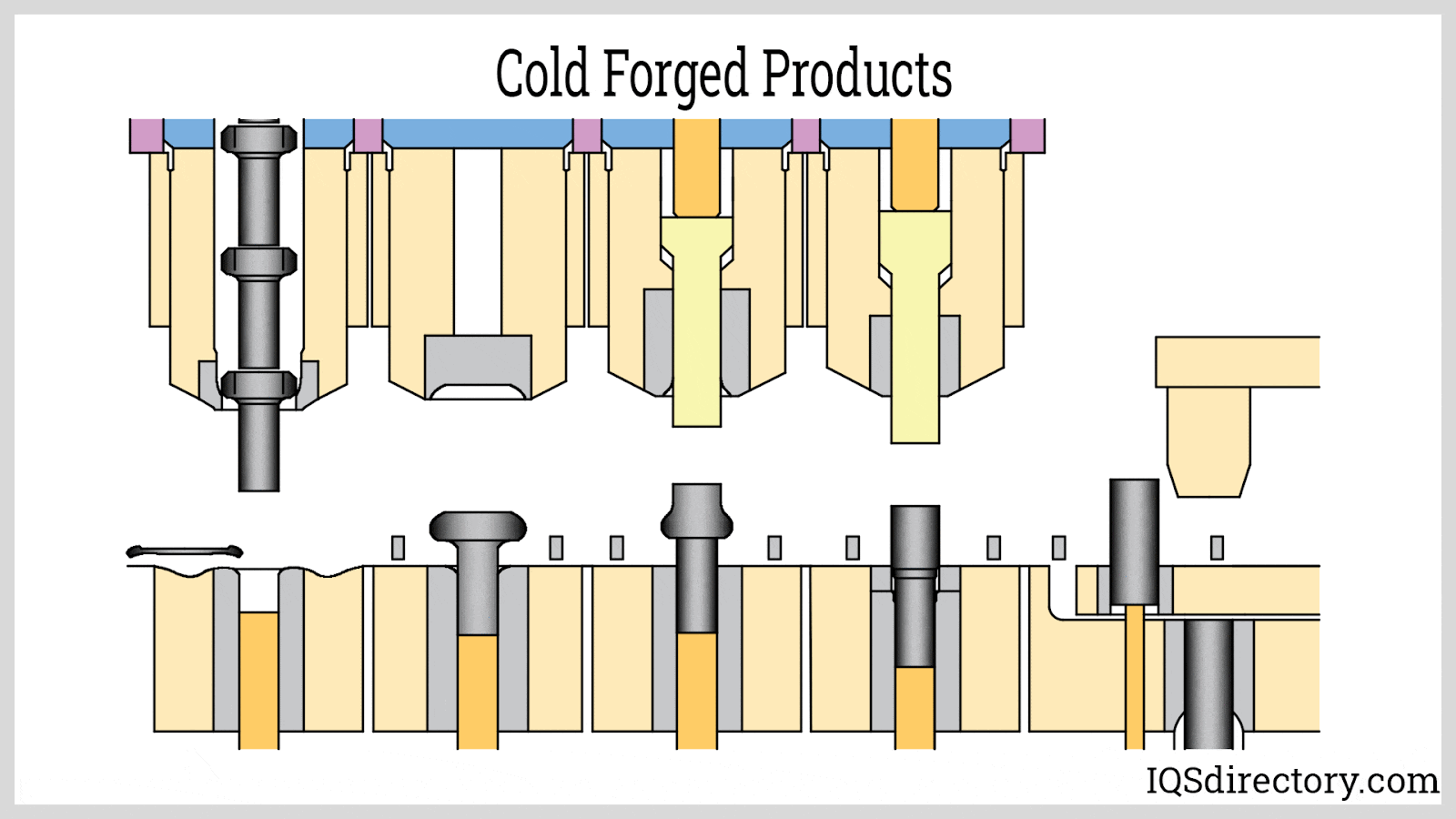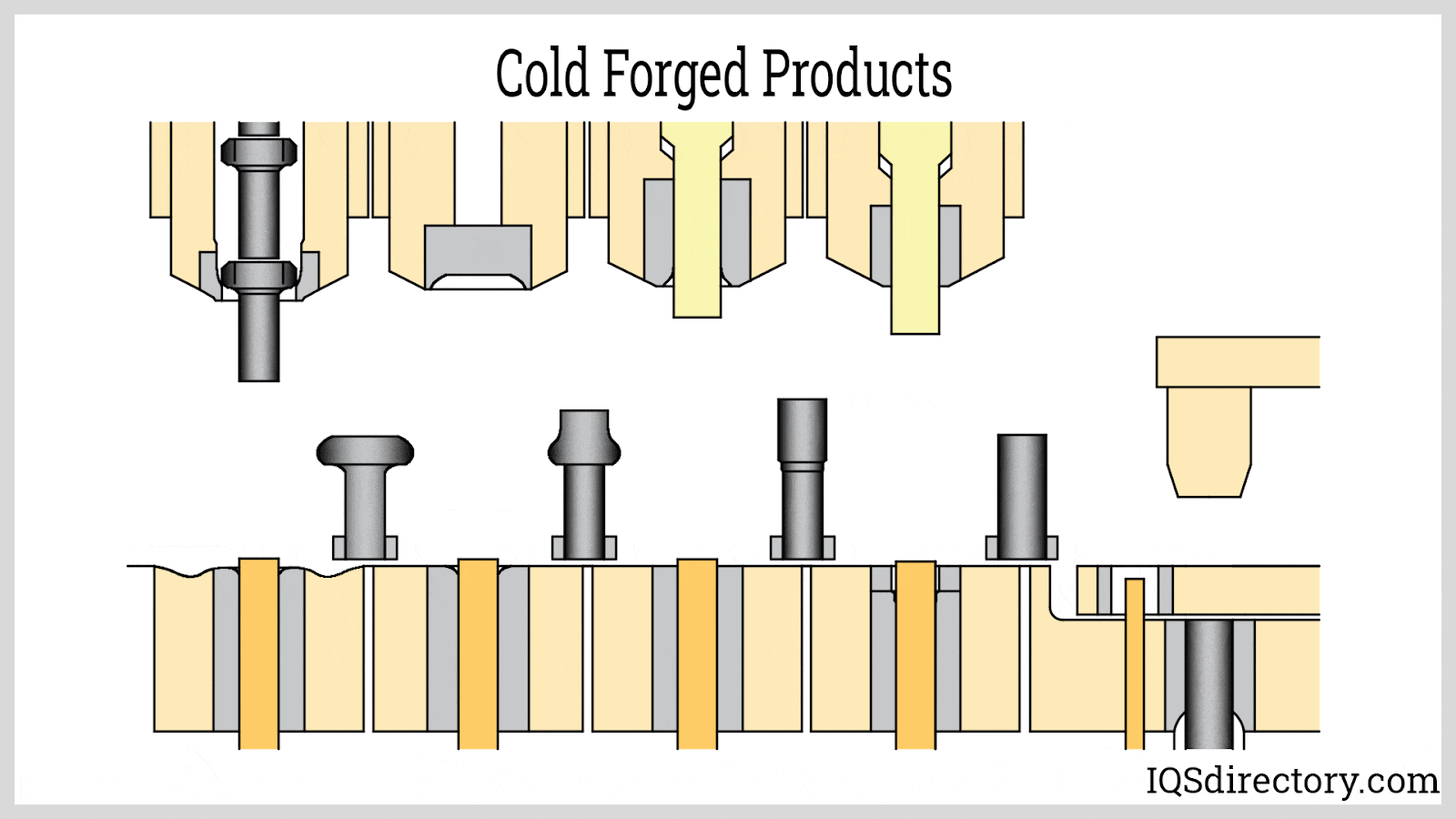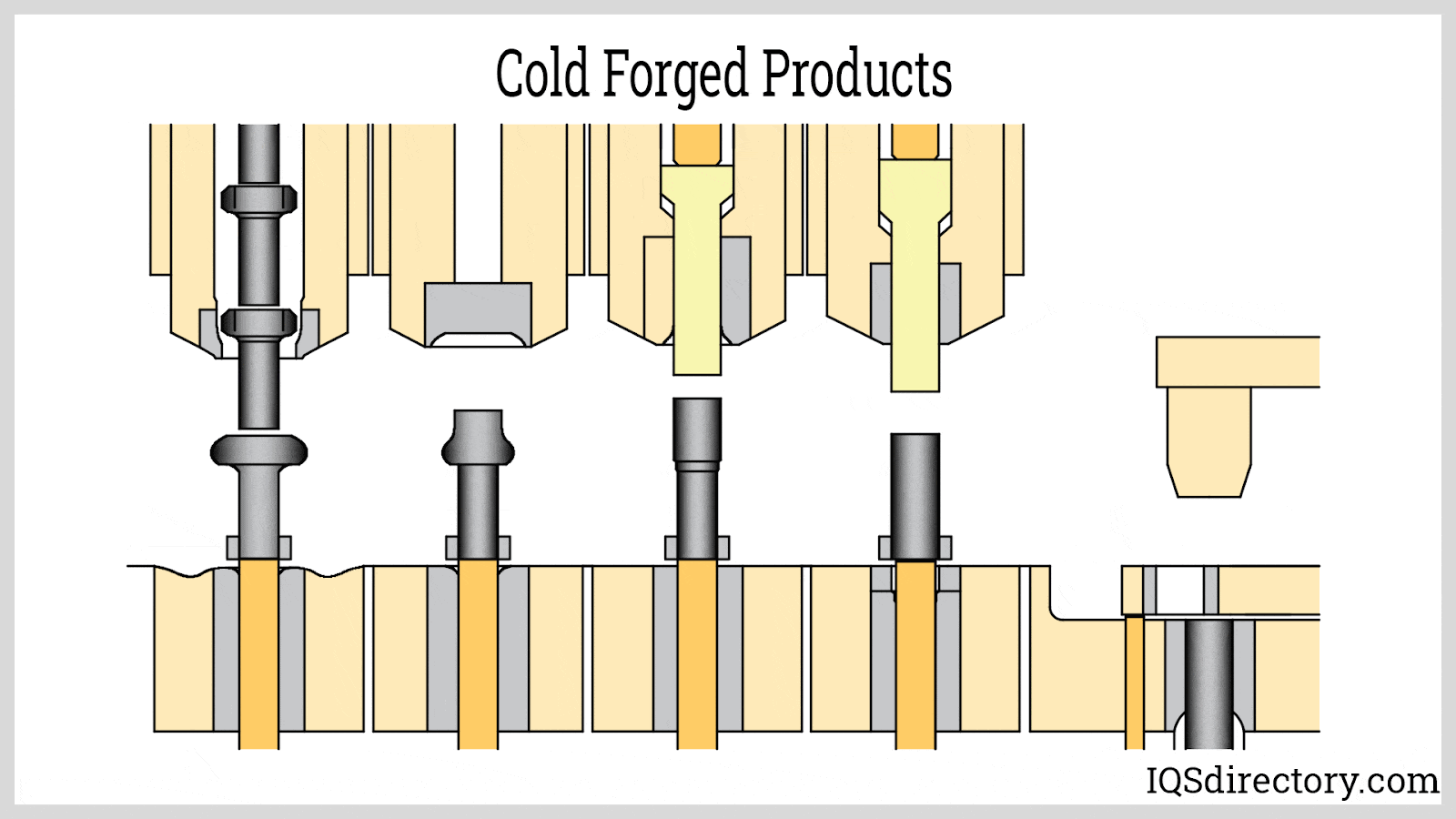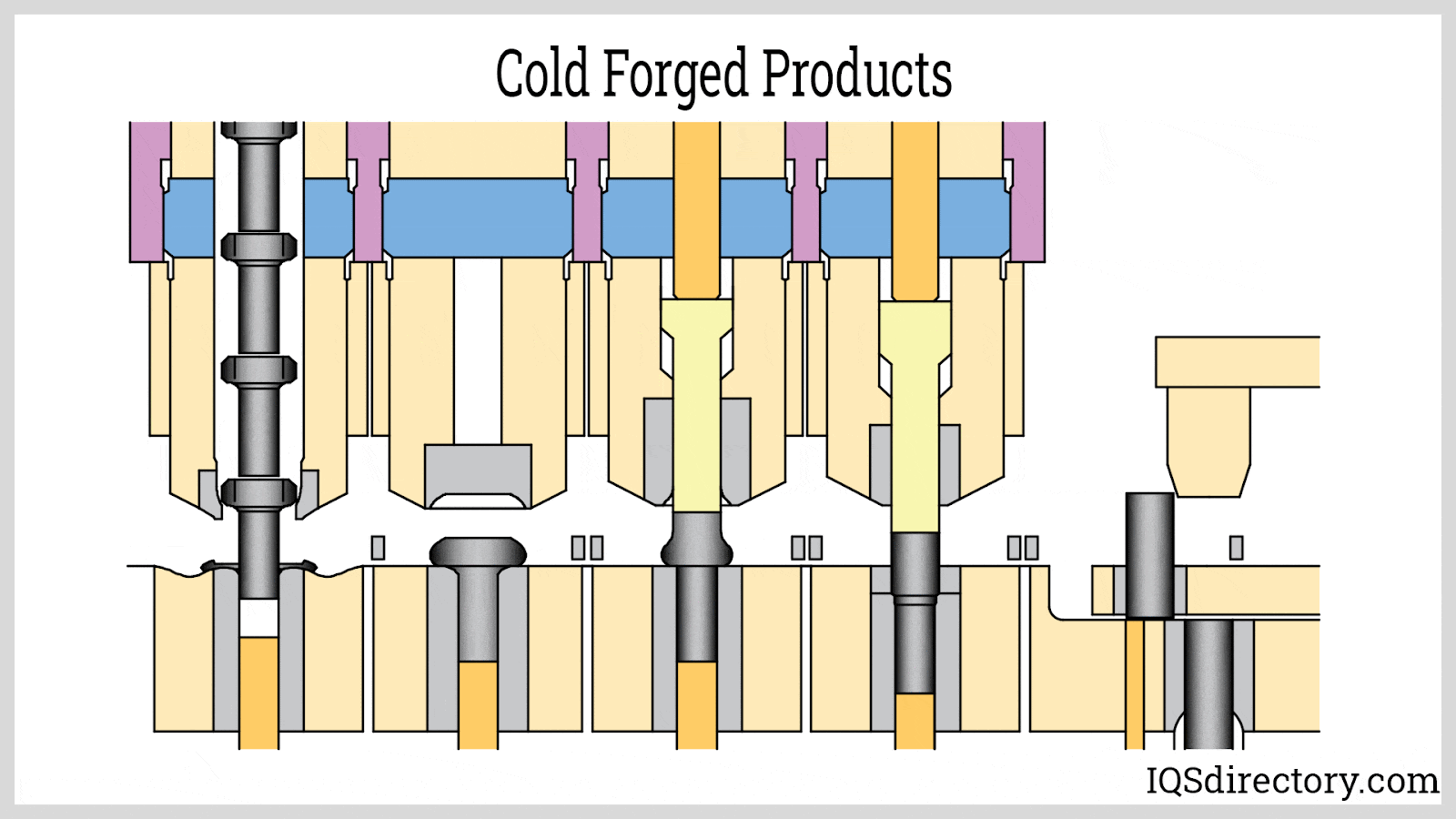
A Deep Dive into Cold Forging Operations Solution
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cold forging operations
Navigating the complexities of sourcing cold forging operations can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, particularly those in emerging markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Vietnam and Nigeria. As manufacturers increasingly seek reliable, cost-effective solutions for producing high-strength components, understanding the nuances of cold forging becomes essential. This guide is designed to empower decision-makers by providing an in-depth exploration of cold forging, including its various types, applications, and the intricacies of supplier vetting.
With a focus on practical insights, this comprehensive resource outlines the benefits of cold forging, such as enhanced material properties, reduced waste, and quick production times. Buyers will gain clarity on evaluating suppliers, understanding cost structures, and identifying the best materials for specific applications. Additionally, the guide addresses potential challenges in the global market, including logistics and compliance issues that are vital for seamless operations.
By leveraging this guide, B2B buyers will be equipped to make informed purchasing decisions that not only meet their immediate manufacturing needs but also position them for long-term success in a competitive landscape. Whether you are looking to optimize production efficiency or ensure the quality of your forged components, this resource serves as a vital tool in navigating the global cold forging market effectively.
Understanding cold forging operations Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open-Dye Forging | Uses flat dies without enclosing the workpiece; versatile. | Automotive parts, construction fasteners. | Pros: Lower tooling costs, flexibility. Cons: Less precision than closed-die. |
| Closed-Dye Forging | Employs custom-shaped dies that enclose the workpiece. | Aerospace components, precision machinery parts. | Pros: High precision, reduced waste. Cons: Higher initial tooling costs. |
| Rolled Ring Forging | Involves creating a donut shape, then forming a ring. | Bearings, flanges, and pipe fittings. | Pros: Efficient for circular components. Cons: Limited to ring-shaped products. |
| Multi-Station Forging | Uses multiple stations for complex part features. | Automotive assemblies, complex machinery parts. | Pros: High production speed, complexity. Cons: Higher setup complexity and cost. |
| Thread Rolling | Forms threads on cylindrical parts through deformation. | Fasteners, screws, and bolts. | Pros: Stronger threads, less material waste. Cons: Requires precise initial dimensions. |
What Are the Characteristics and Suitability of Open-Dye Forging?
Open-die forging is characterized by the use of flat dies that do not completely enclose the workpiece. This method allows for a high degree of flexibility in shaping larger and more complex parts. It is particularly suitable for industries like automotive manufacturing, where custom fasteners and components are frequently needed. Buyers should consider the lower tooling costs and adaptability of open-die forging, although it may sacrifice some precision compared to closed-die methods.
How Does Closed-Dye Forging Enhance Precision in Manufacturing?
Closed-die forging involves the use of custom-shaped dies that completely encase the workpiece, allowing for precise shaping and minimal material waste. This method is ideal for high-precision applications, such as aerospace components and intricate machinery parts. B2B buyers should weigh the initial investment in tooling against the long-term benefits of reduced waste and superior quality. While the cost may be higher upfront, the enhanced precision can lead to significant savings in downstream processes.
What Advantages Does Rolled Ring Forging Offer for Circular Components?
Rolled ring forging is a specialized process where a solid metal piece is transformed into a ring shape through a series of compressive forces. This method is particularly advantageous for producing circular components like bearings and flanges. For B2B buyers, the efficiency of this process can lead to lower production times and costs for ring-shaped products. However, it is essential to note that this method is limited to circular designs, which may not suit all manufacturing needs.
How Does Multi-Station Forging Improve Production Efficiency?
Multi-station forging utilizes several stations to execute various processes on a single workpiece, allowing for the creation of complex parts in a single run. This method is especially beneficial in the automotive sector, where intricate assemblies are common. Buyers should consider the high production speed and ability to incorporate multiple features into a single part. However, the complexity of setup and higher costs associated with this method may be a drawback for smaller operations.
Why is Thread Rolling a Cost-Effective Method for Fasteners?
Thread rolling is a cold forging technique that creates threads on cylindrical components through deformation rather than cutting. This method is particularly suited for producing fasteners like screws and bolts. B2B buyers benefit from the increased strength of rolled threads and reduced material waste. It is crucial to ensure that the initial dimensions of the workpiece are precise, as any discrepancies can lead to complications in the rolling process.
Key Industrial Applications of cold forging operations
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of cold forging operations | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Production of gears and fasteners | Enhanced strength and durability of components | Sourcing high-quality raw materials and precision tooling |
| Aerospace | Manufacturing of critical structural parts | Lightweight components with high fatigue resistance | Compliance with strict industry standards and certifications |
| Oil & Gas | Creation of valves and fittings | High corrosion resistance and reliability | Supplier reliability and capacity for large-scale production |
| Electronics | Production of connectors and terminals | High precision and minimal finishing required | Quality assurance processes and testing capabilities |
| Construction | Fabrication of rebar and structural elements | Cost-effective, strong, and durable components | Local sourcing capabilities and logistical efficiency |
How Is Cold Forging Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, cold forging is pivotal for producing gears and fasteners that require high strength and durability. This process addresses challenges such as the need for lightweight components that can withstand high-stress environments. Buyers in this industry should consider sourcing from suppliers that offer high-quality raw materials and precision tooling, ensuring that the final products meet stringent safety and performance standards.
What Are the Applications of Cold Forging in Aerospace?
Cold forging is essential in aerospace for manufacturing critical structural components that must be both lightweight and robust. The process helps solve issues related to fatigue resistance, which is crucial for safety and performance in flight. International buyers should prioritize suppliers who comply with rigorous industry standards and can provide certifications to guarantee the quality and reliability of their products.
How Is Cold Forging Beneficial for the Oil & Gas Sector?
In the oil and gas industry, cold forging is used to create valves and fittings that require high corrosion resistance and reliability under extreme conditions. This method effectively addresses the need for durable components that can withstand harsh environments. When sourcing, companies should focus on supplier reliability and their ability to handle large-scale production runs, ensuring consistent quality across all components.
What Role Does Cold Forging Play in Electronics Manufacturing?
Cold forging is utilized in the electronics industry for producing connectors and terminals that demand high precision and minimal finishing. The process reduces material waste and ensures that parts meet tight tolerances, which is critical for performance in electronic applications. Buyers should seek suppliers with robust quality assurance processes and testing capabilities to ensure that the components meet their specific requirements.
How Does Cold Forging Impact the Construction Industry?
In construction, cold forging is employed for fabricating rebar and other structural elements, providing cost-effective solutions that are both strong and durable. This method helps solve the challenges of material waste and production efficiency, making it an attractive option for builders. Buyers should consider local sourcing capabilities and logistical efficiency when selecting suppliers to minimize lead times and transportation costs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cold forging operations’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Quality of Forged Parts
The Problem: B2B buyers often grapple with the challenge of inconsistent quality in forged parts. Variability in strength, durability, and precision can lead to significant operational issues, especially in industries like automotive or aerospace, where safety and reliability are paramount. This inconsistency can stem from various factors, including variations in raw materials, improper machine settings, or inadequate quality control processes. Buyers may find themselves facing increased costs due to rework, scrap, or delays in production as they attempt to rectify these issues.
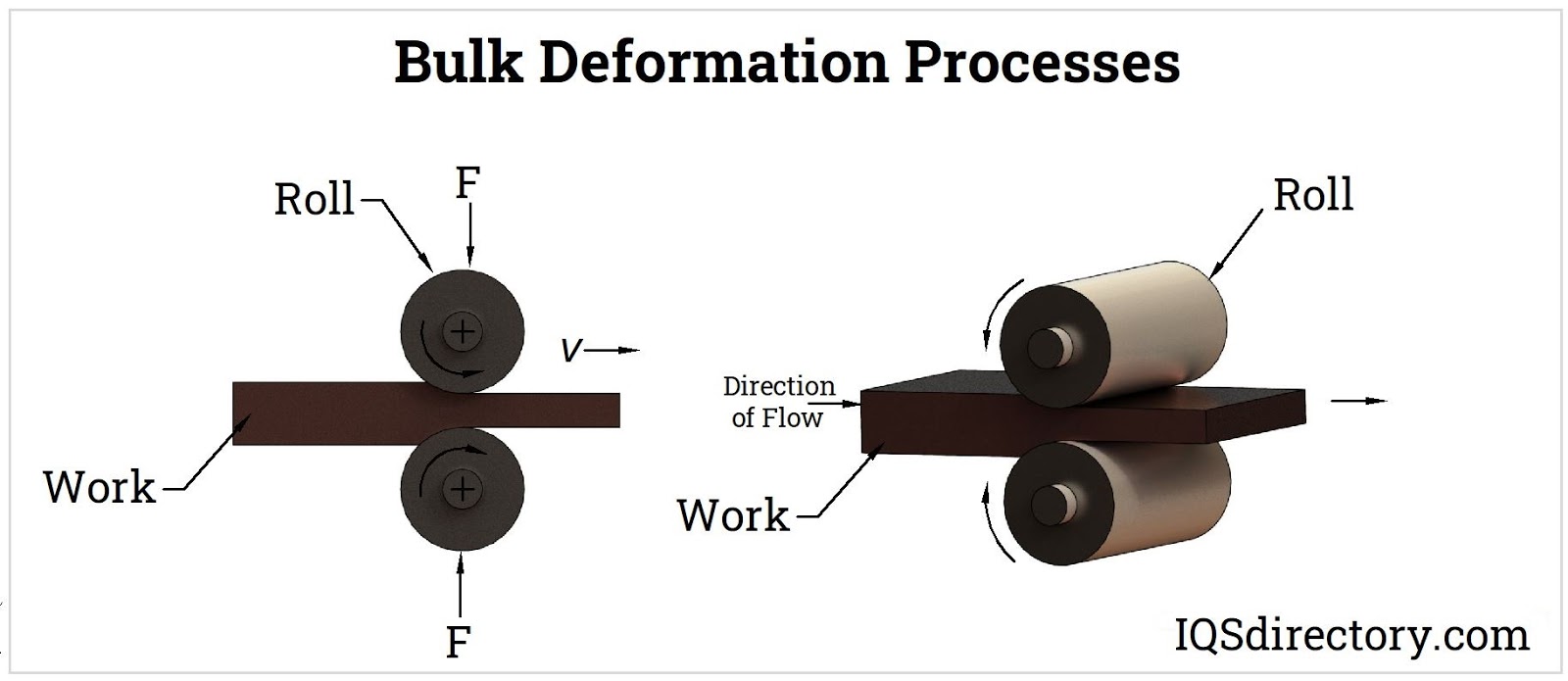
Illustrative image related to cold forging operations
The Solution: To mitigate quality inconsistencies, buyers should prioritize establishing robust supplier relationships with manufacturers who employ stringent quality control measures. This can include requiring detailed reports on material properties and performance testing of samples before full-scale production. Additionally, investing in advanced manufacturing technologies like automated inspection systems can help ensure consistent quality throughout the forging process. Buyers should also implement a comprehensive quality assurance program that includes regular audits of suppliers and periodic reviews of production processes to identify and rectify potential issues proactively.
Scenario 2: High Production Costs and Waste
The Problem: Another prevalent challenge faced by B2B buyers is the high production costs associated with cold forging operations, often exacerbated by material waste. The costs can escalate due to inefficient processes, excessive scrap, or the need for secondary operations to achieve the desired finish. This is particularly concerning for buyers in competitive markets where profit margins are tight, making it essential to minimize costs without compromising quality.
The Solution: Buyers can address high production costs by collaborating with manufacturers who specialize in optimizing cold forging processes. This includes selecting the right die configuration—closed-die forging, for instance, can significantly reduce waste compared to open-die methods. Furthermore, integrating advanced process simulation software can help identify the most efficient production methods, reducing material waste and improving yield rates. Buyers should also consider leveraging bulk purchasing agreements with suppliers to lower raw material costs, further enhancing their overall production efficiency.
Scenario 3: Limited Material Options Affecting Design Flexibility
The Problem: B2B buyers often find themselves constrained by the limited range of materials available for cold forging, which can impede their ability to innovate and meet specific design requirements. This limitation can be particularly pronounced in regions where access to high-quality raw materials is restricted, or in cases where specialized alloys are necessary for specific applications. As a result, buyers may struggle to achieve the desired mechanical properties or surface finishes, leading to dissatisfaction with the final product.
The Solution: To enhance material options and design flexibility, buyers should engage with suppliers who can provide a wider selection of metals suitable for cold forging, including advanced alloys and composites. Establishing partnerships with suppliers that specialize in custom materials can also facilitate access to unique compositions tailored to specific application needs. Buyers should work closely with their suppliers during the design phase to explore alternative materials and processes that can achieve the desired performance characteristics without compromising on the manufacturing capabilities. Additionally, investing in research and development can help identify innovative solutions that expand material choices and improve product performance.
Illustrative image related to cold forging operations
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cold forging operations
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Cold Forging Operations?
Cold forging operations rely on a variety of materials, each offering distinct advantages and limitations. Understanding these materials is crucial for B2B buyers looking to optimize their production processes and ensure product performance.
How Does Steel Perform in Cold Forging Applications?
Steel, particularly carbon steel and alloy steel, is one of the most commonly used materials in cold forging. Its key properties include high tensile strength, excellent ductility, and good corrosion resistance when treated. Steel can withstand high pressure and temperature, making it suitable for demanding applications.
Pros: Steel’s durability and strength make it ideal for producing components that require high performance, such as automotive parts and industrial machinery. It is also relatively cost-effective compared to other materials.
Cons: The primary drawback is that steel can be susceptible to corrosion if not properly treated, which may limit its use in certain environments. Additionally, the complexity of manufacturing processes can increase costs if specialized treatments are required.
Impact on Application: Steel components are compatible with various media, including oils and fuels, making them versatile for different industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of compliance with international standards such as ASTM and ISO. The availability of high-quality steel may vary, so sourcing from reputable suppliers is essential.
What Advantages Does Aluminum Offer for Cold Forging?
Aluminum is another popular choice for cold forging, known for its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. It is also a good conductor of heat and electricity, which can be advantageous in specific applications.
Pros: Aluminum’s low density translates to lighter parts, which is particularly beneficial in the aerospace and automotive industries. Its resistance to corrosion reduces the need for protective coatings, thus lowering overall manufacturing costs.
Cons: However, aluminum has a lower tensile strength compared to steel, which may limit its use in high-stress applications. Additionally, the cost of aluminum can be higher than that of steel, depending on market fluctuations.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is particularly suited for applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in aircraft components and automotive parts. Its compatibility with various media, including water and chemicals, enhances its usability.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of aluminum alloys that meet specific standards such as JIS and DIN. Understanding local market conditions is vital for cost-effective procurement.
How Do Copper and Brass Compare in Cold Forging?
Copper and brass are often used in cold forging for applications requiring excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance. Copper has a high melting point and can withstand significant stress, while brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, offers additional strength and machinability.
Pros: The primary advantage of copper and brass is their superior electrical and thermal conductivity, making them ideal for electrical components and plumbing fittings. They also exhibit good corrosion resistance.
Cons: However, both materials can be more expensive than steel and aluminum, which may deter some buyers. Additionally, they are less suitable for high-strength applications due to lower tensile strength compared to steel.
Impact on Application: Copper and brass components are commonly used in electrical connectors, plumbing fixtures, and decorative applications due to their aesthetic appeal.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B16 for brass and ASTM B170 for copper is essential. Buyers should also be aware of the varying availability of these materials in different regions.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Cold Forging Operations
| Material | Typical Use Case for cold forging operations | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Automotive parts, industrial machinery | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion without treatment | Medium |
| Aluminum | Aerospace components, automotive parts | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower tensile strength compared to steel | High |
| Copper | Electrical connectors, plumbing fittings | Excellent electrical conductivity | Higher cost and lower strength | High |
| Brass | Plumbing fixtures, decorative applications | Good corrosion resistance and machinability | More expensive than steel and aluminum | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of key materials used in cold forging, facilitating informed decision-making for their operations.

Illustrative image related to cold forging operations
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cold forging operations
What Are the Main Stages of Cold Forging Manufacturing Processes?
Cold forging is a sophisticated manufacturing process that involves several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a crucial role in ensuring the final product meets the required specifications and quality standards.
How Is Material Prepared for Cold Forging?
The first step in cold forging is material preparation, which involves selecting the appropriate raw materials, typically in the form of metal slugs or blanks. Common materials used in cold forging include carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. The chosen material is often subjected to quality checks to ensure it meets the required mechanical properties and chemical composition.
Once the material is selected, it undergoes cutting or blanking processes to achieve the desired dimensions. This preparation may also include surface treatments to enhance lubricity and prevent sticking during the forging process.
What Techniques Are Used in the Cold Forging Forming Stage?
The core of cold forging lies in the forming stage, where the prepared metal is shaped into the desired components. This can be achieved through two primary techniques: open-die forging and closed-die forging.
-
Open-Die Forging: This technique involves placing the raw material between flat dies that do not enclose the workpiece. The compressive force applied deforms the metal until the desired shape is achieved. Open-die forging is ideal for larger components and allows for flexibility in design.
-
Closed-Die Forging: In this method, the workpiece is confined within custom-shaped dies. The metal flows to fill the die cavity, allowing for intricate shapes and high precision. This method is widely used for mass production of complex components, as it minimizes material waste and enhances the mechanical properties of the forged parts.
During the forming process, lubrication is applied to reduce friction and heat, ensuring a smooth operation. The use of hydraulic, pneumatic, or mechanical mechanisms generates the necessary force to shape the metal.
How Is Assembly Managed in Cold Forging Operations?
After forming, components may undergo assembly if they are part of a larger product. This stage involves joining multiple forged parts using various methods, such as welding, riveting, or threading. The assembly process is critical for ensuring that the final product functions as intended and meets the design specifications.
What Finishing Techniques Are Common in Cold Forging?
The finishing stage involves additional processes that enhance the surface quality and functionality of the forged parts. Common finishing techniques include:
- Trimming: Excess material, known as flash, is removed from closed-die forged parts.
- Machining: Precision machining may be applied to achieve tighter tolerances or specific surface finishes.
- Surface Treatment: Processes such as plating, anodizing, or coating may be employed to improve corrosion resistance or aesthetic appearance.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for Cold Forging?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to cold forging operations, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations. The QA process can be broken down into several checkpoints and testing methods.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Cold Forging?
To maintain high-quality production, cold forging operations often adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems. Additionally, industry-specific standards may apply, including:
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European safety, health, and environmental protection legislation.
- API Standards: Relevant for manufacturers producing parts for the oil and gas industry, ensuring they meet specific performance criteria.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) is typically structured around three main checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of raw materials before production begins. Inspectors verify that materials meet specified standards and perform necessary tests, such as chemical composition analysis and mechanical property assessments.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, continuous monitoring is essential. Operators conduct checks during the forming and assembly stages to identify any deviations from quality standards. This may include dimensional inspections and visual checks for surface defects.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, a comprehensive inspection ensures that finished products meet all specifications. This stage may involve functional testing, dimensional verification, and surface quality assessments.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Cold Forging Quality Control?
Cold forging manufacturers utilize various testing methods to ensure product integrity, including:
- Mechanical Testing: Tensile tests, hardness tests, and fatigue tests assess the material’s performance under stress.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle inspection identify internal flaws without damaging the component.
- Dimensional Inspection: Calipers, gauges, and coordinate measuring machines (CMM) are used to verify that parts meet specified dimensions and tolerances.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is critical to ensuring product reliability. Here are some actionable strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes, quality control systems, and overall operational practices of potential suppliers. This firsthand evaluation can provide insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can help buyers understand a supplier’s QC processes. These reports should outline testing results, compliance with standards, and any corrective actions taken to address quality issues.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control measures. These inspections typically cover raw materials, production processes, and finished products, providing buyers with confidence in their sourcing decisions.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local regulations and quality expectations is essential. Each market may have specific compliance requirements that suppliers must meet. Buyers should consider the following:
- Cultural Factors: Different regions may have varying approaches to quality assurance. Establishing clear communication about expectations and standards is crucial.
- Regulatory Compliance: Being aware of the specific regulatory requirements in the buyer’s region can help in selecting suppliers that are compliant and reliable.
- Certification Recognition: Ensure that certifications held by suppliers are recognized in the buyer’s market, as this can impact the acceptance of products.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices in cold forging operations, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that ensure they receive high-quality products tailored to their needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cold forging operations’
The following checklist serves as a comprehensive guide for B2B buyers looking to procure cold forging operations. This step-by-step approach will help you ensure that your sourcing process is efficient, cost-effective, and aligned with your technical requirements.
Illustrative image related to cold forging operations
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical specifications for the cold forged parts you need. This includes material types, dimensions, tolerances, and surface finishes. Providing precise requirements helps suppliers understand your needs and reduces the risk of receiving subpar products.
- Material Considerations: Specify whether you need aluminum, brass, copper, or various grades of steel based on the application.
- Dimensional Tolerances: Indicate the acceptable tolerances to ensure the parts fit correctly in your assembly.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in cold forging. Look for companies with a strong reputation and proven experience in your industry.
- Industry Presence: Check their years of operation, client base, and market reach, especially in your target regions such as Africa, South America, and Europe.
- Online Reviews and Ratings: Utilize platforms like LinkedIn and industry-specific forums to gauge supplier reliability.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before proceeding, verify that the suppliers possess relevant certifications. Certifications such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific standards demonstrate a commitment to quality and operational excellence.
- Quality Assurance: Ensure that the supplier has a documented quality management system in place.
- Compliance: Check for compliance with international standards, especially if you operate in regulated industries.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Ask for samples or prototypes of the cold forged parts you intend to purchase. This step allows you to assess the quality and performance of the products firsthand.
- Functional Testing: Evaluate the samples under real-world conditions to ensure they meet your operational needs.
- Feedback Loop: Use this opportunity to provide feedback to the supplier for any necessary adjustments.
Step 5: Assess Production Capabilities
Understand the production capabilities of your shortlisted suppliers. This includes their capacity for high-volume production, lead times, and technology used in the cold forging process.
- Automation Level: Inquire about the extent of automation in their processes, as higher automation often leads to faster and more consistent production.
- Flexibility: Evaluate their ability to adapt to changes in order sizes or specifications.
Step 6: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, engage in negotiations to discuss pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Ensure that the terms align with your budget and operational timelines.
- Volume Discounts: Inquire about discounts for bulk orders to maximize your cost savings.
- Payment Options: Consider flexible payment terms that align with your cash flow needs.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Finally, set up a clear communication plan with the chosen supplier. Effective communication is key to a successful partnership and can help preempt potential issues during production.
- Regular Updates: Schedule regular check-ins to monitor progress and address any concerns.
- Point of Contact: Designate a specific point of contact from both sides to streamline communication.
By following this checklist, you can effectively source cold forging operations that meet your specific needs while ensuring quality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cold forging operations Sourcing
Analyzing the cost structure and pricing dynamics of cold forging operations is essential for international B2B buyers looking to optimize their sourcing strategies. The following breakdown includes key cost components, price influencers, and actionable tips for buyers.
Illustrative image related to cold forging operations
What Are the Key Cost Components in Cold Forging Operations?
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly influences overall costs. Common materials used in cold forging include steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. Prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, availability, and specific material grades. Buyers should consider the total material costs, including any potential wastage during the forging process.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass not only the wages of skilled operators but also the training and ongoing development of staff. In regions with lower labor costs, such as certain parts of Africa and South America, this can lead to significant savings. However, the quality and expertise of the labor force can also affect the quality of the finished product.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with the facility, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Given that cold forging is a high-speed process, efficient machinery can enhance productivity and reduce overhead costs. Regular maintenance schedules are crucial to avoid unexpected downtime.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are a substantial part of the cold forging process. High-quality dies and molds are necessary for precision and durability. Custom tooling can be more expensive but may be justified by improved product quality and reduced waste.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes is vital to ensure product specifications are met. This can include testing, inspections, and certifications, which contribute to overall costs but are essential for maintaining quality standards, especially for international markets that may have stringent regulations.
-
Logistics: The logistics of transporting raw materials and finished goods also play a critical role in cost structure. International shipping costs, tariffs, and local transportation can significantly affect pricing. It is vital to consider Incoterms to understand responsibilities regarding shipping and risk.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically build in a profit margin that reflects their operational costs, market position, and the competitive landscape. Understanding the standard margin in the cold forging sector can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Cold Forging Sourcing?
-
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often have minimum order quantities (MOQ) that can affect pricing. Higher volume orders can lead to discounts, making it essential for buyers to evaluate their needs and negotiate accordingly.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized parts typically incur higher costs due to the additional tooling and labor required. Buyers should assess whether the added functionality justifies the increased expense.
-
Material Selection: The choice of material can drastically alter costs. Specialty metals or alloys may have higher market prices, which should be factored into total project budgets.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that require specific quality certifications or compliance with international standards may come at a premium. Buyers should ensure they understand the certifications needed for their target markets.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, location, and operational efficiency can influence pricing. Engaging with established suppliers often leads to better quality and reliability, albeit at a higher initial cost.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in terms of shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Choosing the right terms can significantly impact the overall cost.
What Are the Best Tips for Buyers Negotiating Cold Forging Prices?
-
Negotiate Wisely: Leverage volume commitments and long-term contracts to negotiate better pricing. Suppliers often appreciate the security of guaranteed orders.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just upfront costs. Consider factors like durability, maintenance, and potential waste reduction.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers should account for currency fluctuations and regional market conditions that may affect pricing.
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Gather quotes from multiple suppliers to understand the competitive landscape. This can provide leverage in negotiations.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the cost structure, price influencers, and strategic negotiation techniques is essential for international B2B buyers in the cold forging sector. By focusing on these areas, companies can optimize their sourcing strategies and achieve better pricing outcomes.
Disclaimer: Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on specific project requirements and market conditions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cold forging operations With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Metal Forming Solutions
When considering metal forming processes, it’s essential to evaluate various methods beyond cold forging operations. While cold forging is known for its efficiency and cost-effectiveness, other alternatives such as hot forging and die casting can also provide viable solutions depending on specific project requirements. In this section, we will compare cold forging with hot forging and die casting to help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Cold Forging Operations | Hot Forging | Die Casting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength, precision, and low waste | Excellent ductility and malleability | High precision and complex shapes |
| Cost | Lower operational costs, minimal waste | Higher energy costs due to heating | Moderate tooling costs, but efficient for high volumes |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized machinery, but straightforward | More complex setup with heating equipment | Requires precise molds and setup |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to fewer moving parts | Higher maintenance due to heating elements | Moderate maintenance, mold wear can be an issue |
| Best Use Case | High-volume production of small to medium parts | Large, complex parts needing ductility | High-volume production of intricate shapes |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Hot Forging
Hot forging involves shaping metal at elevated temperatures, which allows for greater malleability and ductility. This method is ideal for producing larger, more complex components that require reshaping without cracking. However, the need for heating equipment increases operational costs and energy consumption. The process also requires careful temperature control to ensure quality, making it less straightforward to implement compared to cold forging. While hot forging can produce robust parts, its higher energy costs and complex setup may not be suitable for all B2B applications.
Die Casting
Die casting is a method that forces molten metal into a mold to create intricate shapes with high precision. This technique excels in producing complex geometries with smooth finishes, making it suitable for high-volume production runs. However, the initial investment in molds can be significant, and while the operational costs are generally manageable, the setup can be labor-intensive. Die casting is best utilized for parts that require fine detail and dimensional accuracy, but it may not match the strength characteristics of cold forged components.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Metal Forming Solution
When deciding between cold forging, hot forging, and die casting, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including the intended application, production volume, and budget constraints. Cold forging stands out for its cost-effectiveness and strength, particularly for high-volume, precision parts. Hot forging may be preferable for larger components requiring enhanced ductility, while die casting is best for intricate designs with high volume requirements. Each method has its unique advantages and trade-offs, making it crucial to align the choice with specific project needs to achieve optimal results.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cold forging operations
When engaging in cold forging operations, understanding the essential technical properties and industry jargon is crucial for effective decision-making and procurement. Here’s a breakdown of the key specifications and terminology that B2B buyers should be familiar with.
What Are the Key Technical Properties in Cold Forging?
-
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific classification of the metal being used in cold forging, such as stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum, or copper alloys. Each grade has unique mechanical properties, such as tensile strength and corrosion resistance, which directly impact the performance and longevity of the final product. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade is essential for meeting application requirements and ensuring product reliability. -
Tolerance
Tolerance is the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension of a forged part. In cold forging, tight tolerances can be achieved, which is critical for parts that must fit precisely in assemblies. Understanding tolerance levels helps buyers specify their needs accurately, leading to reduced waste and rework, ultimately saving costs and time in the production process. -
Surface Finish
Surface finish refers to the texture and quality of the surface of the forged part. Cold forging generally results in a smoother finish compared to other methods, which can minimize the need for additional machining or finishing processes. For manufacturers and buyers, a good surface finish can enhance aesthetics and functional performance, particularly in applications where friction or wear is a concern. -
Yield Strength
Yield strength is the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically. In cold forging, parts are produced under conditions that enhance their yield strength compared to their original state. Higher yield strength translates to better performance under load, making it essential for applications in automotive and aerospace industries. Buyers must consider yield strength to ensure the components can withstand operational demands. -
Production Rate
This refers to the speed at which parts can be produced during the cold forging process. High production rates can significantly lower costs per unit, making cold forging a competitive option for high-volume manufacturing. Understanding production rates allows buyers to align their procurement strategies with production capabilities, ensuring they meet market demand efficiently.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Cold Forging?
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In cold forging, OEMs often require high-quality, custom components that meet specific industry standards. Buyers should be aware of OEM requirements to ensure compatibility and compliance with their end products. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. In cold forging, MOQs can vary based on the complexity of the part and the production setup. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers to avoid overstocking or underordering, which can affect cash flow and inventory management. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a price quote for specific products or services. In the context of cold forging, issuing an RFQ helps buyers gather essential pricing information and understand supplier capabilities. It is a vital step in the procurement process, allowing for informed decision-making. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in global trade transactions. In cold forging, understanding Incoterms is essential for determining who bears the risk and costs during shipping and delivery. This knowledge helps buyers negotiate better terms and avoid unexpected expenses. -
Flash
Flash refers to the excess material that is squeezed out of the die during the cold forging process. This byproduct must be trimmed away, but it can often be recycled for further use. For buyers, understanding flash can impact material costs and production efficiency, making it an important consideration in the overall manufacturing process.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions regarding their cold forging operations, leading to improved product quality and operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cold forging operations Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Impacting Cold Forging Operations?
The cold forging operations sector is witnessing significant growth driven by several global factors. The increasing demand for high-strength, lightweight components in automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications is a primary driver. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to optimize production processes, cold forging stands out for its cost-effectiveness and efficiency. Emerging technologies such as Industry 4.0, which integrates automation and data exchange in manufacturing, are facilitating faster production cycles and reducing lead times. This trend is particularly relevant for manufacturers looking to scale operations without compromising on quality.
Furthermore, the rise of advanced materials, including high-performance alloys and composites, is shaping sourcing strategies. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can provide tailored solutions that meet specific material requirements. The trend towards digital sourcing platforms is also gaining traction, allowing buyers to connect with manufacturers globally, streamline procurement processes, and enhance supply chain visibility. Understanding these dynamics enables international B2B buyers to make informed decisions, ensuring they leverage the advantages of cold forging to enhance their competitive edge.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing Cold Forging Operations?
Sustainability has emerged as a critical concern in the cold forging operations sector, driven by both regulatory pressures and consumer demand for environmentally responsible practices. Cold forging itself is considered more sustainable than traditional manufacturing methods due to its lower energy consumption and minimal waste generation. The process often results in higher material utilization rates, which is particularly appealing to environmentally conscious buyers.
Moreover, ethical sourcing is becoming increasingly important in the B2B landscape. Buyers are prioritizing suppliers who adhere to ethical labor practices and demonstrate transparency in their supply chains. Certifications such as ISO 14001, which focuses on effective environmental management systems, and other ‘green’ certifications are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to appeal to the modern buyer. As the market evolves, B2B buyers are encouraged to assess their suppliers based on sustainability credentials and ethical practices, ensuring they align with both corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals and consumer expectations.
What Is the Historical Context of Cold Forging Operations?
Cold forging has its roots in traditional metalworking, evolving significantly since the industrial revolution of the 19th century. Initially, this process was labor-intensive and limited in scope, primarily used for creating simple shapes. However, advancements in technology have transformed cold forging into a sophisticated method capable of producing complex, high-strength components at scale. The introduction of automated machinery and computer-aided design (CAD) has further enhanced precision and efficiency in the manufacturing process.
As industries grew and diversified, the applications for cold forging expanded beyond simple fasteners to include intricate parts for the automotive and aerospace sectors. This evolution has made cold forging a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, offering a blend of durability and cost-effectiveness that appeals to a wide range of B2B buyers globally. Today, the cold forging sector is not only recognized for its historical significance but also for its pivotal role in meeting the demands of contemporary manufacturing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cold forging operations
-
How do I choose the right cold forging supplier for my business needs?
Selecting a cold forging supplier requires careful consideration of their experience, capabilities, and quality assurance processes. Evaluate their production capacity, technical expertise, and previous projects to ensure they can meet your specifications. Request samples to assess the quality of their work and inquire about their certifications, such as ISO standards, which indicate adherence to international quality management practices. Additionally, consider their location and logistics capabilities, especially if you are sourcing from different continents, to ensure timely delivery. -
What are the advantages of using cold forging over other metal forming processes?
Cold forging offers several advantages, including improved mechanical properties, cost-effectiveness, and high production rates. The process creates parts with superior strength due to work hardening, reduces material waste, and often eliminates the need for extensive finishing. Additionally, cold forging can be performed at room temperature, which means there is no need for heating equipment, thus saving on energy costs. This makes it an efficient option for high-volume production of complex parts. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for cold forging operations?
Minimum order quantities for cold forging can vary significantly based on the supplier, the complexity of the parts, and the materials used. Typically, MOQs can range from a few hundred to several thousand units. It’s essential to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers, as many are willing to accommodate smaller orders for custom projects, especially if they see potential for future business. Be prepared to negotiate terms based on your production requirements. -
How can I ensure quality assurance in cold forging parts?
To ensure quality assurance in cold forging parts, establish clear specifications and standards before production begins. Request detailed inspection reports and certifications from your supplier, including material traceability and testing results. Many suppliers implement rigorous quality control processes, including dimensional inspections, material testing, and surface finish evaluations. Additionally, consider conducting on-site audits or third-party inspections to verify compliance with your quality requirements. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing cold forging services internationally?
Payment terms for international cold forging services can vary widely depending on the supplier and the nature of the order. Common terms include upfront deposits, payment upon delivery, or payment after inspection. It’s advisable to discuss and agree on payment terms that protect both parties, such as using a Letter of Credit for larger orders. Ensure you understand any potential additional costs related to shipping, customs, and tariffs that may affect the overall pricing. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing cold forged parts?
When sourcing cold forged parts, logistics play a crucial role in ensuring timely delivery and cost management. Consider the shipping methods available, transit times, and the reliability of freight carriers. If your supplier is located internationally, factor in customs clearance times and potential tariffs. It’s also wise to discuss packaging methods to prevent damage during transit. Establishing a good communication channel with your supplier and logistics partner can help mitigate delays. -
Can I customize my cold forged parts to meet specific design requirements?
Yes, most cold forging suppliers offer customization options to meet specific design requirements. You can collaborate with them to create custom dies and tooling that will allow for the production of parts tailored to your specifications. Be clear about your design needs, material preferences, and any performance requirements. Keep in mind that customization may impact lead times and costs, so it’s important to discuss these factors upfront. -
What industries commonly utilize cold forging, and what types of products are produced?
Cold forging is widely used across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, construction, and electronics. Common products include gears, shafts, fasteners, and intricate components that require high strength and precision. The versatility of cold forging allows it to accommodate a wide range of materials, including steel, aluminum, and copper alloys, making it suitable for manufacturing components that need to withstand high-stress environments.
Top 6 Cold Forging Operations Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Cornell Forge – High-Quality Forged Steel Solutions
Domain: cornellforge.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Cornell Forge Company specializes in hot and cold forging processes, producing high-quality forged steel and alloy products. They offer closed die hot forging, microalloy forging, stainless steel forgings, forged alloys, and custom forged steel parts. The company has over 90 years of experience and is ISO 9001:2015 certified, ensuring rigorous quality standards. Hot forging allows for increased du…
2. Force Beyond – Cold Forging Solutions
Domain: forcebeyond.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Cold forging products supplied to multiple industries for over a decade. Helps maximize supply chain efficiency and improve production costs. Industries served include energy, automotive, bus, heavy-duty truck, marine, and rail. Cold forging deforms metal below its recrystallization point, preferred for softer metals like aluminum. Produces forged parts requiring little to no finishing. Equipment …
3. TFG USA – Cold Forging Solutions
Domain: tfgusa.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Cold forging is a metal forging technique that processes bar stock and squeezes it into an open die at ambient temperature or below the metal’s recrystallization temperature. It is an efficient and cost-effective method for manufacturing large volumes of parts with minimal waste, achieving material savings of up to 70%. Cold forging can produce near-perfect surface finishes and increased dimension…
4. Netform – Cold Forming Solutions
Domain: netform.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Cold forming (also known as cold forging or coining) is a process that transforms material into new shapes at room temperature using high-tonnage presses. It is used to produce powertrain components such as planetary carriers and splined hubs. Key benefits include work hardening, which increases strength and allows for weight savings or stronger parts within the same packaging constraints. The pro…
5. TIRapid – Cold Forging Solutions
Domain: tirapid.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Cold forging is a metal shaping process performed at room temperature to 500°F (260°C) using dies. It is ideal for producing small, high-precision parts such as gears and engine components. The process involves preparing the metal, placing it in a die, hammering or pressing it into shape, and finishing the surface. Key types include impression die forging and roll forging, with advantages such as …
6. Ferralloy – Cold Forging Solutions
Domain: ferralloy.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Cold forging is a metal shaping method that involves inserting bar stock into a die and squeezing it into a closed die at room temperature or below the metal’s melting point. It is suitable for high production rates, particularly in automotive applications. Key steps in the cold forging process include: 1. Cutting the Material: Requires proper heat treatment to soften bars before delivery; only ce…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cold forging operations
In navigating the complexities of cold forging operations, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal factor for international B2B buyers. By leveraging the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of cold forging, companies can enhance their production capabilities while minimizing waste. The ability to produce high volumes of durable, high-quality parts at room temperature not only streamlines manufacturing processes but also ensures faster turnaround times, which is crucial for maintaining competitive advantage in global markets.
Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize partnerships with reputable cold forging suppliers who offer customized solutions tailored to specific industry needs. The diverse range of metals applicable in cold forging further allows for flexibility in product development, enabling businesses to innovate and meet evolving market demands.
As we look to the future, investing in advanced cold forging technologies and fostering collaborative relationships with suppliers will be essential for achieving sustainable growth. By embracing these strategies, international buyers can position themselves at the forefront of the manufacturing landscape, driving both efficiency and profitability. Engage with trusted partners today to unlock the full potential of cold forging in your operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.