A B2B Buyer’s Guide to Rf Shields: Price, Quality, and Suppliers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for rf shields
In an increasingly interconnected world, sourcing reliable RF shields has emerged as a critical challenge for B2B buyers across diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As electronic devices proliferate and regulatory standards tighten, the demand for effective electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding solutions becomes paramount. This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted landscape of RF shields, covering various types, applications, and innovative materials designed to meet industry standards and specific client needs.
Navigating this complex market requires a nuanced understanding of the options available, as well as the ability to assess potential suppliers. This guide equips international buyers with the necessary tools to make informed purchasing decisions. We will explore essential criteria for supplier vetting, including quality assurance processes, certifications, and customization capabilities, ensuring that your sourcing strategy aligns with your operational requirements. Additionally, we will analyze cost factors associated with RF shields, helping you identify budget-friendly solutions without compromising on quality.
Whether you’re based in Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, or any part of Europe, this guide aims to empower your procurement strategy by providing actionable insights and expert recommendations. By leveraging this knowledge, you can confidently navigate the global RF shield market, ensuring that your electronic systems are protected against interference while optimizing performance and compliance.
Understanding rf shields Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conductive Gaskets | Made from conductive elastomers; seals gaps between metal surfaces | Enclosures, cabinets, and panels | Pros: Effective sealing, reusable; Cons: Limited lifespan under heavy use. |
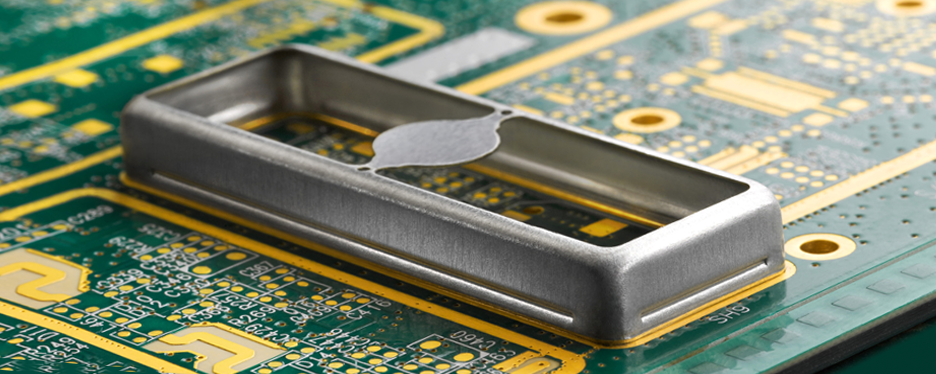
| RF Shielded Enclosures | Fully enclosed structures designed to block RF signals | Telecommunications, medical equipment | Pros: High effectiveness; Cons: Higher initial cost, requires precise installation. |
| Honeycomb Filters | Hexagonal structure allowing airflow while blocking RF | HVAC systems in sensitive environments | Pros: Maintains airflow; Cons: Limited frequency range. |
| Shielded Vent Panels | Allows air exchange while preventing RF leakage | Data centers, laboratories | Pros: Efficient design; Cons: Installation complexity. |
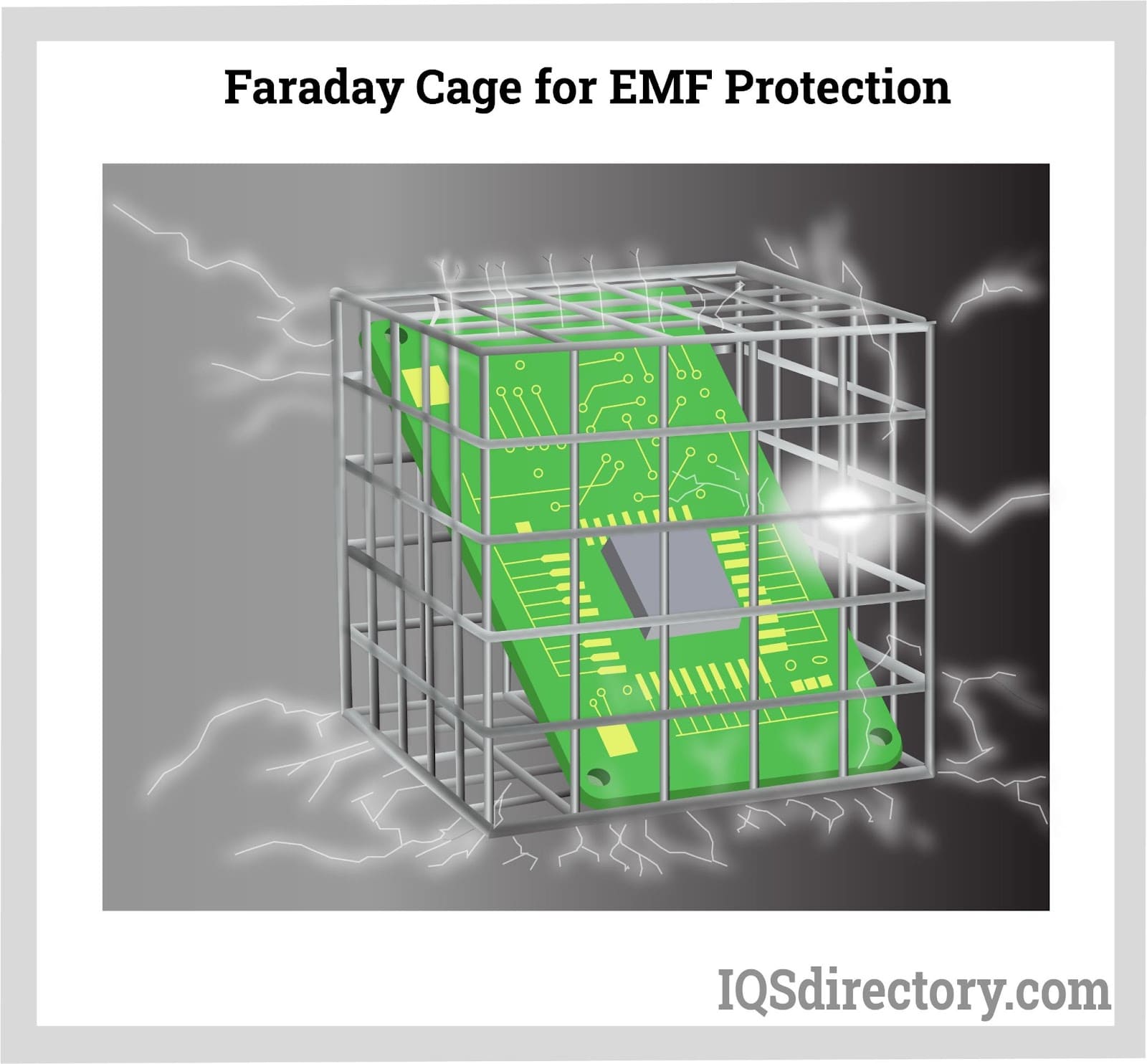
| Faraday Cages | Enclosures that block external electromagnetic fields | Military, aerospace, research labs | Pros: Comprehensive shielding; Cons: Bulkier design, higher costs. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Conductive Gaskets for RF Shielding?
Conductive gaskets are essential for providing a reliable seal between metal surfaces, preventing electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). These gaskets are typically made from conductive elastomers that ensure a low-impedance path for electrical continuity. In B2B applications, they are widely used in enclosures, cabinets, and panels, where maintaining EMI/RFI integrity is crucial. When purchasing, buyers should consider the gasket’s durability and the specific environmental conditions, as these factors can influence performance over time.
How Do RF Shielded Enclosures Function in Industrial Settings?
RF shielded enclosures are specifically designed to block radio frequency signals, creating a secure environment for sensitive electronic equipment. These enclosures are critical in industries such as telecommunications and medical technology, where interference can lead to operational failures. Buyers should evaluate the enclosure’s effectiveness based on shielding effectiveness (SE) ratings and installation requirements. While these enclosures offer high protection, the initial investment can be significant, and precise installation is necessary for optimal performance.
What Are the Advantages of Using Honeycomb Filters in RF Applications?
Honeycomb filters are engineered to allow airflow while effectively blocking RF signals, making them ideal for HVAC systems in sensitive environments. Their unique hexagonal structure provides a balance between maintaining air quality and minimizing electromagnetic interference. When considering honeycomb filters, B2B buyers should assess their specific frequency range and airflow requirements. While these filters are advantageous for maintaining environmental control, they may have limitations regarding the frequencies they can effectively attenuate.

Illustrative image related to rf shields
How Do Shielded Vent Panels Enhance RF Protection?
Shielded vent panels are designed to facilitate air exchange while preventing RF leakage in environments such as data centers and laboratories. These panels are crucial for maintaining the operational efficiency of sensitive equipment while ensuring compliance with electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards. Buyers should focus on the panel’s design and installation complexity, as these factors can affect overall performance. While shielded vent panels are efficient, their installation can be more complex compared to traditional venting solutions.
What Makes Faraday Cages Essential for Sensitive Operations?
Faraday cages are structures that provide comprehensive shielding against external electromagnetic fields, making them indispensable in military, aerospace, and research laboratory applications. They effectively prevent interference from external RF signals, ensuring that sensitive equipment operates without disruption. When purchasing Faraday cages, B2B buyers should consider the size, material, and design, as these factors influence shielding effectiveness and practicality. Despite their advantages, Faraday cages can be bulkier and more expensive than alternative shielding solutions, which may impact budget considerations.
Key Industrial Applications of rf shields
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of rf shields | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Telecommunications | Shielded enclosures for communication devices | Reduces signal interference, ensuring reliable connectivity | Compliance with international EMI regulations, material durability, and custom sizes |
| Healthcare | RF shielding in medical imaging equipment | Enhances image quality by minimizing noise and interference | Certifications for biocompatibility, compatibility with existing equipment, and maintenance requirements |
| Automotive | RF shields in electronic control units (ECUs) | Improves performance and reliability of vehicle electronics | Temperature resistance, weight considerations, and integration with existing systems |
| Aerospace | Shielding for avionics systems | Protects sensitive electronics from EMI, enhancing safety | Lightweight materials, adherence to aerospace standards, and custom fabrication capabilities |
| Military and Defense | RF shielding in communication and radar systems | Ensures secure and reliable operations in sensitive environments | Compliance with military specifications, durability under extreme conditions, and rapid prototyping capabilities |
How are RF Shields Used in Telecommunications?
In the telecommunications industry, RF shields are essential for protecting communication devices from electromagnetic interference (EMI). By employing shielded enclosures, businesses can maintain signal integrity and ensure reliable connectivity, which is crucial for operations across various sectors. International buyers, especially from regions like Africa and the Middle East, must consider compliance with local EMI regulations and the durability of materials used in these shields to withstand environmental challenges.
Why are RF Shields Important in Healthcare?
RF shielding plays a critical role in medical imaging equipment, such as MRI machines, where minimizing noise and interference is paramount for achieving high-quality images. These shields prevent external RF signals from distorting the imaging process, thus enhancing diagnostic accuracy. Buyers in the healthcare sector should prioritize sourcing materials that meet biocompatibility standards and are compatible with existing medical technologies, particularly in regions with stringent health regulations.
What Role do RF Shields Play in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, RF shields are increasingly used in electronic control units (ECUs) to mitigate interference that can affect vehicle performance. These shields ensure that critical electronic components operate reliably, which is vital for safety and functionality in modern vehicles. Buyers must focus on temperature resistance and weight considerations, especially in regions like South America where diverse climates can impact materials.
How are RF Shields Beneficial in Aerospace Applications?
Aerospace applications require robust RF shielding to protect avionics systems from EMI, which can compromise the safety and reliability of aircraft operations. The use of lightweight materials that comply with aerospace standards is crucial for maintaining performance without adding unnecessary weight. International buyers should seek suppliers capable of custom fabrication to meet specific design needs while ensuring adherence to stringent aerospace regulations.
Why are RF Shields Critical for Military and Defense?
In military and defense applications, RF shielding is vital for secure communication and radar systems, protecting sensitive electronics from interference. This enhances operational reliability in challenging environments. Buyers in this sector should ensure that sourced materials comply with military specifications, offer durability under extreme conditions, and provide rapid prototyping capabilities for urgent needs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘rf shields’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Compromised Equipment Performance Due to EMI
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face the challenge of electromagnetic interference (EMI) negatively affecting their electronic equipment’s performance. This interference can stem from various sources, such as nearby machinery, communication devices, or even natural phenomena. For manufacturers in sectors like telecommunications or aerospace, this interference can lead to data loss, equipment malfunction, and ultimately, costly downtime. Buyers often find themselves struggling to pinpoint the source of the EMI and determine how to effectively shield their sensitive electronics.
The Solution: To mitigate EMI issues, buyers should prioritize sourcing high-quality RF shields tailored to their specific equipment and environment. The first step is to conduct a thorough EMI assessment to identify the frequencies and types of interference affecting their systems. Once the interference profile is established, selecting the appropriate RF shielding materials becomes crucial. For instance, conductive elastomers or metal enclosures can provide effective barriers against specific frequencies. Engaging with suppliers who offer custom solutions can also ensure that the RF shields are designed to fit the unique shapes and sizes of the equipment being protected. Regular testing post-installation is essential to ensure that the shielding is performing as intended, and adjustments should be made as necessary.
Scenario 2: Budget Constraints Leading to Inadequate Shielding Solutions
The Problem: Budget constraints are a common concern for B2B buyers, especially in emerging markets in Africa and South America. Many companies may opt for lower-cost RF shielding solutions that do not provide adequate protection, leading to ongoing EMI issues and potential compliance violations. This decision can result in long-term financial repercussions, such as increased repair costs, regulatory fines, and damage to the company’s reputation.
The Solution: Buyers should approach RF shielding purchases with a cost-benefit analysis mindset. Instead of focusing solely on upfront costs, they should consider the long-term value of investing in high-quality RF shields that offer better performance and durability. Collaborating with suppliers who understand the local market can lead to cost-effective solutions without compromising quality. Additionally, leveraging bulk purchasing agreements or exploring government grants for technology improvements can help alleviate financial pressures. Buyers should also engage in open discussions with their suppliers about their specific needs and constraints, as many manufacturers offer scalable solutions that can fit various budget sizes while still providing effective EMI protection.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Compliance with International Standards
The Problem: For international B2B buyers, particularly those in regulated industries, ensuring compliance with various electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards is a significant pain point. Different regions have specific regulations that dictate how much EMI can be emitted by equipment, and failing to comply can result in penalties, product recalls, or market entry barriers. Buyers often feel overwhelmed by the complexities of these regulations and how they impact the choice of RF shielding materials.
The Solution: To navigate the compliance landscape effectively, buyers should familiarize themselves with the relevant international standards, such as IEC and FCC regulations. Partnering with RF shielding manufacturers who have experience in compliance can provide valuable insights into selecting materials that meet specific regulatory requirements. It is also beneficial to request documentation and certifications from suppliers to ensure that the selected RF shields have been tested and verified to meet these standards. Conducting pre-compliance testing before final product deployment can help identify potential issues early in the design process. Moreover, maintaining a close relationship with regulatory bodies and industry associations can provide ongoing updates on changes to compliance requirements, allowing businesses to adapt their shielding strategies proactively.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for rf shields
When selecting materials for RF shields, it’s crucial to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and how they align with specific applications. This guide analyzes four common materials used in RF shielding, providing actionable insights for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Which Materials Are Commonly Used for RF Shields?
1. Copper
Copper is a widely used material for RF shielding due to its excellent electrical conductivity and ability to attenuate electromagnetic interference (EMI).
- Key Properties: High electrical conductivity (approximately 59 S/m), good thermal conductivity, and resistance to corrosion.
- Pros & Cons: Copper is durable and provides effective shielding, but it can be expensive and may require additional coatings to prevent oxidation. Its weight can also be a disadvantage in applications where lightweight materials are preferred.
- Impact on Application: Copper is highly effective for high-frequency applications, making it suitable for telecommunications and aerospace industries.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B187 is essential. Buyers should also consider the availability of copper in their regions, as supply chain issues can affect pricing and lead times.
2. Aluminum
Aluminum is another popular choice for RF shielding, known for its lightweight and good corrosion resistance.
- Key Properties: Lightweight, moderate electrical conductivity (approximately 37 S/m), and excellent corrosion resistance.
- Pros & Cons: Aluminum is less expensive than copper and easier to fabricate, but it has lower shielding effectiveness compared to copper. Its lower weight can be advantageous in portable applications.
- Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for a variety of applications, including consumer electronics and automotive industries, where weight is a critical factor.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards like EN 573. The availability of aluminum may vary based on local manufacturing capabilities.
3. Nickel
Nickel is often used in combination with other metals for RF shielding due to its unique properties.
- Key Properties: Good corrosion resistance, moderate conductivity, and high melting point.
- Pros & Cons: Nickel is durable and provides decent shielding, but it is generally more expensive than aluminum and requires careful handling during manufacturing due to its brittleness.
- Impact on Application: Nickel is commonly used in environments where corrosion resistance is critical, such as in marine applications and harsh industrial settings.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM B162 is important. Buyers should also consider the environmental regulations regarding nickel usage in their regions.
4. Conductive Plastics
Conductive plastics, often infused with metal powders, provide a lightweight alternative for RF shielding.
- Key Properties: Lightweight, flexible, and varying levels of conductivity depending on the formulation.
- Pros & Cons: These materials can be less expensive and easier to mold into complex shapes, but they generally offer lower shielding effectiveness compared to metals. Their durability can also be a concern in high-stress applications.
- Impact on Application: Conductive plastics are ideal for consumer electronics and automotive applications where weight and design flexibility are prioritized.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the conductive plastics meet relevant standards such as ISO 11469. The availability of specific formulations may vary by region.
Summary of Material Selection for RF Shields
| Material | Typical Use Case for RF Shields | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Telecommunications, Aerospace | Excellent conductivity and shielding | High cost, weight | High |
| Aluminum | Consumer Electronics, Automotive | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower shielding effectiveness | Medium |
| Nickel | Marine, Harsh Industrial Environments | Good corrosion resistance | Higher cost, brittleness | High |
| Conductive Plastics | Consumer Electronics, Automotive | Lightweight and moldable | Lower shielding effectiveness | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides an overview of common materials used in RF shielding, highlighting their properties, advantages, and limitations. By understanding these factors, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific applications and regional requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for rf shields
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of RF Shields?
The manufacturing process for RF shields typically involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets stringent performance and quality standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Selected and Processed?
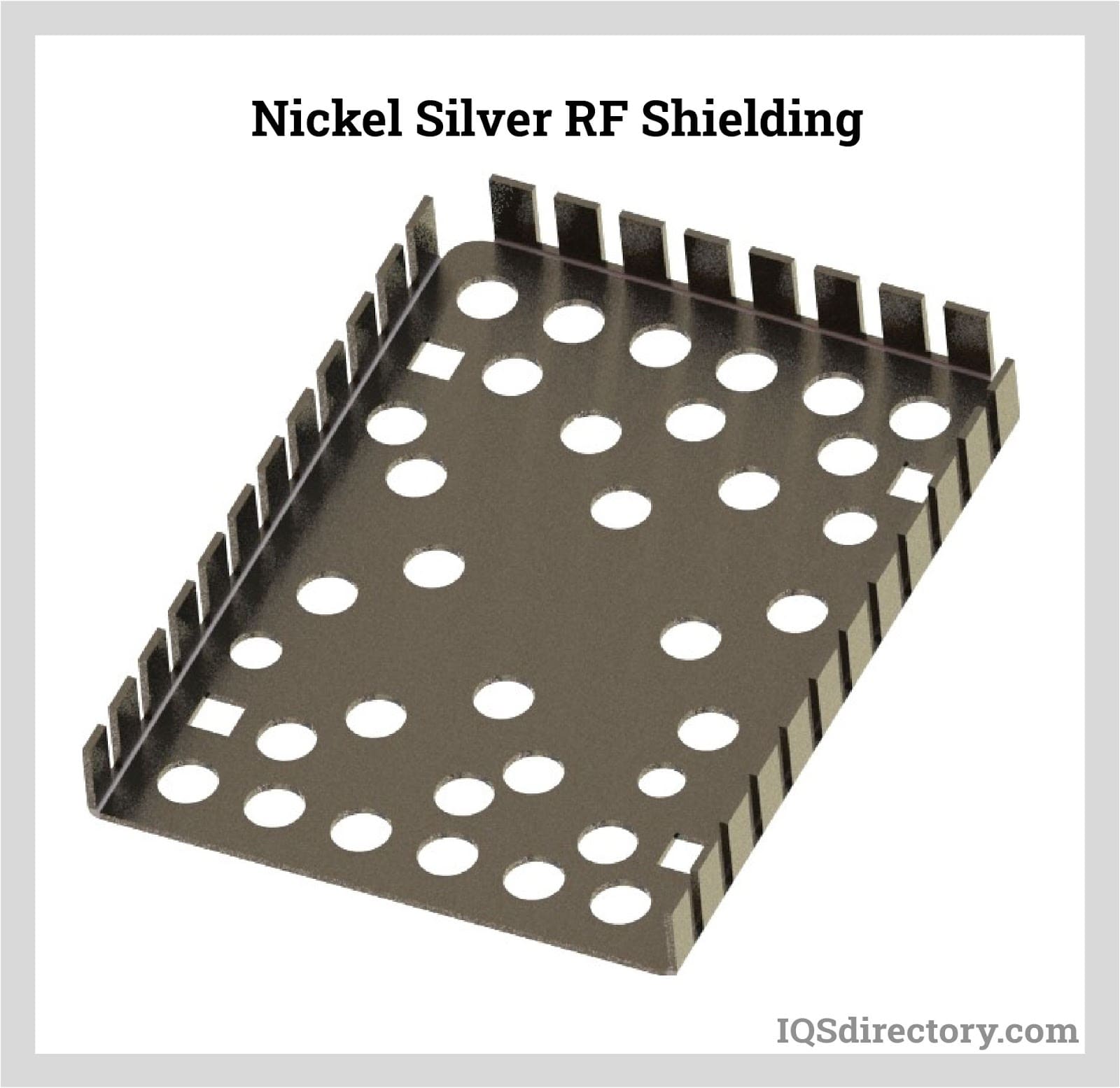
The first step in manufacturing RF shields is the selection and preparation of raw materials. Common materials used include conductive metals such as aluminum, copper, and specialized alloys like Beryllium Copper (BeCu). These materials are chosen based on their electrical conductivity, mechanical properties, and resistance to corrosion.
Once selected, materials undergo a series of processes, including cutting, shearing, and punching, to create the desired shapes and sizes. This initial processing is crucial, as any defects at this stage can propagate through the manufacturing process, affecting the shield’s performance.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming RF Shields?
After material preparation, the next stage is forming. This involves techniques such as stamping, bending, and molding, depending on the complexity of the design. Stamping is often used for high-volume production, while bending is suitable for creating specific shapes that fit into electronic enclosures.
Advanced manufacturing technologies, such as CNC machining and laser cutting, allow for greater precision in forming RF shields. These techniques ensure that the shields meet strict dimensional tolerances, which are essential for effective electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding.
Illustrative image related to rf shields
How Are RF Shields Assembled?
Assembly is a critical stage where individual components are brought together to form the final RF shield. This process may involve welding, soldering, or using conductive adhesives, depending on the design requirements and materials used. For example, finger stock gaskets made from BeCu may be attached to the edges of the shields to enhance their sealing capabilities.
Careful attention to detail during assembly is necessary to maintain the integrity of the shielding. Any misalignment or poor bonding can lead to leakage paths for electromagnetic waves, reducing the effectiveness of the shield.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Employed?
The final stage in manufacturing RF shields is finishing. This can include surface treatments such as anodizing, plating, or painting, which not only enhance the shield’s aesthetics but also improve its resistance to corrosion and wear. Surface treatments can also influence the electrical properties of the shield, making it essential to choose the appropriate finishing process based on the application.
Additionally, finishing processes may include testing for surface conductivity to ensure that the shield meets specific electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) requirements.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for RF Shield Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing of RF shields, ensuring that products meet both international and industry-specific standards. For B2B buyers, understanding these QA processes can provide confidence in the reliability of their suppliers.

Illustrative image related to rf shields
Which International Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
The ISO 9001 standard is one of the most recognized international quality management systems, applicable across various industries, including electronics and manufacturing. It emphasizes a process-oriented approach to quality management, focusing on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
In addition to ISO 9001, RF shield manufacturers may also comply with industry-specific standards such as CE marking for European markets, which indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards, and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for applications in the oil and gas sector.
What Are the Critical Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) during the manufacturing process typically includes several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint verifies the quality of raw materials before they enter the manufacturing process. It ensures that only materials meeting specified criteria are used.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, IPQC measures various parameters to ensure that production remains within specified tolerances. This may involve regular inspections and tests at different stages of manufacturing.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before the RF shields are shipped, FQC involves comprehensive testing to confirm that they meet all design specifications and performance standards. This may include electrical testing for shielding effectiveness, dimensional checks, and visual inspections for surface defects.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers have robust quality assurance processes in place. Here are several methods to verify supplier QC:
What Auditing Practices Should Buyers Consider?
Conducting supplier audits is one of the most effective ways to assess a manufacturer’s quality control processes. These audits can be performed by the buyer’s quality assurance team or through third-party organizations specializing in supplier assessments. During an audit, buyers can evaluate the supplier’s adherence to quality standards, manufacturing processes, and overall operational effectiveness.
What Reports and Documentation Should Buyers Request?
Buyers should request documentation such as quality control reports, compliance certifications, and test results for products. These documents provide insight into the supplier’s manufacturing capabilities and adherence to quality standards. Regularly reviewing these reports can help buyers identify any trends or areas of concern.
How Important Are Third-Party Inspections?
Engaging third-party inspection services can further assure B2B buyers of product quality. These independent entities can conduct inspections and tests at various stages of the manufacturing process, providing an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures. This is particularly vital for international buyers who may not have the resources to conduct on-site inspections.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding quality control nuances is essential. Variations in manufacturing practices, regulatory requirements, and cultural differences can impact the quality of RF shields.
How Do Regional Standards Affect Quality Assurance?
Different regions may have specific regulatory requirements that affect the design and manufacturing of RF shields. For instance, the EU imposes strict EMC regulations that suppliers must adhere to, while other regions may have different standards. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers are familiar with and compliant with the relevant regulations in their target markets.
What Cultural Considerations Should Buyers Keep in Mind?
Cultural differences can also influence business practices and communication styles. Establishing a strong relationship with suppliers and clearly articulating quality expectations can help mitigate misunderstandings. Regular communication and feedback can foster a collaborative approach to quality assurance.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for RF shields is crucial for B2B buyers. By being aware of the key stages in manufacturing, relevant quality standards, and effective verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions and ensure they are selecting reliable suppliers that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘rf shields’
Introduction
This guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in navigating the procurement process for RF shields. It outlines essential steps to ensure that you select the right products and suppliers that meet your specific technical requirements, compliance standards, and business needs. Following this checklist will help streamline your sourcing process and mitigate potential risks.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial before engaging with suppliers. Identify the frequency range, material requirements, and specific shielding effectiveness needed for your application. This clarity not only helps in communicating your needs to suppliers but also ensures that you receive products that meet your operational standards.
- Consider factors such as:
- Operating environment (e.g., temperature, humidity)
- Required attenuation levels (dB)
- Compliance with industry standards (e.g., MIL-STD, IEC)
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers of RF shields. Look for companies with a proven track record in providing similar products and services. Utilize online directories, industry forums, and trade shows to gather a list of suppliers that align with your needs.
Illustrative image related to rf shields
- Focus on:
- Supplier experience and reputation in the market
- Range of products offered, including custom options
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before proceeding with a supplier, verify their certifications and compliance with relevant standards. Certifications like ISO 9001 or specific industry-related standards demonstrate a commitment to quality and reliability.
- Key certifications to look for:
- EMC compliance certifications
- Quality management certifications
- Environmental and safety standards
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Once you’ve narrowed down your list of suppliers, request samples or prototypes of their RF shields. This step allows you to evaluate the quality, performance, and suitability of the products for your specific application.
- Assess:
- Physical characteristics (e.g., material integrity, finish)
- Performance metrics (e.g., attenuation levels)
Step 5: Analyze Pricing and Terms
Gather detailed quotations from your shortlisted suppliers, ensuring they include all costs associated with the purchase. Compare pricing but also take into account the terms of delivery, warranty, and after-sales support.
- Considerations include:
- Total cost of ownership (including shipping and duties)
- Payment terms and conditions
- Lead times for delivery
Step 6: Check Customer Reviews and References
Request references from previous customers and check online reviews to gauge the reliability and customer service of the suppliers. Positive feedback from clients in similar industries can provide valuable insights into the supplier’s performance.
- Look for:
- Case studies showcasing successful implementations
- Testimonials addressing quality and service reliability
Step 7: Finalize Your Decision and Place the Order
After thorough evaluation and consideration of all factors, make your final decision. Ensure that you have a clear agreement in place, covering all aspects of the order, including delivery schedules and post-purchase support.
- Key points to confirm:
- Final specifications and quantities
- Any additional service agreements (e.g., installation, maintenance)
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing process for RF shields, ensuring they make informed decisions that support their business objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for rf shields Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of RF Shields?
When sourcing RF shields, understanding the cost structure is critical for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts pricing. Common materials for RF shields include conductive metals like copper and aluminum, as well as specialized composites. The quality and certification of materials can also affect costs, with higher-grade materials typically leading to enhanced shielding performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the workforce involved in the manufacturing process. Skilled labor is essential for custom fabrication and intricate designs, which can increase overall costs. Automation may help reduce labor costs but could require significant upfront investment.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to the operation of the manufacturing facility, such as utilities, maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient production processes can mitigate overhead costs, making it essential to partner with suppliers who emphasize operational efficiency.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs cover the creation of molds and dies necessary for production. Custom designs may require specialized tooling, which can be a significant upfront expense but is crucial for achieving precise specifications.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that RF shields meet industry standards and customer specifications involves rigorous quality control processes. Investments in QC can lead to higher upfront costs but ultimately reduce defects and returns.
-
Logistics: Transporting RF shields from the manufacturer to the buyer incurs shipping and handling costs. International shipping may involve customs duties and tariffs, which should be factored into the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a profit margin to their costs, which can vary widely based on market conditions, competition, and the perceived value of their products.
How Do Price Influencers Affect RF Shields Sourcing?
Several factors influence pricing in the RF shields market:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to economies of scale, reducing the per-unit cost. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with their needs and budget constraints.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs tailored to specific applications typically command higher prices. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected costs during production.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The quality of materials and the presence of industry certifications (e.g., ISO, RoHS) can significantly impact prices. Higher-quality materials often provide better performance and longevity, which may justify the increased upfront costs.
-
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers with a strong reputation may charge a premium due to their reliability and quality assurance. Conversely, emerging suppliers may offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is crucial for managing logistics costs. Different Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) dictate who is responsible for shipping costs and risks, impacting the overall pricing structure.
What Are the Best Tips for Negotiating RF Shields Pricing?
For B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost-efficiency:

Illustrative image related to rf shields
-
Negotiate Volume Discounts: Leverage larger order quantities to negotiate better pricing. Establishing a long-term relationship with suppliers can also lead to favorable terms.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond initial purchase prices. Analyze the long-term costs associated with installation, maintenance, and potential replacements. Investing in higher-quality RF shields may reduce TCO over time.
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Conduct thorough research on multiple suppliers to understand market pricing. This knowledge empowers buyers to negotiate more effectively and secure the best possible deal.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers should consider fluctuations in currency exchange rates, tariffs, and local taxes that can affect the final price. Understanding these nuances can help in budgeting and financial planning.
-
Seek Local Suppliers When Possible: Sourcing from local manufacturers can reduce shipping costs and lead times. Additionally, it may simplify communication and support services.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for RF shields can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. This analysis provides a framework for understanding costs and pricing, but buyers should obtain specific quotes from suppliers for accurate pricing tailored to their needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing rf shields With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to RF Shields for Electromagnetic Interference Management
In the realm of electromagnetic interference (EMI) management, RF shields are a popular choice due to their effectiveness in blocking unwanted signals. However, several alternative solutions exist that can also mitigate EMI effects. Understanding these alternatives allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and implementation capabilities.
Comparison of RF Shields and Alternative Solutions
| Comparison Aspect | RF Shields | Conductive Coatings | EMI Filters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High attenuation of RF signals; effective in diverse environments | Moderate attenuation; varies based on coating thickness and material | Effective in filtering specific frequency ranges but may not block all EMI |
| Cost | Higher initial investment; long-term durability can offset costs | Generally lower cost; requires periodic reapplication | Moderate cost; depends on the complexity of the filtering solution |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires precise installation and fitting; may need professional assistance | Easy to apply but requires surface preparation; DIY-friendly | Installation may require expertise, particularly for complex systems |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; robust and long-lasting | May require reapplication over time; susceptible to wear | Regular checks needed to ensure effectiveness; may need replacement |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for high-frequency environments and critical applications | Suitable for less demanding applications or surfaces needing aesthetic appeal | Best for systems where specific frequency filtering is required, like power lines |
Understanding Conductive Coatings as an Alternative to RF Shields
Conductive coatings offer a cost-effective solution for EMI management. These coatings, which can be applied to various surfaces, provide a level of attenuation against EMI. One of the key advantages of conductive coatings is their versatility; they can be used on both metal and non-metal surfaces. However, their performance can be inconsistent, as it often depends on the thickness and uniformity of the application. Maintenance can be a concern, as these coatings may wear over time, necessitating reapplication.
Evaluating EMI Filters for Electromagnetic Interference Management
EMI filters are another alternative that specifically targets unwanted frequencies. They can be integrated into power lines or signal lines to filter out noise, making them particularly effective in environments where specific frequency interference is a concern. One of the significant benefits of EMI filters is their ability to be tailored for specific applications, allowing for precise control over which frequencies are blocked. However, they may not provide comprehensive protection against all forms of EMI, and their effectiveness can diminish if not regularly maintained.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right EMI Solution for Your Needs
When considering the best solution for EMI management, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific requirements, including the nature of the EMI they face, budget constraints, and installation capabilities. RF shields may be the best option for critical applications requiring robust protection, while conductive coatings and EMI filters can offer viable alternatives for less demanding environments. Ultimately, the choice will depend on a careful assessment of performance needs, cost-effectiveness, and maintenance considerations, ensuring that the selected solution aligns with operational goals and long-term strategies.
Illustrative image related to rf shields
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for rf shields
What Are the Key Technical Properties of RF Shields?
When evaluating RF shields, understanding specific technical properties is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and compliance with industry standards. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material used in RF shields significantly affects their effectiveness. Common materials include aluminum, copper, and specialized alloys like Beryllium Copper (BeCu). Each material offers distinct benefits such as conductivity, durability, and corrosion resistance. For B2B buyers, selecting the right material grade can mean the difference between achieving the required shielding effectiveness and facing potential electromagnetic interference (EMI) issues.
2. Shielding Effectiveness (SE)
Shielding effectiveness is a measure of an RF shield’s ability to block electromagnetic fields, typically expressed in decibels (dB). A higher SE indicates better protection against interference. For businesses, understanding the SE of a product is vital when ensuring that sensitive electronic equipment operates without disruption. This metric directly influences product reliability and regulatory compliance.

Illustrative image related to rf shields
3. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension or property of the shield. For RF shields, maintaining tight tolerances is essential to ensure a proper fit and effective sealing against EMI. In a B2B context, high tolerance levels can reduce the need for additional modifications, thereby lowering overall project costs and minimizing delays in production.
4. Insertion Loss
Insertion loss quantifies the loss of signal strength that occurs when a filter or shield is introduced into a circuit. This property is critical for RF shields used in communication systems. Understanding insertion loss helps businesses assess how effectively a shield will perform without compromising signal integrity, which is especially important for industries relying on high-frequency data transmission.
5. Frequency Range
The frequency range specifies the spectrum of electromagnetic frequencies over which the shield is effective. RF shields must be designed to operate within the specific frequency bands relevant to the application. For B2B buyers, confirming that a shield covers the necessary frequency range is essential to ensure that their equipment remains protected against interference across all operational conditions.
6. Environmental Resistance
This property includes factors such as resistance to moisture, temperature extremes, and chemical exposure. Environmental resistance ensures that the shield maintains its performance in various conditions, which is particularly important for applications in harsh environments. Businesses must consider this property to avoid costly failures and ensure long-term reliability.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the RF Shielding Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology is vital for effective communication and negotiation in the RF shielding market. Here are several key terms that B2B buyers should understand:
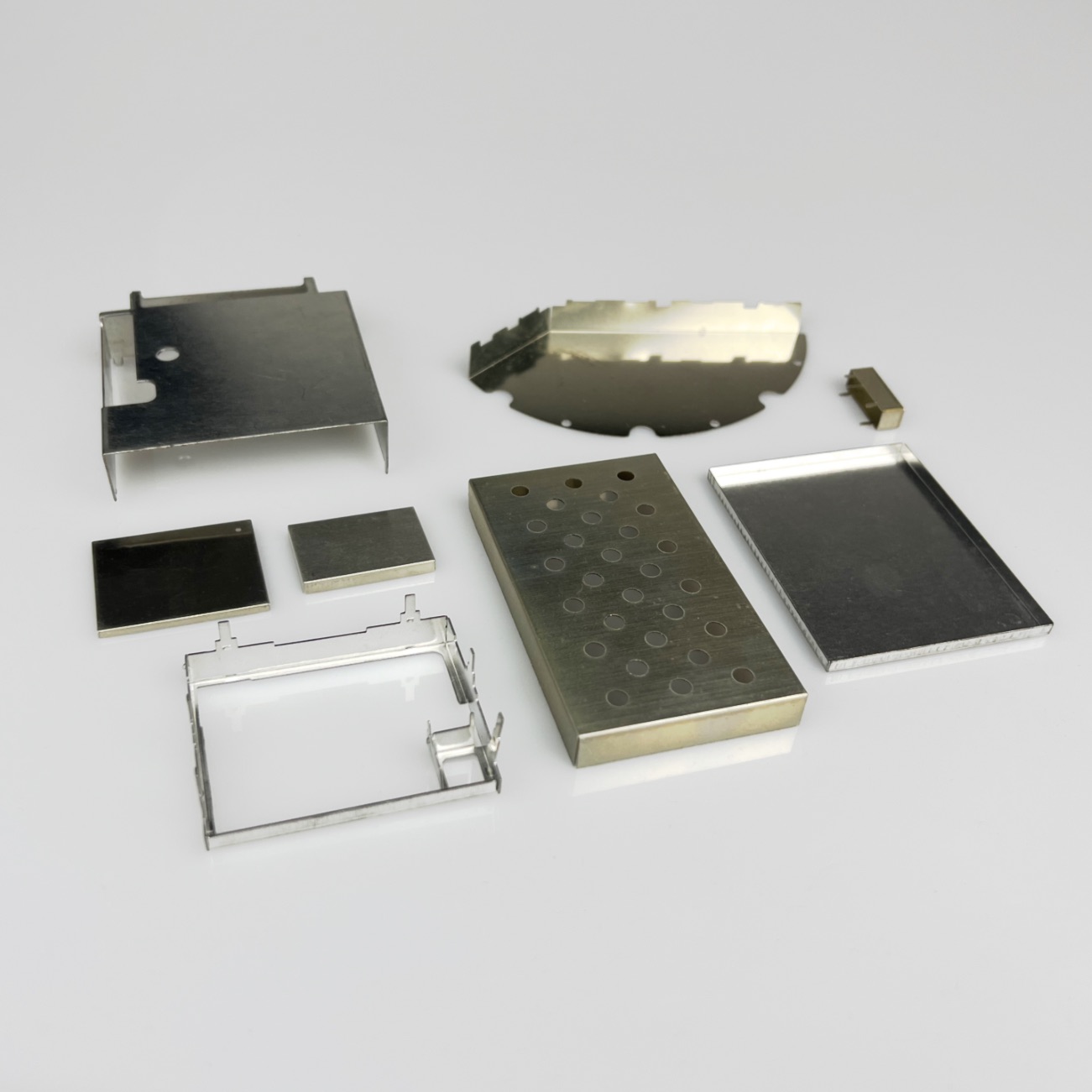

Illustrative image related to rf shields
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that manufactures products or components that are sold by another company under its brand name. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers seeking custom RF shielding solutions, as it can affect pricing, lead times, and product quality.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and supply chain planning, especially for smaller businesses or those entering new markets.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent by a buyer to suppliers requesting price quotes for specific products or services. Crafting a detailed RFQ can streamline the procurement process and ensure that buyers receive competitive pricing and terms.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, delivery, and risk management. Familiarity with these terms helps businesses mitigate risks associated with international transactions and understand their obligations during shipping.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is crucial for planning and inventory management, particularly for businesses with tight project deadlines.
6. Certification Standards
Certification standards refer to the specifications that products must meet to be deemed compliant with industry regulations (e.g., ISO, IEC). Buyers should prioritize suppliers who can provide relevant certifications, ensuring that their RF shields meet quality and safety requirements.
By understanding these properties and terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and product reliability in the competitive RF shielding market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the rf shields Sector
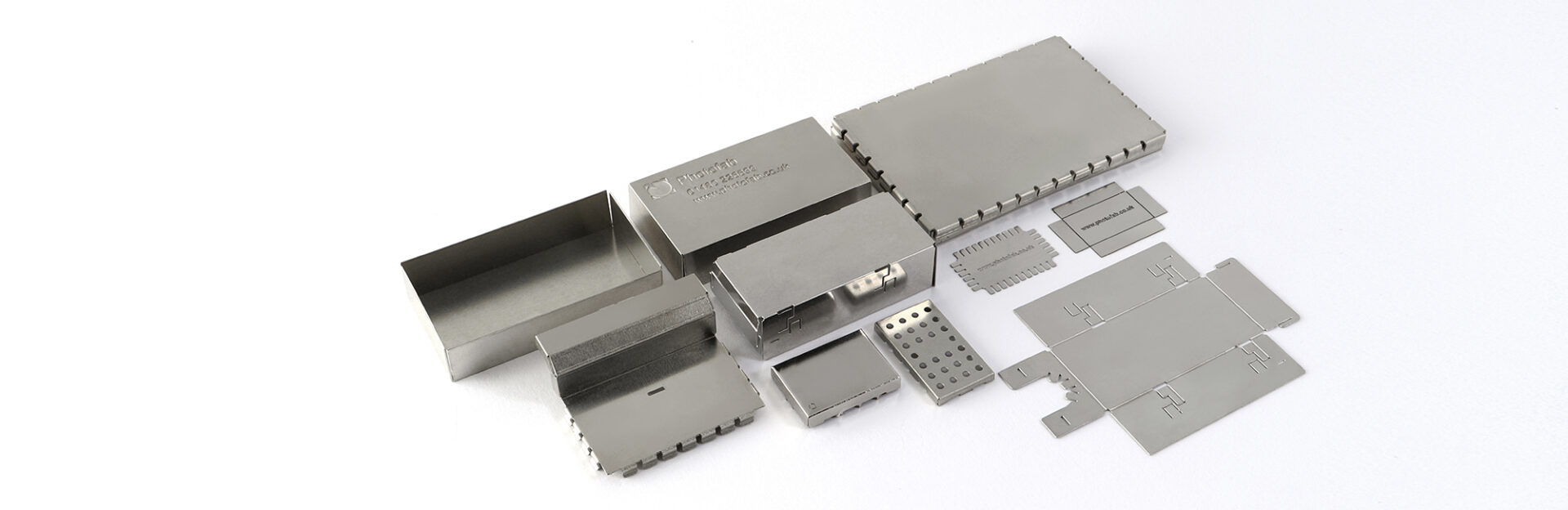
What Are the Current Trends and Dynamics in the RF Shields Market?
The RF shields market is experiencing robust growth driven by the increasing demand for electronic devices, particularly in sectors such as telecommunications, automotive, and healthcare. As global connectivity expands, so does the need for effective electromagnetic interference (EMI) solutions. International B2B buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are keenly aware of the regulatory pressures surrounding electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) in their respective regions. This regulatory landscape encourages the adoption of high-quality RF shielding solutions to ensure compliance and maintain operational efficiency.
Emerging technologies like 5G and the Internet of Things (IoT) are also reshaping sourcing trends. These technologies require advanced RF shielding materials to mitigate interference and enhance performance. As a result, manufacturers are increasingly investing in innovative materials, such as conductive elastomers and advanced composites, which offer superior shielding effectiveness and flexibility. Furthermore, the rise of customized solutions tailored to specific applications is becoming prevalent, enabling buyers to meet their unique operational requirements.
The market is also witnessing a shift towards digital sourcing platforms that facilitate streamlined procurement processes. These platforms allow buyers to compare product specifications, pricing, and supplier ratings, making it easier to make informed decisions. Additionally, collaboration between suppliers and manufacturers is essential for fostering innovation and addressing the evolving needs of end-users.

Illustrative image related to rf shields
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the RF Shields Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the RF shields sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, from raw material extraction to product disposal, is under scrutiny. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, including the use of eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient manufacturing processes.
Ethical sourcing is another key aspect, as businesses seek to ensure that their supply chains are free from exploitative labor practices and harmful environmental impacts. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to appeal to conscientious buyers. Additionally, the use of green materials, such as recyclable composites and biodegradable elastomers, is gaining traction. These materials not only reduce environmental footprints but also enhance the marketability of products in an eco-conscious marketplace.
The integration of sustainability into procurement strategies not only aligns with corporate social responsibility goals but also enhances brand reputation and fosters customer loyalty. As more companies commit to sustainable practices, the demand for RF shields made from responsibly sourced materials will continue to rise, compelling suppliers to adapt their offerings accordingly.

Illustrative image related to rf shields
What Is the Historical Context of RF Shields in B2B Transactions?
The evolution of RF shielding can be traced back to the early days of electronics, where the need for reducing electromagnetic interference became apparent with the proliferation of radio technology. Initially, basic metal enclosures were employed to shield sensitive components. However, as technology advanced, the demand for more sophisticated solutions grew, leading to the development of specialized materials and designs that cater to specific frequency ranges and application requirements.
In the 1980s and 1990s, the emergence of personal computing and telecommunications further accelerated innovation in RF shielding technologies. Manufacturers began to explore diverse materials like conductive plastics and composites, expanding the possibilities for design and application. Today, the market has matured into a highly specialized sector, with a focus on custom solutions that meet stringent regulatory standards and performance expectations.
This historical context highlights the ongoing need for innovation and adaptation in the RF shields sector, driven by technological advancements and evolving market demands. For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions that align with current and future industry trends.
Illustrative image related to rf shields
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of rf shields
-
How do I solve electromagnetic interference issues in my facility?
To effectively address electromagnetic interference (EMI) issues, start by conducting a thorough assessment of your facility to identify sources of interference. Implement RF shields, such as conductive enclosures or gaskets, to mitigate EMI. Ensure that all electronic equipment is properly grounded and consider using EMI filters on power lines and signal cables. Regularly monitor your environment with EMI measuring devices to assess the effectiveness of your shielding solutions and make adjustments as necessary. -
What is the best RF shield for protecting sensitive electronic equipment?
The best RF shield for sensitive electronic equipment depends on the frequency range of the EMI you are dealing with. For most applications, a combination of conductive enclosures and gaskets, such as those made from copper or aluminum, offers excellent protection. Additionally, consider double-shielded enclosures for environments with high interference levels. Always ensure that the materials used meet the necessary attenuation requirements for your specific application to maintain performance. -
What customization options are available for RF shields?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for RF shields to meet specific requirements. Customizations may include tailored dimensions, unique shapes, and specific materials designed for particular frequency ranges. You can also request additional features like ventilation systems, mounting options, or integrated EMI filtering. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications to the supplier to ensure that the final product meets your operational needs. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for RF shields?
Minimum order quantities for RF shields can vary significantly among suppliers. Generally, MOQs range from a few units for standard products to larger quantities for customized solutions. It’s important to communicate your specific needs and budget with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that suit your purchasing strategy. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for first-time buyers or bulk orders, so be sure to inquire about available options. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing RF shields internationally?
Payment terms for international RF shield purchases vary by supplier and region. Common options include advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Always clarify payment terms before finalizing your order, as this can affect your cash flow and financial planning. Consider establishing a relationship with suppliers who offer favorable terms, including extended payment periods or discounts for early payment, especially when ordering large quantities. -
How can I vet suppliers of RF shields for quality assurance?
To vet suppliers of RF shields effectively, start by checking their certifications and quality management systems, such as ISO 9001. Request samples to evaluate material quality and shielding effectiveness against industry standards. Additionally, seek references from other clients in your industry to gauge their experience. Consider visiting the supplier’s facility if possible, or ask for a virtual tour to inspect their production processes and capabilities firsthand. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing RF shields?
When sourcing RF shields, consider logistics factors such as shipping costs, delivery times, and customs clearance procedures. Work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping to ensure smooth transportation of goods. Be aware of import regulations in your country and factor in potential duties and taxes. Establish clear communication with your supplier regarding packaging, labeling, and documentation to avoid delays in the shipping process. -
How do I ensure compliance with international standards when sourcing RF shields?
To ensure compliance with international standards, familiarize yourself with the relevant regulations and certifications required in your industry and region, such as CE, FCC, or RoHS. Request documentation from suppliers that demonstrates compliance with these standards. It’s also advisable to stay informed about changes in regulations that may affect your products. Collaborating with suppliers who are experienced in navigating compliance can help streamline this process and reduce risk.
Top 8 Rf Shields Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. East Coast Shielding – EMI Shielding Products
Domain: eastcoastshielding.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: East Coast Shielding provides high-quality RF Shields, EMI Shield, and RFI materials. Key products include: 1. EMI Shielding Products 2. Custom Fabrication 3. Shielded Vent Panels 4. Optical Filters for Electronic Displays 5. 300 Series RF Shields 6. Conductive Elastomer 7. Electrical Gaskets 8. EMI Filters 9. Finger Stock Gaskets 10. Conduct-O-Knit Knitted Wire Mesh 11. Conduct-O-Seal Combo Gaske…
2. IQS Directory – RF Shielding Solutions
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: RF shielding, or radiofrequency shielding, is designed to prevent radiofrequency electromagnetic signals from causing radio frequency interference (RFI) that disrupts electronic devices. It involves enclosing electronic components and wiring with barriers made from conductive and magnetic materials. Key factors influencing RF shielding performance include the characteristics of the materials, desi…
3. Digi-Key – RF Shields
Domain: digikey.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: This company, Digi-Key – RF Shields, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. FotoFab – RF Shields & Prototype Kits
Domain: fotofab.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Standard RF Shields and RF Prototype Kits available in 72 different dimensional combinations. 27 different RF shield sizes and shield heights in the prototyping kit. 18 sizes of standard RF shields with a height of 0.125″. Minimum purchase of two sheets. Quick and easy shielding solution, in stock and ready to order. Made from tin plated brass material for excellent shielding and solderability. De…
5. Masach – Custom EMI/RFI Shields
Domain: masach.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Custom EMI/RFI Shields from Masach are designed for efficient and cost-effective development. They offer a range of standard shields that can save on custom design costs and reduce delivery times. The engineering department can design shields from scratch or review existing designs, focusing on simplification while maintaining functionality and shielding levels. Masach utilizes innovative CNC tech…
6. Reddit – RF Shields for Home Electronics
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: RF shields in home electronics protect devices from electromagnetic (EM) radiation and interference. They are necessary because electronic components, such as processors and graphics cards, can generate significant power spikes and act like antennas, potentially disrupting communication on various frequency bands (e.g., WiFi, Bluetooth, cell phone frequencies). Devices undergo testing in RF chambe…
7. Signals Defense – RF Shielding Solutions
Domain: signalsdefense.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: RF Shielding Products: RF / IR Shielding Films, RF Shielding Products, RFoil RF Shielding Paint, RF Shielding Tapes, RF Shielding Caulk, Architectural Window Films, Decorative Window Film, Security and Safety Films, Solar Control Window Film, Cloaking Film, DAS Shield Glass and Polycarbonate Laminates, Window Treatments, Spray-Lock FRP Adhesive. Key Features: Blocks radiofrequency radiation, provi…
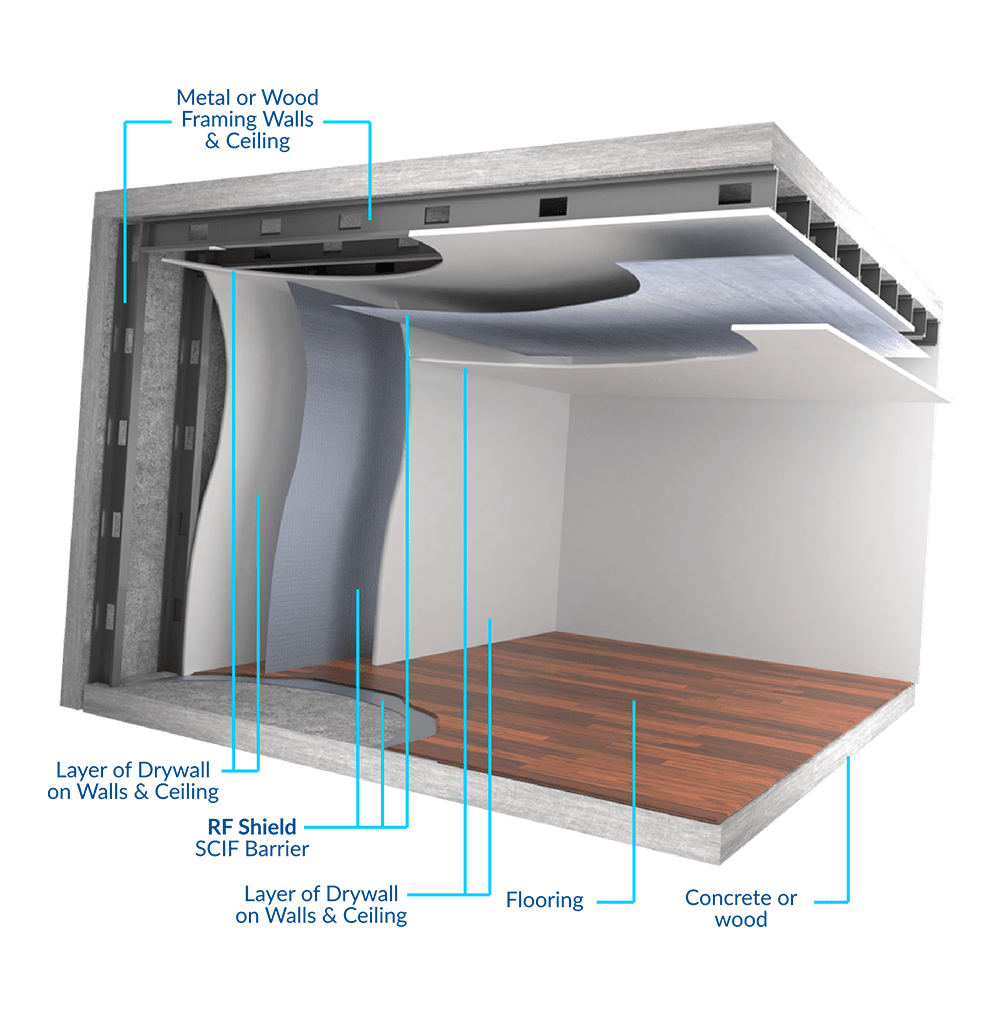
8. FIFOIL – RF Shield™ SCIF Barrier
Domain: fifoil.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: RF Shield™ SCIF Barrier is designed for Sensitive Compartmented Information Facilities (SCIFs). It features a tear-resistant layer of woven polyethylene material sandwiched between two highly reflective aluminum surfaces. Key specifications include: 2 outer layers of 99% Pure Aluminum Foil, an inner layer of Fiberglass reinforcing and Kraft paper, made in the USA. It provides RF protection with an…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for rf shields
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electronic devices, the strategic sourcing of RF shields is essential for businesses aiming to ensure compliance with electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) regulations and to protect sensitive equipment from electromagnetic interference (EMI). As outlined in this guide, effective sourcing strategies can significantly enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and foster innovation. By selecting high-quality RF shielding solutions that meet specific industry standards, businesses can mitigate risks associated with signal degradation and interference.
For international buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of RF shield sourcing is crucial. Factors such as regional compliance, supplier reliability, and material quality should be prioritized to secure the best outcomes. Collaborating with established manufacturers and leveraging local partnerships can also streamline logistics and improve responsiveness to market demands.
As we look to the future, the demand for advanced RF shielding solutions is set to grow alongside the increasing complexity of electronic systems. Now is the time for businesses to evaluate their sourcing strategies, invest in robust RF shielding products, and position themselves as leaders in their respective markets. Engage with trusted suppliers and explore innovative solutions to stay ahead in this competitive environment.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

Illustrative image related to rf shields