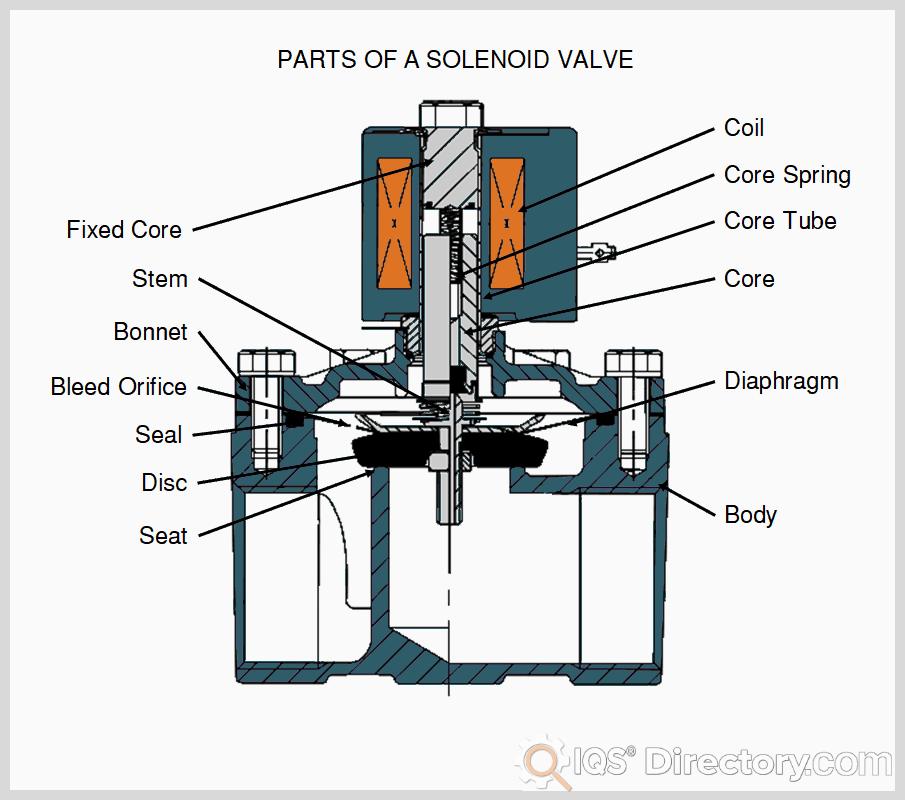
A B2B Buyer’s Guide to Solenoid Valve Diagram: Price, Quality, and Suppliers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for solenoid valve diagram
In the intricate landscape of industrial automation and fluid control, understanding the solenoid valve diagram is crucial for B2B buyers navigating the global market. One of the key challenges faced by international buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, is sourcing the right valve solutions that align with their operational needs and regulatory standards. This guide aims to demystify the complexities surrounding solenoid valve diagrams, offering insights into various types, applications, and the significance of accurate representations in piping and instrumentation diagrams (P&IDs).
As you delve into this comprehensive resource, you will explore the different classifications of solenoid valves, including 2-way and 3-way configurations, and their specific functionalities within fluid power systems. Additionally, the guide will provide valuable information on supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and best practices for integrating these components into your operations. By equipping B2B buyers with the knowledge to interpret solenoid valve diagrams effectively, this guide empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions that enhance operational efficiency and compliance with local standards.
Whether you are a seasoned procurement professional or new to the industry, understanding solenoid valve diagrams is essential for optimizing your fluid control systems and ensuring seamless operations across diverse applications. Join us on this journey to unlock the potential of solenoid valves in your business.
Understanding solenoid valve diagram Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2/2 Way Solenoid Valve | Two ports, two states (open/closed) | Simple on/off control in various industries | Pros: Simple design, cost-effective. Cons: Limited functionality. |
| 3/2 Way Solenoid Valve | Three ports, two states, allows switching between circuits | Pneumatic control, hydraulic applications | Pros: Versatile for multiple applications. Cons: More complex than 2/2 valves. |
| Proportional Solenoid Valve | Variable flow control, precise positioning | Automation, process control | Pros: Accurate flow regulation. Cons: Higher cost and complexity. |
| Pneumatic Solenoid Valve | Designed for air or gas applications | Pneumatic systems, industrial automation | Pros: Efficient for gas control. Cons: Not suitable for liquid applications. |
| 4/2 Way Solenoid Valve | Four ports, two states, can control multiple circuits | HVAC systems, fluid control | Pros: Flexible for complex systems. Cons: Requires careful installation. |
What are the Characteristics of 2/2 Way Solenoid Valves?
The 2/2 way solenoid valve is a fundamental component in fluid control systems, featuring two ports and two states—open and closed. This simplicity makes it ideal for straightforward on/off applications across various industries, such as water management and irrigation systems. When considering a purchase, buyers should evaluate the valve’s compatibility with their specific fluid type and pressure requirements, as well as its energy consumption, which can impact operational costs.
How Does a 3/2 Way Solenoid Valve Operate?
A 3/2 way solenoid valve includes three ports and two states, allowing it to effectively switch between two circuits. This design is particularly beneficial in pneumatic and hydraulic applications where fluid direction needs to be controlled. Buyers should consider the valve’s actuation method and the materials used in construction, as these factors significantly influence durability and performance under varying operational conditions.
What Makes Proportional Solenoid Valves Unique?
Proportional solenoid valves offer variable flow control, allowing for precise adjustments between fully open and fully closed positions. This feature is crucial in automation and process control applications where maintaining specific flow rates is essential. When purchasing, buyers should focus on the valve’s response time and control accuracy, as these characteristics directly affect system efficiency and performance.
In What Scenarios are Pneumatic Solenoid Valves Preferred?
Pneumatic solenoid valves are engineered specifically for air and gas applications, making them a staple in pneumatic systems and industrial automation setups. Their design ensures efficient control of gas flow, which is vital in sectors like manufacturing and packaging. Buyers should assess the valve’s pressure rating and compatibility with the intended gas type to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Why Choose 4/2 Way Solenoid Valves for Complex Systems?
The 4/2 way solenoid valve features four ports and two states, enabling it to control multiple circuits simultaneously. This versatility is particularly useful in HVAC systems and complex fluid control applications. Buyers should pay attention to the valve’s installation requirements and ensure that it fits seamlessly into their existing systems, as improper installation can lead to inefficiencies and operational challenges.
Key Industrial Applications of solenoid valve diagram
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of solenoid valve diagram | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Control of hydraulic systems in assembly lines | Increased efficiency and automation in production processes | Compatibility with existing systems and reliability |
| Water Treatment | Flow regulation in filtration and pumping systems | Enhanced water quality and resource management | Compliance with local regulations and durability |
| Oil & Gas | Safety shut-off in pipeline operations | Prevention of leaks and environmental hazards | Material compatibility with various fluids and pressures |
| HVAC Systems | Temperature control in climate control systems | Improved energy efficiency and user comfort | Response time and power consumption of solenoid valves |
| Agriculture | Irrigation control in automated farming systems | Optimized water usage and crop yield | Environmental resilience and ease of integration |
How is the ‘solenoid valve diagram’ utilized in manufacturing processes?
In the manufacturing sector, solenoid valve diagrams are crucial for controlling hydraulic systems within assembly lines. These diagrams provide a visual representation of the fluid pathways and valve functions, enabling engineers to design systems that enhance automation and efficiency. By accurately mapping the flow of hydraulic fluids, manufacturers can troubleshoot issues quickly, ensuring minimal downtime. Buyers in this sector should consider the compatibility of solenoid valves with existing machinery and the reliability of suppliers to maintain operational continuity.
What role do solenoid valve diagrams play in water treatment applications?
In water treatment facilities, solenoid valve diagrams are essential for regulating flow in filtration and pumping systems. These diagrams help operators visualize the interactions between various components, ensuring optimal flow rates and pressure levels. The precise control of water flow not only improves treatment efficiency but also enhances the overall quality of water delivered to consumers. Buyers should focus on sourcing valves that comply with local regulations regarding water safety and are durable enough to withstand harsh operating conditions.
How are solenoid valve diagrams critical for safety in the oil and gas industry?
In the oil and gas sector, solenoid valve diagrams serve as vital tools for implementing safety shut-off mechanisms in pipeline operations. These diagrams illustrate how valves function in emergency scenarios, preventing leaks and reducing the risk of environmental hazards. By providing clear visibility into valve operations, they facilitate better safety protocols and compliance with industry standards. B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing valves that are compatible with various fluids and can operate under high-pressure conditions to ensure safety and reliability.
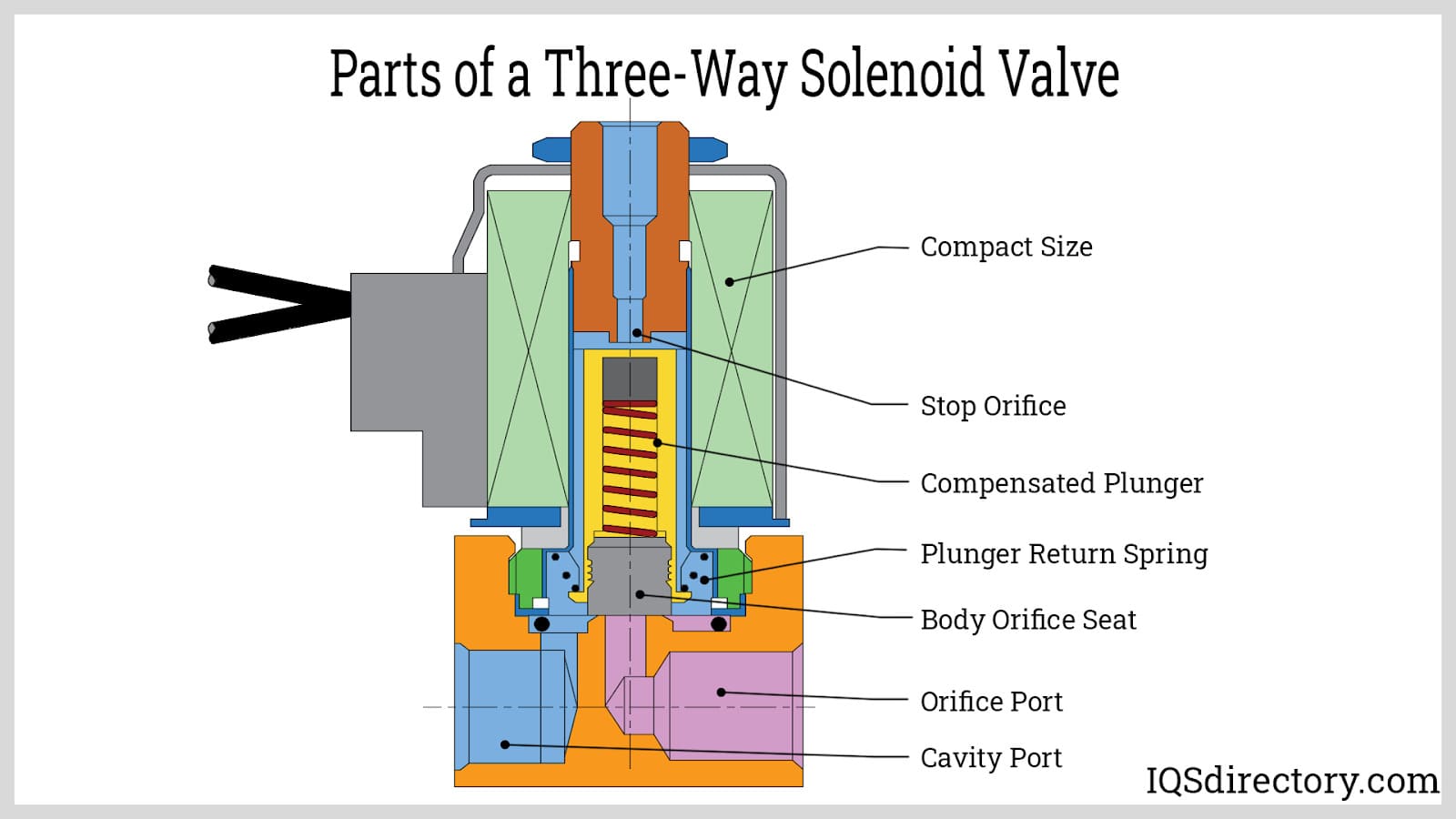
Illustrative image related to solenoid valve diagram
How do solenoid valve diagrams improve HVAC system efficiency?
In HVAC systems, solenoid valve diagrams are used to control temperature and airflow effectively. These diagrams provide a clear understanding of how valves interact within the system, allowing for precise adjustments to maintain optimal indoor conditions. The ability to automate temperature control not only enhances user comfort but also leads to significant energy savings. Buyers should consider the response time and power consumption of solenoid valves to ensure they meet the specific demands of their HVAC applications.
What benefits do solenoid valve diagrams bring to agricultural automation?
In agriculture, solenoid valve diagrams are used to automate irrigation systems, allowing for precise water control based on crop needs. These diagrams help farmers visualize the irrigation layout, optimizing water usage and ultimately improving crop yield. By automating irrigation, farmers can respond quickly to environmental changes, ensuring optimal growth conditions. Buyers in this sector should look for environmentally resilient valves that can integrate seamlessly with existing systems to enhance operational efficiency.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘solenoid valve diagram’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misinterpretation of Solenoid Valve Symbols in Diagrams
The Problem: Many international B2B buyers encounter significant difficulties when interpreting solenoid valve symbols within technical diagrams, such as Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams (P&ID). Different manufacturers may use varying representations for the same valve type, leading to confusion. This misinterpretation can result in incorrect installation, operational inefficiencies, or even costly downtime. For example, a buyer in Brazil might mistakenly assume a valve is normally closed when it is actually normally open, leading to critical errors in fluid control systems.
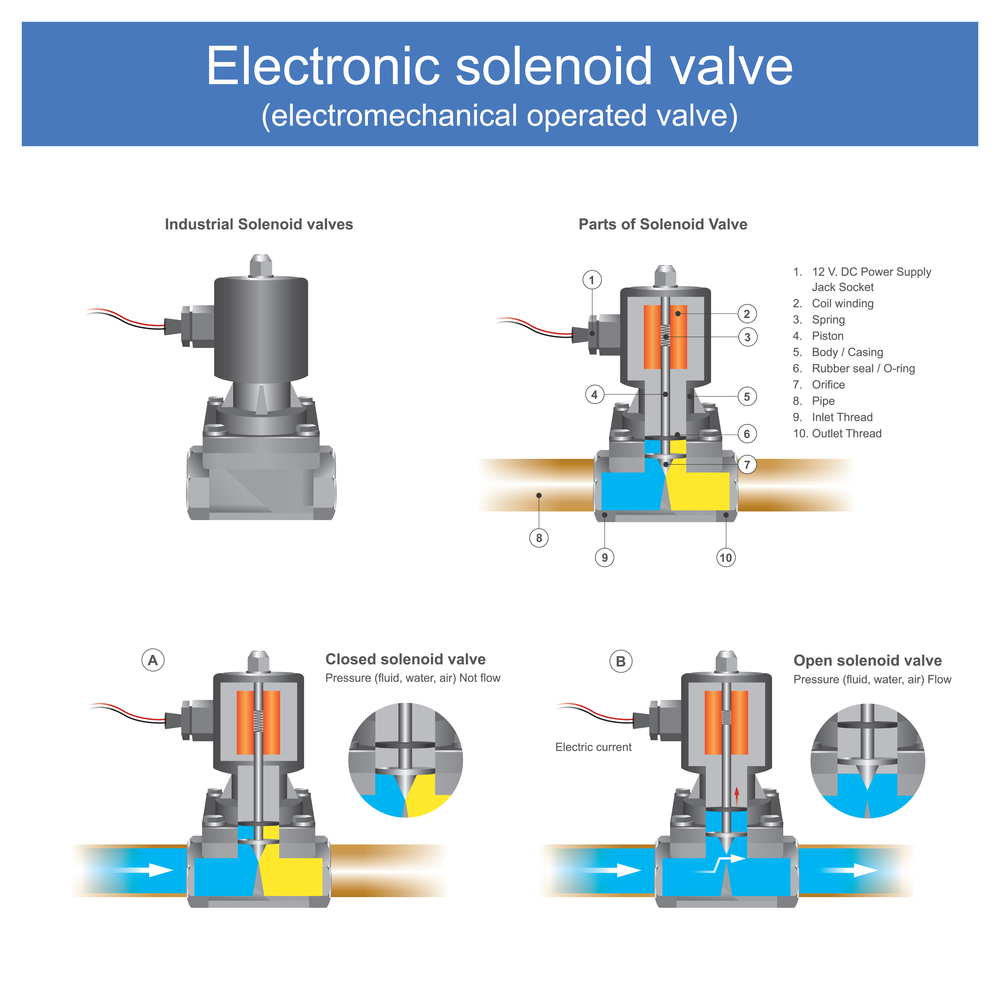
Illustrative image related to solenoid valve diagram
The Solution: To mitigate misinterpretation issues, buyers should invest in comprehensive training for their engineering and technical teams on standard solenoid valve symbols and their meanings. It is advisable to refer to recognized international standards such as ISO 1219 or ANSI/ISA-5.1, which provide clear definitions and diagrams for fluid power components. Additionally, maintaining a catalog of standard symbols and a reference guide at their workspace can enhance understanding. When sourcing solenoid valves, buyers should ask for detailed documentation that includes accurate diagrams with clearly defined symbols. This practice ensures that everyone involved in the project is on the same page, minimizing the risks of operational errors.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Solenoid Valve for Specific Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle to select the appropriate solenoid valve for their specific applications due to the vast array of options available. For instance, a company in the Middle East may require a solenoid valve that can operate under high temperatures and pressures but finds it challenging to filter through the specifications of multiple products. This can lead to delays in project timelines and increased costs, as unsuitable valves may need to be replaced after installation.
The Solution: To streamline the selection process, buyers should develop a structured approach to define their application requirements before consulting suppliers. This includes outlining critical factors such as the type of fluid, pressure ratings, temperature ranges, and environmental conditions. Engaging with suppliers who provide a comprehensive selection wizard or configurator tool on their websites can also facilitate the identification of suitable products. Furthermore, buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer expert consultancy services, as this can provide invaluable insights into which valve types are best suited for their unique needs. Creating a checklist that encompasses all technical requirements can further assist buyers in making informed decisions.
Scenario 3: Inadequate Documentation and Support for Solenoid Valve Diagrams
The Problem: In many cases, B2B buyers find that the solenoid valve diagrams they receive lack sufficient detail or clarity, making it difficult to implement or maintain the systems effectively. For example, a manufacturing plant in South America might receive diagrams that do not adequately explain the control mechanism or fail to illustrate the flow paths clearly. This inadequacy can lead to maintenance challenges, misalignments in systems, and ultimately, increased operational costs.
The Solution: To address these documentation issues, buyers should insist on receiving comprehensive documentation from suppliers, including not just diagrams but also operational manuals, maintenance guidelines, and troubleshooting tips. When reviewing diagrams, buyers should seek out those that clearly delineate all components, flow paths, and control mechanisms. Additionally, it can be beneficial to establish a communication channel with the supplier for clarification on any diagram-related queries. Implementing a regular review process of the diagrams against the actual installations can help identify discrepancies early and facilitate timely corrections. By ensuring that they have complete and precise documentation, buyers can enhance their operational efficiency and reduce the risk of costly errors.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for solenoid valve diagram
What Are the Key Materials Used in Solenoid Valve Diagrams?
When selecting materials for solenoid valves, several common options stand out due to their unique properties and performance characteristics. Understanding these materials is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
How Do Brass Solenoid Valves Perform in Various Applications?
Brass is a widely used material for solenoid valves due to its excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical strength. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 200°C and can withstand pressures up to 16 bar.
Pros: Brass offers durability and is relatively easy to machine, making it suitable for various applications, including water, air, and gas. Its cost-effectiveness also makes it a popular choice among manufacturers.
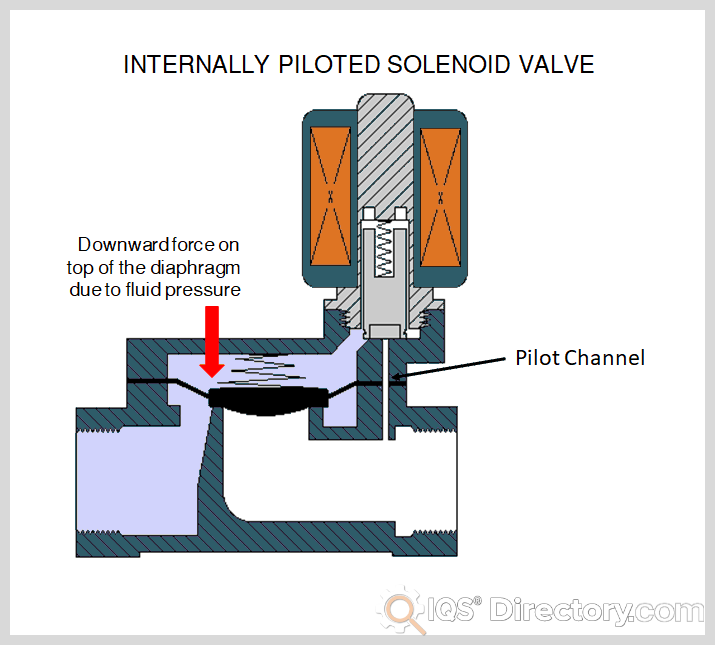
Illustrative image related to solenoid valve diagram
Cons: However, brass can be susceptible to dezincification in certain environments, which can lead to premature failure. Additionally, while it is generally less expensive than stainless steel, it may not be suitable for highly corrosive media.
Impact on Application: Brass is compatible with water and gas applications but may not be ideal for aggressive chemicals. Buyers should check compatibility with specific media to avoid operational issues.
What Role Does Stainless Steel Play in Solenoid Valve Design?
Stainless steel is another common material choice for solenoid valves, known for its superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature performance, typically rated up to 300°C and capable of handling pressures exceeding 20 bar.
Pros: Its robustness and resistance to a wide range of chemicals make stainless steel ideal for harsh environments, including those found in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries.
Cons: The main downside is its higher cost compared to brass, along with increased manufacturing complexity due to its hardness.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel valves are suitable for applications involving aggressive chemicals or high-temperature environments, making them a preferred choice for international buyers in industries with stringent safety and compliance requirements.
Why Consider Plastic Materials for Solenoid Valves?
Plastic materials, such as PVC or polypropylene, are increasingly used in solenoid valves, especially in applications involving corrosive chemicals or where weight is a concern. They typically operate effectively at temperatures up to 60°C and pressures around 10 bar.
Pros: The primary advantage of plastic is its excellent chemical resistance and lightweight nature, which can reduce shipping costs and ease installation.
Cons: However, plastics generally have lower temperature and pressure ratings compared to metals, which may limit their use in certain applications.
Impact on Application: Plastic solenoid valves are ideal for handling aggressive media like acids or bases, making them suitable for the chemical processing industry. Buyers should ensure that the selected plastic material meets relevant international standards.
How Do Aluminum Solenoid Valves Compare?
Aluminum is also a viable option for solenoid valves, offering a good balance of strength, weight, and cost. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 150°C and can handle pressures around 10-15 bar.
Pros: Aluminum is lightweight and has good corrosion resistance, making it suitable for applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in mobile equipment.
Cons: Its lower corrosion resistance compared to stainless steel can be a limitation in certain environments, and it may require protective coatings for extended use in corrosive applications.
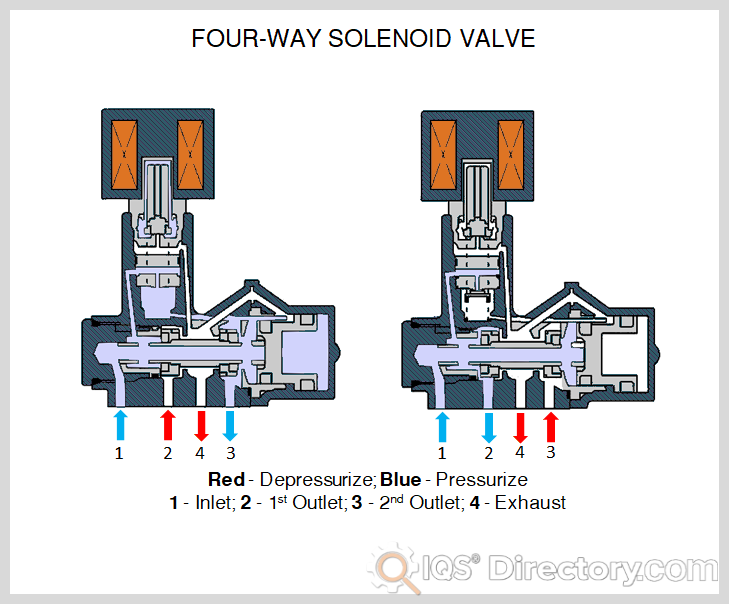
Illustrative image related to solenoid valve diagram
Impact on Application: Aluminum valves are often used in pneumatic applications and environments where weight savings are essential. Buyers should consider the environmental conditions to ensure longevity.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Solenoid Valves
| Material | Typical Use Case for solenoid valve diagram | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brass | Water, air, and gas applications | Cost-effective and durable | Susceptible to dezincification | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Chemical and pharmaceutical industries | Superior corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Plastic | Chemical processing applications | Excellent chemical resistance | Lower temperature and pressure ratings | Medium |
| Aluminum | Pneumatic and mobile equipment applications | Lightweight and good corrosion resistance | Requires protective coatings in harsh environments | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of various materials used in solenoid valves, helping them make informed decisions tailored to their specific applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for solenoid valve diagram
What are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Solenoid Valves?
The manufacturing process of solenoid valves is multifaceted, involving several crucial stages that ensure the final product meets industry standards and customer expectations. Understanding these stages is vital for B2B buyers looking to source high-quality solenoid valves.
Material Preparation: What Materials are Commonly Used?
The first stage in the manufacturing process is material preparation. Solenoid valves are typically made from materials like brass, stainless steel, or plastic, depending on their intended application and environmental conditions.
-
Material Selection: The choice of material affects the valve’s durability, resistance to corrosion, and overall performance. For instance, stainless steel is preferred for applications involving harsh chemicals, while brass might be used for water or air applications.
-
Quality of Raw Materials: Suppliers should ensure that the raw materials meet specific industry standards, such as ASTM or equivalent. B2B buyers should request certifications to verify material quality.
Forming: How are Solenoid Valves Shaped?
The forming stage involves shaping the raw materials into the components needed for the solenoid valve. This process typically includes several techniques:
-
Machining: Precision machining is employed to create the valve body, ports, and other intricate components. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are often utilized for their accuracy and efficiency.
-
Casting and Molding: In some cases, components may be cast or molded. For instance, plastic solenoid valves are often produced through injection molding, which allows for complex shapes and reduced waste.
-
Assembly Preparation: Once components are formed, they are cleaned and prepared for assembly. This may involve deburring, sanding, or applying protective coatings.
Assembly: What are the Steps in Assembling Solenoid Valves?
The assembly stage is where all the prepared components come together to create the final product. This process typically includes:
-
Component Integration: Individual parts such as the solenoid coil, valve body, and actuator are assembled. Each component must fit precisely to ensure proper functionality.
-
Sealing and Testing: After assembly, solenoid valves often undergo sealing processes to prevent leaks. This can involve O-rings, gaskets, or other sealing materials.
-
Initial Testing: Some manufacturers conduct preliminary tests at this stage to ensure that the assembly is functioning correctly before moving on to more rigorous quality checks.
Finishing: How is the Final Product Enhanced?
Finishing processes enhance the appearance and functionality of solenoid valves. This stage may include:
-
Coating and Plating: Protective coatings or plating (such as nickel or chrome) are often applied to improve corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
-
Final Quality Checks: Before packaging, valves are subjected to final quality inspections to ensure they meet specifications.
What International Standards and Quality Assurance Practices are Relevant for Solenoid Valves?
Quality assurance (QA) is a crucial aspect of the manufacturing process for solenoid valves, ensuring that products meet both international standards and customer expectations. B2B buyers should be familiar with the following standards and practices:
Which International Standards Should Buyers Look For?
-
ISO 9001: This is the most recognized international standard for quality management systems. Suppliers adhering to ISO 9001 demonstrate their commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
-
CE Marking: For products sold in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) provides standards specifically for valves used in the oil and gas industry, ensuring reliability and safety.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Solenoid Valve Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is embedded throughout the manufacturing process, with specific checkpoints designed to catch defects and ensure compliance with standards:
What Are the Main QC Checkpoints?
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified quality standards. Suppliers should have documented procedures for IQC.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, regular inspections are conducted to monitor the quality of the assembly and ensure compliance with specifications.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the solenoid valves are fully assembled, they undergo rigorous testing to check for functionality, leakage, and adherence to specifications. This may include pressure tests, electrical testing, and performance evaluations.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used to Ensure Quality?
Various testing methods are employed to validate the performance and safety of solenoid valves:
-
Hydraulic and Pneumatic Testing: These tests check for leaks and ensure that the valve can withstand specified pressures.
-
Electrical Testing: For electrically actuated valves, testing verifies coil resistance and functionality to ensure reliable operation.
-
Functional Testing: This involves operating the valve under conditions that simulate real-world applications to confirm it performs as intended.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Measures?
To ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards, B2B buyers should implement the following verification strategies:
What Steps Can Buyers Take?
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. This is essential for ensuring compliance with international standards.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should be willing to provide quality control reports and documentation demonstrating adherence to relevant standards.
-
Third-party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures, ensuring that products meet specified requirements.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is essential:
-
Regional Compliance: Different regions may have specific regulations regarding product safety and environmental impact. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these requirements to avoid compliance issues.
-
Language Barriers: Documentation and communication may pose challenges due to language differences. Buyers should ensure that all quality-related documentation is available in a language they can understand.
-
Cultural Considerations: Understanding the cultural context of suppliers can facilitate better communication and collaboration, ultimately leading to improved quality outcomes.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for solenoid valves, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers, ensuring that they receive high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘solenoid valve diagram’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure solenoid valve diagrams. Understanding the proper specifications and requirements is crucial to ensure that the solenoid valves meet your operational needs, particularly in sectors such as manufacturing, automation, and fluid control.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is essential for successful procurement. This includes identifying the type of solenoid valve needed (e.g., 2/2-way, 3/2-way, proportional) and understanding the application requirements, such as pressure ratings, flow rates, and voltage specifications. Ensure to document these requirements in detail to avoid miscommunication with suppliers.
Step 2: Research Industry Standards and Symbols
Familiarize yourself with industry standards related to solenoid valve diagrams and the relevant symbols used in P&IDs (Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams). Knowing the symbols, such as those for normally open or normally closed configurations, will help you accurately interpret the diagrams and ensure they align with your project’s requirements. This knowledge also aids in effective communication with engineers and suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request company profiles, certifications, and references from previous clients within your industry or region. Assess their experience with solenoid valves and their ability to provide detailed diagrams that align with your specifications. A reliable supplier should have a track record of delivering quality products on time.
Step 4: Verify Compliance with Local Regulations
Ensure that the solenoid valve diagrams and the products they represent comply with local regulations and standards relevant to your industry. This may include certifications for safety, environmental impact, and operational efficiency. Compliance not only mitigates legal risks but also enhances the reliability and performance of the solenoid valves.
Step 5: Request Samples and Technical Documentation
Request samples of solenoid valve diagrams and relevant technical documentation from shortlisted suppliers. This should include detailed specifications, installation instructions, and maintenance guidelines. Reviewing this documentation allows you to assess the clarity and usability of the diagrams, ensuring they meet your operational needs.
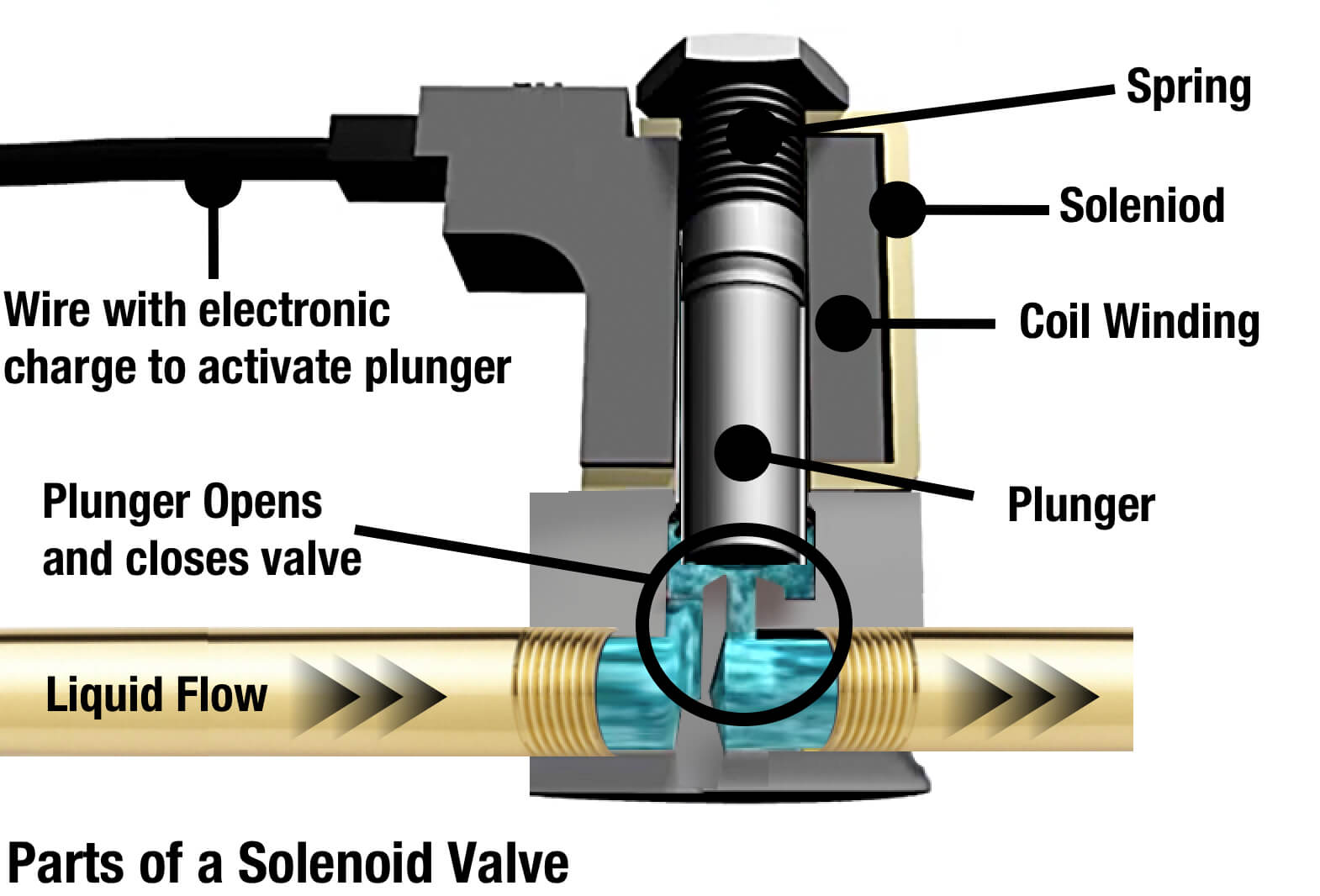
Illustrative image related to solenoid valve diagram
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support and Training
Inquire about the after-sales support and training offered by the supplier. Effective support can significantly impact the operational success of your solenoid valves. Look for suppliers that provide comprehensive training on installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting, as well as readily available customer service for ongoing assistance.
Step 7: Compare Pricing and Terms
Finally, compare pricing and terms from multiple suppliers before making a decision. Look beyond just the cost; consider factors such as payment terms, lead times, and warranty conditions. A slightly higher price may be justified by better quality or support, making it essential to evaluate the overall value offered by each supplier.
By following these steps, you can ensure a thorough and effective procurement process for solenoid valve diagrams that meet your technical and operational requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for solenoid valve diagram Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Solenoid Valve Diagrams?
When sourcing solenoid valve diagrams, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and decision-making. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used in solenoid valves significantly impact costs. For instance, brass and stainless steel are commonly used materials, with stainless steel typically incurring higher costs due to its durability and resistance to corrosion.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the region and the expertise required for design and manufacturing. Skilled labor in regions with higher wage standards will increase overall costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with facilities, utilities, and indirect labor. Manufacturers in regions with higher operational costs may pass these expenses onto buyers.
-
Tooling: The cost of molds and tools necessary for production can be significant, especially for customized designs. Investing in high-quality tooling can lead to better product quality and consistency.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that the solenoid valves meet industry standards. However, these processes add to the overall cost, reflecting the importance of reliability in B2B transactions.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs are critical, especially for international shipments. Factors like shipping distance, mode of transport, and customs duties can significantly influence logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. Understanding the supplier’s margin can help buyers gauge the fairness of the pricing.
How Do Volume and Customization Affect Pricing for Solenoid Valve Diagrams?
Volume and customization are two of the most influential factors in pricing.
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes often lead to reduced unit costs due to economies of scale. Suppliers may offer discounts for larger purchases, making it beneficial for buyers to consolidate orders when possible.
-
Specs/Customization: Custom designs or specific technical requirements can increase costs due to the need for specialized manufacturing processes or materials. Buyers should clearly define their specifications upfront to obtain accurate quotes.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products that meet international quality standards or certifications may come at a premium. Buyers in regions with stringent regulations should factor in these additional costs when sourcing.
What Supplier Factors Should Buyers Consider in Pricing?
Supplier-related factors can also have a significant impact on pricing:
-
Supplier Reputation: Established suppliers with a track record of quality and reliability may charge higher prices but offer peace of mind and better service.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can affect the total landed cost of products. Understanding terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) is crucial for accurate cost estimation.
What Buyer Tips Can Help with Negotiation and Cost Efficiency?
To optimize sourcing strategies, buyers should consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Build relationships with suppliers and be transparent about your needs. This can lead to better pricing and terms, especially for repeat orders.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: International buyers, especially from Africa, South America, and the Middle East, should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local taxes that can affect the final cost.
What Is the Disclaimer Regarding Indicative Prices?
It’s important for buyers to note that prices can vary widely based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. While this analysis provides a framework for understanding costs and pricing, actual prices should be confirmed through direct communication with suppliers to ensure accuracy and relevance to individual sourcing needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing solenoid valve diagram With Other Solutions
Introduction: What Are the Alternatives to Solenoid Valve Diagrams?
When evaluating fluid control systems, solenoid valve diagrams are essential for understanding the operation and integration of valves within a system. However, there are alternative solutions and methods available that may offer different advantages depending on specific application needs. This analysis will compare solenoid valve diagrams with two viable alternatives: pneumatic control diagrams and motorized valve systems. Each alternative presents unique benefits and challenges that can impact decision-making for B2B buyers in various industries.
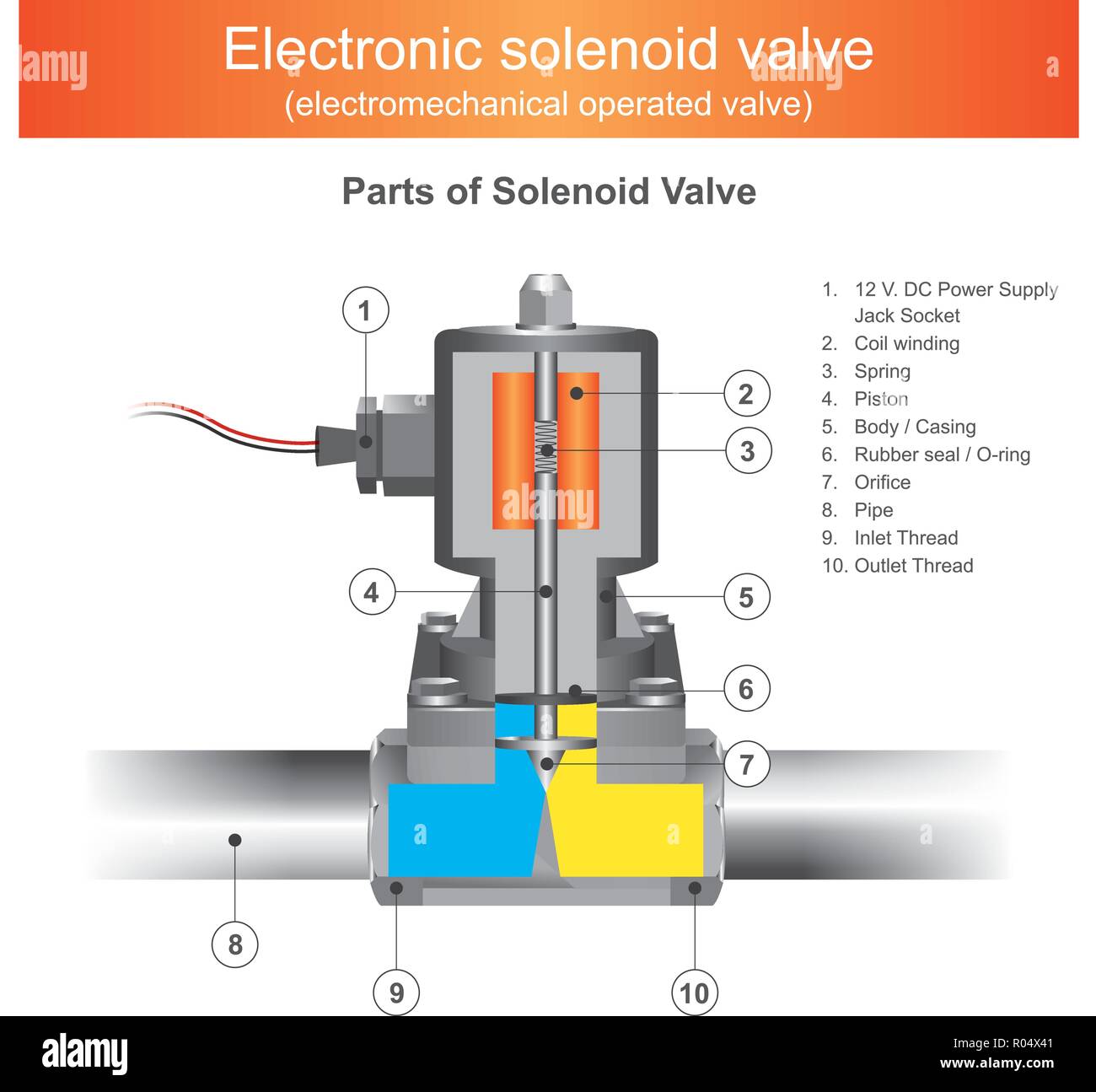
Illustrative image related to solenoid valve diagram
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Solenoid Valve Diagram | Pneumatic Control Diagram | Motorized Valve Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision control; quick response time | Reliable, suitable for high flow rates | Moderate precision; slower response compared to solenoids |
| Cost | Generally low cost for components | Moderate to high cost due to compressor systems | High initial investment and operational costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple to implement with standard symbols | Requires specialized knowledge for setup | More complex installation; may require additional infrastructure |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; typically reliable | Moderate maintenance; requires regular checks | Higher maintenance needs due to mechanical components |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for automated systems needing rapid control | Best for high-volume applications and pneumatic systems | Suitable for large systems requiring precise flow control |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are Pneumatic Control Diagrams?
Pneumatic control diagrams utilize compressed air to operate valves, cylinders, and other components in a system. They are particularly effective in applications where high flow rates are necessary, such as in manufacturing and assembly lines.
Pros: Pneumatic systems are known for their reliability and ability to handle large volumes of fluid or air, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. Their operation is generally straightforward for experienced technicians familiar with pneumatic principles.
Cons: However, they require additional infrastructure, such as air compressors, which can increase both initial setup costs and ongoing operational expenses. Moreover, the need for regular maintenance checks adds to the overall complexity.
How Do Motorized Valve Systems Differ?
Motorized valve systems utilize electric motors to control valve positions. They can achieve precise control over flow rates and are often used in applications where variability in flow is essential, such as in HVAC systems and water treatment facilities.
Pros: The primary advantage of motorized systems is their ability to provide accurate control over flow, making them ideal for applications where precision is crucial. They can also be integrated with modern automation and control systems easily.
Cons: The drawbacks include a higher initial investment and increased operational costs due to energy consumption. Installation can be complex, requiring specialized knowledge and potentially additional infrastructure to support motor operation.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting between solenoid valve diagrams and their alternatives, B2B buyers should assess their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and the complexity of implementation and maintenance. Solenoid valves are often the best choice for applications requiring quick and precise control at a lower cost. However, pneumatic control diagrams might be more suitable for high-volume operations, while motorized valve systems offer precision for complex fluid management tasks. Ultimately, the choice will depend on the specific requirements of the application, ensuring that the selected solution aligns with both current and future operational demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for solenoid valve diagram
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Solenoid Valves?
Understanding the critical specifications of solenoid valves is vital for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential technical properties that B2B buyers should consider:
-
Material Grade
Solenoid valves are typically made from various materials, including brass, stainless steel, and plastic. The choice of material affects the valve’s durability, resistance to corrosion, and suitability for specific media (e.g., water, oil, or chemicals). For example, stainless steel valves are preferred in harsh environments due to their resistance to oxidation and high-pressure applications. Selecting the right material is crucial for ensuring operational longevity and compliance with industry standards. -
Pressure Rating
The pressure rating indicates the maximum pressure the valve can handle without failure. Common ratings include low-pressure (up to 150 psi) and high-pressure (over 150 psi) classifications. This specification is vital for applications in industries such as oil and gas, where pressure fluctuations can impact safety and performance. Ensuring that the valve meets the required pressure standards for your specific application is essential to avoid costly failures. -
Flow Coefficient (Cv Value)
The flow coefficient (Cv) quantifies the flow capacity of the valve. A higher Cv value indicates a greater flow capacity, allowing for efficient operation in systems requiring significant fluid movement. This metric is particularly important for optimizing system performance and energy efficiency, especially in large-scale industrial applications. -
Actuation Type
Solenoid valves can be actuated electrically or manually, with options such as normally closed (NC) and normally open (NO) configurations. Understanding the actuation type is critical for ensuring compatibility with existing control systems. For instance, normally closed valves are ideal for applications requiring a fail-safe mode, where the valve defaults to a closed position without power. -
Temperature Range
Each solenoid valve is designed to operate within a specific temperature range. This specification is crucial for ensuring that the valve functions correctly in various environmental conditions. Choosing a valve that can withstand the operational temperatures of the application helps prevent malfunctions and extends the product’s lifespan. -
Wattage
The wattage of the solenoid coil determines its power consumption and response time. Lower wattage valves are energy-efficient, while higher wattage options provide faster actuation. Evaluating wattage is essential for balancing performance with energy costs, especially in applications where multiple valves are in operation.
What Are the Common Trade Terminology and Jargon in Solenoid Valve Procurement?
Familiarizing yourself with industry terminology can enhance communication with suppliers and streamline the procurement process. Here are some common terms relevant to solenoid valves:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce components that are used in another company’s end product. Understanding OEM specifications is crucial for ensuring compatibility and quality when sourcing solenoid valves, especially for industries that require custom solutions. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ helps B2B buyers manage inventory levels and avoid overcommitting to large orders that may not align with current needs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. Crafting a clear RFQ can facilitate better negotiations and help ensure that all technical requirements are met, leading to more accurate quotes. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, insurance, and liability, thereby reducing the risk of disputes. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order until its delivery. Understanding lead times is essential for project planning and inventory management, especially in industries with tight deadlines. -
Certification Standards
Certification standards, such as ISO or CE marking, indicate that a product meets specific safety and quality benchmarks. Ensuring that solenoid valves are certified can safeguard against compliance issues and enhance product reliability.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the solenoid valve diagram Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Influencing the Solenoid Valve Diagram Sector?
The solenoid valve diagram market is experiencing dynamic shifts driven by technological advancements and changing customer needs. Key global drivers include the increasing demand for automation across various industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and HVAC systems. This demand is further fueled by the rise of Industry 4.0, where interconnected systems and smart technologies are becoming the norm. International buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking solenoid valves that integrate seamlessly with automated systems.
Emerging trends include the adoption of digital twin technology, which allows for the simulation of solenoid valve performance in real-time, enhancing predictive maintenance capabilities. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce platforms is reshaping sourcing strategies, enabling buyers to access a broader range of suppliers and products. As manufacturers focus on customization and adaptability, B2B buyers are looking for solenoid valves that can be tailored to specific applications.
Moreover, the shift towards modular designs is gaining traction, as these allow for easier upgrades and replacements, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. The emphasis on quality and reliability remains paramount, particularly for buyers in developing markets where operational efficiency directly impacts profitability.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact My B2B Decisions in the Solenoid Valve Diagram Market?
Sustainability is becoming a crucial consideration for B2B buyers in the solenoid valve diagram sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including resource consumption and waste generation, is under increased scrutiny. International buyers are now prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices. This includes the use of eco-friendly materials and production methods that minimize carbon footprints.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as buyers seek to ensure their supply chains are free from exploitation and environmental degradation. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other green credentials can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Incorporating ‘green’ materials, such as recyclable metals and environmentally friendly coatings, not only enhances the sustainability profile of solenoid valves but also meets the growing consumer demand for responsible products. As global regulations tighten around environmental impact, aligning with suppliers who prioritize sustainability will not only mitigate risks but also enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty.
What Is the Historical Evolution of Solenoid Valve Diagrams and Their Relevance Today?
The solenoid valve diagram has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially used in basic mechanical applications, the introduction of electrical solenoids marked a turning point, allowing for remote and automated control of fluid systems. Over the decades, advancements in materials and technology led to more sophisticated designs, enabling solenoid valves to operate in diverse environments, from industrial settings to consumer appliances.
Today, solenoid valve diagrams are critical for engineers and operators, providing a clear visual representation of how these components function within broader systems. The integration of digital technologies has further enhanced their utility, allowing for real-time monitoring and control. This evolution underscores the importance of understanding solenoid valve diagrams for B2B buyers, as they play a vital role in system design, troubleshooting, and maintenance. Understanding this history can help buyers appreciate the technological advancements that continue to shape the market, guiding their sourcing and procurement strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of solenoid valve diagram
-
How do I interpret solenoid valve symbols in diagrams?
Understanding solenoid valve symbols in diagrams is crucial for effective system design and operation. Each symbol represents specific functions, such as the number of ports and switching states. For instance, a 2/2-way valve has two ports and two states (open and closed). Familiarize yourself with the standard symbols used in Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams (P&ID) to accurately read and communicate system designs. It’s advisable to consult a reference guide or standard documentation to ensure clarity and prevent misinterpretations during installation and maintenance. -
What are the key features to look for in solenoid valve diagrams?
When reviewing solenoid valve diagrams, focus on key features such as the number of ports, the type of actuation (normally open or closed), and flow direction indicators. Understanding the operational states of the valves, represented by various symbols, is also critical. Additionally, check for any annotations that might indicate specific functionalities or operational instructions. This information will help ensure that the valves meet your application’s requirements and facilitate smoother integration into your systems. -
What should I consider when sourcing solenoid valves internationally?
When sourcing solenoid valves internationally, consider factors such as compliance with local regulations, quality certifications, and supplier reliability. Research the manufacturer’s background, including their experience in the industry and customer reviews. Additionally, assess shipping logistics, lead times, and potential tariffs or duties that may affect costs. Establishing clear communication with suppliers can also help clarify specifications and reduce the risk of misunderstandings regarding product quality and delivery timelines. -
How can I ensure the quality of solenoid valves from suppliers?
To ensure the quality of solenoid valves, request certifications such as ISO 9001 or specific industry standards relevant to your application. Conduct supplier audits or request product samples for testing before placing large orders. Additionally, ask for references from previous clients to gauge satisfaction levels. Implementing a quality assurance process that includes regular inspections and testing upon receipt can also help maintain high standards for your equipment. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for solenoid valves?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for solenoid valves can vary significantly between suppliers and regions. Typically, MOQs may range from 50 to several hundred units, depending on the manufacturer’s production capabilities and the specific type of valve. Discussing your needs with suppliers can sometimes lead to flexibility in MOQs, especially for long-term partnerships or bulk orders. Always clarify the MOQ before finalizing any agreements to avoid unexpected costs. -
What payment terms should I negotiate with solenoid valve suppliers?
When negotiating payment terms, consider options such as net 30 or net 60 days, which allow time for inspection and quality checks before full payment. Some suppliers may require a deposit upfront, especially for custom orders. Additionally, explore options for letter of credit or escrow services to safeguard your interests. Establishing clear payment terms in your contract can prevent misunderstandings and ensure a smooth transaction process. -
How can I customize solenoid valves to meet my specific needs?
Customizing solenoid valves typically involves selecting specific features such as port sizes, actuation types, and materials suited to your application. When engaging with suppliers, provide detailed specifications and requirements to facilitate the customization process. Many manufacturers offer engineering support to help design valves tailored to specific operational environments. It’s essential to confirm lead times and any additional costs associated with customization during your discussions. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing solenoid valves?
When importing solenoid valves, logistics considerations include shipping methods, delivery timelines, and customs clearance processes. Choose a reliable logistics partner familiar with international shipping regulations to streamline the process. Ensure that all necessary documentation, such as invoices and shipping manifests, is in order to avoid delays. Additionally, factor in warehousing and distribution arrangements upon arrival to ensure timely delivery to your operations.
Top 3 Solenoid Valve Diagram Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Tameson – Solenoid Valves
Domain: tameson.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Solenoid valves are represented in fluid power diagrams using unique symbols to indicate their functions and connections. Key details include: 1. Valve Types: 2-Way Solenoid Valves, 3-Way Solenoid Valves, Proportional Valves, Pneumatic Solenoid Valves, and Solenoid Valve Accessories. 2. Valve Designation: Valves are designated with two numbers (e.g., 2/2-way), where the first number indicates the …
2. Connexion Developments – Solenoid Valve Symbols
Domain: connexion-developments.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Solenoid Valve Symbols UK Free : 0800 808 7799 Int : +44 1454 334 990. General Purpose Manufacturers. Media Type: Air and Inert Gases, Light Oil, Natural Gas, Slightly Aggressive Media, Steam, Thick Viscous Liquids, Vacuum, Very Aggressive Media, Water. Common Solenoid Valve Symbols: 2/2 Valve (2 Ports, 2 Positions), 3/2 Valve (3 Ports, 2 Positions), 4/2 Valve (4 Ports, 2 Positions), 4/3 Valve (4 …
3. AutomationDirect – Pneumatic Circuit Symbols
Domain: library.automationdirect.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Pneumatic circuit symbols represent directional air control valves, indicating methods of actuation, number of positions, flow paths, and number of ports. Valve symbols consist of three parts: actuators, position boxes, and flow boxes. Each valve has at least two positions and flow paths, shown by arrows in the flow boxes. The number of ports is indicated by endpoints in the boxes, with labels suc…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for solenoid valve diagram
In the realm of solenoid valves, strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in optimizing operational efficiency and ensuring the reliability of fluid control systems. By understanding the diverse applications of 2-way and 3-way solenoid valves, as well as their symbols in P&ID and fluid power diagrams, international buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific operational needs. Furthermore, selecting the right type of valve—whether for automation or manual control—can significantly impact process reliability and safety.
As the global market continues to evolve, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for high-quality solenoid valves is expected to rise. Buyers are encouraged to leverage strategic sourcing not only to enhance their supply chain resilience but also to build partnerships with reputable manufacturers that prioritize innovation and quality assurance.
Looking ahead, investing in advanced solenoid valve technologies and understanding their diagrams will empower businesses to enhance their operational capabilities. Engage with trusted suppliers today to position your organization for success in an increasingly competitive landscape. Embrace the future of fluid control with confidence and clarity.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
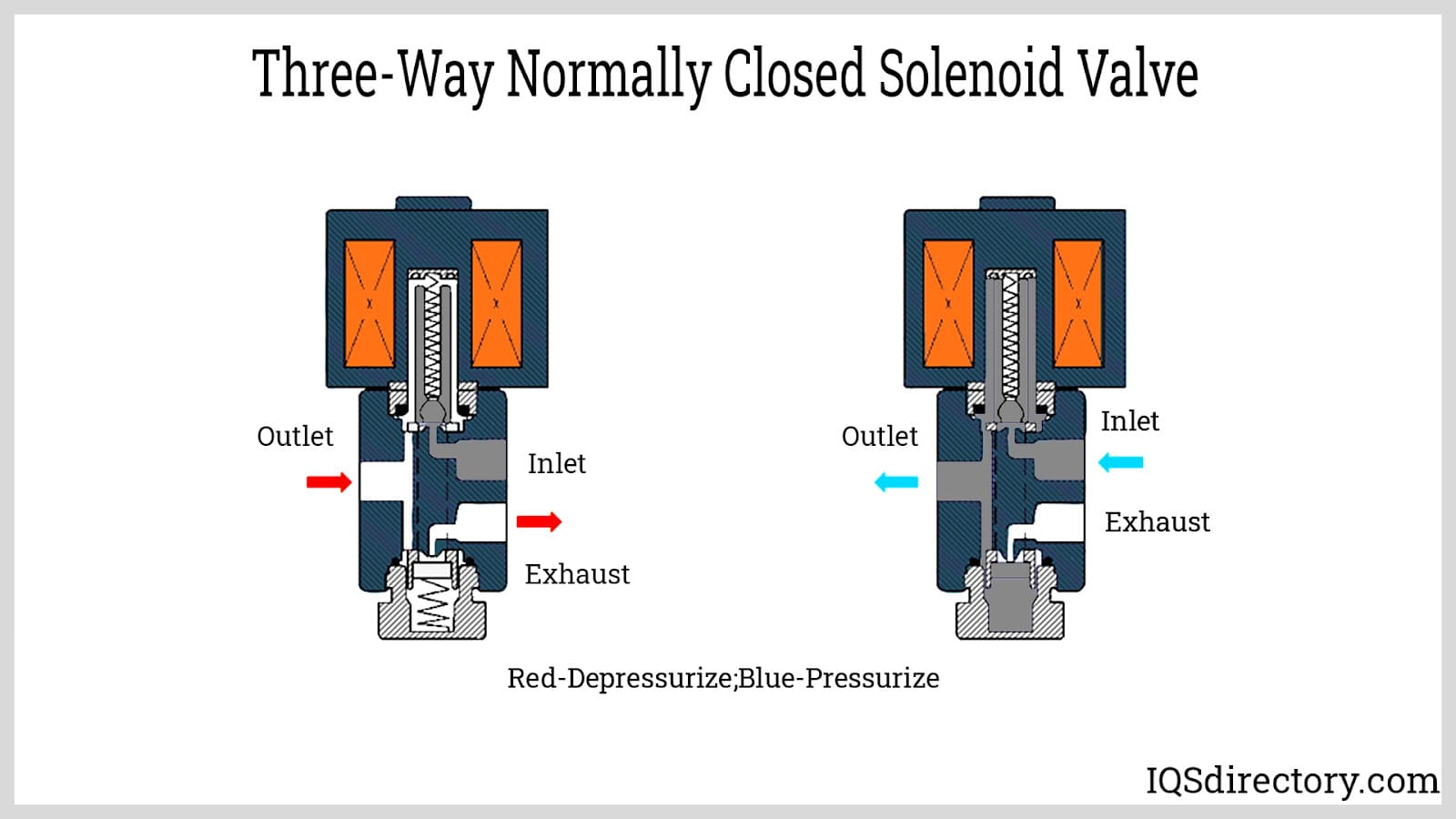
Illustrative image related to solenoid valve diagram
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.