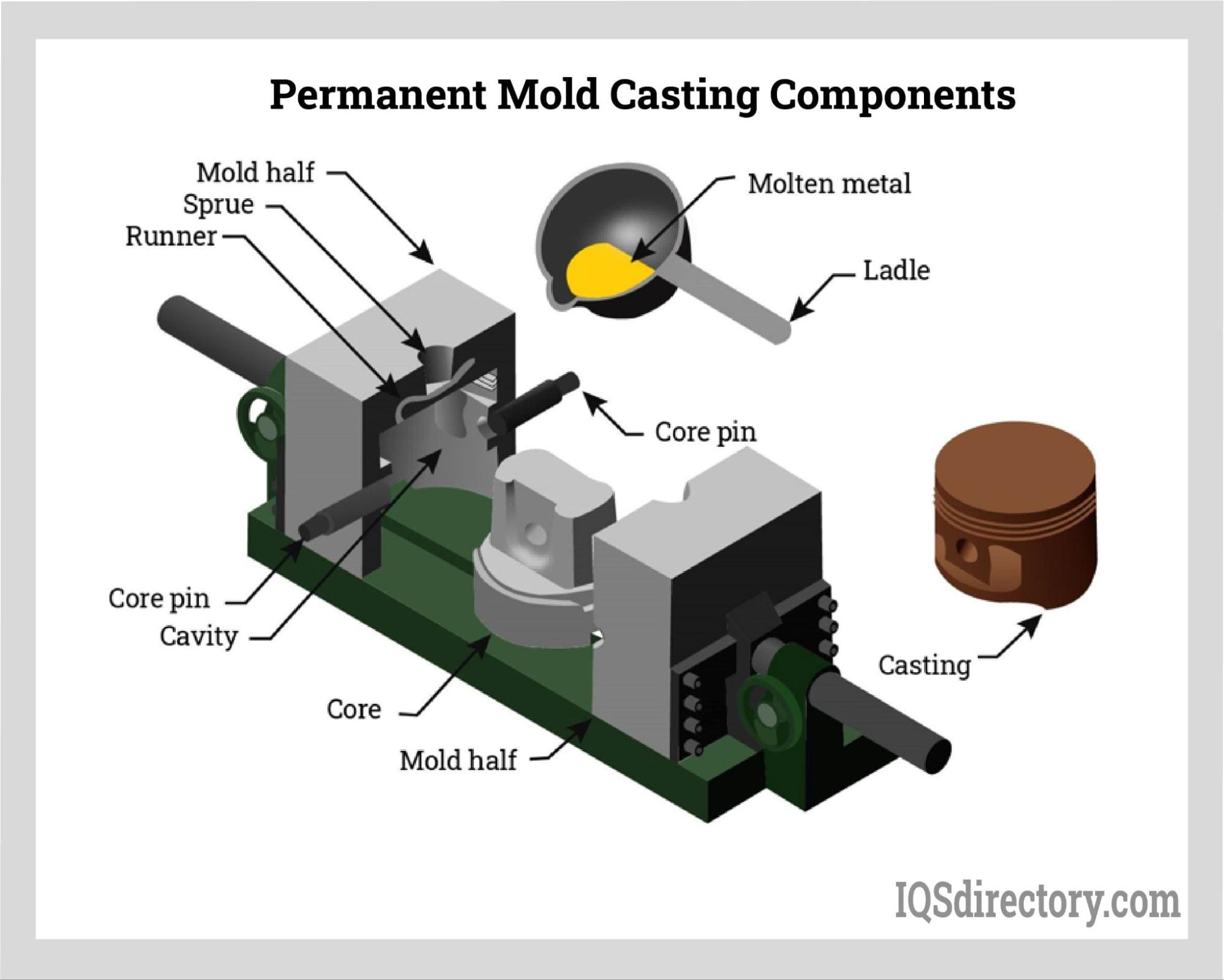
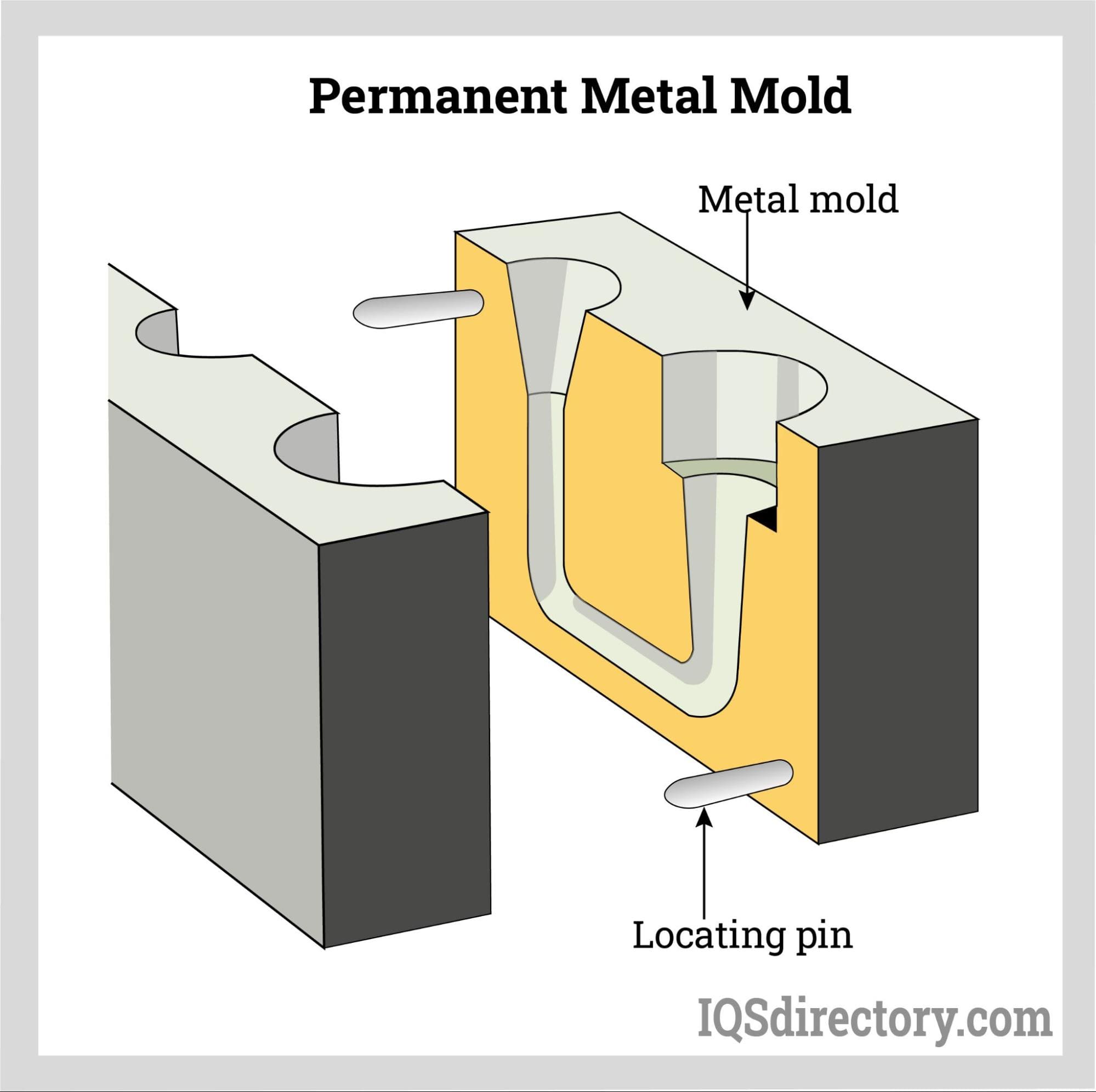
A Deep Dive into Casting Mold Solution
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for casting mold
In the competitive landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing high-quality casting molds can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The intricacies of identifying the right molds that meet specific production needs—whether for silicone, HDPE, or other materials—can complicate decision-making. This guide aims to streamline that process by providing an in-depth exploration of the casting mold market, encompassing various types, applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
By navigating through this comprehensive resource, international buyers will gain valuable insights into the nuances of mold selection, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions that align with their business objectives. From understanding the differences between mold materials to learning about the production capabilities of potential suppliers, this guide empowers you to mitigate risks and maximize efficiency in your sourcing strategy.
Additionally, we delve into the best practices for mold maintenance and usage, which are crucial for achieving optimal casting results. With our expert insights, B2B buyers can confidently engage with suppliers and enhance their product offerings, ultimately leading to improved operational outcomes and customer satisfaction in an increasingly interconnected market.
Understanding casting mold Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silicone Molds | Flexible, reusable, and can create intricate designs | Crafting, jewelry, and custom product design | Pros: Easy to demold, versatile. Cons: Can be costly upfront. |
| HDPE Molds | Durable, resistant to chemicals, and suitable for high-volume production | Industrial applications, mass production | Pros: Long-lasting, excellent for high volumes. Cons: Limited design flexibility. |
| Aluminum Molds | Excellent thermal conductivity and durability | Automotive parts, aerospace components | Pros: High precision, reusable. Cons: Heavier and more expensive. |
| 3D Printed Molds | Customizable designs created through additive manufacturing | Prototyping, low-volume production | Pros: Highly customizable, quick turnaround. Cons: May not withstand high temperatures. |
| Plaster Molds | Inexpensive and easy to create but less durable | Art casting, decorative items | Pros: Low cost, simple to use. Cons: Fragile, limited lifespan. |
What Are the Characteristics of Silicone Molds and Their Suitability for B2B Buyers?
Silicone molds are prized for their flexibility and ability to capture intricate details, making them ideal for crafting and jewelry applications. They can be reused multiple times, which provides cost savings over time. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment, as high-quality silicone molds may come at a premium. However, their versatility and ease of demolding often justify the cost, especially for businesses focused on custom product designs.
How Do HDPE Molds Serve Industrial Applications Effectively?
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) molds are robust and chemical-resistant, making them suitable for industrial applications, including mass production of plastic components. They are known for their durability and capacity to handle high volumes, which is essential for manufacturers looking to scale operations. While HDPE molds offer long-lasting performance, buyers should be aware of their limited design flexibility compared to silicone molds. However, for straightforward applications, HDPE remains a go-to choice.
What Advantages Do Aluminum Molds Offer for Precision Manufacturing?
Aluminum molds are recognized for their excellent thermal conductivity and high durability, making them suitable for precision applications like automotive and aerospace components. They provide a high degree of precision and can be reused multiple times, which is advantageous for B2B buyers focused on quality. Although they come with a higher price tag and added weight, the benefits in terms of accuracy and longevity can outweigh these drawbacks for businesses requiring reliable production standards.
Illustrative image related to casting mold
Why Are 3D Printed Molds Gaining Popularity in Prototyping?
3D printed molds have emerged as a game-changer in prototyping and low-volume production due to their customizable nature. These molds can be rapidly produced, allowing businesses to bring designs to market quickly. However, buyers should consider that while they are highly adaptable, 3D printed molds may not withstand high temperatures as well as traditional materials. For companies prioritizing innovation and speed, 3D printed molds are an attractive option.
What Are the Key Considerations for Using Plaster Molds in Casting?
Plaster molds are an economical option for businesses involved in art casting and decorative items. They are straightforward to create and use, making them accessible for small-scale operations. However, their fragility and limited lifespan can pose challenges for B2B buyers looking for durability. While plaster molds are ideal for low-cost applications, businesses should assess their long-term needs to determine if the trade-offs are acceptable.
Key Industrial Applications of casting mold
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Casting Mold | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine components, such as cylinder heads and blocks | Enhanced performance and weight reduction | Material specifications, durability, and precision |
| Aerospace | Structural components for aircraft | High strength-to-weight ratio, compliance with safety standards | Aerospace-grade materials, certifications, and testing |
| Consumer Goods | Custom packaging solutions for products | Improved brand presentation and protection | Customization options, material compatibility |
| Construction | Architectural elements like decorative facades | Aesthetic appeal and structural integrity | Design flexibility, local regulations, and scalability |
| Jewelry and Crafting | Unique artistic pieces and molds for small items | Customization and personalization opportunities | Material quality, detail precision, and versatility |
How is Casting Mold Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, casting molds are crucial for producing engine components like cylinder heads and blocks. These molds allow manufacturers to create complex shapes with high precision, ensuring optimal performance and weight reduction. International buyers must consider specific material requirements, such as aluminum or iron, along with durability and thermal resistance. Additionally, sourcing from suppliers that comply with industry standards can enhance product reliability.
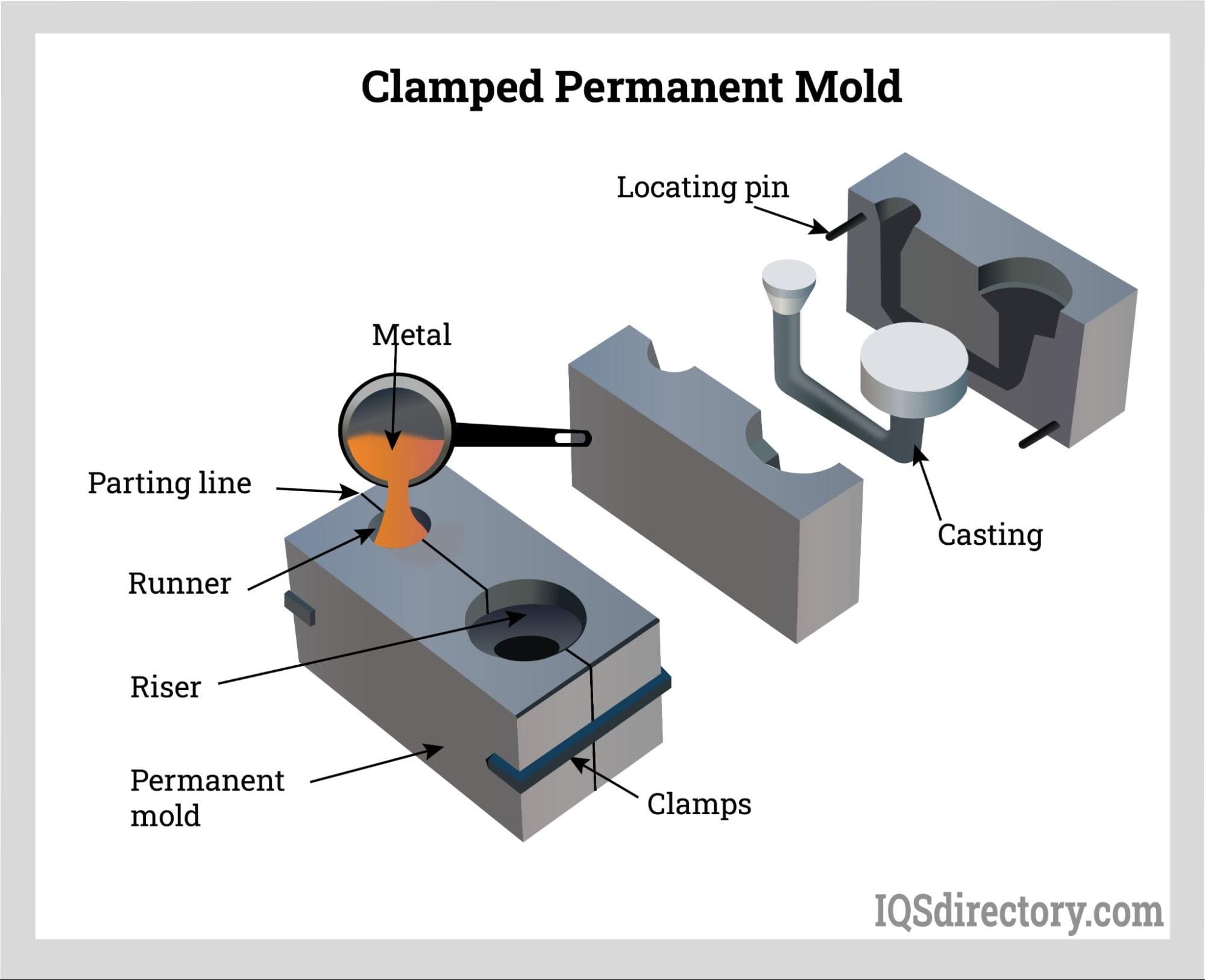
Illustrative image related to casting mold
What Role Does Casting Mold Play in Aerospace Applications?
Casting molds are essential in the aerospace industry for fabricating structural components that require high strength-to-weight ratios, such as brackets and housings. The use of advanced materials and techniques ensures compliance with stringent safety regulations. Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should prioritize suppliers with aerospace certifications and a proven track record in quality assurance to mitigate risks associated with high-stakes applications.
How Are Casting Molds Used in Consumer Goods Manufacturing?
In the consumer goods industry, casting molds are employed to create custom packaging solutions that enhance product presentation and protection. This application allows brands to differentiate their products in competitive markets. Buyers should focus on suppliers that offer customization options and are capable of producing molds in various materials. Additionally, understanding local regulations regarding packaging can be critical for compliance and market entry.
What are the Benefits of Casting Molds in Construction?
Casting molds are widely used in the construction industry for producing architectural elements, such as decorative facades and structural components. These molds offer design flexibility and can create intricate details that enhance aesthetic appeal while maintaining structural integrity. International buyers must consider local building regulations and the scalability of production when sourcing these molds, as well as the ability to adapt designs for specific project needs.
How Do Jewelry and Crafting Industries Utilize Casting Molds?
In the jewelry and crafting sectors, casting molds are utilized to create unique artistic pieces and intricate designs for small items. This application provides artisans with the opportunity to customize and personalize products, catering to diverse consumer preferences. Buyers should seek suppliers that offer high-quality materials and precision in detail, ensuring that molds can accommodate complex designs without compromising quality. Versatility in mold options is also vital for meeting various crafting needs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘casting mold’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Quality Assurance in Casting Projects
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, especially those in regions with emerging manufacturing capabilities, struggle with inconsistent quality in their casting products. The challenge often arises from using inferior molds that can lead to defects such as bubbles, blemishes, or uneven surfaces in the final castings. This inconsistency not only affects product quality but can also lead to costly reworks, delays, and diminished customer satisfaction.
The Solution: To mitigate quality issues, it’s essential to invest in high-grade molds designed for specific casting materials. Buyers should prioritize molds made from durable materials like high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or premium silicone, which can withstand various casting processes. When selecting molds, consider those with features that prevent defects, such as disassemblable designs that facilitate easy cleaning and maintenance. Additionally, utilizing mold release agents can enhance mold longevity and ensure smoother finishes. Engaging with manufacturers that offer trials or samples can also help ascertain quality before making larger investments.
Scenario 2: Sourcing the Right Mold for Diverse Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of sourcing molds that cater to a diverse range of applications, from automotive parts to artistic crafts. This difficulty is compounded in international markets where local suppliers may not offer specialized molds, leading to a reliance on generic options that do not meet specific project requirements.
The Solution: To address this sourcing issue, companies should develop strategic partnerships with reliable mold manufacturers that offer custom solutions tailored to unique applications. Conducting thorough market research to identify suppliers with a proven track record in your specific industry can yield better results. Additionally, leveraging online platforms that connect businesses with specialized mold makers can provide access to innovative designs and materials. When negotiating with suppliers, consider discussing your specific needs upfront to explore custom mold options that can enhance production efficiency and product quality.
Scenario 3: Navigating the Learning Curve for New Users
The Problem: New users entering the casting mold market often encounter a steep learning curve, leading to confusion over the correct usage of molds, casting materials, and finishing techniques. This lack of knowledge can result in poor outcomes, wasted resources, and frustration, particularly for businesses looking to scale their production quickly.
The Solution: To overcome this barrier, B2B buyers should invest in comprehensive training resources and engage with manufacturers that provide instructional materials, workshops, or online tutorials. Utilizing resources that explain the nuances of different casting materials, mold types, and best practices can significantly enhance user proficiency. Additionally, joining industry forums or online communities can facilitate knowledge sharing and provide insights from experienced users. For companies looking to streamline the onboarding process, consider appointing a dedicated expert or consultant to guide new team members through initial projects, ensuring they gain confidence and competence in using casting molds effectively.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for casting mold
What Are the Key Materials Used for Casting Molds?
Selecting the right material for casting molds is crucial for ensuring the quality and efficiency of the final product. Here, we analyze four common materials used in casting molds: silicone, high-density polyethylene (HDPE), aluminum, and epoxy resin. Each material presents distinct properties, advantages, and limitations that can significantly impact production and application.
How Does Silicone Perform in Casting Applications?
Silicone is a popular choice for casting molds due to its flexibility and high-temperature resistance. It can withstand temperatures ranging from -60°C to 200°C, making it suitable for various casting applications, including resin and concrete. Silicone molds are also resistant to corrosion and can produce intricate designs with a smooth finish.
Pros: Silicone molds are durable and reusable, which reduces long-term costs. They also require minimal release agents, making them easy to work with.
Cons: The initial cost of silicone molds can be high, and they may not be suitable for high-pressure applications, limiting their use in certain industries.
International Considerations: Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure that the silicone used complies with relevant standards such as REACH and RoHS, especially for food-grade applications.
What Advantages Does High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Offer?
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) is a thermoplastic known for its strength and durability. It is resistant to impact, moisture, and chemicals, making it ideal for casting molds that require longevity and robustness. HDPE molds can typically handle temperatures up to 120°C.
Pros: HDPE molds are cost-effective and easy to manufacture, which is advantageous for high-volume production. They also have a lower environmental impact compared to other plastics.
Cons: While HDPE is durable, it may not provide the same level of detail in casting as silicone, which can be a drawback for intricate designs.
International Considerations: Compliance with ASTM standards is essential for HDPE products, especially in regions like South America where regulations can vary significantly.
How Does Aluminum Compare in Terms of Casting Mold Applications?
Aluminum is a metal commonly used for casting molds, particularly in high-volume production settings. It offers excellent thermal conductivity, allowing for quicker cooling times, which can enhance production efficiency. Aluminum molds can withstand high pressures and temperatures, making them suitable for a variety of casting materials, including metals and plastics.
Pros: Aluminum molds are highly durable and can produce consistent results over time. They are also easier to machine compared to other metals, which can reduce manufacturing complexity.
Illustrative image related to casting mold
Cons: The initial investment for aluminum molds can be substantial, and they may require additional surface treatments to prevent corrosion.
International Considerations: Buyers should be aware of the need for compliance with international standards like ISO 9001 for quality management systems, particularly in Europe and the Middle East.
What Role Does Epoxy Resin Play in Casting Mold Production?
Epoxy resin is often used to create molds for casting due to its high strength and resistance to chemicals and moisture. It can be formulated to withstand high temperatures, making it versatile for various applications, including jewelry and art pieces.
Pros: Epoxy molds can achieve a high level of detail and clarity, making them ideal for decorative applications. They also allow for customization in terms of color and finish.
Cons: The curing process can be time-consuming, and the molds may not be as durable as silicone or aluminum, leading to a shorter lifespan.
International Considerations: Compliance with environmental standards is crucial, especially for epoxy products, as many regions enforce strict regulations on chemical usage.
Summary Table of Casting Mold Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for casting mold | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicone | Resin and concrete casting | Flexible and reusable | High initial cost | High |
| High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) | General-purpose molds for low to medium detail | Cost-effective and durable | Limited detail in casting | Medium |
| Aluminum | High-volume production for metals/plastics | Excellent thermal conductivity | High initial investment | High |
| Epoxy Resin | Decorative items and jewelry casting | High detail and clarity | Time-consuming curing process | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of key materials for casting molds, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for casting mold
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Casting Molds?
Manufacturing casting molds is a meticulous process that involves several critical stages to ensure high-quality outputs. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to source reliable molds that meet their production needs.
Material Preparation: How Are Casting Materials Selected and Processed?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. Casting molds can be made from various materials, including silicone, high-density polyethylene (HDPE), and metal alloys. Each material has its specific properties that make it suitable for different casting applications.
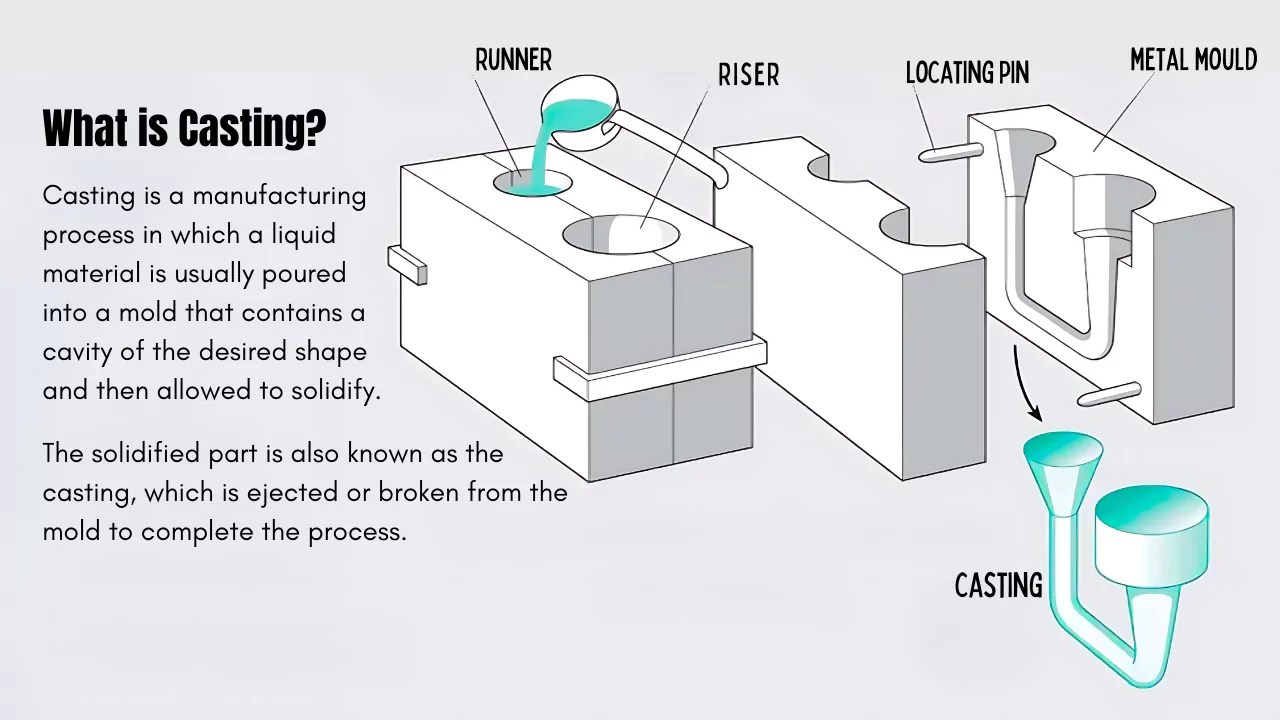
Illustrative image related to casting mold
For example, silicone molds are favored for their flexibility and ease of release, while HDPE molds are known for their durability and strength. The selection of raw materials often depends on the intended use of the mold, the type of casting material to be used, and the required precision.
Once the materials are selected, they undergo a preparation process that may include cutting, mixing, or heating, depending on the specific requirements of the mold design. This stage is crucial as it lays the foundation for the subsequent forming process.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of Casting Mold Production?
The forming stage is where the actual shape of the mold is created. This can involve various techniques such as injection molding, CNC machining, and handcrafting, each chosen based on the complexity and volume of the required molds.
-
Injection Molding: This method is commonly used for mass production of plastic molds, where molten material is injected into a mold cavity. It allows for precise shapes and high repeatability.
-
CNC Machining: For more complex designs, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is employed. This technique offers high precision and is often used for creating metal molds.
-
Handcrafting: In cases where customization is essential, handcrafting may be utilized. This method allows for bespoke designs but is generally more labor-intensive and time-consuming.
The choice of technique significantly impacts the cost, lead time, and quality of the final product. Buyers should assess their specific needs to determine which manufacturing method aligns best with their production goals.
How Is the Assembly Process Managed for Casting Molds?
After the forming stage, the next step is assembly. For molds that consist of multiple components, precise assembly is critical to ensure that all parts fit together seamlessly.
The assembly process may involve:
-
Aligning and Securing Components: This ensures that the mold operates correctly and produces consistent results. Fasteners, adhesives, or interlocking designs may be used to secure components.
-
Quality Checks: Conducting inspections at this stage helps to identify any issues that could affect mold performance.
Effective assembly not only enhances the functionality of the mold but also contributes to its longevity and reliability in the casting process.
What Finishing Techniques Are Used to Enhance the Quality of Casting Molds?
Finishing is the final stage in the manufacturing process and plays a vital role in the overall quality of casting molds. This stage may involve polishing, sanding, or applying coatings to improve surface finish and durability.
-
Polishing: A smooth surface finish is essential to prevent defects in cast products. Polishing techniques can help achieve a glass-like finish, which is particularly important for visible components.
-
Coatings: Applying a mold release agent or protective coating can enhance the mold’s longevity and performance. This is especially true for molds used with resins, where release agents help prevent sticking and extend the mold’s life.
Investing in quality finishing processes can reduce the need for post-production work, ensuring that the final castings meet the desired specifications.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in the Production of Casting Molds?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for casting molds. B2B buyers must understand how suppliers implement QA to ensure that the molds meet international standards and specific industry requirements.
What International Standards and Certifications Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems, are essential for ensuring that manufacturers maintain consistent quality in their processes. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE for European markets or API for the oil and gas sector can provide further assurance of quality and safety.
These certifications indicate that the manufacturer adheres to strict guidelines and undergoes regular audits to maintain compliance. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers with these certifications, as they reflect a commitment to quality and reliability.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that defects are caught early and that the final product meets specifications. Common QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet required specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during the manufacturing process help catch any deviations from quality standards early on.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection of the finished molds is conducted to verify their quality and performance before they are shipped to customers.
Implementing these checkpoints allows manufacturers to maintain high-quality standards and minimize waste, which is critical for B2B buyers seeking cost-effective solutions.
Illustrative image related to casting mold
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers should take an active role in verifying the quality control practices of their suppliers. Here are some actionable steps:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of the manufacturing facility can provide insights into the supplier’s processes and quality management systems.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide detailed reports on their quality control processes, including results from inspections and tests.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent inspectors can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality practices and product reliability.
By taking these steps, B2B buyers can ensure that they are partnering with suppliers who prioritize quality and compliance.
What Nuances Should International Buyers Consider Regarding Quality Control?
When sourcing casting molds from international suppliers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers should consider the following nuances:
-
Cultural Differences: Different regions may have varying standards and practices for quality assurance. Understanding these cultural differences can help buyers navigate expectations and communication more effectively.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different countries may have specific regulations that must be adhered to. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers are compliant with local laws and international standards.
-
Language Barriers: Communication can be challenging when dealing with international suppliers. Clear documentation and open lines of communication are essential to avoid misunderstandings.
By being aware of these nuances, B2B buyers can foster stronger relationships with suppliers and ensure that their quality requirements are met consistently.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for casting molds are crucial for ensuring that B2B buyers receive reliable, high-quality products. Understanding these aspects not only aids in selecting the right suppliers but also contributes to the overall success of their operations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘casting mold’
This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure casting molds. By following these steps, you can ensure that you make informed decisions, select the right suppliers, and ultimately acquire high-quality molds that meet your production needs.
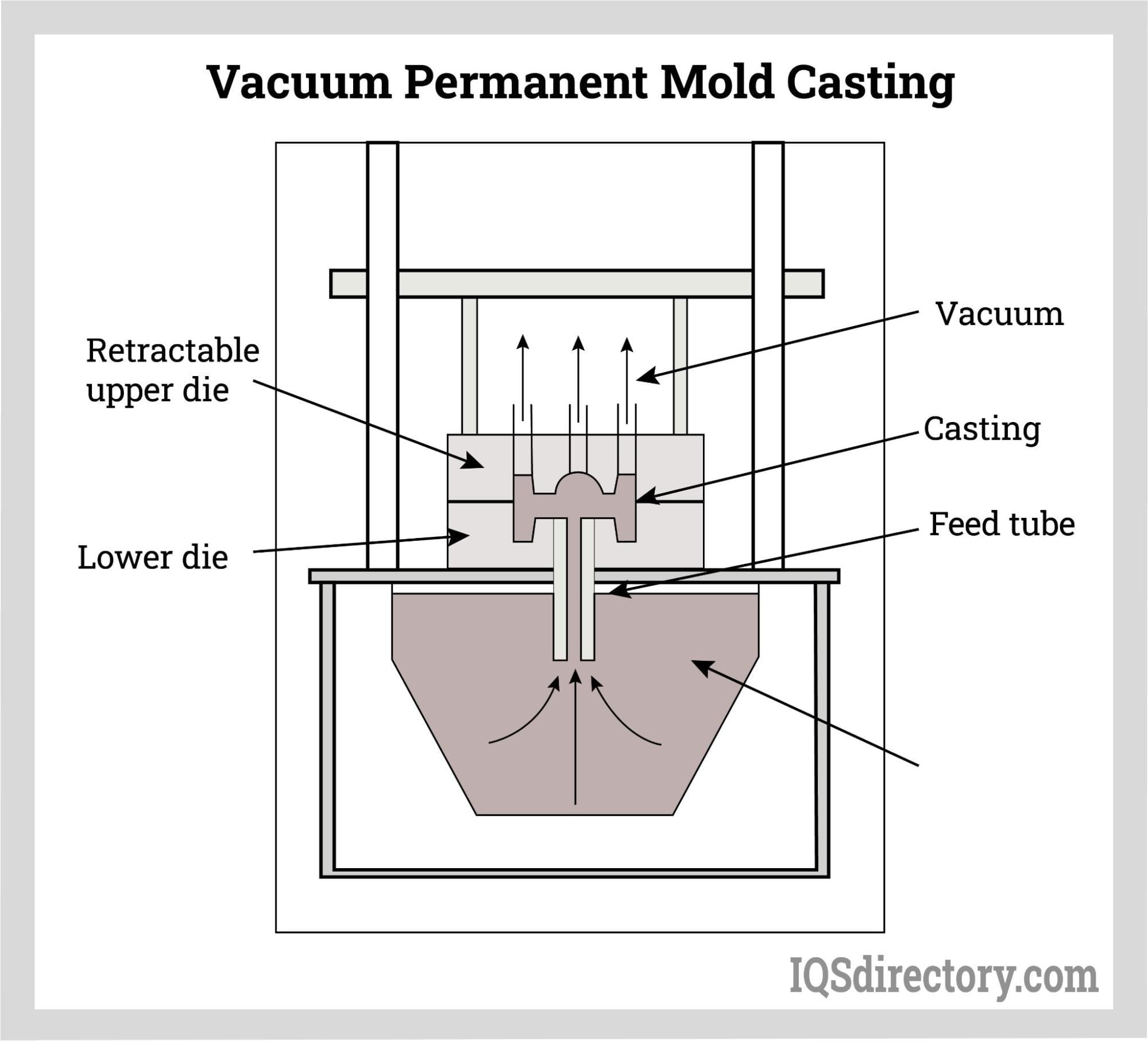
Illustrative image related to casting mold
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by outlining the specific requirements for the casting molds you need. Consider factors such as the type of material you will be casting (e.g., resin, metal), the dimensions and shapes of the molds, and any unique features like adjustable plugs or multiple cavities. Clearly defined specifications will help you communicate your needs to suppliers and ensure you receive appropriate options.
Step 2: Research Material Options
Understanding the different materials used in casting molds is crucial for your sourcing decision. Common materials include silicone and high-density polyethylene (HDPE), each offering distinct benefits. For instance, silicone molds provide flexibility and ease of use, while HDPE molds are known for their durability and stability. Evaluate which material aligns best with your production processes and end-product requirements.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s essential to conduct thorough evaluations of potential suppliers. Look for established companies with a proven track record in the industry. Request company profiles, client testimonials, and case studies that demonstrate their experience with similar products. Additionally, check if they have the necessary certifications and quality assurance processes in place.
Step 4: Request Samples
Obtaining samples of the molds you are considering is an important step. This allows you to assess the quality of the materials and craftsmanship firsthand. Evaluate how the molds perform with your intended casting material and whether they meet your dimensional and finish specifications. Be prepared to provide feedback to suppliers based on your testing.
Step 5: Verify Production Capabilities
Ensure that the supplier can meet your production volume requirements. Ask about their manufacturing processes, lead times, and capacity to scale production as your needs grow. A supplier who can adapt to your demands will be invaluable for maintaining consistent supply without compromising quality.
Step 6: Discuss After-Sales Support
Inquire about the after-sales support offered by the supplier. This includes warranty information, replacement parts availability, and technical support for troubleshooting. A supplier with robust after-sales services can help you minimize downtime and ensure a smooth production process.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve selected a supplier, it’s crucial to negotiate clear terms and conditions. Discuss pricing, payment terms, delivery schedules, and any penalties for late delivery or quality issues. Ensure that all agreements are documented to prevent misunderstandings down the line.
By following this checklist, you will be well-equipped to navigate the procurement process for casting molds effectively, ensuring you select the right suppliers and products for your business needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for casting mold Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Casting Mold Manufacturing?
When sourcing casting molds, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type of material used significantly influences cost. Common materials for casting molds include silicone and high-density polyethylene (HDPE). Silicone molds, known for their flexibility and durability, may have a higher initial cost but can offer better performance and longevity compared to less expensive alternatives.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary depending on the location of manufacturing. Regions with lower wage rates may offer more competitive pricing, but it is essential to consider the trade-offs in quality and expertise.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to the production facility, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient factories may have lower overhead costs, allowing them to provide more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, especially for custom molds. Investing in high-quality tooling can lead to better mold performance and longer life, ultimately reducing the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures that molds meet specifications and quality standards. This may add to initial costs but can save money in the long run by minimizing defects and rework.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely depending on the origin and destination of the molds. Factors such as weight, dimensions, and shipping method will impact overall logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a markup to cover their costs and ensure profitability. Understanding the typical margin in your target market can aid in negotiating better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Casting Mold Costs?
Several factors can significantly influence the pricing of casting molds:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk orders often lead to lower per-unit costs. Negotiating minimum order quantities (MOQs) can result in significant savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom molds tailored to specific applications may come at a premium. Standard molds are generally more cost-effective, but buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the costs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and molds that meet international quality certifications (like ISO) may command higher prices. However, investing in certified products can enhance reliability and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier play a critical role in pricing. Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge more, but they often provide better support and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for managing shipping costs and responsibilities. Different terms may affect the final price and the risk associated with transportation.
What Tips Can B2B Buyers Use for Cost-Efficiency in Sourcing Casting Molds?
To maximize cost-efficiency when sourcing casting molds, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Build strong relationships with suppliers and be transparent about your needs. Discuss pricing openly and explore volume discounts or long-term contracts for better terms.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership: Instead of focusing solely on the initial purchase price, assess the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational efficiency, and lifespan of the molds. This holistic view can reveal the most cost-effective options.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Be aware of regional market dynamics. For example, sourcing from Southeast Asia may offer lower costs due to favorable labor rates, while European suppliers might provide higher quality and faster delivery times.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Regularly monitor market trends and supplier capabilities to identify potential cost-saving opportunities. Keeping abreast of innovations in materials and manufacturing techniques can lead to better sourcing decisions.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for casting molds can vary significantly based on the factors discussed. The information provided is indicative and should be used as a guideline for negotiation and planning purposes. Always request quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing tailored to your specific requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing casting mold With Other Solutions
When it comes to manufacturing and production, choosing the right method for creating components is crucial. While casting molds are a popular choice for many applications, there are several viable alternatives that can achieve similar results. Understanding these alternatives can help businesses make informed decisions based on their specific needs and constraints.
| Comparison Aspect | Casting Mold | 3D Printing | CNC Machining |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High detail and durability | Good for complex geometries | Excellent precision and finish |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment | High setup costs, lower per unit | High initial costs, variable per unit |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires mold design and production | Requires CAD design skills | Requires skilled operators |
| Maintenance | Regular care needed to prolong life | Minimal maintenance | Regular calibration and upkeep |
| Best Use Case | High-volume production of consistent parts | Custom, low-volume runs, prototypes | Precision parts in small to medium runs |
What are the Benefits and Drawbacks of 3D Printing as an Alternative?
3D printing offers an innovative approach to manufacturing, particularly advantageous for creating complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible with traditional casting methods. The initial costs for 3D printing can be high, especially for industrial-grade printers, but the cost per unit decreases significantly with lower production volumes. Additionally, 3D printing allows for rapid prototyping, enabling businesses to test designs before committing to full production. However, the materials used in 3D printing may not always match the durability of those produced with casting molds, which can limit its application in high-stress environments.
Illustrative image related to casting mold
How Does CNC Machining Compare to Casting Molds?
CNC machining stands out for its precision and ability to produce high-quality finishes. This method is particularly well-suited for producing parts with tight tolerances and complex shapes. The downside is that the initial investment in CNC machinery can be substantial, along with the need for skilled operators to manage the process. CNC machining is typically more efficient for small to medium production runs, but it may not be cost-effective for high-volume production compared to casting molds, which excel in producing large quantities of consistent parts.
Which Option is Best for Your Business Needs?
Selecting the right manufacturing method depends on various factors, including production volume, design complexity, budget, and material requirements. Casting molds are ideal for high-volume production where uniformity and durability are paramount. In contrast, 3D printing is more suitable for businesses focusing on customization and rapid prototyping, while CNC machining is best for precision engineering applications.
In conclusion, B2B buyers should carefully evaluate their unique requirements and constraints when choosing between casting molds, 3D printing, and CNC machining. By considering factors such as performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases, companies can align their manufacturing processes with their business goals, ensuring a competitive edge in their respective markets.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for casting mold
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Casting Molds?
Understanding the technical specifications of casting molds is essential for international buyers to ensure product quality and compatibility. Here are some critical properties to consider:
1. Material Grade
Casting molds are typically made from various materials, including silicone, high-density polyethylene (HDPE), and urethane. Each material has distinct properties that affect durability, flexibility, and cost. For example, silicone molds are known for their flexibility and ease of demolding, making them ideal for intricate designs. In contrast, HDPE molds offer rigidity and long-term durability, suitable for repeated use in high-volume production.
2. Dimensional Tolerance
Dimensional tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in mold dimensions. This specification is crucial for ensuring that the final castings meet the required specifications and fit correctly in their intended applications. A tighter tolerance can lead to higher manufacturing costs but is often necessary for precision components, particularly in industries such as automotive and aerospace.
3. Temperature Resistance
The ability of a mold to withstand high temperatures is vital, especially when working with materials that require curing or hardening at elevated temperatures. Molds made from heat-resistant materials can maintain their shape and structural integrity under stress, preventing defects in the final product. This property is particularly important in regions with high ambient temperatures or when using thermosetting resins.
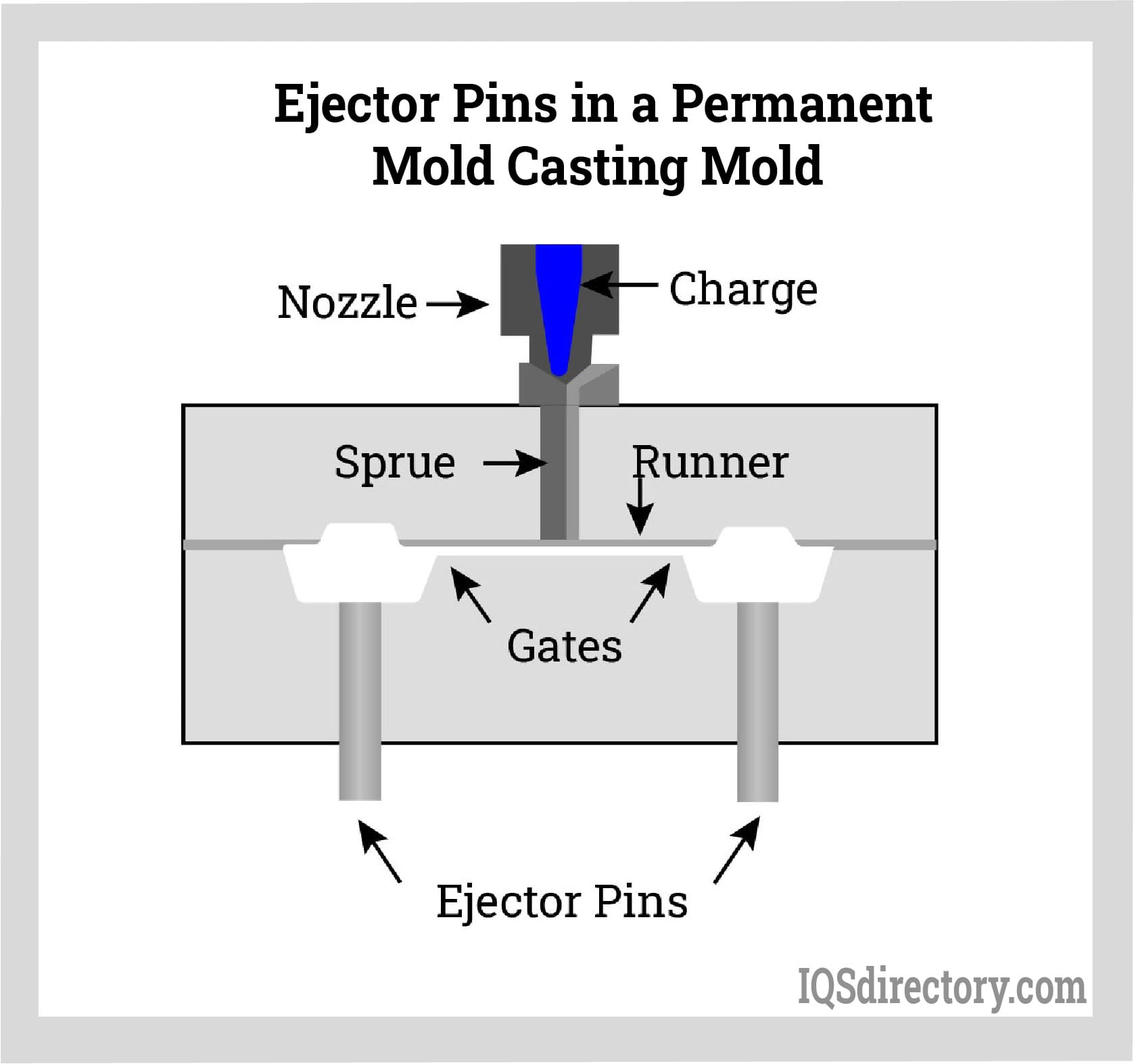
Illustrative image related to casting mold
4. Surface Finish
The surface finish of a mold affects the final appearance and quality of the cast product. A smooth surface finish can lead to a glass-like finish on the final casting, while a rough surface may require additional finishing processes, such as sanding or polishing. Understanding the required surface finish can help buyers choose the right mold for their specific casting needs, ultimately impacting production efficiency and cost.
5. Cavity Design
The design of the mold cavity plays a critical role in the type and complexity of the castings produced. Factors such as the number of cavities, shape, and size directly influence production volume and cycle time. Buyers should consider their production needs when selecting molds to ensure they can achieve the desired output efficiently.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Casting Mold Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B marketplace. Here are several key terms to know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers seeking specific components or molds tailored to their product lines.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is particularly significant for international buyers, as it can impact inventory management and upfront investment costs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. This process helps buyers compare offers and negotiate better deals, ensuring they receive the best value for their investment.

Illustrative image related to casting mold
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping and delivery. Understanding these terms can help international buyers navigate logistics and reduce the risk of misunderstandings during the purchasing process.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. This is a critical factor for businesses that rely on just-in-time inventory systems, as longer lead times can disrupt production schedules.
By grasping these essential technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing casting molds, ensuring they select the right products for their specific applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the casting mold Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Casting Mold Sector?
The casting mold market is witnessing transformative changes driven by technological advancements and evolving buyer preferences. Key global drivers include the increasing demand for customized and intricate designs across various industries, such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods. The rise of 3D printing technology is revolutionizing mold production, enabling faster prototyping and reducing waste. This trend is particularly beneficial for international buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where cost-effective and efficient sourcing is critical.
Another significant trend is the integration of digital solutions in the sourcing process. Platforms that offer real-time inventory management and supplier performance tracking are gaining traction among B2B buyers. This shift not only enhances transparency but also aids in making informed purchasing decisions, especially for companies in Europe and the Middle East looking for reliable suppliers. Additionally, the market is seeing a surge in demand for high-quality materials, such as silicone and high-density polyethylene (HDPE), which are favored for their durability and versatility in various applications.
Furthermore, sustainability is becoming a central theme, with buyers increasingly prioritizing eco-friendly options. This focus on sustainable practices is reshaping sourcing strategies, compelling manufacturers to adopt greener production methods and materials. The ongoing digitalization of the supply chain is also streamlining operations, making it easier for buyers to connect with suppliers who align with their sustainability goals.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Casting Mold Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are no longer optional considerations in the casting mold sector; they are essential for maintaining competitive advantage and meeting regulatory requirements. The environmental impact of traditional mold production processes, including high energy consumption and waste generation, has prompted many international buyers to seek greener alternatives. By prioritizing sustainable materials, such as recycled plastics and bio-based resins, companies can significantly reduce their carbon footprints.
Ethical supply chains also play a crucial role in enhancing brand reputation and customer loyalty. Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East are particularly focused on suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to ethical labor practices and environmental stewardship. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and FSC certification for sustainable sourcing of materials can serve as important indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, the growing consumer awareness around environmental issues is influencing purchasing decisions. Companies that embrace green certifications and sustainable materials not only comply with regulations but also attract a more conscientious customer base. This shift is particularly relevant for B2B buyers in markets with stringent environmental standards, such as Germany, where sustainability is a key driver of business success.
What Is the Brief Evolution of the Casting Mold Industry?
The casting mold industry has evolved significantly over the decades, transitioning from traditional manual methods to advanced automated processes. Initially dominated by metal molds, the industry saw a gradual shift towards the use of synthetic materials like silicone and HDPE, which offer greater flexibility and ease of use. The introduction of CNC machining and 3D printing technologies has further transformed mold manufacturing, enabling unprecedented precision and customization.

Illustrative image related to casting mold
Historically, the casting process was labor-intensive, often leading to longer lead times and higher costs. However, advancements in technology have streamlined production, allowing for rapid prototyping and shorter turnaround times. Today, the industry is characterized by a blend of craftsmanship and technology, where skilled artisans and engineers collaborate to create innovative solutions tailored to specific market needs. As the demand for customized products continues to rise, the evolution of the casting mold sector is expected to accelerate, paving the way for new opportunities in global markets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of casting mold
-
How do I choose the right casting mold for my production needs?
Selecting the appropriate casting mold depends on several factors, including the material being cast, the desired finish, and production volume. For example, silicone molds are great for small batches and intricate designs due to their flexibility, while HDPE molds are ideal for larger production runs due to their durability and ease of use. Assess your project requirements, including the type of resin or material you will use, the complexity of the design, and whether you need a reusable mold. Consulting with suppliers can provide insights based on their expertise and product offerings. -
What are the benefits of using silicone vs. HDPE casting molds?
Silicone molds offer flexibility and are excellent for detailed designs, making them suitable for small-scale productions. They can withstand a variety of resins and are easy to demold. On the other hand, HDPE molds are more rigid and designed for high-volume production, providing durability and a longer lifespan. They are often more cost-effective for bulk casting projects. The choice ultimately depends on your production scale, design complexity, and budget constraints. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQs) should I expect when sourcing casting molds?
MOQs for casting molds can vary significantly by supplier and the type of mold. Generally, custom molds may have higher MOQs due to the costs associated with their production. Standard molds might have lower MOQs, sometimes as few as 10-50 units. When negotiating with suppliers, inquire about their MOQs upfront and whether they offer discounts for larger orders. This is crucial for managing costs, especially for international purchases. -
How can I ensure quality control when sourcing casting molds internationally?
Quality assurance is critical when sourcing casting molds from international suppliers. Start by vetting suppliers through online reviews, industry certifications, and asking for samples of their molds. Consider conducting factory audits or hiring third-party inspection services to verify manufacturing standards. Establish clear quality expectations in your purchase agreements, including tolerances and finish specifications, to minimize discrepancies upon receipt. -
What payment terms should I negotiate with suppliers for casting molds?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier and the nature of the order. Common arrangements include a deposit upfront (often 30-50%) with the balance due upon shipment. For larger orders, you might negotiate extended payment terms or letter of credit options to reduce upfront cash flow pressure. Always discuss payment methods (e.g., wire transfer, PayPal) and ensure they align with your company’s financial practices and international trade regulations. -
What are the logistics considerations when importing casting molds?
Logistics is a crucial aspect of sourcing casting molds internationally. Consider shipping methods (air vs. sea), which can affect costs and delivery times. Ensure you understand customs regulations and potential tariffs in your country, which can impact total costs. Collaborating with a freight forwarder can help streamline the shipping process, from documentation to delivery. Lastly, factor in lead times for production and shipping when planning your inventory. -
Can I customize casting molds to fit my specific product requirements?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for casting molds. This can include modifications in size, shape, or even the materials used. Custom molds are particularly beneficial for unique product designs or specific production requirements. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and, if possible, prototypes or sketches to ensure the supplier understands your vision. Be aware that custom molds may require longer lead times and higher costs. -
What common issues should I be aware of when using casting molds?
Common issues with casting molds include bubbles, blemishes, and incomplete casts, often resulting from improper mixing of resin or inadequate mold release agents. To mitigate these problems, ensure thorough mixing and apply appropriate mold release sprays to extend the lifespan of your molds. Additionally, consider post-processing methods, such as sanding or polishing, to achieve the desired finish. Regular maintenance and proper storage of molds can also help prevent deterioration and ensure consistent quality in your casts.
Top 3 Casting Mold Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Smooth-On – Mold Max™ Silicones
Domain: smooth-on.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Smooth-On, Inc. offers a wide range of mold making and casting materials including rubbers, plastics, foams, and more. Key products include Mold Max™ Silicones for capturing fine details, Si-Tac II Silicone Fabric and Textile Adhesive, and Alja-Safe™ Acrobat Fiber-Reinforced “Non-Sag” Life Casting Alginate. They also provide polymer gypsum for various applications such as hand lay up, rotocasting,…
2. ACTÍVA – Key Products
Domain: activaproducts.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: ACTÍVA offers a wide selection of casting and mold making materials that are 100% Wheat & Gluten Free, Non-Toxic & Non-Carcinogenic. Key products include:
1. InstaMold – A temporary mold-making compound safe for body casting, allowing for 3D replication of solid objects.
2. PermaStone – A durable casting compound that acts like plaster but dries like stone, can be painted.
3. Li-Qua-Che – Desig…
3. Oomoo – Silicone Molding Essentials
Domain: instructables.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Oomoo 30 silicone for molding; 1-to-1 ratio mixing; resin for casting; mold release agent; blue tape for mold preparation; tools for cutting and pouring; vacuum chamber for air bubble removal; sander for vibration to release bubbles.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for casting mold
In the dynamic landscape of casting mold procurement, strategic sourcing emerges as a crucial component for international buyers. Understanding the diverse offerings—ranging from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) molds to silicone options—enables businesses to select products that align with their specific production needs. Key takeaways include the importance of quality in mold construction, which directly impacts the final output’s finish and durability. Leveraging established suppliers who offer customizable solutions can significantly enhance operational efficiency and reduce production costs.
As B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate the complexities of sourcing, maintaining a focus on innovation and sustainability will be vital. The global market is leaning towards environmentally friendly materials and manufacturing processes, underscoring the need for strategic partnerships with suppliers who prioritize these values.
Looking ahead, the casting mold industry is poised for growth, driven by advancements in materials and technology. Buyers are encouraged to engage proactively with suppliers, explore new product lines, and invest in training for optimal mold usage. By doing so, businesses can not only enhance their production capabilities but also position themselves competitively in an increasingly interconnected marketplace.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.