A Deep Dive into Diagram Solenoid Solution
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for diagram solenoid
In the dynamic landscape of industrial automation, sourcing the right diagram solenoid can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers. With a myriad of options available, understanding the intricacies of solenoid valve types, their applications, and the specific needs of different industries is crucial. This guide aims to demystify the complexities associated with diagram solenoids, offering a comprehensive overview that includes various types, operational mechanisms, and application scenarios.
Buyers will find detailed insights into the vetting process for suppliers, ensuring they choose reliable partners who meet international standards. Additionally, we delve into cost considerations, helping businesses navigate budget constraints while ensuring quality and efficiency. This resource is tailored for international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including markets like Saudi Arabia and Germany.
By equipping stakeholders with actionable information and best practices, this guide empowers informed purchasing decisions, enhancing operational efficiency and effectiveness in fluid control systems. Whether you are looking to upgrade existing systems or implement new solutions, understanding the nuances of diagram solenoids will enable you to make strategic choices that align with your business objectives.
Understanding diagram solenoid Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2/2 Way Solenoid Valve | Two ports, two positions (normally open/closed) | Fluid control in simple systems | Pros: Simple design; Cons: Limited functionality |
| 3/2 Way Solenoid Valve | Three ports, two positions, can control two circuits | Pneumatic applications, cylinder control | Pros: Versatile; Cons: More complex than 2/2 valves |
| Proportional Solenoid Valve | Variable flow control based on input signals | Industrial automation, precise fluid control | Pros: High precision; Cons: Higher cost |
| Pneumatic Solenoid Valve | Operated by compressed air, often used in automation | Manufacturing, packaging machinery | Pros: Fast operation; Cons: Requires air supply |
| Modulating Solenoid Valve | Adjustable opening between fully open and closed | HVAC systems, flow rate control | Pros: Flexible control; Cons: Complexity in setup |
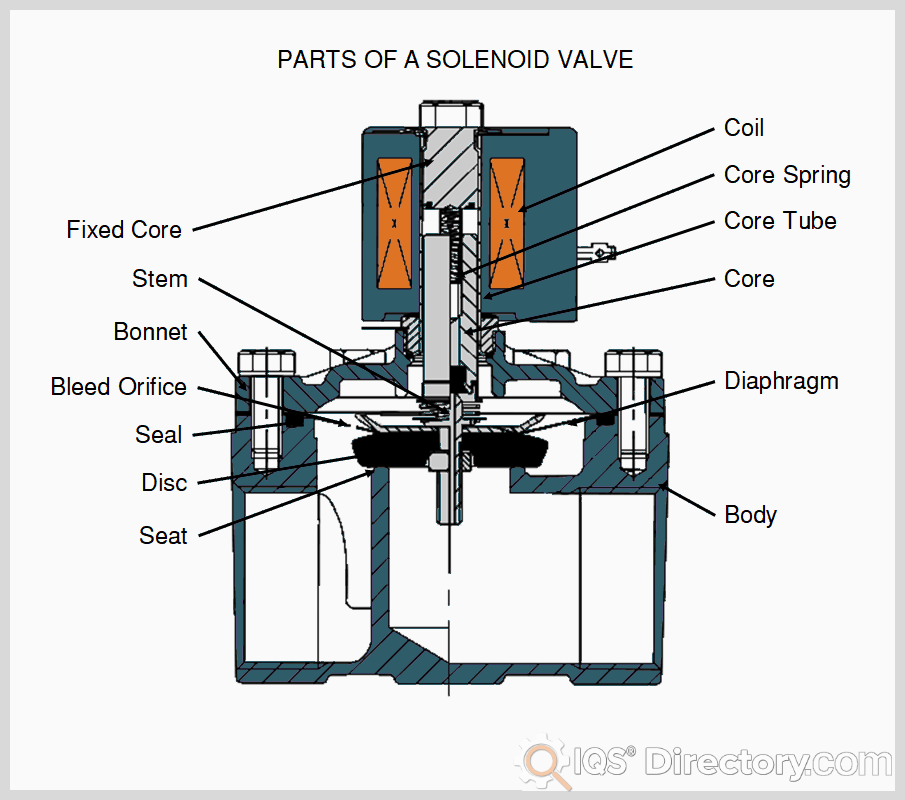
What are the Characteristics of 2/2 Way Solenoid Valves?
2/2 Way Solenoid Valves are among the most straightforward types of solenoid valves, featuring two ports and two states: open and closed. They are primarily used in fluid control applications where simple on/off operation is sufficient. Buyers should consider the valve’s compatibility with their specific fluids and operating pressures. While they are cost-effective and easy to implement, their limited functionality may not suit more complex applications requiring variable flow control.
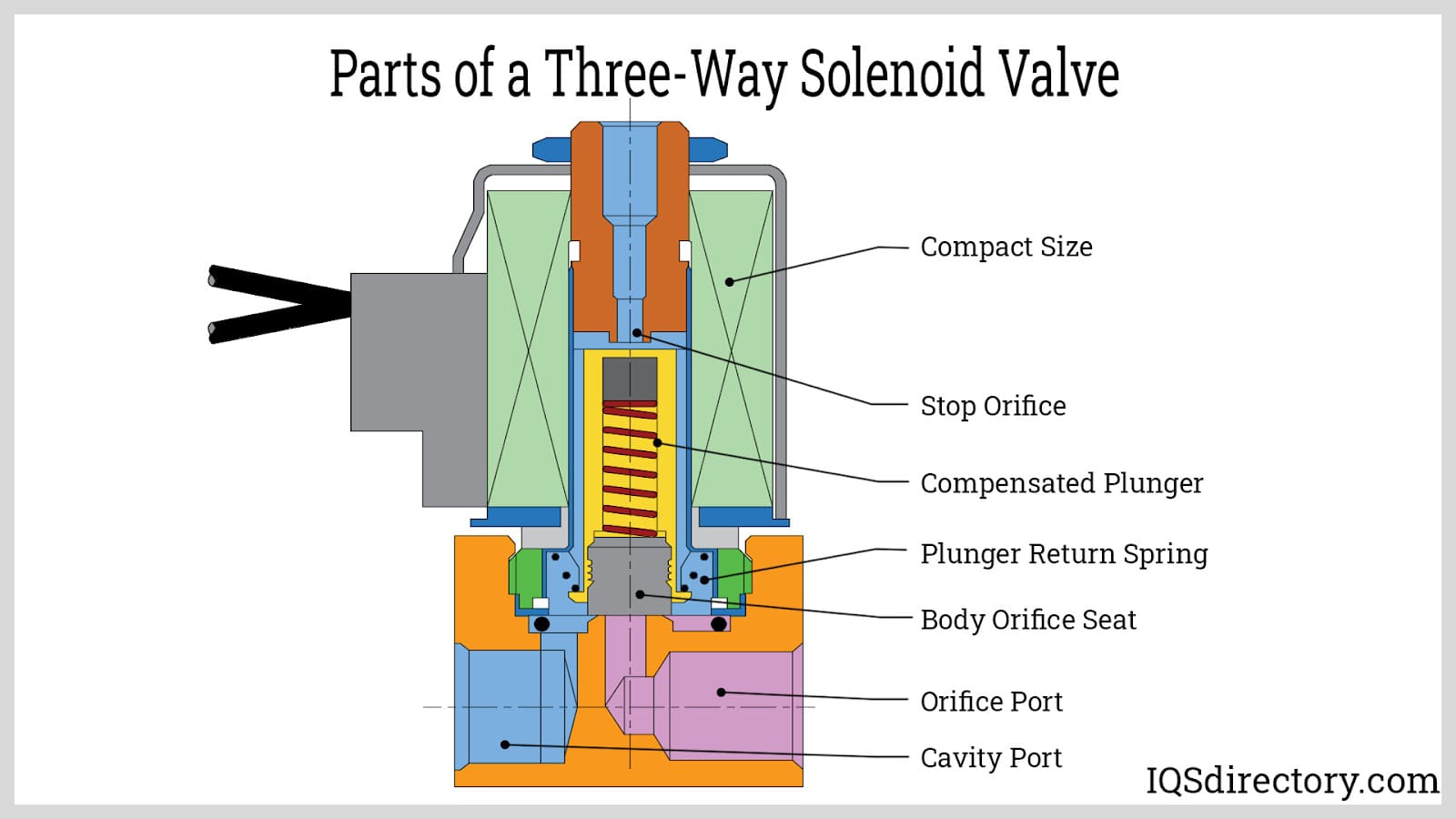
How Do 3/2 Way Solenoid Valves Operate?
3/2 Way Solenoid Valves have three ports and two positions, allowing them to control two separate circuits. This versatility makes them ideal for applications such as pneumatic systems and hydraulic cylinders. When purchasing, buyers should assess their specific circuit requirements and the valve’s compatibility with the intended medium. Although they offer greater functionality than 2/2 valves, their increased complexity may require additional considerations in installation and maintenance.
What Makes Proportional Solenoid Valves Unique?
Proportional Solenoid Valves provide variable flow control based on electrical input signals, making them suitable for industrial automation and processes requiring precise fluid management. These valves are often employed in applications where maintaining a specific pressure or flow rate is critical. Buyers should evaluate the precision needs of their applications and the associated costs, as these valves typically come at a higher price point due to their advanced features.
In What Applications are Pneumatic Solenoid Valves Most Effective?
Pneumatic Solenoid Valves are specifically designed to operate using compressed air, making them a common choice in manufacturing and packaging machinery. They are known for their rapid actuation speed, which enhances operational efficiency. Buyers should consider the availability of air supply and the valve’s suitability for their pneumatic systems. While these valves excel in speed, they may require additional infrastructure for air supply, which could increase overall costs.
Why Choose Modulating Solenoid Valves?
Modulating Solenoid Valves allow for adjustable openings, providing control between fully open and fully closed states. This feature is particularly beneficial in HVAC systems and applications where precise flow rate adjustments are necessary. When considering a purchase, buyers should assess the complexity of setup and the specific control requirements of their systems. Although they offer flexible control options, the complexity may lead to higher installation and maintenance costs.
Key Industrial Applications of diagram solenoid
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of diagram solenoid | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Control of automated assembly lines | Enhances efficiency and reduces downtime | Quality certifications, compatibility with existing systems |
| Water Treatment | Regulation of water flow in treatment plants | Ensures optimal operation and compliance with regulations | Durability under harsh conditions, maintenance support |
| Oil & Gas | Actuation of valves in pipeline systems | Increases safety and reliability in operations | Explosion-proof ratings, resistance to corrosive environments |
| HVAC Systems | Temperature control in heating/cooling systems | Improves energy efficiency and comfort for users | Energy efficiency ratings, responsiveness to control signals |
| Agriculture & Irrigation | Automation of irrigation systems | Optimizes water usage and crop yield | Adaptability to local conditions, reliability in remote areas |
In the manufacturing sector, diagram solenoids are integral to the automation of assembly lines. They control the flow of compressed air or fluids that actuate machinery, enhancing overall efficiency and reducing downtime. International buyers should consider sourcing solenoids that are compatible with their existing systems and meet quality certifications to ensure reliable performance.
In water treatment facilities, diagram solenoids regulate water flow and manage the chemical dosing process. This application is critical for ensuring optimal operation and compliance with environmental regulations. Buyers need to focus on sourcing solenoids that demonstrate durability under harsh conditions, as well as those that come with maintenance support to minimize operational interruptions.
Within the oil and gas industry, diagram solenoids are used to actuate valves in pipeline systems, providing essential control over fluid flow. This application is vital for maintaining safety and reliability in operations, especially in high-pressure environments. Buyers should prioritize solenoids with explosion-proof ratings and those designed to resist corrosive environments, particularly in regions with extreme weather conditions.
In HVAC systems, diagram solenoids play a key role in temperature control. They are used to regulate the flow of refrigerants or heated air, thereby improving energy efficiency and ensuring comfort for users. Buyers should look for solenoids that have high energy efficiency ratings and quick responsiveness to control signals, as these features contribute to better system performance and lower operating costs.
In agriculture and irrigation, diagram solenoids automate irrigation systems, allowing for precise control over water delivery. This application helps optimize water usage and enhance crop yield, particularly in regions where water is scarce. Buyers should consider the adaptability of solenoids to local conditions and their reliability in remote areas, as these factors are crucial for successful agricultural operations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘diagram solenoid’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Confusion Over Solenoid Valve Symbols in Diagrams
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter confusion when interpreting solenoid valve symbols in piping and instrumentation diagrams (P&ID). This can lead to miscommunication among engineering teams, incorrect installations, and costly operational errors. For example, a buyer might receive a diagram where the symbols for a normally closed valve and a normally open valve are misrepresented. This confusion can result in selecting the wrong type of valve for a critical application, jeopardizing system efficiency and safety.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should invest time in understanding standardized solenoid valve symbols and their meanings. Engaging with resources that explain the symbols used in P&IDs can enhance clarity. Furthermore, it’s advisable to collaborate closely with suppliers to ensure that the specifications provided in the diagrams are accurate and consistent. Buyers should also consider requesting detailed documentation or symbol key charts from their suppliers when placing orders. This proactive approach helps ensure that everyone involved in the project has a clear understanding of the components, minimizing the risk of errors during installation and operation.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Sourcing the Right Solenoid Valves for Specific Applications
The Problem: Many international buyers struggle to find solenoid valves that meet specific requirements for diverse applications, particularly when it comes to pressure ratings, flow capacities, and environmental conditions. For instance, a buyer in a South American manufacturing facility may need valves that can withstand high humidity and corrosive environments but finds limited options in their local market. This difficulty can delay projects and increase costs, as buyers often resort to suboptimal alternatives.
The Solution: To address sourcing challenges, buyers should leverage global supply chains by researching and connecting with reputable manufacturers who specialize in solenoid valves. Utilizing online platforms and industry-specific trade shows can provide access to a broader range of products. Buyers should also communicate their specific needs clearly to suppliers, including detailed environmental conditions and operational parameters. Establishing relationships with multiple suppliers can ensure access to customized solutions and expedite the procurement process. Additionally, buyers may consider forming partnerships with local distributors who can facilitate access to international brands while providing local support.
Scenario 3: Challenges with Installation and Maintenance of Solenoid Valves
The Problem: Installation and maintenance of solenoid valves can pose significant challenges, especially for B2B buyers who may not have in-house expertise. A buyer in Europe, for example, might face difficulties in properly wiring and configuring solenoid valves within a larger control system. Missteps during installation can lead to system failures, unexpected downtimes, and increased operational costs. Furthermore, maintenance procedures can be unclear, leading to longer repair times and potential safety hazards.
The Solution: To enhance installation and maintenance processes, buyers should prioritize training for their technical teams. Investing in workshops or online training sessions offered by valve manufacturers can provide valuable insights into best practices. Buyers should also request comprehensive installation manuals and maintenance guidelines from their suppliers, ensuring that all relevant personnel are equipped with the necessary knowledge. Implementing a routine maintenance schedule can also prevent potential issues, allowing teams to identify wear and tear before they escalate into major problems. By fostering a culture of continuous learning and adherence to manufacturer guidelines, organizations can improve system reliability and efficiency.
Illustrative image related to diagram solenoid
Strategic Material Selection Guide for diagram solenoid
What Are the Key Materials Used in Diagram Solenoids?
Selecting the appropriate material for diagram solenoids is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity in diverse applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in manufacturing solenoids, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
1. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high tensile strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures (up to 800°F or 427°C). It also has good pressure ratings, making it suitable for various fluid applications.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of stainless steel is a significant advantage, as it can withstand harsh environments without degrading. However, it is more expensive than other materials, which may increase the overall cost of the solenoid. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, as stainless steel requires specialized machining.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including aggressive chemicals and high-temperature fluids. This makes it ideal for industries like oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, and food processing.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A276 or DIN 17440, which govern stainless steel grades. Understanding local corrosion factors is also critical for selecting the right grade.
Illustrative image related to diagram solenoid
2. Brass
Key Properties:
Brass offers good corrosion resistance, moderate strength, and excellent machinability. It typically operates well under moderate temperatures (up to 400°F or 204°C) and pressures.
Pros & Cons:
Brass is less expensive than stainless steel, making it a cost-effective choice for many applications. However, it has lower corrosion resistance compared to stainless steel, which can limit its use in aggressive environments. Its manufacturing process is simpler, allowing for efficient production.
Impact on Application:
Brass is suitable for applications involving water, air, and non-aggressive chemicals. It is commonly used in plumbing and HVAC systems.
Considerations for International Buyers:
In regions like South America, buyers should verify compliance with local standards, such as JIS H3250 for brass materials. The lower cost of brass can be appealing, but buyers must consider the specific media compatibility to avoid premature failure.
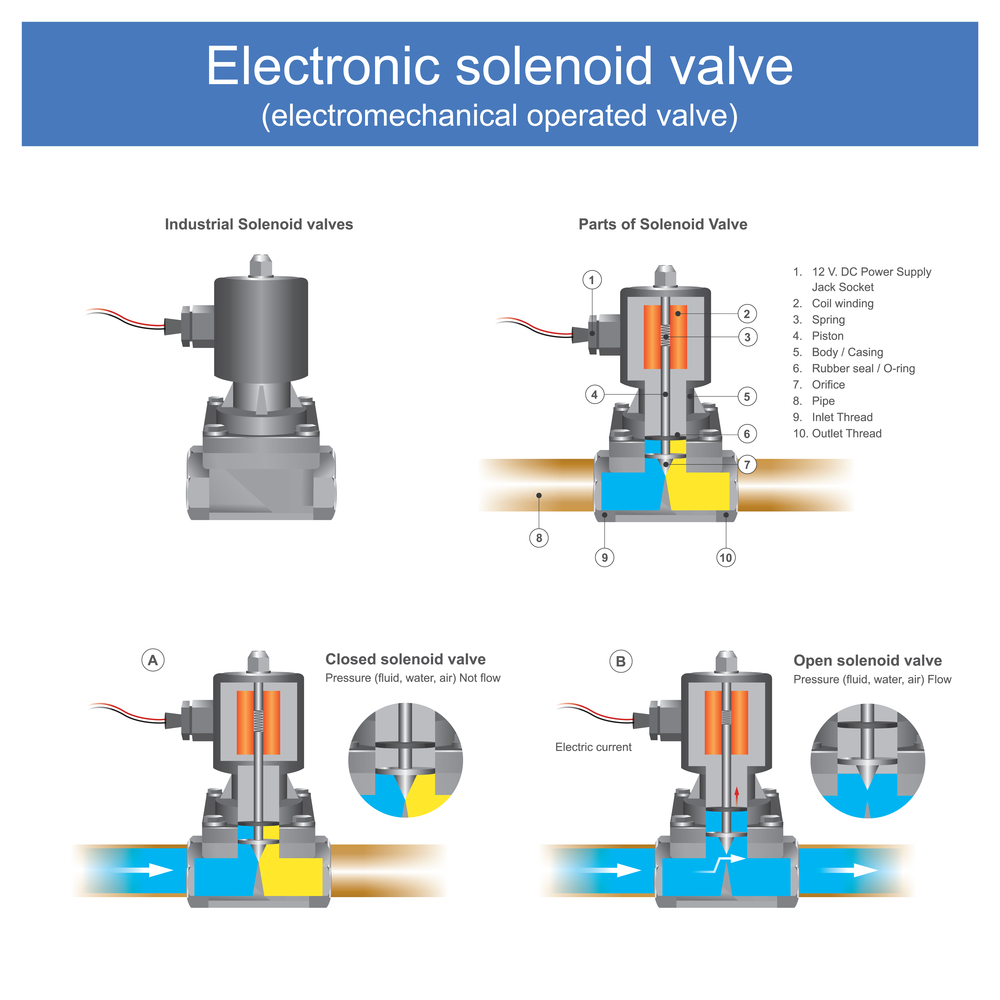
3. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight, has good corrosion resistance, and can operate at moderate temperatures (up to 300°F or 149°C). It is also known for its excellent thermal conductivity.
Illustrative image related to diagram solenoid
Pros & Cons:
The lightweight nature of aluminum makes it ideal for applications where weight is a concern. However, its lower strength and pressure ratings compared to stainless steel and brass can be limiting factors. Manufacturing complexity is generally low, as aluminum is easy to machine.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is suitable for air and low-pressure fluid applications but may not be ideal for high-temperature or high-pressure environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in Africa and Europe should consider the specific alloy used, as various aluminum grades have different properties. Compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 is essential for ensuring quality.
4. Plastic (Polymer)
Key Properties:
Plastics, particularly engineering polymers, offer excellent chemical resistance, low weight, and good electrical insulation properties. They can operate in a range of temperatures (typically up to 200°F or 93°C) and pressures.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of plastic solenoids is their resistance to corrosion and low cost. However, they may not be suitable for high-pressure applications and can be less durable than metal alternatives. Manufacturing processes for plastic parts can be complex, requiring specialized techniques.
Impact on Application:
Plastic solenoids are ideal for applications involving corrosive fluids or where weight savings are critical, such as in consumer products or medical devices.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that the selected plastic complies with relevant standards, such as FDA regulations for food-related applications. Understanding the specific chemical compatibility is crucial for ensuring product longevity.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for diagram solenoid | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Oil & gas, pharmaceuticals | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, moderate manufacturing complexity | High |
| Brass | Plumbing, HVAC systems | Cost-effective, good machinability | Lower corrosion resistance | Medium |
| Aluminum | Air and low-pressure applications | Lightweight, good thermal conductivity | Lower strength and pressure ratings | Medium |
| Plastic | Consumer products, medical devices | Corrosion-resistant, low cost | Not suitable for high-pressure applications | Low |
In summary, selecting the right material for diagram solenoids involves balancing performance, cost, and application requirements. International buyers should consider local standards and specific media compatibility to ensure optimal functionality and compliance.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for diagram solenoid
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Diagram Solenoids?
The manufacturing process of diagram solenoids involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the required specifications and quality standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing solenoids for their operations.
Material Preparation
The manufacturing process begins with the selection and preparation of materials. Common materials used in solenoid manufacturing include brass, stainless steel, and various plastics. The choice of material depends on the solenoid’s intended application, such as resistance to corrosion or temperature variations.
After material selection, the components are cut, machined, or molded into the required shapes and sizes. Precision is crucial at this stage, as any deviations can affect the solenoid’s performance. For example, the coil must fit precisely around the core to ensure efficient operation.
Forming Techniques: How Are Solenoids Shaped?
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage involves forming the components. This may include processes such as:
- Stamping: Used for creating metal parts, stamping is a cost-effective method for producing high volumes of identical components.
- Injection Molding: Ideal for plastic parts, this technique allows for complex shapes and high precision.
- Winding: The coil is wound around the solenoid core. This is a critical step, as the number of turns and the wire gauge directly influence the solenoid’s electromagnetic properties.
Each of these techniques requires skilled operators and specialized machinery to ensure consistency and quality.
Assembly: What Goes Into the Assembly of Diagram Solenoids?
The assembly process is where various components come together to form the final product. This typically involves:
- Coil Installation: The wound coil is carefully positioned onto the core.
- Housing Assembly: The solenoid is housed in a protective casing, which may also include mounting brackets.
- Electrical Connections: Proper electrical connections are made to ensure the solenoid can be easily integrated into the end-user’s system.
Quality control checks are integrated at this stage to verify that components fit together correctly and that there are no defects in assembly.
Finishing: How Are Solenoids Prepared for Market?
The finishing stage includes processes that enhance the solenoid’s durability and aesthetics. This may involve:
- Surface Treatment: Processes such as anodizing or plating can improve corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity.
- Quality Checks: Final inspections are conducted to ensure all specifications are met. This includes checking for leaks, electrical continuity, and mechanical functionality.
Finishing touches can significantly impact the performance and longevity of solenoids, making this stage critical for B2B buyers looking for reliable products.
What Are the Quality Assurance Standards for Diagram Solenoids?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of diagram solenoids, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations. Buyers should be aware of various certifications and quality control practices that manufacturers should adhere to.
International Standards: What Certifications Should Buyers Look For?
ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized international quality management standards. It outlines a framework for consistent quality in manufacturing processes, which can be crucial for B2B buyers. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) are important for solenoids used in specific applications, such as oil and gas.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Solenoid Manufacturing?
Quality control in solenoid manufacturing typically involves several checkpoints throughout the production process:
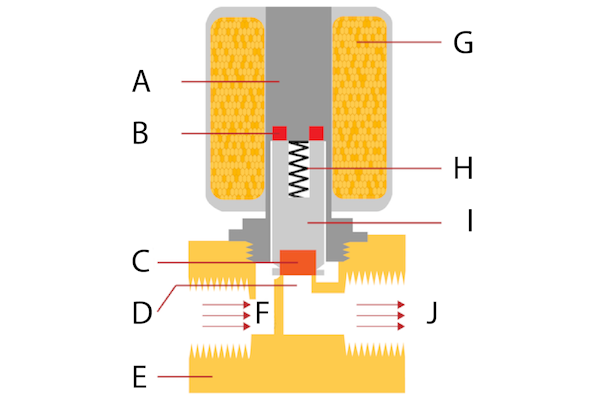
Illustrative image related to diagram solenoid
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous checks during manufacturing help identify and rectify issues before they escalate.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection of the finished product to verify it meets all design specifications and quality standards.
These checkpoints provide multiple layers of assurance that the final product will perform reliably in its intended application.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Solenoid Quality?
To validate the quality of solenoids, manufacturers employ various testing methods, including:
- Electrical Testing: Measures the solenoid’s resistance and ensures it meets specifications.
- Leak Testing: Ensures the solenoid is airtight, which is crucial for applications involving fluids.
- Functional Testing: Verifies that the solenoid operates correctly under expected load conditions.
These tests are vital for ensuring that solenoids can withstand the operational demands they will face in the field.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to ensure their suppliers adhere to rigorous quality control standards. Here are some effective strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to directly assess the manufacturing processes and quality control measures in place. This is particularly important for international suppliers where standards may vary.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can provide insights into the supplier’s performance metrics, including defect rates and compliance with quality standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices and product quality.
These measures can help mitigate risks associated with sourcing from international suppliers, ensuring that the solenoids meet the buyer’s standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control. Variations in local regulations, manufacturing practices, and cultural expectations can influence product quality. Buyers should:
- Understand Regional Standards: Familiarize themselves with local and international regulations that may apply to solenoid use in their specific industries.
- Establish Clear Communication: Clear communication regarding quality expectations and specifications can help bridge gaps between buyers and suppliers from different regions.
- Leverage Technology: Utilizing digital platforms for tracking quality metrics and communication can enhance collaboration and transparency in the supply chain.
By understanding these nuances, B2B buyers can foster better relationships with suppliers and ensure they receive high-quality products that meet their needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘diagram solenoid’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist international B2B buyers in procuring diagram solenoids efficiently. By following these steps, buyers can ensure they select the right products from reliable suppliers, aligning with their technical requirements and operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Start by clearly outlining the technical specifications required for your application. This includes understanding the type of solenoid valve (e.g., 2-way or 3-way), pressure ratings, and materials that will be compatible with your system. Accurate specifications will help you avoid costly mistakes and ensure that the solenoids meet operational demands.
- Consider Environmental Factors: Assess the operational environment, including temperature, humidity, and exposure to chemicals, as these will influence material choice.
- Determine Actuation Requirements: Decide whether you need normally closed or normally open valves based on your system’s requirements.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in solenoid valves. Look for companies with a strong reputation and experience in your industry.
- Check Online Reviews: Utilize platforms like LinkedIn, industry forums, and trade associations to find reviews and testimonials from other buyers.
- Evaluate Their Product Range: Ensure the supplier offers a variety of solenoid types and brands to meet your specific needs.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before proceeding, verify that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications that demonstrate quality control and compliance with international standards.
- ISO Certification: Look for ISO 9001 or similar certifications which indicate a commitment to quality management systems.
- Industry-Specific Certifications: Depending on your industry, additional certifications may be necessary, such as ATEX for explosive environments or FDA for food-grade applications.
Step 4: Request Samples or Prototypes
Request samples or prototypes of the solenoid valves you are considering. This allows you to assess their quality, functionality, and compatibility with your existing systems.
- Test Performance: Conduct tests under your operational conditions to ensure the solenoid performs as required.
- Check for Documentation: Ensure that the supplier provides detailed documentation, including installation guides and operating manuals.
Step 5: Inquire About Lead Times and Availability
Discuss lead times and product availability with your shortlisted suppliers. Understanding these factors is critical for planning your operations and avoiding delays.
- Consider Stock Levels: Ask about their inventory management practices and whether they can fulfill large orders quickly.
- Evaluate Shipping Options: Ensure that the supplier can deliver to your location efficiently, considering any potential customs or import regulations.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, payment terms, and warranties.
- Compare Offers: Don’t hesitate to compare quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure you receive the best value for your investment.
- Clarify Warranty Conditions: Ensure that warranty terms are clearly outlined, particularly concerning defects and performance issues.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Finally, establish a clear communication plan with your chosen supplier to facilitate ongoing support and issue resolution.
Illustrative image related to diagram solenoid
- Designate Points of Contact: Identify key contacts for technical support, order tracking, and customer service.
- Schedule Regular Updates: Arrange for periodic check-ins to discuss performance, future orders, and any potential issues that may arise.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the procurement process for diagram solenoids, ensuring they choose the right products and suppliers for their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for diagram solenoid Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Diagram Solenoids?
When considering the sourcing of diagram solenoids, it’s crucial to understand the various cost components involved. The primary elements include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly affects the price. Common materials for solenoids include brass, stainless steel, and various plastics. Higher-grade materials often lead to increased durability and performance but come at a premium.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly based on the manufacturing location. Regions with lower labor costs may offer more competitive pricing, but this could impact quality and consistency.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses expenses related to facilities, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead, which is beneficial for pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial cost of tooling can be substantial, especially for custom solenoids. Buyers should consider whether the tooling costs can be amortized over larger production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing robust QC measures ensures product reliability. However, stringent QC processes can increase costs, which may be reflected in the final price.
-
Logistics: Transporting solenoids from the manufacturer to the buyer involves shipping costs, customs duties, and insurance. The choice of Incoterms can significantly influence these logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a margin to cover their operational expenses and profit. Understanding the standard margins in your industry can help in negotiations.
What Factors Influence Pricing for Diagram Solenoids?
Several key influencers affect the pricing of diagram solenoids:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate for volume discounts when possible.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific technical specifications can raise costs. It’s vital for buyers to balance their needs against budget constraints.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Solenoids that meet international quality standards or certifications, such as ISO, may cost more but offer better reliability and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier play a significant role in pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their proven track record.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can influence total costs. Understanding these terms can help buyers avoid unexpected expenses related to shipping and customs.
How Can Buyers Negotiate Effectively for Diagram Solenoids?
Effective negotiation strategies can lead to cost savings:
-
Research and Benchmarking: Understand market rates and use this information to negotiate better prices. Benchmark against similar suppliers to establish a fair price range.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but the TCO, which includes installation, maintenance, and operational costs. Emphasizing TCO can lead to better long-term value.
-
Build Long-term Relationships: Establishing a solid relationship with suppliers can yield benefits like better pricing, priority service, and access to new products.
-
Be Clear on Requirements: Provide clear specifications to avoid misunderstandings that could lead to additional costs. Well-defined requirements can streamline production and reduce the need for costly revisions.
What Pricing Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, pricing nuances are crucial:
-
Currency Fluctuations: Be aware of currency exchange rates, as they can significantly impact costs. Locking in prices in a stable currency can mitigate risks.
-
Customs Duties and Taxes: Understand the import duties and taxes that may apply in your country. These can add considerable costs to the purchase price.
-
Shipping Times and Costs: Longer shipping times may necessitate higher logistics costs. Plan ahead to avoid expedited shipping fees.
-
Cultural Differences: Different regions may have varying negotiation styles and business practices. Being culturally aware can facilitate smoother negotiations and better business relationships.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for diagram solenoids can vary widely based on numerous factors, including specifications, order volume, and supplier conditions. This analysis is intended to provide indicative insights and should not be viewed as a definitive pricing guide. Always consult with suppliers for accurate quotes tailored to specific needs and circumstances.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing diagram solenoid With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to Diagram Solenoids
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial automation and fluid control, diagram solenoids have become a popular choice for controlling fluid flow due to their reliability and efficiency. However, several alternative solutions exist that can achieve similar objectives. Understanding these alternatives allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific operational needs.
Comparison of Diagram Solenoid with Alternative Solutions
| Comparison Aspect | Diagram Solenoid | Pneumatic Actuators | Mechanical Valves |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and quick response time | Moderate speed and control, dependent on air supply | Reliable but slower response time |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost, low operational costs | Higher initial costs due to compressor and installation | Low initial cost, but maintenance can add up |
| Ease of Implementation | Straightforward installation with electrical connections | Requires additional air supply setup and maintenance | Simple installation, but may require manual operation |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, minimal wear parts | Regular maintenance needed for air supply systems | Moderate maintenance, can be prone to wear |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for automated systems requiring precise control | Suitable for high-speed applications needing rapid cycling | Best for manual control applications or low-speed operations |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
Pneumatic Actuators
Pneumatic actuators utilize compressed air to produce mechanical motion, making them suitable for high-speed applications. They offer moderate precision but can be affected by fluctuations in air pressure. While the initial investment is higher due to the need for an air compressor and related infrastructure, operational costs can be lower in high-volume applications. Their primary drawback is the need for regular maintenance of the air supply system, which can complicate implementation and increase downtime.
Mechanical Valves
Mechanical valves, which can be operated manually or automatically, provide a simple and cost-effective solution for fluid control. They are reliable and straightforward to install, making them appealing for applications where automation is not critical. However, their slower response time and potential wear issues can be disadvantages in dynamic environments. They are best suited for operations where manual control is preferred or where the speed of operation is not a primary concern.
How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting a fluid control solution, B2B buyers should assess their specific operational requirements, including the necessary speed, precision, and control of fluid flow. Consideration of initial costs versus long-term maintenance and operational expenses is crucial. Buyers should also evaluate the complexity of implementation and the availability of necessary infrastructure, such as air supply for pneumatic systems. By aligning these factors with the unique demands of their operations, companies can make an informed choice that enhances efficiency and productivity.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for diagram solenoid
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Diagram Solenoids?
When considering the procurement of diagram solenoids, understanding their technical properties is crucial for ensuring compatibility and performance in your specific application. Here are several key specifications that should be taken into account:
-
Material Grade
The material of a solenoid valve significantly affects its durability and compatibility with various fluids. Common materials include brass, stainless steel, and plastic. Brass is often used for general applications, while stainless steel is preferred for corrosive environments. Understanding the material grade helps in assessing the solenoid’s longevity and maintenance requirements, which is vital for minimizing operational downtime. -
Pressure Rating
This specification indicates the maximum pressure the solenoid can handle without failure. It is typically measured in psi (pounds per square inch) or bar. Choosing a solenoid with an appropriate pressure rating ensures safe operation within the system’s parameters, preventing leaks or catastrophic failures that could lead to costly damage and liability issues. -
Electrical Specifications
Solenoid valves require specific voltage and current ratings for proper operation. Common voltages include 12V, 24V, and 110V. Understanding these electrical specifications is essential for selecting a solenoid that will function correctly within your existing electrical infrastructure, thereby avoiding electrical failures and inefficiencies. -
Flow Rate
The flow rate, often measured in liters per minute (L/min) or gallons per minute (GPM), determines how much fluid can pass through the valve when it is open. This specification is critical for applications requiring precise fluid control, as an inadequate flow rate can lead to performance bottlenecks in your operations. -
Actuation Type
Solenoid valves can be classified as normally open (NO) or normally closed (NC). Understanding the actuation type is vital for ensuring that the valve will perform correctly within the intended application. For example, an NC valve will remain closed until energized, making it suitable for safety applications where the default state should be closed. -
Temperature Range
The operational temperature range of a solenoid valve indicates the environments in which it can function effectively. This specification is particularly important in industries where extreme temperatures may be encountered, such as food processing or chemical manufacturing. Selecting a valve with an appropriate temperature range is crucial for maintaining operational integrity.
What Are Common Trade Terms Associated with Diagram Solenoids?
Familiarity with industry jargon can enhance communication and negotiations with suppliers. Here are several common terms you should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the solenoid valve industry, OEMs often provide components to larger manufacturers. Understanding OEM relationships can help in sourcing high-quality components that meet specific standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is important for budget planning and inventory management, particularly for businesses that require a large number of solenoids for production but want to avoid overstock. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers asking for pricing and terms for specific products. It is a crucial step in the procurement process, enabling businesses to compare offers from different suppliers and make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are a set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Understanding Incoterms is essential for managing logistics and ensuring that both parties are aware of their obligations regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. -
Lead Time
This term refers to the time it takes from placing an order until it is delivered. Knowing the lead time is essential for project planning and ensuring that you have the necessary components on hand when needed, thereby preventing delays in your operations. -
P&ID (Piping and Instrumentation Diagram)
A P&ID is a detailed graphical representation of a process, showing how equipment is interconnected. Familiarity with P&IDs is crucial for engineers and operators, as they provide essential information about how solenoid valves fit into larger systems, influencing design and maintenance decisions.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terminology will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing diagram solenoids, ultimately leading to more efficient operations and successful project outcomes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the diagram solenoid Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Influencing the Diagram Solenoid Sector?
The global diagram solenoid market is experiencing robust growth driven by several key factors. Firstly, the increasing automation in various industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and agriculture is propelling demand for solenoid valves that facilitate efficient fluid control. International B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly investing in advanced solenoid technologies to enhance operational efficiency and reliability. Furthermore, the rise of Industry 4.0 has led to the adoption of smart solenoid valves equipped with IoT capabilities, allowing for real-time monitoring and data analytics.
Emerging sourcing trends indicate a shift towards digital procurement platforms that enhance transparency and streamline the purchasing process. These platforms provide access to a diverse range of suppliers, enabling B2B buyers to compare products and prices easily, thus optimizing their supply chain strategies. Additionally, sustainability is becoming a significant consideration, with buyers favoring suppliers that demonstrate eco-friendly practices and products. This trend is particularly evident in Europe and parts of the Middle East, where regulatory pressures are prompting companies to adopt greener solutions.
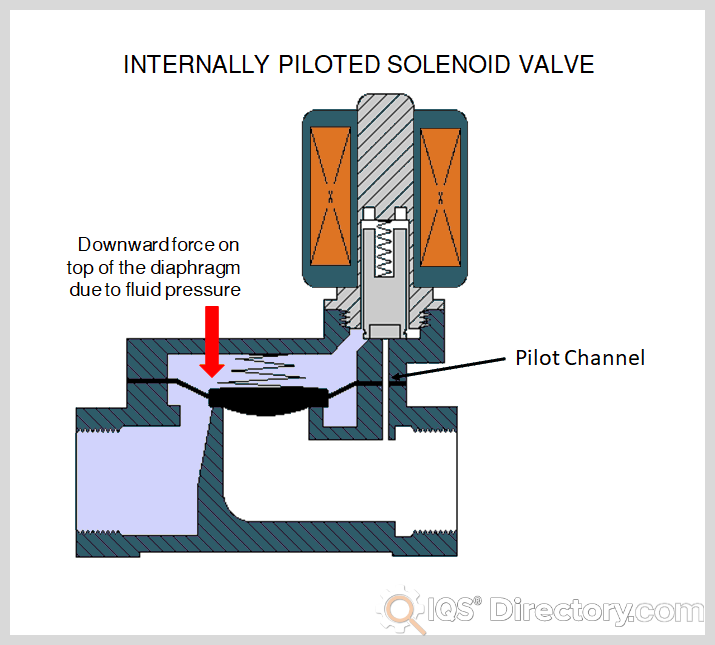
Illustrative image related to diagram solenoid
Lastly, geopolitical factors, such as trade agreements and tariffs, are shaping market dynamics. Buyers from different regions must navigate these complexities to ensure a stable supply chain while mitigating risks associated with price volatility and supply disruptions.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Diagram Solenoid Market?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are increasingly vital in the diagram solenoid sector as businesses face growing scrutiny regarding their environmental impact. The production of solenoid valves involves materials and processes that can have significant ecological footprints, prompting buyers to seek suppliers committed to minimizing these effects. Sustainable practices include the use of recyclable materials, energy-efficient manufacturing processes, and waste reduction strategies.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. B2B buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who adhere to ethical labor practices and demonstrate corporate social responsibility. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety are becoming essential indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
In addition, there is a notable trend toward using ‘green’ materials in the production of solenoids, which can enhance a company’s sustainability profile. As global markets shift toward eco-conscious products, B2B buyers who prioritize ethical sourcing are not only contributing to environmental protection but also enhancing their brand reputation and customer loyalty.
What Is the Historical Evolution of the Diagram Solenoid Sector and Its Relevance to Today’s B2B Buyers?
The diagram solenoid sector has evolved significantly since the introduction of solenoid technology in the early 19th century. Initially, solenoids were primarily used in telegraph systems and simple mechanical devices. Over the decades, advancements in materials and electronic control systems have transformed solenoid valves into sophisticated components integral to various industrial applications.
The introduction of automation in the late 20th century marked a pivotal moment for solenoid technology. With the rise of computer-aided design (CAD) and programmable logic controllers (PLCs), solenoid valves became essential in automated systems, allowing for precise control over fluid dynamics. This evolution is crucial for today’s B2B buyers, who seek solutions that enhance efficiency and reliability in increasingly complex industrial environments.
As the market continues to innovate, understanding the historical context of solenoid technology can provide valuable insights into current trends and future developments. B2B buyers must recognize the importance of selecting suppliers with a strong track record of innovation and quality to ensure they remain competitive in their respective industries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of diagram solenoid
-
How do I choose the right solenoid valve for my application?
Choosing the right solenoid valve involves understanding your specific application requirements, such as fluid type, pressure, and temperature. Start by determining the valve’s configuration (2/2-way, 3/2-way, etc.) based on how you need to control the flow. Consider factors like voltage ratings, actuation methods (normally open vs. normally closed), and the materials of construction to ensure compatibility with your fluid. Consulting with a supplier who specializes in solenoid valves can provide additional insights and recommendations tailored to your needs. -
What are the common applications for solenoid valves in industrial settings?
Solenoid valves are widely used in various industrial applications, including automation systems, fluid control in manufacturing processes, HVAC systems, and irrigation systems. They play a critical role in controlling the flow of liquids and gases, making them essential in sectors such as oil and gas, food and beverage, and pharmaceuticals. Their ability to provide precise control and rapid switching capabilities makes them invaluable in enhancing efficiency and reliability in these applications. -
What customization options are available for solenoid valves?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for solenoid valves to meet specific operational needs. Customizations may include modifications to valve size, material selection, coil voltage, and specific actuation types. Additionally, you can request features such as integrated sensors or specific connection types to align with your existing systems. Discussing your requirements with suppliers can help you identify the best customization options available for your application. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for solenoid valves when sourcing internationally?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for solenoid valves can vary significantly between suppliers and regions. While some manufacturers may offer low MOQs for standard products, custom valves often have higher MOQs due to production costs. It’s essential to clarify MOQs during your initial discussions with suppliers, especially when considering bulk purchases to optimize your supply chain. Some suppliers may also offer flexibility for first-time buyers or ongoing partnerships. -
How can I ensure the quality of solenoid valves sourced from international suppliers?
To ensure the quality of solenoid valves from international suppliers, request certifications such as ISO 9001 or specific industry standards relevant to your application. Consider conducting a thorough supplier audit, including factory visits if feasible. Request samples for testing before placing large orders, and inquire about warranty terms and return policies. Establishing a clear communication channel for quality expectations can also help mitigate risks. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing solenoid valves internationally?
Payment terms for international sourcing can vary widely among suppliers. Common terms include upfront payment, partial payment with the balance upon delivery, or net 30/60 days after invoice. It’s advisable to discuss payment options during negotiations to align with your financial processes. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services to protect your investment and ensure supplier reliability. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing solenoid valves?
When importing solenoid valves, consider shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations in your country. Air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is cost-effective for larger shipments but may take longer. Be aware of import duties and taxes that may apply to your shipment. Working with a reliable logistics provider can streamline the process and help ensure compliance with all regulations. -
How do I verify the reliability of a supplier for solenoid valves?
To verify a supplier’s reliability, start by researching their reputation through online reviews, industry certifications, and references from previous clients. Engage in discussions about their production processes, quality control measures, and customer service responsiveness. Request documentation demonstrating their experience in your industry and inquire about their ability to provide support post-purchase. Establishing a relationship with suppliers who prioritize transparency and communication is crucial for long-term partnerships.
Top 4 Diagram Solenoid Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Tameson – Solenoid Valves
Domain: tameson.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
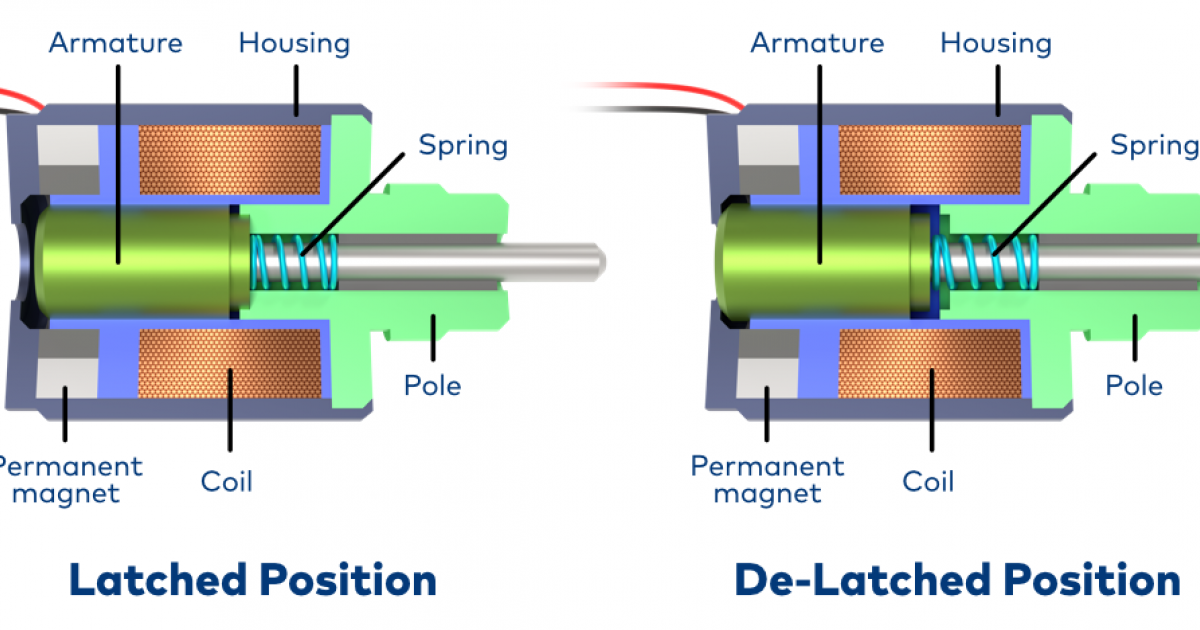
Introduction: Solenoid valves are represented by unique symbols in fluid power diagrams, indicating their functions and connections. Key details include: 2/2-way valves have two connection ports and two switching states (open and closed), while 3/2-way valves have three ports and two switching states. Symbols consist of squares representing valve states, with arrows indicating fluid flow direction. Common types…
2. Pinterest – 4 Pole Starter Solenoid Wiring Diagram
Domain: pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: 4 Pole Starter Solenoid Wiring Diagram
3. Connexion Developments – Solenoid Valve Symbols
Domain: connexion-developments.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Solenoid Valve Symbols: Common symbols for solenoid valves and pneumatic systems include 2/2 Valve (2 Ports, 2 Positions), 3/2 Valve (3 Ports, 2 Positions), 4/2 Valve (4 Ports, 2 Positions), 4/3 Valve (4 Ports, 3 Positions), 5/2 Valve (5 Ports, 2 Positions), and 5/3 Valve (5 Ports, 3 Positions). Media types include Air and Inert Gases, Light Oil, Natural Gas, Slightly Aggressive Media, Steam, Thic…
4. Reddit – Motor and Coil Solutions
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: This company, Reddit – Motor and Coil Solutions, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for diagram solenoid
In today’s competitive landscape, strategic sourcing of diagram solenoids presents a significant opportunity for international B2B buyers to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. Understanding the various solenoid valve configurations, such as 2/2 and 3/2-way valves, alongside their specific applications, is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Engaging with reliable suppliers who can provide detailed specifications and certifications will ensure that your sourcing strategy aligns with industry standards, fostering reliability and performance in your operations.
Moreover, leveraging local and international suppliers can enhance supply chain resilience, especially for businesses operating in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As industries increasingly prioritize automation and efficiency, investing in high-quality solenoid valves becomes not just beneficial, but essential for sustaining competitive advantage.
Looking ahead, consider forming strategic partnerships with trusted manufacturers and suppliers to stay ahead of technological advancements in solenoid applications. By doing so, you will not only secure a reliable supply chain but also position your business for future growth and innovation. Embrace the potential of strategic sourcing today to unlock new efficiencies and capabilities in your operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.