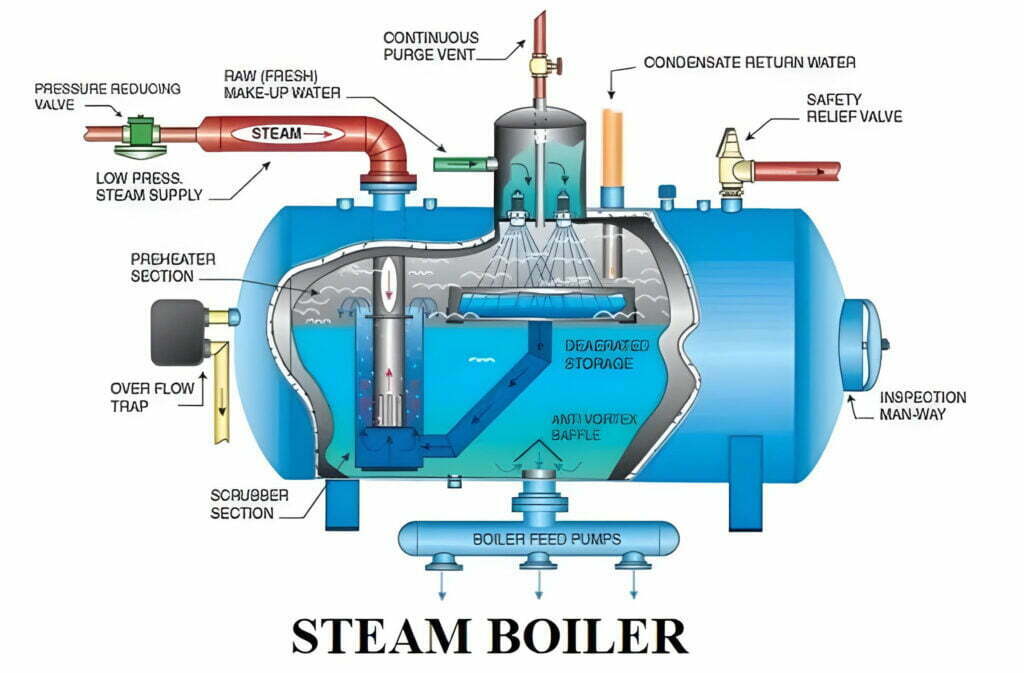
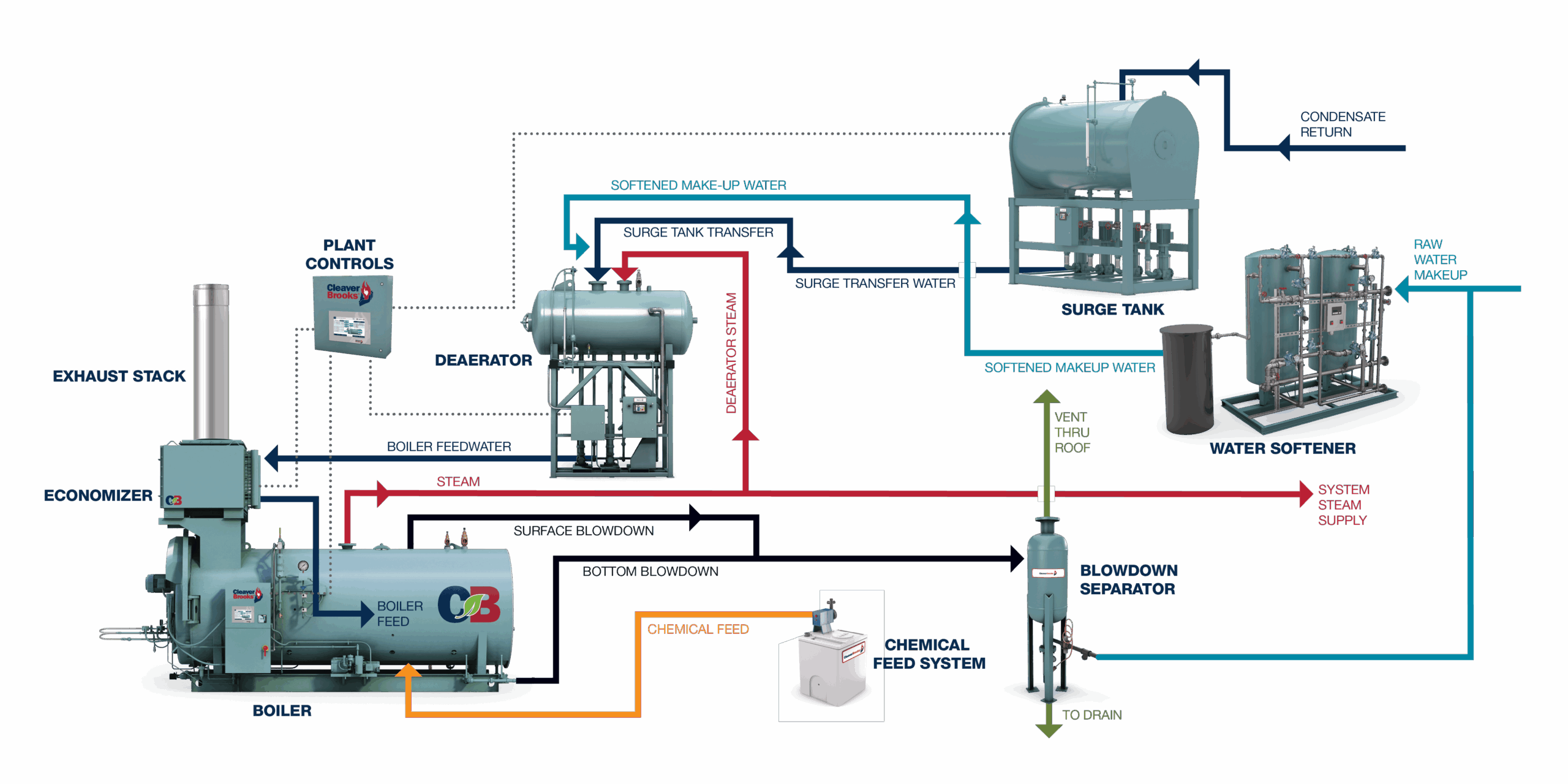
A Deep Dive into Diagram Of A Steam Boiler Solution
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for diagram of a steam boiler
Navigating the complex landscape of the global market for steam boiler diagrams presents a significant challenge for B2B buyers, particularly when sourcing reliable equipment that meets diverse industrial needs. Understanding the intricacies of a steam boiler, from its various types to their operational applications, is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This comprehensive guide covers everything from the fundamental types of steam boilers—such as fire-tube and water-tube boilers—to critical factors like supplier vetting, cost considerations, and maintenance requirements.
For international B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—countries such as Saudi Arabia and Brazil—this guide serves as an essential resource. It empowers you to navigate the market with confidence, ensuring that you select the right steam boiler that not only aligns with your operational demands but also adheres to regional regulations and sustainability goals. By delving into the specifications and functionalities of different boiler types, along with practical tips for supplier engagement, this guide equips you with the knowledge necessary to optimize your procurement strategy.
With a focus on actionable insights, you will be better positioned to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs, ultimately driving your business forward in a competitive global market.
Understanding diagram of a steam boiler Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fire Tube Boiler | Water flows around heated tubes; simpler design | Food processing, textile, and beverage | Pros: Lower initial cost; Cons: Limited efficiency at high pressures |
| Water Tube Boiler | Water circulates through tubes, heated externally | Power generation, chemical processing | Pros: Higher efficiency; Cons: More complex and costly |
| Electric Boiler | Uses electric elements for heating | Hospitals, schools, and residential | Pros: Low emissions; Cons: Higher operational costs |
| Low Pressure Boiler | Operates at lower pressure (10-15 psi) | Heating applications, small industries | Pros: Quick steam generation; Cons: Limited to low-pressure applications |
| High Pressure Boiler | Generates steam at pressures above 15 psi | Large manufacturing, power plants | Pros: High efficiency and output; Cons: Requires rigorous safety measures |
What are the Key Characteristics of Fire Tube Boilers?
Fire tube boilers are characterized by their design, where water flows around heated tubes. This straightforward structure makes them a popular choice for industries like food processing and textiles. B2B buyers should consider their lower initial costs and simpler maintenance requirements. However, they may not be suitable for high-pressure applications, limiting their efficiency in some industrial settings.
How Do Water Tube Boilers Stand Out?
Water tube boilers differ by circulating water through tubes that are heated externally, allowing for higher efficiency and steam output. This design is ideal for power generation and chemical processing, where high pressure and steam quality are crucial. Buyers should weigh the benefits of efficiency and output against the complexity and higher costs associated with installation and maintenance.
What are the Benefits of Electric Boilers?
Electric boilers offer a cleaner alternative as they use electric components for heating, making them ideal for environments with strict emissions regulations, such as hospitals and schools. They require minimal maintenance and are easier to install. However, buyers should be aware of the higher operational costs associated with electricity and the potential for scale buildup in the tank.
Why Choose Low Pressure Boilers?
Low pressure boilers operate at pressures between 10 and 15 psi, making them suitable for heating applications in smaller industries. Their ability to generate steam quickly is a significant advantage for operations requiring consistent temperature control. However, their limitations in pressure output may restrict their application in more demanding environments.
What Makes High Pressure Boilers Essential for Large Industries?
High pressure boilers are designed to produce steam at pressures exceeding 15 psi, making them essential for large manufacturing facilities and power plants. Their ability to deliver high efficiency and significant steam output can enhance productivity. However, B2B buyers must consider the stringent safety measures and maintenance protocols necessary to operate these systems effectively.
Key Industrial Applications of diagram of a steam boiler
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of diagram of a steam boiler | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Steam generation for food processing and sterilization | Ensures product safety and quality through effective sterilization | Compliance with health standards, energy efficiency, and capacity |
| Pharmaceuticals | Steam supply for sterilizing equipment and manufacturing | Guarantees sterile environments essential for drug production | Precision in temperature control, reliability, and maintenance needs |
| Textile Manufacturing | Steam for dyeing and finishing processes | Enhances product quality and operational efficiency | Material compatibility, energy source type, and pressure ratings |
| Power Generation | Steam for driving turbines in power plants | Increases energy output and efficiency in electricity generation | Boiler type (firetube vs. watertube), fuel type, and emissions standards |
| Chemical Processing | Steam for heating and reaction processes | Facilitates chemical reactions and improves production rates | Safety standards, chemical compatibility, and operational reliability |
How is the diagram of a steam boiler applied in the food and beverage industry?
In the food and beverage sector, steam boilers are crucial for processes such as cooking, pasteurization, and sterilization. The diagram of a steam boiler illustrates how steam is generated and distributed to ensure that food products are safely processed. This application helps mitigate the risk of contamination and enhances product quality. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing boilers that meet local health regulations and energy efficiency standards is vital for compliance and cost-effectiveness.
What role does the diagram of a steam boiler play in pharmaceuticals?
Pharmaceutical manufacturing relies heavily on steam boilers for sterilizing equipment and maintaining sterile environments. The diagram provides insights into the boiler’s operational mechanisms, ensuring that the steam produced meets stringent quality standards. This is critical as any contamination can lead to significant financial losses and regulatory issues. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should prioritize suppliers who can demonstrate reliability, precision in temperature control, and adherence to pharmaceutical regulations.
How is steam utilized in textile manufacturing?
In textile manufacturing, steam is essential for dyeing, finishing, and other processes that require precise temperature control. The diagram of a steam boiler showcases the system’s ability to deliver consistent steam pressure and temperature, which is vital for achieving high-quality fabric finishes. For B2B buyers, especially in developing regions, it is important to consider the boiler’s efficiency and the compatibility of materials used to ensure long-term operational success and reduced downtime.
How does steam generation impact power generation facilities?
In power generation, steam boilers are fundamental for driving turbines that convert thermal energy into electricity. The diagram illustrates the flow of steam and the interaction with turbine systems. This application is crucial for maximizing energy output and overall efficiency. International buyers, particularly in Europe, should consider the type of boiler, emissions standards, and the potential for integrating renewable energy sources to enhance sustainability in operations.
What is the significance of steam in chemical processing?
In chemical processing, steam is utilized for heating and facilitating various chemical reactions. The diagram of a steam boiler aids in understanding how steam is generated and controlled for these applications. This is particularly important for maintaining reaction conditions and improving production rates. Buyers from regions like South America should focus on sourcing boilers that comply with safety standards and can handle the specific chemical processes involved, ensuring operational reliability and safety.
Illustrative image related to diagram of a steam boiler
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘diagram of a steam boiler’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Understanding Boiler Diagrams for Optimal Operation
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, especially those new to steam boiler systems, often struggle to interpret complex diagrams. This can lead to miscommunication among team members and hinder effective operation or maintenance of the boiler. For instance, an engineer may misread the flow of steam in the diagram, resulting in improper setup or failure to identify critical components such as safety valves or pressure gauges. Such misunderstandings can jeopardize safety, efficiency, and operational reliability, potentially leading to costly downtime.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should invest in comprehensive training sessions that focus on reading and understanding steam boiler diagrams. This training can include hands-on workshops where engineers and operators can practice interpreting various types of diagrams in real-world scenarios. Additionally, sourcing high-quality, user-friendly manuals and digital resources that break down each component of the diagram can provide valuable reference materials. Buyers should also consider collaborating with suppliers who offer detailed diagrams and support services, ensuring that their teams have the knowledge to correctly interpret and implement the diagrams effectively.
Scenario 2: Incompatibility Between Boiler Design and Operational Needs
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of selecting a steam boiler whose design does not align with their operational needs, primarily due to vague or generic diagrams. For example, a manufacturing plant in Brazil may require a high-capacity boiler for its production line but purchases a model based on a diagram that emphasizes compact size rather than output capacity. This mismatch can result in inadequate steam supply, leading to decreased productivity and increased operational costs.
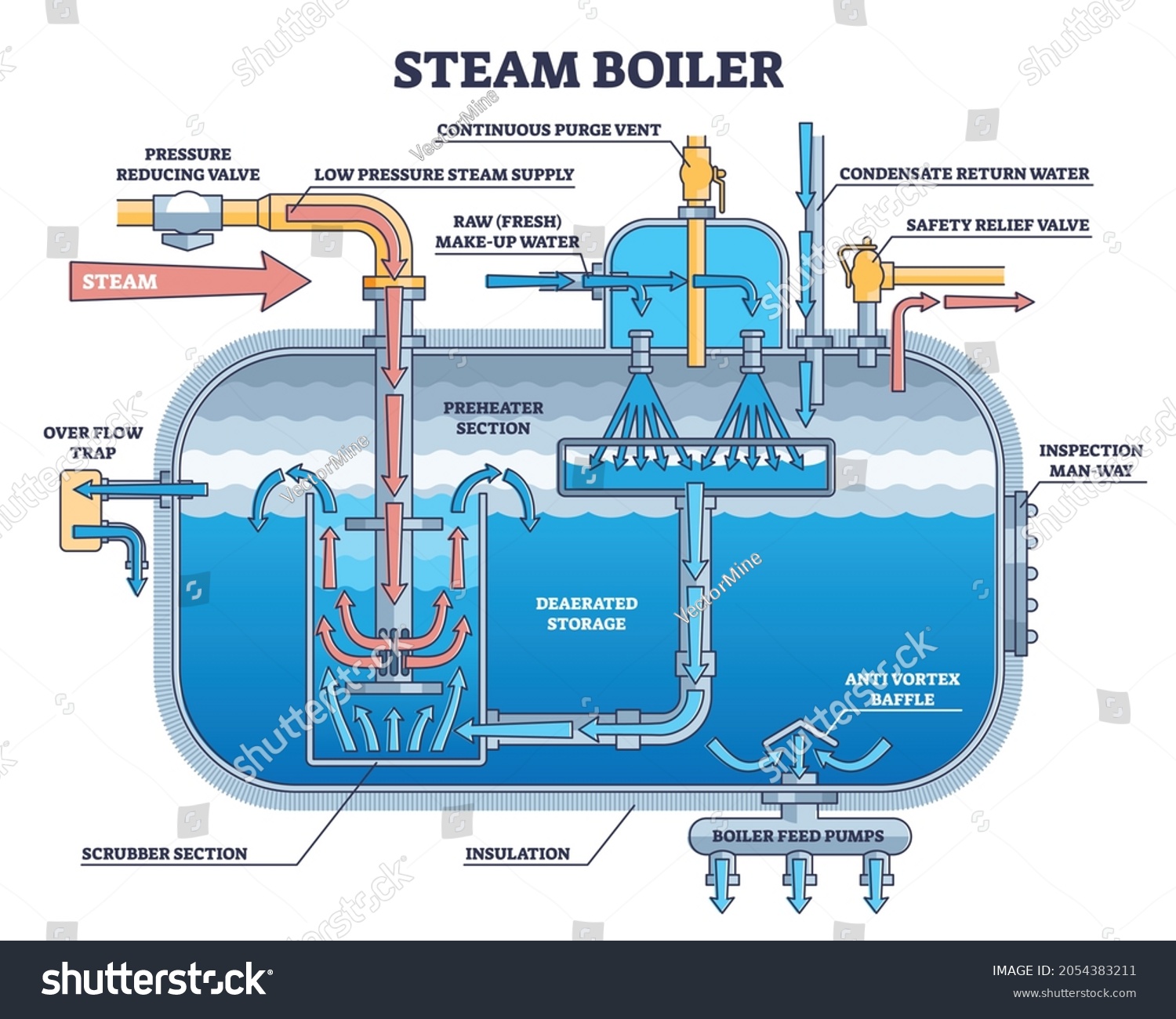
Illustrative image related to diagram of a steam boiler
The Solution: To avoid this scenario, it is crucial for buyers to conduct a thorough needs assessment before sourcing a steam boiler. This involves specifying the required steam output, pressure, and temperature based on their specific applications. When reviewing diagrams, buyers should focus on those that clearly indicate capacity ratings and performance specifications. Collaborating with reputable manufacturers who provide tailored diagrams that reflect the boiler’s operational capabilities can also ensure a better fit. Additionally, engaging with industry experts to validate the chosen specifications against operational requirements can help prevent costly errors.
Scenario 3: Maintenance Challenges Due to Poorly Designed Diagrams
The Problem: Maintenance teams often encounter difficulties when the steam boiler diagrams provided are outdated or lack sufficient detail. This can lead to incorrect servicing practices, resulting in increased wear and tear or even hazardous situations. For instance, if the diagram does not clearly indicate the location of critical maintenance points, technicians may overlook necessary inspections, leading to unexpected failures or safety incidents.
The Solution: To mitigate these issues, B2B buyers should prioritize acquiring the most recent and detailed diagrams from their boiler suppliers. It’s beneficial to request diagrams that are specific to the model in use, highlighting maintenance points, troubleshooting tips, and common failure modes. Regular updates and revisions should be part of the service agreement with suppliers, ensuring that the diagrams remain relevant. Additionally, implementing a preventive maintenance program that incorporates these diagrams can help in systematic inspections and repairs, further enhancing the reliability and safety of the boiler operation.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for diagram of a steam boiler
When selecting materials for a steam boiler, it’s essential to consider the specific properties and performance requirements of each material. The following analysis focuses on four common materials used in the construction of steam boilers: carbon steel, stainless steel, cast iron, and copper. Each material offers distinct advantages and disadvantages that can significantly impact the performance and longevity of the boiler system.
What are the Key Properties of Carbon Steel in Steam Boilers?
Carbon steel is widely used in steam boilers due to its excellent mechanical properties and cost-effectiveness. It typically has high strength and can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various applications. Carbon steel is also relatively easy to fabricate and weld, which simplifies manufacturing processes.
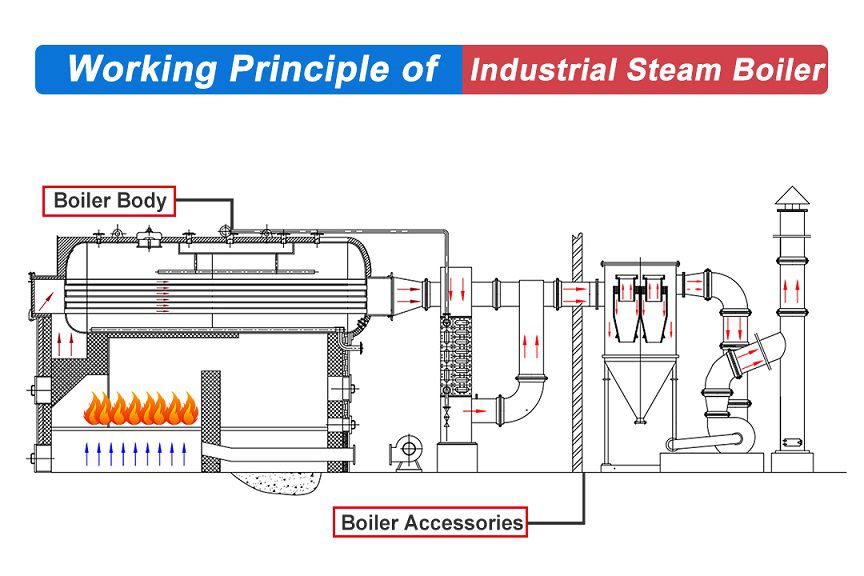
Illustrative image related to diagram of a steam boiler
Pros: Carbon steel is durable and has good tensile strength, making it ideal for high-pressure applications. Its low cost compared to other materials makes it a popular choice for many industrial applications.
Cons: One of the main drawbacks of carbon steel is its susceptibility to corrosion, especially in high-moisture environments. Proper protective coatings or treatment methods are essential to enhance its corrosion resistance.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is compatible with steam and water but may require additional treatments to prevent rust and corrosion.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards (e.g., ASTM A106 for seamless carbon steel pipes) to meet safety and performance requirements.
How Does Stainless Steel Compare for Steam Boiler Applications?
Stainless steel is another popular choice for steam boiler construction, known for its excellent corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength. It is particularly advantageous in environments where corrosion is a significant concern.
Pros: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its resistance to oxidation and corrosion, making it suitable for high-humidity and high-temperature applications. It also has a longer lifespan compared to carbon steel.
Cons: Stainless steel tends to be more expensive than carbon steel and can be more challenging to fabricate due to its hardness.
Impact on Application: This material is highly compatible with various media, including steam and water, and is ideal for applications requiring high cleanliness and hygiene standards.
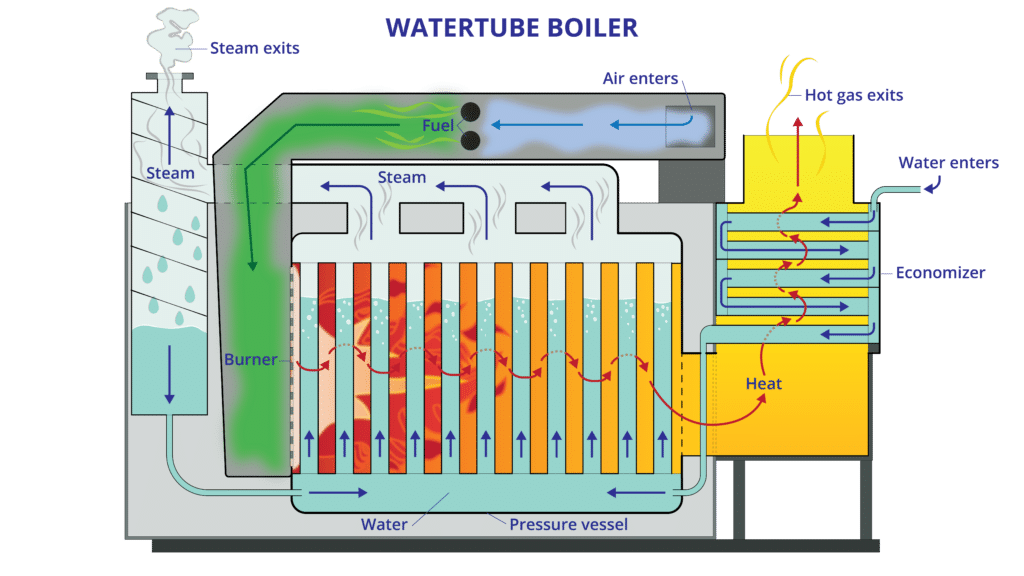
Illustrative image related to diagram of a steam boiler
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should look for compliance with standards such as ASTM A312 for seamless stainless steel pipes, ensuring that the material meets local regulatory requirements.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Cast Iron in Steam Boilers?
Cast iron is traditionally used in steam boilers due to its excellent thermal conductivity and ability to withstand high pressures. It is particularly effective in applications where heat retention is a priority.
Pros: Cast iron has excellent durability and can handle high temperatures, making it ideal for steam generation. It also has good resistance to thermal shock.
Cons: The main limitation of cast iron is its brittleness, which can lead to cracking under certain conditions. Additionally, it is heavier than other materials, which may complicate installation.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is compatible with steam and water but may require careful handling to prevent damage during installation.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A48, which governs the specifications for gray iron castings.
Why is Copper a Viable Material for Steam Boilers?
Copper is less commonly used for large steam boilers but is still relevant in specific applications, particularly in smaller, residential systems. Its excellent thermal conductivity makes it an efficient choice.
Pros: Copper offers superior heat transfer capabilities and is resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for various applications.
Cons: The primary disadvantage is its high cost compared to other materials and its relatively low strength under high-pressure conditions.
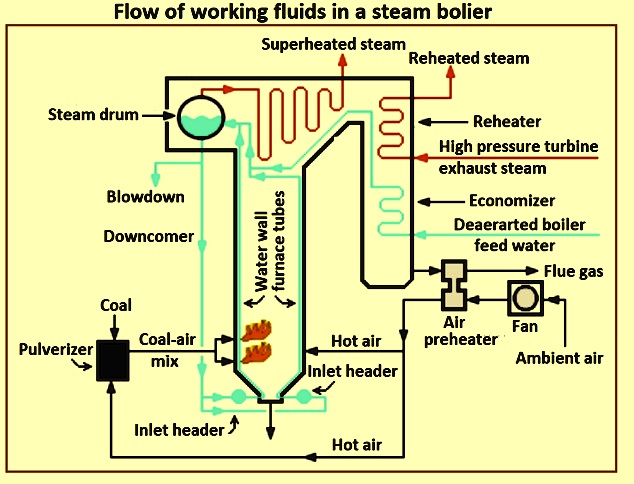
Illustrative image related to diagram of a steam boiler
Impact on Application: Copper is compatible with steam and hot water but is typically used in lower-pressure applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with standards such as ASTM B88 for copper tubing, particularly in regions where copper is preferred for its thermal efficiency.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Steam Boilers
| Material | Typical Use Case for diagram of a steam boiler | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | High-pressure steam applications | Cost-effective and durable | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | High-humidity and high-temperature applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and difficult to fabricate | High |
| Cast Iron | Heat retention in steam generation | Good thermal conductivity and durability | Brittle and heavy | Medium |
| Copper | Smaller residential systems | Superior heat transfer capabilities | High cost and lower strength under pressure | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides critical insights for international B2B buyers, allowing them to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for diagram of a steam boiler
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of a Steam Boiler?
The manufacturing of steam boilers is a complex process that involves several critical stages, each contributing to the quality and reliability of the final product. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers evaluate suppliers effectively.
Material Preparation: What Types of Materials Are Used?
The manufacturing process begins with the careful selection and preparation of materials. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steels, which are chosen for their strength and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. The material is often subjected to rigorous inspections and tests to ensure it meets industry standards before it enters the manufacturing stage.
How Is the Forming Process Conducted?
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into the desired components of the steam boiler. Techniques such as forging, rolling, and bending are commonly employed. Advanced technologies like CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining may also be used for precision. This stage is crucial as it determines the structural integrity of the boiler, ensuring that all components can handle the operational stresses they will face.
What Does the Assembly Process Entail?
After forming, the next step is assembly, where various components are brought together to create the complete steam boiler. This stage often includes welding, bolting, and fitting parts such as the combustion chamber, heat exchangers, and control systems. Skilled technicians typically oversee this process to ensure that all components are aligned correctly and securely attached, which is vital for both safety and efficiency.
What Are the Finishing Techniques Used?
The finishing stage involves several processes designed to enhance the boiler’s durability and efficiency. This may include surface treatments like painting or coating to prevent corrosion, as well as insulation to improve energy efficiency. Quality checks are often integrated into this stage to verify that the finishing meets specified standards.
What International Standards Apply to Steam Boiler Manufacturing?
Quality assurance in steam boiler manufacturing is governed by various international and industry-specific standards. Understanding these standards is essential for B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Which International Quality Standards Should Buyers Consider?
ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized international standards for quality management systems. It emphasizes the need for consistent quality in products and services, which is particularly important in the manufacturing of steam boilers. Compliance with ISO 9001 assures buyers that the manufacturer follows a structured approach to quality management.
What Are Industry-Specific Certifications Like CE and API?
In addition to ISO 9001, steam boiler manufacturers may also need to meet specific industry standards such as CE marking in Europe, which indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. The American Petroleum Institute (API) standards are crucial for manufacturers catering to the oil and gas sectors. These certifications demonstrate that the product has undergone rigorous testing and meets the necessary safety and performance criteria.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is an integral part of the steam boiler manufacturing process. Various checkpoints help ensure that the product meets all specified standards.
How Do Incoming Quality Control (IQC) and In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) Work?
Incoming Quality Control (IQC) involves inspecting raw materials before they enter the manufacturing process. This ensures that only materials that meet quality standards are used. In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) takes place throughout the manufacturing stages, where periodic checks are performed to identify any defects or deviations from specifications early in the process.
What Is Final Quality Control (FQC) and Its Importance?
Final Quality Control (FQC) is the last checkpoint before the steam boiler is shipped to the customer. During this stage, the entire unit undergoes thorough testing, including pressure tests, leak tests, and performance evaluations. FQC ensures that the boiler operates safely and efficiently, providing peace of mind to buyers.
Which Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Steam Boilers?
Testing methods play a vital role in ensuring that steam boilers meet operational and safety standards. Understanding these methods can help buyers assess the credibility of their suppliers.
What Are the Standard Testing Procedures?
Common testing procedures for steam boilers include hydrostatic testing, where the boiler is filled with water and pressurized to check for leaks. Additionally, non-destructive testing (NDT) methods such as ultrasonic and radiographic testing are used to identify any internal flaws without damaging the material. These tests are critical for ensuring the structural integrity of the boiler.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, verifying the quality control processes of potential suppliers is crucial. Here are some actionable insights.
What Steps Can Buyers Take to Conduct Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to ensure that manufacturers adhere to quality standards. Buyers should develop a checklist based on relevant certifications and quality control practices. Regular audits can help identify any potential issues before they affect product quality.
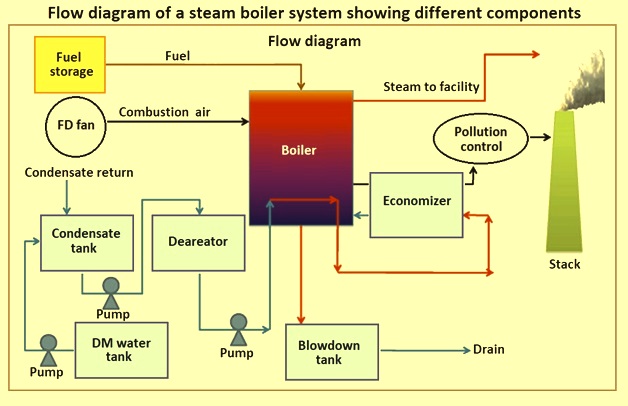
Illustrative image related to diagram of a steam boiler
Why Are Quality Reports and Third-Party Inspections Important?
Requesting quality reports from suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Additionally, third-party inspections can add an extra layer of verification, ensuring that the products meet the required standards. Buyers should look for suppliers who are willing to provide documentation and allow external audits.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
Navigating quality control can be more complex for international buyers due to varying standards and regulations across different regions.
How Do Regional Standards Affect Quality Assurance?
In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, different countries may have their own regulations regarding steam boiler manufacturing. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local standards to ensure compliance. For example, while CE marking is essential for European markets, other regions may have different certification requirements.
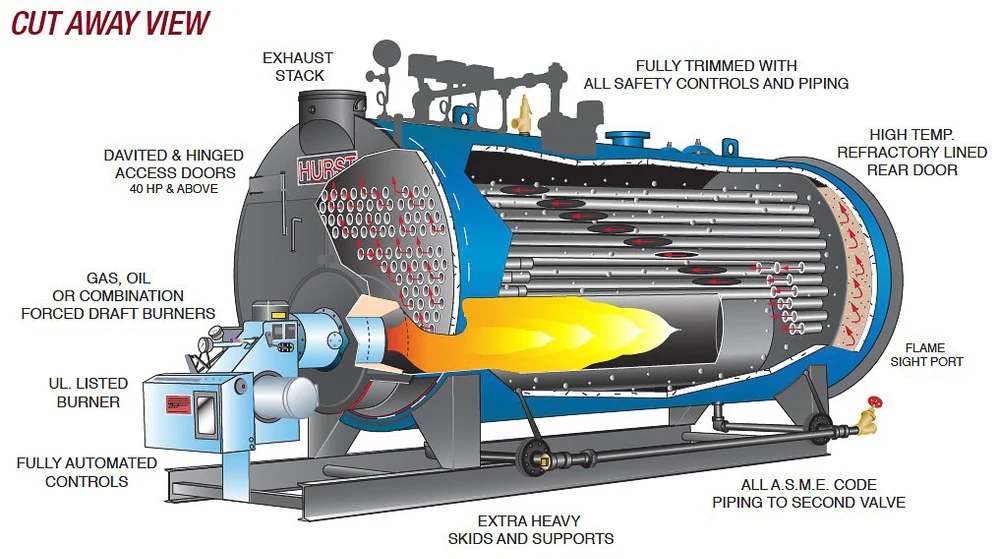
Illustrative image related to diagram of a steam boiler
What Should Buyers Keep in Mind Regarding Cultural and Operational Differences?
Cultural differences can impact communication and expectations in quality control. B2B buyers should ensure that they clearly communicate their quality expectations and understand the operational capabilities of their suppliers. Building strong relationships can also facilitate better quality assurance throughout the procurement process.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and select suppliers who meet their quality expectations for steam boilers.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘diagram of a steam boiler’
To assist B2B buyers in effectively procuring a steam boiler, this practical sourcing guide outlines essential steps to follow. Each step is designed to ensure a comprehensive understanding of requirements and to facilitate informed decision-making.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outlining your technical specifications is crucial to ensure the steam boiler meets your operational needs. Consider factors such as the required steam pressure, capacity, and the type of fuel that will be used. Additionally, assess whether you need a low-pressure or high-pressure boiler based on your industry requirements.
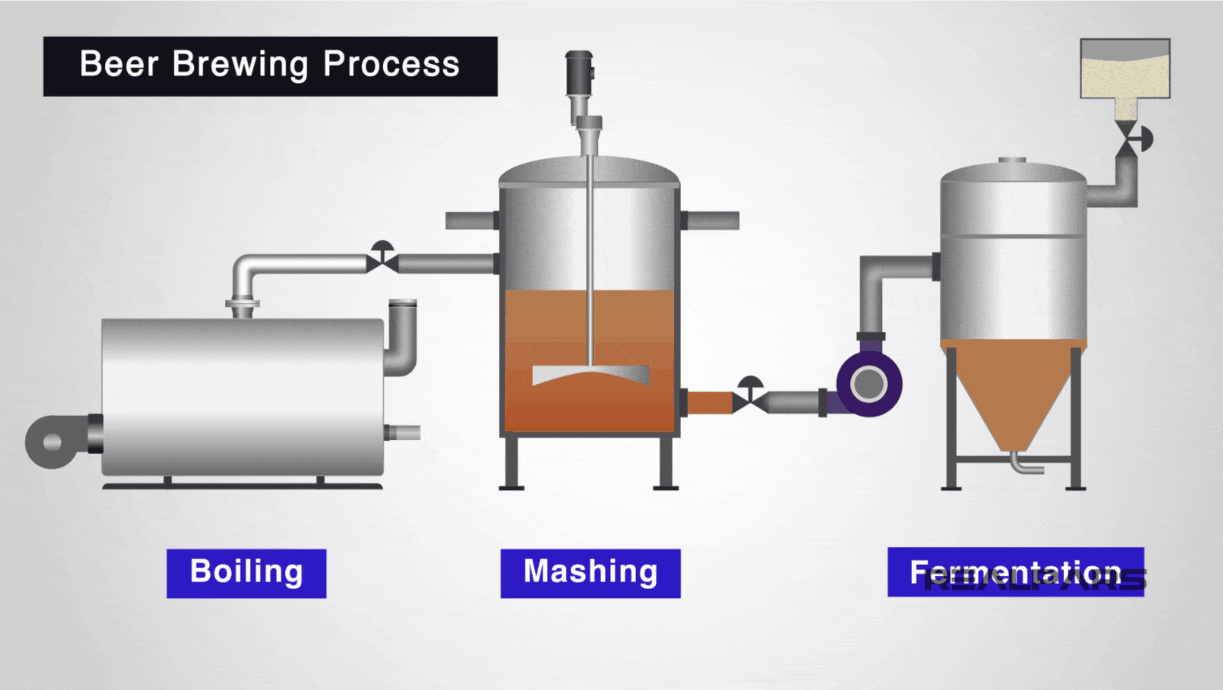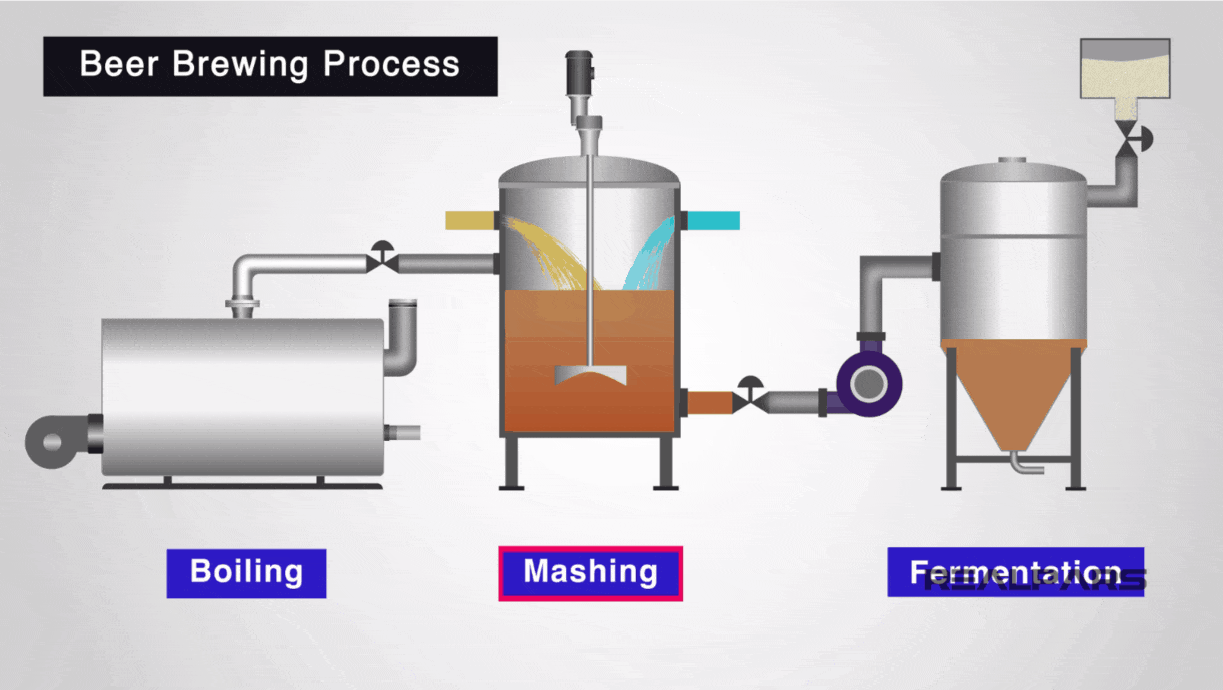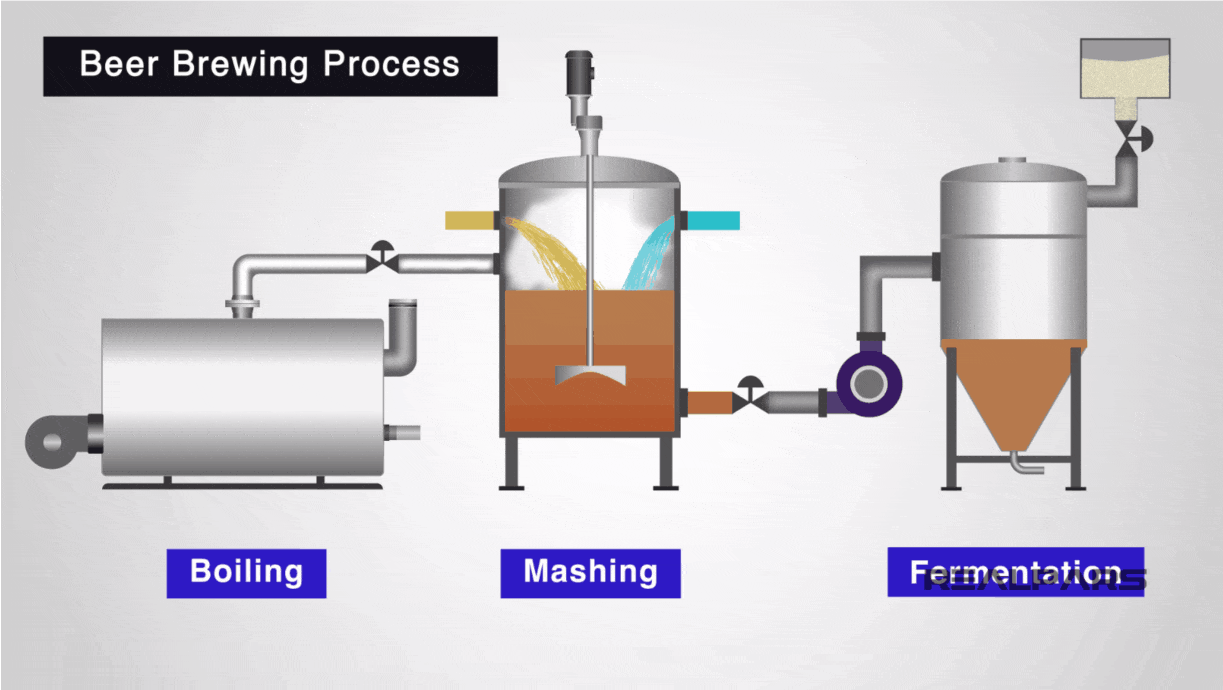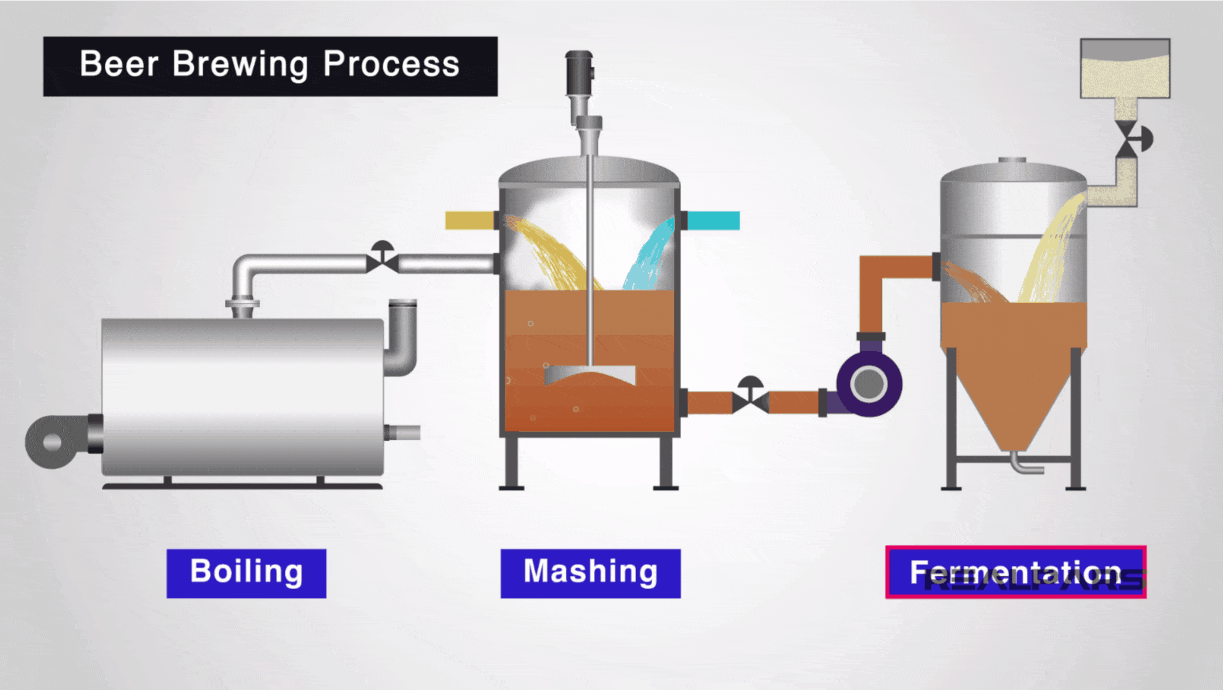
Illustrative image related to diagram of a steam boiler
Step 2: Conduct Market Research
Thorough market research enables you to identify potential suppliers and understand the current trends in steam boiler technology. Look for suppliers that specialize in your industry and have a solid reputation. Pay attention to the types of boilers they offer, their efficiency ratings, and any innovative features that may benefit your operations.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, it’s essential to evaluate potential suppliers rigorously. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from clients in similar industries or regions. Additionally, verify their track record regarding delivery times, after-sales support, and warranty terms, as these factors significantly impact your long-term satisfaction.
Step 4: Check Compliance and Certifications
Ensure that the suppliers you consider comply with international standards and local regulations regarding steam boiler manufacturing and safety. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, ASME, or CE marking, which indicate adherence to quality and safety protocols. This step is crucial to mitigate risks associated with equipment failure and legal compliance.
Step 5: Assess Maintenance and Support Services
Inquire about the maintenance and support services offered by suppliers. A reliable supplier should provide comprehensive after-sales service, including installation, training, and ongoing maintenance. Consider whether they offer remote monitoring and diagnostics, which can enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime.
Step 6: Request Detailed Quotations
Once you have narrowed down your options, request detailed quotations from your shortlisted suppliers. Ensure that these quotes include all relevant costs, such as installation, shipping, and any additional components required for operation. Compare these quotes not only on price but also on the value offered, including warranties and support.
Step 7: Finalize Your Decision
After thorough evaluation, make your final decision based on a combination of price, supplier reliability, and technical compatibility. Engage in discussions with the chosen supplier to clarify any remaining questions and negotiate terms where possible. Once a mutual agreement is reached, ensure that all terms are documented in a contract to protect both parties.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the procurement process for steam boilers, ensuring they choose the best equipment for their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for diagram of a steam boiler Sourcing
Analyzing the cost structure and pricing for sourcing a steam boiler diagram involves understanding various components that contribute to the overall expense. This analysis is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where market dynamics can differ significantly.
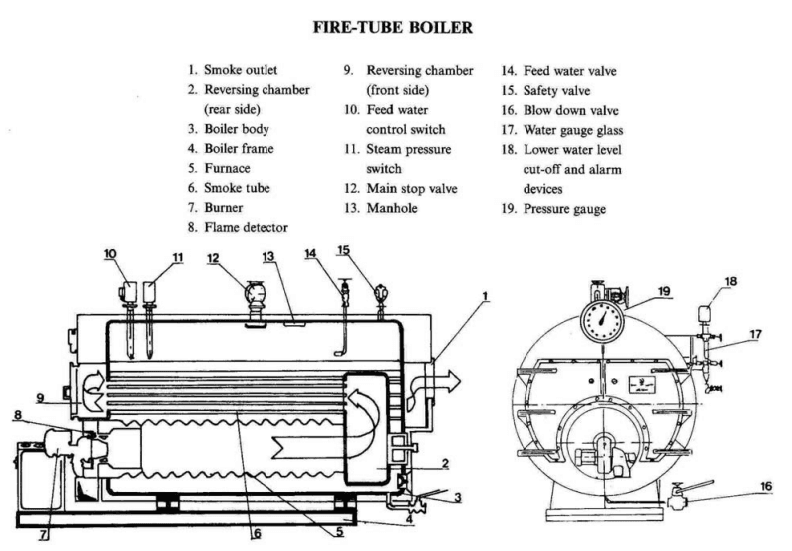
Illustrative image related to diagram of a steam boiler
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing a Steam Boiler Diagram?
-
Materials: The primary cost component in the production of steam boiler diagrams is the materials used. High-quality steel, insulation, and other components like valves and gauges are essential. The choice of materials affects durability, efficiency, and compliance with international standards.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is necessary for both the design and manufacturing processes. Labor costs can vary significantly based on geographic location and the complexity of the design. In regions with high labor costs, such as Western Europe, this component can significantly impact the total price.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient production facilities can lower overhead costs, making the final product more competitive.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling and machinery is a crucial cost factor. Custom tooling for specific designs can lead to higher upfront costs but may be justified by improved efficiency and reduced long-term production costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that steam boilers meet safety and efficiency standards is vital. Rigorous QC processes add to the cost but are necessary to prevent future liabilities and maintain a good market reputation.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely, especially for international shipments. Factors such as distance, transportation mode, and customs clearance can significantly influence overall logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and generate profit. This margin can vary based on supplier reputation, market demand, and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Steam Boiler Diagrams?
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should consider negotiating MOQ terms to benefit from reduced pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific performance requirements can increase costs. It’s essential for buyers to define their needs clearly to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and recognized certifications (e.g., ISO, ASME) can elevate costs but are crucial for ensuring safety and reliability, especially in regions with stringent regulations.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their experience and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital for international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, influencing the final cost.
What Are the Best Practices for Buyers in Negotiating Prices?
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of focusing solely on the initial purchase price, consider the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational efficiency, and lifespan. A slightly higher upfront cost for a more efficient boiler can result in significant savings over time.
-
Negotiate Terms: Don’t hesitate to negotiate pricing, especially for larger orders. Discussing payment terms, delivery schedules, and warranties can lead to more favorable arrangements.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: Sourcing from local suppliers can reduce logistics costs and lead times. Additionally, local suppliers may have a better understanding of regional regulations and standards.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Understanding market conditions and trends in the steam boiler industry can provide leverage in negotiations. Awareness of raw material price fluctuations can also help buyers time their purchases effectively.
Conclusion
When sourcing steam boiler diagrams, understanding the intricate cost structure and price influencers is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. By considering material quality, labor, manufacturing overhead, and logistics, B2B buyers can optimize their procurement strategies. Engaging in thorough negotiation and being aware of the total cost of ownership can lead to significant long-term savings. Buyers should always approach sourcing with a clear understanding of their needs and market dynamics, particularly when operating across diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing diagram of a steam boiler With Other Solutions
Understanding the Importance of Alternative Solutions in Steam Generation
In the quest for efficient steam generation, businesses often explore various technologies beyond traditional steam boilers. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of these alternatives is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to optimize operational efficiency, reduce costs, and meet sustainability goals. This analysis compares steam boilers with electric boilers and hot water boilers, providing insights into each solution’s performance, cost, implementation ease, maintenance requirements, and best use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | Diagram Of A Steam Boiler | Electric Boiler | Hot Water Boiler |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High pressure steam generation, suitable for large-scale applications | Quick heating, ideal for smaller applications | Efficient for heating spaces but not for high pressure |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment, ongoing fuel costs | Higher upfront cost, lower operational costs | Moderate investment, fuel costs depend on type |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires significant infrastructure and safety measures | Easier installation with minimal infrastructure | Moderate; requires plumbing and heating system integration |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed for safety and efficiency | Low maintenance; fewer moving parts | Moderate; regular checks required for plumbing |
| Best Use Case | Industrial applications needing large steam outputs | Commercial and residential heating, quick steam needs | Space heating, lower temperature applications |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Electric Boilers?
Electric boilers utilize electric components to generate heat, making them a cleaner alternative to traditional steam boilers. They excel in environments where reducing carbon footprints is a priority. Their low maintenance needs and ease of installation are significant advantages, as they do not require fuel storage or combustion processes. However, the initial investment can be higher than that of steam boilers, and they may not be suitable for high-demand industrial applications due to lower steam output capacities.
How Do Hot Water Boilers Compare to Steam Boilers?
Hot water boilers are designed primarily for space heating and lower temperature applications. They are generally less complex and can be more cost-effective than steam boilers, making them a viable option for residential and commercial settings. However, they are not designed for high-pressure steam applications and may not meet the needs of industries requiring significant steam production. While installation and maintenance are manageable, their efficiency diminishes in scenarios demanding rapid steam generation.
Making the Right Choice: How to Select the Best Solution for Your Needs
Choosing the right solution for steam generation depends on various factors, including the scale of operations, specific heating requirements, budget constraints, and sustainability goals. B2B buyers should assess their operational needs and long-term objectives when comparing steam boilers with alternatives like electric and hot water boilers. A thorough analysis of performance metrics and cost implications, alongside an understanding of the unique advantages each solution offers, will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational strategies. Ultimately, the right choice will facilitate improved efficiency, cost savings, and environmental compliance in the long run.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for diagram of a steam boiler
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Steam Boiler?
Understanding the essential technical specifications of steam boilers is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when making decisions about equipment procurement. Here are some of the most important technical properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
The materials used in steam boilers, such as carbon steel, stainless steel, or alloy steel, determine their durability, corrosion resistance, and overall lifespan. Higher-grade materials can withstand higher temperatures and pressures, which is critical for operational safety and efficiency. Choosing the right material grade can minimize maintenance costs and extend the boiler’s operational life, making it a significant consideration for buyers looking for long-term investments. -
Pressure Rating
This specification indicates the maximum pressure the boiler can safely handle. Common ratings include low-pressure (up to 15 psi) and high-pressure (over 15 psi). Understanding pressure ratings is essential for ensuring that the selected boiler meets the specific requirements of the application, whether it’s for industrial processes or heating systems. Overlooking this can lead to operational failures or safety hazards. -
Efficiency Rating
The efficiency of a steam boiler is typically expressed as a percentage, indicating how effectively it converts fuel into steam. Higher efficiency ratings mean lower fuel consumption and reduced operational costs, which are critical for businesses focused on sustainability and profitability. Buyers should assess efficiency ratings to calculate potential savings over the boiler’s lifespan. -
Heat Transfer Surface Area
The size and design of the heat transfer surface area directly affect the boiler’s performance. A larger surface area allows for more effective heat transfer, leading to faster steam production. Buyers need to consider this property to ensure that the boiler can meet the specific steam output requirements of their operations. -
Safety Features
Safety is paramount in boiler operations. Essential safety features include pressure relief valves, water level indicators, and automatic shut-off systems. These elements help prevent accidents and ensure compliance with industry regulations. Buyers should prioritize these features to protect their investments and maintain a safe working environment.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Steam Boiler Industry?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology is vital for effective communication and negotiation in the steam boiler market. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce equipment that may be marketed by another company. Understanding OEM specifications is crucial when sourcing replacement parts or complete boiler systems to ensure compatibility and reliability. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For buyers, knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, particularly when considering bulk purchases for large projects. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document issued by buyers to solicit price quotes from suppliers. This process helps buyers compare costs and terms from different vendors, facilitating informed purchasing decisions. It’s important for buyers to clearly outline their specifications in an RFQ to receive accurate quotes. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping and insurance costs. Familiarity with Incoterms is critical for B2B buyers involved in cross-border purchases to understand their obligations and minimize risks. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is essential for project planning and ensuring timely delivery, particularly in industries where downtime can be costly. -
Warranties and Service Agreements
These terms refer to the guarantees provided by manufacturers regarding the performance and maintenance of the steam boiler. Buyers should thoroughly review warranty terms to understand coverage and service expectations, which can impact long-term operational costs.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when selecting steam boilers that align with their operational needs and strategic goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the diagram of a steam boiler Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Steam Boiler Sector?
The global steam boiler market is witnessing significant growth, driven by increasing industrialization and the demand for efficient heating solutions. Key drivers include the expansion of sectors such as manufacturing, energy, and food processing, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. For international B2B buyers, understanding the dynamics of this market is crucial.
Emerging technologies such as IoT-enabled steam boilers are reshaping sourcing trends. These advanced systems offer predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring, which significantly enhance operational efficiency. Furthermore, the shift toward automation in industries is compelling manufacturers to adopt smarter steam solutions, allowing for better integration into existing production processes. As such, buyers should prioritize suppliers who can offer innovative, technologically advanced products tailored to their specific operational needs.
In addition, the market is increasingly influenced by regulatory frameworks aimed at reducing carbon emissions. Buyers are urged to consider suppliers who comply with international standards and can provide equipment that meets stringent environmental regulations. This not only ensures compliance but also positions organizations favorably in a competitive market.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Steam Boiler Sector?
Sustainability has become a pivotal concern in the steam boiler sector, with both suppliers and buyers focusing on reducing environmental impact. The production and operation of steam boilers can significantly contribute to greenhouse gas emissions if not managed properly. Therefore, it is essential for B2B buyers to seek out manufacturers that prioritize sustainable practices, such as using eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient technologies.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as it reflects a company’s commitment to social responsibility. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers adhere to ethical labor practices and transparent supply chains. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 9001 (Quality Management) are indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices. Furthermore, the use of alternative fuels, such as biomass or waste-to-energy technologies, can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of steam boiler operations, making them more appealing to environmentally conscious buyers.
As the demand for sustainable products grows, buyers are encouraged to collaborate with suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through innovation and ethical sourcing strategies. This not only aligns with global trends but also enhances brand reputation and marketability.
What Is the Historical Context of Steam Boilers in B2B Markets?
The steam boiler has a rich history dating back to the early industrial revolution when it played a crucial role in powering factories and driving machinery. Initially, steam boilers were rudimentary and often dangerous, leading to numerous accidents. However, advancements in technology, including the introduction of safety valves and improved materials, transformed the steam boiler into a reliable and efficient energy source.
As industries evolved, so did the design and functionality of steam boilers. The introduction of water tube and fire tube boilers allowed for greater efficiency and capacity, catering to the needs of expanding industries. Today, steam boilers are integral to various sectors, including power generation, chemical processing, and food manufacturing, with ongoing innovations enhancing their performance and safety. For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is key to recognizing the importance of selecting modern, efficient systems that meet current operational demands while also adhering to regulatory standards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of diagram of a steam boiler
-
How do I choose the right steam boiler for my industry needs?
Selecting the right steam boiler involves evaluating several factors, including the type of fuel available, the required steam pressure, and the specific applications of the steam. First, assess the energy requirements of your operations and the compatibility of different fuel types with local regulations. Additionally, consider the boiler’s efficiency, maintenance requirements, and the expected lifespan. Consulting with manufacturers or industry experts can provide tailored insights to ensure your choice meets both operational and compliance standards. -
What are the key components of a steam boiler diagram?
A steam boiler diagram typically includes essential components such as the combustion chamber, heat exchanger, water supply system, steam outlet, and safety valves. Understanding these components is crucial for troubleshooting and maintenance. The combustion chamber is where fuel is burned to generate heat, while the heat exchanger transfers this heat to water. Safety valves prevent pressure build-up, ensuring operational safety. Familiarizing yourself with these parts can help in efficient boiler management and adherence to safety protocols. -
What are the common types of steam boilers available in the market?
The market offers various steam boiler types, including fire-tube, water-tube, electric, and biomass boilers. Fire-tube boilers are popular for low-pressure applications, while water-tube boilers are preferred for high-pressure needs due to their efficiency. Electric boilers provide a cleaner alternative, and biomass boilers are increasingly favored for their sustainability. Assessing your specific requirements, including steam capacity and fuel availability, will guide you in selecting the most suitable type for your operations. -
How can I ensure the quality of steam boilers from international suppliers?
To ensure quality, conduct thorough vetting of potential suppliers by checking their certifications, customer reviews, and previous project experience. Request product samples or detailed specifications to assess their manufacturing standards. Additionally, consider visiting the supplier’s facility if possible, or using third-party inspection services to verify quality before making a purchase. Establishing clear communication about quality expectations and testing procedures will also help mitigate risks associated with international procurement. -
What are the typical payment terms when sourcing steam boilers internationally?
Payment terms can vary significantly based on the supplier and the nature of the transaction. Common arrangements include a deposit upon order confirmation and the balance upon shipment or delivery. Some suppliers may offer letters of credit or payment through escrow services for added security. It is essential to negotiate terms that protect both parties, ensuring you understand the implications of each payment method. Always document agreements to avoid disputes later in the transaction process. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for steam boilers?
Minimum order quantities for steam boilers can vary widely depending on the manufacturer and the specific model. Some suppliers may have no MOQ for standard models, while custom or specialized boilers might require larger orders to justify production costs. When negotiating, consider your immediate needs and future requirements to ensure you are not over-committing. Discussing flexibility in MOQs can also help in building a long-term relationship with suppliers. -
How do logistics and shipping affect the procurement of steam boilers?
Logistics play a critical role in the procurement process, impacting delivery times and costs. Factors such as the origin of the boiler, shipping method, and customs regulations in your country can influence overall logistics. It is advisable to work closely with suppliers to understand their shipping capabilities and to choose a logistics partner experienced in handling heavy industrial equipment. Consider potential delays in customs clearance and plan accordingly to avoid disruptions in your operations. -
What customization options are available for steam boilers?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for steam boilers to meet specific operational needs. Customization can include adjustments to size, capacity, fuel type, and additional features such as automated controls or advanced safety systems. Discussing your specific requirements with the supplier early in the procurement process can lead to tailored solutions that enhance efficiency and performance. Ensure that any customizations comply with local regulations and standards to avoid compliance issues later on.
Top 6 Diagram Of A Steam Boiler Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. CN Control Valve – Steam Boiler Solutions
Domain: cncontrolvalve.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Steam boilers are heating systems that generate steam by boiling water, converting thermal energy from various fuels such as gas, coal, biomass, and fuel oil. They are characterized by their structure, adaptability, tube type, fuel type, and pressure output. Types of steam boilers include electric boilers, hot water boilers, gas boilers, oil boilers, low pressure boilers, high pressure boilers, wa…
2. Pinterest – Steam Boiler Insights
Domain: pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Steam Boiler Types and Construction, typical steam boiler diagram, components of a steam boiler, resources for electrical and electronic engineers.
3. Cleaver-Brooks – Steam Boilers
Domain: cleaverbrooks.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Steam Boilers: Advanced solutions for industrial and commercial use designed for efficiency and reliability. Types include Firetube Boilers (used in commercial/small industrial applications), Watertube Boilers (ideal for high pressures in demanding industrial processes), Electric and Electrode Boilers (efficient, emission-free alternatives). Key components: Pressure Vessel (meets ASME standards), …
4. Facebook – Industrial Steam Boiler
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This steam boiler is commonly used for industrial heating and power generation. Key features include a fire brick furnace for burning fuel, water tubes for heat transfer, a make-up water inlet for continuous supply, water level control for safe operation, a large steam space for steam accumulation, a steam outlet for release, a draft exhaust stack for removing combustion gases, safety relief valve…
5. Forum Automation – P&ID Diagram for Boiler Components
Domain: forumautomation.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: P&ID diagram for Boiler includes main components: Steam drum, Downcomer, Furnace, Separator/cyclone, Backpass/Heat Recovery Area (HRA), Feed water pipe, Economizer, Superheater (low, medium & high temperature), Connecting Pipes (upper & lower), Main Steam Pipe. The boiler process involves: converting process water into steam, processing fuel (coal, limestone, oil) into ash, and processing air into…
6. SteamForum – Steam Boiler Solutions
Domain: steamforum.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Piping in a hot water base board on a steam boiler, questions and answers related to steam plants and power generation, steam boilers, turbine generators, heating problems, Hartford loop, condensate return lines, low water cut off, residential and small commercial steam boilers, industrial steam background, steam and hot water heating books.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for diagram of a steam boiler
In navigating the complex landscape of steam boiler procurement, international B2B buyers must prioritize strategic sourcing to optimize their investments. Understanding the diverse types of steam boilers, from firetube to watertube and electric models, allows businesses to select the right solution tailored to their operational needs. Key considerations such as fuel efficiency, environmental impact, and maintenance requirements can significantly affect long-term costs and sustainability goals.
Strategic sourcing not only enhances the efficiency of procurement processes but also fosters valuable relationships with suppliers, ensuring access to cutting-edge technologies and competitive pricing. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe increasingly focus on energy efficiency and regulatory compliance, aligning sourcing strategies with these objectives will be crucial.
Looking ahead, the demand for innovative steam boiler solutions is set to rise. By leveraging strategic sourcing practices, buyers can position themselves to capitalize on emerging trends, such as the shift towards renewable energy sources and advanced automation technologies. Engage with trusted suppliers today to ensure your business remains at the forefront of steam boiler advancements and operational excellence.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.