A Deep Dive into Difference Between Air Filter And Cabin Filter Solution
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for difference between air filter and cabin filter
Understanding the distinction between air filters and cabin filters is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to enhance vehicle performance and passenger comfort. As companies across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including key markets like Germany and Saudi Arabia) seek reliable automotive components, the challenge lies in sourcing high-quality filters that meet both operational efficiency and regulatory standards. This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of air filters and cabin filters, exploring their types, applications, and the importance of selecting the right supplier.
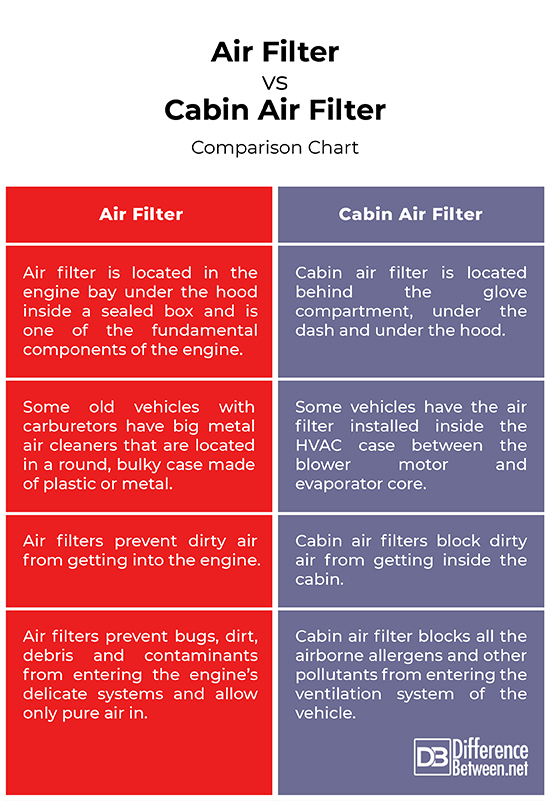
Air filters are essential for engine performance, ensuring clean air intake to optimize combustion, while cabin filters play a critical role in maintaining a healthy and comfortable environment for vehicle occupants. By outlining the varying specifications, replacement cycles, and potential impacts of neglecting these components, this guide empowers international B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Additionally, we will address cost considerations, supplier vetting processes, and the latest market trends to help businesses navigate the complexities of the automotive filter market effectively. With this knowledge, buyers can enhance their product offerings and ensure customer satisfaction through superior air quality, whether on the bustling streets of Johannesburg or the highways of Frankfurt.
Understanding difference between air filter and cabin filter Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
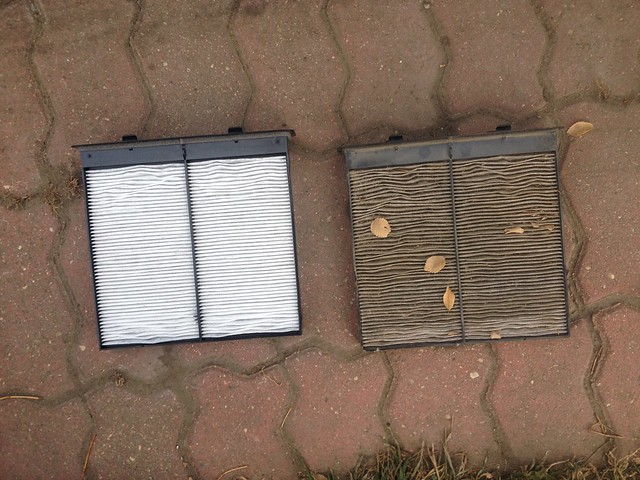
| Engine Air Filter | Located in the engine bay, larger size, designed for high airflow. | Automotive manufacturing, fleet management. | Pros: Enhances engine performance, easy to replace. Cons: Regular replacement needed to maintain efficiency. |
| Cabin Air Filter | Located in the passenger compartment, smaller size, filters allergens and odors. | Automotive service centers, HVAC systems. | Pros: Improves passenger comfort, reduces allergens. Cons: Replacement can be less accessible, may require professional service. |
| HEPA Cabin Air Filter | High-efficiency particulate air filter, captures very fine particles. | Luxury vehicles, healthcare transport. | Pros: Superior filtration, ideal for allergy sufferers. Cons: Higher cost, may reduce airflow if not maintained. |
| Oiled Air Filter | Reusable filter that requires oil for trapping dirt and debris. | Off-road vehicles, performance tuning. | Pros: Long lifespan, eco-friendly option. Cons: Requires maintenance and re-oiling, potential for over-oiling. |
| Carbon-Activated Filter | Contains activated carbon to neutralize odors in addition to filtering. | Urban vehicles, taxi services. | Pros: Effective against odors, enhances air quality. Cons: Higher initial cost, may require more frequent replacements. |
What are the characteristics of Engine Air Filters and their B2B applications?
Engine air filters are essential components located in the engine bay, designed to filter out dust, dirt, and other contaminants from the air entering the engine. Their larger size allows them to handle higher airflow rates, crucial for engine performance. B2B applications primarily include automotive manufacturing and fleet management, where maintaining engine efficiency is vital for operational costs. Buyers should consider the frequency of replacement, typically every 15,000 miles, and the implications of a dirty filter on engine performance, which can lead to reduced fuel economy and power.
How do Cabin Air Filters differ and what are their key B2B purchasing considerations?
Cabin air filters serve a different purpose by cleaning the air entering the passenger compartment, filtering out allergens, dust, and unpleasant odors. Their location behind the dashboard makes them smaller and more straightforward in design. B2B applications often involve automotive service centers and HVAC systems, where customer comfort is a priority. Buyers should assess the filter’s replacement accessibility and the frequency of change, generally recommended every two years. Additionally, the impact of a dirty cabin filter on air quality can significantly affect passenger satisfaction, making regular maintenance essential.
What makes HEPA Cabin Air Filters a preferred choice in certain sectors?
HEPA cabin air filters are designed to capture very fine particles, making them ideal for luxury vehicles and healthcare transport applications. Their ability to trap allergens and pollutants enhances air quality significantly, catering to health-conscious consumers. While they provide superior filtration, B2B buyers must weigh the higher cost against the benefits of improved air quality and passenger comfort. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure they function effectively without restricting airflow.

Illustrative image related to difference between air filter and cabin filter
What are the benefits and drawbacks of Oiled Air Filters in off-road and performance vehicles?
Oiled air filters are reusable and designed for off-road vehicles and performance tuning, offering a sustainable option for buyers. They provide a long lifespan but require regular maintenance, including cleaning and re-oiling. B2B buyers in sectors like off-road vehicle production should consider the trade-off between the environmental benefits and the potential for over-oiling, which can hinder performance. Understanding the maintenance requirements is key to ensuring they remain effective.
Why are Carbon-Activated Filters gaining traction in urban vehicle applications?
Carbon-activated filters are increasingly popular in urban environments, particularly for taxi services and vehicles frequently exposed to pollutants. They not only filter particles but also neutralize odors, enhancing passenger experience. Buyers should consider the initial investment and the potential for more frequent replacements due to their specialized design. The benefits of improved air quality in urban settings can lead to higher customer satisfaction and retention, making them a worthwhile investment for B2B buyers.
Key Industrial Applications of difference between air filter and cabin filter
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of difference between air filter and cabin filter | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Quality control in vehicle assembly lines, ensuring proper filtration. | Enhanced vehicle performance and customer satisfaction. | Reliable suppliers with certifications and quality assurance. |
| Transportation and Logistics | Maintenance of fleet vehicles, focusing on air quality and engine efficiency. | Reduced operational costs through improved fuel efficiency. | Availability of bulk purchasing options and local support. |
| HVAC Systems | Integration of air filtration systems in commercial buildings. | Improved indoor air quality and compliance with health standards. | Sourcing from manufacturers with a range of filtration options. |
| Agriculture | Use in agricultural machinery to protect engines from dust and debris. | Increased machinery lifespan and reduced downtime. | Consideration of filters suitable for specific environmental conditions. |
| Heavy Equipment | Application in construction and mining equipment to ensure efficient operation. | Enhanced performance and reduced maintenance costs. | Need for filters that can withstand harsh working conditions. |
How Are Air Filters and Cabin Filters Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive manufacturing sector, understanding the difference between air filters and cabin filters is crucial for quality control during vehicle assembly. Engine air filters are essential for ensuring optimal engine performance by preventing contaminants from entering the engine, while cabin filters are vital for maintaining air quality within the passenger compartment. This differentiation helps manufacturers enhance vehicle reliability and customer satisfaction, leading to a competitive edge in the market. International buyers should prioritize suppliers who provide certified filters that meet specific automotive standards.
Why Is Air Filter and Cabin Filter Maintenance Important for Transportation and Logistics?
For transportation and logistics companies operating fleets, the maintenance of air filters is critical for ensuring vehicle efficiency and safety. Engine air filters directly impact fuel efficiency, while cabin filters are essential for passenger comfort. By regularly replacing these filters, businesses can reduce operational costs, as cleaner filters lead to better fuel economy and lower emissions. Buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East should seek suppliers that offer bulk purchasing options to streamline their maintenance processes.
How Do Air Filters Enhance HVAC Systems in Commercial Buildings?
In the HVAC industry, the difference between air filters and cabin filters translates to improved indoor air quality in commercial buildings. Air filters clean the air circulating through heating and cooling systems, while cabin filters (often referred to in this context as air filters for indoor environments) help reduce allergens and pollutants. This is particularly important for compliance with health and safety regulations. B2B buyers in Europe, especially Germany, should focus on sourcing from manufacturers that provide a wide range of filter options to cater to various system designs and requirements.

Illustrative image related to difference between air filter and cabin filter
What Role Do Air Filters Play in Agriculture?
In agriculture, the distinction between engine air filters and cabin filters is significant for the maintenance of agricultural machinery. Engine air filters protect engines from dust and debris, which can lead to costly repairs and downtime. Cabin filters ensure that operators are not exposed to harmful airborne particles while working. Buyers in South America should consider filters designed for specific environmental conditions, ensuring durability and effectiveness in challenging agricultural settings.
How Are Air Filters Critical for Heavy Equipment Operations?
Heavy equipment in construction and mining heavily relies on the proper functioning of air filters and cabin filters. Engine air filters prevent dust and debris from damaging sensitive engine components, while cabin filters protect operators from harmful airborne particles. This differentiation is vital for maintaining equipment performance and safety. Buyers in these sectors should prioritize filters that can withstand harsh working conditions and provide long-lasting performance, sourcing from suppliers with a proven track record in heavy machinery applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘difference between air filter and cabin filter’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Confusion Over Air Filter Types in Fleet Maintenance
The Problem: B2B buyers managing vehicle fleets often encounter confusion regarding the distinction between engine air filters and cabin air filters. This confusion can lead to mismanagement in maintenance schedules, resulting in suboptimal vehicle performance and increased operational costs. For example, a fleet manager might neglect to replace cabin air filters due to a lack of understanding about their importance, leading to poor air quality for drivers and passengers. This can not only affect comfort but also potentially harm the health of employees, leading to decreased productivity.
The Solution: To alleviate this issue, fleet managers should develop a comprehensive training program for their maintenance teams that clearly outlines the roles and functions of both types of filters. Implementing a systematic approach to filter replacement based on the manufacturer’s recommendations will ensure that both engine and cabin air filters are regularly checked and replaced. Additionally, using a fleet management software can help automate reminders for filter inspections and replacements, making it easier to keep track of maintenance schedules. Establishing a partnership with a reliable supplier who provides detailed product information and support can also enhance understanding and help in making informed decisions regarding filter purchases.
Scenario 2: Overlooking the Financial Impact of Dirty Filters
The Problem: Many B2B buyers fail to recognize the financial ramifications of neglecting air filter maintenance, especially in regions with high dust levels, such as parts of Africa and the Middle East. A dirty engine air filter can significantly reduce fuel efficiency, leading to higher operational costs. Additionally, a compromised cabin air filter can lead to increased wear and tear on HVAC systems, resulting in expensive repairs or replacements down the line. This oversight can impact a company’s bottom line and overall profitability.
The Solution: To mitigate these financial impacts, businesses should conduct a cost-benefit analysis that emphasizes the importance of regular filter maintenance. Investing in quality air filters might seem costly upfront, but it can save significant amounts in fuel and repair costs over time. Establishing a routine maintenance schedule that includes filter checks, along with using high-quality filters designed for specific environmental conditions, can enhance vehicle performance and longevity. Moreover, educating drivers about the signs of dirty filters, such as reduced airflow or strange odors, can empower them to report issues promptly, further preventing costly repairs.
Scenario 3: Difficulty Sourcing the Right Filters for Diverse Vehicles
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with sourcing the correct air filters for a diverse fleet of vehicles, especially when the fleet includes models from various manufacturers. This challenge can lead to delays in maintenance and increased downtime for vehicles, which can severely impact business operations. Additionally, buyers may find it difficult to navigate the myriad of options available in the market, leading to confusion and potential procurement errors.
The Solution: To streamline the sourcing process, businesses should establish a standardized inventory system that categorizes air filters by vehicle make and model. Leveraging digital platforms or supplier portals that provide detailed specifications and compatibility information can greatly simplify the procurement process. Additionally, forming strategic partnerships with filter manufacturers or authorized distributors can ensure access to high-quality filters while also providing expert guidance on the best options for specific vehicles. Regularly reviewing and updating the inventory based on vehicle acquisitions and retirements will further optimize the supply chain, ensuring that maintenance needs are met efficiently and effectively.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for difference between air filter and cabin filter
What Are the Common Materials Used in Air Filters and Cabin Filters?
When selecting materials for air filters and cabin filters, it’s essential to understand the properties, advantages, and limitations of various media. This knowledge can guide international B2B buyers in making informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regulatory requirements.
What Are the Key Properties of Synthetic Fiber in Air Filters?
Synthetic fibers, often made from polyester or polypropylene, are commonly used in both engine air filters and cabin filters. These materials exhibit excellent filtration efficiency, capable of capturing fine particles while maintaining airflow. They typically have a high temperature resistance, making them suitable for engine environments, and are resistant to moisture, which is vital for cabin filters exposed to humidity.
Pros: Synthetic fibers are lightweight and can be manufactured in various thicknesses, allowing for flexibility in design. They also tend to have a longer lifespan compared to natural fibers, reducing replacement frequency.
Cons: The manufacturing process can be more complex and costly, which may impact the final product price. Additionally, synthetic materials are less biodegradable, raising environmental concerns.
Impact on Application: Synthetic fibers are compatible with HEPA filtration requirements, making them ideal for high-performance applications. They can efficiently filter allergens and pollutants in cabin environments, enhancing passenger comfort.

Illustrative image related to difference between air filter and cabin filter
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Europe may prioritize compliance with environmental standards such as REACH, while those in the Middle East may focus on durability in extreme temperatures. Understanding local regulations can influence material selection.
How Does Cellulose Material Perform in Air Filters?
Cellulose, derived from natural plant fibers, is another common material used in air filters. It is particularly favored for its cost-effectiveness and good filtration capabilities.
Pros: Cellulose filters are generally less expensive to produce, making them an attractive option for budget-conscious buyers. They can effectively filter larger particles and are biodegradable, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
Cons: However, cellulose filters have lower moisture resistance and can degrade more quickly in humid conditions, which may lead to reduced performance in cabin filters. They also have a shorter lifespan compared to synthetic options.
Impact on Application: Cellulose is suitable for applications where cost is a primary concern, but it may not meet the stringent filtration standards required for high-performance engines or allergy-sensitive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Africa and South America may find cellulose filters advantageous due to lower costs, but they should consider the local climate’s impact on filter performance.
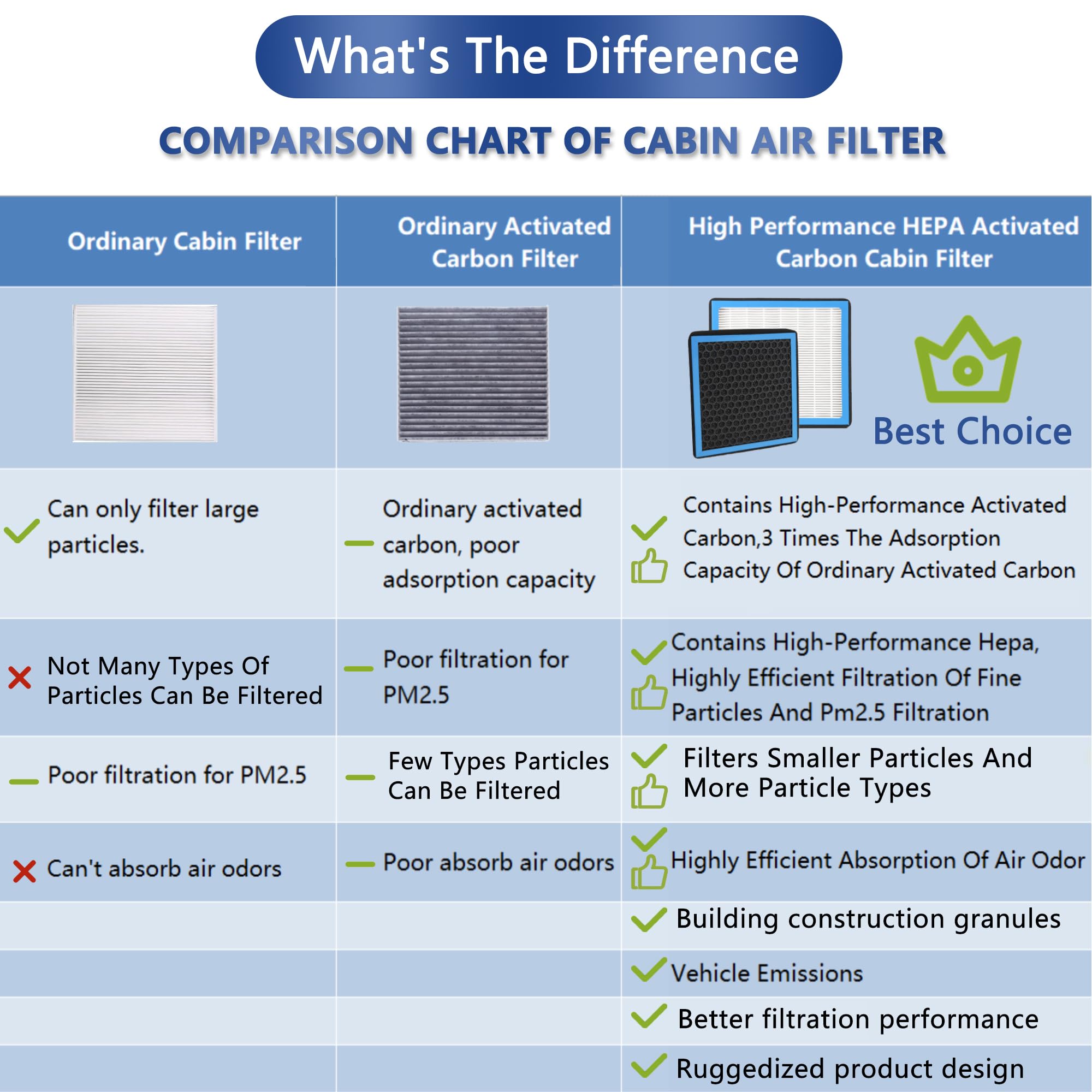
What Are the Benefits of Activated Carbon in Cabin Filters?
Activated carbon is often incorporated into cabin filters to provide additional odor removal capabilities. This material is treated to create a large surface area, allowing it to adsorb various gases and odors effectively.
Pros: The primary advantage of activated carbon is its ability to neutralize unpleasant smells, improving the passenger experience. It also enhances the filter’s ability to capture volatile organic compounds (VOCs).

Illustrative image related to difference between air filter and cabin filter
Cons: Activated carbon filters can be more expensive than standard filters and may require more frequent replacement due to saturation. They may also have lower particulate filtration efficiency compared to synthetic or cellulose filters.
Impact on Application: Activated carbon is particularly beneficial in urban areas with high pollution levels, making it a suitable choice for cabin filters in cities across Europe and the Middle East.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with air quality standards is crucial for buyers in regions like Germany, where stringent regulations exist. Understanding local preferences for air quality can guide material selection.
How Does Foam Material Compare in Air Filters?
Foam is another material used in air filters, particularly in applications requiring high airflow and low resistance. Foam filters can be made from polyurethane or other synthetic materials.
Pros: Foam filters are reusable and can be washed, making them cost-effective over time. They provide excellent airflow, which is beneficial for performance applications.
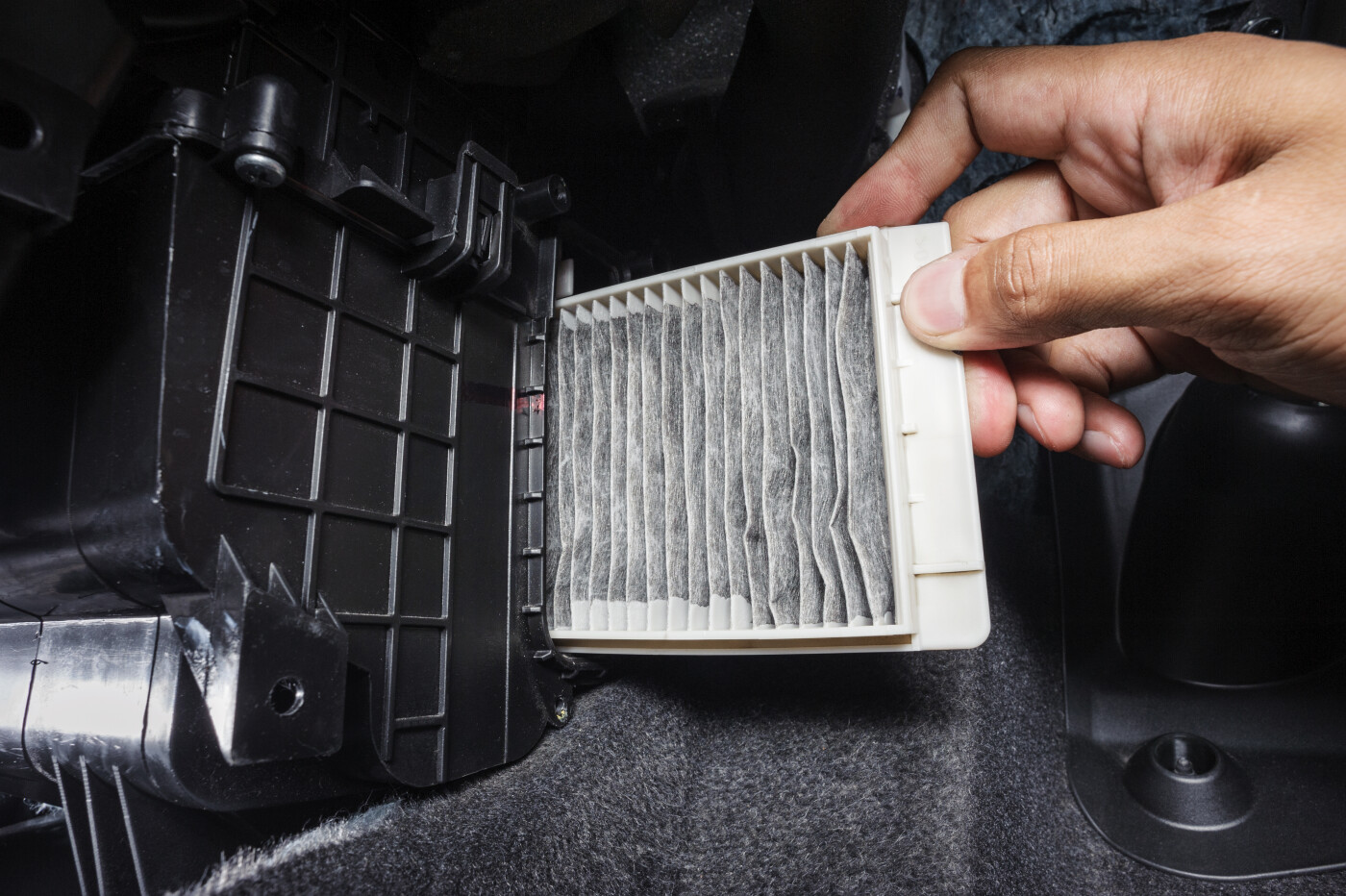

Illustrative image related to difference between air filter and cabin filter
Cons: However, foam filters may not capture fine particles as effectively as other materials, potentially compromising filtration efficiency. They can also degrade under extreme temperatures or chemical exposure.
Impact on Application: Foam is often used in racing or high-performance vehicles where airflow is prioritized over fine filtration.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions with extreme climates should assess the durability of foam filters in their specific conditions, as well as compliance with relevant automotive standards.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Air Filters and Cabin Filters
| Material | Typical Use Case for difference between air filter and cabin filter | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synthetic Fiber | Engine air filters, cabin filters | High filtration efficiency, durable | Higher manufacturing costs | Medium |
| Cellulose | Budget-friendly engine air filters | Cost-effective, biodegradable | Lower moisture resistance | Low |
| Activated Carbon | Cabin filters for odor removal | Effective odor neutralization | Higher cost, frequent replacement | High |
| Foam | High-performance air filters | Reusable, excellent airflow | Lower filtration efficiency | Medium |
This comprehensive analysis provides B2B buyers with the insights needed to make informed decisions on material selection for air and cabin filters, considering performance, cost, and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for difference between air filter and cabin filter
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Air Filters and Cabin Filters?
Understanding the manufacturing processes for air filters and cabin filters is essential for B2B buyers looking to source quality products. The production of these filters involves multiple stages, each critical to ensuring that the final product meets performance and durability standards.
-
Material Preparation
The first stage in manufacturing involves selecting and preparing raw materials. Engine air filters typically utilize a combination of synthetic and natural fibers, designed to trap larger particles while allowing airflow. Cabin air filters, on the other hand, often incorporate activated carbon to neutralize odors and filter out smaller particles like pollen. Suppliers should ensure that the materials meet international standards such as ISO 9001, which emphasizes quality management systems. -
Forming
In this stage, the prepared materials are shaped into the appropriate filter dimensions. For engine air filters, pleating is a common technique used to increase the surface area, thereby enhancing filtration efficiency. Cabin air filters may employ a simpler flat design, but they also utilize pleating to maximize their filtration capacity in confined spaces. Advanced techniques like hot-pressing or ultrasonic welding may be employed to enhance the integrity and performance of the filters. -
Assembly
After forming, the various components of the filters are assembled. This may involve bonding layers of material together or adding frames to provide structural stability. In the case of cabin filters, the integration of activated carbon layers requires precise assembly to ensure effective filtration. Quality checks should be conducted during this stage to verify that all components fit properly and adhere to design specifications. -
Finishing
The final stage involves quality finishing processes, such as trimming excess material, applying protective coatings, or packaging the filters for distribution. This stage is crucial for ensuring that the filters maintain their integrity during shipping and storage. Proper labeling and documentation are also important to provide buyers with essential product information and compliance certifications.
What International Standards and Quality Control Measures Are Relevant for Air and Cabin Filters?
Quality assurance in the manufacturing of air filters and cabin filters is vital for ensuring that products meet both performance and safety standards. International standards and industry-specific certifications play a key role in this process.
-
ISO 9001 Certification
This international standard specifies requirements for a quality management system (QMS) and is applicable to any organization. For air filter manufacturers, obtaining ISO 9001 certification signifies a commitment to consistent quality and continuous improvement. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers with this certification to ensure reliability. -
CE Marking
For products sold in the European market, CE marking indicates that a product meets EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards. This is particularly relevant for cabin filters, which directly impact passenger comfort and health. Buyers in Europe should ensure that their suppliers provide CE certification for compliance. -
API Certification
The American Petroleum Institute (API) provides certification for engine air filters. This certification ensures that filters meet specific performance standards, particularly in terms of efficiency and dirt-holding capacity. B2B buyers sourcing filters for engines should look for this certification to ensure optimal engine performance.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Filter Manufacturing?
Implementing rigorous quality control (QC) measures is essential throughout the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:

Illustrative image related to difference between air filter and cabin filter
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. Suppliers should verify that materials meet specified standards and are free from defects. Proper documentation and supplier audits can help ensure compliance. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
During the manufacturing process, IPQC involves monitoring various parameters, such as temperature and pressure, to ensure they remain within acceptable limits. Regular sampling and testing of filter performance can help identify any deviations from quality standards before the final product is completed. -
Final Quality Control (FQC)
Before packaging, FQC involves comprehensive testing of finished products. This may include airflow tests, particle retention tests, and odor neutralization tests for cabin filters. Suppliers should provide detailed reports of these tests to B2B buyers, enabling them to assess product quality.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international buyers, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is crucial for ensuring product reliability. Here are some effective strategies:
-
Supplier Audits
Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes and quality control measures in place. This firsthand observation can provide insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality and compliance with international standards. -
Requesting Quality Control Reports
Buyers should request detailed QC reports from suppliers, which should include results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC stages. These reports can help buyers understand the supplier’s quality assurance processes and identify any potential risks. -
Engaging Third-Party Inspection Services
For additional assurance, B2B buyers can engage third-party inspection services to evaluate the supplier’s manufacturing processes and product quality. These independent assessments can provide an unbiased view of the supplier’s capabilities and adherence to standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
Navigating quality control nuances can be particularly challenging for B2B buyers operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Here are some considerations:
-
Cultural and Regulatory Differences
Quality standards and regulations may vary significantly across regions. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and ensure that their suppliers comply with both international and regional standards. -
Language Barriers
Communication can pose challenges, especially when discussing technical specifications and quality standards. It is advisable for buyers to work with suppliers who can provide documentation and support in multiple languages. -
Logistical Considerations
Shipping and logistics may affect product quality. Buyers should consider suppliers’ capabilities in handling transportation and storage to minimize the risk of damage or contamination during transit.
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and verification strategies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing air filters and cabin filters. Prioritizing suppliers who adhere to stringent quality standards ensures that they receive reliable products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘difference between air filter and cabin filter’
Introduction
Understanding the difference between air filters and cabin filters is essential for B2B buyers involved in automotive parts procurement. This guide provides a practical checklist to help you make informed decisions when sourcing these critical components. By following these steps, you can ensure that your purchases meet the necessary quality and performance standards for your market.
Step 1: Identify Your Market Needs
Begin by assessing the specific requirements of your target market. Different regions may have varying environmental conditions that affect filter performance, such as dust levels or pollen counts. Understanding these needs will help you select the right type of filters that cater to your customer base.
- Sub-bullet: Analyze local air quality reports to gauge the common contaminants.
- Sub-bullet: Consider regional vehicle types to determine the most frequently used filters.
Step 2: Define Technical Specifications
Establish clear technical specifications for both air filters and cabin filters. This includes dimensions, materials, and filtration capabilities. Accurate specifications are crucial for ensuring compatibility with various vehicle models.
- Sub-bullet: Specify the filter’s micron rating to ensure it meets the required filtration standards.
- Sub-bullet: Include information on whether the filters need to be washable or disposable.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before committing to a supplier, verify their certifications. Look for ISO certifications or other industry-specific standards that indicate quality control measures. These certifications can assure you that the products meet international quality benchmarks.
- Sub-bullet: Ask for documentation of compliance with local and international automotive standards.
- Sub-bullet: Check if the supplier has a robust quality assurance process in place.
Step 4: Request Sample Products
Always request samples before finalizing your order. Testing these samples can provide insight into their performance and quality, allowing you to compare them with competing products.
- Sub-bullet: Conduct performance tests to evaluate filtration efficiency.
- Sub-bullet: Assess the durability of the filters under simulated operating conditions.
Step 5: Analyze Pricing Structures
Evaluate the pricing structures of potential suppliers. Understanding the price range for both air filters and cabin filters is crucial for budgeting and margin calculations.
- Sub-bullet: Compare prices across multiple suppliers to identify competitive rates.
- Sub-bullet: Consider the total cost of ownership, including shipping and potential duties.
Step 6: Check Customer Reviews and References
Investigate customer feedback and seek references from previous buyers. This step can provide valuable insights into the reliability and performance of the filters supplied by potential vendors.
Illustrative image related to difference between air filter and cabin filter
- Sub-bullet: Look for testimonials from businesses in similar industries or geographical locations.
- Sub-bullet: Utilize platforms like industry forums to gauge supplier reputation.
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Ensure there are clear communication channels with your chosen supplier. Effective communication can prevent misunderstandings and facilitate smooth transactions.
- Sub-bullet: Set expectations for response times and updates on order status.
- Sub-bullet: Discuss protocols for handling issues related to product quality or delivery delays.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing air filters and cabin filters, ensuring they meet the needs of their clients while maintaining high standards of quality and performance.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for difference between air filter and cabin filter Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Air Filters and Cabin Filters?
When sourcing air filters and cabin filters, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The composition of filters varies significantly. Engine air filters often use a combination of paper, foam, and synthetic fibers, while cabin filters may incorporate activated carbon for odor removal. The quality of these materials directly impacts the price, with higher-grade materials commanding a premium.
-
Labor: Labor costs are incurred during the manufacturing process, including assembly and quality control (QC). These costs can vary based on the region where the filters are produced. For instance, labor costs in countries with higher wages may lead to increased filter prices.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the costs associated with factory operations, including utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs, influencing overall pricing.
-
Tooling: The design and fabrication of molds and tools for filter production can be a significant upfront cost. Custom designs or unique specifications will increase tooling expenses, which may be reflected in the final product price.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous testing and quality assurance processes are vital to ensure that filters meet performance standards. The costs associated with QC procedures, including testing equipment and personnel, contribute to the overall price.
-
Logistics: Transporting filters from manufacturers to distribution centers or end-users can add substantial costs, especially for international shipments. Factors such as shipping methods, distance, and customs duties must be considered.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and generate profit. This margin can vary based on the competitive landscape and the perceived value of the filters.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Air Filters and Cabin Filters?
Several factors can influence the pricing of air filters and cabin filters:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Purchasing in larger quantities often leads to discounts. Buyers should negotiate MOQs with suppliers to optimize costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom filters designed for specific applications may incur additional charges. Buyers should weigh the need for customization against potential cost increases.
-
Materials: The choice of materials impacts pricing significantly. Filters made with premium materials, such as HEPA or specialized synthetic fibers, will be priced higher than standard options.
-
Quality and Certifications: Filters that meet specific industry standards or certifications (e.g., ISO, SAE) may be priced higher due to the added assurance of quality and performance. Buyers should assess the importance of certifications based on their operational needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge more due to their reliability and service quality.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can affect the final price, as they determine the responsibilities of buyers and sellers during shipping. Understanding these terms is crucial for managing costs effectively.
What Tips Can B2B Buyers Use to Optimize Their Sourcing of Air Filters and Cabin Filters?
-
Negotiate Wisely: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing. Engage in negotiations that consider long-term partnerships, which may yield favorable terms.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just upfront costs. Consider factors such as filter lifespan, maintenance needs, and performance efficiencies.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of regional pricing variations and currency fluctuations that may affect overall costs.
-
Seek Multiple Quotes: Obtaining quotes from multiple suppliers helps in understanding the market rate and identifying competitive pricing. It also allows for better negotiation leverage.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Keeping abreast of industry trends and innovations can provide insights into potential cost-saving opportunities, such as new materials or manufacturing methods.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for air filters and cabin filters can vary significantly based on the factors discussed above. The ranges provided (typically $10-$80 for engine air filters and $15-$50 for cabin filters) are indicative and may not reflect current market conditions. Always confirm with suppliers for the most accurate pricing tailored to specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing difference between air filter and cabin filter With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Air and Cabin Filters
In the automotive sector, maintaining clean air for both engine performance and passenger comfort is critical. While traditional air and cabin filters serve this purpose, businesses may consider alternative solutions that can enhance performance, reduce costs, or simplify maintenance. Here, we will compare the differences between air filters and cabin filters with several viable alternatives, providing insights into each option’s benefits and drawbacks.
| Comparison Aspect | Difference Between Air Filter And Cabin Filter | Alternative 1 Name: HEPA Filters | Alternative 2 Name: Oiled Filters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Filters engine air and cabin air separately, ensuring optimal engine function and passenger comfort. | Captures smaller particles, including allergens and pollutants, providing superior air quality. | Enhances engine performance by allowing better airflow and filtration, often reusable. |
| Cost | Engine air filters: $10-$80; Cabin filters: $15-$50. | Generally higher upfront cost, around $50-$150 depending on vehicle type. | Moderate cost, typically $20-$60, plus cleaning supplies. |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to replace for engine air; cabin filter may require professional help. | Installation similar to cabin filters; requires careful handling to avoid damage. | DIY-friendly; requires cleaning and re-oiling periodically. |
| Maintenance | Engine air filters need replacement every 15,000 miles; cabin filters every 2 years. | Requires replacement every 1-2 years, depending on use and environment. | Cleaning needed every 15,000 miles; re-oiling required after cleaning. |
| Best Use Case | Essential for all vehicles for optimal performance and comfort. | Ideal for vehicles in polluted urban areas or for individuals with allergies. | Best for performance vehicles or users seeking a long-term, cost-effective solution. |
HEPA Filters: Pros and Cons
HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters offer superior filtration, capturing particles as small as 0.3 microns. This makes them particularly effective for users concerned about allergens, dust, and pollutants, especially in urban environments. However, HEPA filters tend to have a higher upfront cost and may require more frequent replacement, depending on the vehicle usage and air quality conditions. While they enhance passenger comfort significantly, they may not be necessary for all applications, particularly in less polluted areas.
Oiled Filters: Advantages and Disadvantages
Oiled filters are designed to be reusable, providing an eco-friendly alternative to traditional filters. They enhance engine performance by allowing better airflow and filtration efficiency. This can lead to increased horsepower and fuel efficiency. The primary downside is the need for regular maintenance, including cleaning and re-oiling, which may not appeal to all users. Additionally, improper maintenance can lead to engine damage if not done correctly, making it essential for users to be diligent about upkeep.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between air filters, cabin filters, and their alternatives, B2B buyers should consider factors such as vehicle type, operating environment, and maintenance capabilities. For those prioritizing air quality, HEPA filters may provide significant benefits, while oiled filters offer a longer-term solution for performance-focused applications. Ultimately, understanding the specific needs of your fleet or customer base will guide you in choosing the most effective and efficient filtration solution.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for difference between air filter and cabin filter
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Air Filters and Cabin Filters?
When assessing air filters and cabin filters, several technical properties are essential for B2B buyers to consider. These specifications not only affect product performance but also influence purchasing decisions and operational efficiency.

Illustrative image related to difference between air filter and cabin filter
1. Material Composition
Air filters are typically made from a combination of paper, foam, or synthetic fibers. Engine air filters often use pleated paper for higher dirt-holding capacity, while cabin filters frequently incorporate activated carbon for odor absorption. Understanding the material composition is crucial for evaluating filter effectiveness and longevity, impacting maintenance schedules and overall vehicle performance.
2. Filtration Efficiency
Filtration efficiency is usually expressed as a percentage, indicating the filter’s ability to capture particles of specific sizes. For instance, HEPA cabin filters can trap particles as small as 0.3 microns with an efficiency of 99.97%. B2B buyers should prioritize filters with high filtration efficiency to ensure optimal air quality, particularly in regions with high levels of dust or allergens.
3. Flow Rate
The flow rate measures the volume of air that passes through the filter within a specific time, often expressed in cubic feet per minute (CFM). Engine air filters generally have higher flow rates to meet engine demands, while cabin filters are designed for lower flow rates. Understanding flow rate is vital for ensuring that the vehicle maintains performance without compromising air quality.
4. Size and Fitment
Filters must fit correctly to function effectively. Engine air filters are usually larger and more complex than cabin filters, which are designed to fit into tight spaces within the dashboard. B2B buyers should confirm specifications such as dimensions and compatibility with various vehicle models to avoid costly returns and ensure proper installation.
5. Replacement Interval
Replacement intervals indicate how often filters should be replaced for optimal performance. Engine air filters typically require replacement every 15,000 miles, while cabin filters may last up to 24 months, depending on usage conditions. Understanding these intervals aids in effective inventory management and scheduling maintenance, impacting operational costs.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Air Filters and Cabin Filters?
Familiarity with industry jargon can enhance communication and negotiation between B2B buyers and suppliers. Here are several key terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to parts made by the original manufacturer of the vehicle. For air filters, OEM parts are often preferred for their compatibility and reliability. Buyers should consider OEM filters when looking for quality assurance and performance consistency.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ denotes the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for B2B buyers to manage inventory effectively and negotiate better pricing, especially when dealing with multiple filter types.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document requesting a price quote from suppliers. It is a critical step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare pricing and terms from different manufacturers, ensuring cost-effectiveness.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, covering aspects like shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms helps B2B buyers navigate logistics and understand their obligations, reducing the risk of miscommunication.
5. HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air)
HEPA filters are a specific type of cabin air filter known for their high filtration efficiency. These filters are particularly advantageous in environments with high allergen concentrations, making them a popular choice for health-conscious buyers.
6. Aftermarket
The aftermarket refers to parts and accessories sold after the original sale of the vehicle. Understanding the aftermarket landscape is crucial for B2B buyers looking to offer a range of filter options to their customers, balancing quality and cost.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their product offerings, improve customer satisfaction, and streamline operations.
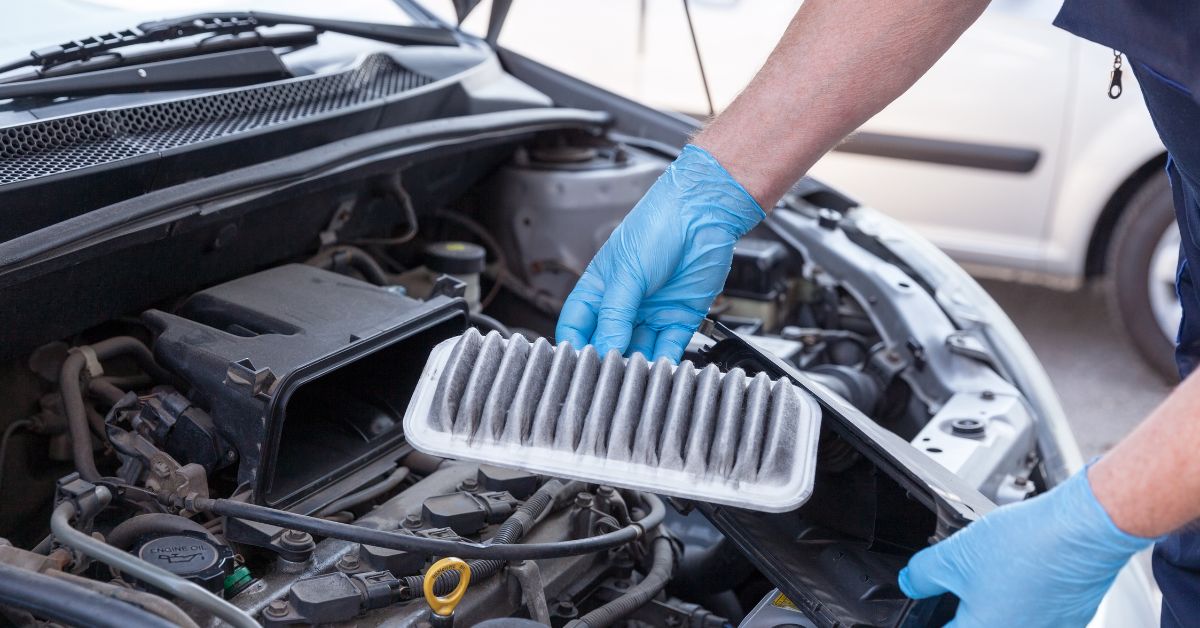

Illustrative image related to difference between air filter and cabin filter
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the difference between air filter and cabin filter Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Air Filter and Cabin Filter Sector?
The global market for air filters and cabin filters is experiencing dynamic growth driven by several key factors. Increasing vehicle production and rising awareness about air quality significantly influence the demand for both engine and cabin air filters. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, urbanization and industrialization are accelerating vehicle usage, which in turn propels the need for effective filtration systems. The growing emphasis on vehicle maintenance and performance optimization is further enhancing the market landscape, making air filters a critical component for both manufacturers and suppliers.
Emerging technologies such as smart filters equipped with sensors that monitor filter performance are transforming sourcing trends. B2B buyers are increasingly looking for advanced filtering solutions that provide real-time data, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime. Additionally, the adoption of e-commerce platforms for sourcing automotive components is on the rise, enabling international buyers to access a broader range of products and suppliers. This shift towards digital procurement is particularly beneficial for businesses in regions with developing markets, as it simplifies the sourcing process and promotes competitive pricing.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Air Filter Industry?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of procurement strategies in the air filter sector. With growing environmental concerns, buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adhere to ethical sourcing practices. The environmental impact of production processes, particularly concerning the materials used in air filters, has come under scrutiny. For instance, the use of non-toxic, biodegradable, and recyclable materials is gaining traction, aligning with global efforts to reduce carbon footprints.
Moreover, certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and various green product certifications are becoming essential in supplier evaluations. B2B buyers are not only looking for products that meet performance standards but also those that contribute to sustainability goals. This trend is particularly relevant in Europe, where regulatory frameworks are stringent regarding environmental practices. By integrating sustainability into their sourcing strategies, companies can improve brand reputation, appeal to environmentally conscious consumers, and potentially reduce costs associated with waste management and compliance.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Air Filters and Cabin Filters in the Automotive Industry?
The evolution of air filters and cabin filters has been marked by significant technological advancements and changing consumer expectations. Initially, air filters were simple components designed solely to protect engine performance. However, as vehicle technology progressed, the focus expanded to include the passenger experience, leading to the development of cabin filters that address indoor air quality.
Over the years, innovations such as HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters and activated carbon filters have emerged, enhancing the ability to trap smaller particles and odors. The introduction of these advanced filtration systems reflects a broader trend toward improving air quality in vehicles, driven by consumer demand for healthier environments. As regulatory standards for emissions and air quality become more stringent, the air filter and cabin filter market is expected to continue evolving, incorporating new materials and technologies that align with both performance and sustainability objectives.
In conclusion, understanding the market dynamics, sustainability considerations, and historical context of air filters and cabin filters is crucial for B2B buyers looking to navigate this evolving sector effectively. By prioritizing ethical sourcing and staying abreast of technological advancements, businesses can position themselves favorably in a competitive landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of difference between air filter and cabin filter
-
What are the key differences between an engine air filter and a cabin air filter?
The engine air filter is designed to protect the vehicle’s engine by filtering out dirt, dust, and debris from the air that enters the combustion chamber. It is typically located under the hood and is larger and more complex in design. In contrast, the cabin air filter cleans the air that circulates within the passenger compartment, removing allergens, pollutants, and odors. It is usually smaller and found within the vehicle’s HVAC system, often behind the glove box. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for maintaining vehicle performance and passenger comfort. -
How often should I replace engine air filters and cabin air filters?
Engine air filters are generally recommended for replacement every 15,000 miles or annually, depending on driving conditions. Conversely, cabin air filters may require replacement every two years or based on specific environmental factors. Regular inspections of both filters are essential to ensure optimal vehicle performance and air quality. Buyers should consider climate and usage patterns in their region when determining replacement intervals to maintain efficiency. -
What factors should I consider when sourcing air filters for international trade?
When sourcing air filters, consider factors such as compliance with international standards and regulations, quality assurance processes, and the supplier’s reliability. It’s vital to evaluate certifications and testing procedures that ensure the filters meet performance criteria specific to your market. Additionally, assess the supplier’s ability to provide timely delivery and responsive customer service, which are essential for maintaining inventory and meeting client demands in your region. -
How can I vet suppliers for air filters effectively?
To vet suppliers, start by researching their reputation through reviews, testimonials, and industry references. Request samples to evaluate product quality and performance. Inquire about their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and certifications. Additionally, consider their experience in international trade, including logistics capabilities and familiarity with customs regulations in your region. Establishing clear communication and transparency in operations will help build a trustworthy supplier relationship. -
What customization options are available for air filters?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for air filters, including size, filtration media, and additional features like activated carbon for odor removal. Customization can be tailored to meet specific vehicle requirements or regional environmental conditions. When sourcing, communicate your needs clearly to suppliers to ensure they can accommodate your specifications. This flexibility can enhance customer satisfaction and differentiate your offerings in competitive markets. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for air filters?
Minimum order quantities for air filters can vary significantly based on the supplier and the type of filter. Generally, MOQs can range from 100 to several thousand units. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs and order volumes with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms. Some suppliers may offer lower MOQs for first-time buyers or for custom orders, making it essential to clarify this aspect during the procurement process. -
What payment terms are standard for international air filter transactions?
Payment terms for international transactions typically include options such as advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Common practices involve a deposit upfront, with the balance payable upon shipment or delivery. Discussing payment terms early in negotiations can help manage cash flow and establish trust between buyers and suppliers. Always ensure that payment methods are secure and offer sufficient protection against potential disputes. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for air filters sourced internationally?
Implementing a robust quality assurance process is crucial when sourcing air filters. This includes establishing clear specifications and testing protocols prior to production. Requesting third-party testing or certifications can further validate the product’s quality. Regular communication with the supplier during production and conducting final inspections before shipping will help ensure that the filters meet the agreed-upon standards. Establishing a return policy for defective products can also safeguard your business interests.
Top 3 Difference Between Air Filter And Cabin Filter Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Capitol Acura – Engine Air Filter
Domain: capitolacura.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Engine Air Filter: Cleans dirt, dust, sand, and contaminants from entering the engine. Signs of failure include reduced acceleration, misfiring spark plugs, black smoke from exhaust, and Service Engine light activation. Recommended replacement schedule varies; consult owner’s manual. Cabin Air Filter: Cleans air passing through heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. Signs of failure i…
2. Reddit – Cabin Air Filter and Aircon Filter
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Cabin air filter and aircon filter are two different components in a vehicle’s HVAC system. The cabin air filter is designed to filter the air that enters the passenger compartment, removing dust, pollen, and other pollutants. The aircon filter, often referred to as the air conditioning filter, is specifically for filtering the air that circulates through the air conditioning system. In the contex…
3. Sarasota Dodge – Engine Air Filter
Domain: sarasotadodge.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Engine Air Filter: Responsible for cleaning the air that circulates around the engine. Recommended to change every 12,000 to 15,000 miles, or more frequently in heavy traffic or dusty conditions. Signs of a clogged engine air filter include slow acceleration, spark plug misfires, black smoke from the exhaust, and the Service Engine light coming on. Cabin Air Filter: Responsible for cleaning the ai…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for difference between air filter and cabin filter
In summary, understanding the differences between engine air filters and cabin air filters is critical for optimizing vehicle performance and ensuring passenger comfort. Engine air filters play a vital role in maintaining engine efficiency by preventing harmful contaminants from entering, while cabin air filters focus on providing clean air for occupants by filtering out allergens and odors.
For international B2B buyers, strategic sourcing of these components can lead to significant cost savings and enhanced vehicle reliability. By prioritizing quality and compatibility when selecting air filters, buyers can improve maintenance schedules and reduce the likelihood of performance issues that can arise from dirty or improperly functioning filters.
As the automotive market continues to evolve, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there is an increasing demand for high-quality filtration solutions. Now is the time to leverage insights gained from this guide to make informed sourcing decisions that align with industry standards and regional needs. Engage with trusted suppliers and manufacturers to ensure your fleet operates at peak performance, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
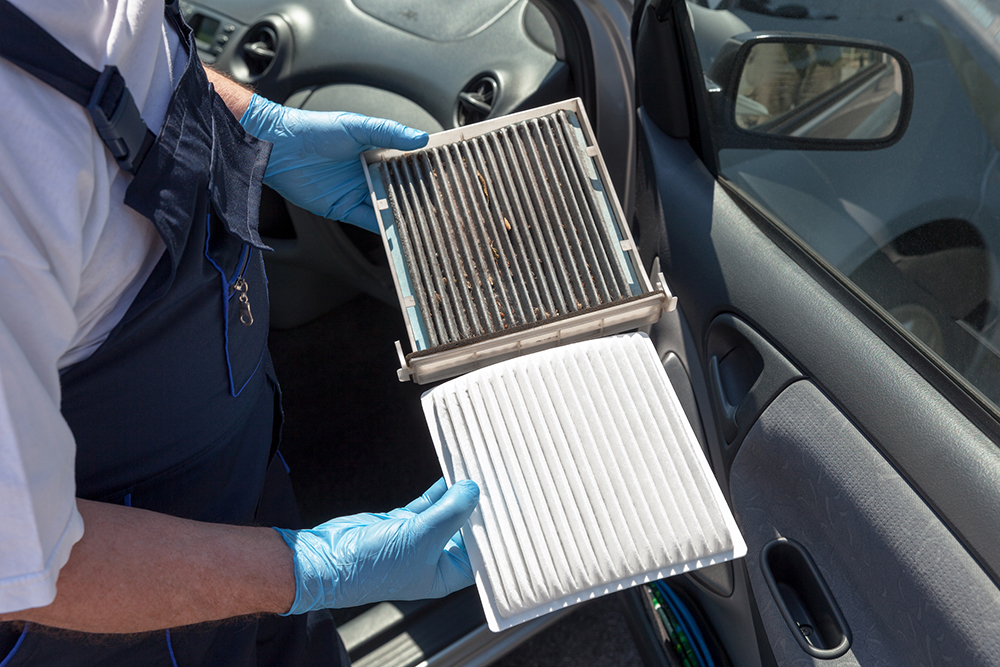

Illustrative image related to difference between air filter and cabin filter
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.