A Deep Dive into Air To Air Heat Exchanger Solution
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for air to air heat exchanger
In an increasingly competitive global market, sourcing an efficient air-to-air heat exchanger can be a daunting task for B2B buyers. The challenge lies not only in identifying the right technology but also in ensuring that the chosen solution meets specific operational requirements, complies with local regulations, and delivers optimal energy efficiency. This guide aims to demystify the complexities surrounding air-to-air heat exchangers, offering insights into various types, applications, and the nuances of supplier vetting.
We delve into the critical factors that influence purchasing decisions, including cost considerations, installation complexities, and performance metrics tailored to different climates and industries. From the energy-efficient systems ideal for residential ventilation in Europe to robust models suited for high-temperature applications in the Middle East, this guide equips international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, and Europe with actionable knowledge.
By synthesizing expert insights and practical advice, we empower businesses to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their unique operational needs. Whether you are seeking to enhance indoor air quality or reduce energy costs, understanding the diverse landscape of air-to-air heat exchangers is essential for achieving sustainable and profitable outcomes.
Understanding air to air heat exchanger Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crossflow | Simple design with two air streams crossing each other | HVAC systems, residential ventilation | Pros: Cost-effective, straightforward installation. Cons: Lower efficiency compared to counterflow. |
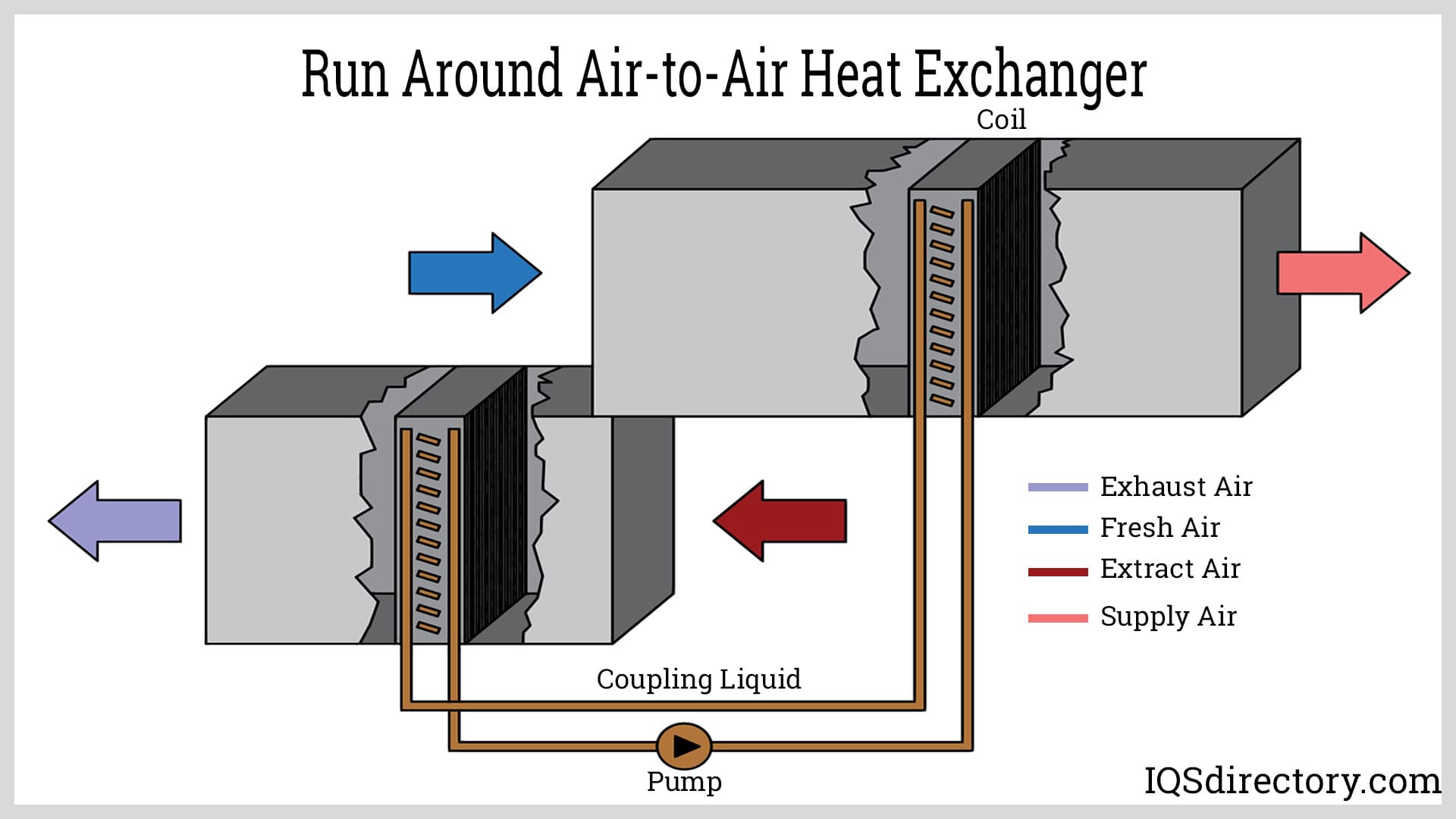
| Counterflow | Air flows in opposite directions, maximizing heat transfer | Industrial heating, large commercial buildings | Pros: Higher efficiency, better heat recovery. Cons: More complex design, potentially higher installation costs. |
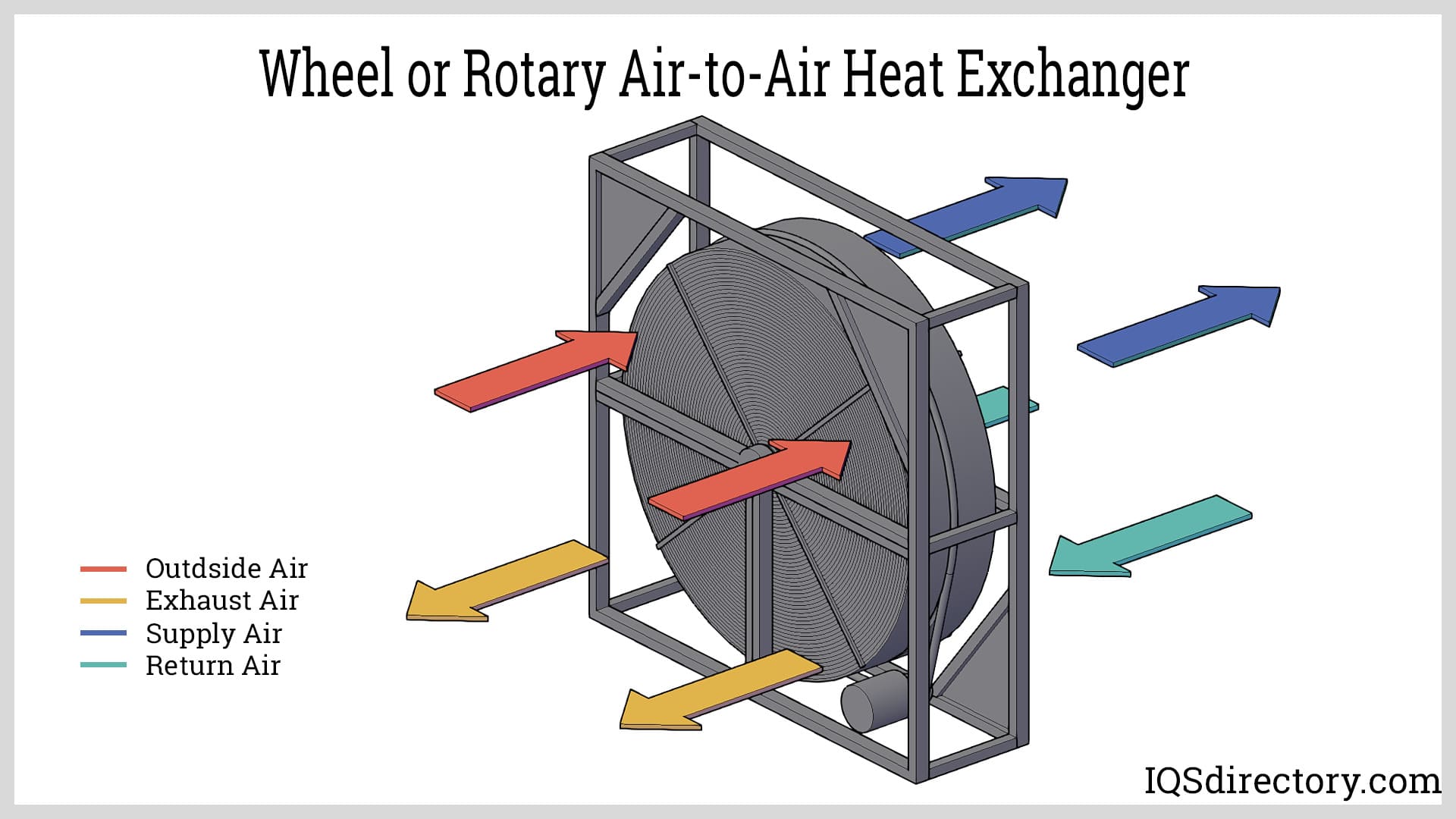
| Rotary Heat Exchanger | Uses a rotating wheel to transfer heat between air streams | Large-scale ventilation systems, data centers | Pros: High efficiency, suitable for variable loads. Cons: Requires regular maintenance, larger footprint. |
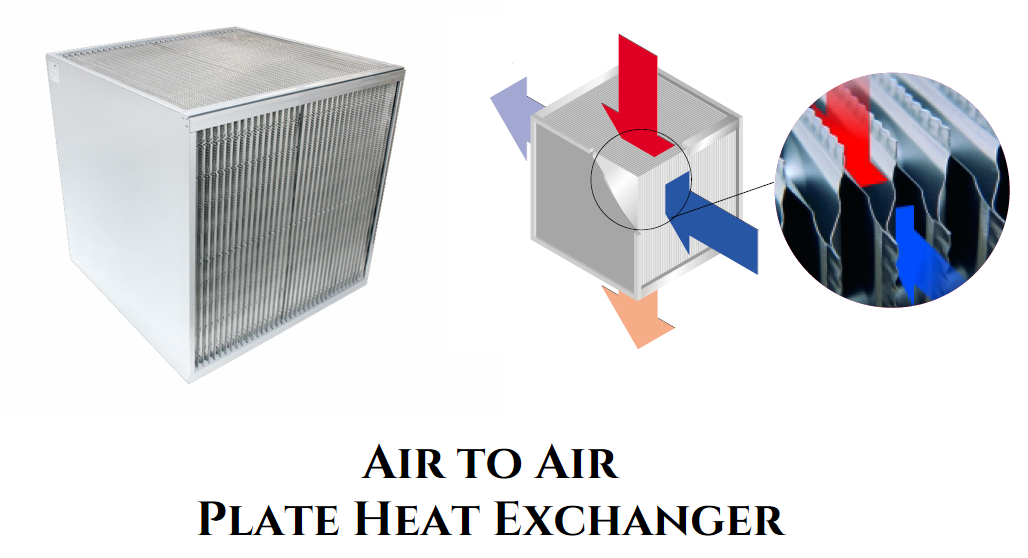
| Glued Heat Exchanger | Lightweight design using silicon-free glue for connections | Low to medium temperature applications | Pros: Easy to install, cost-effective. Cons: Limited to lower temperatures, potential durability concerns. |
| Welded Heat Exchanger | Strong construction suitable for high temperatures and loads | Food processing, chemical plants | Pros: High durability, customizable designs. Cons: Heavier, more complex installation process. |
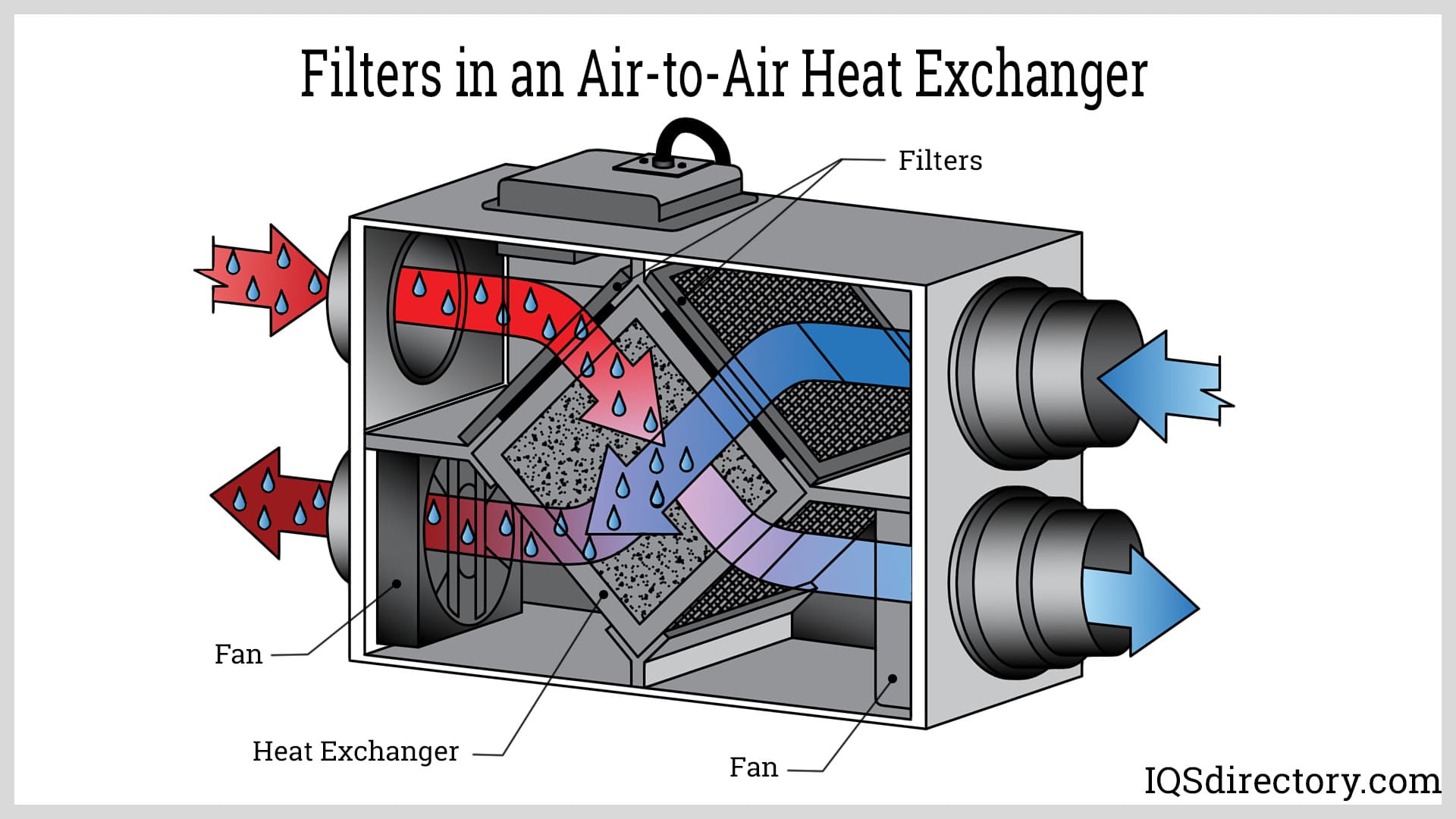
What Are the Key Characteristics of Crossflow Heat Exchangers?
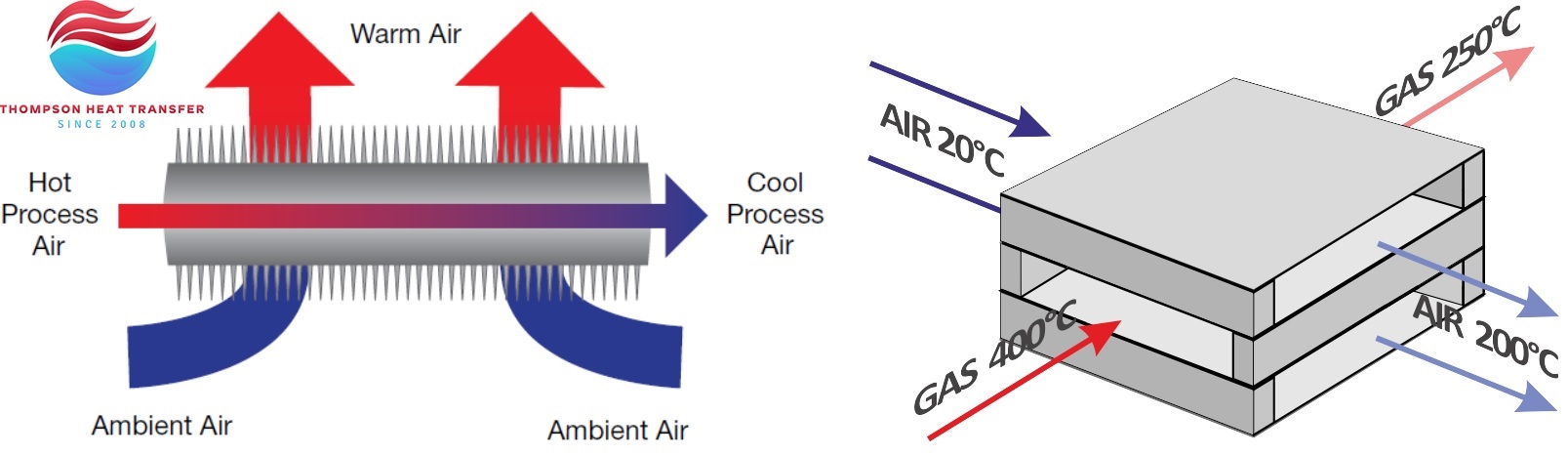
Crossflow heat exchangers feature a straightforward design where two air streams intersect at right angles. This type is primarily used in HVAC systems and residential ventilation due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of installation. However, while crossflow exchangers are budget-friendly, they often deliver lower efficiency in heat recovery compared to more advanced designs. Buyers should consider the specific heating and cooling needs of their applications, especially in regions with extreme climates.
Illustrative image related to air to air heat exchanger
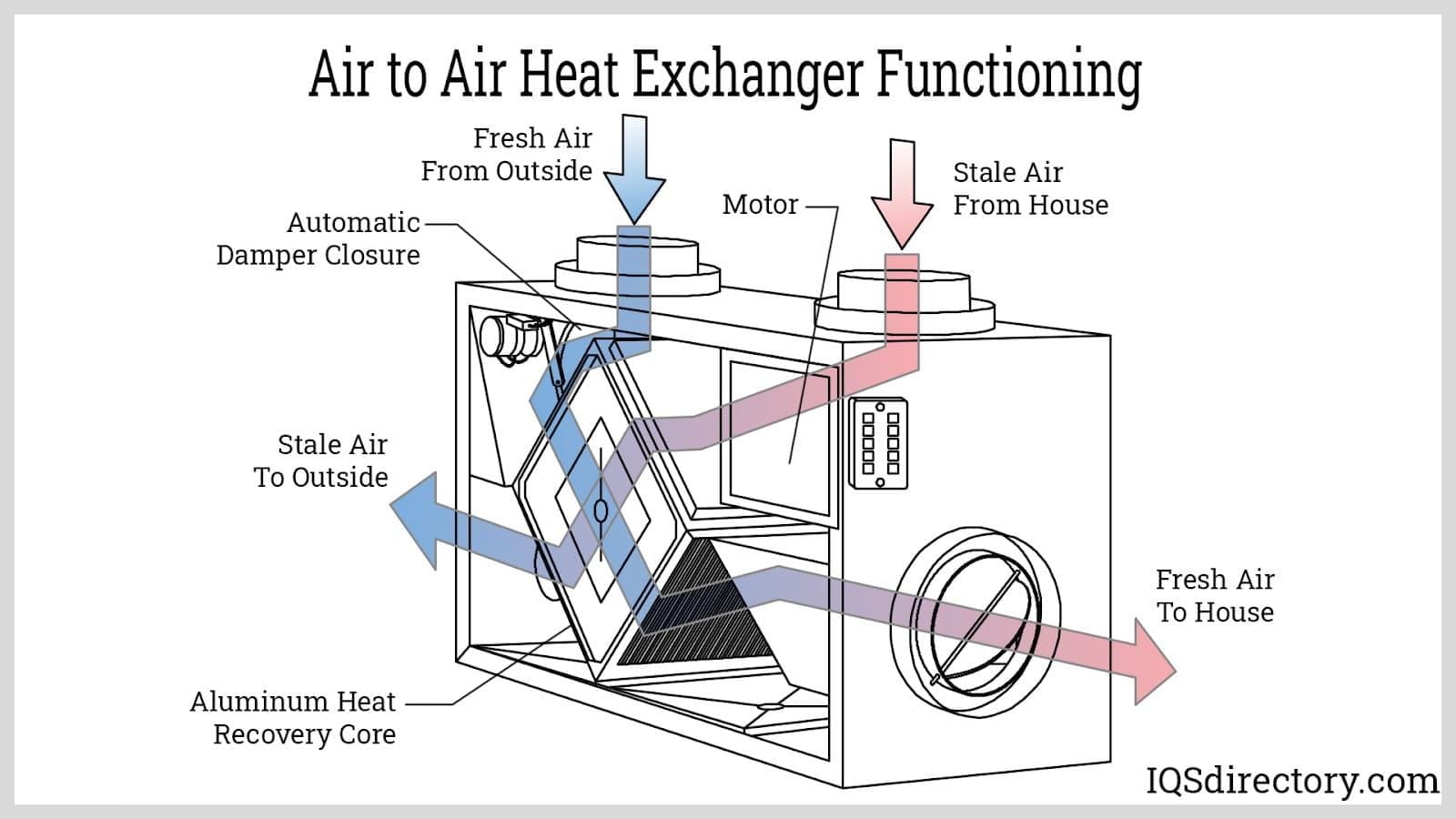
How Do Counterflow Heat Exchangers Maximize Efficiency?
Counterflow heat exchangers operate with air flowing in opposite directions, allowing for a more effective heat transfer process. This design is ideal for industrial heating and large commercial buildings where energy efficiency is paramount. Although they tend to have higher upfront costs and more complex installation requirements, the long-term energy savings can justify the investment. B2B buyers should evaluate their operational demands and potential energy savings when considering this option.
Why Choose Rotary Heat Exchangers for Large-Scale Applications?
Rotary heat exchangers utilize a rotating wheel to facilitate heat exchange, making them highly efficient for large-scale ventilation systems, such as those found in data centers. They are particularly effective in scenarios with fluctuating air loads. While they offer exceptional energy recovery, regular maintenance is necessary to ensure optimal performance, and their larger footprint may require more space. Businesses should assess their operational scale and maintenance capabilities before opting for this solution.
What Are the Benefits of Glued Heat Exchangers?
Glued heat exchangers utilize a lightweight construction method where silicon-free glue connects the components, making them suitable for low to medium temperature applications. Their ease of installation and cost-effectiveness make them attractive for businesses looking to minimize upfront expenses. However, they are limited to lower temperature ranges, which may not be suitable for all industrial applications. Buyers should consider their temperature requirements and installation constraints when evaluating this option.
Illustrative image related to air to air heat exchanger
When Should Welded Heat Exchangers Be Considered?
Welded heat exchangers are designed for high-temperature applications and can withstand greater loads, making them ideal for industries such as food processing and chemical plants. Their robust construction offers high durability and can be customized to meet specific operational needs. However, they are typically heavier and involve a more complex installation process. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of durability and customization against the installation challenges and costs associated with this type of heat exchanger.
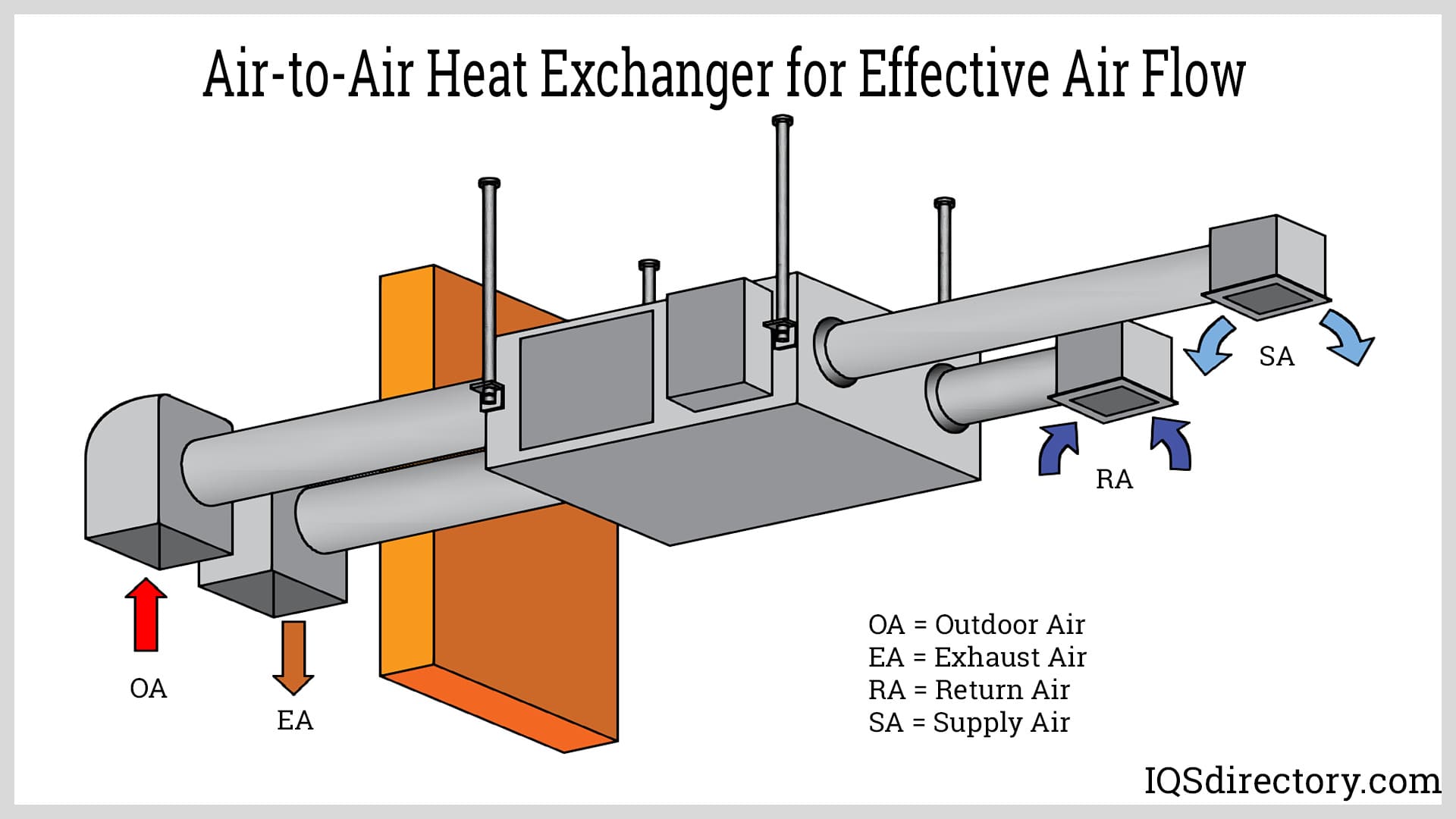
Key Industrial Applications of air to air heat exchanger
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of air to air heat exchanger | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Processing | Preheating air for drying processes in food production | Increases energy efficiency by recovering heat from exhaust air, reducing operational costs. | Need for robust materials to handle high humidity and temperatures; compliance with food safety standards. |
| HVAC Systems | Ventilation in commercial buildings | Enhances indoor air quality while reducing heating and cooling costs through efficient heat recovery. | Consideration for unit size and airflow capacity based on building design; energy efficiency ratings. |
| Pharmaceutical Manufacturing | Climate control in clean rooms | Maintains stringent temperature and humidity levels essential for product integrity and compliance. | Specifications for low contamination risk; materials resistant to chemical exposure. |
| Data Centers | Cooling of IT equipment | Prevents overheating by efficiently managing airflow, thus improving equipment reliability and lifespan. | Requirements for high air volume flow and energy efficiency; compatibility with existing cooling systems. |
| Automotive Industry | Temperature regulation in paint booths | Ensures optimal conditions for paint application, enhancing finish quality and reducing waste. | Durability under high temperatures and potential exposure to solvents; customization for specific booth sizes. |
In the food processing industry, air-to-air heat exchangers are used primarily for preheating air in drying processes. By recovering heat from exhaust air, these systems significantly enhance energy efficiency, leading to lower operational costs. Buyers in this sector must consider the robustness of materials to handle high humidity and temperatures, as well as compliance with food safety standards to ensure product integrity.
In HVAC systems for commercial buildings, air-to-air heat exchangers play a critical role in ventilation. They improve indoor air quality while simultaneously reducing heating and cooling costs through effective heat recovery. For B2B buyers, key considerations include the unit’s size and airflow capacity, which must align with the specific building design, as well as the energy efficiency ratings to ensure long-term savings.
Pharmaceutical manufacturing relies heavily on maintaining strict climate control in clean rooms. Air-to-air heat exchangers help regulate temperature and humidity levels, which are essential for product integrity and regulatory compliance. Buyers in this sector need to focus on specifications that minimize contamination risk and select materials that can withstand potential chemical exposure.
Data centers utilize air-to-air heat exchangers to manage airflow and prevent overheating of IT equipment. These systems enhance equipment reliability and lifespan by ensuring optimal cooling. When sourcing, businesses should prioritize high air volume flow capabilities and energy efficiency to align with their existing cooling systems while minimizing operational costs.
In the automotive industry, air-to-air heat exchangers are vital for temperature regulation in paint booths. These systems create optimal conditions for paint application, which enhances finish quality and reduces waste. Buyers must consider the durability of the exchangers under high temperatures and their ability to withstand exposure to solvents, as well as the need for customization to fit specific booth sizes.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘air to air heat exchanger’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inefficient Energy Recovery Leading to High Operational Costs
The Problem: Many businesses investing in air-to-air heat exchangers face the challenge of inefficient energy recovery, which can significantly inflate operational costs. In regions with extreme temperatures, such as the Middle East or Europe during winter, the inability of the heat exchanger to efficiently transfer heat from exhaust air to incoming fresh air can result in higher energy consumption. This inefficiency not only affects the bottom line but also raises concerns regarding sustainability and compliance with energy efficiency regulations.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should prioritize selecting air-to-air heat exchangers that feature high thermal efficiency ratings, typically above 80%. When sourcing these systems, it’s crucial to consult technical specifications and performance data provided by manufacturers. Look for units with advanced features such as variable-speed fans and integrated control systems that can adapt to changing conditions, optimizing energy recovery in real-time. Additionally, consider conducting regular maintenance checks and cleaning of filters and heat exchange surfaces to ensure peak performance. Investing in training for staff on operational best practices can further enhance system efficiency, ultimately reducing energy costs.
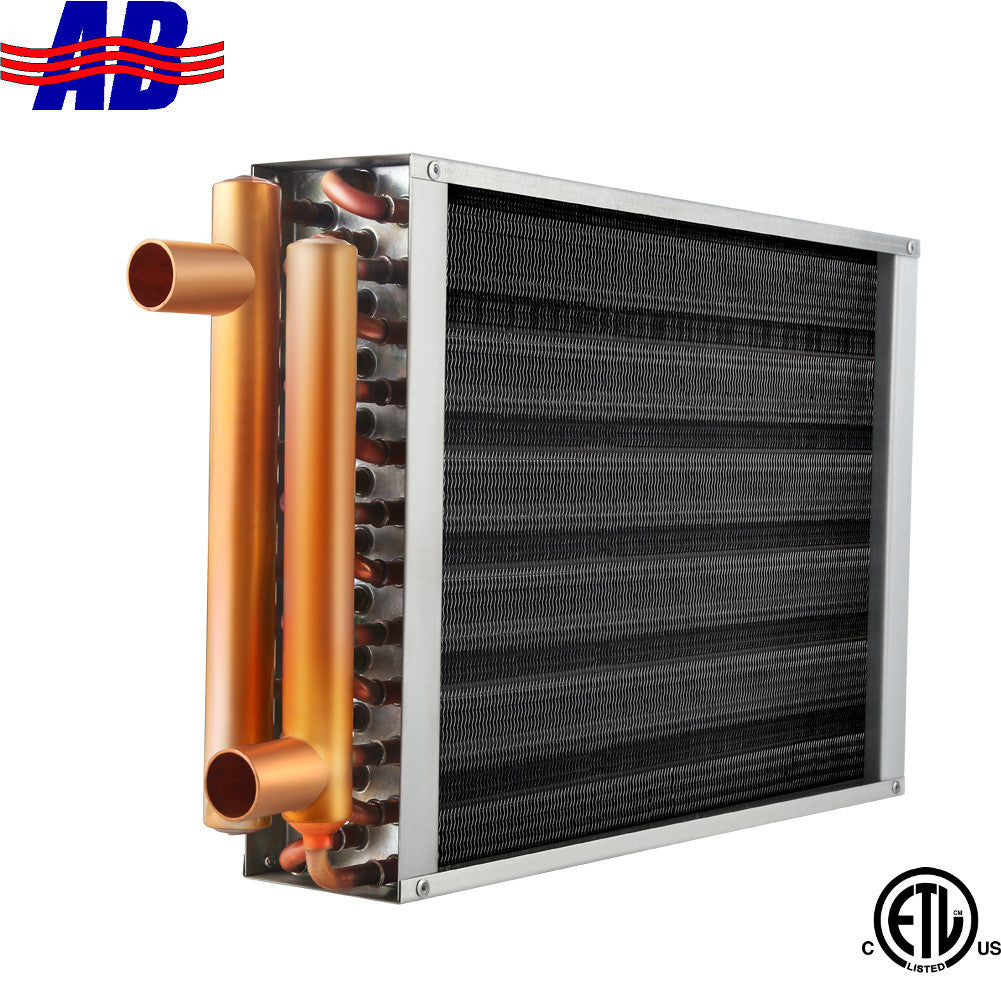

Illustrative image related to air to air heat exchanger
Scenario 2: Complications in Installation and Integration with Existing Systems
The Problem: For businesses planning to upgrade their HVAC systems, integrating a new air-to-air heat exchanger can be fraught with complications. Factors such as the layout of existing ductwork, the need for structural modifications, and compatibility with current systems can lead to unexpected delays and additional costs. This situation can be particularly daunting for companies in sectors like food processing or pharmaceuticals, where maintaining a specific indoor climate is critical for product safety and compliance.
The Solution: To mitigate installation challenges, buyers should engage with manufacturers early in the planning phase to assess compatibility with existing systems. A thorough site survey can help identify potential integration issues, allowing for tailored solutions. Opting for modular air-to-air heat exchangers can simplify installation, as these units are designed for flexibility and easier adaptation to various setups. Furthermore, investing in professional installation services with experience in similar projects can ensure that the system is correctly configured and optimized for performance from the outset. Detailed documentation and training provided by the manufacturer can also facilitate smoother transitions and minimize operational disruptions.
Scenario 3: Poor Indoor Air Quality Affecting Employee Health and Productivity
The Problem: In many industries, maintaining high indoor air quality (IAQ) is crucial not only for compliance with health regulations but also for ensuring employee well-being and productivity. Businesses using air-to-air heat exchangers may find that, without proper filtration and humidity control, these systems can inadvertently circulate pollutants and allergens, leading to poor IAQ. This is especially problematic in environments like schools, hospitals, and office buildings, where air quality directly impacts health and productivity.
The Solution: To enhance IAQ, it’s essential for buyers to select air-to-air heat exchangers equipped with high-quality filtration systems capable of removing particulates, allergens, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). When sourcing these systems, inquire about the types of filters used and their efficiency ratings (MERV ratings), as well as any additional features like humidity control mechanisms. Regular maintenance schedules should include filter replacement and cleaning of heat exchange components to prevent the buildup of contaminants. Implementing a continuous monitoring system for air quality can also help facilities proactively address IAQ issues, ensuring a healthier work environment for employees and compliance with health standards.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for air to air heat exchanger
What are the Key Materials Used in Air to Air Heat Exchangers?
When selecting materials for air to air heat exchangers, it’s essential to consider factors such as thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, weight, and cost. Here, we analyze four common materials—aluminum, stainless steel, carbon steel, and copper—each with distinct properties and applications.
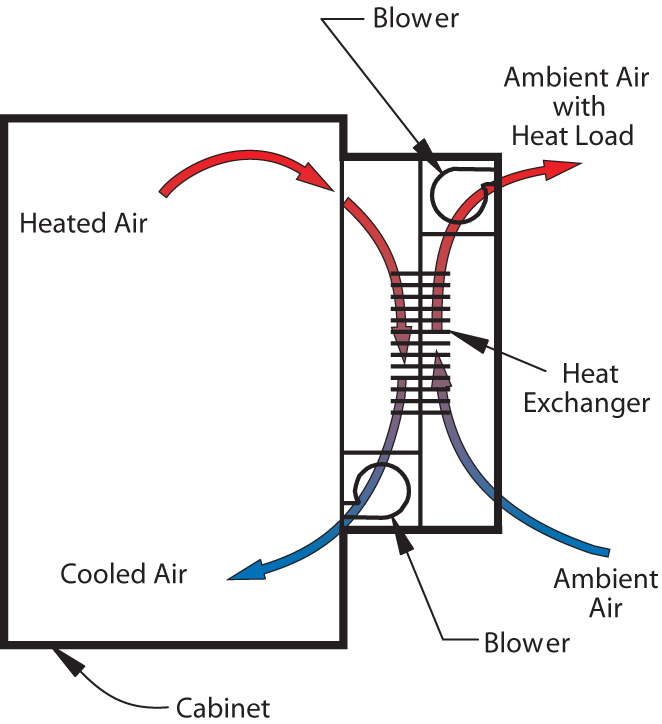
How Does Aluminum Perform in Air to Air Heat Exchangers?
Aluminum is a popular choice for air to air heat exchangers due to its excellent thermal conductivity and lightweight nature. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 200°C and is resistant to corrosion, especially when anodized.
Pros: Aluminum’s lightweight characteristic allows for easier installation and reduced structural support requirements. Its high thermal conductivity translates into efficient heat transfer, making it suitable for various applications, including residential and commercial ventilation systems.
Cons: While aluminum is durable, it can be susceptible to mechanical damage and may not withstand highly corrosive environments without protective coatings. Additionally, the cost can be higher than carbon steel, which may be a consideration for budget-conscious buyers.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various air media, making it versatile for different ventilation systems. However, it may not be ideal for high-temperature applications exceeding its rating.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial, especially in regions like Europe and the Middle East. Buyers should ensure that suppliers can provide certifications for their aluminum products.
Illustrative image related to air to air heat exchanger
What Advantages Does Stainless Steel Offer for Heat Exchangers?
Stainless steel is renowned for its strength and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for demanding environments. It can handle temperatures up to 600°C and is often used in industrial applications where hygiene is paramount, such as food processing.
Pros: The durability of stainless steel ensures a long lifespan, even in harsh conditions. Its resistance to corrosion and staining makes it ideal for applications involving moisture and contaminants.
Cons: The primary drawback is its higher cost compared to aluminum and carbon steel. Additionally, stainless steel can be heavier, which may complicate installation and increase support structure requirements.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with various air and fluid media, making it suitable for diverse applications, including high-temperature processes.
Illustrative image related to air to air heat exchanger
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Germany and Saudi Arabia should verify compliance with local standards and certifications, as stainless steel products often require specific grades for food and pharmaceutical applications.
How Does Carbon Steel Compare in Terms of Cost and Performance?
Carbon steel is a cost-effective material commonly used in air to air heat exchangers. It can handle moderate temperatures and is often treated with coatings to enhance corrosion resistance.
Pros: The primary advantage of carbon steel is its low cost, making it an attractive option for large-scale projects. Its strength allows for robust construction, suitable for various industrial applications.
Cons: Carbon steel is less resistant to corrosion compared to stainless steel and aluminum, which may limit its use in humid or corrosive environments. Additionally, it typically requires protective coatings, adding to maintenance costs.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is suitable for applications where cost is a primary concern, but its limitations in corrosion resistance may restrict its use in specific environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the need for protective coatings and compliance with local regulations, especially in regions with high humidity or corrosive conditions.
What Role Does Copper Play in Heat Exchanger Applications?
Copper is known for its superior thermal conductivity, making it an excellent choice for heat exchangers. It can operate effectively at temperatures up to 300°C and is often used in specialized applications.
Pros: The high thermal efficiency of copper allows for compact designs and effective heat transfer. Its antimicrobial properties also make it suitable for applications requiring high hygiene standards.
Cons: The primary disadvantage is its high cost compared to other materials. Additionally, copper is prone to corrosion in certain environments, which may necessitate protective measures.
Impact on Application: Copper is ideal for applications where thermal performance is critical, such as in HVAC systems. However, its susceptibility to corrosion may limit its use in specific environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that copper products comply with relevant standards and consider the implications of corrosion in their specific applications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Air to Air Heat Exchangers
| Material | Typical Use Case for air to air heat exchanger | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Residential and commercial ventilation systems | Lightweight and high thermal conductivity | Susceptible to mechanical damage | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing and industrial applications | High strength and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and weight | High |
| Carbon Steel | Large-scale industrial applications | Low cost and robust construction | Requires protective coatings | Low |
| Copper | HVAC systems and specialized applications | Superior thermal conductivity | High cost and corrosion susceptibility | High |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for air to air heat exchanger
What are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Air-to-Air Heat Exchangers?
The manufacturing of air-to-air heat exchangers is a complex process that involves several critical stages. Each stage contributes to the efficiency and durability of the final product, which is essential for B2B buyers looking for reliable and energy-efficient solutions.
Illustrative image related to air to air heat exchanger
Material Preparation: What Materials are Used and How are They Prepared?
The manufacturing process begins with the careful selection and preparation of materials. Common materials include stainless steel and carbon steel, chosen for their durability and resistance to corrosion. For applications involving higher temperatures or pollutants, stainless steel is often preferred, while carbon steel may be used in less demanding environments.
Once materials are selected, they undergo processes such as cutting, bending, and surface treatment to enhance their performance. For instance, thin-walled tubes are often pre-treated to ensure optimal heat transfer efficiency and to prevent corrosion. This meticulous preparation is crucial for ensuring that the heat exchanger performs effectively and meets industry standards.
How are Air-to-Air Heat Exchangers Formed?
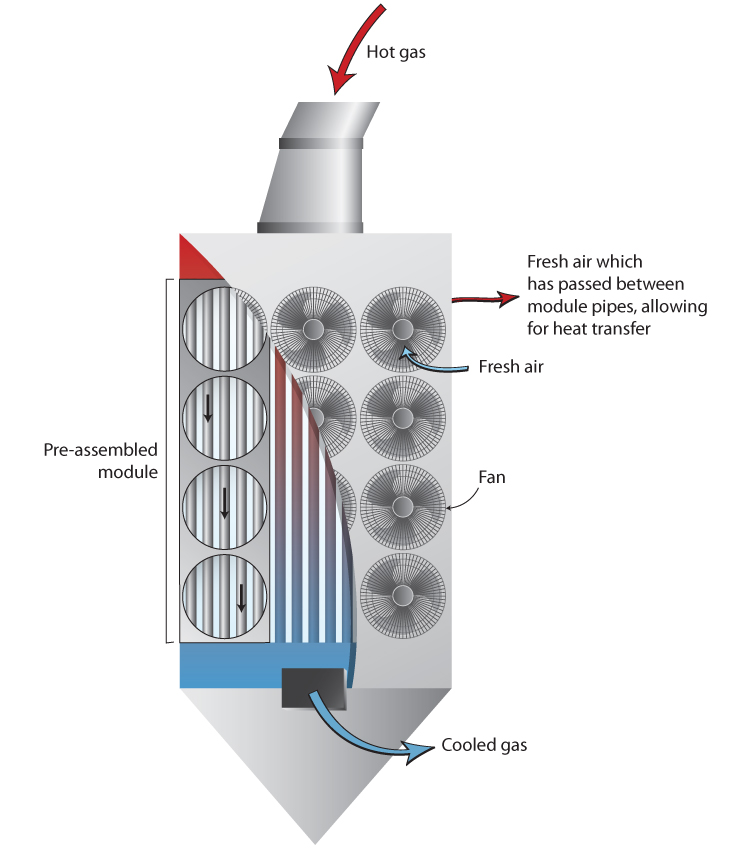
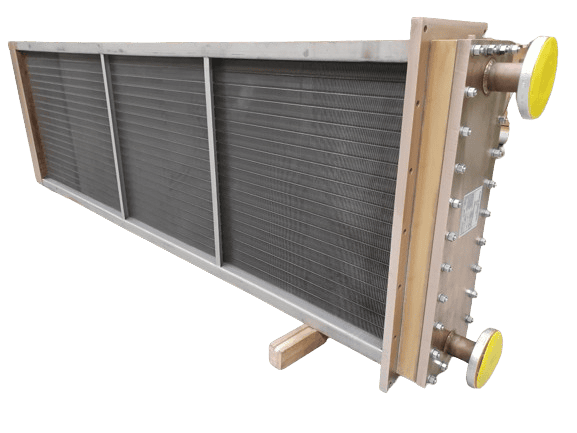
The forming stage involves several key techniques. Depending on the design, heat exchangers may be constructed using either glued or welded connections. The glued option utilizes a silicon-free adhesive to bond components, offering a lightweight solution ideal for low to medium temperature applications. This method reduces the overall weight, allowing for easier installation in restricted spaces.
Conversely, welded heat exchangers are designed for high-temperature or high-load applications. The welding process creates robust connections that can withstand extreme conditions. This stage is vital for ensuring structural integrity and longevity of the heat exchanger, which is particularly important for industries that operate under rigorous conditions, such as food processing or petrochemicals.
What is Involved in the Assembly of Air-to-Air Heat Exchangers?
During the assembly phase, all components, including the heat exchange tubes, fans, and casing, are meticulously put together. Each component is checked for compatibility and alignment to ensure optimal airflow and heat transfer efficiency. Advanced techniques such as computer-aided design (CAD) may be employed to simulate airflow and thermal dynamics, allowing manufacturers to optimize designs before physical assembly.

Illustrative image related to air to air heat exchanger
Quality control during assembly is critical. Each stage involves detailed inspections to verify that components meet specified tolerances and performance criteria. This minimizes the risk of defects and ensures that the final product will operate as intended in various applications.
What Finishing Processes Are Essential for Quality and Performance?
Finishing processes include cleaning, coating, and final inspections. Cleaning is essential to remove any contaminants that may affect performance or lead to corrosion. Coating processes may be applied to enhance corrosion resistance or to provide additional insulation.
Final inspections involve comprehensive testing of the assembled unit. This includes pressure testing to ensure there are no leaks, as well as performance tests to verify that the heat exchanger operates efficiently under specified conditions. These final steps are crucial for guaranteeing that the product meets both the manufacturer’s and industry standards.
How is Quality Assurance Implemented in Air-to-Air Heat Exchanger Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of the manufacturing process for air-to-air heat exchangers. It ensures that products not only meet customer expectations but also comply with international and industry-specific standards.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Air-to-Air Heat Exchangers?
Manufacturers typically adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. This certification indicates that a manufacturer has consistent processes in place to ensure product quality.
In addition to ISO standards, specific industry certifications like CE marking and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards may apply, particularly for products used in specific sectors such as construction or energy. Compliance with these standards is crucial for B2B buyers, as it assures them of the reliability and safety of the heat exchangers they procure.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Production?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process. These typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Regular inspections are conducted during manufacturing to identify any defects early on.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The completed heat exchangers undergo extensive testing and inspections to confirm they meet performance and safety standards.
These checkpoints help maintain high-quality standards and minimize the risk of defects that could lead to product failures.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Assurance?
Testing methods for air-to-air heat exchangers include:
- Performance Testing: Evaluating heat transfer efficiency under various conditions to ensure optimal performance.
- Leak Testing: Identifying any potential leaks in the system that could compromise efficiency.
- Durability Testing: Assessing the product’s ability to withstand extreme temperatures and environmental conditions.
These testing methods are crucial for ensuring that the final product meets or exceeds customer expectations and industry standards.
Illustrative image related to air to air heat exchanger
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is essential to verify the quality control practices of suppliers. Here are actionable steps:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits can provide insights into the supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This can help identify any potential risks associated with their operations.
-
Request Quality Assurance Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation of their quality control processes, including certifications and test results.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent inspectors can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s compliance with quality standards.
-
Understand Certification Nuances: Different regions may have specific certification requirements. It’s crucial for buyers to be aware of these nuances to ensure compliance with local regulations and standards.
By taking these steps, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and establish reliable partnerships with manufacturers of air-to-air heat exchangers.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘air to air heat exchanger’
This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure air-to-air heat exchangers. With the increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions in various industries, selecting the right system is crucial for optimizing energy use and maintaining a healthy indoor climate. Follow these steps to ensure a successful procurement process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your specific needs is essential before you start sourcing. Consider factors such as the required airflow capacity, efficiency ratings, and operational temperatures. This information will help you narrow down your options and ensure compatibility with existing systems.
- Airflow Capacity: Determine the volume of air that needs to be exchanged to meet your building’s requirements.
- Efficiency Ratings: Look for systems with high energy recovery efficiency to reduce operational costs.
Step 2: Research Industry Standards and Regulations
Compliance with local and international standards is crucial for ensuring safety and efficiency. Familiarize yourself with relevant regulations in your region, particularly in sectors like HVAC and building management.
Illustrative image related to air to air heat exchanger
- Local Codes: Check local building codes to ensure that your chosen system meets legal requirements.
- Energy Efficiency Standards: Investigate standards such as ISO or ASHRAE to find products that enhance sustainability.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct a thorough evaluation. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from businesses in similar industries or regions. This step is vital to gauge the supplier’s reliability and expertise.
- Supplier Reputation: Look for reviews and feedback from existing customers to assess product performance and service quality.
- Experience in Your Sector: Choose suppliers who have a proven track record in your specific market to ensure they understand your unique challenges.
Step 4: Request Detailed Quotations
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request detailed quotations that include pricing, lead times, and warranty terms. This information is essential for comparing options and making an informed decision.
- Pricing Transparency: Ensure that the quotation breaks down costs, including installation and maintenance.
- Warranty and Support: Look for comprehensive warranty coverage and ongoing support options to mitigate future risks.
Step 5: Assess Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Understanding installation and maintenance needs will help you avoid unexpected costs and downtime. Evaluate the complexity of installation and the availability of maintenance services in your area.
- Installation Complexity: Determine if specialized skills or equipment are needed for installation.
- Maintenance Schedule: Inquire about recommended maintenance practices and the availability of service contracts.
Step 6: Verify Supplier Certifications
Supplier certifications can provide assurance of quality and compliance with industry standards. Verify that your chosen suppliers hold relevant certifications to ensure reliability and performance.
Illustrative image related to air to air heat exchanger
- Quality Certifications: Look for ISO certifications or similar quality assurance marks that validate their manufacturing processes.
- Environmental Certifications: Check for certifications that demonstrate commitment to sustainability, such as LEED or ENERGY STAR.
Step 7: Finalize the Purchase Agreement
Once you’ve selected a supplier, finalize the purchase agreement. Ensure all terms, including delivery timelines, payment schedules, and penalties for non-compliance, are clearly outlined to protect your interests.
- Clear Terms: Review all clauses carefully to avoid misunderstandings in the future.
- Payment Flexibility: Negotiate payment terms that align with your budget and cash flow needs.
By following this structured checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the procurement process for air-to-air heat exchangers, ensuring they make well-informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and sustainability goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for air to air heat exchanger Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Air-to-Air Heat Exchangers?
When sourcing air-to-air heat exchangers, it is crucial to understand the various cost components that contribute to the overall pricing. These components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts costs. Common materials like stainless steel and carbon steel are used for their durability and resistance to corrosion. The complexity of the design, such as the use of thin-walled tubes or advanced coatings, can also drive up material costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the region and the level of expertise required for manufacturing. Skilled labor is necessary for precise assembly and quality control, particularly for customized solutions.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with utilities, depreciation of machinery, and facility maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead costs, thus lowering overall prices.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific designs can be a significant initial investment, impacting the unit cost, especially for lower volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC measures ensures product reliability and compliance with international standards, which may add to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs can vary widely based on the shipping distance and the Incoterms used. These factors should be considered when evaluating total costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically build a profit margin into their pricing, which can vary depending on market conditions and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Air-to-Air Heat Exchangers?
Several factors influence the pricing of air-to-air heat exchangers beyond the basic cost components:

Illustrative image related to air to air heat exchanger
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Suppliers may offer discounts for minimum order quantities (MOQs), making it essential for buyers to assess their volume requirements.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized products tailored to specific operational needs may incur higher costs due to additional engineering and production time. Buyers should carefully evaluate whether standard models could meet their requirements to optimize costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet international quality standards or specific certifications (e.g., ISO, ASME) may command higher prices. However, investing in higher-quality products often results in lower maintenance costs over the lifespan of the equipment.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reliability, reputation, and after-sales service can influence pricing. Buyers should consider the total value offered by a supplier, including support and warranty terms.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects shipping responsibilities and costs. Understanding the implications of terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) is crucial for budgeting.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Achieve Cost-Efficiency in Air-to-Air Heat Exchanger Sourcing?
To navigate the complexities of sourcing air-to-air heat exchangers effectively, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers to negotiate prices based on volume, long-term relationships, or bundled services. Building rapport can lead to better pricing terms.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also installation, maintenance, and operational costs over the product’s lifecycle. A higher initial investment may lead to substantial savings in energy efficiency and durability.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Sourcing: International buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should account for currency fluctuations, import duties, and local regulations that may impact final costs. Working with local representatives or consultants can help navigate these challenges.
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Conduct thorough market research to compare suppliers, prices, and product offerings. Utilizing online platforms can facilitate the identification of potential vendors and their capabilities.
Disclaimer
Prices for air-to-air heat exchangers can vary significantly based on specifications, supplier factors, and market conditions. The information provided is indicative and should be used as a guideline for preliminary assessments. Buyers are encouraged to obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing air to air heat exchanger With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Heat Recovery
In the pursuit of energy efficiency and cost savings, businesses often explore various heat recovery solutions to optimize their HVAC systems. The air-to-air heat exchanger is a prominent technology that recovers heat from outgoing air to precondition incoming fresh air. However, several alternative methods exist that can also achieve similar goals, each with its unique advantages and drawbacks. This analysis compares air-to-air heat exchangers with two viable alternatives: shell and tube heat exchangers and cooling towers.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Air To Air Heat Exchanger | Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger | Cooling Towers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency (up to 86% recovery) | Moderate efficiency (up to 70% recovery) | Variable efficiency (depends on design) |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment | Higher initial investment | Lower initial investment |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively straightforward installation | Complex installation due to piping | Simple setup, requires adequate space |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, filter changes needed | Moderate maintenance, requires cleaning | High maintenance, water treatment necessary |
| Best Use Case | Residential and commercial buildings | Industrial applications with high heat loads | Large-scale cooling for processes or buildings |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers?
Shell and tube heat exchangers consist of a series of tubes, one set carrying the hot fluid and the other carrying the cold fluid. They are renowned for their effectiveness in transferring heat in industrial settings.
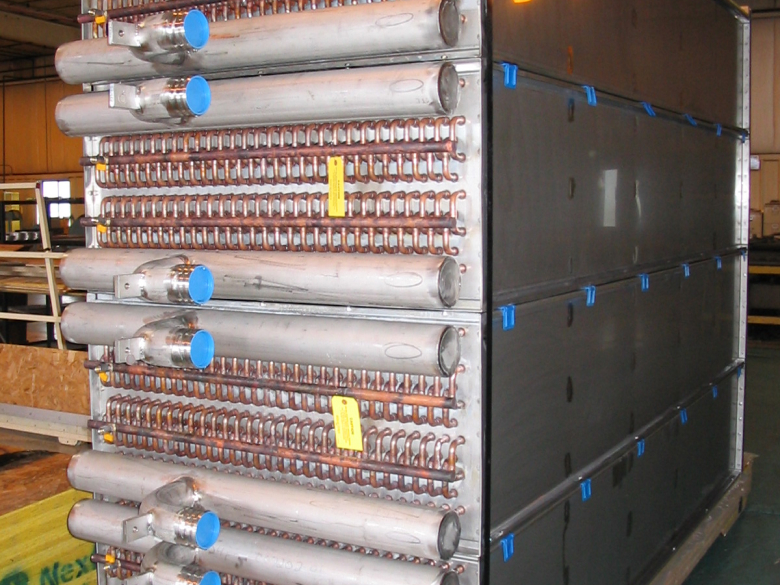

Illustrative image related to air to air heat exchanger
Pros: They offer high heat transfer efficiency and can handle high-pressure applications. They are also versatile and can be customized for various processes.
Cons: The initial costs can be significant, and the installation process is more complex due to the required piping and space considerations. Maintenance can also be a concern, as cleaning the tubes is essential to maintain efficiency.
How Do Cooling Towers Work?
Cooling towers are designed to remove heat from water through evaporation and heat exchange with air. They are commonly used in large-scale applications, such as power plants and HVAC systems.
Pros: They provide a cost-effective solution for cooling large volumes of water and can be highly efficient in heat removal. Their lower initial investment compared to shell and tube systems makes them appealing for budget-conscious projects.
Illustrative image related to air to air heat exchanger
Cons: Cooling towers require significant maintenance, including regular water treatment to prevent algae growth and corrosion. Their effectiveness can vary based on environmental conditions, making them less reliable in certain climates.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Heat Recovery Solution
Selecting the appropriate heat recovery system involves evaluating specific business needs, including budget constraints, installation complexity, and operational requirements. For businesses focused on maximizing indoor air quality and energy efficiency, air-to-air heat exchangers are an excellent choice, particularly in climates with significant temperature fluctuations. Conversely, shell and tube heat exchangers may be more suitable for industrial applications requiring robust heat transfer capabilities, while cooling towers offer a cost-effective solution for large-scale cooling needs. By carefully considering these factors, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and financial objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for air to air heat exchanger
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Air to Air Heat Exchangers?
Air to air heat exchangers are integral components in HVAC systems, providing efficient heat transfer and energy savings. Understanding their technical properties can help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
1. Material Grade
The material used in air to air heat exchangers, such as stainless steel or carbon steel, directly affects durability, corrosion resistance, and heat transfer efficiency. Stainless steel is preferred for its resistance to oxidation and high temperatures, making it suitable for a variety of applications, especially in harsh environments. For buyers, selecting the right material ensures longevity and minimizes maintenance costs.
2. Heat Transfer Efficiency
This specification indicates how effectively a heat exchanger can transfer heat from one air stream to another. Efficiency ratings often range from 70% to over 90%, with higher ratings leading to greater energy savings. In a B2B context, understanding heat transfer efficiency is crucial for calculating potential energy savings and return on investment (ROI) for HVAC systems.
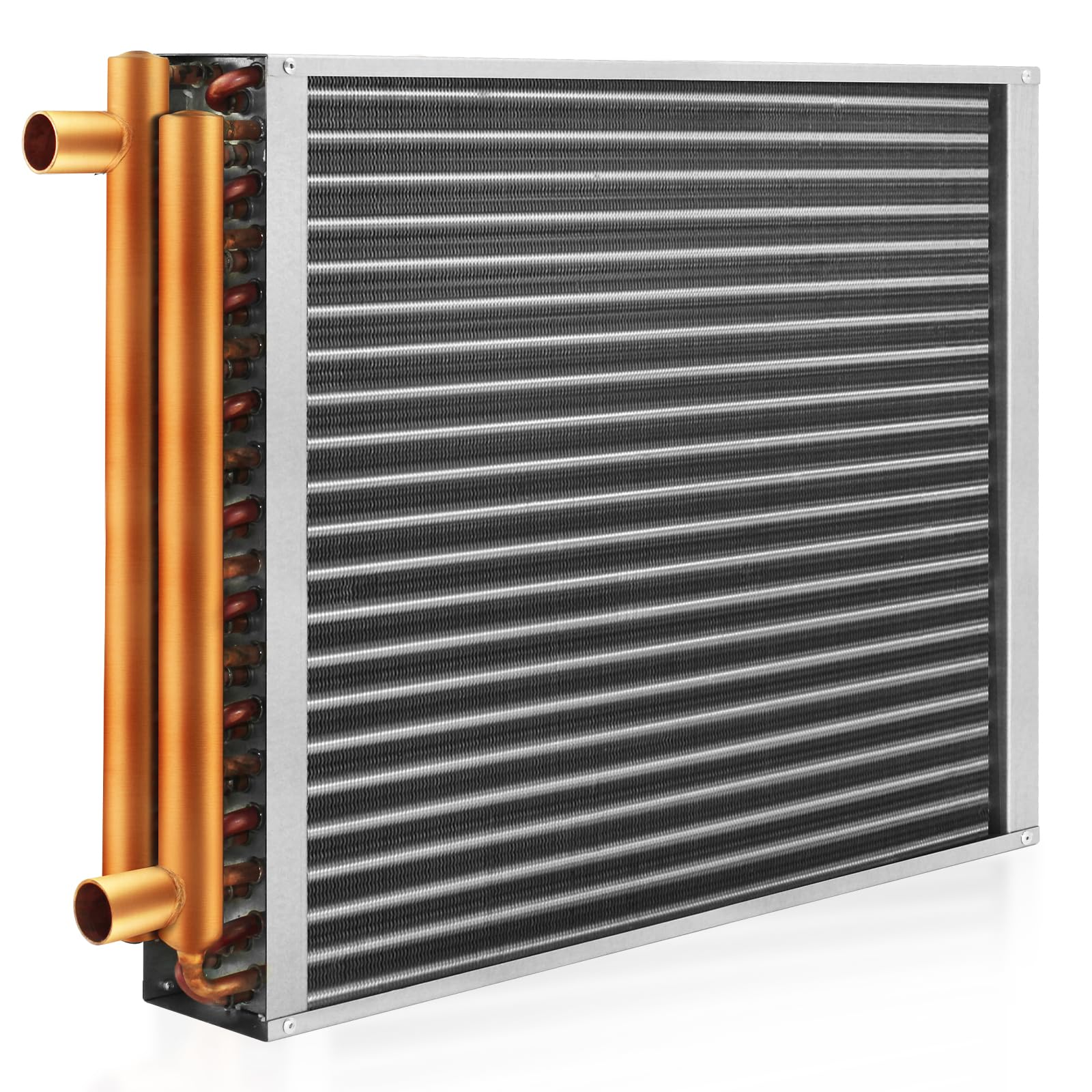

Illustrative image related to air to air heat exchanger
3. Airflow Capacity
Airflow capacity is the maximum volume of air that can pass through the heat exchanger, typically measured in cubic meters per hour (m³/h). This property is vital for ensuring that the system can meet the ventilation requirements of a given space. Buyers should assess airflow capacity to ensure compatibility with existing HVAC systems, optimizing performance and comfort levels.
4. Operating Temperature Range
This specification defines the range of temperatures in which the heat exchanger can operate effectively. Different applications may require different temperature tolerances, with some systems capable of handling temperatures up to 1000°C. Understanding the operating temperature range is essential for buyers to ensure the heat exchanger can handle the specific conditions of their industry.
5. Pressure Drop
Pressure drop refers to the reduction in pressure as air flows through the heat exchanger. A lower pressure drop indicates better efficiency and less energy consumption by fans. For B2B buyers, evaluating pressure drop is crucial for assessing the overall energy efficiency of the system and potential impacts on operational costs.
6. Size and Weight
The dimensions and weight of an air to air heat exchanger can affect installation and space requirements. Lightweight designs are easier to install and can be placed in areas with limited access. Buyers should consider size and weight for practical installation and integration within existing systems.
What Are the Common Trade Terms in Air to Air Heat Exchanger Transactions?
Navigating the procurement process for air to air heat exchangers involves understanding industry-specific jargon.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. For buyers, partnering with OEMs can ensure high-quality components that meet specific standards and performance criteria.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ helps buyers plan their purchases, particularly when considering inventory and budget constraints. It also influences negotiation strategies with suppliers.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document requesting pricing and terms from suppliers for specified products. For B2B buyers, issuing RFQs is crucial for comparing prices and terms from multiple suppliers, ensuring they secure the best deal.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risk transfer, and delivery responsibilities, which can significantly impact the total cost of ownership.

Illustrative image related to air to air heat exchanger
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times is essential for project planning and ensuring timely delivery, which can be critical in maintaining operational schedules.
6. Warranty Period
The warranty period is the duration during which a manufacturer guarantees the performance of their product. Knowing the warranty terms is important for buyers as it affects maintenance planning and potential costs associated with repairs or replacements.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that lead to improved energy efficiency and cost savings in their operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the air to air heat exchanger Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Air to Air Heat Exchanger Sector?
The air to air heat exchanger market is currently experiencing significant growth, driven by global trends in energy efficiency, sustainability, and regulatory compliance. As energy costs rise and environmental regulations tighten, businesses across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly investing in heat recovery solutions to reduce operational costs and improve energy performance. Key trends include the adoption of advanced technologies such as IoT-enabled heat exchangers, which facilitate real-time monitoring and optimize performance, leading to enhanced energy savings.
Emerging markets are witnessing a surge in demand for air to air heat exchangers, particularly in sectors such as food processing, HVAC, and industrial applications. In regions like Germany and Saudi Arabia, local industries are prioritizing energy-efficient solutions, further propelling the market forward. Additionally, the shift towards decentralized energy systems and building automation is influencing sourcing strategies, as buyers seek equipment that integrates seamlessly with existing infrastructure while offering flexibility and scalability.
Another notable trend is the increasing preference for lightweight and customizable heat exchangers, which enable easier installation and maintenance. Manufacturers are responding by developing products that cater to diverse applications, from residential ventilation systems to large-scale industrial processes, ensuring that international buyers can find tailored solutions to meet their specific needs.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Air to Air Heat Exchanger Sector?
Sustainability has become a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the air to air heat exchanger market. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, energy consumption, and lifecycle emissions are now at the forefront of purchasing decisions. Companies are increasingly seeking suppliers that prioritize sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and implementing energy-efficient manufacturing methods.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, with buyers looking for transparency in supply chains to ensure that materials are sourced responsibly. Certifications such as LEED and ISO 14001 are gaining traction as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. By choosing suppliers with recognized ‘green’ certifications, businesses can enhance their corporate social responsibility profiles and comply with stringent regulations in their respective regions.
Furthermore, the push for eco-friendly products is leading to innovations in material selection. For example, the use of stainless steel in air to air heat exchangers not only improves durability but also reduces the environmental footprint compared to traditional materials. This trend reflects a broader shift toward sustainable engineering practices that resonate with environmentally conscious consumers and regulatory bodies alike.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Air to Air Heat Exchangers in the B2B Context?
The evolution of air to air heat exchangers dates back to the early 20th century, when the need for energy-efficient solutions in industrial processes began to gain recognition. Initially, these systems were rudimentary, focusing primarily on basic heat recovery functions. However, as energy costs soared and environmental concerns escalated in the latter half of the century, technological advancements transformed the landscape.
The introduction of more sophisticated designs, such as cross-flow and counterflow heat exchangers, allowed for improved efficiency and versatility across various applications. The 21st century marked a significant turning point with the integration of digital technologies, enabling real-time monitoring and enhanced performance analytics. This progression has established air to air heat exchangers as vital components in modern HVAC systems, ensuring that they remain relevant and essential in today’s energy-conscious market.
Illustrative image related to air to air heat exchanger
As the industry continues to innovate, international B2B buyers can expect to see ongoing advancements in design, material science, and smart technology integration, further solidifying the role of air to air heat exchangers in achieving energy efficiency and sustainability objectives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of air to air heat exchanger
-
How do I determine the right size of an air-to-air heat exchanger for my facility?
To select the appropriate size of an air-to-air heat exchanger, consider the volume of air to be exchanged, the temperature difference between the incoming and outgoing air, and the specific heating or cooling requirements of your application. Conducting a thermal load calculation will help you determine the necessary capacity, ensuring optimal energy efficiency and performance. Additionally, consult with suppliers who can provide guidance based on your facility’s unique requirements and local climate conditions. -
What is the best type of air-to-air heat exchanger for industrial applications?
The best type of air-to-air heat exchanger for industrial applications often depends on the operating conditions and specific needs of your process. Crossflow and counterflow designs are commonly used in industrial settings, with counterflow typically offering higher efficiency. Evaluate factors such as temperature ranges, air volume flows, and the potential for condensation when choosing. Consulting with a manufacturer or supplier experienced in your industry can help you identify the most suitable solution. -
What are the key factors to consider when sourcing an air-to-air heat exchanger internationally?
When sourcing internationally, consider the supplier’s reputation, certifications, and experience in your specific industry. Look for companies with a proven track record of quality and reliability. Additionally, assess their ability to provide custom solutions tailored to your needs, including material selection and design variations. Logistics, including shipping times and costs, as well as compliance with local regulations, are also crucial factors to ensure a smooth procurement process. -
How can I ensure the quality of air-to-air heat exchangers from suppliers?
To ensure quality, request certifications and test results demonstrating compliance with international standards, such as ISO or ASME. Conduct site visits or audits if possible, and seek references from previous clients to gauge supplier reliability. Engaging with suppliers who offer warranties and robust after-sales support is also beneficial. Implementing a quality assurance process, including pre-shipment inspections, can further safeguard your investment. -
What customization options are typically available for air-to-air heat exchangers?
Most manufacturers offer various customization options, including size, material (stainless steel, carbon steel), design configurations (crossflow, counterflow), and specific features tailored to your operational needs. You can also request modifications to accommodate unique temperature ranges or specific air flow requirements. Discussing your requirements upfront with suppliers will help ensure that the final product meets your expectations and operational standards. -
What are common minimum order quantities (MOQs) for air-to-air heat exchangers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for air-to-air heat exchangers can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer and the complexity of the product. Typically, MOQs range from 1 to 10 units for standard models, while custom designs may require larger orders. Always clarify MOQs with potential suppliers during your initial discussions to ensure alignment with your purchasing strategy and inventory management. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing air-to-air heat exchangers?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and region. Common options include advance payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, and balance upon delivery. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow needs while also considering the supplier’s policies. Establishing clear terms in a written agreement can prevent misunderstandings and ensure a smoother transaction process. -
How can I streamline the logistics of importing air-to-air heat exchangers?
To streamline logistics, work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping and can provide comprehensive shipping solutions. Ensure that all necessary documentation, such as customs declarations and compliance certificates, is in order to avoid delays. Consider partnering with a freight forwarder who can manage the logistics process for you, helping to navigate customs regulations and optimize shipping routes for timely delivery.
Top 6 Air To Air Heat Exchanger Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Swegon – Air-to-Air Heat Exchange Ventilation System
Domain: swegon.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Air-to-air heat exchange ventilation system with energy class A, recovering 86% of energy from extract air. Features include: mechanical system with two fans (supply air fan and extract air fan), heat exchanger for energy transfer, high-quality filters for supply air, and balanced ventilation. It provides energy-efficient heating and passive cooling, ensuring a healthy indoor climate. Typical ener…
2. IQS Directory – Air-to-Air Heat Exchangers
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
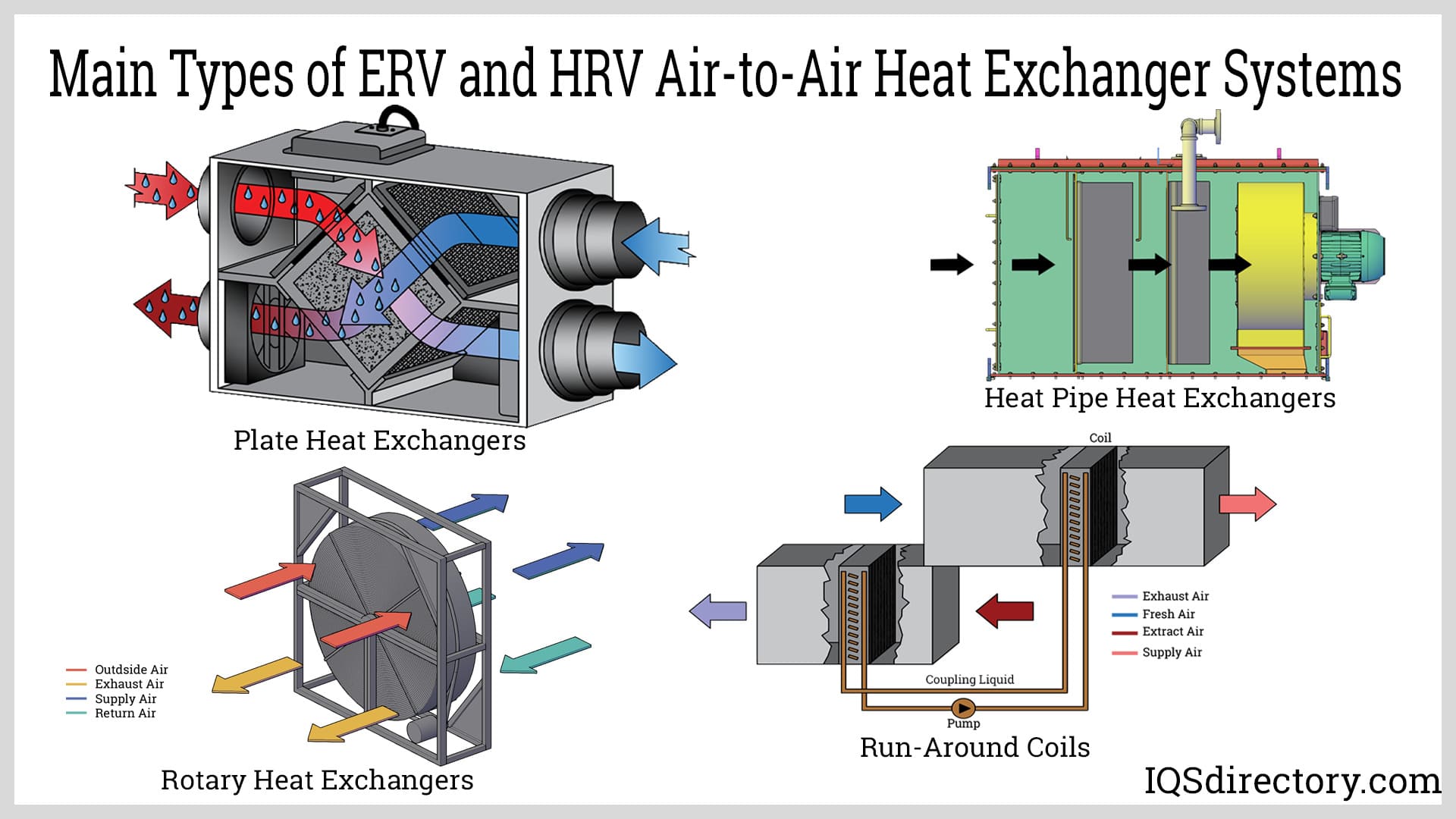
Introduction: Air-to-Air Heat Exchangers (AAHXs) are essential for balanced ventilation systems, transferring heat from warm extracted air to incoming cold air. They operate through a mechanical ventilation system with two fans (supply and extraction) and a heat transfer unit. Key types include: 1. Plate Air-to-Air Heat Exchangers: Separate supply and exhaust air with flat or profiled plates, offering energy re…
3. Loud Dawson – DIY Air to Air Cross-Flow Heat Exchanger
Domain: loudawson.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: DIY Air to Air Cross-Flow Heat Exchanger (HRV) designed by Lou Dawson. Core made of 3-inch aluminum ribbed expandable dryer duct for high heat conductivity. Shell constructed from 4-inch thin wall CL200 white PVC plumbing pipe, allowing sufficient air space around the core. Features variable speed fans for airflow control. Recommended length of 8 feet for the shell, with flexibility in size based …
4. Pfannenberg – PKS 3000 Series Air to Air Heat Exchangers
Domain: pfannenbergusa.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Air to Air Heat Exchangers – PKS 3000 Series: 5 models available (PKS 313X, PKS 320X, PKS 330X, PKS 336X, PKS Mini 30X2). Cooling capacity ranges from 22 Watts/°C to 100 Watts/°C. Ideal for cooling electronics in contaminated environments (dust, liquid, gas). Utilizes lower temperature ambient air for cooling without a compressor, reducing energy consumption. Compact and lightweight design allows …
5. Boyd Corporation – Air to Air Heat Exchangers
Domain: boydcorp.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Air to Air Heat Exchangers are thermal management solutions that transfer heat between two separate air systems. They consist of two sets of fins separated by an air blocker to seal the airflows. Heat is absorbed from the hotter airflow through one set of fins and transferred to the cooler airflow via conduction or passive two-phase systems like heat pipes or vapor chambers. Boyd’s heat exchangers…
6. NYC Energy Tools – Air-to-Air Heat Exchanger Calculator
Domain: uat-pnp.nycenergytools.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Air-to-air Heat Exchanger Heat Transfer Calculation Methodology based on the 2020 ASHRAE Handbook – Systems and Equipment, Chapter 26. Assumes use of a variable speed supply fan and a rotary wheel energy recovery component. Includes a calculator for estimating annual sensible and latent heat transfer in an energy recovery ventilation (ERV) system. Requires hourly data collection for a minimum of s…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for air to air heat exchanger
In the rapidly evolving landscape of energy efficiency, air-to-air heat exchangers stand out as a vital component for businesses aiming to optimize their HVAC systems. These systems not only facilitate significant energy savings—up to 40 kWh/sq. m. annually—but also contribute to healthier indoor environments by ensuring proper ventilation and air filtration. Strategic sourcing of air-to-air heat exchangers allows companies to leverage advanced technologies that enhance heat recovery processes, catering to diverse applications across various industries, from food processing to commercial buildings.
As international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is essential to evaluate suppliers based on their innovation, reliability, and ability to provide tailored solutions. Engaging with manufacturers that offer customizable designs, such as welded or glued constructions, can further ensure that your specific operational needs are met without compromising on efficiency.
Looking ahead, the demand for energy-efficient systems will only intensify as regulatory pressures and environmental concerns grow. Now is the time to invest in air-to-air heat exchangers that align with your sustainability goals and operational efficiency. Explore partnerships with leading manufacturers to stay ahead in this competitive market and drive both cost savings and environmental benefits for your organization.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.