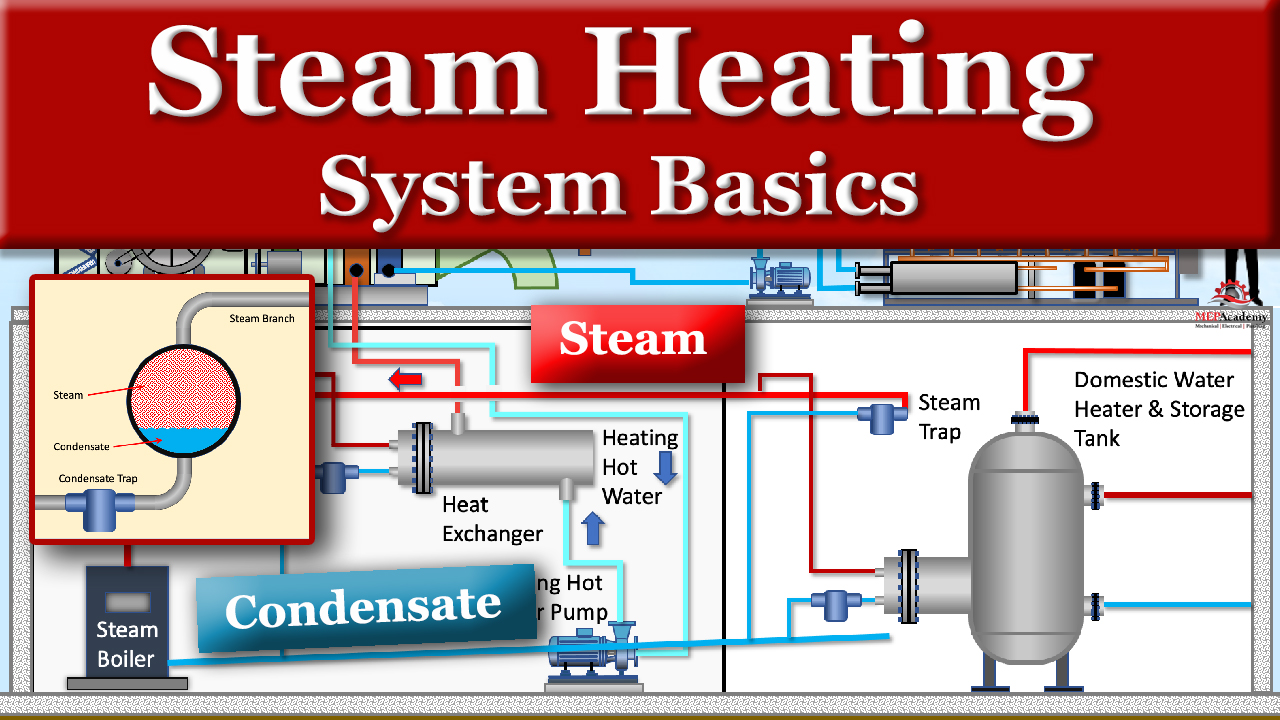
A B2B Buyer’s Guide to Steam Heating System Diagram: Price, Quality, and Suppliers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for steam heating system diagram
In the rapidly evolving landscape of industrial infrastructure, sourcing an effective steam heating system diagram presents a significant challenge for B2B buyers. The complexity of steam heating systems, which serve critical roles in diverse sectors—from food processing to pharmaceuticals—requires a deep understanding of various designs and functionalities. This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of steam heating systems, exploring different types such as single pipe systems, steam trap systems, and their specific applications.
By providing insights into supplier vetting, cost considerations, and performance metrics, this guide equips international buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Brazil and Germany—with the knowledge necessary to make informed purchasing decisions. Understanding the nuances of steam heating systems not only aids in selecting the right technology but also enhances operational efficiency and energy management.
Navigating the global market for steam heating systems can be daunting, but with the right information at hand, B2B buyers can confidently assess their options and choose systems that align with their operational goals. This guide empowers you to decipher complex diagrams, evaluate suppliers effectively, and ultimately secure the most efficient steam heating solutions for your business needs.
Understanding steam heating system diagram Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single Pipe Steam System with Main Pipes Pitched Towards the Boiler | Uses the same pipes for steam and condensate; simple design | Warehouses, garages, temporary heating | Pros: Low installation costs; Cons: Poor heat modulation |
| Single Pipe Steam System with Main Steam Pipes Pitched Away from the Boiler | Improved separation of steam and condensate; better flow | Industrial facilities, larger buildings | Pros: Better efficiency; Cons: Limited control over heating |
| Single Pipe Steam System with Overhead Steam Distribution | Completely separates steam and condensate; overhead design | Factories, commercial buildings | Pros: Enhanced heat control; Cons: More complex installation |
| Steam Trap System | Uses traps to hold steam in heating elements; improved modulation | Manufacturing, food processing | Pros: Better individual control; Cons: Higher equipment costs |
| High Pressure Steam Boiler | Operates at pressures above 15 psi; suitable for heavy-duty applications | Power generation, large-scale industrial processes | Pros: High efficiency and output; Cons: Safety considerations |
What Are the Characteristics of a Single Pipe Steam System with Main Pipes Pitched Towards the Boiler?
This system is characterized by a straightforward design where steam and condensate share the same piping. It’s ideal for applications such as warehouses and garages, where heat modulation is not a primary concern. However, buyers should be aware that while installation costs are low, the lack of control over heat emission can lead to inefficiencies, making it less suitable for environments requiring precise temperature management.
How Does the Single Pipe Steam System with Main Steam Pipes Pitched Away from the Boiler Improve Efficiency?
This variation enhances the separation of steam and condensate, leading to improved flow and efficiency. It is suitable for larger industrial facilities and buildings where better heating control is necessary. While it offers better performance than the simpler design, buyers must consider that it may still have limitations in individual radiator control, making it less ideal for applications demanding precise temperature regulation.
What Advantages Does the Single Pipe Steam System with Overhead Steam Distribution Offer?
This system separates steam and condensate entirely and utilizes an overhead design to optimize space and efficiency. It is particularly advantageous in factories and commercial buildings, where heat control is critical. Although it provides enhanced modulation capabilities, the complexity of installation and potential for higher costs may deter some buyers, necessitating a careful cost-benefit analysis.
Why Consider a Steam Trap System for Better Heating Control?
The Steam Trap System is designed to retain steam within heating elements, allowing for better modulation of heat output. This system is particularly useful in manufacturing and food processing industries, where individual control over radiators is essential. Despite the advantages of improved efficiency and control, the increased equipment costs may be a consideration for budget-conscious buyers.
What Makes High Pressure Steam Boilers Suitable for Heavy-Duty Applications?
High Pressure Steam Boilers are engineered to operate at pressures exceeding 15 psi, making them ideal for power generation and large-scale industrial processes. These systems offer high efficiency and output, which are crucial for demanding applications. However, buyers must be cognizant of the safety considerations associated with high-pressure operations, including the need for rigorous maintenance and monitoring protocols.
Key Industrial Applications of steam heating system diagram
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of steam heating system diagram | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Pasteurization of liquids | Ensures product safety and extends shelf life | Compliance with health regulations, energy efficiency |
| Chemical Manufacturing | Process heating for reactions | Increases efficiency and control over chemical processes | Material compatibility, pressure and temperature ratings |
| Textile Industry | Dyeing and finishing processes | Enhances color quality and consistency | Temperature control, steam quality, maintenance support |
| Pharmaceuticals | Sterilization of equipment and products | Guarantees product integrity and compliance | Quality certifications, reliability of supply |
| Energy Sector | Steam generation for power plants | Maximizes energy output and operational efficiency | Fuel type compatibility, emissions standards |
How is the Steam Heating System Diagram Used in the Food and Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage sector, steam heating systems are critical for pasteurization processes, which require precise temperature control to eliminate pathogens. By utilizing a steam heating system diagram, manufacturers can ensure that steam is effectively distributed throughout the pasteurization equipment. This not only enhances food safety but also extends the shelf life of products. B2B buyers in this industry must consider compliance with health regulations and the energy efficiency of the systems to minimize operational costs.
What Role Does Steam Heating Play in Chemical Manufacturing?
Chemical manufacturers rely on steam heating systems for various processes, including heating and maintaining reaction temperatures. The steam heating system diagram illustrates the flow of steam and its interaction with chemical reactors, ensuring optimal conditions for reactions. This leads to improved efficiency and control over production. Buyers in this sector should prioritize material compatibility with steam, as well as the specific pressure and temperature ratings necessary for their processes to ensure safety and effectiveness.
How is Steam Heating Beneficial for the Textile Industry?
In the textile industry, steam heating systems are essential for dyeing and finishing processes, where consistent temperature control is vital for achieving high-quality colors and finishes. The steam heating system diagram provides a visual representation of the steam distribution, allowing for precise adjustments. For international buyers, key considerations include the need for reliable temperature control and the quality of steam to prevent fabric damage. Furthermore, maintenance support is crucial to minimize downtime in production.
Why is Steam Heating Important in Pharmaceuticals?
Pharmaceutical companies use steam heating systems for sterilization, ensuring that equipment and products are free of contaminants. The steam heating system diagram helps visualize the sterilization process, allowing manufacturers to maintain compliance with stringent regulatory standards. This guarantees product integrity and safety. B2B buyers in this industry must focus on sourcing systems with quality certifications and a proven track record of reliability, as any failure could have significant consequences on public health.
How Does Steam Generation Impact the Energy Sector?
In the energy sector, steam heating systems are fundamental for generating power in steam turbines. The steam heating system diagram outlines the generation and distribution of steam, maximizing energy output and operational efficiency. Buyers must consider the compatibility of fuel types used in the system, as well as adherence to emissions standards, which are increasingly important in global markets. Efficient steam systems can significantly enhance the profitability of energy operations by reducing fuel costs and improving overall performance.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘steam heating system diagram’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Visualizing Complex Steam Heating System Layouts
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle to comprehend intricate steam heating system diagrams, particularly when integrating these systems into existing infrastructures. This challenge is exacerbated in regions with varying industrial standards, such as those found in Africa or South America, where buyers may have less exposure to advanced engineering practices. A lack of clarity can lead to misinterpretation, resulting in improper installations that can affect system efficiency and safety.
The Solution: To overcome this issue, buyers should invest in high-quality, detailed steam heating system diagrams that not only illustrate the layout but also explain the functions of each component. When sourcing these diagrams, look for those that include annotations, color coding, and legends to enhance understanding. Additionally, consider engaging with suppliers who offer technical support or training sessions. This hands-on approach can help teams visualize the systems better and make informed decisions about integration and installation.
Scenario 2: Inadequate Control Over Heat Distribution
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges in managing heat distribution effectively within their steam heating systems. In a simple single-pipe steam system, heat modulation can be hard to control, leading to uneven heating in different areas of a facility. This can be particularly problematic in environments like warehouses or manufacturing plants, where consistent temperatures are crucial for operational efficiency and product quality.
The Solution: To address the inadequacies of basic steam heating systems, buyers should consider more advanced configurations, such as a steam trap system or a two-pipe steam system. These systems provide better separation of steam and condensate, allowing for improved heat control. When reviewing steam heating system diagrams, pay close attention to those that illustrate these advanced systems and their components. Collaborating with experienced engineers or consultants can also facilitate the design of a system tailored to specific heating needs, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
Scenario 3: Uncertainty Around Maintenance and Safety Protocols
The Problem: Another significant pain point for B2B buyers is the uncertainty surrounding the maintenance and safety of steam heating systems. Many buyers may lack expertise in identifying potential issues, such as leaks or pressure irregularities, which can lead to costly downtime or safety hazards. This concern is particularly pronounced in regions where regulatory compliance varies significantly, making it crucial for companies to prioritize safety.
The Solution: To mitigate these risks, it is essential to incorporate comprehensive maintenance protocols into the steam heating system design. Buyers should source diagrams that include maintenance schedules, safety checks, and troubleshooting tips. Training staff on these protocols is equally important; consider organizing workshops that focus on the interpretation of steam heating system diagrams and routine maintenance practices. Additionally, establishing a relationship with a reliable service provider can ensure regular inspections and immediate support when issues arise, ultimately enhancing system longevity and safety.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for steam heating system diagram
When selecting materials for steam heating systems, it is crucial to consider properties that directly influence performance, durability, and overall system efficiency. Below, we analyze four common materials used in steam heating systems, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
Illustrative image related to steam heating system diagram
Which Materials Are Commonly Used in Steam Heating Systems?
1. Carbon Steel
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its high strength and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for steam applications. It typically has a temperature rating up to 400°C (752°F) and can handle pressures exceeding 200 psi.
Pros & Cons: Carbon steel is relatively inexpensive and widely available, making it a cost-effective choice for many applications. However, it is prone to corrosion, especially in humid or acidic environments, which can lead to premature failure if not properly maintained.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is compatible with steam and water but may require additional protective coatings or treatments in corrosive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM A106 for seamless carbon steel pipes. In Europe, adherence to EN standards is crucial.
2. Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand high temperatures, with some grades rated for temperatures up to 800°C (1472°F). It also maintains structural integrity under high pressures.
Illustrative image related to steam heating system diagram
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to oxidation, making it ideal for environments with moisture. However, it is significantly more expensive than carbon steel and can be more complex to manufacture and weld.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is suitable for high-purity steam applications, such as in pharmaceutical or food processing industries, where contamination must be avoided.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM A312 for stainless steel pipes is essential. Buyers in Germany may prefer grades that meet DIN standards, ensuring compatibility with local regulations.
3. Copper
Key Properties: Copper has excellent thermal conductivity, making it highly efficient for heat transfer in steam heating systems. It can operate effectively at temperatures up to 200°C (392°F) and pressures around 100 psi.
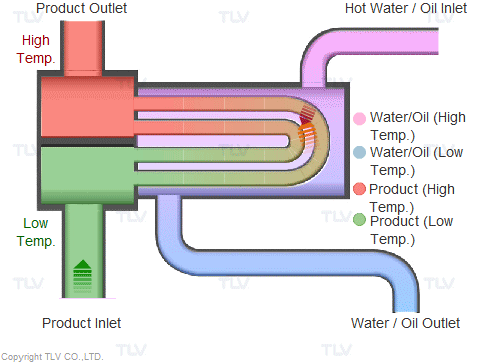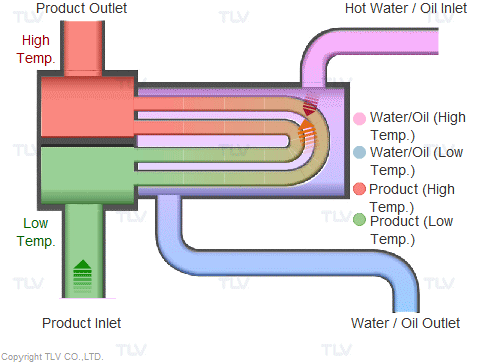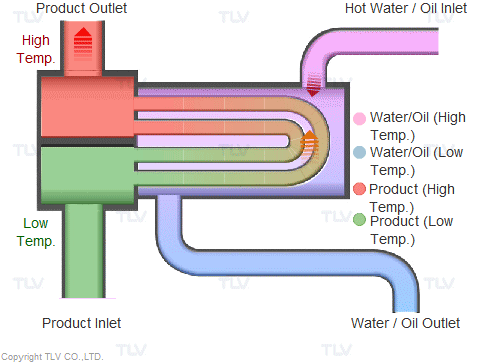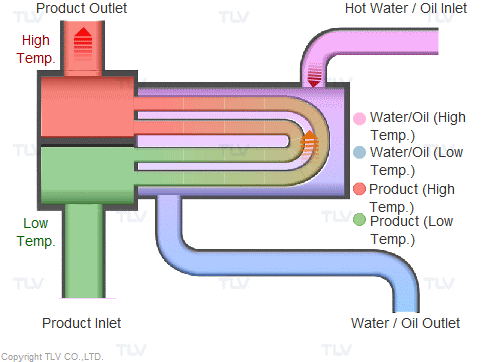
Illustrative image related to steam heating system diagram
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of copper is its superior heat transfer capabilities, leading to energy savings. However, it is more expensive than carbon steel and can be susceptible to corrosion if exposed to certain chemicals.
Impact on Application: Copper is often used in smaller-scale applications, such as residential heating systems or specialized industrial processes where efficient heat transfer is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific standards governing copper materials, such as ASTM B280 for copper tubing. In regions with high humidity, additional protective measures may be necessary to prevent corrosion.
4. Cast Iron
Key Properties: Cast iron is known for its excellent thermal retention and ability to withstand high pressures, with typical ratings up to 300 psi and temperatures around 400°C (752°F).
Pros & Cons: Cast iron is durable and provides good heat retention, making it suitable for large-scale heating applications. However, it is heavy and can be brittle, leading to potential breakage during installation or operation.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is often used in large industrial steam heating systems, where weight and structural integrity are less of a concern compared to performance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM A48 for cast iron is important. Buyers in the Middle East should consider the impact of environmental conditions on the longevity of cast iron systems.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Steam Heating Systems
| Material | Typical Use Case for steam heating system diagram | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | General industrial steam applications | Cost-effective and strong | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | High-purity applications (e.g., food, pharma) | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Copper | Residential and small-scale industrial systems | Superior heat transfer | Expensive and corrosion-prone | Med |
| Cast Iron | Large industrial heating systems | Good thermal retention | Heavy and brittle | Med |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of material options for steam heating systems, equipping international B2B buyers with the insights needed to make informed decisions based on their specific applications and regional requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for steam heating system diagram
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Steam Heating System Diagrams?
The manufacturing of steam heating systems involves several key stages that ensure the final product meets both performance and safety standards. Each stage is critical in delivering a system that operates efficiently and reliably.
Material Preparation: What Is Involved in Preparing Materials for Steam Heating Systems?
Material selection is paramount in the steam heating system manufacturing process. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and copper, chosen for their thermal conductivity and resistance to corrosion.
- Material Sourcing: Suppliers must provide materials that meet international standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO). This includes checking for certifications that guarantee material quality.
- Cutting and Shaping: Once sourced, materials are cut to specific dimensions using techniques like plasma cutting or laser cutting, which provide precision and reduce waste.
How Is the Forming Process Executed in Manufacturing Steam Heating Systems?
Forming processes shape the raw materials into functional components. These processes can involve:
- Bending and Forming: Pipes and tubes are bent using hydraulic benders to create the desired shapes for steam distribution. This is crucial for maintaining flow efficiency.
- Welding: Components are joined through welding techniques, such as TIG or MIG welding, ensuring strong, leak-proof connections. Automated welding systems are increasingly employed for consistency and quality.
What Are the Key Steps in the Assembly of Steam Heating Systems?
Assembly is where individual components come together to form the complete steam heating system.
- Component Assembly: Each part, including the boiler, piping, valves, and traps, is assembled in a systematic manner. A checklist ensures that all components are present and correctly oriented.
- Integration of Control Systems: Control valves and sensors are integrated into the system. This step is vital for ensuring the system can modulate heating effectively.
What Finishing Techniques Are Used in Steam Heating System Manufacturing?
The finishing stage enhances the system’s durability and aesthetic quality.
- Surface Treatment: Components may undergo treatments such as galvanization or powder coating to prevent corrosion and enhance thermal efficiency.
- Final Inspections: Each unit undergoes a visual inspection for defects and a functional test to verify that it meets specified operating parameters.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for Steam Heating Systems?
Quality assurance is crucial in the manufacturing of steam heating systems to ensure safety, reliability, and compliance with international standards.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Quality Control in Steam Heating Systems?
Manufacturers must adhere to various international and industry-specific standards:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems, ensuring consistent quality in products and services.
- CE Marking: In Europe, products must meet health, safety, and environmental protection standards to gain CE certification.
- API Standards: For those dealing with oil and gas applications, American Petroleum Institute standards provide guidelines for the design and manufacturing of components.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Implementing checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process helps maintain quality:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications before processing begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the assembly process, inspections are conducted to monitor adherence to specifications and quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive evaluation of the finished product ensures it meets all performance and safety criteria.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures directly.
- Review of Quality Reports: Requesting quality control reports and documentation can provide insight into a supplier’s compliance with relevant standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection services can validate the supplier’s quality claims and ensure that products meet international standards.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Assurance for Steam Heating Systems?
Testing is integral to quality assurance and can include:
- Pressure Testing: This checks for leaks and ensures that the system can handle operational pressures safely.
- Hydraulic Testing: Components are filled with water and pressurized to validate structural integrity.
- Functional Testing: The complete system is operated under controlled conditions to ensure that all components work as intended.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Be Aware of Regarding Quality Control?
B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of specific nuances:
- Regional Standards: Different regions may have varying standards and regulations. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local requirements to ensure compliance.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Understanding the supply chain can help in assessing the reliability of the materials and components used in the manufacturing process.
- Cultural Considerations: Communication styles and business practices may differ across regions. Building strong relationships with suppliers can facilitate better quality assurance processes.
In conclusion, the manufacturing and quality assurance of steam heating systems are multifaceted processes that require careful attention to detail at every stage. By understanding these processes and implementing effective quality control measures, B2B buyers can ensure they procure reliable, efficient, and compliant steam heating systems tailored to their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘steam heating system diagram’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of a steam heating system diagram can be complex, especially for international B2B buyers. This guide provides a practical checklist to streamline your sourcing process, ensuring you make informed decisions that align with your technical requirements and budget constraints.
1. Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clarify the specific technical requirements for your steam heating system. This includes understanding the types of steam systems you may need (e.g., single-pipe or two-pipe systems) and their application (industrial, commercial, etc.). Knowing your requirements upfront helps you communicate effectively with potential vendors and ensures they can meet your needs.
2. Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers with a proven track record in steam heating systems. Look for manufacturers or distributors who specialize in your required technology and have experience in your geographical region. An extensive search will help you compile a shortlist of reputable companies.
3. Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Standards
Ensure that potential suppliers comply with industry standards and hold necessary certifications. This may include ISO certifications, safety standards, or environmental compliance certifications. Such credentials are critical as they demonstrate the supplier’s commitment to quality and reliability, reducing the risk of future operational issues.
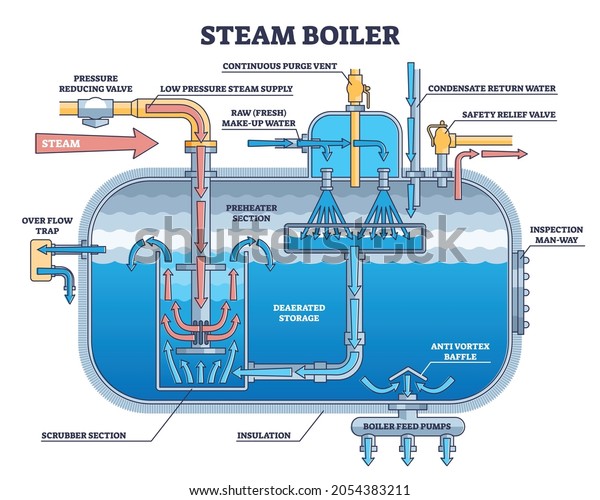
Illustrative image related to steam heating system diagram
4. Request Detailed Product Documentation
When you have narrowed down your options, request detailed product documentation from suppliers. This should include installation guides, maintenance manuals, and technical specifications for the steam heating system diagrams. Comprehensive documentation is vital for understanding how to implement the systems effectively and ensures that you are aware of any specific installation requirements.
5. Assess Customization Options
Consider whether the supplier can customize the steam heating system diagram to meet your specific operational needs. Some projects may require unique configurations or adaptations based on the facility layout or heating requirements. Suppliers offering customization can provide better alignment with your operational goals.
6. Compare Pricing and Payment Terms
Once you have gathered quotes, compare the pricing structures and payment terms offered by different suppliers. Look for transparency in pricing, including any additional costs for shipping, installation, or support services. Understanding the total cost of ownership will help you budget effectively and avoid unexpected expenses down the line.
7. Seek Customer References and Case Studies
Finally, ask potential suppliers for references or case studies from previous clients, especially those in similar industries or regions. Engaging with past customers can provide valuable insights into the supplier’s reliability, product performance, and customer service. This step is crucial in ensuring you choose a supplier who can deliver on their promises.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can approach the procurement of steam heating system diagrams with confidence, ensuring they select the right solutions for their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for steam heating system diagram Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Steam Heating Systems?
When sourcing steam heating systems, understanding the cost structure is paramount for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margins.
Materials are often the most significant expense, encompassing various components like pipes, valves, boilers, and steam traps. The choice of materials—whether they are standard or specialized—can greatly affect pricing. For instance, using high-grade stainless steel for pipes may increase costs but will enhance durability and efficiency.
Labor costs vary widely based on the region and skill level required. In regions with higher labor costs, such as parts of Europe, sourcing from countries with lower labor rates can lead to significant savings.
Manufacturing overhead includes expenses related to factory operation, maintenance, and utilities. This cost is typically factored into the pricing of the system and can differ depending on the efficiency of the manufacturing process.
Tooling costs are often overlooked but can significantly impact the final price, especially for customized solutions. The need for specialized tools and molds will increase initial expenditures.
Quality control is essential for ensuring the reliability and safety of steam heating systems. Buyers should assess the QC processes of potential suppliers, as rigorous QC can lead to higher costs but ultimately reduce risks associated with equipment failure.
Logistics encompasses shipping, handling, and storage costs. For international buyers, understanding the full logistics chain is crucial, as these costs can vary based on distance, mode of transport, and local regulations.
Margins added by suppliers can fluctuate based on market demand and competition. Buyers should be aware of the typical margin ranges in their region to ensure they are receiving fair pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Sourcing of Steam Heating Systems?
Several factors influence the pricing of steam heating systems. Volume and minimum order quantity (MOQ) play a critical role; larger orders often yield better unit prices due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs while maximizing cost efficiency.
Specifications and customization can significantly affect costs. Custom systems tailored to specific applications may incur additional design and manufacturing expenses. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unnecessary expenses related to last-minute changes.
Material choices directly impact pricing. For example, opting for eco-friendly materials may be more expensive initially but can lead to lower operating costs over time. Buyers should weigh the long-term benefits against upfront costs.
Quality certifications are another pricing influencer. Systems that meet international standards or certifications may command higher prices but provide assurance of performance and safety, which is particularly important for critical applications.
Supplier factors such as reputation, experience, and geographical location can also affect pricing. Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge a premium, but their reliability can lead to cost savings in the long run.
Incoterms impact logistics costs and responsibilities between buyers and sellers. Familiarity with these terms can help buyers negotiate better shipping deals and avoid unexpected costs.
What Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency for International Buyers?
For B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost-efficiency.
Negotiation is crucial. Engaging suppliers in discussions about pricing, terms, and conditions can lead to favorable agreements. Buyers should be prepared with market data to support their negotiation positions.
Understanding Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is essential. This includes not just the initial purchase price but also installation, maintenance, and operational costs over the lifespan of the system. Buyers should evaluate all these factors to make informed decisions.
Pricing nuances for international buyers can vary. Currency fluctuations, import duties, and local taxes can significantly affect the final cost. Buyers should factor these into their budgeting process to avoid financial surprises.
Lastly, always seek multiple quotes from different suppliers. This practice not only fosters competition but also provides a broader perspective on market pricing, enabling better purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer: Prices mentioned in sourcing discussions are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Always consult directly with suppliers for the most accurate pricing.
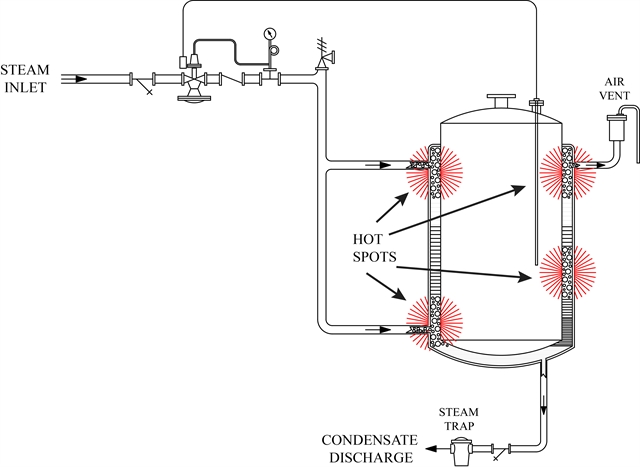
Illustrative image related to steam heating system diagram
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing steam heating system diagram With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Heating Solutions
When evaluating heating systems, understanding the alternatives to a steam heating system is crucial for B2B buyers. Different heating technologies can offer varying benefits and drawbacks, depending on specific operational needs, installation environments, and budget constraints. This analysis compares the steam heating system diagram with other viable heating solutions: electric boilers and hot water boilers.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Steam Heating System Diagram | Electric Boiler | Hot Water Boiler |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Efficient for large areas but less precise in temperature control | Quick heating with precise temperature control | Good for consistent heating but slower to respond |
| Cost | Lower initial costs but higher operational costs | Higher initial investment, lower operational costs | Moderate initial and operational costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively straightforward installation, requires skilled labor | Simple installation, minimal infrastructure | Requires more complex plumbing and space |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed for steam traps and boiler | Low maintenance with occasional checks | Moderate maintenance, depends on water quality |
| Best Use Case | Industrial applications with high heat demand | Residential or small commercial applications | Commercial applications requiring consistent heating |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Electric Boiler
Electric boilers are increasingly popular due to their efficiency and environmental benefits. They convert electricity into heat, offering a cleaner solution as they do not involve combustion. The primary advantages include precise temperature control and lower operational costs in the long term. However, the initial investment can be significantly higher than steam systems, which may deter some buyers. Additionally, electric boilers can be limited by the availability of electrical infrastructure, especially in regions with less developed power grids.
Hot Water Boiler
Hot water boilers serve as another alternative, utilizing water as a heat transfer medium. They are effective for providing consistent heating across larger spaces, making them suitable for commercial environments. The advantages include their ability to maintain steady temperatures and lower operational costs than steam systems. However, the installation process can be complex, requiring careful planning and plumbing, which may lead to higher initial costs. Additionally, hot water systems may not respond as quickly to temperature changes, potentially leading to inefficiencies in operations that require rapid heating adjustments.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the right heating solution requires a careful assessment of your specific operational requirements, budget, and long-term goals. Steam heating systems are ideal for high-demand industrial applications where initial costs are a priority. However, for buyers focused on efficiency and precision, electric boilers may be more suitable. Meanwhile, hot water boilers can serve well in commercial settings requiring steady heating. Ultimately, understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each system will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational objectives and budgetary constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for steam heating system diagram
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Steam Heating Systems?
When evaluating steam heating systems, understanding critical technical properties is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several key specifications that significantly impact system performance and reliability:
1. Material Grade
The material used in steam heating systems, typically stainless steel or carbon steel, plays a vital role in durability and corrosion resistance. For B2B buyers, selecting the right material grade can affect the lifespan of the system and its maintenance requirements. A higher-grade material may incur higher initial costs but can lead to lower long-term expenses due to reduced corrosion and maintenance needs.
2. Pressure Rating
The pressure rating indicates the maximum pressure the system can safely operate under. Common classifications include low-pressure (10-15 psi) and high-pressure (over 15 psi). Understanding the pressure requirements for specific applications is crucial, as it affects the boiler’s efficiency and safety. Buyers must ensure that the pressure rating aligns with their operational needs to avoid operational failures or inefficiencies.
3. Thermal Efficiency
Thermal efficiency measures how effectively a boiler converts fuel energy into steam energy. High-efficiency models reduce fuel consumption and lower operational costs, making them attractive for B2B buyers focused on cost-effectiveness. Evaluating the thermal efficiency is essential for industries looking to minimize energy expenses while maximizing output.
4. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels refer to the acceptable variations in dimensions and performance specifications. This is critical for ensuring compatibility with existing systems and components. For international buyers, understanding tolerance levels can prevent costly delays and modifications during installation, ensuring a smoother procurement process.
5. Capacity
Capacity, often measured in BTUs or kilowatts, indicates the amount of steam the system can generate. Choosing the right capacity is crucial for meeting specific heating demands. Oversized systems can lead to inefficiencies and higher costs, while undersized systems may not meet heating needs, leading to operational disruptions.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Steam Heating Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the steam heating market. Here are several key terms that buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure they are sourcing high-quality components that meet industry standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. For B2B buyers, understanding MOQs is crucial for budgeting and inventory management. It can also affect the cost per unit; larger orders often lead to better pricing.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing and terms for specific products or services. Crafting a detailed RFQ helps buyers receive accurate proposals and enables them to compare offers effectively, ensuring they secure the best deal.
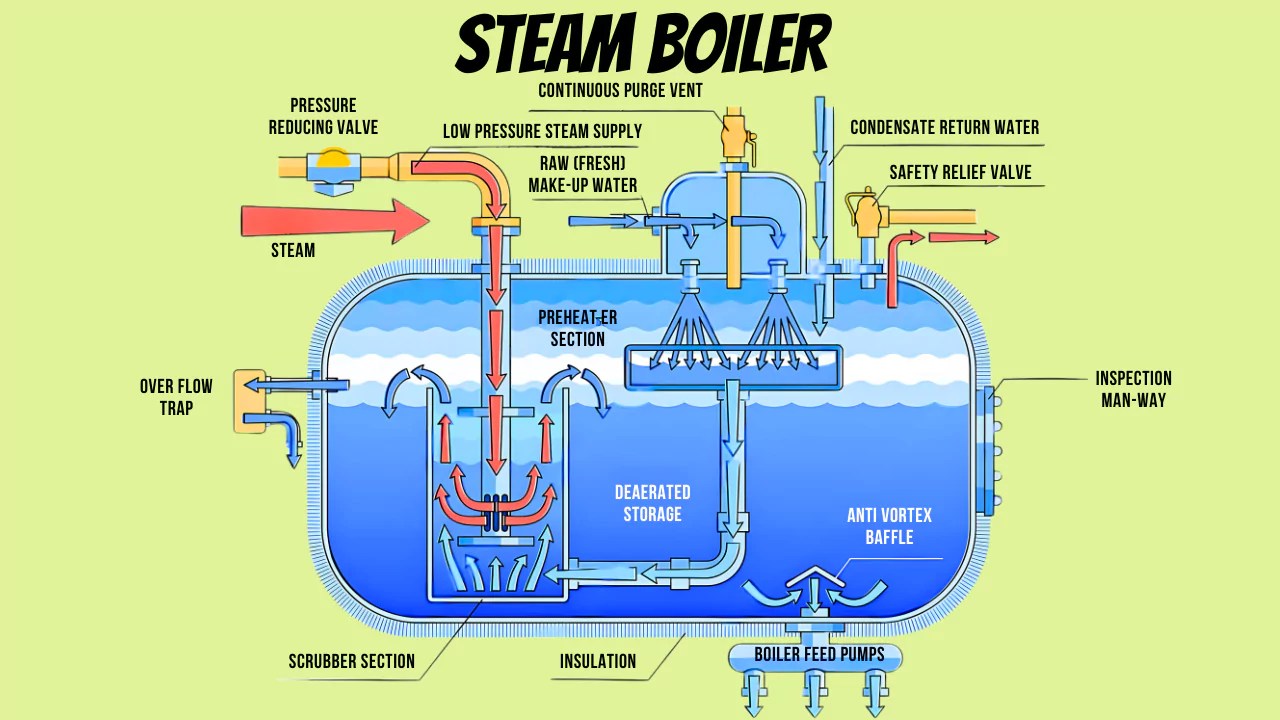
Illustrative image related to steam heating system diagram
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international trade terms that outline the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and obligations, facilitating smoother cross-border transactions.
5. BTU (British Thermal Unit)
BTU is a measurement of thermal energy, specifically the amount needed to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. Understanding BTUs is vital for evaluating the heating capacity of steam systems and ensuring they meet operational demands.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of steam heating systems more effectively, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the steam heating system diagram Sector
What Are the Global Drivers Influencing the Steam Heating System Diagram Market?
The steam heating system diagram market is witnessing significant shifts driven by various global factors. One of the primary drivers is the increasing demand for energy-efficient heating solutions across industries, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Countries such as Brazil and Germany are pushing for modernized infrastructure that incorporates advanced steam heating technologies, which optimize energy use and reduce operational costs. This trend is also reflected in the growing popularity of modular steam systems, which offer flexibility and scalability for businesses of all sizes.
Emerging technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things) and AI (Artificial Intelligence) are reshaping how steam heating systems are designed and monitored. These innovations enable real-time data analytics for performance optimization and predictive maintenance, thereby enhancing system reliability and efficiency. Furthermore, the integration of renewable energy sources into steam heating systems is gaining traction, especially in Europe, where there is a strong regulatory push towards sustainability.
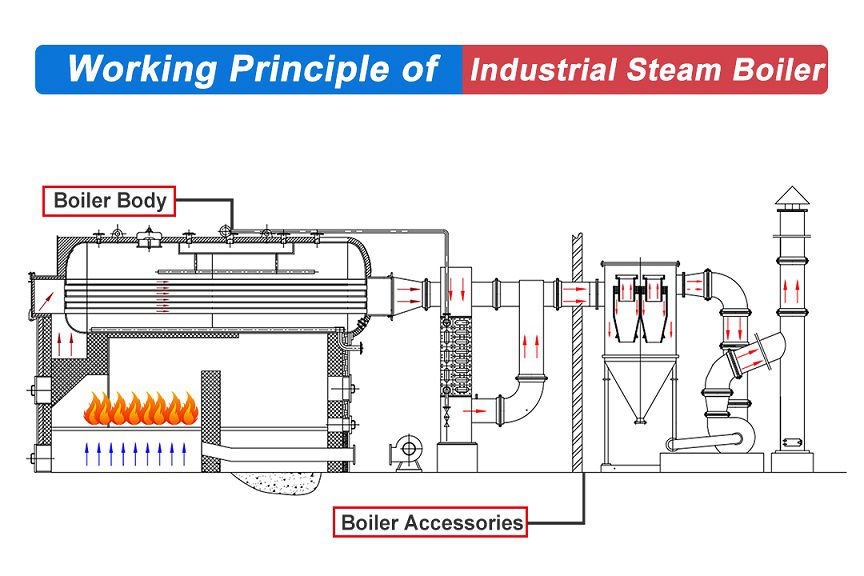
Illustrative image related to steam heating system diagram
Market dynamics are also influenced by supply chain considerations, where international B2B buyers are increasingly looking for local suppliers to reduce lead times and transportation costs. This local sourcing trend is particularly relevant in developing regions, where establishing reliable supply chains can lead to significant competitive advantages.
How Is Sustainability Shaping Sourcing Decisions in the Steam Heating Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone in the sourcing strategies of B2B buyers in the steam heating system sector. The environmental impact of traditional heating methods has prompted businesses to reevaluate their choices. Steam heating systems that utilize cleaner fuel options or are designed for energy efficiency are now preferred, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Moreover, ethical sourcing is critical as companies face increasing scrutiny from consumers and regulatory bodies regarding their supply chain practices. Buyers are seeking suppliers who adhere to ethical labor practices and environmental stewardship. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 50001 (Energy Management) are becoming essential for suppliers to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability.
Investing in “green” materials, such as low-emission fuel options and energy-efficient components, can significantly enhance a company’s brand reputation and marketability. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who offer sustainable solutions, as these choices not only meet regulatory requirements but also resonate with environmentally conscious consumers.
How Have Steam Heating Systems Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of steam heating systems dates back to the industrial revolution, where they were pivotal in powering factories and providing heating solutions. Early systems were simple, often using a single pipe to transport steam and condensate. While cost-effective, these systems lacked the ability to modulate heat output effectively, leading to inefficiencies.
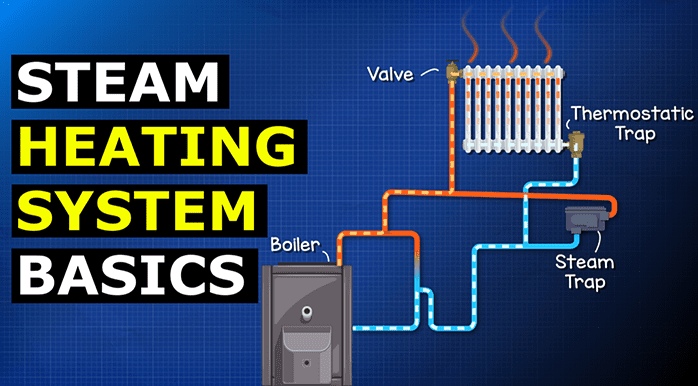
Illustrative image related to steam heating system diagram
As technology advanced, so did steam heating systems. The introduction of multi-pipe systems and steam traps allowed for better separation of steam and condensate, enhancing efficiency and control. The modern landscape now includes sophisticated steam boilers that utilize various fuels, including natural gas and biomass, catering to a diverse range of industrial applications.
Today, the focus is on integrating smart technologies and renewable energy sources, making steam heating systems not only more efficient but also aligned with the global push towards sustainability. The ongoing evolution signifies an ongoing commitment to meeting the energy needs of industries while minimizing environmental impact.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of steam heating system diagram
-
1. How do I choose the right steam heating system for my industrial application?
Selecting the appropriate steam heating system hinges on your specific operational requirements. Assess factors such as the size of your facility, the types of processes needing heat, and the level of temperature control required. For environments where precise temperature modulation is necessary, consider advanced systems like those utilizing steam traps for better control. Additionally, evaluate the fuel types available in your region, as well as the efficiency and maintenance requirements of different boiler types, to ensure compatibility with your operations. -
2. What are the key components of a steam heating system diagram?
A steam heating system diagram typically includes essential components such as steam boilers, steam pipes, condensate return lines, radiators or heat exchangers, and steam traps. Understanding these components helps in visualizing the flow of steam and condensate within the system. Each element plays a critical role in ensuring efficient heat distribution and condensation management. A well-structured diagram can serve as a valuable reference for troubleshooting and system optimization. -
3. How can I ensure the quality of steam heating systems from international suppliers?
To ensure quality, start by conducting thorough research on potential suppliers. Look for certifications, industry experience, and customer reviews. Request samples or detailed specifications of their products, and inquire about their quality assurance processes. Establish communication channels to discuss your specific needs and confirm that the supplier understands them. Additionally, consider visiting the manufacturing facility, if feasible, to evaluate their operations firsthand. -
4. What customization options are available for steam heating systems?
Most manufacturers offer customization to meet the unique requirements of your application. Customization can include modifications in size, capacity, fuel type, and control systems. Discuss your specific needs with the supplier to explore available options, such as heat exchanger designs or integrated control systems. Be sure to communicate any regulatory compliance requirements pertinent to your region, as this may influence available customization choices. -
5. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for steam heating systems?
The MOQ for steam heating systems can vary significantly between suppliers and is often influenced by factors such as production capacity and material costs. Some manufacturers may have a low MOQ for standard models, while custom orders might require larger quantities. It’s advisable to discuss your project requirements directly with suppliers to negotiate MOQs that fit your budget and timeline, especially if you are looking to scale your operations. -
6. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing steam heating systems internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely based on the supplier and the nature of the transaction. Common terms include partial upfront payments, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Discuss these terms early in negotiations to avoid misunderstandings. Consider your cash flow and financial capabilities when agreeing to terms. Some suppliers may offer financing options or discounts for early payments, which can also be advantageous. -
7. How can I manage logistics for importing steam heating systems?
Managing logistics requires careful planning, particularly when dealing with international suppliers. Coordinate with your supplier to understand shipping timelines and costs. Engage a reliable freight forwarder who specializes in industrial equipment to handle customs clearance and delivery. Additionally, ensure that you have all necessary import permits and comply with local regulations regarding steam heating systems. Clear communication with all parties involved will streamline the logistics process. -
8. What are the common challenges in operating steam heating systems, and how can they be mitigated?
Common challenges include steam leaks, inefficient heat transfer, and inadequate control over temperature regulation. Regular maintenance and inspections can help identify potential issues early. Implementing a comprehensive training program for operators on system components and troubleshooting techniques can further mitigate problems. Additionally, investing in advanced control systems can enhance efficiency and ensure optimal operation, reducing the likelihood of operational disruptions.
Top 4 Steam Heating System Diagram Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Engineering Toolbox – Steam Heating Systems
Domain: engineeringtoolbox.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Steam Heating Systems are designed for efficient heating applications, with various configurations available. The simplest system is the Single Pipe Steam System with Main Pipes Pitched Towards the Boiler, where steam and condensate share the same pipes, making it cost-effective but challenging to control heat emission. This system is suitable for applications like warehouses and garages but not f…
2. CN Control Valve – Steam Boiler Solutions
Domain: cncontrolvalve.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Steam boilers are heating systems that generate steam by boiling water. They convert thermal energy from various fuels, including gas, coal, biomass, and fuel oil, into steam for industrial and domestic purposes. Key types of steam boilers include: 1. Electric Boilers – Utilize electric components for heating, offering a cleaner and more efficient solution. 2. Hot Water Boilers – Composed of stain…
3. Pinterest – Steam Boiler Parts
Domain: pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Steam Boilers Parts – Steam Boiler Indonesian. Related interests include Steam Boiler Parts And Functions, Steam Boiler Wiring Diagram, Steam Boiler Parts Diagram, Steam Boiler Diagram, Steam Boiler Schematic Diagram. Available documents include PEG-E GAS-FIRED STEAM BOILERS Models PARTS AND PEG112EID from uticaboilers.com and STEAM SYSTEMS from cleaverbrooks.com.
4. Heating Help – Steam Boiler Piping Guide
Domain: heatinghelp.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Steam Boiler Piping Diagram: The right way to pipe takeoffs from a header. Published on February 20, 2018. Related content includes a seminar on old steam heating systems and various articles by Dan Holohan on steam heating topics.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for steam heating system diagram
As the demand for efficient heating solutions continues to rise across various industries, understanding the intricacies of steam heating systems becomes paramount for B2B buyers. The strategic sourcing of these systems—whether opting for simple single-pipe designs or advanced steam trap systems—can significantly impact operational efficiency, energy consumption, and overall cost-effectiveness. By prioritizing systems that allow for better modulation and control, businesses can ensure tailored heating solutions that meet their specific needs.
Moreover, the choice of fuel sources—ranging from natural gas to biomass—can influence both environmental sustainability and operational costs, thus presenting an opportunity for buyers to align with global energy trends. As you consider your sourcing strategy, keep in mind the importance of evaluating the long-term benefits of investing in reliable and efficient steam heating technologies.
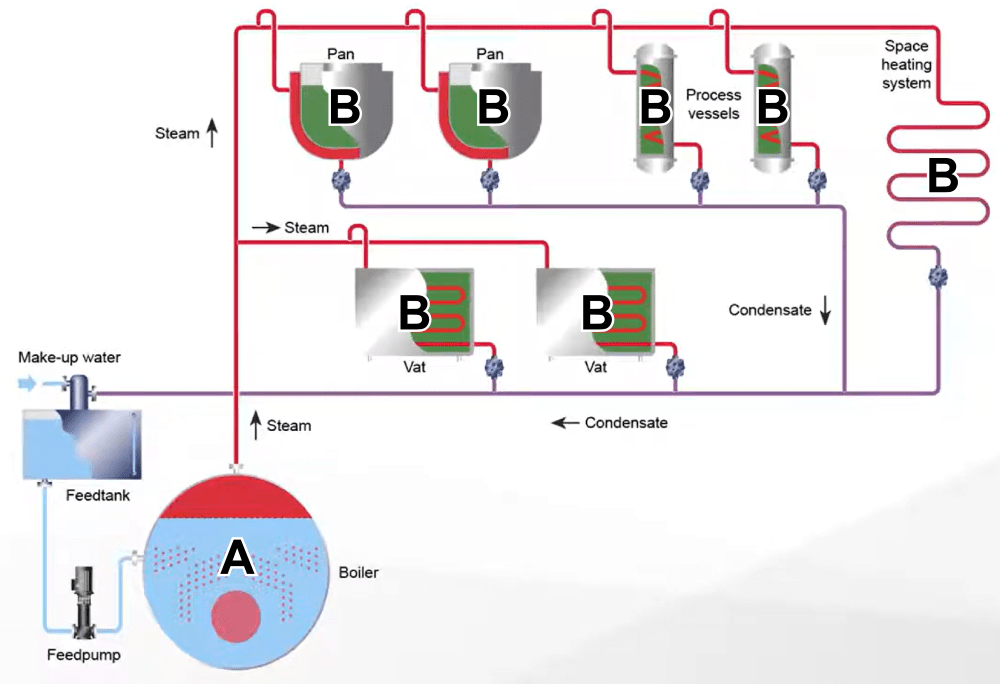
Illustrative image related to steam heating system diagram
Looking ahead, the evolution of steam heating systems will be shaped by innovations in energy efficiency and environmental compliance. Engaging with trusted suppliers and leveraging their expertise can pave the way for smarter investments in this critical infrastructure. Take the next step in optimizing your heating solutions—connect with industry leaders and explore the diverse offerings tailored to your market needs.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.