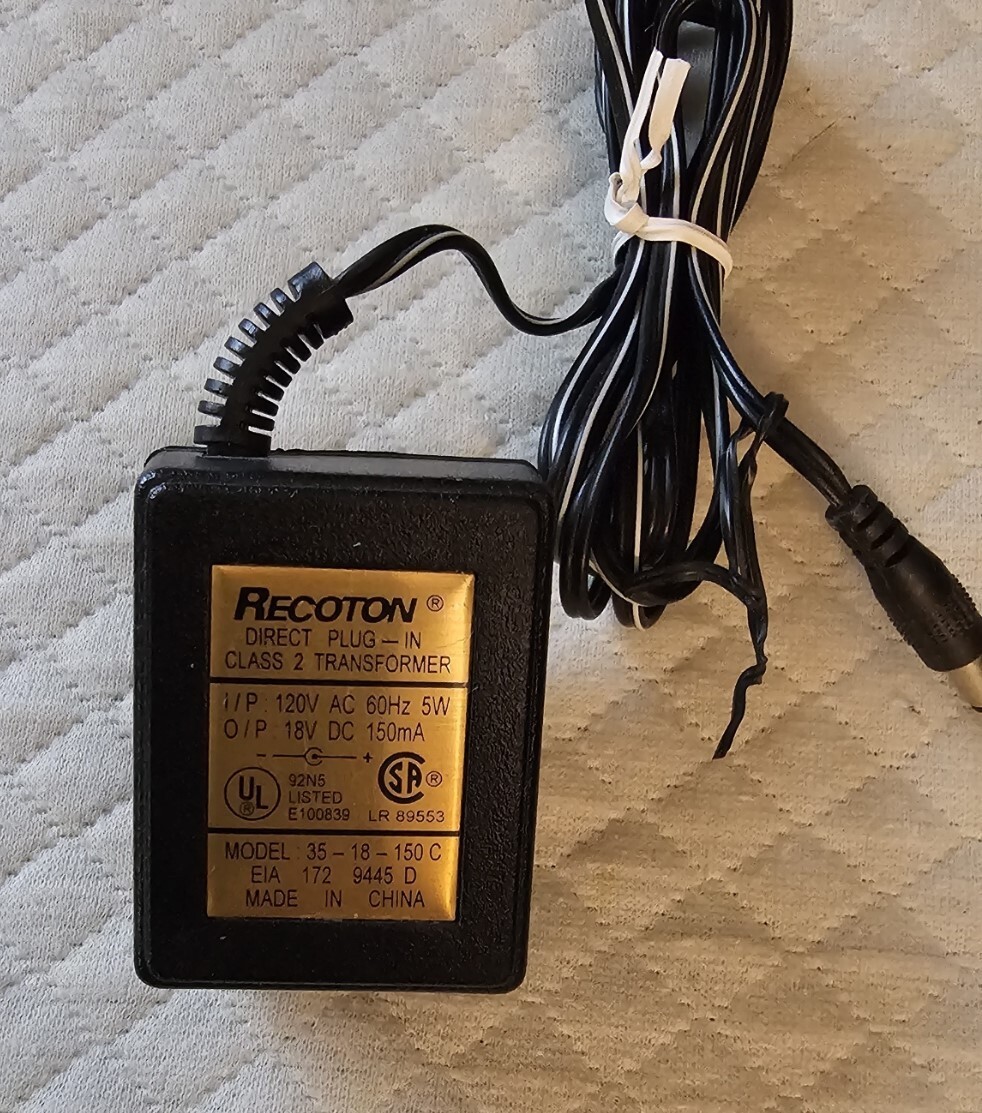
A Deep Dive into Direct Plug In Class 2 Transformer Solution
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for direct plug in class 2 transformer
In an increasingly interconnected world, sourcing reliable direct plug-in Class 2 transformers poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. Whether you’re operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, the complexities of navigating diverse supply chains, regulatory compliance, and product specifications can be daunting. This guide aims to simplify the sourcing process by offering a comprehensive overview of Class 2 transformers, including various types, applications, and essential features that align with your specific needs.
Our exploration delves into the intricacies of different transformer models, highlighting their suitability for various applications—from powering low-voltage lighting systems to supporting sensitive electronic devices. Moreover, we provide actionable insights on how to effectively vet suppliers, ensuring that you partner with reputable manufacturers who adhere to international quality standards.
Cost considerations are also addressed, equipping you with the knowledge to make informed purchasing decisions that enhance your operational efficiency and budget management. By leveraging this guide, B2B buyers will gain the confidence to navigate the global market for direct plug-in Class 2 transformers, facilitating smarter investments that drive business success. Whether you are based in Germany, Nigeria, or beyond, this resource is designed to empower you with the tools needed for strategic sourcing in today’s dynamic marketplace.
Understanding direct plug in class 2 transformer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard AC Class 2 Transformer | 120V input with various output voltages; basic design | General-purpose electronic devices | Pros: Cost-effective; Cons: Limited features |
| Dimmable Class 2 Transformer | Adjustable output for lighting control; integrated dimming feature | Lighting systems in commercial spaces | Pros: Enhances ambiance; Cons: Higher cost |
| Multi-Voltage Class 2 Transformer | Supports multiple output voltages; versatile | Diverse applications across industries | Pros: Flexible use; Cons: Complexity in selection |
| Water-Resistant Class 2 Transformer | Designed for damp or wet environments; rugged casing | Outdoor lighting, wet locations | Pros: Durable; Cons: Typically pricier |
| Smart Class 2 Transformer | Wi-Fi connectivity; remote control capabilities | Smart home and IoT applications | Pros: Modern features; Cons: Requires network setup |
What are the Characteristics of Standard AC Class 2 Transformers?
Standard AC Class 2 transformers are fundamental devices that convert 120V AC input into lower DC or AC output voltages. Their simplicity makes them a go-to solution for powering a variety of electronic devices. These transformers are widely used in general-purpose applications, such as powering small appliances and electronics in both commercial and residential settings. When purchasing, buyers should consider the specific voltage requirements and load capacity to ensure compatibility with their devices.
How Do Dimmable Class 2 Transformers Enhance Lighting Systems?
Dimmable Class 2 transformers feature adjustable output capabilities, allowing users to control the brightness of their lighting systems effectively. These transformers are particularly beneficial in commercial environments where ambiance is crucial, such as restaurants and retail spaces. When selecting a dimmable transformer, B2B buyers should evaluate the dimming technology (e.g., trailing edge, leading edge) to ensure it aligns with their lighting fixtures for optimal performance.
Why Choose Multi-Voltage Class 2 Transformers for Versatility?
Multi-voltage Class 2 transformers can output various voltages, making them highly versatile for different applications. They are ideal for businesses that require a single power supply to support multiple devices with varying voltage needs. This flexibility can reduce inventory costs and simplify procurement processes. Buyers should assess the transformer’s voltage range and current ratings to match their specific operational requirements.
What Makes Water-Resistant Class 2 Transformers Suitable for Outdoor Use?
Water-resistant Class 2 transformers are designed to withstand damp conditions, making them perfect for outdoor lighting applications. Their rugged construction protects against moisture, ensuring reliability in challenging environments. B2B buyers should consider the IP rating of these transformers to ensure they meet the environmental demands of their intended installations, especially in regions with high humidity or precipitation.
How Do Smart Class 2 Transformers Integrate with Modern Technology?
Smart Class 2 transformers offer advanced features such as Wi-Fi connectivity and remote control capabilities, making them ideal for smart home and IoT applications. These transformers enable seamless integration with smart devices, allowing users to control their lighting and appliances from anywhere. When purchasing, businesses should consider compatibility with existing smart home systems and the potential need for additional setup or configuration.
Key Industrial Applications of direct plug in class 2 transformer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of direct plug in class 2 transformer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lighting | Powering LED lighting systems in commercial spaces | Ensures consistent and reliable power for lighting solutions | Compliance with international safety standards and certifications |
| Telecommunications | Supplying power to communication devices and routers | Reliable power supply enhances system uptime and reliability | Voltage compatibility and power ratings specific to equipment |
| Medical Equipment | Providing power for diagnostic and monitoring devices | Critical for patient safety and operational efficiency | Strict adherence to medical device regulations and certifications |
| Consumer Electronics | Charging and powering small appliances and gadgets | Facilitates user convenience and product versatility | Consideration of regional voltage standards and plug types |
| Security Systems | Powering surveillance cameras and alarm systems | Enhances security and monitoring capabilities | Robustness and durability in various environmental conditions |
In the lighting industry, direct plug-in class 2 transformers are widely used to power LED lighting systems in commercial spaces, such as offices and retail environments. These transformers provide a stable power supply that enhances energy efficiency and reduces maintenance costs. For international buyers, ensuring compliance with local safety standards and certifications is crucial, as these factors can significantly impact the installation and operation of lighting solutions.

Illustrative image related to direct plug in class 2 transformer
In the telecommunications sector, direct plug-in class 2 transformers are essential for supplying power to communication devices, including routers and modems. A reliable power source is vital for maintaining system uptime and ensuring the integrity of data transmission. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should focus on voltage compatibility and power ratings to match their specific equipment requirements, which can vary widely across different markets.
Within the medical equipment field, these transformers are critical for powering diagnostic and monitoring devices, where reliability is paramount. Ensuring a continuous power supply is not only essential for operational efficiency but also for patient safety. International buyers must navigate strict regulations and certifications governing medical devices, necessitating thorough due diligence when sourcing transformers for this application.
In the realm of consumer electronics, direct plug-in class 2 transformers are commonly used for charging and powering small appliances and gadgets. This application offers significant user convenience and enhances product versatility. Buyers should consider regional voltage standards and plug types to ensure compatibility with local electrical systems, which is particularly important for international sourcing.
Lastly, in the security systems industry, these transformers power surveillance cameras and alarm systems, thereby enhancing security and monitoring capabilities. The reliability and durability of these transformers are critical, especially in regions with varying environmental conditions. Buyers should prioritize sourcing robust transformers that can withstand local challenges, ensuring effective security solutions.

Illustrative image related to direct plug in class 2 transformer
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘direct plug in class 2 transformer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Incompatibility with Local Power Standards
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, face challenges when sourcing direct plug-in Class 2 transformers due to variations in local voltage and frequency standards. Transformers designed for 120V and 60Hz systems may not work optimally or at all in countries where 220V or 50Hz is the norm. This incompatibility can lead to equipment failures, increased costs due to returns, and delays in project timelines, significantly impacting operational efficiency and profitability.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should prioritize sourcing transformers that are explicitly rated for the local electrical standards of their operational regions. Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that offer transformers compatible with 220V/50Hz specifications. Additionally, consider investing in adjustable transformers or those equipped with universal voltage input features. This will not only ensure compatibility but also provide flexibility for future projects in different regions. Establishing strong relationships with local distributors can also help in obtaining the right specifications and support when needed.
Scenario 2: Overheating and Safety Concerns
The Problem: Overheating is a significant concern with direct plug-in Class 2 transformers, especially in industrial applications where multiple devices may draw power simultaneously. This can lead to premature equipment failure, potential fire hazards, and costly downtimes. B2B buyers may struggle to find transformers that offer adequate safety features, increasing anxiety about their equipment’s reliability and the safety of their facilities.
The Solution: When selecting a transformer, it is crucial to look for models that incorporate advanced safety features such as thermal protection, overload protection, and short-circuit prevention. Buyers should evaluate the transformer’s specifications, including the wattage and amp ratings, to ensure it can handle the load of all connected devices without overheating. Additionally, consider transformers that come with a built-in cooling mechanism or that have been tested for high-temperature environments. Implementing regular maintenance checks can further enhance safety, ensuring that any signs of wear or damage are addressed before they lead to failures.
Scenario 3: Complex Installation and Configuration Processes
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter difficulties during the installation and configuration of direct plug-in Class 2 transformers, particularly when they involve multiple outputs for various devices. Complicated wiring diagrams and unclear instructions can lead to installation errors, resulting in further costs for troubleshooting and potential damage to connected equipment.
The Solution: To simplify the installation process, buyers should seek transformers that are designed for ease of use, featuring clear, concise installation manuals and labeled connectors. Additionally, consider opting for plug-and-play transformers that require minimal setup and can accommodate multiple devices without complex wiring. If possible, engaging a qualified electrician for installation can ensure that the transformer is set up correctly and safely, reducing the risk of errors. Furthermore, investing in training for in-house technical staff on the specifics of the transformers being utilized can foster greater confidence and competence in handling future installations.
By addressing these common pain points with informed solutions, B2B buyers can enhance their operational reliability and effectiveness when utilizing direct plug-in Class 2 transformers.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for direct plug in class 2 transformer
What Are the Key Materials Used in Direct Plug-In Class 2 Transformers?
When selecting materials for direct plug-in Class 2 transformers, several factors must be considered, including electrical performance, durability, cost, and compliance with international standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of these transformers, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Copper
Key Properties: Copper is known for its excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and resistance to corrosion. It can operate efficiently at high temperatures, making it suitable for transformers that may experience heat buildup.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, which leads to reduced energy losses during operation. However, copper is relatively expensive compared to other conductive materials, which can increase the overall manufacturing cost of the transformer. Additionally, copper components can be more complex to manufacture, especially when intricate designs are required.
Impact on Application: Copper is particularly effective in applications requiring high efficiency and reliability. It is compatible with various media, including electrical insulation materials, ensuring optimal performance.
International Considerations: Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as DIN and IEC for electrical safety. In Africa and South America, local regulations may also dictate the use of specific materials, emphasizing the need for thorough market research.
2. Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, has good electrical conductivity (though not as high as copper), and exhibits excellent corrosion resistance. It is also more malleable than copper, allowing for easier manufacturing processes.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its lower cost compared to copper, making it a more budget-friendly option for manufacturers. However, its lower conductivity can lead to higher energy losses, which may affect the efficiency of the transformer. Additionally, aluminum can be less durable under high-temperature conditions compared to copper.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for applications where weight is a concern, such as portable devices. However, it may not be ideal for high-performance transformers that require maximum efficiency.
International Considerations: Compliance with ASTM standards is crucial for aluminum components, especially in markets like Germany and Nigeria, where quality assurance is paramount. Buyers should also consider the availability of aluminum in their local markets to avoid supply chain disruptions.
3. Plastic (Polycarbonate)
Key Properties: Polycarbonate is a thermoplastic known for its high impact resistance, thermal stability, and electrical insulation properties. It can withstand a wide range of temperatures, making it suitable for various environmental conditions.

Illustrative image related to direct plug in class 2 transformer
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of polycarbonate is its lightweight nature and excellent electrical insulation, which enhances the safety of transformers. However, it may not be as durable as metals under extreme conditions and can be more susceptible to UV degradation if not treated.
Impact on Application: Polycarbonate is often used in the casing of transformers, providing protection against physical damage and electrical hazards. Its compatibility with various media makes it a versatile choice for different applications.
International Considerations: Buyers should verify that polycarbonate materials meet local safety and environmental regulations, particularly in Europe, where strict compliance with REACH regulations is enforced. Understanding local preferences for material safety can also guide purchasing decisions.

Illustrative image related to direct plug in class 2 transformer
4. Steel
Key Properties: Steel is a strong and durable material that provides excellent mechanical strength and can withstand high pressure and temperatures. It is often used in transformer cores for its magnetic properties.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of steel is its durability and strength, which enhances the overall robustness of the transformer. However, it is heavier than other materials, which can be a disadvantage in portable applications. Additionally, steel components may require additional treatment to prevent corrosion.
Impact on Application: Steel is essential for applications requiring structural integrity and magnetic efficiency. Its compatibility with various insulating materials ensures effective performance in high-load scenarios.
International Considerations: Compliance with international standards such as JIS and ASTM is crucial for steel materials, especially in markets like Germany and South America, where quality standards are rigorously enforced. Buyers should also consider the availability of treated steel to ensure long-term durability.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for direct plug in class 2 transformer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Windings and connectors | Superior electrical conductivity | High cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Windings and lightweight applications | Cost-effective and lightweight | Lower conductivity than copper | Medium |
| Plastic | Transformer casing and insulation | Excellent electrical insulation | Less durable under extreme conditions | Low |
| Steel | Transformer cores | High strength and durability | Heavier and may require corrosion treatment | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for direct plug-in Class 2 transformers, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for direct plug in class 2 transformer
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Direct Plug-In Class 2 Transformers?
The manufacturing process for direct plug-in Class 2 transformers involves several critical stages that ensure the end product meets performance and safety standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing transformers.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used?
The first stage in manufacturing involves the selection and preparation of materials. High-quality copper wire is often used for windings due to its excellent electrical conductivity. Insulating materials, such as polycarbonate or thermoplastics, are selected for their heat resistance and durability. Steel or aluminum may be used for the casing, which provides structural integrity and protection. Suppliers should verify that all materials comply with relevant safety and environmental standards, such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances).
Forming: How Are Components Shaped and Assembled?
Once materials are prepared, the next step is forming. This involves winding the copper wire around a magnetic core, which is typically made from silicon steel to enhance magnetic efficiency. The winding process is critical; precise control over the number of turns and the tension applied can significantly impact the transformer’s performance.
After winding, the magnetic core is assembled with the winding in a manner that minimizes air gaps, enhancing efficiency. This stage may also involve the use of automated machines to ensure accuracy and reduce human error. B2B buyers should inquire about the technology used in this phase to gauge the quality assurance capabilities of their suppliers.

Illustrative image related to direct plug in class 2 transformer
Assembly: What Happens During the Assembly Process?
The assembly phase combines all individual components into a complete transformer unit. This includes integrating the casing, attaching the input and output connectors, and ensuring that all electrical connections are secure. It is during this stage that key safety features, such as overcurrent protection and thermal fuses, are installed.
Quality assurance during assembly is vital. Manufacturers often employ techniques such as automated optical inspection (AOI) to detect defects in soldering or component placement. Buyers should consider requesting detailed documentation of assembly procedures to ensure adherence to best practices.
Finishing: How Is the Final Product Prepared for Market?
The finishing stage includes testing and final assembly checks. Transformers are typically coated with protective finishes to resist environmental factors like moisture and dust. This coating also enhances the aesthetic appeal of the product.
Before the transformers are packaged for shipment, they undergo a series of functional tests to ensure they meet specified voltage and current outputs. B2B buyers should look for suppliers who provide detailed testing reports, as these documents serve as proof of compliance with performance standards.
What Quality Assurance Processes Are in Place for Direct Plug-In Class 2 Transformers?
Quality assurance (QA) is a crucial aspect of manufacturing direct plug-in Class 2 transformers. It ensures that products are safe, reliable, and meet international standards.

Illustrative image related to direct plug in class 2 transformer
What International Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
Manufacturers must comply with various international standards, including ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems. Additionally, certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) are essential for products sold in Europe, as they indicate compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
In regions like Africa and South America, compliance with local regulatory bodies may also be necessary. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers have the relevant certifications to avoid potential legal issues and enhance product marketability.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) is divided into several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials before they are used in production. It ensures that only materials meeting specified standards are allowed into the manufacturing process.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During assembly, various tests are conducted to monitor the quality of the product at different stages. This can include visual inspections and functional tests to detect defects early.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, final testing is conducted to verify that the transformer meets all operational specifications. This includes load testing to confirm that the transformer can handle the rated voltage and current.
B2B buyers should inquire about the specific QC processes their suppliers employ, as rigorous testing can mitigate risks associated with product failures.
How Can Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
Verifying a supplier’s quality control measures is essential for B2B buyers. Here are several methods to ensure that suppliers adhere to high standards:
-
Audits: Conducting regular audits of the manufacturing facility can help assess compliance with quality standards and operational practices. Buyers can schedule these audits or hire third-party services to perform them.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports, including testing results and certification documentation, can provide insights into the supplier’s QA practices.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s manufacturing processes and product quality.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers must navigate various nuances when dealing with QC and certification. Different regions may have specific requirements that affect how transformers are manufactured and tested. For instance, European markets may require CE marking, while North American markets often look for UL certification.
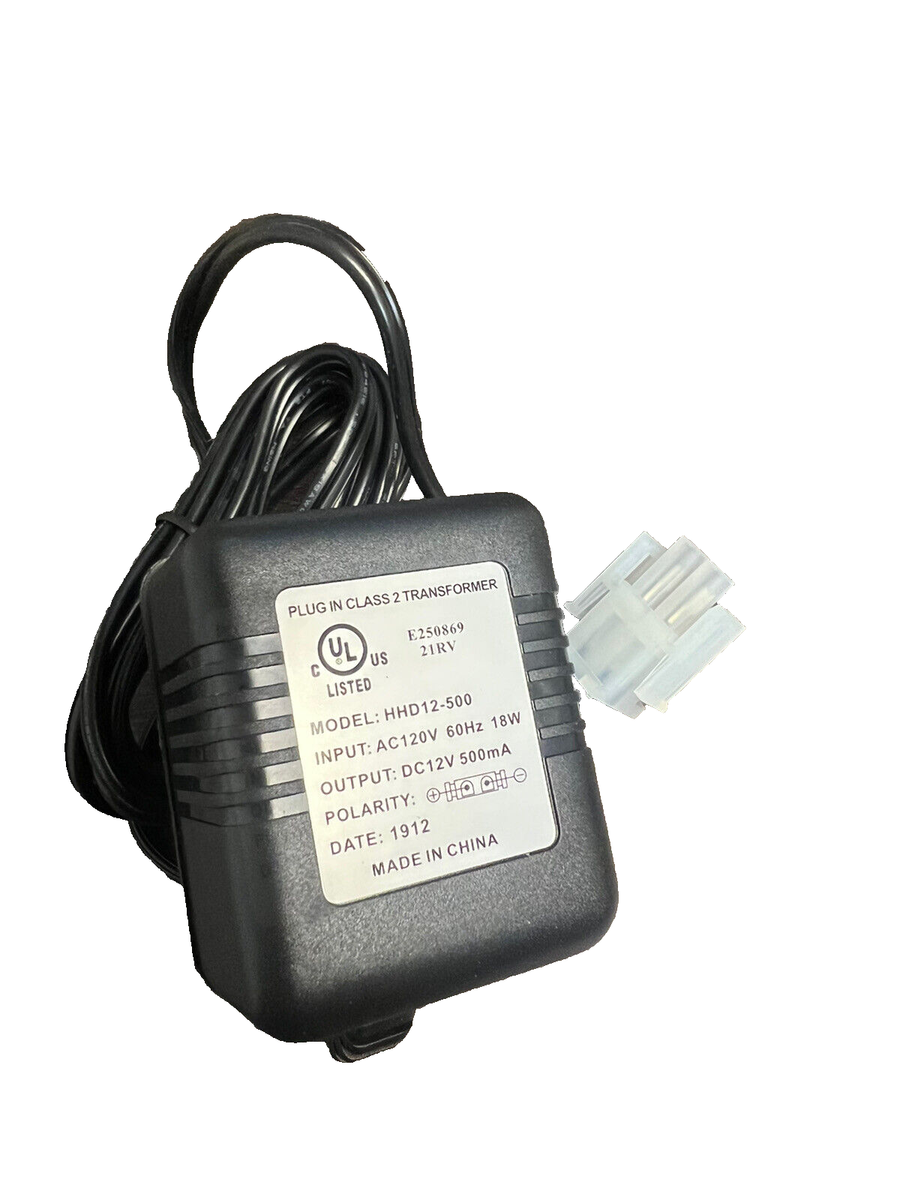

Illustrative image related to direct plug in class 2 transformer
Moreover, communication barriers can complicate the understanding of QC processes. It is advisable for buyers to establish clear lines of communication with suppliers and consider working with local representatives who understand regional compliance requirements.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for direct plug-in Class 2 transformers is essential for B2B buyers looking to source reliable and compliant products. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing stages, along with rigorous quality control checkpoints, buyers can ensure they partner with manufacturers that meet high standards. As international markets evolve, staying informed about certifications and regional requirements will further enhance sourcing decisions.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘direct plug in class 2 transformer’
Introduction
When sourcing a direct plug-in Class 2 transformer, it’s essential for B2B buyers to follow a structured approach. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to ensure you select the right product and supplier, thereby minimizing risks and enhancing operational efficiency. Whether you’re in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, these steps will help you navigate the procurement process effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding the specific requirements of your project is the first step in sourcing a Class 2 transformer. Consider factors such as voltage, wattage, and output current. This clarity ensures that you choose a transformer that meets your equipment needs and complies with local regulations.
- Voltage Requirements: Common voltages include 120V and 24V; ensure compatibility with your devices.
- Wattage Capacity: Determine the total wattage needed to power all connected devices to avoid overload.
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
Once you have your specifications, the next step is to identify potential suppliers. A thorough market analysis will help you find reliable manufacturers or distributors.
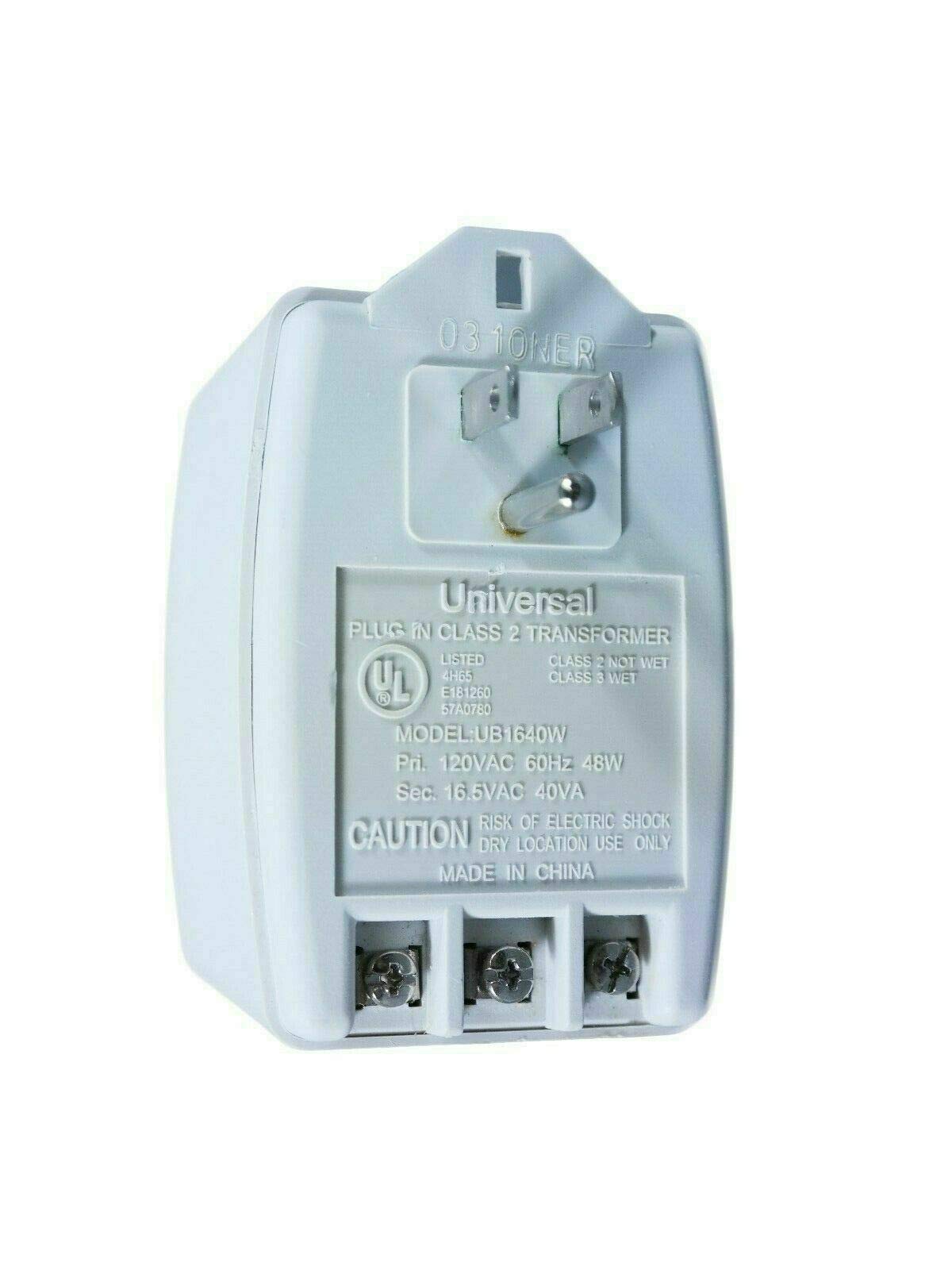

Illustrative image related to direct plug in class 2 transformer
- Industry Reputation: Look for suppliers with strong industry presence and positive reviews.
- Product Range: Ensure they offer a variety of transformers to meet different specifications and applications.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before making any commitments, verify that your selected suppliers have the necessary certifications. This is crucial for ensuring product safety and compliance with international standards.
- Safety Certifications: Look for UL, CE, or RoHS certifications that indicate compliance with safety standards.
- Quality Assurance: Check if the supplier follows ISO 9001 standards for quality management.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Obtaining samples is a vital step to assess the quality and performance of the transformers. Testing samples allows you to ensure they meet your technical specifications before bulk purchasing.
- Functional Testing: Verify that the transformer operates effectively under expected load conditions.
- Material Quality: Inspect the construction materials and design for durability and reliability.
Step 5: Understand Pricing and Payment Terms
Pricing can vary significantly among suppliers, so it’s essential to understand the cost structure and payment terms. This step helps you manage your budget effectively.
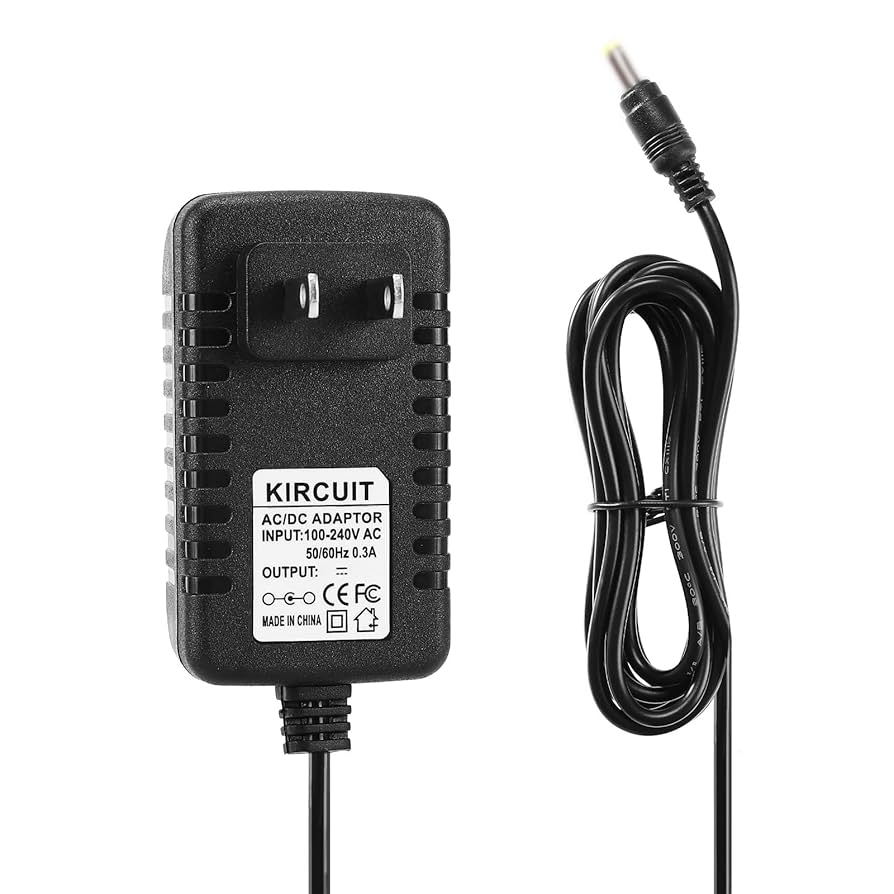

Illustrative image related to direct plug in class 2 transformer
- Bulk Discounts: Inquire about volume pricing or discounts for larger orders.
- Payment Flexibility: Look for suppliers that offer favorable payment terms, such as net 30 or net 60 options.
Step 6: Review Shipping and Delivery Options
Confirm the shipping methods and delivery timelines offered by your suppliers. This is critical for planning your inventory and ensuring timely project execution.
- Shipping Costs: Get detailed quotes to avoid unexpected expenses.
- Lead Times: Understand the typical lead times for delivery to align with your project schedule.
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Effective communication with your supplier is key to a successful procurement process. Establishing clear channels helps in resolving issues quickly and ensures all parties are aligned.
- Point of Contact: Designate a specific person for all communications to streamline information flow.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Implement feedback loops to address any concerns during the sourcing process, ensuring a smooth transaction.
Following this checklist will empower you to make informed decisions when sourcing direct plug-in Class 2 transformers, ultimately contributing to the success of your projects.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for direct plug in class 2 transformer Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components of Direct Plug-In Class 2 Transformers?
The cost structure for direct plug-in class 2 transformers involves several critical components that B2B buyers should understand for effective sourcing.
-
Materials: The primary materials for manufacturing these transformers include high-grade copper for windings, durable plastic for casings, and various electronic components such as capacitors and circuit boards. The quality of these materials can significantly impact the performance and longevity of the transformer, thus influencing the cost.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and manufacturer. Countries with lower labor costs might offer competitive pricing, but this can be offset by potential quality concerns. Skilled labor is essential for assembly and quality control, impacting overall production costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, utilities, and maintenance of manufacturing equipment. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs, which can be reflected in the pricing of the transformers.
-
Tooling: The cost of tooling can vary significantly based on the complexity of the transformer design. Custom tooling for specialized transformers will increase initial costs but can lead to better production efficiency and lower long-term costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures ensures that the transformers meet required standards. While this adds to the cost, it is essential for reducing returns and enhancing customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing costs can vary based on the location of the manufacturer and the destination market. For international buyers, understanding logistics costs, including tariffs and shipping fees, is crucial for accurate pricing.
-
Margin: Finally, suppliers will add a profit margin to cover their costs and generate profit. This margin can fluctuate based on market demand, competition, and supplier positioning.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Sourcing Decisions?
Several factors can influence the pricing of direct plug-in class 2 transformers, which are critical for B2B buyers to consider:
-
Volume/MOQ: Manufacturers often provide tiered pricing based on the order volume. Higher volumes can lead to significant discounts, making it essential for buyers to analyze their needs and negotiate accordingly.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications or unique features can increase costs. Buyers should clarify their requirements upfront to avoid unexpected expenses and ensure that they receive quotes that reflect their needs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Transformers with advanced materials or certifications (like UL or CE) often come at a premium. Buyers must weigh the benefits of these features against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a history of quality may charge more, but they can also provide better service and support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) agreed upon in the contract is vital. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight) can affect the total landed cost of the product.
What Negotiation Strategies Can Buyers Use for Cost-Efficiency?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation strategies can lead to better pricing:
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Buyers should consider not just the upfront cost but the TCO, which includes maintenance, energy efficiency, and lifespan. Presenting a TCO analysis can strengthen negotiation positions.
-
Research Market Prices: Having a benchmark of market prices for similar transformers allows buyers to negotiate more effectively. Utilize resources and market reports to understand the price range.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and favorable terms. Long-term partnerships often yield better service and reliability.
-
Be Open to Alternatives: If a specific transformer model exceeds budget constraints, consider alternative models that meet essential specifications. Discussing these alternatives with suppliers can result in cost savings.
-
Request Samples: Before committing to large orders, requesting samples can ensure the product meets quality standards without a significant financial commitment.
Conclusion
Understanding the cost structure and pricing influencers of direct plug-in class 2 transformers is crucial for B2B buyers. By considering the various cost components, leveraging negotiation strategies, and being aware of the nuances in international sourcing, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their financial and operational goals. Always remember that prices are indicative and can vary based on numerous factors, including market conditions and supplier negotiations.
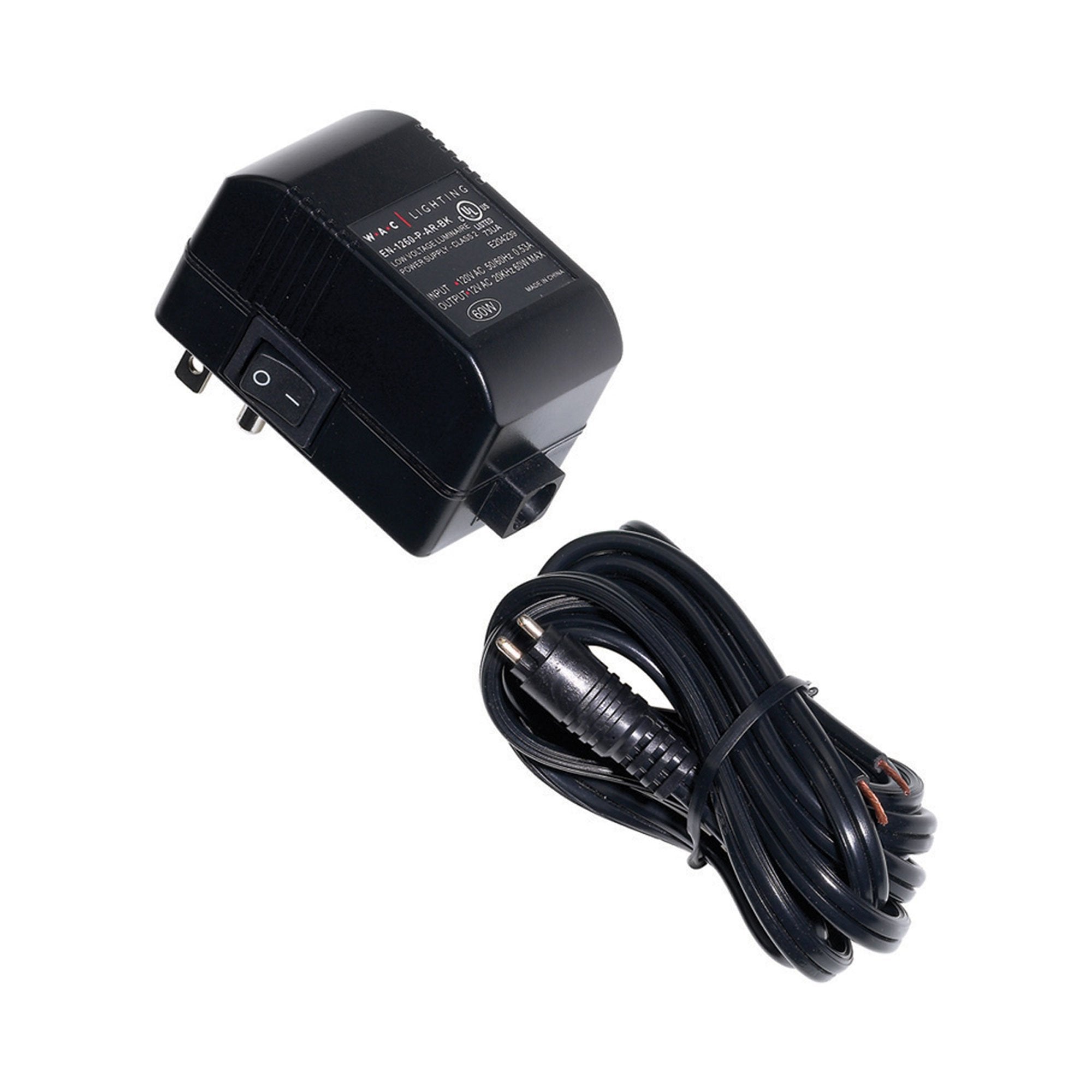

Illustrative image related to direct plug in class 2 transformer
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing direct plug in class 2 transformer With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Direct Plug In Class 2 Transformers
In the realm of electrical solutions, the direct plug-in Class 2 transformer serves as a common choice for low-voltage applications. However, various alternatives exist that may better suit specific operational needs or constraints. This analysis explores two viable alternatives—switching power supplies and hardwired transformers—comparing them across critical aspects to help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Direct Plug In Class 2 Transformer | Switching Power Supply | Hardwired Transformer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Provides stable, low-voltage output; suitable for small devices. | Highly efficient; can support a wide range of output voltages. | Offers robust power delivery; ideal for larger systems. |
| Cost | Generally low upfront cost; varies by wattage. | Typically higher initial cost but lower long-term operational costs. | Higher installation costs due to complexity. |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple plug-and-play setup; minimal installation required. | Requires some technical knowledge for integration. | Requires professional installation; not suitable for DIY. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; generally reliable over time. | Minimal maintenance; long lifespan with proper usage. | Requires periodic checks and maintenance; can be complex. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for small electronic devices and low-power applications. | Best for applications requiring variable voltage and high efficiency. | Suitable for commercial applications needing high power and durability. |
Understanding the Advantages and Disadvantages of Alternatives
Switching Power Supply
Switching power supplies are known for their efficiency and flexibility. They convert electrical power using high-frequency switching, which allows them to provide a wide range of output voltages and currents. This adaptability makes them ideal for applications with varying power demands. However, their complexity may require specialized knowledge for installation, which could pose a barrier for some businesses. Additionally, while they are efficient, they can generate electromagnetic interference, which may not be suitable for sensitive electronic environments.
Hardwired Transformer
Hardwired transformers are robust solutions often used in larger commercial or industrial applications. They are designed to handle significant power loads, making them suitable for systems that require high voltage and current. Their durability is a key advantage, as they are built to last under demanding conditions. However, they come with higher installation costs and require professional expertise for setup, which may not be feasible for smaller businesses or projects with limited budgets. Maintenance can also be more complex, necessitating periodic inspections to ensure optimal performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business Needs
When evaluating the best solution for your specific requirements, consider factors such as application scale, budget constraints, and technical expertise available within your organization. A direct plug-in Class 2 transformer may be the most straightforward choice for low-power applications, while a switching power supply could provide greater flexibility and efficiency for varied power needs. For larger systems, a hardwired transformer may offer the robustness required but at a higher investment in both installation and maintenance.
Ultimately, understanding the nuances of each option will empower B2B buyers to select the most appropriate solution that aligns with their operational goals and resource capabilities.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for direct plug in class 2 transformer
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Direct Plug-In Class 2 Transformers?
When evaluating direct plug-in Class 2 transformers, several technical specifications are crucial for ensuring compatibility and performance in various applications. Understanding these properties helps B2B buyers make informed purchasing decisions.
1. Input Voltage and Frequency
The input voltage, typically 120V, and frequency (60Hz in North America) are essential specifications. These values determine the compatibility of the transformer with the electrical systems in different regions. For international buyers, it’s important to confirm that the transformer meets local voltage and frequency standards to prevent equipment malfunction.

Illustrative image related to direct plug in class 2 transformer
2. Output Voltage and Current Rating
Output voltage and current ratings, such as 24V and 1.25A, define the transformer’s capacity to supply power to connected devices. This specification is crucial for ensuring that the transformer can adequately power the intended application, such as lighting systems or electronic devices, without causing damage or performance issues.
3. Power Rating (Watts)
The power rating, often expressed in watts (e.g., 54W), indicates the maximum load the transformer can handle. For B2B buyers, selecting a transformer with an appropriate power rating is vital to ensure it can support the total load of the connected devices, providing reliability and efficiency in operation.
4. Material and Build Quality
The materials used in the transformer, such as polycarbonate housing, play a significant role in durability and safety. Quality construction can enhance resistance to environmental factors and extend the lifespan of the transformer. Buyers should consider this aspect, especially for applications in challenging environments.
5. Protection Features
Modern transformers often include protection features such as short-circuit protection, overload protection, and thermal shutdown. These specifications are critical for safeguarding connected devices from damage due to electrical faults, making them essential for buyers concerned with safety and reliability.
6. Efficiency Rating
Efficiency ratings measure how much of the input power is converted into usable output power. Higher efficiency translates to lower energy costs and less heat generation, which is beneficial for long-term operational savings. B2B buyers should prioritize transformers with high efficiency to enhance sustainability and reduce operational expenses.

Illustrative image related to direct plug in class 2 transformer
What Are Common Trade Terms Associated with Direct Plug-In Class 2 Transformers?
Familiarity with industry terminology is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Below are common terms that buyers may encounter.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of transformers, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify trusted suppliers and ensure they are purchasing high-quality products.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ signifies the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for buyers to plan their inventory and budget effectively, especially when sourcing transformers for large projects.

Illustrative image related to direct plug in class 2 transformer
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers request pricing and terms from suppliers. This document is critical for obtaining competitive bids and ensuring that all potential suppliers understand the requirements for the transformers needed.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms helps B2B buyers navigate the complexities of international transactions, ensuring clarity and reducing the risk of disputes.
5. UL Listing
A UL listing indicates that the product has been tested and meets specific safety standards set by Underwriters Laboratories. For B2B buyers, this certification can significantly influence purchasing decisions, as it ensures compliance with safety regulations and enhances the product’s credibility.

Illustrative image related to direct plug in class 2 transformer
6. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product. Understanding lead times is vital for effective project planning and inventory management, ensuring that transformers arrive on schedule to meet operational needs.
By comprehensively understanding the technical properties and trade terminology associated with direct plug-in Class 2 transformers, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and market demands.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the direct plug in class 2 transformer Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics Affecting the Direct Plug In Class 2 Transformer Sector?
The global market for direct plug in class 2 transformers is shaped by several key drivers and emerging trends. As industries increasingly adopt automation and smart technology, the demand for reliable power supplies like class 2 transformers continues to rise. This trend is particularly evident in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where infrastructural development is accelerating. For instance, in emerging markets like Nigeria, there is a growing need for efficient and safe power solutions in both commercial and residential sectors.
Moreover, advancements in technology are enabling the development of more compact and efficient transformers, which are essential for modern applications such as LED lighting and electronic devices. The shift towards renewable energy sources is also influencing sourcing trends, as manufacturers seek to create transformers that comply with sustainability standards. B2B buyers must remain vigilant about the evolving technological landscape and the regulatory requirements that accompany it, as these factors can significantly impact sourcing decisions.
Another critical trend is the rise of e-commerce platforms, which facilitate easier access to a broader range of suppliers and products. International buyers can now leverage digital channels to compare prices, specifications, and certifications, enhancing their purchasing power. As a result, understanding the dynamics of global supply chains is essential for B2B buyers to ensure timely procurement and cost-effectiveness.
How Is Sustainability Impacting the Sourcing of Direct Plug In Class 2 Transformers?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal factor in the sourcing of direct plug in class 2 transformers. As environmental concerns gain traction globally, B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices. This includes using eco-friendly materials, minimizing waste, and ensuring ethical labor practices throughout the supply chain.
The environmental impact of transformers can be significant, particularly in terms of energy consumption and waste generation. Buyers should look for products that feature energy-efficient designs, such as those with lower standby power consumption. Additionally, certifications like Energy Star or RoHS can provide assurance that the products meet stringent environmental standards.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining importance, as stakeholders demand transparency in supply chains. Buyers are encouraged to engage with manufacturers who prioritize responsible sourcing of materials, ensuring that they do not contribute to environmental degradation or exploitative labor practices. By choosing suppliers with green certifications and ethical practices, B2B buyers can not only enhance their brand reputation but also contribute positively to the global push for sustainability.
What Has Been the Evolution of Direct Plug In Class 2 Transformers?
The evolution of direct plug in class 2 transformers has been marked by technological advancements and changing industry needs. Initially designed for basic power supply functions, these transformers have evolved to meet the demands of modern electronic devices that require compact, efficient, and reliable power solutions.

Illustrative image related to direct plug in class 2 transformer
Over the years, improvements in materials and design have led to the development of transformers that are not only smaller and lighter but also more energy-efficient. The introduction of smart technology has further transformed the landscape, allowing for features like remote monitoring and control. This evolution reflects the broader trend towards smarter, more integrated systems in various sectors, emphasizing the importance of adapting to technological advancements in the B2B market.
In summary, the direct plug in class 2 transformer sector is poised for continued growth driven by technological innovation, sustainability, and evolving market needs. B2B buyers must stay informed about these trends to make strategic sourcing decisions that align with their operational goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of direct plug in class 2 transformer
-
How do I determine the right specifications for a Class 2 transformer?
When selecting a Class 2 transformer, assess the voltage and power requirements of your application. Consider the input voltage (typically 120V) and the desired output voltage (commonly 12V or 24V). Additionally, evaluate the wattage needed for your devices, ensuring the transformer can handle the load without overheating. It’s essential to check for compliance with local regulations and certifications, especially when importing products to regions like Africa, South America, and Europe. -
What is the best type of Class 2 transformer for low-voltage applications?
For low-voltage applications, a plug-in Class 2 transformer is often the best choice due to its ease of installation and compact design. Look for transformers that offer features like short circuit protection, overload protection, and energy efficiency. Models with built-in dimming capabilities can also provide added functionality for lighting applications. Always ensure compatibility with your specific devices and check for local standards to ensure safety and performance. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for Class 2 transformers?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their experience in manufacturing Class 2 transformers and check for relevant certifications (e.g., UL, CE). Review customer testimonials and case studies to assess their reliability. Also, inquire about their production capabilities, lead times, and quality assurance processes. For international buyers, understanding their export experience and logistics capabilities is crucial to ensuring smooth transactions and delivery. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for Class 2 transformers?
MOQs for Class 2 transformers can vary widely depending on the supplier and the specific model. Generally, MOQs may range from 50 to 500 units. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with the supplier, as some may offer flexibility for first-time buyers or smaller businesses. Consider the implications of larger orders on storage and inventory management before committing to an MOQ. -
What payment terms are commonly offered for international orders of Class 2 transformers?
Payment terms for international orders often include options such as advance payment, letters of credit, or net terms (30, 60, or 90 days). Many suppliers may require a deposit upfront, particularly for custom orders. Discussing payment options early in negotiations can help establish trust and ensure smooth financial transactions. Be aware of any additional fees related to currency exchange or international banking. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for my Class 2 transformer order?
To ensure quality assurance, request samples before placing a bulk order. Verify that the transformers meet international standards and certifications. It’s also beneficial to establish a clear quality control process, including inspections during production and pre-shipment checks. Maintaining open communication with the supplier throughout the production process can help address any issues promptly. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing Class 2 transformers?
When importing Class 2 transformers, consider shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations in your destination country. Evaluate the total landed cost, including shipping, duties, and taxes. Working with a freight forwarder familiar with your region can streamline the logistics process. Additionally, ensure that the packaging is robust to withstand transit conditions and that the documentation is complete to avoid delays at customs. -
Can I customize Class 2 transformers for my specific applications?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for Class 2 transformers, such as specific output voltages, wattages, or connector types. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers and inquire about their capabilities for custom designs. Keep in mind that custom orders may have longer lead times and higher MOQs, so plan accordingly to align with your project timelines.
Top 4 Direct Plug In Class 2 Transformer Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Class 2 Transformer AC Wall Adapter
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: AC wall-adapter labeled as “class 2 transformer”; may use an isolation transformer or a switch-mode supply; class 2 indicates it operates under 60V for DC with specific amperage limits; output wiring considered low voltage, adhering to different safety standards than class 1 or high voltage.
2. Unbranded – AC DC Adaptor Model 35A-D05-140
Domain: electronicsflip.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: {“Title”:”AC DC Adaptor Direct Plug In Class 2 Transformer Model 35A-D05-140 AC120V 60HZ 2W”,”Price”:”$8.07″,”UPC”:”371671695568″,”Type”:”Electronics”,”Condition”:”Used: Very Good”,”Notes”:”Very Good Condition”,”Output Voltage”:”5 V”,”Color”:”Black”,”Brand”:”Unbranded”,”Country/Region of Manufacture”:”Unknown”}
3. WAC Lighting – 120V/24V 60W Plug-In Electronic Transformer
Domain: citylightssf.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: {“name”:”120V/24V 60W Plug-In Electronic Transformer Class 2 Power Supply”,”brand”:”WAC Lighting”,”price”:”$101.95″,”availability”:”In Stock”,”shipping”:”Free Shipping on most orders over $75″,”description”:”Plug-In Electronic Transformer for Class 2 Power Supply”}
4. West Florida Components – A41808 AC Adapter
Domain: westfloridacomponents.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: {‘model’: ‘A41808’, ‘type’: ‘AC Adapter’, ‘class’: ‘Class 2 Transformer’, ‘input_voltage’: ‘120V’, ‘frequency’: ’60Hz’, ‘output_voltage’: ’18VDC’, ‘output_current’: ‘800mA’, ‘power’: ’35W’, ‘lead_terminal_type’: ‘Cord’, ‘number_of_leads’: ‘1’, ‘color’: ‘Black’, ‘termination_method’: ‘Plug’, ‘price’: ‘$13.50’, ‘availability’: ’21 available for immediate delivery’, ‘weight’: ‘32.00oz’, ‘dimensions’:…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for direct plug in class 2 transformer
In the evolving landscape of electrical components, strategic sourcing of direct plug-in Class 2 transformers has emerged as a pivotal consideration for B2B buyers. By prioritizing high-quality, compliant products, businesses can mitigate risks associated with equipment failure and enhance operational efficiency. The focus on reliable suppliers ensures adherence to international standards, which is particularly crucial for markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where varying regulations may apply.
As companies seek to optimize their supply chains, the importance of building strong relationships with manufacturers cannot be overstated. This collaboration can lead to better pricing, improved lead times, and enhanced product support. Moreover, understanding regional market dynamics can provide a competitive edge, allowing buyers to leverage local insights for informed decision-making.
Looking ahead, it is essential for international B2B buyers to stay proactive in sourcing strategies, embracing innovation and sustainability as core principles. By investing in reliable Class 2 transformers, businesses not only enhance their operational capabilities but also position themselves for long-term growth and success in a rapidly changing marketplace. Engage with reputable suppliers today to ensure your electrical needs are met with quality and efficiency.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.