsions. Homogenizers equipped with advanced temperature control systems can maintain the desired temperature during processing, minimizing the risk of thermal degradation. This feature is particularly valuable for B2B buyers in the dairy and cosmetic sectors, where product integrity is crucial.
5. Particle Size Reduction Capability
The ability of a homogenizer to achieve specific particle sizes is essential for product quality. Machines may be rated for achieving particle sizes in microns or nanometers, which directly impacts the texture and stability of emulsions. Buyers must assess their end-product requirements to select a homogenizer that meets their particle size specifications.
6. Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is becoming increasingly important in industrial operations, both for cost savings and sustainability. Homogenizers with energy-efficient designs reduce operational costs and environmental impact. Buyers should inquire about the energy consumption ratings of potential machines to align with their sustainability goals.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Homogenizer Machines?
Understanding industry jargon can significantly enhance communication and negotiation between buyers and suppliers. Here are some essential terms to know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of homogenizers, knowing the OEM helps buyers identify reputable suppliers and ensures they receive quality equipment backed by manufacturer support.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ specifies the smallest quantity of an item that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it can impact inventory management and cash flow. Understanding the MOQ helps in budgeting and ensures that production needs are met without overcommitting resources.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers request pricing information from suppliers for specific products or services. This term is significant for buyers looking to compare costs and negotiate better terms before finalizing a purchase.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized international trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms is essential for B2B transactions, especially for international buyers, as they clarify who bears the risk and costs at various points in the shipping process.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times is critical for planning and ensuring that production schedules are maintained. It can vary significantly based on the supplier’s location and production capacity.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of acquiring homogenizer machines more effectively, ensuring they select the right equipment for their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the homogenizer machine Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Homogenizer Machine Sector?
The homogenizer machine sector is witnessing significant growth driven by several global factors. Increased demand for processed food and beverages, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, and the Middle East, has propelled the need for efficient homogenization technologies. High-pressure homogenizers, known for their ability to create stable emulsions and enhance product quality, are particularly sought after in dairy and beverage applications. The trend toward automation and smart technologies is also reshaping sourcing strategies, with manufacturers increasingly integrating IoT capabilities into homogenizers to improve efficiency and real-time monitoring.
Another emerging trend is the customization of homogenizer machines to meet specific industry requirements. Companies are looking for equipment that can handle diverse materials—from dairy to pharmaceuticals—while ensuring consistent quality and compliance with regulatory standards. For international buyers, particularly from regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia, understanding local market dynamics, such as regulatory frameworks and technological advancements, is crucial when sourcing these machines.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing Homogenizer Purchases?
Sustainability is becoming an essential consideration for B2B buyers in the homogenizer machine sector. The environmental impact of production processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, is under scrutiny. Buyers are increasingly favoring manufacturers that prioritize sustainable practices, such as energy-efficient designs and the use of recyclable materials. This shift is particularly relevant in markets with stringent environmental regulations.
Moreover, ethical sourcing is gaining traction, with an emphasis on transparent supply chains. Buyers are encouraged to evaluate the sourcing of materials used in homogenizer machines, seeking suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to ethical labor practices and sustainable resource management. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and certifications for materials can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
What Is the Evolution and Historical Context of Homogenizer Technology?
The evolution of homogenizer technology dates back to the early 20th century, initially developed to improve milk processing. Over the decades, advancements have transformed homogenizers into versatile machines capable of processing a wide range of materials. The introduction of high-pressure and ultrasonic homogenizers marked a significant milestone, enabling more efficient emulsification and particle size reduction.
As industries evolved, so did the technology, with a focus on enhancing performance, reducing energy consumption, and meeting the specific needs of diverse applications, from food and beverage to pharmaceuticals. This historical context is vital for B2B buyers as it highlights the continuous innovation within the sector, paving the way for more efficient and sustainable solutions in homogenization processes. Understanding this evolution can help buyers make informed decisions when selecting equipment that meets current industry standards and future demands.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of homogenizer machine
-
How do I select the right homogenizer for my application?
Selecting the right homogenizer requires a thorough understanding of your specific application. Consider factors such as the type of materials you will be processing (liquids, solids, or both), the desired particle size reduction, and the volume of production. High-pressure homogenizers are ideal for emulsions and cell lysis, while high-shear mixers excel in breaking down solid particles. It’s also crucial to evaluate the machine’s compatibility with your existing processes and whether it can be customized to meet your unique production requirements. -
What are the key features to look for in a homogenizer machine?
When sourcing a homogenizer, focus on features such as pressure capabilities, flow rates, and the type of homogenizing technology (high-pressure, high-shear, or ultrasonic). Additionally, consider ease of maintenance, energy efficiency, and the machine’s ability to handle varying viscosities. Advanced features like customizable valves and control systems can enhance performance and adaptability. Always review the manufacturer’s specifications and customer feedback to ensure the machine meets your operational needs. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for homogenizers?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between manufacturers and models. Generally, larger suppliers may have higher MOQs, while niche manufacturers might offer flexibility for smaller orders. It’s essential to communicate your requirements clearly during the inquiry process. Additionally, consider the benefits of bulk purchasing, such as cost savings and better lead times, especially if you anticipate ongoing needs for replacement parts or additional machines. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing a homogenizer?
Payment terms will vary based on the supplier’s policies, your negotiation skills, and your established relationship with the manufacturer. Common terms include a percentage deposit upfront, with the balance due upon delivery or installation. In international transactions, consider using secure payment methods like letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks. Always clarify payment terms in your contract to avoid misunderstandings and ensure a smooth transaction process. -
How can I verify the reliability of a homogenizer supplier?
To vet a homogenizer supplier, start by researching their industry reputation and customer reviews. Check for certifications and compliance with international standards, such as ISO or CE, which indicate quality assurance. Engaging with existing clients for testimonials can provide insights into the supplier’s reliability and service quality. Additionally, consider visiting their facility or requesting a demonstration of their equipment to assess their production capabilities firsthand. -
What is the typical lead time for ordering a homogenizer machine?
Lead times for homogenizer machines can range from a few weeks to several months, depending on the manufacturer, model, and customization level. Standard models may have shorter lead times, while specialized or high-capacity machines often require more time for production. It’s advisable to discuss lead times upfront and plan your procurement schedule accordingly, especially if your production timelines are tight or if you are entering a new market. -
Are there options for customizing homogenizers to fit my needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for homogenizers to better suit specific applications. Customizations may include adjustments to flow rates, pressure settings, and material selection for parts that contact product. Discuss your specific needs with the supplier to explore available options. This collaboration can lead to a more efficient machine that enhances your production process and meets your quality standards. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing a homogenizer machine?
When importing a homogenizer, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs duties, and local regulations. It’s crucial to work with suppliers who provide clear shipping terms and can assist with documentation for customs clearance. Be aware of any import restrictions or requirements in your country, which may affect lead times and costs. Partnering with a reliable logistics provider can streamline the process and help ensure timely delivery of your equipment.
Top 5 Homogenizer Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. IQS Directory – Homogenizers
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Homogenizers are specialized mixing devices designed to create a uniform and consistent blend by forcing substances through a restricted passage. They utilize various forces such as turbulence and cavitation, along with high pressure, to homogenize solution contents evenly. Key features include a positive displacement pump and a homogenizing valve configuration. Homogenizers are used across multip…
2. GEA – Industrial Homogenizers
Domain: gea.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: GEA Industrial Homogenizers are machines consisting of a compression block for high-pressure pumping and a homogenizing valve for micronizing dispersed particles to micrometers and nanometers. They are versatile, suitable for various applications in food & beverage, dairy, pharmaceutical, chemical, and cosmetics industries. GEA offers customized homogenizers tailored to specific product needs, uti…
3. Fisher Scientific – Mechanical Homogenizers
Domain: fishersci.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Mechanical homogenizers are powered devices used for grinding, lysing, and homogenization of biological samples prior to molecular extraction. They come in handheld and benchtop models and are available in complete kits with stands, motors, and probes, as well as pestle accessories. Product types include: Aggregate, Bead Mill Homogenizer, Cordless Homogenizer Unit, Dispersing Aggregate, Dissolver,…
4. Quadro – HV High Shear Homogenizer
Domain: quadroliquids.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: High Shear Homogenizer and Wet Mill by Quadro® HV
– Submicron homogenizing, high shear wet milling, micronization
– Low cost per kg-hr in the industry
– High shear mixing results without high-pressure processing
– More process shear energy than conventional rotor-stator mills
– Lower capital costs compared to high-pressure homogenizers or media mills
– Optimized for homogenizing or wet milling
– T…
5. Silverson – Homogenizer Mixers
Domain: silverson.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Silverson Homogenizer Mixers are designed for homogenizing various products such as creams, ointments, sauces, flavoring emulsions, and pharmaceutical suspensions. The ideal droplet size for uniformity is between 2 – 5 microns. The mixers utilize a three-stage mixing/homogenizing process: 1) Rapid Ingredient Intake using a high-speed rotor, 2) Uniform Size Reduction through centrifugal force and p…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for homogenizer machine
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers in the Homogenizer Market?
In today’s competitive landscape, strategic sourcing of homogenizer machines is vital for optimizing production efficiency and product quality. High-pressure homogenizers, for instance, are essential for industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics, where achieving uniformity and stability in emulsions is paramount. By understanding the specific needs of your operation and aligning them with the right technology—whether it be high shear, ultrasonic, or mechanical homogenizers—you can significantly enhance your product offerings.
How Can International Buyers Leverage Strategic Sourcing?
For international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the opportunity to collaborate with reputable manufacturers can lead to customized solutions that cater to local market demands. This strategic sourcing approach not only improves operational efficiency but also ensures compliance with international quality standards.
What’s Next for Your Homogenizer Procurement Strategy?
As you consider your next investment in homogenizer technology, prioritize partnerships with suppliers who offer both innovative solutions and robust support. Engage with manufacturers that are willing to customize their offerings to meet your unique requirements. This proactive approach will not only streamline your sourcing process but also position your business for sustainable growth in a rapidly evolving market. Embrace this opportunity to enhance your production capabilities and drive your business forward.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

Illustrative image related to homogenizer machine