A B2B Buyer’s Guide to Types Of Centrifugal Pump: Price, Quality, and Suppliers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for types of centrifugal pump
In an increasingly interconnected world, sourcing the right types of centrifugal pumps can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. With diverse applications across industries such as water treatment, oil and gas, and HVAC, selecting the appropriate pump not only affects operational efficiency but also impacts overall project costs. This comprehensive guide delves into various centrifugal pump types, including single-stage, multi-stage, axial flow, and submersible pumps, while highlighting their unique applications and advantages.
Moreover, we will explore critical factors such as supplier vetting, maintenance considerations, and cost implications that are essential for making informed purchasing decisions. For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—countries such as Brazil and Saudi Arabia—understanding the nuances of centrifugal pump selection is vital. This guide equips you with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of the global market, ensuring you choose pumps that align with your specific operational needs and budget constraints. Whether you are upgrading existing systems or embarking on new projects, this resource will empower you to make strategic decisions that enhance productivity and drive success in your business operations.
Understanding types of centrifugal pump Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-stage Centrifugal Pump | One impeller, designed for low to moderate pressure applications | Water supply, HVAC systems | Pros: Cost-effective, simple design. Cons: Limited head generation, less efficient for high-viscosity fluids. |
| Multi-stage Centrifugal Pump | Multiple impellers for high-pressure applications | Boiler feed systems, water treatment | Pros: High pressure capabilities, efficient for higher viscosities. Cons: Higher cost, complex maintenance. |
| Axial Flow Centrifugal Pump | Fluid moves parallel to the shaft, high flow rates | Irrigation, flood control | Pros: Efficient for large volumes, compact design. Cons: Limited pressure generation, less efficient at low flow rates. |
| Radial Flow Centrifugal Pump | Fluid moves radially outward from the impeller | Industrial processes, chemical processing | Pros: Handles moderate viscosities, wide range of flow rates. Cons: Susceptible to clogging, not suitable for very high pressures. |
| Submersible Centrifugal Pump | Operates submerged, sealed unit with waterproof motor | Sewage treatment, deepwater pumping | Pros: No priming needed, efficient for submerged conditions. Cons: Higher initial cost, requires careful sealing and maintenance. |
What Are the Characteristics of Single-stage Centrifugal Pumps?
Single-stage centrifugal pumps feature a single impeller, making them ideal for low to moderate pressure applications. Their straightforward design allows for easy installation and operation, making them a cost-effective choice for various industries. B2B buyers should consider their suitability for clean or slightly contaminated fluids, as well as their limitations in handling high-viscosity materials and generating high pressures. These pumps are commonly used in water supply systems, HVAC applications, and irrigation.
How Do Multi-stage Centrifugal Pumps Differ in Performance?
Multi-stage centrifugal pumps consist of several impellers arranged in series, enabling them to produce higher pressures than single-stage pumps. They are particularly effective in applications requiring significant pressure boosts, such as boiler feed systems and water treatment facilities. For B2B buyers, the upfront investment is higher due to the complex design and maintenance requirements, but the efficiency in high-pressure scenarios often justifies the cost, especially for handling thicker fluids.
What Applications Benefit from Axial Flow Centrifugal Pumps?
Axial flow centrifugal pumps are designed to move fluids parallel to the pump shaft, making them suitable for applications requiring high flow rates with low head. They are often found in irrigation systems and flood control projects. B2B purchasers should note their compact design and efficiency in moving large volumes of liquid. However, these pumps may not perform well in high-pressure applications and can be less efficient at lower flow rates.
Why Choose Radial Flow Centrifugal Pumps for Industrial Applications?
Radial flow centrifugal pumps push fluid radially outward, making them versatile for various applications, including industrial process circulation and chemical processing. They can handle moderate viscosities and provide a wide range of flow rates, which is beneficial for diverse operational needs. B2B buyers must consider their susceptibility to clogging when dealing with solids and their limitations in high-pressure scenarios when selecting these pumps for their applications.

Illustrative image related to types of centrifugal pump
What Are the Advantages of Submersible Centrifugal Pumps?
Submersible centrifugal pumps are designed to operate while submerged in the fluid they are pumping, making them ideal for applications like sewage treatment and deepwater pumping. Their sealed construction eliminates the need for priming and allows for efficient operation in confined spaces. B2B buyers should evaluate the higher initial costs and the need for diligent maintenance to prevent motor damage, balancing these factors against the advantages of their unique operational capabilities.
Key Industrial Applications of types of centrifugal pump
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of types of centrifugal pump | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water and Wastewater Treatment | Sludge transfer in wastewater treatment plants | Efficient removal of sludge, reducing operational costs | Reliability, corrosion resistance, and maintenance support |
| Oil and Gas | Enhanced oil recovery using multi-stage pumps | Increased oil yield and operational efficiency | Pressure ratings, material compatibility, and energy efficiency |
| Agriculture | Irrigation systems utilizing axial flow pumps | Improved water distribution for crops, boosting yield | Flow rate requirements, energy consumption, and durability |
| Power Generation | Cooling water circulation in power plants | Maintains optimal operating temperatures, enhancing efficiency | Temperature tolerance, flow capacity, and maintenance needs |
| Chemical Processing | Chemical transfer in manufacturing processes | Safe and efficient handling of hazardous materials | Material compatibility, flow control, and safety certifications |
How Are Types of Centrifugal Pumps Used in Water and Wastewater Treatment?
In wastewater treatment plants, centrifugal pumps are crucial for transferring sludge and other fluids. They help maintain efficient operations by ensuring the timely removal of waste materials, which is essential for regulatory compliance and environmental protection. Buyers in this sector must prioritize reliability and corrosion resistance, as these pumps operate in harsh environments. Additionally, sourcing pumps with robust maintenance support can significantly reduce downtime and operational costs.
What Role Do Multi-Stage Pumps Play in Oil and Gas Operations?
Multi-stage centrifugal pumps are vital in the oil and gas sector, particularly for enhanced oil recovery processes. These pumps generate the high pressures needed to extract oil from reservoirs, thereby increasing yield and operational efficiency. For international buyers, especially in regions like Saudi Arabia and Brazil, key considerations include pressure ratings and material compatibility to handle various fluid properties. Energy efficiency is also critical, as it directly impacts operational costs.
How Do Axial Flow Pumps Benefit Agricultural Irrigation?
In agriculture, axial flow centrifugal pumps are commonly used in irrigation systems. Their design allows for high flow rates with low head requirements, making them ideal for distributing water across large fields. This efficiency can lead to improved crop yields and reduced water wastage. Buyers in the agricultural sector should consider flow rate requirements and energy consumption when sourcing these pumps, ensuring they select models that can withstand varying field conditions.
Why Are Centrifugal Pumps Important in Power Generation Cooling Systems?
Centrifugal pumps play a significant role in cooling water circulation within power plants. They help maintain optimal operating temperatures, which is crucial for maximizing efficiency and preventing equipment damage. When sourcing pumps for this application, considerations should include temperature tolerance, flow capacity, and maintenance needs. Buyers must ensure that the selected pumps can handle the specific conditions of their operations to avoid costly failures.
What Are the Key Considerations for Chemical Processing Applications?
In the chemical processing industry, centrifugal pumps are used for the safe transfer of various chemicals. These pumps must be designed to handle hazardous materials while ensuring efficiency and safety. Buyers should focus on material compatibility to prevent corrosion and leaks, as well as flow control mechanisms to manage the varying viscosities of chemicals. Additionally, obtaining pumps with the necessary safety certifications is crucial for compliance with industry regulations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘types of centrifugal pump’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Pump Performance in Viscous Fluids
The Problem: A manufacturing plant in Brazil relies on centrifugal pumps to transport viscous fluids like oils and slurries. However, they experience frequent fluctuations in pump performance, leading to inconsistent flow rates and pressure drops. This inconsistency not only disrupts production but also increases operational costs due to the need for emergency maintenance and replacements. The plant manager is frustrated, as these performance issues also affect the quality of the final product.
The Solution: To address this problem, it is crucial for the plant to select multi-stage centrifugal pumps specifically designed for high-viscosity applications. These pumps can generate the necessary pressure to maintain a steady flow rate despite the fluid’s thickness. When sourcing pumps, buyers should consult with manufacturers to ensure that the pump’s materials, such as impeller design and casing, are optimized for handling viscous fluids. Additionally, regular maintenance should include checking for wear on seals and bearings, which can contribute to performance inconsistencies. Implementing a monitoring system to track flow rates and pressures can also help identify performance deviations early, enabling preemptive actions before they escalate into significant issues.
Illustrative image related to types of centrifugal pump
Scenario 2: High Energy Costs from Inefficient Pump Systems
The Problem: An oil and gas company in Saudi Arabia faces rising energy costs attributed to their outdated centrifugal pump systems. The pumps are inefficient, consuming more energy than necessary to move fluids through their operations. This inefficiency not only impacts the company’s bottom line but also raises environmental concerns related to their carbon footprint, leading to pressure from stakeholders for more sustainable practices.
The Solution: The company should conduct a comprehensive energy audit to identify which pumps are underperforming and assess the potential for energy savings. Transitioning to modern, high-efficiency multi-stage or mixed-flow centrifugal pumps can significantly reduce energy consumption. Buyers should look for pumps with advanced designs that minimize hydraulic losses and incorporate variable frequency drives (VFDs) to optimize energy use based on real-time demand. Additionally, training staff on best practices for pump operation and maintenance can ensure that systems run efficiently. Establishing a routine review of energy performance can help maintain efficiency gains over time.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Sourcing Reliable Spare Parts
The Problem: A water treatment facility in South Africa struggles with prolonged downtimes due to delays in sourcing reliable spare parts for their centrifugal pumps. This issue arises from using pumps from multiple manufacturers, leading to a lack of standardized parts inventory. As a result, the facility faces increased maintenance costs and extended outages, disrupting service to the community.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, the facility should standardize the types of centrifugal pumps in use, preferably selecting models from a single reputable manufacturer that offers comprehensive support and readily available spare parts. This approach simplifies inventory management and speeds up repair times. It is also beneficial to establish a long-term relationship with the manufacturer or authorized distributor to ensure a reliable supply chain for parts and technical support. Implementing a preventive maintenance schedule, which includes regular inspections and timely replacements of components, can also help minimize breakdowns and extend the lifespan of the pumps. Creating a partnership with the supplier for emergency support can further enhance operational resilience.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for types of centrifugal pump
What are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Centrifugal Pumps?
When selecting materials for centrifugal pumps, it is crucial to consider their properties in relation to the specific application requirements. Here, we analyze four common materials: cast iron, stainless steel, bronze, and thermoplastics, focusing on their performance characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Cast Iron Perform in Centrifugal Pumps?
Key Properties: Cast iron is known for its excellent wear resistance and ability to withstand high pressures and temperatures, typically rated up to 300°F (150°C) and pressures around 150 psi. Its inherent strength makes it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of cast iron is its durability and cost-effectiveness, making it a popular choice for standard applications. However, it is prone to corrosion and may not perform well in aggressive chemical environments. Additionally, cast iron can be heavy, which may complicate installation and maintenance.

Illustrative image related to types of centrifugal pump
Impact on Application: Cast iron is ideal for water supply, irrigation, and wastewater applications, where the fluid is generally non-corrosive. However, it is less suitable for applications involving corrosive or abrasive media.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM or DIN, particularly for pressure ratings. Cast iron pumps are widely accepted, but regional preferences for corrosion resistance may necessitate additional coatings or linings.
What Advantages Does Stainless Steel Offer for Pump Applications?
Key Properties: Stainless steel is highly resistant to corrosion and can withstand high temperatures (up to 1000°F or 540°C) and pressures (up to 300 psi), making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and resistance to a variety of chemicals, making it ideal for food processing, pharmaceuticals, and corrosive environments. However, it is more expensive than cast iron and may require more complex manufacturing processes.
Illustrative image related to types of centrifugal pump
Impact on Application: Stainless steel pumps are commonly used in industries requiring high hygiene standards, such as food and beverage processing, as well as in chemical processing where fluid compatibility is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards like ASTM and JIS is essential for stainless steel pumps. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe may prefer stainless steel for its reliability in harsh environments, while also considering the higher upfront costs.
How Does Bronze Compare for Centrifugal Pump Applications?
Key Properties: Bronze offers excellent corrosion resistance, particularly against seawater and other saline environments. It typically operates effectively at temperatures up to 400°F (204°C) and pressures around 200 psi.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of bronze is its resistance to corrosion and wear, making it suitable for marine applications. However, it is more expensive than cast iron and may not be as readily available in some regions.
Impact on Application: Bronze pumps are ideal for applications involving seawater, chemicals, and other corrosive fluids. They are often used in marine and industrial applications where durability is paramount.
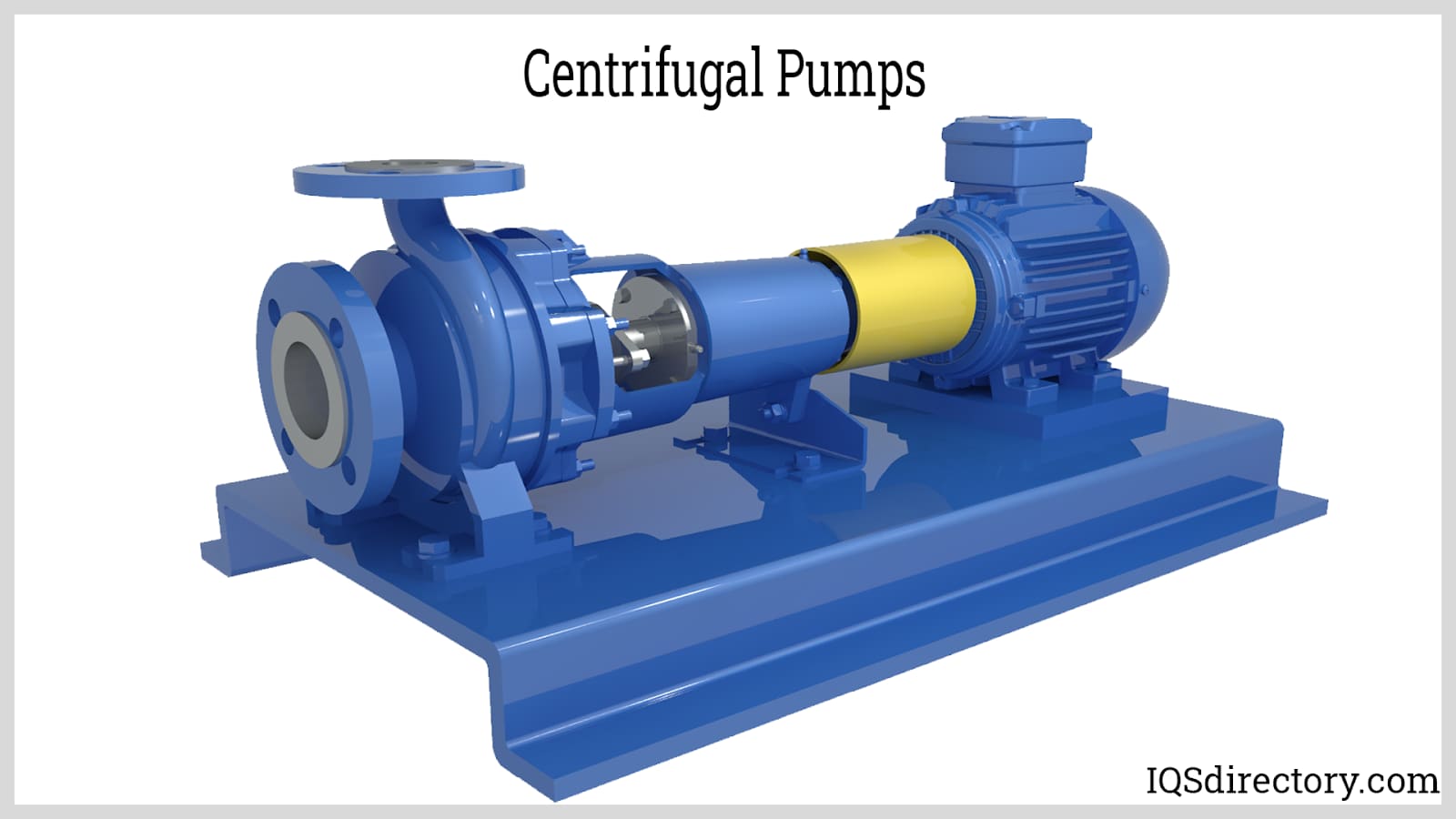
Illustrative image related to types of centrifugal pump
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in coastal regions, such as Brazil and parts of Europe, should consider bronze for its corrosion resistance. Compliance with marine standards and certifications is also critical for these applications.
What Role Do Thermoplastics Play in Centrifugal Pumps?
Key Properties: Thermoplastics, such as PVC and polypropylene, are lightweight and resistant to a wide range of chemicals. They can typically handle temperatures up to 180°F (82°C) and pressures around 100 psi.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of thermoplastics is their chemical resistance and lightweight nature, which simplifies installation and maintenance. However, they may not be suitable for high-temperature or high-pressure applications and can be less durable than metals.
Impact on Application: Thermoplastic pumps are commonly used in chemical processing and wastewater treatment, where fluid compatibility is crucial. They are ideal for transporting corrosive chemicals and are often used in laboratory settings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions with strict chemical handling regulations, such as the Middle East, should ensure compliance with local standards for plastic materials. The lightweight nature of thermoplastics may also appeal to buyers looking for easy transport and installation.

Illustrative image related to types of centrifugal pump
Summary Table of Material Selection for Centrifugal Pumps
| Material | Typical Use Case for types of centrifugal pump | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Iron | Water supply, irrigation, wastewater | Durable and cost-effective | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, pharmaceuticals, chemicals | High corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Bronze | Marine applications, chemicals | Excellent corrosion resistance | More expensive and less available | Medium |
| Thermoplastics | Chemical processing, wastewater treatment | Lightweight and chemical resistant | Limited high-temp/pressure capacity | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for centrifugal pumps, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for types of centrifugal pump
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Centrifugal Pumps?
The manufacturing process of centrifugal pumps is a complex and multi-stage operation that ensures each pump meets the rigorous demands of various industrial applications. The process generally consists of four main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Centrifugal Pump Manufacturing?
The first step in manufacturing centrifugal pumps involves selecting the appropriate materials, which typically include high-grade stainless steel, cast iron, or specialized alloys. These materials are chosen based on their corrosion resistance, strength, and thermal stability, which are crucial for the pump’s performance in different fluid environments.
Illustrative image related to types of centrifugal pump
Once materials are selected, they undergo preparation, which includes cutting, machining, and treating to achieve the desired specifications. For instance, machining components like impellers and casings to precise dimensions is critical to ensure optimal fluid dynamics and efficiency.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Pump Manufacturing?
After material preparation, the next stage is forming. This process can involve casting, forging, or machining, depending on the component.
-
Casting: This is commonly used for pump casings and volutes, where molten metal is poured into molds to create complex shapes. Investment casting is often employed for intricate parts like impellers.
-
Machining: For parts requiring high precision, such as shafts and bearings, machining processes like turning and milling are utilized. This ensures that the components fit together perfectly, which is vital for minimizing wear and maximizing efficiency.
-
Forging: This technique may be used for critical components that require enhanced strength. Forged parts typically offer better mechanical properties compared to cast components.
How Is the Assembly Process Conducted for Centrifugal Pumps?
The assembly stage is where all the manufactured components come together to create the final product. This process typically involves:
- Sub-Assembly: Individual components such as impellers, shafts, and bearings are first assembled into sub-units.
- Final Assembly: Sub-assemblies are then brought together. Precision is paramount here; misalignment can lead to operational inefficiencies or failures.
- Sealing and Testing: After assembly, pumps are sealed to prevent leaks, and initial testing is conducted to ensure functionality.
What Finishing Processes Are Essential for Centrifugal Pumps?
Finishing processes are crucial for enhancing both the aesthetic and functional aspects of centrifugal pumps. These processes include:
- Surface Treatment: Techniques such as polishing, coating, or anodizing are employed to improve corrosion resistance and reduce friction.
- Painting: Protective coatings are often applied to prevent corrosion and enhance durability.
- Final Inspection: Before leaving the factory, each pump undergoes a final inspection to ensure it meets all specifications and quality standards.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Followed in Pump Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) in centrifugal pump manufacturing is critical to ensure reliability and efficiency. Key international standards, such as ISO 9001, serve as a framework for quality management systems, helping manufacturers implement best practices.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Centrifugal Pumps?
Manufacturers often comply with various international standards that govern product quality and safety:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is crucial for ensuring consistent product quality.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, ensuring they meet safety and health requirements.
- API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute provides standards specifically for pumps used in oil and gas applications, ensuring safety and efficiency.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Pump Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is integrated throughout the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during manufacturing processes helps identify and rectify issues in real-time.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection stage assesses the completed pumps against quality standards, ensuring they are ready for shipment.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Quality Assurance?
Testing methods for centrifugal pumps can include:
- Hydrostatic Testing: Pumps are subjected to high-pressure water to check for leaks and structural integrity.
- Performance Testing: This involves measuring flow rate, pressure, and efficiency to verify that the pump meets performance specifications.
- Vibration Analysis: This technique assesses the mechanical balance and operational integrity of the pump to prevent future failures.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to ensure the quality of centrifugal pumps from suppliers, especially in international markets. Here are some effective strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of potential suppliers can help assess their quality control processes and adherence to international standards.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should request detailed quality assurance reports, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC stages.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturing processes and quality control measures in place.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it’s crucial to understand the nuances of quality control and certification. Factors to consider include:
- Regional Standards: Familiarize yourself with both local and international standards that apply to your industry.
- Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Be aware of the different regulatory environments in various countries, which may affect quality control practices.
- Supply Chain Reliability: Assess the supplier’s ability to consistently meet quality standards over time, considering potential disruptions in the supply chain.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting centrifugal pumps that meet their specific needs and regulatory requirements.
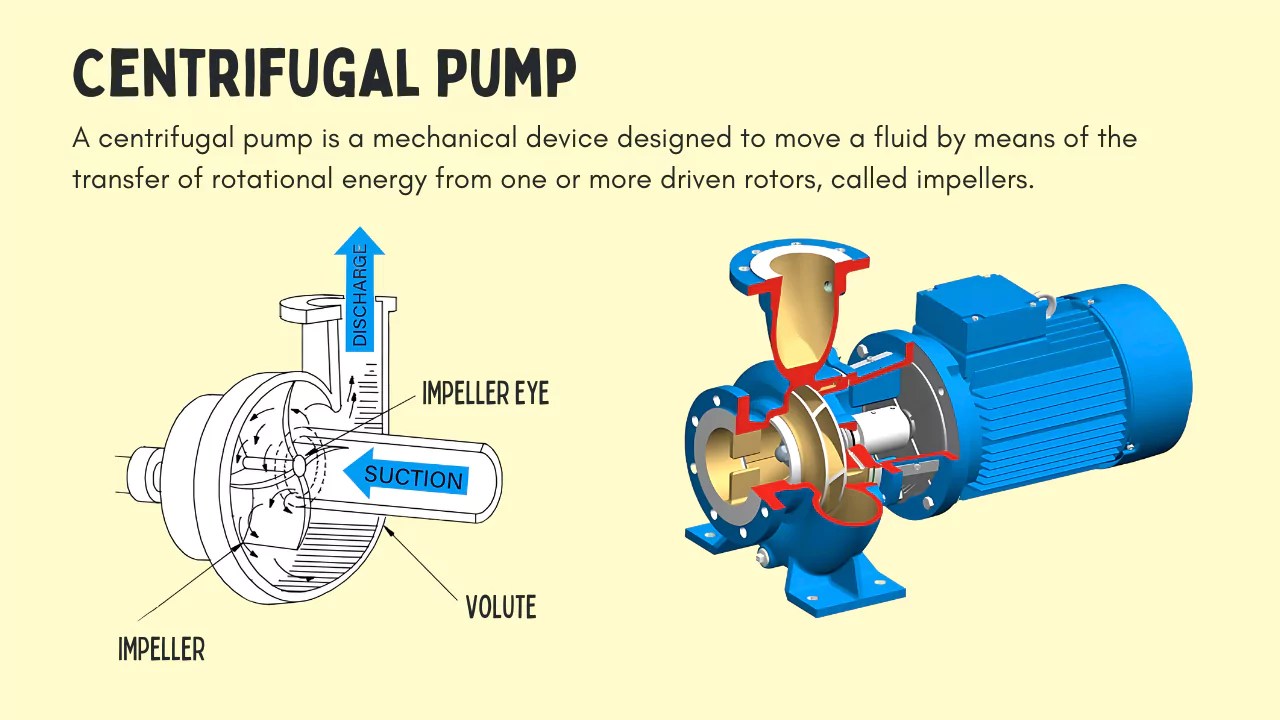
Illustrative image related to types of centrifugal pump
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘types of centrifugal pump’
To assist B2B buyers in procuring centrifugal pumps effectively, this guide provides a structured checklist to ensure that all critical aspects are covered during the sourcing process. By following these steps, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the requirements for your centrifugal pump. Consider factors such as flow rate, head pressure, fluid characteristics, and operational conditions. By defining these specifications upfront, you can narrow down the types of pumps that are suitable for your application, whether it be a single-stage, multi-stage, or a specialized type like a submersible pump.
Step 2: Assess Application Requirements
Evaluate the specific applications where the pump will be used. Identify whether the pump will handle clean fluids, wastewater, or chemicals, as this will dictate the material and design specifications needed. This step is crucial for ensuring that the selected pump can withstand the operational environment and meet performance expectations.
Step 3: Research and Shortlist Suppliers
Compile a list of potential suppliers that specialize in centrifugal pumps. Look for companies with a proven track record and experience in your industry. Consider their geographic location, especially if you are sourcing from regions like Africa or the Middle East, as this can impact lead times and shipping costs.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your shortlisted suppliers possess relevant certifications. Certifications such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific standards demonstrate a commitment to quality and safety. This validation is vital to mitigate risks associated with equipment failure and ensure compliance with local regulations.

Illustrative image related to types of centrifugal pump
Step 5: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Assess the manufacturing and technical capabilities of the suppliers. Inquire about their production processes, quality control measures, and R&D capabilities. A supplier’s ability to customize pumps for specific needs or provide technical support can be a deciding factor in your selection process.
Step 6: Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
Obtain detailed quotations from your shortlisted suppliers. Ensure that quotes include all relevant costs, such as shipping, installation, and after-sales support. Comparing pricing helps to identify the best value for your budget while ensuring that quality and service levels are not compromised.
Step 7: Review After-Sales Support and Warranty
Investigate the after-sales support and warranty options provided by suppliers. A robust support system can significantly affect your long-term satisfaction and operational efficiency. Check if they offer maintenance services, spare parts availability, and technical assistance to ensure that your pump operates smoothly throughout its lifecycle.
Illustrative image related to types of centrifugal pump
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing centrifugal pumps more effectively, ensuring that they select the right equipment to meet their specific needs while minimizing risks and maximizing value.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for types of centrifugal pump Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Centrifugal Pump Manufacturing?
When sourcing centrifugal pumps, understanding the cost structure is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences costs. For instance, high-quality stainless steel or specialized alloys for corrosive environments can elevate the price. Conversely, standard materials may reduce costs but could compromise durability in demanding applications.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and depend on the complexity of the pump design. Skilled labor is often required for high-precision manufacturing processes, especially in custom configurations. Automation can mitigate labor costs but requires a substantial upfront investment.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, maintenance, and operational expenses of manufacturing facilities. Efficient production processes can lower overhead, thereby reducing overall costs.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for unique pump designs adds to the initial costs. Standardized tooling, on the other hand, helps keep costs down and is suitable for mass production.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure product reliability and compliance with industry standards. While this adds to costs, it can prevent costly failures and recalls in the long run.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs are influenced by distance, shipping methods, and import/export regulations. International buyers should factor in customs duties and tariffs, especially when sourcing from overseas suppliers.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover risks and profits. This margin can vary based on market conditions and competitive pricing strategies.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Centrifugal Pump Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of centrifugal pumps, particularly for B2B buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk often leads to discounts. Suppliers may have minimum order quantities (MOQ) that affect pricing, making it advantageous to consolidate orders.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized pumps that meet specific operational requirements generally incur higher costs due to the additional design and manufacturing efforts. Standard models tend to be more cost-effective.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Pumps constructed from premium materials or those with necessary quality certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) may come at a premium. Buyers must weigh the benefits of enhanced durability against the additional costs.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, production capacity, and geographical location can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their reliability and service levels.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is essential for determining who bears the costs and risks during shipping. Terms such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can significantly influence total costs.
What Are the Best Negotiation Strategies for International Buyers?
International buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider the following tips to optimize costs:
-
Negotiate Volume Discounts: Leverage bulk purchasing to negotiate better terms. Suppliers are often willing to reduce prices for larger orders.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond initial purchase price, consider maintenance, operational efficiency, and longevity of the pump. A higher upfront investment in quality may yield lower TCO over time.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of fluctuating material prices and currency exchange rates, which can affect costs. Establishing contracts that account for these fluctuations can protect against unexpected price hikes.
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Evaluate multiple suppliers to understand market rates and negotiate effectively. Consider factors such as lead times, support services, and previous customer reviews.
-
Request Transparent Pricing: Ask suppliers for a detailed breakdown of costs. Understanding each component can empower buyers to negotiate specific elements, such as logistics or QC costs.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for centrifugal pumps can vary widely based on specifications, supplier, and market conditions. It is advisable to obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing and to consider all cost factors when making purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing types of centrifugal pump With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Fluid Transfer
In the realm of fluid transfer technologies, centrifugal pumps are a popular choice due to their efficiency and versatility. However, there are alternative solutions that may better suit specific applications or operational requirements. This section explores how various types of centrifugal pumps compare to other viable methods, such as positive displacement pumps and diaphragm pumps. By understanding these alternatives, B2B buyers can make informed decisions tailored to their unique needs.
Illustrative image related to types of centrifugal pump
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Types of Centrifugal Pump | Positive Displacement Pump | Diaphragm Pump |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High flow rates, moderate pressures | High pressures, lower flow rates | Variable flow rates, moderate pressures |
| Cost | Generally cost-effective for low-pressure applications | Higher initial costs but lower operating costs | Moderate to high initial costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Straightforward installation | Requires precise sizing and setup | Simple installation but may need frequent calibration |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance required | Low maintenance, but may require periodic overhauls | Moderate maintenance needs, with diaphragm replacement |
| Best Use Case | Water supply, HVAC, irrigation | Oil and gas, high-viscosity fluids | Chemical processing, wastewater treatment |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Positive Displacement Pumps
Positive displacement pumps operate by trapping a fixed amount of fluid and forcing it into the discharge pipe. This technology excels in applications requiring high pressures, making it ideal for scenarios involving thick or viscous fluids, such as those found in oil and gas sectors. While these pumps generally have higher initial costs, they often lead to lower operating costs due to their efficiency in high-pressure applications. However, they may require more meticulous installation and sizing to avoid issues such as cavitation.
Diaphragm Pumps
Diaphragm pumps utilize a flexible diaphragm to create a vacuum that draws fluid into the pump chamber and then expels it. These pumps are known for their ability to handle corrosive and abrasive materials, making them suitable for chemical processing and wastewater treatment applications. They offer variable flow rates, allowing for adaptability in different operational scenarios. However, diaphragm pumps may have moderate to high initial costs and require regular diaphragm replacements, which can add to maintenance efforts.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate fluid transfer solution depends on a variety of factors, including the specific application, required flow rates, pressure conditions, and budget constraints. For B2B buyers, understanding the unique benefits and limitations of centrifugal pumps compared to alternatives like positive displacement and diaphragm pumps is crucial. By evaluating these aspects in relation to their operational requirements, businesses can ensure they invest in a solution that not only meets their immediate needs but also supports long-term efficiency and reliability.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for types of centrifugal pump
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Centrifugal Pumps?
Centrifugal pumps are vital in various industries, and understanding their technical specifications is crucial for B2B buyers. Here are some essential properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material used in pump construction, such as stainless steel, cast iron, or plastic, affects durability, corrosion resistance, and overall performance. For instance, stainless steel is preferred for corrosive fluids, while cast iron is suitable for general applications. Selecting the right material ensures longevity and reduces maintenance costs. -
Flow Rate (Q)
Flow rate, measured in liters per minute (LPM) or gallons per minute (GPM), indicates the volume of fluid the pump can move in a given time. Understanding the required flow rate for specific applications helps in selecting the right pump type, ensuring efficient operation and avoiding underperformance or overloading. -
Total Dynamic Head (TDH)
TDH refers to the total height that the pump must overcome to move the fluid, including vertical lift and friction losses in the system. This specification is critical for determining pump performance and efficiency. Buyers must ensure that the selected pump can achieve the required TDH for their application. -
Efficiency Rating
This rating reflects how effectively the pump converts input power into hydraulic energy. High-efficiency pumps reduce operational costs and energy consumption, making them more sustainable options for long-term use. Evaluating efficiency helps businesses minimize overhead costs while maximizing productivity. -
Operating Temperature and Pressure
Each pump type has specified limits for temperature and pressure. Understanding these limits is essential for ensuring the pump operates within safe parameters, preventing equipment failure and costly downtime. Buyers must assess the environmental conditions of their applications to select the appropriate pump. -
Suction Lift Capability
This property indicates the pump’s ability to draw fluid from a lower elevation than the pump itself. It is crucial for applications where the fluid source is below the pump level. Buyers should consider suction lift capabilities to avoid issues with fluid movement and ensure optimal performance.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Centrifugal Pump Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can significantly enhance communication and decision-making in B2B transactions. Here are several key terms:

Illustrative image related to types of centrifugal pump
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable sources for pumps and components, ensuring quality and compatibility. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for buyers to plan their purchases effectively and manage inventory costs. It can also impact pricing and shipping considerations. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to solicit price bids from suppliers for specific products or services. This process allows buyers to compare offers, negotiate terms, and ensure they receive competitive pricing and favorable conditions for their purchases. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms helps buyers manage logistics, shipping costs, and risk during transportation, ensuring clarity in cross-border dealings. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the period between the initiation of an order and its completion. It is a critical factor in supply chain management, as longer lead times can affect project timelines. Buyers should consider lead times when planning purchases to ensure timely delivery. -
Pump Curve
A pump curve is a graphical representation of a pump’s performance, illustrating the relationship between flow rate and head. Analyzing pump curves helps buyers choose pumps that meet their specific operational needs, ensuring efficient system design and function.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms equips B2B buyers with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions when purchasing centrifugal pumps, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the types of centrifugal pump Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics for Centrifugal Pumps?
The global centrifugal pump market is witnessing substantial growth, driven by increased demand across various sectors including water supply, wastewater treatment, and chemical processing. As industries strive for enhanced efficiency, the adoption of advanced technologies such as IoT integration and automation is becoming prevalent. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial. The rise in infrastructure development in emerging markets, coupled with stringent regulations on water quality and environmental standards, is further fueling the demand for specialized centrifugal pumps.
Emerging trends include the shift towards energy-efficient models and smart pumps that offer real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance capabilities. Buyers should look for suppliers that provide not only a diverse range of centrifugal pump types—such as multi-stage and self-priming—but also those that can offer tailored solutions based on specific industry requirements. Additionally, the trend of digital transformation in supply chains is reshaping sourcing strategies, encouraging buyers to prioritize suppliers with robust online platforms for easier procurement processes.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Centrifugal Pump Market?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of procurement strategies in the centrifugal pump sector. B2B buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that prioritize environmentally friendly practices and materials. The environmental impact of centrifugal pumps, particularly in terms of energy consumption and lifecycle emissions, is prompting a shift towards greener alternatives. Pumps that are designed for lower energy use not only reduce operational costs but also align with global sustainability goals.
Ethical sourcing is equally vital, as buyers are now more aware of the importance of transparent supply chains. They seek suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with sustainability certifications, such as ISO 14001 or Energy Star ratings, which indicate a commitment to environmental management. Furthermore, the use of recyclable materials in pump manufacturing is gaining traction. By focusing on these aspects, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that contribute positively to their corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives.
What Is the Historical Context of Centrifugal Pumps in B2B?
The evolution of centrifugal pumps can be traced back to the late 17th century, with significant advancements occurring during the Industrial Revolution. Initially, these pumps were primarily mechanical devices without the efficiency and sophistication seen today. The introduction of electrical motors in the 20th century marked a turning point, allowing for greater automation and reliability. As industries expanded and diversified, the need for various centrifugal pump types emerged, tailored to specific applications ranging from irrigation to chemical processing.
By understanding the historical context and technological advancements in centrifugal pumps, B2B buyers can better appreciate the innovations that shape current market offerings. This knowledge enables them to make strategic procurement decisions that align with their operational needs and sustainability goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of types of centrifugal pump
-
How do I select the right centrifugal pump for my application?
Selecting the right centrifugal pump involves assessing your specific application requirements, including flow rate, head pressure, and the nature of the fluid being pumped. Consider the viscosity, temperature, and any solids present in the fluid. Additionally, evaluate the installation space and whether a standard or customized solution is necessary. Engaging with suppliers for technical support and detailed specifications can greatly assist in making an informed decision. -
What are the advantages of multi-stage centrifugal pumps over single-stage pumps?
Multi-stage centrifugal pumps are designed to generate higher pressures due to their multiple impellers. This makes them ideal for applications that require significant head pressure, such as boiler feed systems or water treatment plants. While they tend to have a higher initial cost and more complex maintenance requirements, their efficiency in handling higher viscosity fluids and delivering consistent performance makes them a preferred choice for demanding industrial applications. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers of centrifugal pumps?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their experience in the industry, customer reviews, and the range of products they offer. Check if they provide technical support and after-sales services, such as maintenance and spare parts availability. It’s also beneficial to assess their compliance with international standards and certifications, which can ensure product quality and reliability. Engaging with suppliers who have a strong presence in your region can also facilitate smoother logistics and communication. -
Are there minimum order quantities (MOQ) for purchasing centrifugal pumps?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among suppliers. Many manufacturers may set MOQs based on production costs or inventory levels, especially for customized pumps. It is advisable to communicate your needs directly to suppliers, as some may be flexible with MOQs for first-time buyers or smaller businesses. Understanding MOQs can help you plan your procurement strategy and budget effectively. -
What payment terms are typically offered in international trade for centrifugal pumps?
Payment terms in international trade can vary widely based on supplier policies and buyer relationships. Common options include advance payments, letter of credit, and payment upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer net payment terms, allowing for payment within a set period after delivery. It’s essential to negotiate terms that align with your financial capabilities while ensuring security for both parties. -
How do I ensure quality assurance (QA) for centrifugal pumps?
To ensure quality assurance, select suppliers who adhere to recognized international standards, such as ISO certifications. Request documentation of testing and inspection processes, including performance testing and material certifications. Regular communication with the supplier throughout the manufacturing process can also help address any potential issues early. Additionally, consider third-party quality audits to validate product standards before shipment. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing centrifugal pumps internationally?
Logistics considerations include shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Determine whether the supplier can handle shipping logistics or if you’ll need to arrange them independently. Understand the import/export regulations of your country, including tariffs and duties, which can affect the total cost. Ensuring proper packaging to prevent damage during transit is also crucial for maintaining product integrity. -
Can centrifugal pumps be customized for specific industrial applications?
Yes, centrifugal pumps can often be customized to meet specific industrial requirements. This may include adjustments to size, materials, impeller design, or additional features such as variable speed drives. Engaging with suppliers early in the design process can help ensure that the final product aligns with your operational needs. Custom solutions can enhance efficiency and performance, making them a valuable investment for specialized applications.
Top 4 Types Of Centrifugal Pump Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. DXPE – Centrifugal Pumps
Domain: dxpe.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Centrifugal pumps are used in various domestic and industrial processes, including water supply, food and beverage manufacturing, and chemical manufacturing. Key types include radial and axial pumps, ANSI pumps (high-quality, single impeller, easy maintenance, ideal for low fuel flow) and API pumps (heavy-duty, radial, used in oil and gas). Pumps are classified by stages: single-stage (one impelle…
2. Rotech Pumps – Single-stage Centrifugal Pumps
Domain: rotechpumps.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Types of Centrifugal Pumps: 1. Single-stage Centrifugal Pumps – Designed for low to moderate-pressure applications, with components including impeller, casing, volute, shaft, bearings, and mechanical seals. Advantages: Simplicity, cost-effective, suitable for clean fluids. Limitations: Limited head generation, less efficient for high-viscosity fluids. Common applications: Water supply, irrigation,…
3. IQS Directory – Centrifugal Pumps
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Centrifugal pumps are hydraulic mechanisms that convert mechanical energy into hydraulic energy using centrifugal force. Key components include: 1. Shaft – connects to the prime mover and turns with the impeller. 2. Impeller – consists of backwards-curved vanes that transfer velocity to the liquid. 3. Casing – a sealed passage that converts velocity into pressure energy. Types of casings include v…
4. Castle Pumps – Types of Centrifugal Pumps
Domain: castlepumps.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Types of Centrifugal Pumps: Close Coupled, Long Coupled, Vertical Inline, Horizontal, Magnetic Drive, Mechanically Sealed. Applications: Industrial, Marine, Chemical Manufacturing, Water Supply, Seawater Transfer, Boiler Feed, Water Circulation. Key Features: Efficient design, smooth flow, ease of operation, maintenance, suitable for clean low viscosity fluids. Close Coupled: Compact, cost-effecti…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for types of centrifugal pump
Centrifugal pumps are integral to various industries, facilitating efficient fluid transfer across diverse applications. By understanding the specific characteristics and operational capabilities of each type—ranging from single-stage to multi-stage, axial to radial flow—international B2B buyers can strategically source pumps that align with their operational requirements. This knowledge not only enhances efficiency but also drives cost-effectiveness in fluid management processes.
Illustrative image related to types of centrifugal pump
Strategic sourcing of centrifugal pumps should consider factors such as flow rates, pressure requirements, and fluid properties. Engaging with reliable suppliers who offer tailored solutions can lead to improved operational reliability and reduced downtime. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, leveraging local supplier networks can also foster sustainable partnerships that support economic growth.
As industries evolve, the demand for specialized centrifugal pumps will only increase. Buyers are encouraged to stay informed about technological advancements and emerging trends in pump design. By doing so, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and remain competitive in a rapidly changing global marketplace. Take the next step in optimizing your fluid management systems by exploring strategic sourcing opportunities today.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.