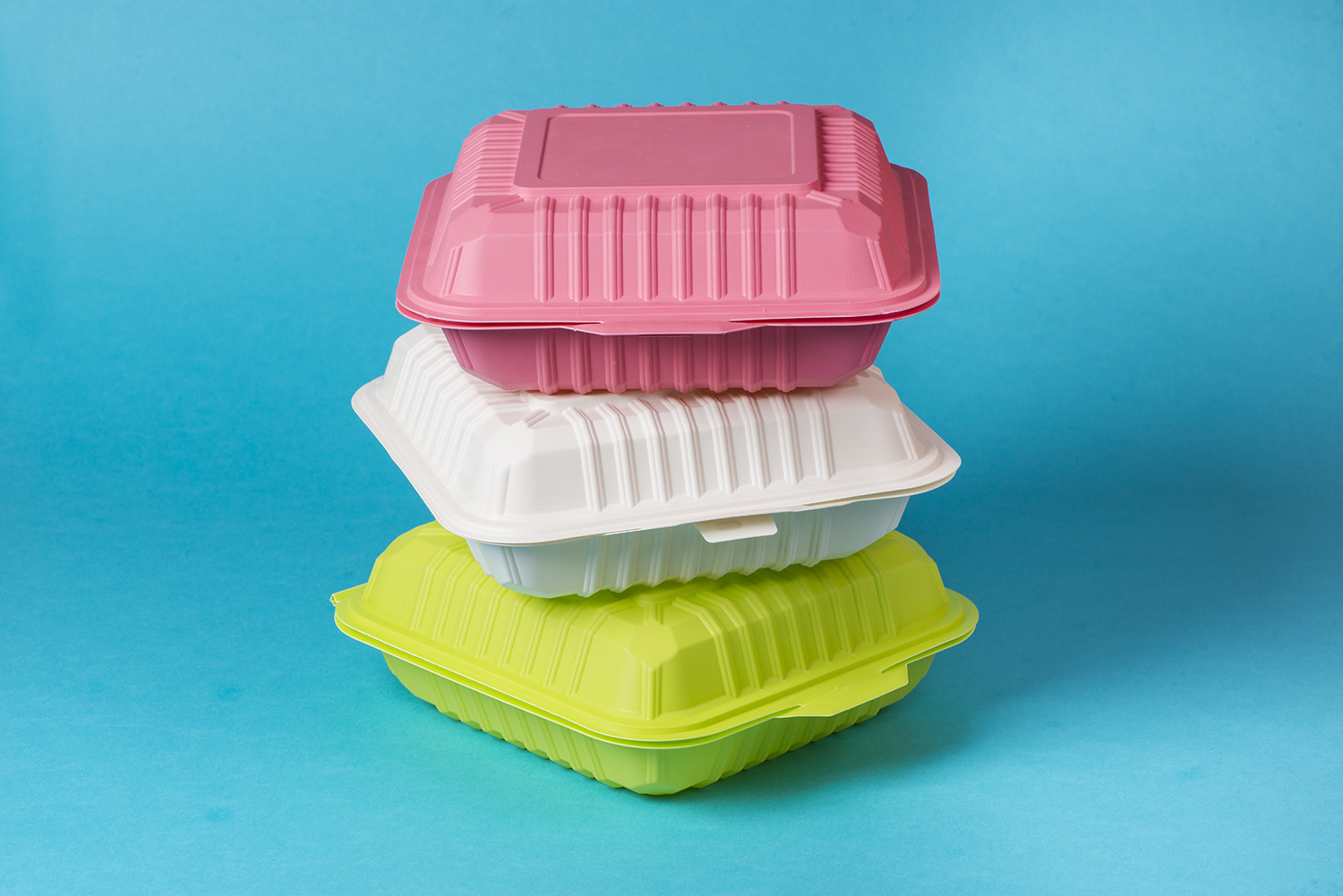
A B2B Buyer’s Guide to Polyethylene Container: Price, Quality, and Suppliers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for polyethylene container
In the fast-evolving global market for polyethylene containers, international B2B buyers face the challenge of sourcing reliable and durable products that meet diverse industry needs. Whether you are looking for pails, drums, or specialized containers, understanding the specifications and applications of polyethylene is crucial. This comprehensive guide delves into various types of polyethylene containers, their applications across multiple sectors, and the essential factors to consider when vetting suppliers.
From food-grade safety regulations to environmental sustainability practices, we cover the critical attributes that define quality polyethylene containers. Furthermore, we provide insights on pricing structures and cost-saving strategies, enabling you to make informed purchasing decisions tailored to your specific market demands.
By equipping buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Saudi Arabia and Germany—with actionable insights, this guide empowers you to navigate the complexities of the polyethylene container market confidently. Whether you are a seasoned procurement professional or a new entrant in the industry, the knowledge shared here aims to streamline your sourcing process and enhance your operational efficiency. Let’s embark on this journey to uncover the best polyethylene container solutions for your business needs.
Understanding polyethylene container Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
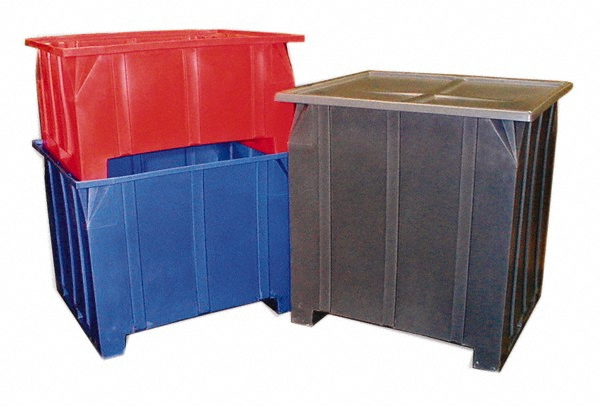
| Pails | Versatile sizes, durable construction, and customizable lids | Food processing, chemicals, industrial goods | Pros: Lightweight, stackable; Cons: Limited capacity for bulk materials. |
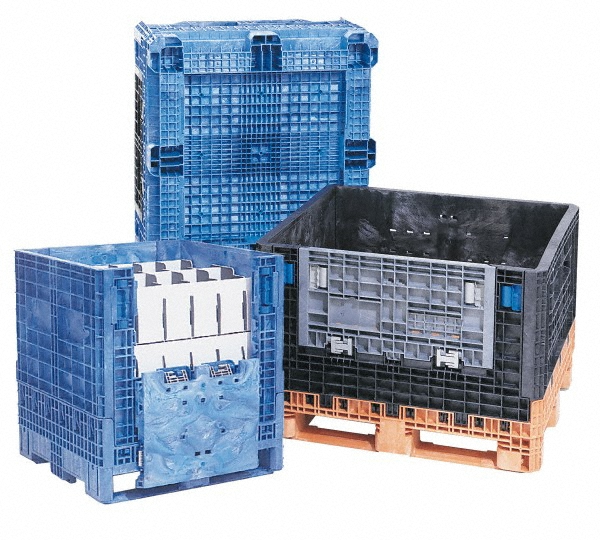
| Drums | Larger capacity, typically 55-gallon, with various closures | Bulk storage, transportation of liquids | Pros: High capacity, robust; Cons: Heavier, may require special handling. |
| IBC Containers | Intermediate bulk containers, often with a valve for discharge | Food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals | Pros: Efficient for bulk transport; Cons: Requires specific storage space. |
| Storage Bins | Stackable, often with built-in handles and latching lids | Retail, warehousing, and logistics | Pros: Easy access, space-saving; Cons: Limited to lighter materials. |
| Custom Containers | Tailored designs for specific needs, including sizes and colors | Niche markets, specialized products | Pros: Perfect fit for unique applications; Cons: Potentially higher costs and longer lead times. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Polyethylene Pails?
Polyethylene pails are lightweight and durable containers, often used in various industries for packaging and transporting a range of products, including food and chemicals. They are available in multiple sizes and can be customized with different lids and handles. For B2B buyers, the ability to stack pails efficiently can save significant storage space, while their resistance to impacts makes them suitable for rigorous handling environments. However, pails may not be ideal for bulk storage due to their limited capacity.
How Do Polyethylene Drums Stand Out in Industrial Applications?
Polyethylene drums are designed for bulk storage, typically holding 55 gallons of liquid. They are robust and often equipped with secure closures to prevent leaks, making them suitable for transporting hazardous materials. For B2B buyers, the high capacity of drums is advantageous for reducing the frequency of deliveries. However, their weight can pose challenges in handling and may require specific equipment for transport, especially in regions with limited infrastructure.
Why Choose Intermediate Bulk Containers (IBCs) for Bulk Transport?
IBCs are designed for the efficient transport and storage of liquids and bulk materials, often featuring valves for easy discharge. They are particularly popular in food and pharmaceutical sectors due to their compliance with hygiene standards. B2B buyers appreciate the significant volume IBCs can hold, which minimizes shipping costs per unit. However, they require adequate space for storage and may necessitate specialized handling equipment, which can be a consideration for businesses with limited resources.
What Are the Benefits of Using Polyethylene Storage Bins?
Polyethylene storage bins are stackable and often come with built-in handles and latching lids, making them ideal for warehousing and retail applications. Their design promotes easy access and organization, which can enhance operational efficiency. For buyers, these bins offer a practical solution for lighter materials and can be an effective way to optimize storage space. However, their capacity may not suffice for heavier or bulkier items, limiting their use in certain industries.
How Can Custom Containers Meet Unique Business Needs?
Custom polyethylene containers can be tailored to fit specific requirements regarding size, shape, and color, catering to niche markets or specialized products. This adaptability makes them a valuable option for businesses looking to differentiate their offerings. B2B buyers should consider the potential for higher costs and longer lead times associated with custom orders, but the investment can lead to a significant competitive advantage in specialized applications.
Key Industrial Applications of polyethylene container
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of polyethylene container | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Storage and transport of bulk ingredients and finished products | Ensures product safety and compliance with food safety standards | Certifications for food safety and transportation standards |
| Chemical Manufacturing | Containment of hazardous materials and chemicals | Provides durability and resistance to chemical reactions | UN certification for hazardous materials handling |
| Agriculture | Packaging and storage of fertilizers and pesticides | Protects contents from moisture and contamination | Customization options for sizes and closures |
| Pharmaceutical | Storage of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) | Maintains product integrity and compliance with regulations | Specifications for sterilization and safety standards |
| Waste Management | Collection and transport of recyclable materials | Facilitates efficient waste sorting and management | Requirements for durability and environmental compliance |
How is Polyethylene Container Used in the Food and Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage sector, polyethylene containers are essential for the safe storage and transport of bulk ingredients such as grains, sugars, and liquids. These containers meet stringent food safety regulations, ensuring that products remain uncontaminated throughout the supply chain. International buyers must consider certifications that comply with local and global food safety standards, such as FDA or EU regulations, to ensure compliance and consumer trust.
What Role Do Polyethylene Containers Play in Chemical Manufacturing?
Chemical manufacturers rely on polyethylene containers for the safe handling of hazardous materials. These containers offer exceptional chemical resistance, ensuring that corrosive substances do not compromise the integrity of the packaging. When sourcing, companies must verify that containers are UN certified for hazardous materials, which guarantees safety during transport and storage. Additionally, the ability to customize container sizes and features is crucial to meet specific operational needs.
How are Polyethylene Containers Utilized in Agriculture?
In agriculture, polyethylene containers are commonly used for the packaging and storage of fertilizers and pesticides. Their waterproof and chemical-resistant properties protect contents from moisture and environmental factors, ensuring product efficacy. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing containers that can be customized for specific chemical compatibility and include features like secure lids to prevent spillage. This is particularly important in regions where environmental conditions can affect product stability.

Illustrative image related to polyethylene container
Why Are Polyethylene Containers Important in the Pharmaceutical Sector?
The pharmaceutical industry utilizes polyethylene containers for the storage of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and other sensitive materials. These containers help maintain the integrity and stability of products while adhering to strict regulatory standards. Buyers must ensure that containers meet requirements for sterilization and are compliant with health regulations, which may vary by region. Customization options for size and closure type are also important to accommodate various pharmaceutical products.
How Do Polyethylene Containers Contribute to Waste Management Solutions?
In the waste management sector, polyethylene containers are vital for collecting and transporting recyclable materials. Their durability and resistance to environmental factors facilitate efficient waste sorting and management. When sourcing these containers, businesses should prioritize options that are designed for easy handling and are compliant with environmental regulations. This ensures that the containers not only serve their purpose effectively but also contribute to sustainability efforts in waste management practices.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘polyethylene container’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Container Size and Type
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges in determining the appropriate size and type of polyethylene container for their specific needs. This can lead to over-purchasing, underutilization, or even product damage during storage and transport. For example, a food manufacturing company may require containers that can withstand certain temperatures and moisture levels, while a chemical processing plant might need containers that meet strict compliance standards. Without a clear understanding of their requirements, buyers risk costly mistakes that can affect their operations and bottom line.
The Solution: To navigate this challenge, buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their material storage and transport needs. Start by evaluating the physical properties of the substances to be stored, such as volume, density, and chemical compatibility. Engage with suppliers to discuss these specifications; many manufacturers offer consultancy services to help identify the optimal container configuration. Utilize standardized sizing charts and consider customizing containers based on unique operational requirements, including features like reinforced handles for easier transport or specific lid types for secure sealing. This proactive approach will ensure you select containers that not only fit your operational needs but also comply with safety and regulatory standards.
Scenario 2: Concerns About Durability and Material Quality
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the durability and quality of polyethylene containers. With varying grades of polyethylene available, some containers may not withstand harsh environmental conditions or the weight of their contents, leading to leaks, breakage, or contamination. This is particularly relevant for industries dealing with hazardous materials or food products, where container integrity is paramount. Buyers may be uncertain about which material grade will meet their specific durability requirements, leading to potential product loss and safety risks.

Illustrative image related to polyethylene container
The Solution: To ensure the selection of durable polyethylene containers, buyers should prioritize sourcing from reputable manufacturers who provide detailed information about the material properties of their products. Look for containers made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) copolymers, which are known for their superior impact resistance and durability. Additionally, request certifications that demonstrate compliance with industry standards, such as UN certifications for hazardous materials or food safety regulations. Buyers should also inquire about the manufacturing processes used, such as precision molding and point-by-point inspection, which can significantly enhance product quality. Finally, consider performing a trial run with a limited order to evaluate the container’s performance under real-world conditions before committing to a larger purchase.
Scenario 3: Sustainability Concerns and Environmental Impact
The Problem: As global awareness of environmental issues increases, B2B buyers are increasingly concerned about the sustainability of their packaging choices, including polyethylene containers. Many businesses want to ensure that their supply chain practices align with sustainability goals. This can be challenging when it comes to sourcing containers that are not only effective but also environmentally friendly, leading to hesitation in purchasing decisions.
The Solution: To address sustainability concerns, buyers should actively seek suppliers that prioritize environmentally responsible practices. This includes opting for containers made from recyclable materials and those that are manufactured using processes aimed at reducing waste. Engage with suppliers to understand their sustainability initiatives, such as using substrates derived from recycled materials or adopting zero landfill waste policies. Additionally, consider investing in containers designed for multiple uses, which can reduce the overall environmental footprint. By aligning purchasing decisions with sustainability criteria, businesses can not only enhance their brand reputation but also contribute positively to the environment, appealing to a growing consumer base that values eco-friendly practices.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for polyethylene container
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Polyethylene Containers?
When selecting materials for polyethylene containers, it is crucial to consider their properties, applications, and compliance with international standards. Here are four common materials used in the production of polyethylene containers, each with unique characteristics that can influence their suitability for various applications.
1. High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
Key Properties:
HDPE is known for its high strength-to-density ratio, making it exceptionally durable. It can withstand temperatures ranging from -40°F to 120°F (-40°C to 49°C) and offers excellent resistance to impact and chemicals, including acids and bases.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of HDPE is its robustness and longevity, which reduces the need for frequent replacements. However, its manufacturing process can be more complex and costly compared to other materials. Additionally, while HDPE is recyclable, its recycling rates can vary depending on local infrastructure.
Impact on Application:
HDPE is ideal for storing and transporting a wide range of products, including food-grade materials, chemicals, and hazardous substances. Its chemical resistance makes it suitable for applications in industries such as pharmaceuticals and agriculture.
Considerations for International Buyers:
For B2B buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East, compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential. HDPE containers often meet these standards, which can facilitate trade and acceptance in local markets.
2. Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE)
Key Properties:
LDPE is characterized by its flexibility and lower density compared to HDPE. It can handle temperatures up to 80°F (27°C) and is resistant to moisture, making it suitable for various applications.

Illustrative image related to polyethylene container
Pros & Cons:
While LDPE offers excellent flexibility and is less expensive than HDPE, it is not as strong or durable. This can limit its use in applications requiring high structural integrity. Additionally, LDPE is less resistant to UV radiation, which can degrade its performance over time.
Impact on Application:
LDPE containers are commonly used for packaging food products and household items. Their moisture resistance makes them suitable for storing liquids, but they may not be ideal for hazardous materials.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in Africa and South America should consider local regulations regarding food safety and packaging materials. LDPE containers often comply with food contact regulations, which can be a selling point in these markets.
3. Polypropylene (PP)
Key Properties:
Polypropylene has a higher melting point than polyethylene, typically around 320°F (160°C), and offers good chemical resistance. It is also lightweight and has a high tensile strength.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of polypropylene is its versatility and ability to withstand higher temperatures, making it suitable for applications that involve heat. However, it can be more expensive than HDPE and LDPE, which may impact budget considerations for buyers.
Impact on Application:
Polypropylene containers are widely used in the pharmaceutical and food industries due to their ability to withstand sterilization processes. They are also suitable for storing chemicals and other sensitive materials.
Considerations for International Buyers:
In regions like Germany, adherence to stringent quality and safety standards is critical. Polypropylene containers that meet these standards can enhance marketability and consumer trust.
4. Recycled Polyethylene (rPE)
Key Properties:
Recycled polyethylene is derived from post-consumer waste and retains many properties of virgin polyethylene, including flexibility and chemical resistance. Its performance can vary based on the quality of the recycled material.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of rPE is its environmental benefits, as it reduces waste and promotes sustainability. However, the variability in quality can lead to inconsistencies in performance, which may be a concern for some applications.
Impact on Application:
Recycled polyethylene is suitable for non-food applications, such as industrial containers and packaging. It can be an excellent choice for companies looking to enhance their sustainability profile.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions focused on sustainability, such as Europe, may prefer rPE containers to meet corporate social responsibility goals. Compliance with local recycling and environmental regulations is also essential.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Polyethylene Containers
| Material | Typical Use Case for polyethylene container | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) | Food-grade materials, chemicals, hazardous substances | High durability and chemical resistance | Higher manufacturing complexity | Medium |
| Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) | Food packaging, household items | Excellent flexibility and low cost | Lower strength and UV resistance | Low |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Pharmaceuticals, food applications | High temperature resistance | Higher cost compared to polyethylene | High |
| Recycled Polyethylene (rPE) | Industrial containers, non-food packaging | Environmental sustainability | Variable quality and performance | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of various materials used in polyethylene containers, helping them make informed purchasing decisions tailored to their specific needs and regional compliance requirements.

Illustrative image related to polyethylene container
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for polyethylene container
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Polyethylene Containers?
The manufacturing of polyethylene containers involves several critical stages, ensuring that the final products are durable, reliable, and meet industry standards.
Material Preparation: What Goes Into Polyethylene Containers?
The first step in the manufacturing process is the preparation of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) resins. These materials are often chosen for their superior strength, flexibility, and resistance to impact and environmental factors. Suppliers should ensure that the resins used are compliant with international quality standards and are suitable for the specific application of the containers, such as food storage or chemical transport.
Once the appropriate resin is selected, it is processed to remove impurities, which can include moisture and contaminants. This step is crucial as it directly affects the integrity of the final product.
How Are Polyethylene Containers Formed?
The forming stage typically utilizes advanced techniques such as blow molding, injection molding, or rotational molding. Each method has its advantages:

Illustrative image related to polyethylene container
-
Blow Molding: This technique is suitable for producing hollow containers, such as bottles and drums. The process involves inflating a heated plastic tube to form the container shape.
-
Injection Molding: This method is ideal for creating smaller, complex shapes. It involves injecting molten resin into a mold, allowing for high precision and uniformity.
-
Rotational Molding: Often used for larger containers, this technique involves rotating a mold around two axes to ensure an even distribution of the material. It is especially beneficial for creating thick-walled containers.
Each of these methods requires specialized equipment and skilled operators to ensure that the containers are formed accurately and efficiently.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Polyethylene Containers?
After the containers are formed, they undergo various finishing processes. These can include trimming, surface treatment, and labeling. Trimming ensures that any excess material is removed, providing a clean finish. Surface treatments may be applied to enhance the container’s durability or appearance, such as UV stabilization for outdoor applications.
Labeling is essential for branding and compliance, especially for containers used in food and chemical industries. Options include direct printing or applying labels, and customization is often available to meet specific branding requirements.
How Is Quality Assurance Maintained Throughout the Manufacturing Process?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing of polyethylene containers, ensuring that they meet international standards and customer specifications.
Which International Standards Apply to Polyethylene Containers?
B2B buyers should be aware of several international standards that govern the quality and safety of polyethylene containers. Key standards include:
-
ISO 9001: This standard outlines criteria for a quality management system, emphasizing the need for consistent quality and customer satisfaction.
-
CE Marking: Relevant in Europe, this certification indicates that a product meets EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: For containers used in the oil and gas industry, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is crucial for safety and performance.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are vital at various stages of the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials for compliance with specifications. Suppliers should provide certificates of analysis for the materials used.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, operators perform regular inspections to ensure that the production is within specified parameters. This may include monitoring temperature, pressure, and material flow rates.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the containers are complete, a final inspection assesses their overall quality, including dimensions, strength, and surface finish. This step often involves testing for leaks, impact resistance, and other critical factors.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential for ensuring product reliability.
What Audit Processes Should Buyers Consider?
Buyers should conduct thorough audits of potential suppliers. These audits can include:
-
On-Site Inspections: Visiting the manufacturing facility allows buyers to assess the production environment, equipment, and adherence to safety and quality standards.
-
Reviewing Quality Assurance Documentation: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality management system, including ISO certifications and internal audit reports.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging a third-party inspection agency can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality practices. This is particularly useful for buyers who may not have the resources to conduct in-depth audits themselves.
What Are the Common Testing Methods for Polyethylene Containers?
Testing methods play a crucial role in ensuring that polyethylene containers meet the required standards. Common tests include:
-
Impact Testing: This assesses the container’s resistance to sudden forces, ensuring that it can withstand rough handling during transport.
-
Leak Testing: Essential for containers used in transporting liquids, this test checks for any signs of leakage under pressure.
-
Environmental Testing: This involves exposing the containers to extreme temperatures, UV light, and other environmental factors to evaluate their durability and longevity.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
B2B buyers operating in different regions may encounter specific challenges related to quality control. It is crucial to understand local regulations and compliance requirements, as these can vary significantly between countries. For instance, buyers in Europe may prioritize CE marking, while those in the Middle East might focus on local certifications.

Illustrative image related to polyethylene container
Additionally, language barriers and differences in business practices can pose challenges. Establishing clear communication channels with suppliers and leveraging technology for real-time updates can mitigate these issues.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for polyethylene containers is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on quality control measures, international standards, and verification processes, buyers can make informed decisions and ensure that their supply chain remains robust and reliable.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘polyethylene container’
In the competitive landscape of B2B procurement, sourcing polyethylene containers requires a strategic approach to ensure quality, compliance, and value. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist tailored for international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.

Illustrative image related to polyethylene container
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly outline the technical requirements for your polyethylene containers. Consider factors such as size, capacity, and intended use (e.g., food-grade, chemical storage). Specificity in your requirements will help suppliers provide accurate quotes and ensure that the containers meet your operational needs.
- Capacity: Determine the volume required for your application.
- Material Requirements: Specify if you need high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or other variants based on durability and application.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Compile a list of potential suppliers who specialize in polyethylene containers. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record and experience in your industry. Conduct online research, read customer reviews, and check their business profiles for credibility.
- Industry Experience: Prioritize suppliers with experience in your specific market or application.
- Customer Feedback: Analyze reviews and testimonials to gauge reliability and service quality.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Ensure that potential suppliers comply with relevant industry standards and certifications. Look for certifications such as ISO, FDA, and UN compliance, which indicate that the containers meet safety and quality benchmarks.
- Quality Assurance: Certifications reflect the supplier’s commitment to quality and regulatory compliance.
- Environmental Standards: Consider suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices, especially if your business prioritizes eco-friendliness.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before making a large purchase, request samples of the polyethylene containers. Testing samples will allow you to evaluate their durability, usability, and compatibility with your products.
- Physical Inspection: Check for defects, material quality, and suitability for your needs.
- Performance Testing: Assess how well the containers perform under your specific handling and storage conditions.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have selected potential suppliers, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Ensure that you understand all costs involved, including shipping and customs duties.
- Bulk Discounts: Inquire about pricing structures for larger orders.
- Payment Flexibility: Seek terms that align with your cash flow requirements.
Step 6: Finalize Your Order with Clear Documentation
When ready to place an order, ensure that all agreements are documented clearly, including specifications, pricing, and delivery timelines. This documentation will protect both parties and help manage expectations.
- Contractual Clarity: A well-documented agreement minimizes the risk of misunderstandings.
- Delivery and Warranty Clauses: Include terms regarding delivery timelines and warranty for defects.
Step 7: Establish Ongoing Communication
After placing your order, maintain open lines of communication with your supplier. Regular updates on production and shipping will help you manage your inventory and address any issues promptly.
- Feedback Loop: Provide feedback on the containers received to help suppliers improve their products.
- Long-term Relationship: Building a strong relationship can lead to better service and pricing in the future.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for polyethylene containers, ensuring they find the right products that meet their business needs while fostering successful supplier relationships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for polyethylene container Sourcing
When sourcing polyethylene containers, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. This section delves into the key components of cost, factors influencing prices, and practical tips for maximizing value during negotiations.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Polyethylene Container Manufacturing?
The cost structure for polyethylene containers encompasses several components:
-
Materials: The primary cost driver is the high-density polyethylene (HDPE) resin, known for its durability and impact resistance. Prices can fluctuate based on market demand and the cost of raw materials. Customization, such as specific colors or additives for UV resistance, can further influence material costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary depending on the manufacturing location. Countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but this should be balanced with quality considerations.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility management. Efficient production processes can help minimize these costs.
-
Tooling: Custom molds for unique container shapes or sizes add to initial costs. However, these costs can be amortized over larger production runs, which is a significant factor for buyers looking for customized solutions.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures that containers meet necessary standards and certifications, such as food safety and UN regulations. These processes add to costs but are essential for maintaining product integrity.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary significantly based on the shipping method, distance, and Incoterms. Buyers should consider logistics as a critical component of total cost, especially when importing from suppliers in different regions.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their operating costs and profit. Understanding the margin expectations of suppliers can help buyers gauge price competitiveness.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Polyethylene Container Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of polyethylene containers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ): Larger orders often qualify for bulk pricing, reducing the per-unit cost. Buyers should assess their needs carefully to balance inventory levels with cost savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features, such as specialized lids, handles, or sizes, can increase costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against budget constraints.
-
Quality and Certifications: Higher quality standards or specific certifications (e.g., food-grade) can command higher prices. It’s essential for buyers to ensure that the quality aligns with their application needs.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reliability, reputation, and service levels can impact pricing. Established suppliers may offer better value through consistent quality and support.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) affects overall costs by determining who is responsible for shipping and insurance. Understanding these terms is vital for accurate cost estimation.
What Are the Best Tips for Buyers to Negotiate Cost-Effectively?
International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can adopt several strategies to optimize costs:
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage in discussions about payment terms, delivery schedules, and pricing structures. Flexibility in these areas can lead to more favorable terms.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the complete lifecycle costs of the containers, including potential disposal and recycling expenses. This approach helps in making informed purchasing decisions.
-
Research Market Prices: Conduct thorough market research to understand typical price ranges and the factors influencing them. This knowledge empowers buyers during negotiations.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: Explore sourcing from local manufacturers to minimize shipping costs and potentially reduce lead times. This can also support local economies.
-
Build Long-term Relationships: Establishing a strong relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service over time. Trust and reliability often translate into cost savings.
Final Thoughts on Pricing Nuances for International Buyers
While this analysis provides a framework for understanding costs and pricing in polyethylene container sourcing, buyers should be aware that prices can vary widely based on the discussed factors. It is advisable to seek multiple quotes and conduct due diligence on potential suppliers to ensure competitive pricing and quality. As market conditions fluctuate, staying informed about industry trends can further aid in making strategic purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing polyethylene container With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Container Solutions
In the realm of industrial packaging and storage, the choice of container material and design can significantly impact operational efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and product integrity. While polyethylene containers are widely recognized for their durability and versatility, various alternative solutions exist that may better meet specific needs based on application, industry requirements, and logistical considerations. This analysis explores how polyethylene containers compare with metal containers and glass containers, focusing on key aspects that matter to B2B buyers.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Polyethylene Container | Metal Container | Glass Container |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Highly durable, resistant to impact and chemicals | Strong, can withstand high pressures and temperatures | Excellent barrier properties, non-reactive |
| Cost | Generally lower initial investment and maintenance costs | Higher upfront cost, potential corrosion issues | Higher initial cost, fragile, expensive to ship |
| Ease of Implementation | Lightweight, easy to transport and handle | Heavier, may require specialized equipment for handling | Requires careful handling and storage to prevent breakage |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, resistant to many chemicals | Requires regular inspection for rust and wear | Requires careful cleaning and inspection; prone to chipping |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for bulk liquids, chemicals, and food applications | Best for high-pressure or high-temperature applications | Suitable for pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food requiring purity |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Metal Containers
Metal containers, often made from steel or aluminum, are known for their strength and ability to withstand extreme conditions. They are often used in industries where durability and pressure resistance are critical, such as in the automotive or aerospace sectors. However, the initial cost is generally higher compared to polyethylene containers. Additionally, metal containers can be prone to corrosion if not properly treated, which may require more maintenance and additional costs over time. Their weight can also complicate transportation and handling, particularly in regions with limited logistics infrastructure.
Glass Containers
Glass containers offer excellent barrier properties and are non-reactive, making them ideal for sensitive products such as pharmaceuticals and certain food items. They provide a high level of protection against contamination and preserve product integrity. However, glass containers are significantly heavier and more fragile than their polyethylene counterparts, which can lead to higher shipping costs and risks of breakage. The initial investment in glass containers can also be steep, making them less appealing for bulk storage solutions. While their recycling potential is high, the costs associated with handling and logistics can deter businesses from choosing glass over more robust options.

Illustrative image related to polyethylene container
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Container Solution for Your Needs
When selecting a container solution, B2B buyers must consider various factors, including the nature of the materials being stored, the required durability, logistical capabilities, and budget constraints. Polyethylene containers stand out for their lightweight, cost-effective nature and versatility across multiple industries. However, for applications requiring high pressure or purity, metal or glass containers may be more appropriate despite their higher costs and handling complexities. Ultimately, understanding the specific needs of your operation will guide you to the most suitable container solution, enhancing efficiency and ensuring product safety throughout the supply chain.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for polyethylene container
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Polyethylene Containers?
When evaluating polyethylene containers, it is crucial to understand their technical properties, as they directly impact performance, safety, and suitability for various applications. Here are some essential specifications:
1. Material Grade
Polyethylene containers are primarily made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or low-density polyethylene (LDPE). HDPE offers superior strength and resistance to impact, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. LDPE, on the other hand, is more flexible and has better resistance to chemicals. Understanding the specific material grade helps buyers select containers that meet their operational demands, especially in industries like food processing or chemical storage.
2. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in the dimensions of a container. It is critical for ensuring that lids fit securely and that the containers can be stacked or transported without risk of failure. Tighter tolerances may be necessary for precision applications, such as pharmaceutical storage, where contamination risk must be minimized. Knowledge of tolerance levels can aid buyers in ensuring compatibility with existing systems and equipment.
3. Capacity
The capacity of polyethylene containers varies widely, from small pails (e.g., 1 liter) to large intermediate bulk containers (IBCs) exceeding 1,800 liters. Selecting the right capacity is essential for efficient storage and transportation, particularly in bulk handling applications. Buyers should assess their specific volume requirements to optimize storage space and reduce handling costs.

Illustrative image related to polyethylene container
4. Chemical Resistance
Polyethylene is known for its excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including acids and bases. This property is particularly important in industries like agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and food processing. Buyers should verify the chemical compatibility of the container material with their specific products to prevent degradation or contamination.
5. UV Resistance
For applications involving outdoor storage or exposure to sunlight, UV resistance is a crucial property. Containers that lack UV protection can degrade over time, leading to structural failures and leaks. Understanding UV resistance helps buyers ensure the longevity and reliability of their containers in outdoor environments.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Polyethylene Containers?
Familiarity with industry jargon can enhance communication and streamline procurement processes. Here are several essential terms:
Illustrative image related to polyethylene container
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of polyethylene containers, buyers often work with OEMs to customize containers tailored to specific applications or branding requirements. Understanding OEM relationships can facilitate better collaboration and product development.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant in B2B transactions, as it helps buyers gauge the scale of their orders and manage inventory costs effectively. Knowing the MOQ is essential for budget planning and stock management.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used by buyers to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. When purchasing polyethylene containers, submitting an RFQ can help buyers compare pricing, specifications, and terms from multiple suppliers, leading to informed purchasing decisions.

Illustrative image related to polyethylene container
4. Incoterms
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in global trade. They clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which is crucial when ordering polyethylene containers from international suppliers. Familiarity with Incoterms can help buyers negotiate better terms and avoid unexpected costs.
5. IBC (Intermediate Bulk Container)
IBCs are large containers designed for the storage and transport of bulk liquids and powders. They are particularly useful in industries such as chemicals, food, and pharmaceuticals. Understanding the IBC specifications, such as capacity and material type, is vital for selecting the appropriate container for bulk handling applications.
By understanding these key technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing polyethylene containers, ensuring they select products that meet their specific needs and industry standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the polyethylene container Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Polyethylene Container Sector?
The polyethylene container market is currently experiencing significant growth driven by a surge in demand across various industries, including food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. Global drivers such as increased consumer demand for sustainable packaging solutions, stringent regulations on food safety, and the growing trend of e-commerce logistics are reshaping market dynamics. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these trends is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions.
Emerging technologies are also influencing the polyethylene container sector. The integration of automation and IoT in manufacturing processes is enhancing efficiency and reducing production costs. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can provide customized solutions, such as tailored sizes, colors, and features that meet specific logistical and branding requirements. The availability of advanced materials, such as high-density polyethylene copolymers, is further driving innovation, as these materials offer superior strength, impact resistance, and recyclability.
In addition, geopolitical factors and trade agreements play a significant role in shaping the sourcing landscape. Buyers must navigate tariffs, import regulations, and local market conditions, particularly when sourcing from different continents. As a result, establishing strong relationships with reliable suppliers who can adapt to changing regulations and market demands is essential for mitigating risks and ensuring a steady supply chain.
How Does Sustainability Impact the Sourcing of Polyethylene Containers?
Sustainability has become a pivotal consideration for B2B buyers in the polyethylene container sector. As awareness of environmental issues grows, companies are increasingly prioritizing ethical sourcing and the use of eco-friendly materials. The environmental impact of traditional plastics is significant, prompting a shift toward containers made from recycled polyethylene or those that are fully recyclable at the end of their lifecycle.
Buyers are now seeking suppliers who can demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and other green certifications. These certifications not only validate a company’s environmental practices but also enhance brand reputation in an increasingly eco-conscious marketplace. Furthermore, companies are exploring partnerships with manufacturers who implement sustainable practices, such as reducing landfill waste and utilizing renewable energy sources in their production processes.
Incorporating sustainability into the supply chain can also lead to cost savings. By opting for durable and recyclable containers, businesses can reduce their overall packaging costs and improve their operational efficiency. This shift towards sustainable practices is not just a trend but a necessary evolution in the industry, as consumers and regulatory bodies alike demand more responsible environmental stewardship.
What Is the Historical Context of the Polyethylene Container Industry?
The polyethylene container industry has evolved significantly since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially, polyethylene was used primarily for low-cost applications, but advancements in polymer technology have transformed it into a versatile material suitable for various applications, including food storage, pharmaceuticals, and industrial use.

Illustrative image related to polyethylene container
The introduction of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) in the 1970s marked a turning point, offering enhanced durability and resistance to chemicals. Over the years, as safety regulations and environmental concerns grew, manufacturers began focusing on producing containers that not only meet stringent safety standards but also prioritize recyclability and sustainability.
Today, the industry is characterized by innovation, with manufacturers investing in advanced technologies and materials to meet the evolving demands of international B2B buyers. This historical context underscores the importance of choosing suppliers who are not only capable of delivering high-quality products but also aligned with the values of sustainability and ethical sourcing in today’s market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of polyethylene container
-
How do I choose the right polyethylene container for my products?
Selecting the ideal polyethylene container involves assessing your product’s specific requirements, such as size, capacity, and intended use. Consider factors like the container’s durability, resistance to chemicals, and compliance with industry regulations (e.g., food safety or hazardous materials). Collaborating with suppliers who offer customization can enhance your choice, allowing you to select features like lids, handles, and colors that align with your brand. It’s also wise to consult with your supplier’s product specification team to ensure optimal configuration for your needs. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for polyethylene containers?
Minimum order quantities for polyethylene containers can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on factors such as container size, customization, and production capabilities. Typically, MOQs range from a few dozen to several hundred units. It is advisable to discuss your requirements directly with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that suit your business needs, especially if you are sourcing for international markets like Africa or Europe. -
How can I ensure the quality of polyethylene containers from suppliers?
To ensure product quality, vet potential suppliers by reviewing their certifications, such as ISO and UN compliance, which indicate adherence to industry standards. Request samples to evaluate material quality and construction. Additionally, inquire about their quality assurance processes, including inspections and testing protocols. Establishing a solid communication channel with suppliers can help address any quality concerns promptly. -
What customization options are available for polyethylene containers?
Many suppliers offer extensive customization options for polyethylene containers, including sizes, shapes, colors, and features like handles, lids, and labeling. Customization can also extend to material specifications, ensuring the container meets your product’s unique requirements. Discuss your needs with the supplier’s design team to explore available options that enhance functionality and branding. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing polyethylene containers internationally?
Payment terms can vary by supplier but typically include options like advance payment, letter of credit, or payment upon delivery. International buyers often face additional considerations, such as currency fluctuations and transaction fees. It is advisable to negotiate favorable terms that protect your interests, and ensure clear communication about payment methods and timelines to avoid misunderstandings. -
How do logistics and shipping work for polyethylene containers?
Logistics and shipping for polyethylene containers involve several steps, including order processing, packaging, and transportation. Suppliers may offer various shipping methods, including air freight for faster delivery or sea freight for cost efficiency. Ensure that you discuss shipping costs, delivery timelines, and customs clearance processes with your supplier to facilitate a smooth transaction, especially for international shipments to regions like South America or the Middle East. -
What are the common applications for polyethylene containers in various industries?
Polyethylene containers are versatile and widely used across industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and agriculture. They are ideal for storing and transporting liquids, powders, and bulk materials due to their durability, resistance to chemicals, and lightweight nature. Understanding the specific requirements of your industry can help you choose the right type of container and ensure compliance with relevant regulations. -
How can sustainability practices influence my choice of polyethylene containers?
Sustainability is increasingly important in B2B sourcing decisions. Many manufacturers are adopting eco-friendly practices, such as using recycled materials in their polyethylene containers and implementing waste reduction strategies. When selecting a supplier, consider their commitment to sustainability, which can enhance your brand’s reputation and meet the growing demand for environmentally responsible products. Inquire about their recycling programs and material sourcing to ensure alignment with your sustainability goals.
Top 3 Polyethylene Container Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Hach – 2.3L Polyethylene Container Set
Domain: hach.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Set of (8) 2.3 Liter Polyethylene Containers with Caps
2. SaniServ – 12 Quart Polyethylene Storage Container
Domain: usplastic.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: {‘product_name’: ’12 Quart Polyethylene Storage Container’, ‘lid_info’: ‘Lid Sold Separately’, ‘item_number’: ‘85125’, ‘catalog_page_number’: ‘P-586’, ‘manufacturer’: ‘SaniServ’, ‘manufacturer_part_number’: ‘H1211200’, ‘country_of_origin’: ‘USA’, ‘color’: ‘White’, ‘material’: ‘HDPE’, ‘type’: ‘Container’, ‘weight’: ‘1 lbs’, ‘dimensions’: ‘8.25” L x 14.25” W x 8.5” H’, ‘temperature_range’: ‘-40°F to…
3. Polyethylene Containers – Employee Insights
Domain: indeed.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: This company, Polyethylene Containers – Employee Insights, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for polyethylene container
In the dynamic landscape of global trade, the strategic sourcing of polyethylene containers presents a significant opportunity for businesses across various sectors. The durability, customization options, and compliance with international standards make these containers an ideal choice for industries ranging from food and pharmaceuticals to manufacturing and logistics. By prioritizing suppliers who emphasize quality, sustainability, and customer service, international B2B buyers can ensure they are making informed decisions that align with their operational goals.

Illustrative image related to polyethylene container
Furthermore, leveraging local suppliers can enhance supply chain resilience and reduce shipping costs, particularly for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As the demand for sustainable packaging solutions grows, partnering with manufacturers committed to environmentally friendly practices will not only meet regulatory requirements but also appeal to increasingly conscious consumers.
As you explore your sourcing options, consider the long-term benefits of investing in high-quality polyethylene containers. Embrace the opportunity to innovate your packaging solutions and strengthen your market position. Connect with reputable suppliers today to secure your supply chain and position your business for future growth.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

Illustrative image related to polyethylene container