A B2B Buyer’s Guide to Titanium Cost: Price, Quality, and Suppliers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for titanium cost
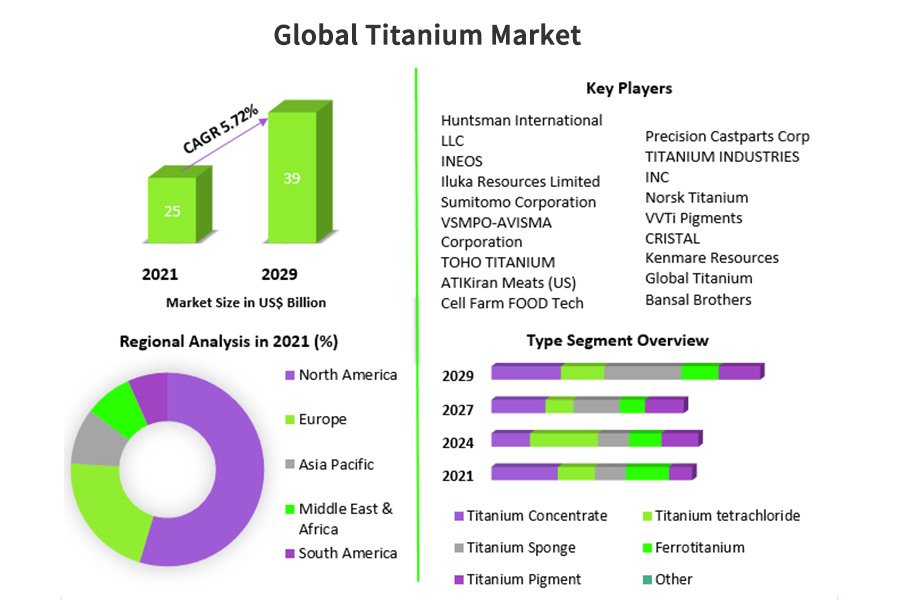
In the dynamic landscape of global trade, understanding titanium cost presents a significant challenge for B2B buyers. The fluctuating prices of this critical metal can impact sourcing decisions, affecting everything from supply chain management to final product pricing. This guide delves into the complexities of titanium costs, offering insights into various types of titanium products, their applications across industries, and effective supplier vetting strategies.
International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia—will find this resource invaluable. It not only provides an overview of current market trends and price benchmarks for titanium products like sponge titanium, alloys, and rutile titanium dioxide but also outlines the essential factors influencing pricing, such as production methods, geopolitical risks, and environmental regulations.
By arming B2B buyers with actionable insights and comprehensive data, this guide empowers informed purchasing decisions, enabling companies to navigate the complexities of the titanium market with confidence. Whether you’re looking to optimize costs, enhance supply chain resilience, or explore new sourcing opportunities, this resource is designed to support your strategic objectives in a competitive global marketplace.
Understanding titanium cost Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium Sponge | Raw form; high purity; used in metal production | Aerospace, Defense, Medical | Pros: High strength-to-weight ratio; essential for alloys. Cons: High cost; complex sourcing process. |
| Titanium Alloy Ingot (TC4) | Pre-processed; combines titanium with other metals | Aerospace components, Medical implants | Pros: Superior mechanical properties; versatile applications. Cons: Price volatility; limited suppliers. |
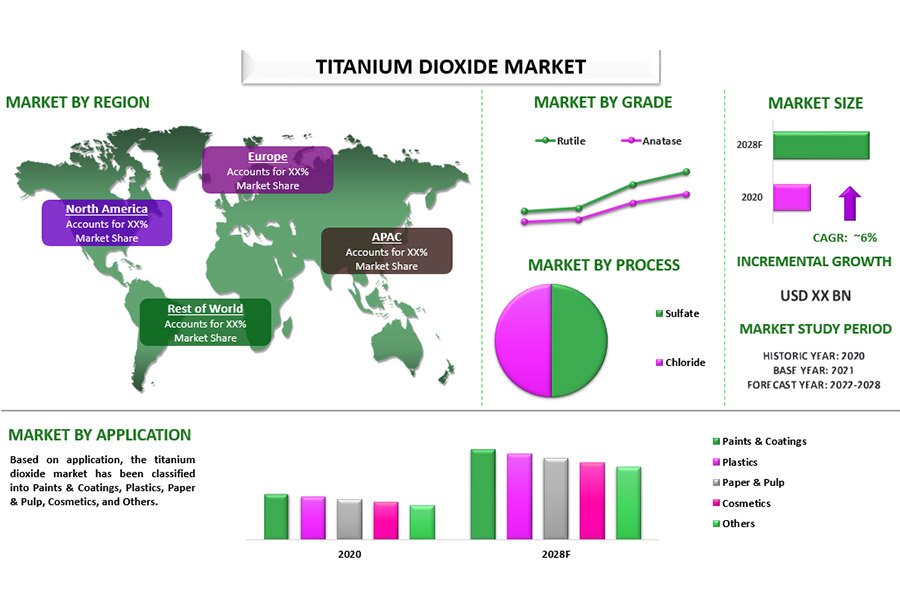
| Rutile Titanium Dioxide (TiO₂) | Widely traded form; utilized in various industries | Paints, Plastics, Cosmetics | Pros: High demand; well-established market. Cons: Price sensitive to raw material costs. |
| Titanium Slag | Intermediate product; lower purity than sponge | Pigment production, Steelmaking | Pros: More cost-effective than pure titanium; easier to source. Cons: Lower performance in high-end applications. |
| Processed Titanium Forms | Semi-finished products like bars, plates, and tubes | Manufacturing, Aerospace, Medical | Pros: Ready for immediate use; wide range of applications. Cons: Pricing varies significantly by form and grade. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Titanium Sponge?
Titanium sponge is the raw, porous form of titanium, characterized by its high purity and strength-to-weight ratio. It serves as the primary feedstock for producing titanium alloys, making it essential in industries such as aerospace, defense, and medical. Buyers should consider the sourcing complexities and high costs associated with titanium sponge, as well as the need for specialized suppliers who can ensure quality and consistency.
How Does Titanium Alloy Ingot (TC4) Differ from Other Types?
Titanium Alloy Ingot, particularly TC4, is a pre-processed form that combines titanium with other metals, enhancing its mechanical properties. This alloy is predominantly used in aerospace components and medical implants due to its superior performance under stress and extreme conditions. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of improved durability against the price volatility and limited supplier options that characterize this product.
What Role Does Rutile Titanium Dioxide (TiO₂) Play in the Market?
Rutile titanium dioxide (TiO₂) is the most widely traded form of titanium, primarily used in paints, plastics, and cosmetics. Its stable demand across various industrial sectors makes it a reliable option for buyers looking for less volatile pricing. However, the cost of rutile TiO₂ is sensitive to fluctuations in raw material prices, which can affect overall procurement strategies.
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Titanium Slag?
Titanium slag is an intermediate product that has a lower purity compared to titanium sponge. It is often used in pigment production and steelmaking, offering a more cost-effective option for buyers. While it is easier to source, its performance in high-end applications may not meet the stringent requirements of sectors like aerospace and medical, making it less suitable for critical applications.
Why Choose Processed Titanium Forms for Manufacturing Needs?
Processed titanium forms include semi-finished products like bars, plates, and tubes, which are ready for immediate use in manufacturing processes. These forms are versatile and cater to a wide range of applications across industries, including aerospace and medical. However, pricing can vary significantly based on the specific form and grade, necessitating careful consideration during procurement to ensure optimal cost-effectiveness.
Key Industrial Applications of titanium cost
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of titanium cost | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Aircraft components (airframes, engines) | High strength-to-weight ratio improves fuel efficiency | Compliance with aerospace standards (e.g., ASTM, AMS) |
| Medical Devices | Surgical implants and prosthetics | Biocompatibility ensures safe integration with human tissue | Certification for medical-grade materials |
| Automotive | Lightweight vehicle parts | Enhances performance and reduces emissions | Supplier reliability and adherence to industry regulations |
| Oil & Gas | Offshore platform components | Corrosion resistance extends lifespan and reduces costs | Understanding of local environmental regulations |
| Chemical Processing | Heat exchangers and reactors | Durability under extreme conditions increases efficiency | Sourcing from certified producers to ensure quality |
How is Titanium Cost Utilized in the Aerospace Industry?
In the aerospace sector, titanium is extensively used for manufacturing critical components like airframes and jet engines. The high strength-to-weight ratio of titanium alloys, such as TC4, significantly enhances fuel efficiency and performance. For international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa and the Middle East, it is crucial to ensure that suppliers comply with stringent aerospace standards such as ASTM and AMS. This not only guarantees product quality but also aligns with regulatory requirements for safety and performance.
What Role Does Titanium Play in Medical Devices?
Titanium’s application in medical devices, particularly in surgical implants and prosthetics, is driven by its biocompatibility and resistance to corrosion. This ensures that implants integrate safely with human tissue, minimizing the risk of rejection. Buyers in South America and Europe must prioritize sourcing from manufacturers that provide certified medical-grade titanium. This certification is essential to meet health regulations and ensure patient safety, making it a critical consideration for procurement.
How is Titanium Used in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, titanium is increasingly favored for lightweight vehicle parts, which help improve overall performance and reduce emissions. The use of titanium components can lead to enhanced fuel efficiency and reduced operational costs. B2B buyers in regions such as Nigeria and Saudi Arabia should focus on sourcing from suppliers who are reliable and adhere to automotive industry regulations. This ensures that the materials meet the necessary performance standards while also providing cost-effective solutions.
What are the Benefits of Titanium in Oil & Gas Applications?
Titanium is invaluable in the oil and gas sector, particularly for offshore platform components, due to its exceptional corrosion resistance. This property extends the lifespan of equipment, thereby reducing maintenance costs and downtime. Buyers must be aware of local environmental regulations when sourcing titanium, as compliance is essential for operational sustainability. Understanding these regulations will aid in selecting suppliers that align with both operational needs and environmental responsibilities.
How is Titanium Applied in Chemical Processing?
In chemical processing, titanium is used to manufacture heat exchangers and reactors that can withstand extreme conditions, thereby increasing operational efficiency. The durability of titanium components leads to longer service life and lower replacement costs. B2B buyers need to ensure that they source titanium from certified producers to guarantee material quality and compliance with industry standards. This consideration is particularly important for businesses looking to optimize their production processes while adhering to safety and regulatory requirements.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘titanium cost’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Price Volatility in Titanium Procurement
The Problem: B2B buyers often face significant challenges due to the volatility of titanium prices. Given that titanium is not traded on public exchanges, its pricing can fluctuate dramatically based on factors such as geopolitical tensions, supply chain disruptions, and changes in demand from key industries like aerospace and medical devices. Buyers in Africa or South America may find it particularly difficult to manage their budgets and forecast costs when negotiating long-term contracts for titanium products. This unpredictability can lead to budget overruns and strained supplier relationships, as buyers may struggle to justify sudden price increases to their stakeholders.
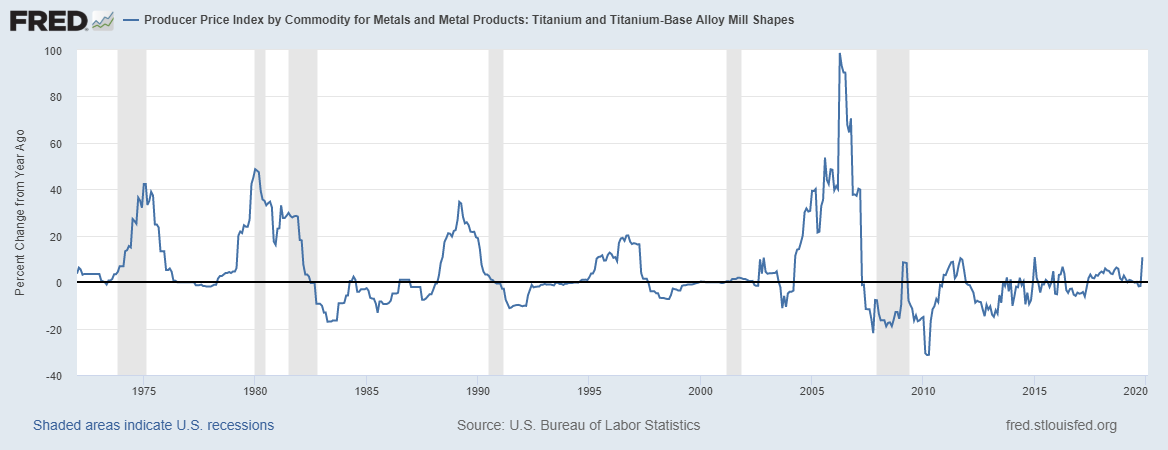
The Solution: To mitigate the risks associated with price volatility, B2B buyers should adopt a proactive procurement strategy that includes price hedging and long-term contracts. Engaging with suppliers to establish fixed pricing agreements or exploring options for futures contracts can help stabilize costs over time. Additionally, utilizing tools such as price trend analysis and real-time market intelligence from platforms like Trading Economics and Shanghai Metals Market can provide valuable insights into market movements. By closely monitoring titanium prices and trends, buyers can make informed decisions and negotiate better terms with suppliers, ultimately safeguarding their budgets against unforeseen fluctuations.
Scenario 2: Understanding the Complexity of Titanium Grades and Their Costs
The Problem: Titanium comes in various grades and forms, each with distinct properties and price points. For B2B buyers, especially those in industries like aerospace and medical manufacturing, selecting the appropriate grade can be a daunting task. Misunderstanding the specifications required for specific applications may lead to purchasing the wrong type of titanium, resulting in higher costs, increased waste, and potential project delays. Buyers from regions like the Middle East may find it particularly challenging to access detailed information on titanium grades and their corresponding costs.
The Solution: To navigate the complexities of titanium grades, buyers should invest time in understanding the specific requirements of their projects. Collaborating closely with engineers and technical teams can help clarify the necessary specifications. Additionally, leveraging online resources and technical documentation from reputable suppliers can provide insights into the properties and applications of various titanium grades. Establishing strong relationships with knowledgeable suppliers who can offer guidance on selecting the right grade based on application needs can also be invaluable. Furthermore, considering bulk purchasing options for commonly used grades can help reduce overall costs while ensuring the right materials are available for production.
Scenario 3: Addressing Supply Chain Disruptions Impacting Titanium Availability
The Problem: The global supply chain for titanium is often subject to disruptions caused by factors such as political instability, environmental regulations, and fluctuations in raw material availability. B2B buyers, especially those in Europe and Africa, may experience delays in receiving titanium supplies, which can halt production lines and lead to missed deadlines. This situation is exacerbated by the fact that titanium is essential for many high-performance applications, making timely availability crucial for manufacturers.
The Solution: To counteract supply chain disruptions, B2B buyers should develop a diversified sourcing strategy. This involves establishing relationships with multiple suppliers across different regions to ensure a steady flow of materials, even if one source is compromised. Implementing inventory management systems that allow for real-time tracking of stock levels can also help buyers anticipate shortages and react accordingly. Additionally, engaging in strategic partnerships with suppliers can foster better communication and collaboration, enabling buyers to stay informed about potential disruptions and plan accordingly. Investing in local suppliers, when possible, can also reduce lead times and enhance supply chain resilience, ensuring that production schedules remain on track despite global challenges.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for titanium cost
When selecting materials for titanium applications, it is essential to consider the specific properties, advantages, and limitations of various titanium grades and forms. Below, we analyze four common materials relevant to titanium costs, providing insights tailored for international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Properties of Titanium Sponge?
Titanium sponge is a porous form of titanium produced through the Kroll process. It has a high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for high-performance applications in aerospace and medical industries. The temperature rating is significant, as it can withstand extreme conditions, which is critical for aerospace components.
Pros: Titanium sponge is the primary raw material for producing titanium alloys, which are essential for high-stress applications. Its lightweight nature reduces overall system weight, enhancing fuel efficiency in aerospace applications.
Cons: The production process is energy-intensive and costly, leading to a high relative cost. Additionally, the manufacturing complexity can limit the availability of certain grades.
Impact on Application: Titanium sponge is particularly compatible with environments that require high strength and corrosion resistance, such as aerospace and high-performance automotive applications.
How Does Titanium Alloy Ingot (TC4) Compare?
Titanium Alloy Ingot, especially TC4 (Ti-6Al-4V), is one of the most widely used titanium alloys due to its superior mechanical properties. It exhibits excellent fatigue resistance and can operate effectively at elevated temperatures.
Pros: TC4 is known for its high strength and lightweight characteristics, making it ideal for aerospace and medical implants. It also offers good weldability, which is beneficial for complex designs.
Cons: The cost is significantly higher than that of pure titanium due to the alloying elements and the complex manufacturing processes involved. Additionally, machining TC4 can be challenging, requiring specialized equipment.
Impact on Application: This alloy is suitable for applications that demand high strength and durability, such as aircraft components and orthopedic implants, where biocompatibility is crucial.
Illustrative image related to titanium cost
What Are the Benefits of Titanium Dioxide (TiO₂)?
Titanium Dioxide is primarily used as a pigment in various industries, including paints, plastics, and cosmetics. It is known for its high refractive index and opacity.
Pros: TiO₂ is abundant and relatively inexpensive compared to titanium metal. It provides excellent whiteness and brightness, making it a preferred choice in coatings and plastics.
Cons: While it offers good properties for pigments, TiO₂ lacks the mechanical strength and corrosion resistance of titanium metal, limiting its use in structural applications.
Impact on Application: TiO₂ is crucial in industries where aesthetics and opacity are important, but it is not suitable for high-stress applications like aerospace or medical devices.
How Does Titanium Grade 2 Compare in Terms of Cost and Performance?
Titanium Grade 2 is a commercially pure titanium with excellent corrosion resistance and moderate strength. It is often used in chemical processing and marine environments.
Pros: This grade is more cost-effective than titanium alloys and provides excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including chemical processing and marine environments.
Cons: While it offers good corrosion resistance, it does not have the same strength-to-weight ratio as titanium alloys, limiting its use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Titanium Grade 2 is ideal for applications requiring corrosion resistance, such as heat exchangers and chemical tanks, particularly in industries prevalent in regions like the Middle East and South America.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Titanium Costs
| Material | Typical Use Case for titanium cost | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium Sponge | Aerospace components | High strength-to-weight ratio | High production cost | High |
| Titanium Alloy Ingot (TC4) | Medical implants | Excellent mechanical properties | Complex machining requirements | High |
| Titanium Dioxide (TiO₂) | Pigment in coatings | Abundant and cost-effective | Limited structural applications | Low |
| Titanium Grade 2 | Chemical processing equipment | Excellent corrosion resistance | Moderate strength | Medium |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the critical materials involved in titanium costs, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for titanium cost
What Are the Main Stages of Titanium Manufacturing?
The manufacturing of titanium is a complex and multi-step process that requires precision and adherence to industry standards. Understanding these stages is crucial for B2B buyers as it directly influences the cost and quality of the final product.
Material Preparation: What Are the Key Steps?
The initial stage involves sourcing raw materials, primarily titanium ores like ilmenite and rutile. The quality of these ores significantly affects the final product. Following sourcing, the ore undergoes crushing and grinding to separate titanium from impurities. The next step is the conversion of titanium ore into titanium tetrachloride (TiCl₄) through a process known as the Kroll process. This process involves chemical reactions that extract titanium, which is then refined into sponge titanium.
How Is Titanium Formed into Usable Products?
Once the titanium sponge is produced, it is melted and formed into various shapes, including ingots, bars, and sheets. This stage typically employs techniques such as vacuum arc remelting (VAR) and electron beam melting (EBM), which ensure a high degree of purity and structural integrity. These methods are particularly favored in industries like aerospace and medical due to the high-performance demands of their applications.
What Does the Assembly Stage Entail?
In the assembly stage, manufacturers combine various titanium components to create finished products. This may involve welding, machining, and other fabrication techniques. The assembly must be meticulously controlled to maintain the strength and durability of the titanium parts, as any defect can lead to significant failures, particularly in critical applications such as aerospace and medical implants.
What Finishing Techniques Are Used to Enhance Titanium Products?
The finishing stage includes processes like surface treatment, coating, and heat treatment. These processes enhance the corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal of titanium products. Techniques such as anodizing and passivation are commonly used to create protective layers that improve longevity and performance, especially in harsh environments.

Illustrative image related to titanium cost
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Titanium Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is an integral part of titanium manufacturing, ensuring that products meet stringent industry standards and customer specifications. For international B2B buyers, understanding the quality assurance processes is essential to mitigate risks associated with product failure.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Manufacturers often adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system. Additionally, industry-specific standards like CE marking for products sold in Europe and API standards for oil and gas applications are critical for compliance. These standards ensure that titanium products are manufactured consistently and reliably.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are critical throughout the manufacturing process to maintain high standards. These include:
Illustrative image related to titanium cost
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage checks the quality of incoming raw materials to ensure they meet specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular checks are performed to monitor the process and detect any deviations from quality standards.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): This final stage involves comprehensive testing of the finished product to ensure it meets all specifications before shipping.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Titanium QC?
Several testing methods are employed to ensure the quality of titanium products:
-
Mechanical Testing: Tensile tests, impact tests, and hardness tests evaluate the physical properties of titanium.
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing and radiographic testing help identify internal defects without damaging the product.
-
Chemical Analysis: Spectrometry and other analytical methods are used to verify the composition of titanium alloys.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is crucial. Here are some actionable steps:
What Are the Best Practices for Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is one of the most effective ways to verify quality control practices. During an audit, buyers can evaluate the manufacturing processes, QC protocols, and adherence to international standards. It is advisable to conduct both initial and periodic audits to ensure ongoing compliance.
How to Request Quality Reports and Documentation?
Buyers should request comprehensive quality documentation from suppliers, including material certifications, test reports, and compliance certificates. Suppliers should be willing to provide this information to ensure transparency and build trust.
What Role Do Third-Party Inspections Play?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control measures. These inspectors can conduct on-site evaluations and provide reports that help buyers make informed decisions.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Transactions?
When sourcing titanium from international suppliers, B2B buyers must navigate various quality control nuances:
Illustrative image related to titanium cost
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have specific regulations that affect the quality standards of titanium products. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these requirements to ensure compliance.
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural practices in quality assurance can aid in better communication with suppliers. Buyers should be aware that practices may vary significantly between regions.
-
Supply Chain Transparency: A transparent supply chain is essential for assessing quality. Buyers should work with suppliers who are open about their sourcing and manufacturing processes.
Conclusion: Why Is Understanding Manufacturing and QC Critical for B2B Buyers?
For B2B buyers in industries where titanium is a critical component, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures is essential. This knowledge not only helps in assessing the cost of titanium but also ensures that the products meet the necessary quality standards for their specific applications. By following best practices in supplier verification and understanding international standards, buyers can make informed decisions that mitigate risks and enhance operational efficiency.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘titanium cost’
Introduction
In the competitive landscape of titanium procurement, understanding the cost implications is crucial for B2B buyers. This guide provides a structured checklist to streamline your sourcing process, ensuring that you make informed decisions while securing the best value for your investment in titanium products.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the specific titanium products you require, including grades, forms, and quantities. This step is vital because different applications—such as aerospace, medical, or industrial—demand varying specifications. By defining your needs upfront, you can better match suppliers’ offerings and avoid unnecessary costs or delays.
Step 2: Research Current Market Prices
Stay informed about the latest titanium prices by consulting reliable market resources like Trading Economics and CarbonCredits.com. Understanding price fluctuations and historical trends helps you anticipate costs and budget accordingly. Regularly monitoring these resources allows you to negotiate effectively with suppliers based on current market conditions.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct thorough due diligence. Look for company profiles, case studies, and testimonials from businesses in similar industries or regions. This evaluation process is essential to ensure the supplier has a proven track record of quality and reliability, which can significantly impact your project’s success.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications and comply with international standards, such as ISO 9001 for quality management. This step is crucial to mitigate risks associated with product quality and regulatory compliance. Ask for documentation that validates their certifications and conduct audits if necessary.
Step 5: Request Samples and Test Products
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the titanium products. Testing these samples against your technical specifications ensures that the materials meet your quality requirements. This step can prevent costly mistakes and ensure that you are investing in the right products for your applications.
Step 6: Negotiate Payment Terms and Conditions
Discuss payment terms, including pricing, delivery schedules, and potential discounts for bulk orders. Clear communication on these terms is essential to avoid misunderstandings later in the procurement process. Establishing favorable terms can also enhance your cash flow management.
Step 7: Plan for Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Develop a logistics plan that considers shipping, storage, and handling of titanium products. Understanding these logistics is critical, especially for international transactions, as it can affect delivery timelines and costs. Collaborate with your supplier to ensure that they can meet your logistical requirements efficiently.
Illustrative image related to titanium cost
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of titanium procurement with confidence, ensuring that they secure the best products at competitive prices while minimizing risks.
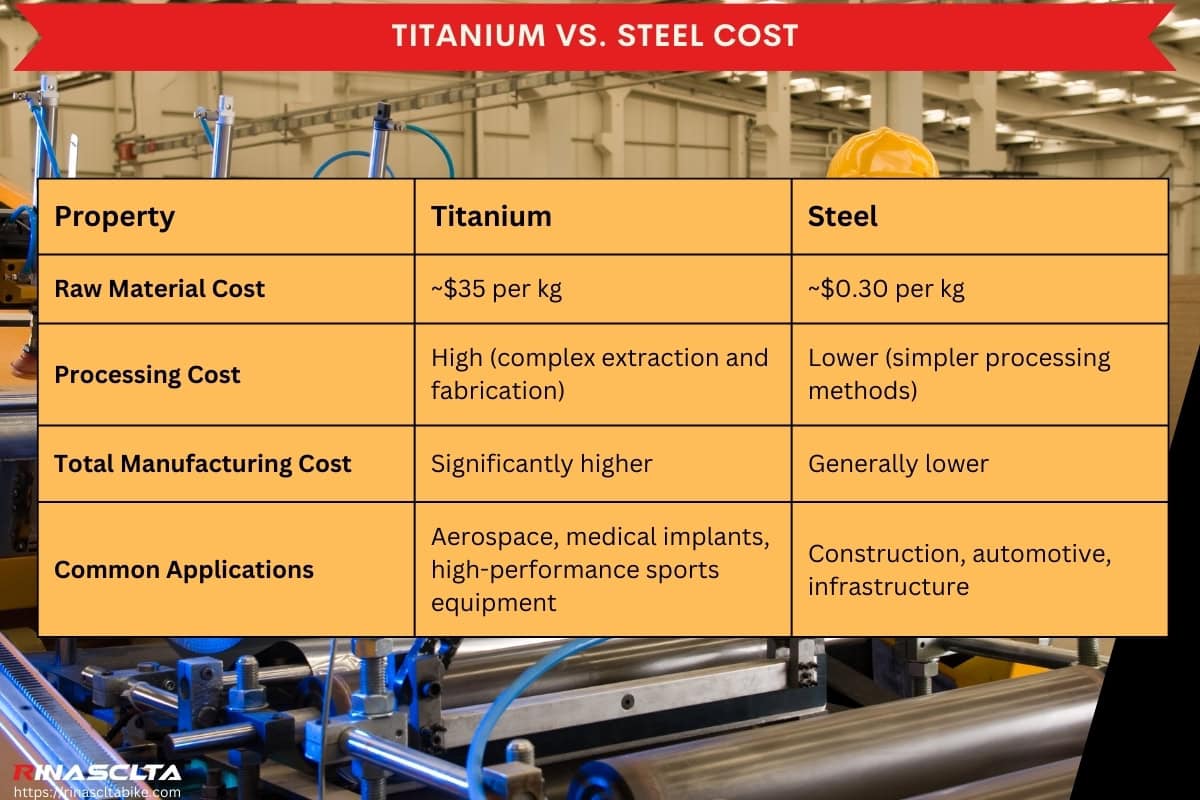
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for titanium cost Sourcing
Analyzing the cost structure and pricing for titanium sourcing reveals a complex interplay of various components that international B2B buyers need to navigate effectively. Understanding these elements can lead to better procurement strategies and cost efficiencies.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Titanium Sourcing?
The cost structure for titanium comprises several critical components:
-
Materials: The primary cost driver is the titanium ore itself, which varies based on purity and form (e.g., titanium sponge vs. titanium alloy). For instance, prices for titanium sponge can range from approximately $5,700 to $6,300 per metric ton depending on quality and supplier.
-
Labor: Labor costs in the extraction and manufacturing processes can significantly impact overall pricing. Countries with lower labor costs may offer more competitive pricing, but this can also affect quality and consistency.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with facilities, equipment maintenance, and energy consumption. Titanium production is energy-intensive, especially in the refining stages, which can lead to fluctuating prices based on energy market conditions.
-
Tooling: The costs related to specialized equipment for processing titanium can be substantial. Investment in high-quality tooling can improve efficiency and reduce waste, ultimately affecting pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the integrity of titanium products through rigorous QC processes incurs additional costs. Certifications for specific industries, such as aerospace or medical, can also add to the overall expense.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs are particularly significant for international shipments. Factors such as Incoterms, shipping routes, and customs duties can alter the final price for buyers.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a margin to cover their operational costs and profit. Understanding the market dynamics can help buyers negotiate better margins.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Titanium Costs?
Several factors can influence titanium pricing, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often attract bulk pricing discounts, making it essential for buyers to assess their needs and negotiate MOQs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Tailoring products to specific requirements can lead to increased costs. Buyers should clarify their specifications early in negotiations to avoid unexpected price hikes.
-
Quality and Certifications: High-grade titanium and certified materials command higher prices. Buyers should evaluate the necessity of certifications based on their intended applications to optimize costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium, but they often offer better quality assurance and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding delivery terms is critical. Different Incoterms can shift cost responsibilities between buyers and suppliers, impacting the overall price.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Titanium Sourcing Costs?
-
Negotiation Strategies: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing structures and be prepared to leverage volume commitments to negotiate better rates.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider all costs associated with procurement, including logistics and potential quality issues, rather than focusing solely on upfront pricing.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Keeping abreast of market conditions, such as shifts in demand from industries like aerospace or medical, can provide insights into pricing trends and help in timing purchases.
-
Explore Multiple Suppliers: Diversifying the supplier base can lead to competitive pricing and reduce dependency on a single source, which is particularly important for international buyers facing geopolitical risks.
-
Understand Regional Pricing Nuances: Pricing dynamics can vary significantly between regions. For instance, buyers in Africa or South America may encounter different cost structures compared to those in Europe or the Middle East, influenced by local market conditions and regulations.
Conclusion
While titanium sourcing presents unique challenges, a thorough understanding of cost components, price influencers, and strategic procurement approaches can empower international B2B buyers to make informed decisions. As the market evolves, staying proactive and adaptable will be key to achieving cost efficiencies and maintaining a competitive edge.
Disclaimer: Prices mentioned are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions and specific supplier agreements.
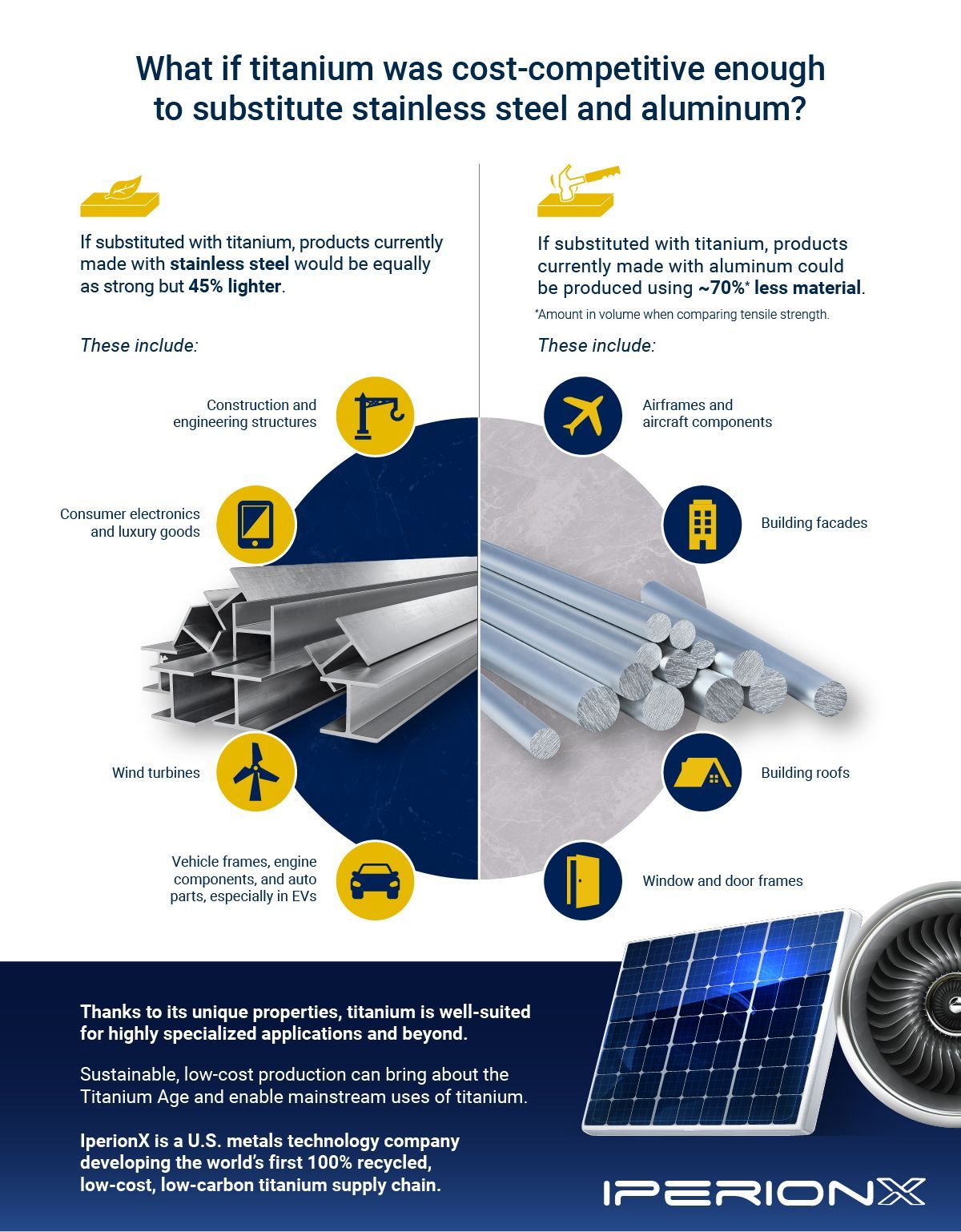
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing titanium cost With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Titanium: Cost Comparison and Insights
In the competitive landscape of materials sourcing, businesses must assess alternatives to titanium, especially in industries where cost efficiency and performance are critical. This section provides a comparative analysis of titanium costs against viable alternatives, focusing on performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | Titanium Cost | Aluminum Alloy | Carbon Fiber |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance | Good strength, lightweight, but less durable than titanium | Very high strength, low weight, excellent stiffness |
| Cost | $5,700 – $7,500+ per metric ton | $2,500 – $3,500 per metric ton | $15,000 – $25,000 per metric ton |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized welding and machining | Easier to work with; conventional methods apply | Requires specialized manufacturing and molding techniques |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; highly durable | Moderate maintenance; susceptible to corrosion | Low maintenance; high durability but can be prone to impact damage |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, medical implants, high-stress applications | Automotive, consumer goods, structural applications | High-performance sporting goods, aerospace, automotive |
In-depth Analysis of Alternatives
Aluminum Alloy
Aluminum alloys are a popular alternative due to their lower cost and ease of use. They offer good strength and are widely used in industries such as automotive and construction. However, while they provide a favorable strength-to-weight ratio, they do not match titanium’s performance in extreme environments, particularly in aerospace applications. Additionally, aluminum alloys are more susceptible to corrosion, requiring surface treatments or coatings to enhance longevity. Overall, aluminum is a suitable choice for applications where cost is a primary concern, but performance requirements are not as stringent.
Carbon Fiber
Carbon fiber is renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness, making it an attractive alternative for high-performance applications. While it offers superior performance, the cost is significantly higher than both titanium and aluminum, making it less accessible for budget-conscious projects. The manufacturing process for carbon fiber components is specialized, often involving complex molding techniques, which can lead to longer lead times and higher production costs. Carbon fiber is ideal for industries like aerospace and high-end sporting goods, where performance justifies the investment.
How to Choose the Right Material for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate material requires a careful evaluation of specific project requirements and constraints. B2B buyers should consider the critical performance needs of their application, budget limitations, and the feasibility of implementation. For applications demanding high strength, corrosion resistance, and durability, titanium remains a top choice despite its higher cost. Conversely, for projects with less demanding performance criteria or tighter budgets, aluminum alloys provide a viable alternative. For high-performance applications where weight and stiffness are paramount, carbon fiber may be worth the investment despite its cost.
In conclusion, understanding the nuances of each material’s advantages and limitations will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and financial considerations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for titanium cost
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Titanium That Impact Cost?
Understanding the essential technical properties of titanium is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when evaluating pricing and suitability for specific applications. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
Titanium is available in various grades, primarily classified by the ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) standard. Common grades include Grade 1 (commercially pure titanium) and Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V alloy). The grade determines the metal’s mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and suitability for various applications. Higher-grade titanium often commands a premium price due to its enhanced performance characteristics, making it essential for industries like aerospace and medical devices. -
Tensile Strength
This property refers to the maximum amount of tensile (stretching) stress that a material can withstand before failure. Titanium’s tensile strength varies by grade, with some alloys capable of withstanding extreme stress, making them ideal for high-performance applications. Understanding tensile strength is vital for B2B buyers as it directly impacts the material’s suitability for specific engineering applications, affecting both safety and cost. -
Corrosion Resistance
Titanium is renowned for its excellent resistance to corrosion, particularly in aggressive environments. This property is crucial for industries such as oil and gas, marine, and chemical processing, where materials are exposed to harsh conditions. Buyers must consider the long-term cost implications of corrosion resistance, as it can significantly affect maintenance and replacement costs. -
Density
Titanium’s low density (approximately 60% of that of steel) makes it a preferred choice in applications requiring a high strength-to-weight ratio, such as aerospace and automotive components. For B2B buyers, understanding density is essential in calculating material costs and evaluating logistics for transportation and handling. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in dimensions and is critical in manufacturing processes. Tight tolerances may increase production costs but are often necessary for applications that require precise fitting. Buyers must assess their tolerance requirements to avoid unexpected costs or delays in production.
What Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Understand When Dealing with Titanium Costs?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective negotiation and procurement. Here are some common trade terms that B2B buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and negotiate better pricing based on production volumes. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it can affect inventory costs and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ can help buyers assess whether a supplier aligns with their purchasing strategy. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. Crafting a clear RFQ can lead to competitive pricing and better terms. It’s a standard practice in B2B transactions and vital for cost management. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Familiarity with Incoterms can help buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, thus influencing overall cost management strategies. -
Lead Time
This term refers to the time taken from placing an order to its delivery. Understanding lead times is crucial for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and project timelines. A longer lead time may necessitate higher inventory levels, impacting overall costs.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when navigating the complexities of titanium procurement, ensuring they secure the best value for their investments.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the titanium cost Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Affecting Titanium Costs?
The titanium market is characterized by a complex interplay of global drivers that significantly influence pricing and sourcing strategies. The demand for titanium, particularly in the aerospace and medical sectors, remains robust due to its unique properties, such as high strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. As of Q2 2025, titanium sponge prices hover around $5,700 to $5,950 per metric ton, while titanium alloy ingots reach approximately $7,500 per metric ton. These figures underscore the metal’s critical role in high-performance applications, especially in regions like Europe, the Middle East, and Africa, where infrastructure and aerospace industries are expanding.
International B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging technology to enhance sourcing strategies. Digital platforms that facilitate real-time pricing and inventory tracking are becoming essential tools for procurement teams. Additionally, private contracts and over-the-counter deals dominate the titanium market, making it crucial for buyers to establish strong relationships with suppliers to negotiate favorable terms. Emerging trends also highlight the importance of diversifying supply chains to mitigate risks associated with geopolitical tensions and trade policies, particularly in light of the growing focus on critical minerals.

Illustrative image related to titanium cost
How Is Sustainability Influencing Titanium Sourcing Practices?
Sustainability has become a pivotal concern in the titanium sector, prompting B2B buyers to prioritize ethical sourcing practices. The environmental impact of titanium mining, which involves energy-intensive processes and significant land disruption, calls for a shift towards more sustainable operations. Companies are increasingly adopting green certifications and seeking suppliers who adhere to environmentally responsible practices. This not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with global sustainability goals.
Moreover, the demand for ‘green’ titanium, produced through environmentally friendly methods, is on the rise. Buyers are encouraged to evaluate suppliers based on their sustainability credentials, which may include reduced carbon footprints, recycling initiatives, and responsible waste management. By investing in sustainable sourcing, B2B buyers can not only reduce environmental impact but also create long-term value by meeting the increasing demand for ethically produced materials from consumers and regulatory bodies.
What Is the Historical Context of Titanium Pricing and Supply?
The titanium market has evolved significantly over the past few decades, transitioning from a niche material to a critical component in various high-tech industries. Initially, titanium was primarily used in military applications, but advancements in technology have broadened its use across sectors such as aerospace, medical, and automotive industries. The classification of titanium as a critical mineral by various governments, including the U.S., underscores its strategic importance and has led to increased scrutiny of supply chains.
Historically, titanium prices have fluctuated based on factors such as production costs, global demand, and availability of raw materials like rutile and ilmenite. As emerging markets in Africa and South America continue to develop, the dynamics of titanium sourcing are likely to shift, offering new opportunities for international buyers to engage with diverse suppliers and innovate in their procurement strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of titanium cost
-
How do I determine the current market price of titanium?
To ascertain the current market price of titanium, regularly check reputable financial news platforms and commodity market resources such as Trading Economics and CarbonCredits.com. These platforms provide real-time updates on titanium prices and historical data, allowing you to monitor fluctuations. Additionally, consider establishing relationships with suppliers and industry analysts who can provide insights into market trends and pricing dynamics specific to your region. -
What factors influence titanium pricing in international markets?
Titanium pricing is influenced by several factors including raw material costs, production methods, demand from key industries (like aerospace and medical), and geopolitical considerations. Environmental regulations can also impact supply chain costs. For B2B buyers, understanding these dynamics can aid in forecasting price trends and making informed procurement decisions. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for titanium products?
Minimum order quantities for titanium products can vary significantly between suppliers and product types. Generally, MOQs can range from a few kilograms for processed forms like bars and plates to several tons for bulk materials. It’s essential to discuss your specific needs with suppliers to negotiate favorable terms that align with your purchasing strategy. -
How can I vet titanium suppliers effectively?
To vet titanium suppliers, consider their industry reputation, certifications, and compliance with international standards. Request references from previous clients and review their production capabilities and quality assurance processes. Additionally, visiting the supplier’s facility, if feasible, can provide valuable insights into their operations and reliability. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing titanium internationally?
Payment terms for international titanium sourcing typically vary based on supplier policies and the nature of the transaction. Common arrangements include letters of credit, advance payments, or payment upon delivery. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that provide sufficient protection against risks while also considering the supplier’s requirements. -
What quality assurance measures should I consider for titanium products?
Quality assurance in titanium sourcing involves ensuring that products meet the required specifications and standards. Look for suppliers who provide certification for their materials, such as ISO or ASTM standards. Additionally, consider implementing third-party inspections and testing to verify the quality and performance of the titanium you are purchasing. -
What are the logistics considerations when importing titanium?
Logistics for importing titanium involve understanding shipping options, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Coordinate with your supplier to determine the most efficient shipping methods and ensure all documentation is accurate to avoid delays. Engaging a logistics partner with experience in handling metal imports can streamline this process significantly. -
How can I customize titanium products to meet specific project requirements?
Many titanium suppliers offer customization options for products to meet specific project needs, such as altering dimensions, alloys, or finishes. When discussing your requirements, provide detailed specifications and any relevant standards. Collaborating closely with the supplier during the design and production phases can help ensure that the final product aligns with your expectations.
Top 7 Titanium Cost Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Trading Economics – Titanium Price Trends
Domain: tradingeconomics.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Titanium traded at 49.01 CNY/KG on September 5, 2025. Over the past month, the price has risen 0.02% and is up 11.39% compared to the same time last year. The all-time high for Titanium was 152.43 CNY/KG in May 2022. It is expected to trade at 49.25 CNY/KG by the end of the current quarter and 49.98 CNY/KG in 12 months. Historical data shows prices ranging from a low of 29.69 CNY/KG to the all-tim…
2. CarbonCredits – Titanium Pricing Insights
Domain: carboncredits.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Live Titanium Prices Today: Rutile Titanium Dioxide (TiO₂) pricing is approximately $2000 USD per metric ton as of Q2 2025. Titanium Alloy Ingot (TC4) is valued at approximately $7500 USD per metric ton. Rutile titanium dioxide averages around $1,772–$2,100 USD per metric ton depending on location and delivery terms. Current average prices for titanium metals (Q2 2025) include: Titanium Sponge (Gr…
3. Metal – Sponge Titanium Pricing
Domain: metal.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: This company, Metal – Sponge Titanium Pricing, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. Luciteria – Titanium Metal 99.5%
Domain: luciteria.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “Titanium metal 99.5%”, “price”: “$1.50”, “description”: “Titanium is as strong as steel yet only half the weight and naturally resistant to corrosion. It is highly prized in large-scale industry. The metal costs approximately $10,000 per ton, making it suitable primarily for well-funded projects. Notable uses include Soviet-era Alpha class submarines. The titanium offered is know…
5. Online Metals – Titanium Sheet/Plate
Domain: onlinemetals.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Titanium Sheet/Plate – Available Grades: Grade 2, Grade 3, Grade 4, 6AL-4V (Grade 5). Key Features: Strong, lightweight, corrosion-resistant, ideal for aerospace and medical applications. Sizes available: 12″ x 12″ ($79.98), 12″ x 24″ ($139.09), 12″ x 36″ ($184.57), 24″ x 24″ ($224.50), 24″ x 36″ ($319.92), 36″ x 36″ ($436.25), 36″ x 48″ ($540.70), 36″ x 96″ ($996.46). Custom cuts available. Fast …
6. Reddit – 4x 6 Ton Titanium Ingots
7. Aixi Hardware – Titanium Pricing Guide
Domain: aixihardware.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: {“Cost of Titanium Per Pound”: {“Price Range”: “$2 – $16”, “Types”: [{“Type”: “Grade 1 & 2 (Pure)”, “Price”: “$6 – $10”}, {“Type”: “Grade 3 & 4 (Pure, stronger)”, “Price”: “$7 – $12”}, {“Type”: “Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V)”, “Price”: “$10 – $16+”}, {“Type”: “Titanium Powder”, “Price”: “$20 – $35”}, {“Type”: “Titanium Scrap”, “Price”: “$2 – $6”}]}}
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for titanium cost
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers on Titanium Costs?
In navigating the complexities of titanium sourcing, understanding the price dynamics is crucial for international buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The current landscape reveals that titanium prices are influenced by a variety of factors, including raw material costs, energy prices, and geopolitical dynamics. With titanium classified as a critical metal, the demand from sectors like aerospace and medical implants continues to drive prices higher.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Procurement Process?
Adopting a strategic sourcing approach can significantly mitigate risks associated with fluctuating prices. By fostering relationships with reliable suppliers and monitoring market trends, buyers can secure more favorable contracts and ensure a steady supply of titanium. Utilizing resources like the Producer Price Index and industry reports can provide valuable insights into pricing trends and help inform your purchasing decisions.
What Should International Buyers Focus on Moving Forward?
As the titanium market evolves, staying informed and adaptable will be key. B2B buyers are encouraged to actively engage with suppliers, assess their sourcing strategies, and leverage market intelligence. By doing so, they can navigate the complexities of titanium procurement effectively, ensuring their businesses remain competitive in an increasingly demanding global landscape.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to titanium cost
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.