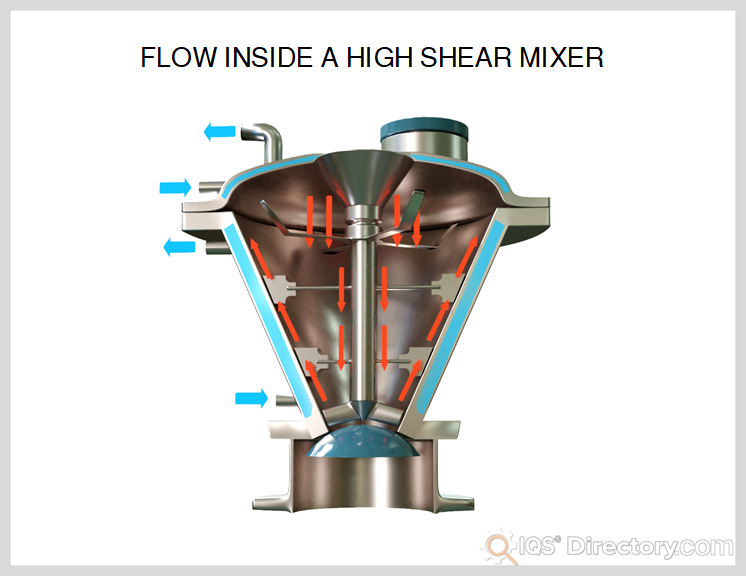
A Deep Dive into High-Shear Mixer Solution
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for high-shear mixer
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing high-shear mixers can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers across various industries. With the demand for precise emulsification and dispersion growing, navigating the global market requires a strategic approach to ensure that the selected equipment meets both operational needs and regulatory standards. This comprehensive guide is designed to empower international buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, by providing detailed insights into the diverse types of high-shear mixers available, their applications across different sectors, and essential considerations for supplier vetting.
Throughout this guide, we will explore the intricacies of high-shear mixing technology, from benchtop laboratory dispersers to large-scale industrial solutions. Buyers will gain an understanding of crucial factors such as cost considerations, performance specifications, and maintenance requirements. Additionally, we will delve into best practices for evaluating suppliers, ensuring that you partner with manufacturers who not only offer quality products but also provide robust support services.
By the end of this guide, you will be equipped with the knowledge necessary to make informed purchasing decisions that align with your business objectives. Whether you are entering a new market or optimizing existing operations, our insights will help you confidently select the right high-shear mixer to enhance your production capabilities and drive business success.
Understanding high-shear mixer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benchtop Lab Dispersers | Compact design, ideal for small batches | R&D, product formulation | Pros: Space-efficient, cost-effective. Cons: Limited capacity for large-scale production. |
| In-Line Rotor Stator Mixers | Continuous mixing, high efficiency | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Pros: Consistent quality, reduced processing time. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Batch Rotor Stators | Versatile operation for varied batch sizes | Cosmetic manufacturing, chemical blending | Pros: Flexible batch sizes, easy to clean. Cons: Potential for longer cycle times. |
| Dual Shaft Mixers | Combines high shear and low shear mixing | Paints, coatings, adhesives | Pros: Handles a wide range of viscosities. Cons: More complex operation may require training. |
| Three Roll Mills | High precision for fine particle dispersion | Ink, pigment, and specialty chemical industries | Pros: Exceptional dispersion quality. Cons: Higher maintenance due to mechanical parts. |
What are Benchtop Lab Dispersers and Their B2B Applications?
Benchtop lab dispersers are designed for small-scale mixing tasks, making them ideal for research and development environments. These mixers are compact and efficient, allowing businesses to conduct product formulation tests without the need for large equipment. When considering a benchtop lab disperser, buyers should evaluate the unit’s horsepower and capacity to ensure it meets their specific production needs while remaining cost-effective.

Illustrative image related to high-shear mixer
How Do In-Line Rotor Stator Mixers Enhance Production Efficiency?
In-line rotor stator mixers are engineered for continuous operation, making them suitable for high-volume applications such as food processing and pharmaceuticals. Their design promotes consistent mixing and emulsification, which can significantly reduce processing times and improve product quality. Buyers should consider the initial investment cost and the required maintenance when selecting in-line mixers, as these factors can impact long-term operational efficiency.
What Makes Batch Rotor Stators Versatile for Various Industries?
Batch rotor stators offer flexibility in processing different batch sizes, making them a valuable asset in industries such as cosmetics and chemical blending. Their ability to accommodate varying viscosities and formulations allows companies to adapt quickly to market changes. However, potential buyers should keep in mind that batch processing may lead to longer cycle times compared to continuous mixing solutions.
Why Choose Dual Shaft Mixers for Diverse Applications?
Dual shaft mixers combine high shear and low shear mixing capabilities, making them effective for handling a wide range of viscosities in applications such as paints and adhesives. This versatility allows businesses to streamline their production processes. However, the complexity of operation may necessitate additional training for staff, which buyers should factor into their purchasing decision.
What Advantages Do Three Roll Mills Offer for Fine Dispersion?
Three roll mills are specialized equipment designed for high precision in dispersing fine particles, particularly in industries like inks and specialty chemicals. Their ability to achieve exceptional dispersion quality is a significant advantage for manufacturers seeking superior product characteristics. Buyers should be aware that while these mills deliver outstanding results, they may require more maintenance due to their mechanical components.
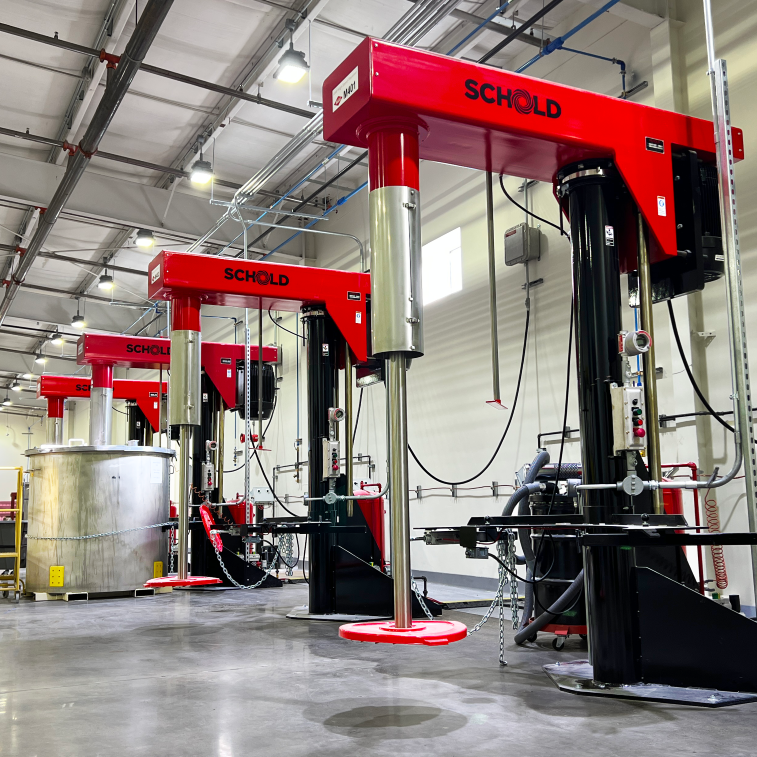

Illustrative image related to high-shear mixer
Key Industrial Applications of high-shear mixer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of high-shear mixer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical | Emulsification of creams and ointments | Ensures uniformity and stability of products, reducing waste and enhancing efficacy. | Compliance with GMP standards, material compatibility, and scalability. |
| Food and Beverage | Production of sauces, dressings, and beverages | Achieves consistent texture and flavor, improving product quality and consumer satisfaction. | Regulatory compliance, hygiene standards, and batch size flexibility. |
| Cosmetics and Personal Care | Mixing of lotions and gels | Enhances product performance and shelf-life by creating stable emulsions. | Sourcing materials that meet safety and quality standards, customization options. |
| Chemicals and Coatings | Dispersing pigments in paints and coatings | Improves product consistency and performance, reducing settling and separation. | Equipment durability, resistance to chemical wear, and energy efficiency. |
| Plastics and Polymers | Mixing of polymer additives and masterbatches | Ensures uniform distribution of additives, enhancing material properties. | High shear capability, heat resistance, and compatibility with various polymer types. |
How is High-Shear Mixing Used in the Pharmaceutical Industry?
In the pharmaceutical sector, high-shear mixers play a crucial role in the emulsification of creams and ointments. These mixers create stable emulsions by combining immiscible liquids, ensuring uniformity in drug distribution. The precision offered by high-shear mixers minimizes waste and enhances the efficacy of pharmaceutical products, which is vital for regulatory compliance. Buyers should prioritize equipment that meets Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) standards and can accommodate the specific viscosity requirements of their formulations.
What Role Does High-Shear Mixing Play in Food and Beverage Production?
High-shear mixers are essential in the food and beverage industry for producing sauces, dressings, and beverages. They ensure a consistent texture and flavor profile, which is critical for consumer satisfaction and brand loyalty. By achieving stable emulsions, these mixers help maintain product quality over time. International buyers should consider sourcing mixers that comply with food safety regulations, ensuring materials are easy to clean and maintain hygiene standards.
Why is High-Shear Mixing Important in Cosmetics and Personal Care?
In the cosmetics industry, high-shear mixers are utilized to create lotions and gels that require precise emulsification. This process enhances product performance and extends shelf life by preventing phase separation. The ability to customize formulations is a significant advantage for brands looking to differentiate themselves in a competitive market. Buyers should focus on sourcing mixers that offer versatility in processing and the ability to handle various ingredient types while adhering to safety standards.
How Does High-Shear Mixing Improve Chemical and Coating Products?
High-shear mixers are pivotal in the chemicals and coatings sector for dispersing pigments in paints and coatings. They ensure a homogenous mixture, which enhances product consistency and performance, reducing issues such as settling and separation. Buyers in this industry should prioritize equipment durability and resistance to chemical wear, as well as energy efficiency to optimize production costs.
What Benefits Does High-Shear Mixing Offer in Plastics and Polymers?
In the plastics industry, high-shear mixers are critical for blending polymer additives and masterbatches. They ensure a uniform distribution of additives, which is essential for enhancing the physical properties of the final product. Buyers should look for high-shear mixers that can handle varying material types and provide the necessary heat resistance, ensuring optimal performance in their applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘high-shear mixer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inefficient Mixing and Emulsion Stability Issues
The Problem: A common challenge faced by manufacturers in industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics is achieving a consistent and stable emulsion or dispersion. Buyers often encounter issues with their current high-shear mixers that fail to produce uniform mixtures, leading to product inconsistencies. This can result in wasted raw materials, extended production times, and ultimately, dissatisfied customers. When emulsions separate or dispersions agglomerate, manufacturers may find themselves facing costly recalls or reformulations, which can severely impact their bottom line.
The Solution: To overcome these mixing inefficiencies, buyers should consider investing in high-shear mixers equipped with advanced rotor-stator technology. When sourcing a mixer, look for models that offer adjustable shear rates, allowing for precise control over the mixing process. Additionally, selecting mixers with a wider range of rotor-stator configurations can help address specific viscosity requirements. For example, a dual-shaft mixer can be particularly effective for high-viscosity applications, providing both high shear and bulk mixing capabilities. Furthermore, regularly calibrating and maintaining the equipment ensures optimal performance, which can mitigate the risk of emulsion breakdown.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Scaling Up Production
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle with scaling up their production processes while maintaining the same quality achieved in smaller batches. This is especially true for companies transitioning from lab-scale to full-scale production. The challenge often lies in the inconsistency of results when increasing batch sizes, leading to variability in product quality and the potential for increased costs. Buyers may feel overwhelmed by the need to replicate successful lab results in larger equipment without losing the desired product characteristics.
The Solution: To successfully scale up, buyers should engage with manufacturers who provide comprehensive testing and validation services. Before making a purchase, conduct pilot runs with the high-shear mixer to evaluate its performance at various scales. This process can help identify the optimal mixer configuration for larger volumes. Additionally, selecting a mixer with in-line capabilities can enhance efficiency and minimize the risk of issues associated with batch-to-batch variations. Buyers should also invest in training for their operators to ensure they understand how to adjust processing parameters as batch sizes change, thus safeguarding product quality across different scales.
Scenario 3: High Maintenance Costs and Downtime
The Problem: High maintenance costs and unexpected downtime are significant pain points for manufacturers utilizing high-shear mixers. Frequent breakdowns not only disrupt production schedules but also lead to unexpected repair costs that can erode profit margins. Many buyers find themselves in a cycle of reactive maintenance rather than proactive management, which can lead to frustration and decreased operational efficiency.
The Solution: To combat high maintenance costs, buyers should prioritize selecting high-shear mixers known for their reliability and ease of maintenance. Look for models that feature modular designs, allowing for quick replacement of parts without extensive downtime. Establishing a regular maintenance schedule is crucial; it ensures equipment is serviced at optimal intervals to prevent unexpected failures. Additionally, investing in a mixer with predictive maintenance capabilities can be beneficial. These mixers often come equipped with sensors that monitor performance in real-time, alerting operators to potential issues before they lead to significant breakdowns. This proactive approach can significantly reduce downtime and overall maintenance expenses, leading to a more efficient production environment.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for high-shear mixer
What Are the Key Materials Used in High-Shear Mixers?
High-shear mixers are critical in various industries, including food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. The choice of materials for these mixers can significantly impact their performance, durability, and overall effectiveness. Below, we analyze four common materials used in high-shear mixers, detailing their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international buyers.
1. Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high tensile strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. It is commonly available in grades such as 304 and 316, with 316 offering superior resistance to chlorides and other corrosive agents.
Pros & Cons: Stainless steel is highly durable and easy to clean, making it ideal for sanitary applications, particularly in the food and pharmaceutical sectors. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may require specialized manufacturing processes, which could affect lead times.
Impact on Application: Its compatibility with various media, including acidic and alkaline substances, makes stainless steel a versatile choice. However, its higher cost might be a limiting factor for smaller manufacturers or those in price-sensitive markets.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East often prefer 316 stainless steel for its enhanced corrosion resistance, while those in Africa and South America may prioritize cost-effectiveness.
2. Carbon Steel
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its strength and toughness, with a good balance of cost and performance. It is less resistant to corrosion compared to stainless steel but can be treated with coatings to enhance its durability.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of carbon steel is its lower cost, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious buyers. However, its susceptibility to rust and corrosion limits its use in applications involving aggressive chemicals or high moisture.
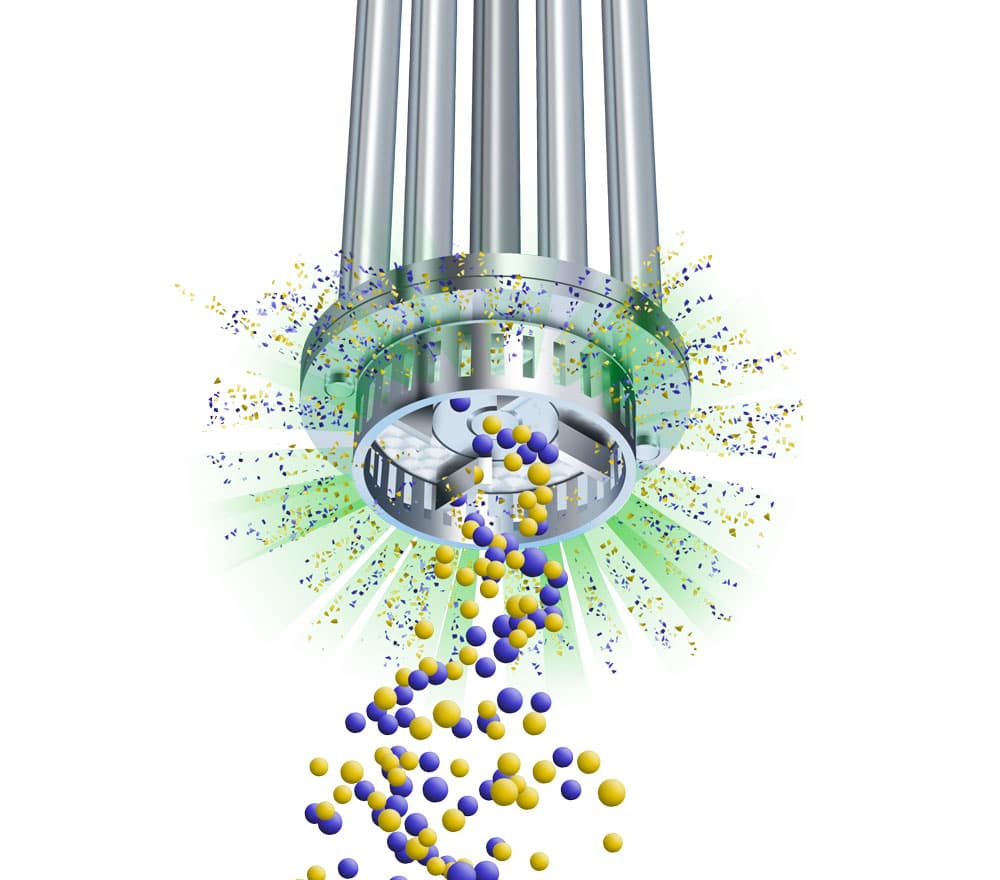
Illustrative image related to high-shear mixer
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is suitable for mixing less corrosive materials but may not be ideal for food or pharmaceutical applications without proper coatings. Its performance can be significantly affected by the media being processed.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that carbon steel mixers meet local compliance standards. In regions like Africa and South America, where cost is a significant factor, carbon steel is often preferred, provided that the application does not involve corrosive substances.
3. Plastic Composites
Key Properties: Plastic composites, such as polypropylene and polyethylene, offer excellent chemical resistance and are lightweight. They can withstand a range of temperatures, but their mechanical strength is generally lower than that of metals.
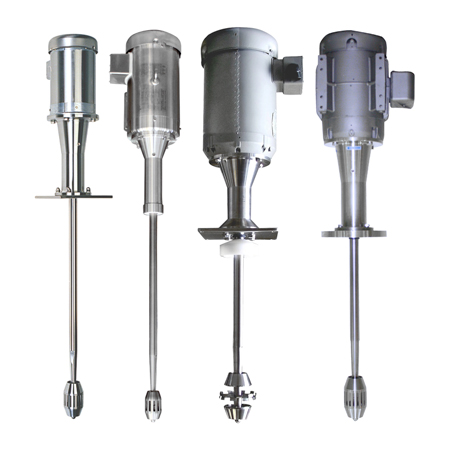

Illustrative image related to high-shear mixer
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of plastic composites is their resistance to corrosion and ease of fabrication, allowing for complex shapes. However, they may not be suitable for high-temperature applications and can degrade over time when exposed to UV light.
Impact on Application: These materials are ideal for mixing aggressive chemicals or in applications where corrosion is a concern. However, their lower strength limits their use in high-stress environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify the chemical compatibility of plastic composites with the intended media. In regions like Vietnam, where chemical processing is prevalent, these materials can be a cost-effective solution.
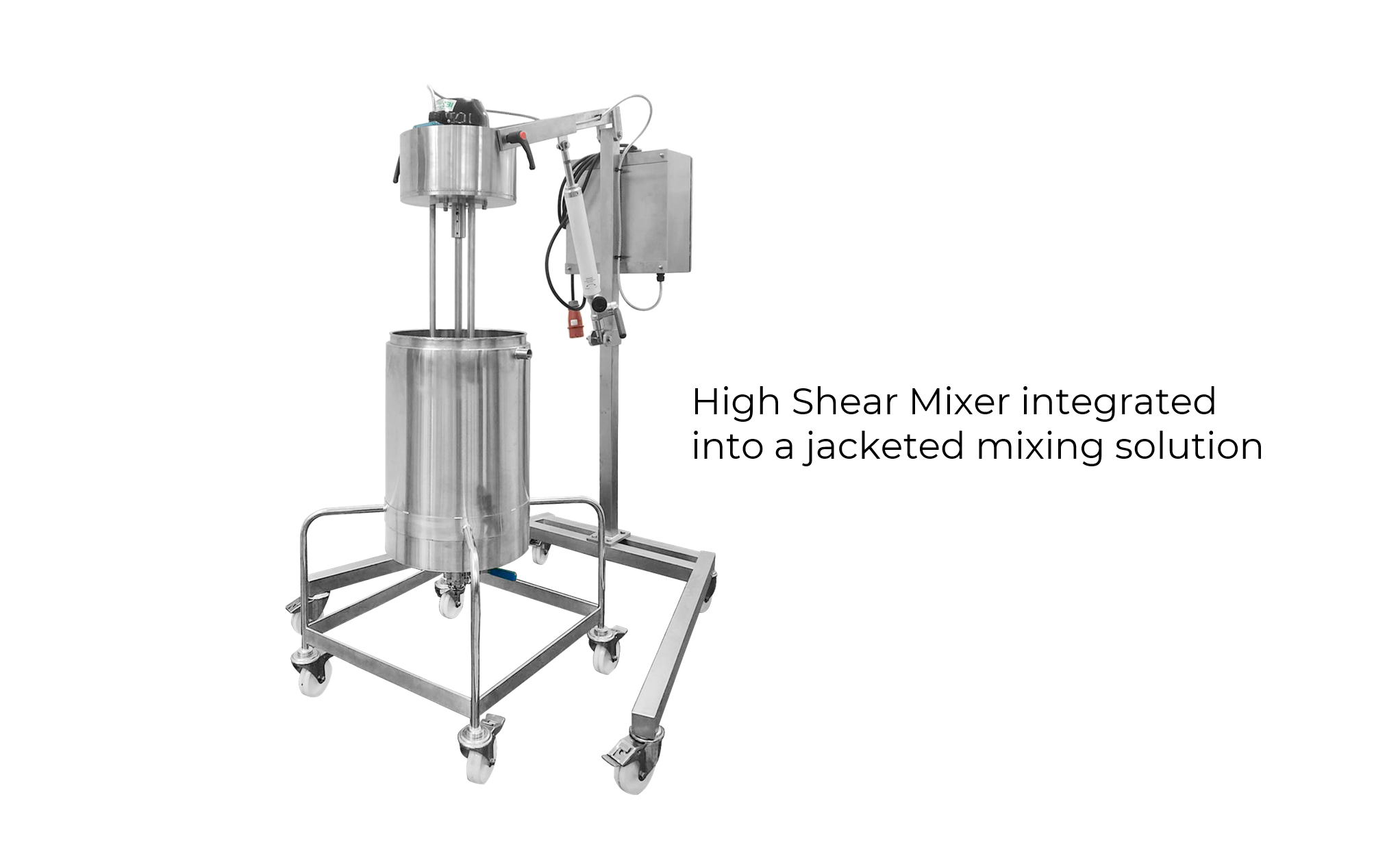

Illustrative image related to high-shear mixer
4. Titanium
Key Properties: Titanium is known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in harsh environments. It can withstand high temperatures and is non-reactive with most chemicals.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of titanium is its durability and longevity in demanding applications. However, it is one of the most expensive materials available, which can be a significant drawback for many businesses.
Impact on Application: Titanium is suitable for high-end applications where performance and longevity are critical, such as in the aerospace and pharmaceutical industries. Its high cost may limit its use to specialized applications.
Illustrative image related to high-shear mixer
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards is essential, particularly for high-value applications. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East may be more inclined to invest in titanium for its long-term benefits, while those in cost-sensitive markets may seek alternatives.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for high-shear mixer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Food and pharmaceutical applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost | High |
| Carbon Steel | Mixing less corrosive materials | Cost-effective | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Plastic Composites | Chemical processing | Corrosion resistant | Lower mechanical strength | Medium |
| Titanium | Aerospace and high-end pharmaceuticals | Exceptional durability | Very high cost | High |
This guide aims to equip international B2B buyers with valuable insights into material selection for high-shear mixers, ensuring informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for high-shear mixer
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of High-Shear Mixers?
The manufacturing process of high-shear mixers is a complex undertaking that involves several key stages, each crucial for ensuring product quality and performance.
Material Preparation: Sourcing and Selection
The first step in manufacturing high-shear mixers is material preparation, where the selection of high-quality materials is essential. Manufacturers typically use stainless steel, known for its durability and resistance to corrosion, especially in applications involving chemicals or food products. Suppliers often source these materials from reputable vendors who provide certifications to guarantee material quality.
Forming: Precision Engineering Techniques
Once materials are sourced, they undergo various forming processes, such as machining and welding. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is commonly employed to achieve the precise dimensions required for components like rotors and stators. The precision in forming is vital because any deviation can affect the efficiency and functionality of the mixer. Advanced laser cutting and plasma cutting techniques may also be utilized to ensure clean edges and minimize material waste.
Assembly: Integration of Components
The assembly stage is where all the components come together. This process involves skilled technicians who meticulously assemble the mixers, ensuring that each part fits together correctly. Special attention is given to the alignment of the rotor and stator, as this affects the shear force generated during mixing. The assembly process may also include the integration of additional features, such as variable speed drives, which are essential for controlling mixing intensity.
Finishing: Surface Treatment and Quality Checks
Finally, the finishing stage encompasses surface treatments, such as polishing or coating, to enhance corrosion resistance and improve aesthetic appeal. This stage is critical, especially for mixers used in the food and pharmaceutical industries, where cleanliness is paramount. After finishing, each unit undergoes thorough quality checks to ensure it meets the specified standards before it is packaged and shipped.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in High-Shear Mixer Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process of high-shear mixers. It encompasses various international standards and industry-specific certifications that help maintain product integrity.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for High-Shear Mixers?
Manufacturers of high-shear mixers often adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO 9001 ensures that the manufacturing processes are consistently monitored and improved. Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking in Europe or API standards in the oil and gas sector, are crucial for demonstrating compliance with regulatory requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) is implemented at multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial phase involves inspecting the raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards. Any non-conforming materials are rejected or re-sourced.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, operators conduct regular checks to ensure that components are being produced according to specifications. This may include dimensional checks and visual inspections.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipping, each high-shear mixer undergoes a final inspection to ensure it meets all quality standards. This can include performance testing under actual working conditions to verify functionality.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for High-Shear Mixers?
Testing methods play a critical role in verifying the performance and reliability of high-shear mixers. Common testing techniques include:
-
Performance Testing: This involves running the mixer under controlled conditions to measure parameters such as shear rate, mixing efficiency, and consistency of emulsions or dispersions produced.
-
Durability Testing: High-shear mixers are subjected to stress tests to evaluate their durability and resistance to wear over time, ensuring they can withstand demanding industrial environments.
-
Safety Testing: Compliance with safety standards is also assessed, ensuring that the mixers meet operational safety requirements to protect operators and facilities.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential. Here are several strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes and quality control measures firsthand. This includes reviewing documentation, observing production lines, and interviewing key personnel.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can provide insight into a supplier’s QC performance. These reports should include data on defect rates, compliance with standards, and any corrective actions taken.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturing processes and product quality. These agencies often have established criteria that align with international standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing high-shear mixers globally, B2B buyers must be aware of various nuances that can affect quality control:
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding local manufacturing practices and quality expectations is crucial. This can vary significantly between regions, affecting communication and quality outcomes.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have varying regulatory requirements. Buyers must ensure that suppliers comply with local and international regulations relevant to their industry.
-
Logistical Challenges: International shipping can introduce risks such as damage during transit. Buyers should consider suppliers’ packaging and shipping practices to minimize these risks.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices involved in high-shear mixers, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and quality standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘high-shear mixer’
Introduction
Sourcing a high-shear mixer requires careful consideration of your specific mixing needs and the capabilities of potential suppliers. This checklist will guide international B2B buyers through the essential steps to ensure you select the right equipment for your operations, whether you’re in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before you begin your search, it’s crucial to outline your technical requirements. Consider the viscosity of the materials you’ll be mixing, the desired particle size, and the scale of production. Knowing these details will help you identify mixers that can meet your specific needs.
- Capacity Needs: Determine the volume you need to process, whether it’s small batches or large-scale production.
- Viscosity Range: Understand the range of viscosities you will be handling to ensure compatibility with the mixer.
Step 2: Research Different Mixer Types
There are various types of high-shear mixers available, each designed for specific applications. Familiarize yourself with the differences between batch and inline mixers, rotor-stator designs, and other configurations.
- Batch Mixers: Ideal for smaller quantities and more precise formulations.
- Inline Mixers: Best for continuous processes and large volumes.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Don’t just rely on their website; investigate their reputation and customer service history.
- Certifications: Ensure suppliers have relevant certifications such as ISO, CE, or others pertinent to your industry.
- Client Feedback: Look for reviews or testimonials from previous clients to gauge their reliability and service quality.
Step 4: Request Product Demonstrations
Seeing the equipment in action can provide valuable insights into its performance and suitability for your needs. Schedule demonstrations with shortlisted suppliers to assess how their mixers handle your specific materials.
- Performance Testing: Ask to observe the mixer with materials that match your production requirements.
- Adjustability: Evaluate how easily the mixer can be adjusted for different processes.
Step 5: Discuss After-Sales Support and Maintenance
Understanding the after-sales support offered by the supplier is essential for long-term satisfaction. Inquire about warranty terms, availability of spare parts, and technical support.
- Maintenance Services: Check if they provide routine maintenance services or training for your team.
- Spare Parts Availability: Confirm the ease of obtaining replacement parts to minimize downtime.
Step 6: Compare Pricing and Value
While cost is a significant factor, it’s important to consider the overall value offered by different suppliers. Ensure you are comparing similar specifications and support services when evaluating prices.
- Total Cost of Ownership: Consider not just the initial purchase price but also operational costs, maintenance, and potential downtime.
- Negotiation Opportunities: Be prepared to negotiate terms, especially if you are placing a large order.
Step 7: Finalize Your Decision and Place Order
Once you have thoroughly evaluated suppliers and their offerings, it’s time to make your decision. Ensure all terms are clearly outlined in the contract before placing your order.
- Contract Review: Have legal counsel review the contract for clarity on warranty, delivery terms, and payment conditions.
- Order Confirmation: Confirm your order details, including specifications, delivery schedules, and any training or support promised by the supplier.
By following this checklist, you can confidently source a high-shear mixer that meets your operational needs while ensuring a reliable partnership with your supplier.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for high-shear mixer Sourcing
When considering the sourcing of high-shear mixers, a comprehensive understanding of the cost structure and pricing elements is essential for B2B buyers. This analysis will cover the major cost components, key price influencers, and practical buyer tips tailored for international markets, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Cost Components for High-Shear Mixers?
The cost structure of high-shear mixers typically comprises several key components:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts costs. High-quality stainless steel, for example, may raise initial expenses but offers durability and corrosion resistance, essential for industries like food and pharmaceuticals.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can be a significant factor in the overall price. Skilled labor is required for assembly and quality control, and labor rates differ substantially across countries.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. A factory’s location can influence these costs, with facilities in regions with higher operational expenses likely passing those costs onto buyers.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific designs or applications can increase initial investment costs. However, it may lead to cost savings in the long run by improving efficiency and reducing waste during production.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures product reliability but adds to costs. Certifications (such as ISO) can also affect pricing, as they require adherence to strict standards.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs are influenced by the size and weight of the mixers, as well as the distance to the buyer. International shipping can incur additional fees and time delays.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their operational risks and profit. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s market position and the competitive landscape.
How Do Price Influencers Affect High-Shear Mixer Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of high-shear mixers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can affect pricing. Larger volumes often lead to bulk discounts, making it essential for buyers to assess their needs accurately.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can significantly alter pricing. Unique designs or additional features may lead to higher costs, but they can also provide enhanced functionality tailored to specific applications.
-
Materials and Quality: The quality of materials used in production will affect both the price and the longevity of the mixer. Buyers should consider the total cost of ownership, factoring in the potential for repairs or replacements over time.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge a premium, but they often provide better service and support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding international commercial terms is vital. Incoterms dictate who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly affect the total landed cost of the mixer.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Sourcing High-Shear Mixers?
To maximize value when sourcing high-shear mixers, consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Engage in discussions with suppliers to negotiate better terms, especially for larger orders. Don’t hesitate to request discounts based on volume or long-term partnerships.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership: Consider not only the purchase price but also maintenance, operation, and potential downtime costs. A higher upfront investment in a reliable mixer may lead to lower overall costs.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations. For instance, suppliers in Europe may have different pricing structures compared to those in Africa or South America, influenced by local market conditions.
-
Request Samples or Trials: If possible, obtain samples or trial periods for mixers to assess performance before committing to a large purchase. This can help ensure the equipment meets your specifications and operational needs.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Keeping abreast of industry trends and technological advancements can provide leverage during negotiations and help you make more informed purchasing decisions.
By understanding these aspects of cost and pricing, B2B buyers can make more strategic sourcing decisions when investing in high-shear mixers. It’s essential to approach the market with a clear strategy to optimize both cost efficiency and operational effectiveness.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing high-shear mixer With Other Solutions
In the realm of industrial mixing, high-shear mixers are widely recognized for their efficiency in creating emulsions and dispersions. However, there are alternative technologies that can also achieve similar results, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these alternatives can help businesses make informed decisions based on their specific operational needs and constraints.
| Comparison Aspect | High-Shear Mixer | Batch Rotor Stator Mixer | Three Roll Mill |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency for emulsions and dispersions; handles high viscosity | Effective for small batch processing; versatile in application | Excellent for reducing particle size and achieving fine dispersions |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment | Generally lower cost; ideal for small-scale operations | High initial cost; suitable for specialized applications |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled setup; may need training | Simple setup; often portable | Requires significant space and setup; complex operation |
| Maintenance | Moderate; regular cleaning required | Low; easy to maintain and clean | High; requires frequent maintenance due to wear and tear |
| Best Use Case | Large-scale production of emulsions | Small batch production in labs or pilot plants | High viscosity materials requiring fine milling |
What Are the Key Advantages and Disadvantages of Batch Rotor Stator Mixers?
Batch rotor stator mixers are designed for small batch processes and are often more cost-effective than high-shear mixers. Their simplicity allows for quick setup and operation, making them a favorite in laboratory settings and pilot plants. However, they may not achieve the same level of efficiency for large-scale production as high-shear mixers, which can limit their application in larger manufacturing environments.
How Do Three Roll Mills Compare in Terms of Performance and Cost?
Three roll mills excel in applications that require fine dispersion and particle size reduction, making them ideal for high-viscosity materials like inks and paints. They can produce extremely uniform products but come with a higher initial cost and require more maintenance due to the mechanical wear of rollers. This makes them a less appealing option for businesses seeking a versatile mixing solution for a variety of applications.
What Should B2B Buyers Consider When Choosing Between These Mixing Solutions?
When evaluating which mixing technology to invest in, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including the scale of production, specific application requirements, and budget constraints. High-shear mixers are excellent for large-scale emulsions and dispersions, while batch rotor stators may be more appropriate for smaller, specialized tasks. Three roll mills are best for applications needing precise particle size control but may not be feasible for all operational setups due to their cost and complexity.
Ultimately, the choice of mixing technology should align with the company’s operational goals, production scale, and the specific properties of the materials being processed. Conducting a thorough analysis of each option’s strengths and weaknesses will empower buyers to make strategic decisions that enhance their production efficiency and product quality.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for high-shear mixer
High-shear mixers play a critical role in various industries, including food processing, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics, where achieving the right consistency and emulsification is vital. Understanding the essential technical properties and trade terminology associated with high-shear mixers can significantly enhance purchasing decisions for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Technical Properties of High-Shear Mixers?
-
Motor Power (HP)
The motor power, measured in horsepower (HP), indicates the strength of the mixer. Common ratings range from 1 HP to 40 HP. This specification is crucial for buyers as it determines the mixer’s capacity to handle different viscosities and batch sizes, ensuring optimal performance in production processes. -
Viscosity Range (cP)
Viscosity, measured in centipoise (cP), represents the thickness of a fluid. High-shear mixers are designed to operate within specific viscosity ranges, typically from 1 cP to over 100,000 cP. Understanding the viscosity range helps buyers select a mixer that can efficiently process their materials, from thin liquids to thick pastes, thereby enhancing production efficiency. -
Mixing Capacity (gallons/liters)
The mixing capacity indicates the maximum volume of material the mixer can handle in a single batch. Capacities can range from small benchtop models (1-5 gallons) to large industrial units (over 1,000 gallons). Selecting the appropriate capacity is essential for aligning with production demands and ensuring that the equipment meets operational needs. -
Material Grade
The material grade of the mixer components (e.g., stainless steel, food-grade plastic) affects durability, corrosion resistance, and compliance with industry standards. For instance, food-grade stainless steel is critical for food applications to prevent contamination. Buyers must assess the material quality to ensure long-term reliability and safety in their processes. -
Rotor/Stator Configuration
The rotor/stator design significantly influences the mixing efficiency and shear force generated. Different configurations, such as batch mixers or inline mixers, cater to various applications. Understanding these designs allows buyers to select the right type of mixer based on their specific mixing requirements. -
Speed Settings (RPM)
The speed of the mixer, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM), determines the intensity of the mixing action. Adjustable speed settings enable flexibility in processing different materials and achieving desired emulsification levels. Buyers should consider the importance of speed variability to optimize their mixing processes.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to High-Shear Mixers?
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. When purchasing high-shear mixers, understanding OEM specifications ensures compatibility and quality assurance, particularly when integrating with existing equipment. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it impacts inventory management and cost-efficiency. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their purchases to avoid excess inventory or stockouts. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing and other details for specific products. This process is essential for obtaining competitive pricing and understanding the terms of sale for high-shear mixers, allowing buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized terms used in international trade to define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. They clarify aspects such as shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers to ensure smooth transactions and minimize potential disputes. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. Understanding lead times is essential for production planning, especially in industries with tight schedules. Buyers should communicate with suppliers to establish realistic timelines for high-shear mixer deliveries. -
Warranty Period
The warranty period is the duration during which the manufacturer guarantees the product against defects. Knowing the warranty terms helps buyers assess the reliability of high-shear mixers and the manufacturer’s commitment to quality, providing peace of mind in their investment.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when investing in high-shear mixers, ultimately enhancing their production capabilities and operational efficiency.
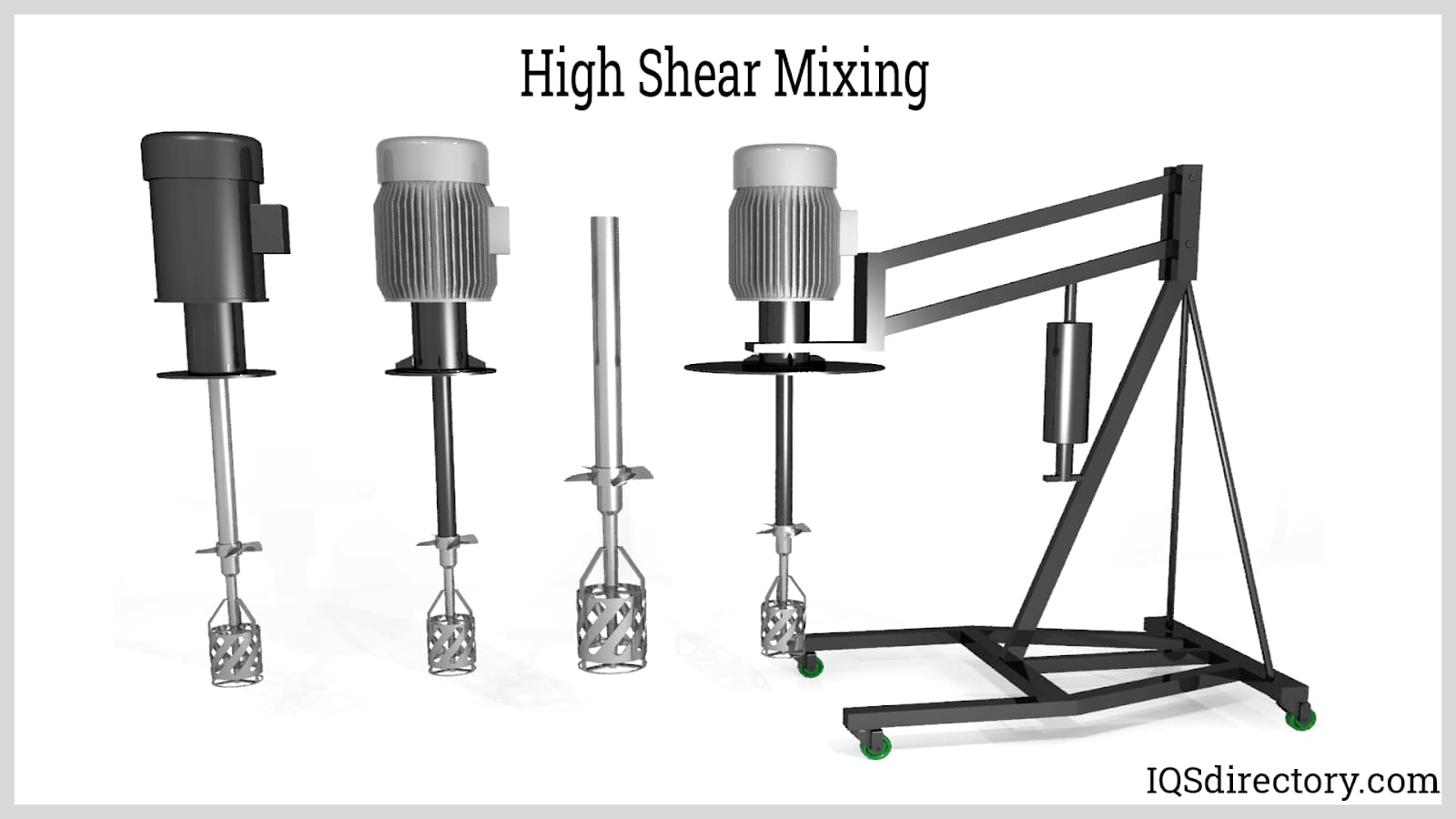

Illustrative image related to high-shear mixer
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the high-shear mixer Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics in the High-Shear Mixer Sector?
The global market for high-shear mixers is experiencing significant growth driven by advancements in processing technologies, increased demand for high-quality emulsions, and the expansion of industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there is a heightened focus on improving production efficiency and product quality, pushing manufacturers to adopt high-shear mixers for their ability to achieve precise emulsification and dispersion. Emerging technologies, such as IoT-enabled mixers, are enhancing monitoring capabilities, allowing businesses to optimize processes and reduce waste.
As international B2B buyers, particularly those in emerging markets, navigate this sector, it’s essential to consider the diverse applications of high-shear mixers. For instance, industries are increasingly utilizing in-line mixers for continuous processing, which not only enhances efficiency but also reduces labor costs. Additionally, the trend toward customization is evident as manufacturers are increasingly offering tailored solutions to meet specific production requirements, thus ensuring scalability and flexibility in operations.
How Is Sustainability Impacting Sourcing Trends for High-Shear Mixers?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount in the high-shear mixer sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, prompting buyers to prioritize suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices. This includes sourcing materials with lower carbon footprints and ensuring that production processes minimize waste and energy consumption.
Buyers should look for suppliers that hold certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and others that focus on sustainable manufacturing practices. Furthermore, the demand for ‘green’ materials—such as recyclable components and energy-efficient designs—is on the rise. By aligning with suppliers committed to sustainability, businesses not only improve their marketability but also contribute to a more responsible supply chain, which is increasingly valued by consumers and regulatory bodies alike.
What Is the Historical Context of High-Shear Mixers Relevant to Today’s Market?
The evolution of high-shear mixers dates back to the early 20th century when the need for efficient mixing solutions became apparent in various manufacturing sectors. Initially utilized in the food industry, the technology quickly expanded into pharmaceuticals and cosmetics as the demand for high-quality emulsions grew. Over the decades, advancements in rotor-stator designs and motor technology have significantly improved mixing efficiency and versatility.
Today, high-shear mixers are recognized for their ability to produce uniform products at high speeds, a capability that has become essential in fast-paced manufacturing environments. The transition from batch processing to continuous mixing systems marks a significant evolution, reflecting the industry’s commitment to enhancing productivity and meeting the needs of modern consumers. Understanding this historical context allows buyers to appreciate the ongoing advancements and innovations that define the current high-shear mixer landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of high-shear mixer
-
1. How do I choose the right high-shear mixer for my application?
Choosing the right high-shear mixer depends on several factors including the viscosity of the materials, batch size, and the desired end product characteristics. Evaluate the mixing process you intend to perform—whether it’s emulsification, dispersion, or homogenization—and match it with the mixer type (e.g., batch or inline). Consider the power requirements, rotor/stator configuration, and any specific features like explosion-proof capabilities if applicable to your industry. Consultation with a supplier can provide insights tailored to your specific needs. -
2. What are the key specifications to look for in high-shear mixers?
When sourcing high-shear mixers, focus on specifications such as horsepower, rotor/stator design, and mixing capacity. Additionally, consider the materials of construction for durability and compatibility with your products. Look for adjustable speed settings to accommodate various mixing tasks and ensure the mixer is easy to clean and maintain. Certifications for safety and quality can also be important, especially for industries like food and pharmaceuticals. -
3. What is the typical lead time for high-shear mixer orders?
Lead times for high-shear mixers can vary based on the supplier, the complexity of the mixer, and customization requirements. Standard models may have shorter lead times, often between 4 to 6 weeks, while customized or high-capacity units may take longer, up to 12 weeks or more. It’s advisable to communicate your timeline clearly with suppliers during the negotiation phase to ensure they can meet your delivery expectations. -
4. How can I ensure the quality of high-shear mixers from international suppliers?
To ensure quality, conduct thorough supplier vetting by checking their certifications, manufacturing processes, and customer reviews. Request samples or case studies of similar applications to evaluate performance. Establish a clear quality assurance process including inspections and testing before shipment. Engaging third-party inspection services can also provide an additional layer of assurance, especially for high-value equipment. -
5. What customization options are available for high-shear mixers?
Many manufacturers offer customization options such as specific rotor/stator designs, sizes, and materials to suit unique processing needs. You can also customize features like speed control, temperature regulation, and mobility (e.g., portable stands). Discuss your specific requirements with suppliers to explore available configurations that enhance performance for your application. -
6. What are the typical payment terms for purchasing high-shear mixers?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers but typically include options like 30% upfront deposit with the balance due before shipment, or net 30/60 days after delivery. Ensure you clarify payment terms early in negotiations and consider using letters of credit or escrow services for large orders to mitigate risk. Always review terms in the context of your cash flow and project timelines. -
7. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing high-shear mixers?
When importing, consider shipping costs, customs duties, and import regulations specific to your country. Collaborate with your supplier to determine the best shipping method (air or sea) based on urgency and budget. Ensure that the packaging is suitable for international transport to prevent damage. Additionally, having a reliable logistics partner can help navigate customs processes smoothly. -
8. How do I troubleshoot common issues with high-shear mixers?
Common issues with high-shear mixers include inadequate mixing, overheating, or unusual noises. Start by checking the power supply and ensuring that all components are properly assembled and functioning. For poor mixing, verify that the rotor/stator is appropriate for your application and that the mixer is operating at the correct speed. Regular maintenance, including cleaning and inspection of wear parts, can also prevent many operational problems. If issues persist, consult the manufacturer’s technical support for guidance.
Top 1 High-Shear Mixer Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Silverson – High Shear Mixers
Domain: silverson.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: High Shear Mixers from Silverson include a versatile lineup designed for various applications, from laboratory to production scale. Key product details include: 1. **Lab Series**: Ideal for laboratory work and R&D, featuring Laboratory Mixers, Laboratory In-Line Mixers, and Laboratory Powder/Liquid Mixers. 2. **Batch Series**: Capable of mixing, emulsifying, homogenizing, disintegrating, and disso…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for high-shear mixer
As global industries continue to evolve, the demand for high-shear mixers is increasingly significant. These advanced mixing solutions are pivotal for achieving superior emulsions and dispersions across diverse applications, from food production to pharmaceuticals. By strategically sourcing high-shear mixers, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency, ensuring consistent product quality while reducing time and costs associated with mixing processes.
Investing in high-shear mixers not only optimizes production capabilities but also aligns with sustainability goals by minimizing waste and energy consumption. Buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize suppliers that offer customizable solutions tailored to their specific needs, ensuring that their operations remain competitive in a dynamic market.
Looking ahead, the integration of innovative technologies and automation within high-shear mixing processes presents exciting opportunities for businesses to scale and adapt. It is imperative for international B2B buyers to engage with reputable suppliers that emphasize quality, reliability, and support. By doing so, companies can position themselves at the forefront of their industries, ready to meet the challenges of tomorrow. Embrace the potential of high-shear mixers—make informed sourcing decisions today to drive your business forward.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.