A B2B Buyer’s Guide to Overhead Conveyor Design: Price, Quality, and Suppliers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for overhead conveyor design
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing the right overhead conveyor design can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. With the ever-evolving demands of production efficiency and space optimization, selecting a conveyor system that meets specific operational needs is crucial. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of overhead conveyor design, covering various types, applications, and the critical considerations for supplier vetting. From understanding the nuances of motorized versus hand-pushed systems to evaluating the cost implications of different track styles, this resource aims to equip buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including industrial hubs like Germany and Vietnam—with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions.
As businesses strive to maximize productivity and streamline operations, having access to a well-rounded overview of overhead conveyor systems is essential. This guide not only highlights the benefits and functionalities of various conveyor types but also addresses the importance of design flexibility, durability, and customization options. With actionable insights into the global market trends and supplier evaluations, readers will gain the confidence to navigate the complexities of overhead conveyor sourcing effectively. Empower your purchasing strategy with this essential resource, ensuring your operations are equipped with the best solutions tailored to your unique requirements.
Understanding overhead conveyor design Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enclosed Track Conveyor | Modular, low-friction chain, enclosed design | Automotive, assembly lines | Pros: Clean operation, space-efficient; Cons: Limited load capacity per trolley. |
| I-Beam Conveyor | Heavy-duty steel tracks, higher load capacity | Manufacturing, heavy assembly | Pros: Robust, high load handling; Cons: Requires more space, complex installation. |
| Power and Free Conveyor | Dual track system allowing independent movement | Warehousing, sorting facilities | Pros: Flexible operations, efficient load management; Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Hand-Pushed Conveyor | Manual operation, simple design | Small workshops, light assembly | Pros: Low cost, easy installation; Cons: Labor-intensive, slower throughput. |
| Inverted Conveyor | Tracks mounted upside down, reducing contamination | Paint shops, cleanroom environments | Pros: Prevents contamination, efficient use of space; Cons: Installation complexity, specialized equipment needed. |
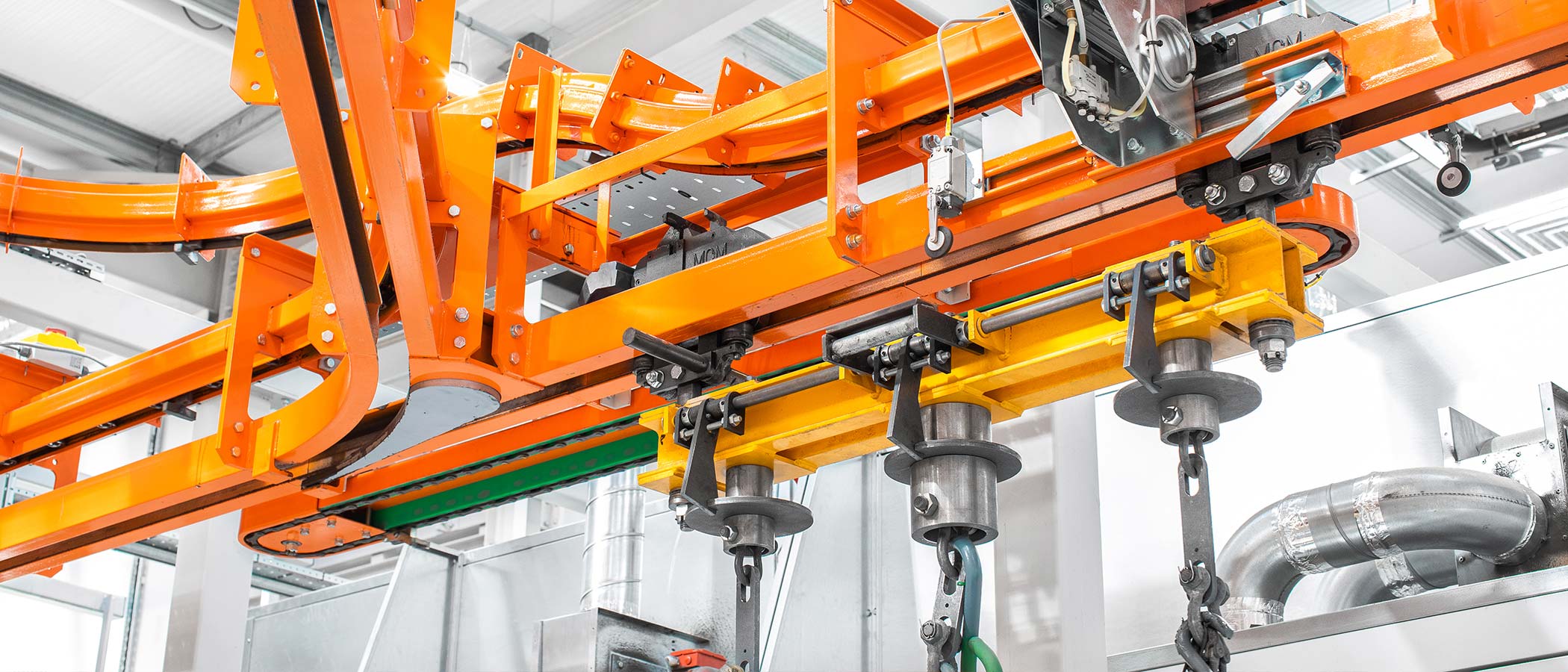
What Are the Key Characteristics of Enclosed Track Conveyors?
Enclosed track conveyors are characterized by their modular design and low-friction chain that runs within a protective track. These systems excel in environments requiring cleanliness and efficiency, making them ideal for automotive assembly lines and similar applications. Buyers should consider the load capacity, which typically maxes out at around 250 pounds per trolley, and the need for regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
How Do I-Beam Conveyors Differ from Other Types?
I-beam conveyors utilize heavy-duty steel tracks, making them suitable for handling significantly heavier loads compared to other overhead systems. Their robust construction is perfect for manufacturing and heavy assembly applications, where durability is paramount. However, buyers must be prepared for a more complex installation process and the requirement for additional space, which can impact overall facility layout.
What Advantages Does a Power and Free Conveyor System Offer?
Power and free conveyors feature a dual-track system that allows the independent movement of trolleys, providing flexibility in operations. This design is particularly beneficial in warehousing and sorting facilities where load management and efficiency are critical. While the initial investment may be higher than simpler systems, the long-term benefits of increased productivity and adaptability often justify the cost for B2B buyers.

Illustrative image related to overhead conveyor design
When Should I Consider a Hand-Pushed Conveyor?
Hand-pushed conveyors are ideal for smaller workshops and light assembly operations where manual labor is feasible. Their simplicity and low cost make them an attractive option for businesses that do not require high throughput. However, buyers should weigh the labor-intensive nature of these systems against their operational needs, as they may not be suitable for larger-scale production environments.
What Makes Inverted Conveyors Unique?
Inverted conveyors are designed with tracks mounted upside down, which helps prevent contamination from dust and debris, making them particularly useful in paint shops and cleanroom settings. This design maximizes vertical space and keeps the load clean, but buyers should consider the complexity of installation and the potential need for specialized equipment to support this system effectively.
Key Industrial Applications of overhead conveyor design
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of overhead conveyor design | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Assembly line for vehicle components | Increases efficiency by streamlining assembly processes, reducing labor costs and cycle time. | Ensure compatibility with existing systems; consider load capacities and track styles. |
| Food Processing | Transporting food products through processing | Enhances hygiene and safety by minimizing manual handling and contamination risks. | Look for systems with easy-to-clean designs and compliance with food safety regulations. |
| Aerospace | Parts handling in assembly and testing | Reduces handling time, improves workflow, and ensures safe transport of sensitive components. | Focus on systems that can accommodate heavy loads and provide precise positioning. |
| Electronics Manufacturing | Assembly of circuit boards and components | Increases production speed and reduces errors through automated handling. | Consider the need for modular designs that can adapt to changing product lines. |
| Textile Industry | Movement of fabrics and garments through stages | Optimizes space and improves material flow, leading to higher productivity. | Evaluate the durability and flexibility of the conveyor design for varying fabric weights. |
How is Overhead Conveyor Design Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive sector, overhead conveyor systems are integral to assembly lines where they transport vehicle components efficiently. These conveyors utilize vertical space, allowing for a streamlined workflow that reduces labor costs and cycle times. Buyers should prioritize systems that are compatible with existing infrastructure and can handle the specific load capacities required for heavy components, ensuring smooth integration and operational efficiency.
What Role Does Overhead Conveyor Design Play in Food Processing?
In food processing, overhead conveyors are essential for transporting products through various stages, from preparation to packaging. These systems enhance hygiene by minimizing manual handling, thereby reducing contamination risks. International buyers should seek conveyors that comply with food safety regulations and feature easy-to-clean designs, as these factors are critical for maintaining operational standards in diverse regulatory environments.

Illustrative image related to overhead conveyor design
How is Overhead Conveyor Design Beneficial in Aerospace Applications?
The aerospace industry relies on overhead conveyor systems for the handling of parts during assembly and testing. These conveyors improve workflow by reducing handling time and ensuring the safe transport of sensitive components. Buyers should focus on systems capable of accommodating heavy loads and providing precise positioning, as the high stakes of aerospace manufacturing demand reliable and efficient solutions.
What Advantages Does Overhead Conveyor Design Offer Electronics Manufacturing?
In electronics manufacturing, overhead conveyors facilitate the assembly of circuit boards and components, significantly increasing production speed and minimizing handling errors. The modularity of these systems allows for adaptability to changing product lines, which is crucial in a fast-paced industry. Buyers should consider the flexibility of the design and its ability to support various load types, ensuring that the conveyor can evolve with their manufacturing needs.
How Does Overhead Conveyor Design Improve Efficiency in the Textile Industry?
Overhead conveyor systems in the textile industry are utilized to transport fabrics and garments through different production stages, optimizing space and improving material flow. This leads to enhanced productivity and reduced bottlenecks in the production process. Buyers should evaluate the durability and flexibility of the conveyor designs to accommodate various fabric weights and types, ensuring that their investment meets the diverse needs of textile manufacturing.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘overhead conveyor design’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inadequate Load Capacity for Heavy Products
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter challenges when selecting overhead conveyor systems that can handle heavy loads. For instance, a manufacturing facility might require the movement of components weighing up to 400 pounds, yet they find that their chosen conveyor system can only support loads up to 250 pounds per trolley. This limitation not only halts operations but also leads to increased costs due to the need for additional equipment or redesigning the workflow. Such scenarios can create delays in production and inefficiencies that are costly in both time and resources.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of their load requirements before selecting an overhead conveyor system. This involves not only considering the maximum weight of the items being transported but also the frequency and speed of movement. Buyers should consult with manufacturers about the specific load capacities of different conveyor types, such as Unibilt or Unibeam systems, which are designed for heavier applications. Additionally, incorporating load bars can enhance the capacity of trolleys, allowing for a combination of trolleys to manage heavier loads safely. A detailed load analysis should also account for the conveyor’s support structures to ensure they are adequate for the intended capacity.
Scenario 2: Inefficient Space Utilization in Production Areas
The Problem: Space is often at a premium in manufacturing and distribution facilities, particularly in regions with high operational costs. B2B buyers frequently face the challenge of designing an overhead conveyor layout that maximizes vertical space while minimizing the footprint of the system. For example, a facility may struggle with a traditional linear conveyor setup that occupies valuable floor space, leading to congestion and inefficiencies in material flow.
The Solution: Buyers can optimize their overhead conveyor design by utilizing modular systems that allow for flexibility in layout. Implementing curved tracks and vertical lifts can facilitate movement through tight spaces and can help navigate around existing equipment. Engaging with an experienced conveyor system designer early in the planning process can yield innovative layout solutions tailored to specific operational needs. Additionally, opting for enclosed track systems can reduce the risk of contamination and improve the overall cleanliness of the production environment, as these systems keep products elevated and shielded from ground-level debris.
Scenario 3: Maintenance and Downtime Concerns
The Problem: One significant pain point for B2B buyers is the maintenance requirements of overhead conveyor systems. Facilities often experience unexpected downtimes due to mechanical failures or misalignments, which can disrupt operations and lead to financial losses. For example, a manufacturing plant might deal with frequent breakdowns of their conveyor system, leading to delays in production schedules and increased labor costs as employees are forced to wait for repairs.

Illustrative image related to overhead conveyor design
The Solution: To address maintenance concerns, buyers should prioritize selecting conveyor systems that incorporate easy access for routine inspections and repairs. Investing in modular components can facilitate quicker replacements and modifications, minimizing downtime. Additionally, integrating predictive maintenance technology can help identify potential issues before they result in failures. Regular training for maintenance staff on the specific systems in use can also enhance their ability to troubleshoot problems quickly. Buyers should consider establishing a maintenance schedule based on the manufacturer’s recommendations and the operational intensity of the conveyor system to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for overhead conveyor design
When selecting materials for overhead conveyor design, it is crucial to consider the specific requirements of the application, including load capacity, environmental conditions, and regulatory compliance. Below, we analyze four common materials used in overhead conveyor systems, highlighting their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international buyers.
What are the Key Properties of Steel in Overhead Conveyor Design?
Steel is a widely used material for overhead conveyor systems due to its strength and durability. Key properties include high tensile strength, temperature resistance, and excellent load-bearing capabilities. Steel can withstand heavy loads and is suitable for high-pressure environments, making it ideal for industrial applications.
Pros: Steel’s durability and load capacity make it suitable for heavy-duty operations. It is also relatively cost-effective compared to other materials.
Cons: Steel is prone to corrosion if not properly treated, which can lead to maintenance issues. Additionally, its weight can complicate installation and require robust support structures.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with various media, including chemicals and oils, but may require protective coatings in corrosive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM or DIN is essential. Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East may prefer galvanized or stainless steel options to enhance corrosion resistance.
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Material for Overhead Conveyors?
Aluminum is another popular choice, particularly for lighter applications. It boasts a favorable strength-to-weight ratio, making it easier to handle and install. Key properties include good corrosion resistance and lightweight characteristics.
Pros: Aluminum is resistant to rust and corrosion, which is beneficial in humid or chemically aggressive environments. Its lightweight nature simplifies installation and reduces structural support needs.
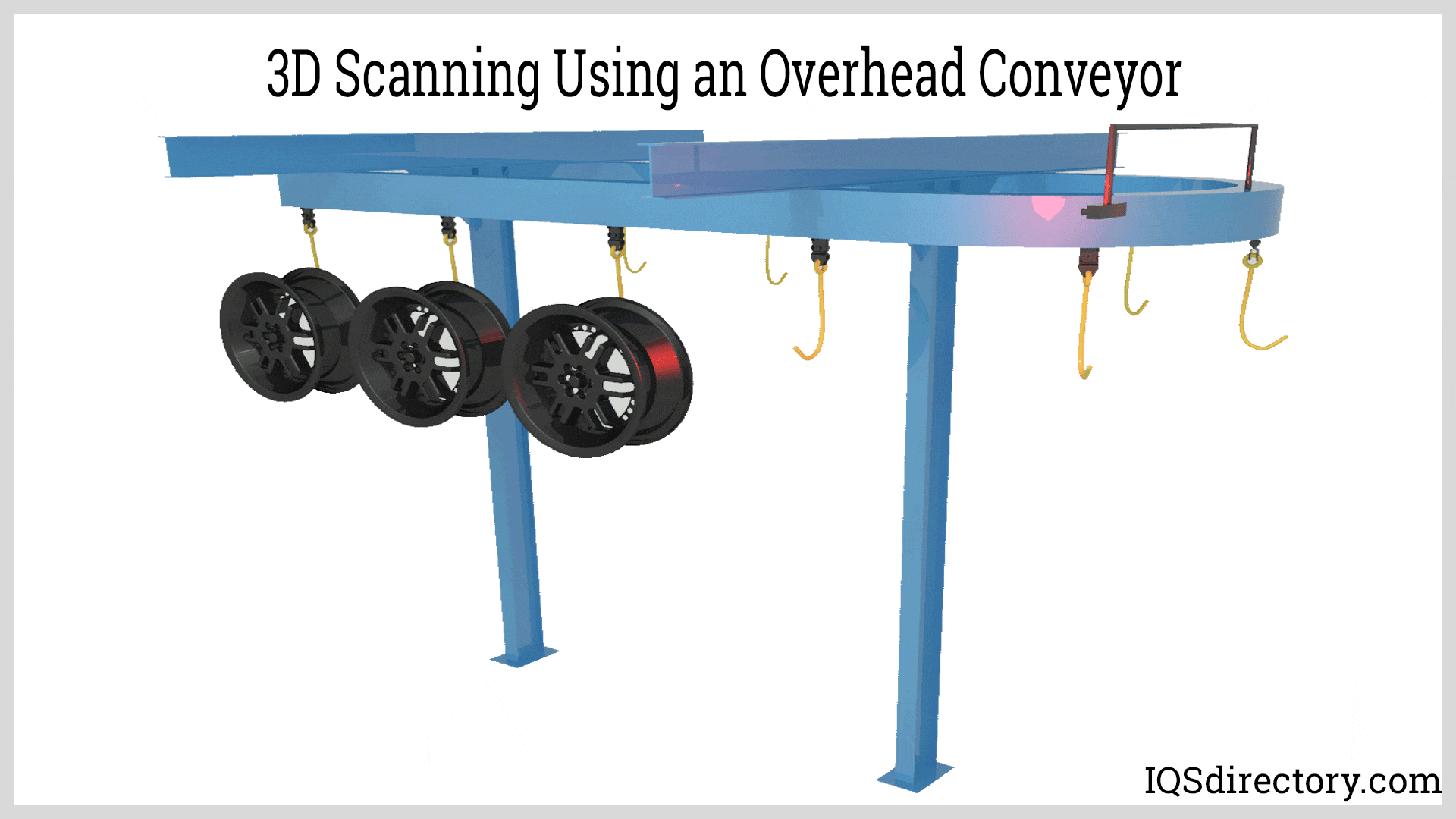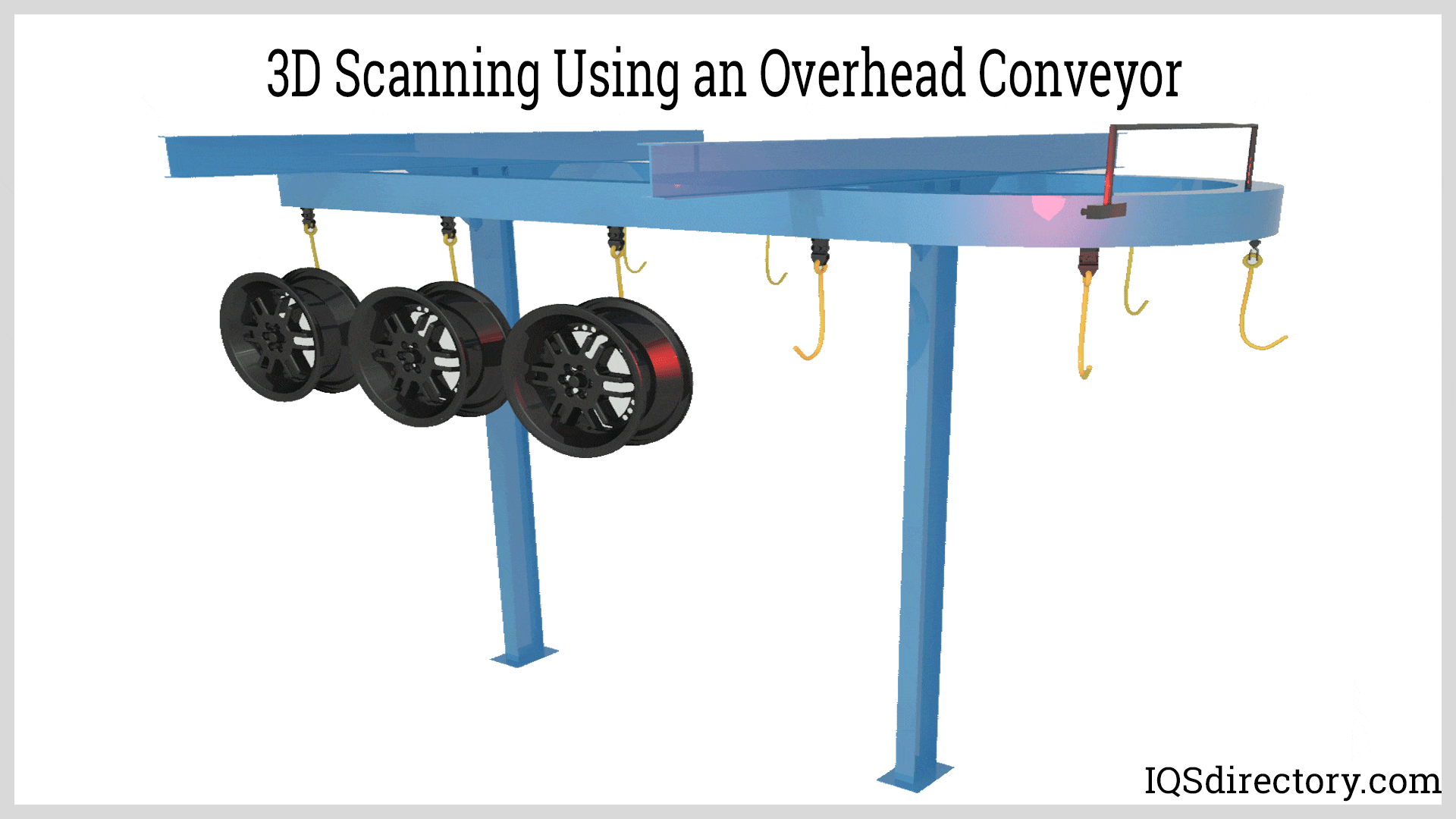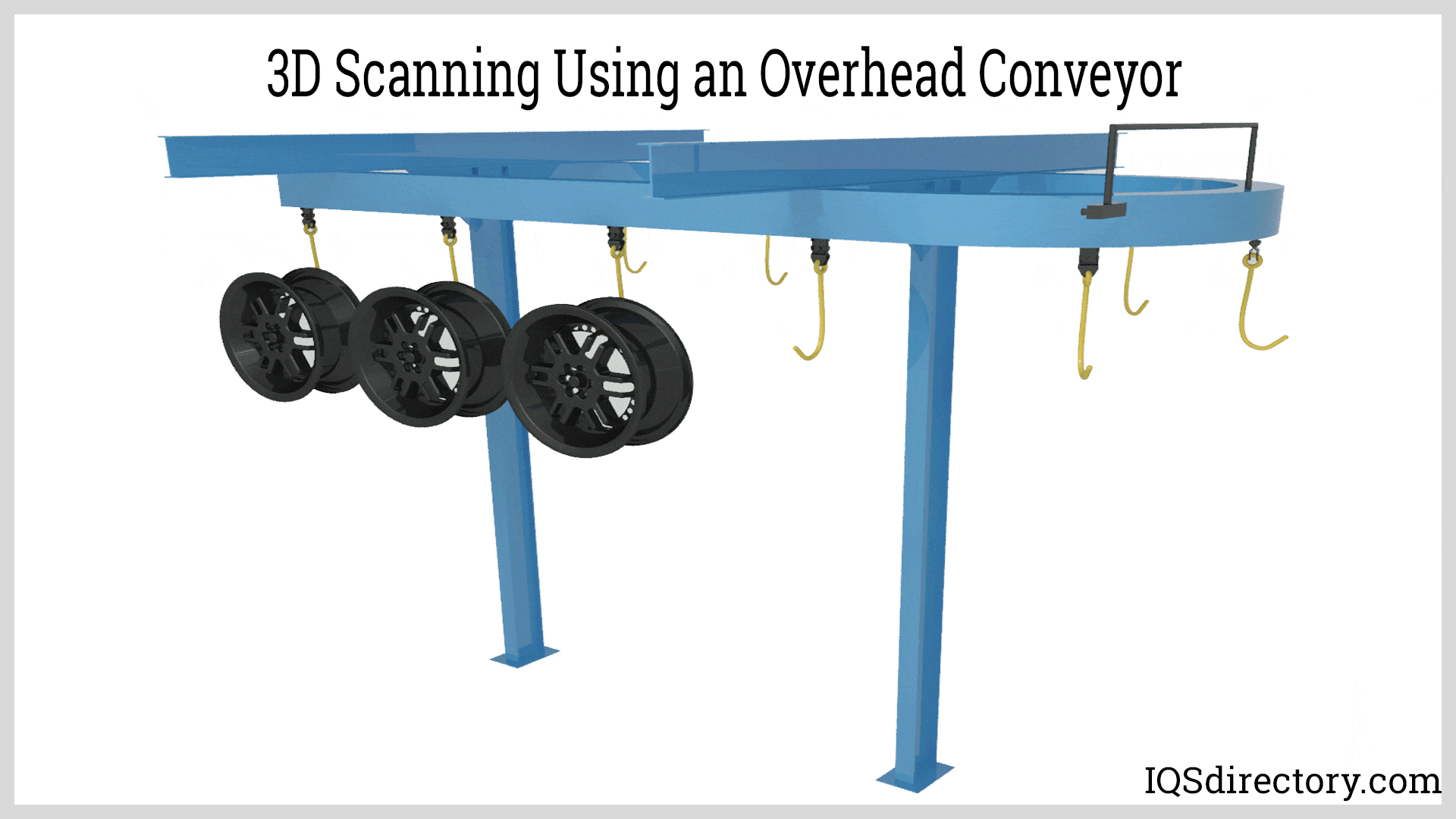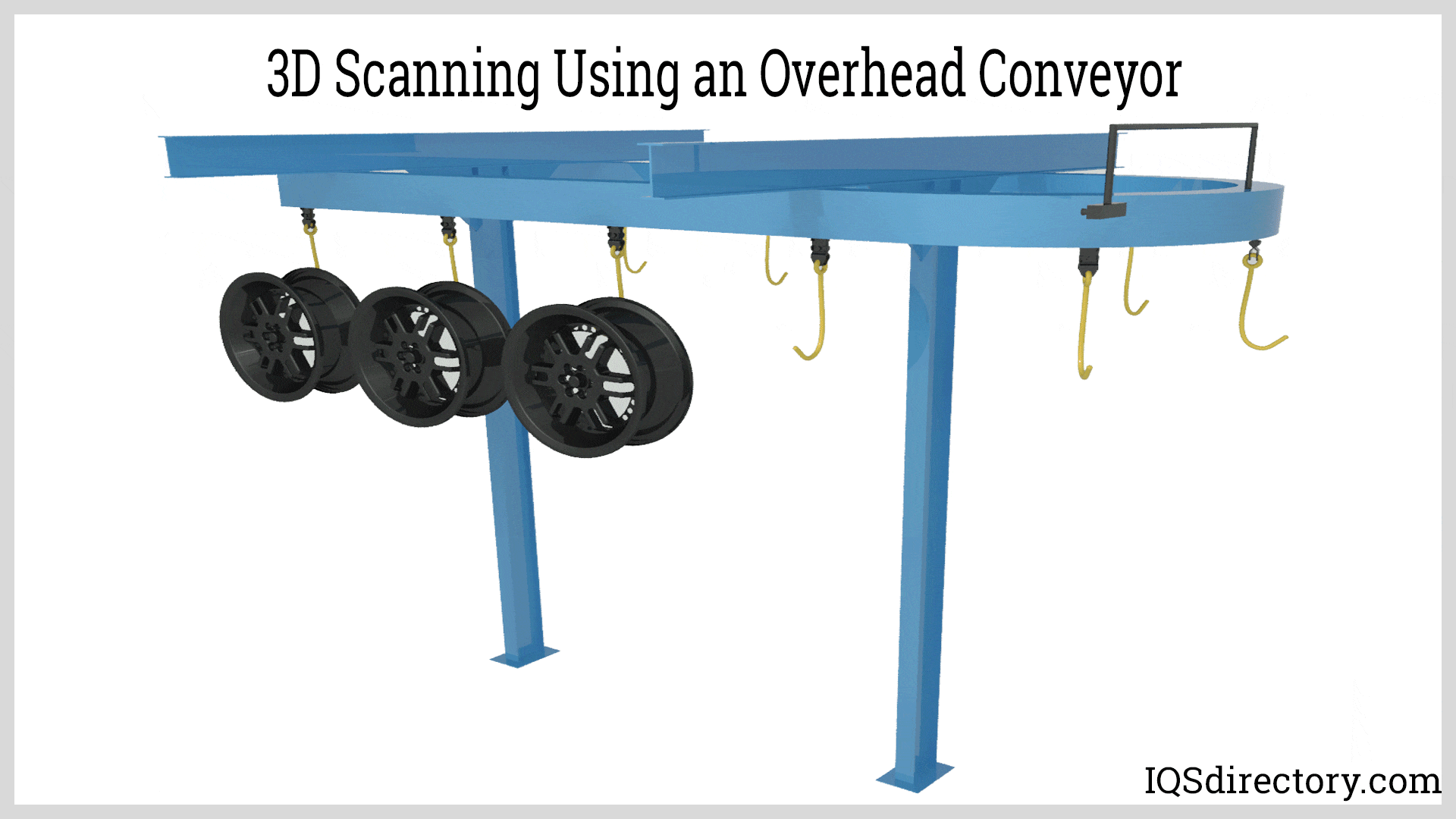
Illustrative image related to overhead conveyor design
Cons: While aluminum is durable, it is not as strong as steel, which limits its use in heavy-load applications. It can also be more expensive than steel, depending on the alloy used.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for transporting lightweight items and in environments where corrosion is a concern. However, it may not be ideal for heavy industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with JIS and other local standards. In regions like Africa and South America, the availability of specific aluminum alloys may vary.
What Role Does Stainless Steel Play in Overhead Conveyor Systems?
Stainless steel is a premium material known for its excellent corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. It is often used in food processing and pharmaceutical applications where hygiene is paramount.
Pros: Stainless steel offers superior durability and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for harsh environments. It also requires less maintenance over time.
Cons: The primary drawback is its cost, which can be significantly higher than both carbon steel and aluminum. Additionally, stainless steel can be more challenging to fabricate.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is suitable for applications involving food, pharmaceuticals, or chemicals due to its non-reactive nature.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with food safety standards (e.g., FDA, EU regulations) is critical. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East may have specific preferences for certain grades of stainless steel.
How Does Plastic Influence Overhead Conveyor Design?
Plastic materials, such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), are increasingly used in overhead conveyor systems, particularly for lighter loads and specialized applications.
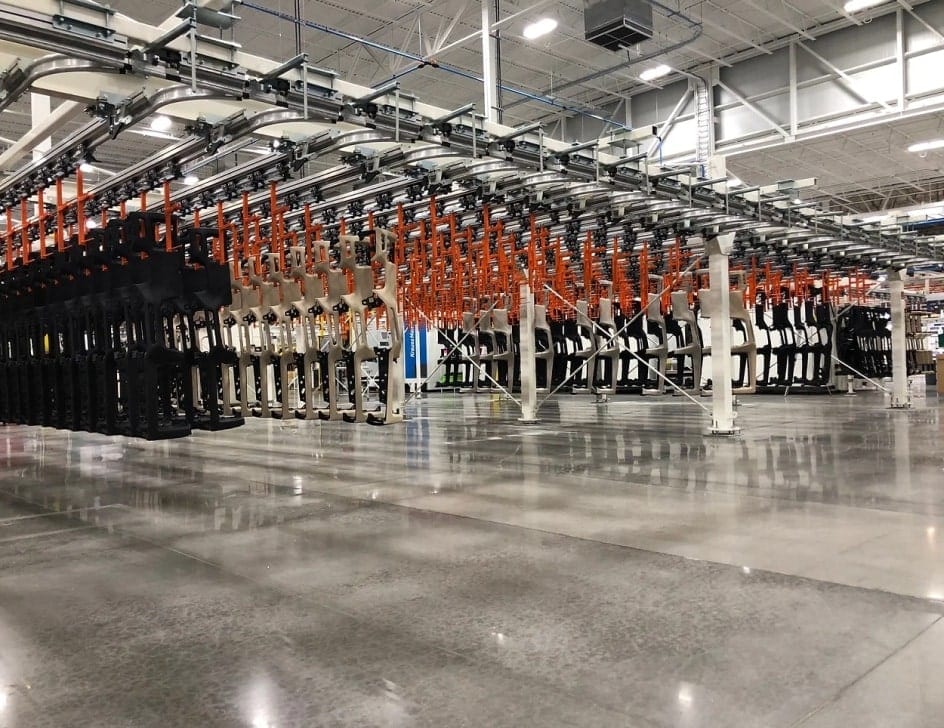

Illustrative image related to overhead conveyor design
Pros: Plastics are lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and can be molded into various shapes, allowing for design flexibility. They are often less expensive than metals.
Cons: Plastics may not withstand high temperatures or heavy loads, limiting their application scope. They can also be susceptible to wear and tear over time.
Impact on Application: Plastic is ideal for transporting lightweight items or in environments where chemical resistance is required. However, they may not be suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local material safety standards. In regions like Africa and South America, the availability of specific plastic materials may vary.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Overhead Conveyor Design
| Material | Typical Use Case for overhead conveyor design | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty industrial applications | High strength and load capacity | Prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight and corrosion-sensitive areas | Lightweight and easy to install | Lower strength compared to steel | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food and pharmaceutical industries | Excellent corrosion resistance | High cost and difficult to fabricate | High |
| Plastic | Lightweight and specialized applications | Lightweight and design flexibility | Limited load capacity and temperature tolerance | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights into the properties and implications of different materials for overhead conveyor design, assisting international B2B buyers in making informed decisions tailored to their specific needs and regional considerations.
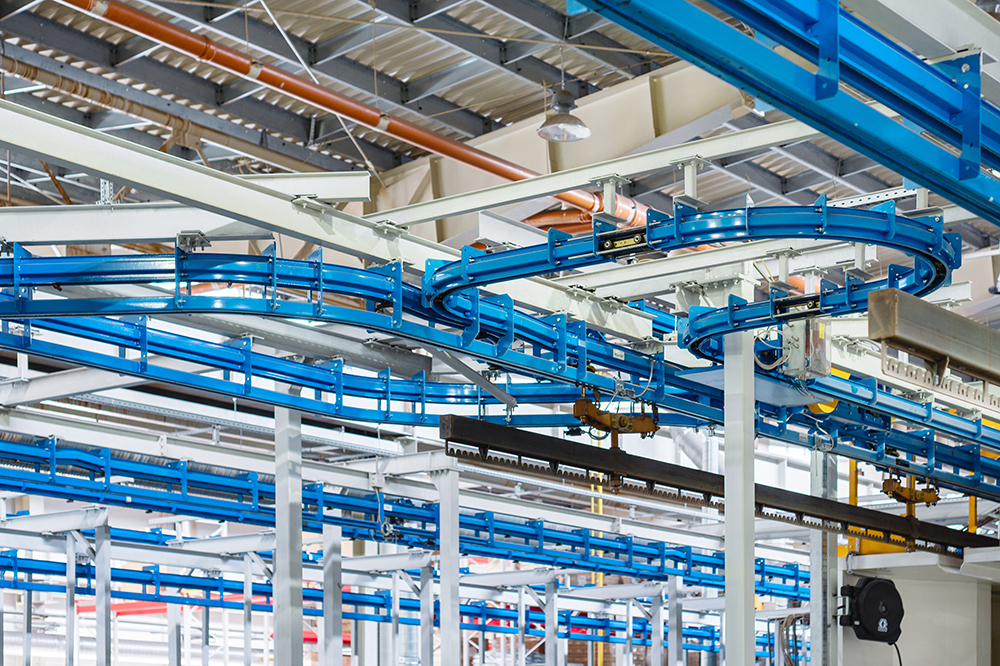

Illustrative image related to overhead conveyor design
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for overhead conveyor design
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Overhead Conveyors?
Manufacturing overhead conveyors involves a series of well-defined stages that ensure the final product meets both functionality and quality standards. Here, we delve into the main stages of the manufacturing process: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Overhead Conveyor Production?
Material preparation is crucial for establishing a strong foundation for overhead conveyor systems. This stage typically involves the selection of high-quality raw materials, such as carbon steel or stainless steel, known for their durability and resistance to wear and corrosion. Manufacturers often perform material inspections to ensure compliance with specifications and standards, eliminating any subpar materials from the production line.
Once selected, materials undergo cutting and machining processes to achieve the required dimensions. Advanced techniques like laser cutting or CNC machining are commonly employed to ensure precision. This stage may also include surface treatments to enhance material properties, such as galvanization or powder coating, which provide additional protection against environmental factors.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of Overhead Conveyors?
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into components that will make up the overhead conveyor system. Key techniques include bending, welding, and forging.
-
Bending: This process shapes the materials into the desired curves and angles needed for tracks and other structural components. Precision bending machines ensure that the angles are consistent and within the required tolerances.
-
Welding: High-strength welding techniques, such as MIG or TIG welding, are employed to join various components. Quality welds are critical as they directly influence the structural integrity and load-bearing capacity of the conveyor system.
-
Forging: For parts that require exceptional strength, such as trolleys and chains, forging processes may be used. This involves deforming metal under pressure to improve its mechanical properties, resulting in components that can withstand heavy loads.
How Does the Assembly Process Work for Overhead Conveyors?
Assembly is the next critical stage in the manufacturing process, where individual components are brought together to form a complete overhead conveyor system. This process typically involves the following steps:

Illustrative image related to overhead conveyor design
-
Component Integration: Each part, from tracks and trolleys to drive units and take-ups, is carefully assembled. Manufacturers often utilize jigs and fixtures to ensure that components are aligned correctly during assembly.
-
Testing During Assembly: Manufacturers may conduct in-process quality checks to verify that each component meets specifications before proceeding to the next assembly stage. This approach minimizes errors and reduces the need for rework later in the process.
-
Final Assembly: The final assembly integrates all components into a functioning system. This may include installing electrical components, such as motors and controls, and ensuring that all moving parts operate smoothly.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Applied to Overhead Conveyors?
Finishing techniques are essential for enhancing the aesthetic and functional qualities of overhead conveyors. Common methods include:
-
Surface Treatments: After assembly, conveyors often undergo surface treatments such as powder coating or painting. These treatments not only improve appearance but also provide additional protection against corrosion and wear.
-
Inspection and Calibration: Before the conveyor systems are shipped, they undergo thorough inspection and calibration. This ensures that all moving parts function correctly and that the system meets operational specifications.
-
Packaging: Finally, conveyors are carefully packaged to prevent damage during transportation. This may involve custom crating or use of protective materials to safeguard against environmental factors.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for Overhead Conveyor Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is vital in manufacturing overhead conveyors, ensuring that they meet international standards and customer expectations. Key quality control (QC) measures include adherence to recognized standards, establishing checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process, and implementing robust testing methods.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
For manufacturers to ensure their overhead conveyors meet global quality expectations, adherence to international standards is crucial. Some key standards include:
-
ISO 9001: This standard specifies requirements for a quality management system (QMS). It is widely recognized and focuses on meeting customer and regulatory requirements while enhancing customer satisfaction.
-
CE Marking: For products sold in Europe, CE marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. Manufacturers must ensure that their products are compliant to gain access to European markets.
-
API Standards: For industries such as oil and gas, compliance with American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is essential. These standards ensure that equipment used in these sectors meets specific safety and performance criteria.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Overhead Conveyor Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early and ensure compliance with specifications. Common checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet predefined specifications. Non-compliant materials are rejected before they enter the production line.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): As components are manufactured and assembled, periodic checks are performed to ensure that each step adheres to quality standards. This might involve dimensional checks or functional tests of subassemblies.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, the finished conveyor systems undergo comprehensive testing to ensure they operate as intended. This includes load testing, functionality checks, and safety inspections.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is critical to ensuring the reliability of overhead conveyor systems. Here are effective strategies for buyers:
Illustrative image related to overhead conveyor design
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of potential suppliers can provide insight into their manufacturing processes, quality control systems, and adherence to international standards. This can be done through on-site visits or third-party audit services.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should request detailed quality assurance reports, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC stages. These documents can offer transparency regarding the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s manufacturing processes and product quality. This can help mitigate risks associated with international sourcing.
What Nuances Should B2B Buyers Consider Regarding Quality Control in Different Regions?
When sourcing overhead conveyors from suppliers in various regions, B2B buyers must navigate specific nuances related to quality control.
-
Africa and South America: Buyers may encounter challenges related to varying levels of regulatory compliance and quality standards. It is essential to verify that suppliers adhere to both local and international standards.
-
Middle East: In this region, certifications such as ISO and CE are increasingly recognized, but local regulations may also apply. Understanding these nuances can help buyers ensure compliance.
-
Europe (e.g., Germany): European suppliers typically have stringent quality control processes in place, often exceeding basic requirements. Buyers can leverage this to their advantage by seeking suppliers with robust certifications and proven track records.
-
Asia (e.g., Vietnam): As manufacturing capabilities in Asia continue to grow, buyers should pay close attention to the supplier’s quality management systems and their ability to meet international standards, particularly for industries with stringent requirements.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance mechanisms for overhead conveyors is paramount for B2B buyers. By being aware of the key stages, quality standards, and verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and product reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘overhead conveyor design’
Introduction
Designing an overhead conveyor system requires careful planning and consideration of various technical and operational factors. This checklist serves as a practical sourcing guide for B2B buyers looking to procure overhead conveyor design solutions. By following these steps, you can ensure that your system meets your operational needs while maximizing efficiency and minimizing costs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for a successful overhead conveyor system. This includes determining the weight and dimensions of the items to be transported, the required speed, and the layout of the facility. Specifying these details upfront helps potential suppliers tailor their offerings to meet your unique operational requirements.
- Load Capacity: Identify the maximum load each section of the conveyor must handle.
- Speed Requirements: Determine the desired speed of movement for optimal workflow.
Step 2: Assess Available Conveyor Types
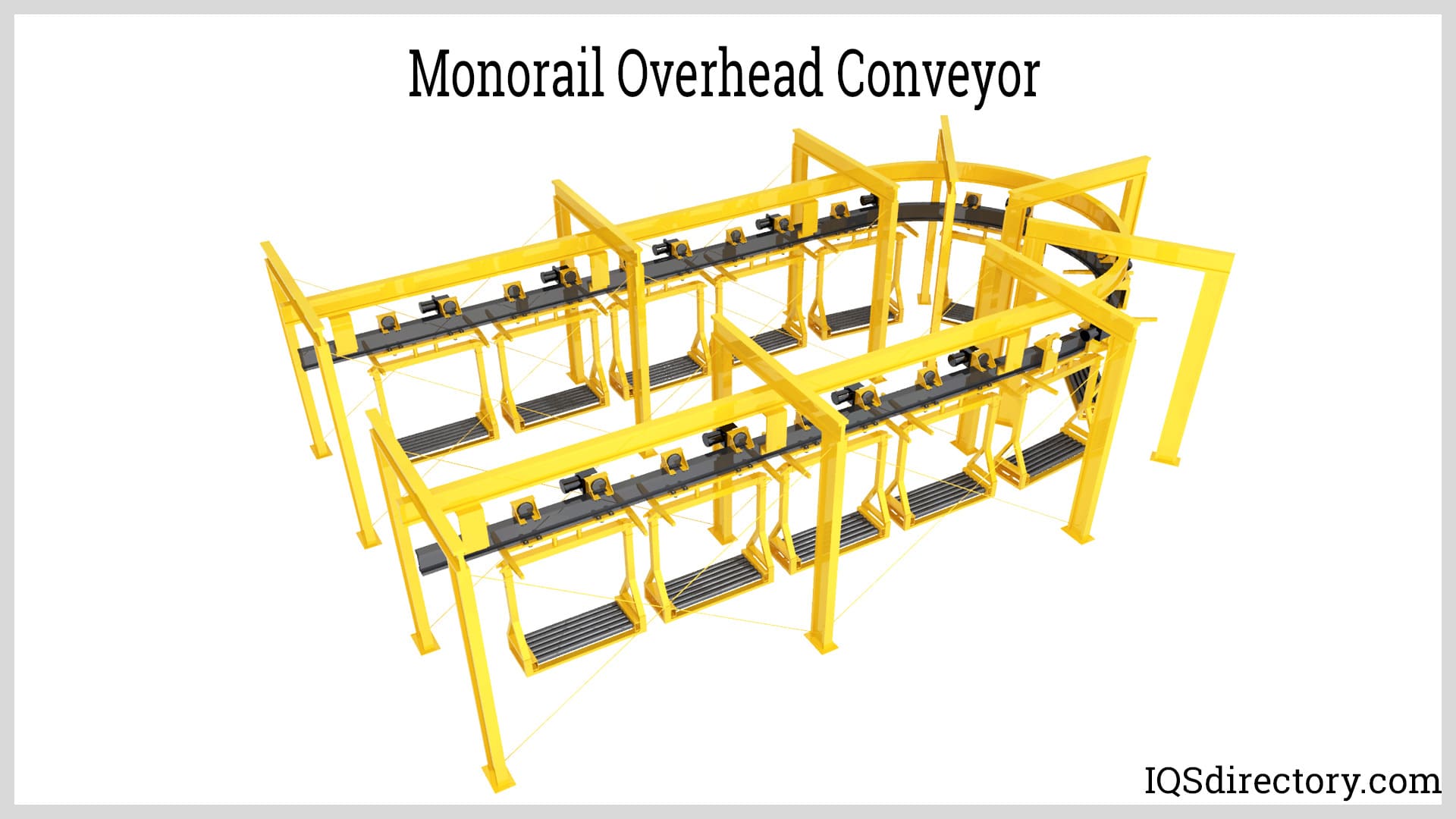
Understanding the different types of overhead conveyors available is essential for making an informed decision. Options include enclosed track systems, I-beam monorail systems, and power and free conveyors, each with distinct advantages based on the application.
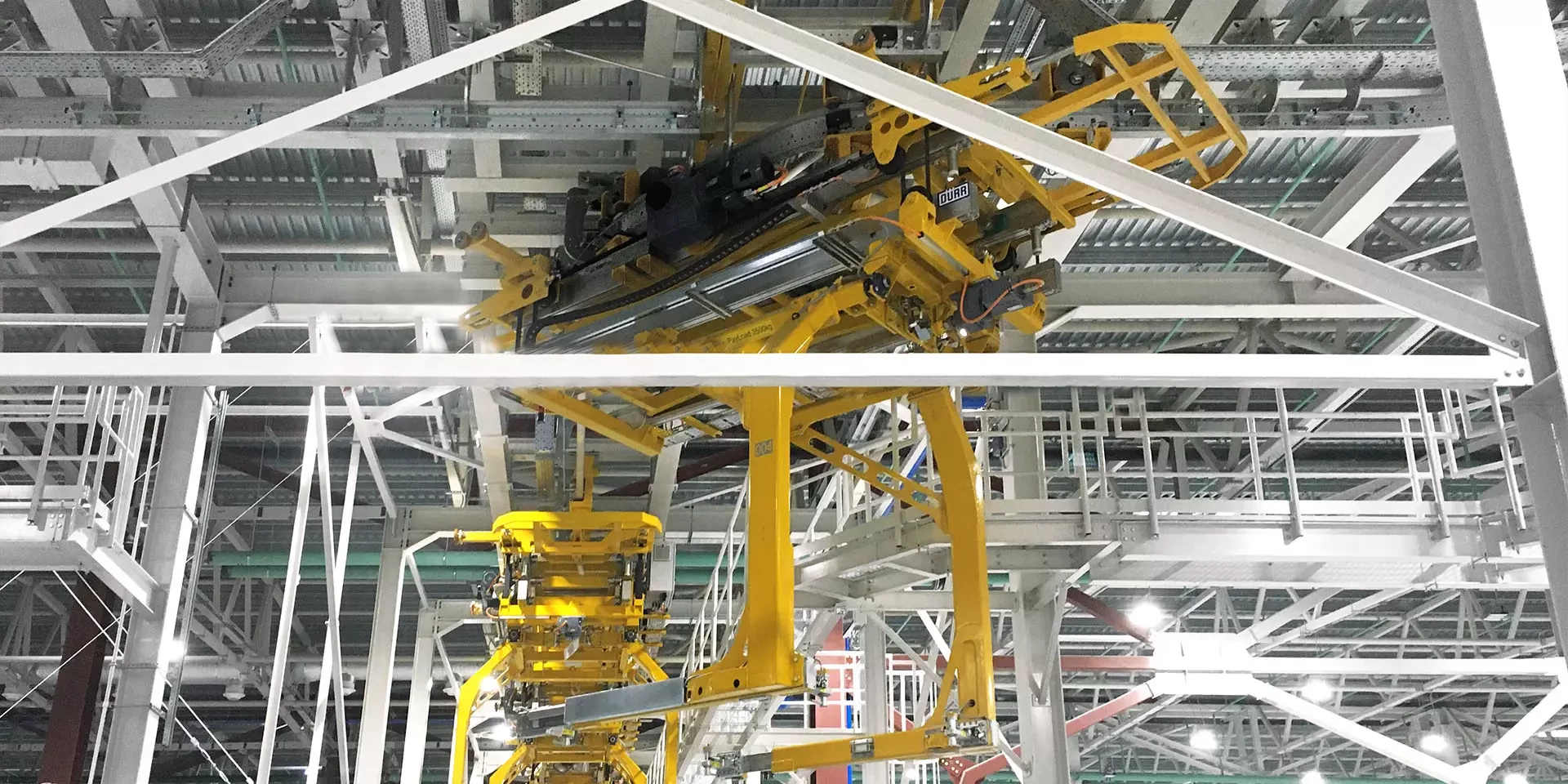

Illustrative image related to overhead conveyor design
- Enclosed Track Systems: Ideal for environments needing protection from contamination.
- I-Beam Systems: Suitable for heavy-duty applications with higher load capacities.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, thorough evaluation is necessary. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from clients in similar industries or geographical regions. This ensures that the supplier has a proven track record of reliability and quality.
- Supplier Experience: Look for suppliers with extensive experience in overhead conveyor systems.
- Client Testimonials: Seek feedback from previous clients to gauge satisfaction and performance.
Step 4: Verify Compliance and Certifications
Ensure that potential suppliers comply with relevant industry standards and hold necessary certifications. This step is vital for ensuring safety and quality in your overhead conveyor system, which can impact your operations significantly.
- ISO Certifications: Verify that suppliers are ISO certified, indicating adherence to international standards.
- Safety Standards: Check for compliance with safety regulations specific to your region and industry.
Step 5: Request Customization Options
Every operation has unique needs, so it’s important to inquire about customization options available for the conveyor system. This can include adjustments to track lengths, load attachments, and motor specifications to better fit your operational workflow.
- Modularity: Look for systems that allow for easy modifications or expansions in the future.
- Customization Flexibility: Ensure the supplier can accommodate specific design requests.
Step 6: Review Installation and Maintenance Support
Consider the level of installation and ongoing maintenance support offered by the supplier. A reliable support system can save time and costs associated with downtime or operational disruptions.

Illustrative image related to overhead conveyor design
- Installation Services: Confirm if the supplier provides on-site installation and training.
- Maintenance Plans: Inquire about available maintenance contracts to keep your system running efficiently.
Step 7: Compare Total Cost of Ownership
Lastly, assess the total cost of ownership (TCO) for the overhead conveyor system. This includes not only the initial purchase price but also installation, maintenance, and operational costs over time.
- Lifecycle Costs: Evaluate the expected lifespan of the conveyor and associated costs.
- Operational Efficiency: Consider how the system’s efficiency can impact overall production costs.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing overhead conveyor designs, ensuring they select the best solution for their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for overhead conveyor design Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Overhead Conveyor Design?
When sourcing overhead conveyor systems, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: This encompasses the raw materials used in manufacturing conveyor components, such as steel for tracks and trolleys, motors, and other mechanical parts. The quality and specifications of these materials can significantly affect the overall cost.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary depending on the complexity of the conveyor system and the expertise required for assembly and installation. Skilled labor is essential for ensuring that the system is built to specifications and operates efficiently.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. These costs are typically spread across all products manufactured, impacting pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be necessary for specialized conveyor designs, which can add to the initial investment. Tooling costs can be amortized over larger production runs, making it critical to consider the volume of orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the conveyor system meets industry standards and customer specifications requires investment in quality control processes. This might include testing materials and final products, which can influence pricing.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary based on the size and weight of the conveyor system, as well as the distance to the buyer’s location. International shipping may involve additional tariffs and customs fees, affecting the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically apply a profit margin to cover their costs and risks. Understanding the market rates can help buyers negotiate better prices.
What Influences Prices of Overhead Conveyors?
Several factors can influence the pricing of overhead conveyor systems, including:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to discounts due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to optimize cost savings, especially when planning for future expansions.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs tailored to specific operational needs can increase costs. Buyers should assess whether standard solutions could meet their requirements to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO standards) typically come at a premium. However, investing in certified components may lead to lower maintenance costs and longer system lifespans.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established manufacturers may charge more for their products but often provide better warranties and support.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping and delivery can significantly affect the final price. Understanding Incoterms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) is crucial for calculating total landed costs.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices?
Buyers can enhance their purchasing strategy by considering the following tips:
-
Negotiation: Open discussions with suppliers about pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules can lead to better deals. Be prepared to discuss volume commitments or long-term contracts for favorable pricing.
-
Cost Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not only the purchase price but also installation, maintenance, and operational costs. Sometimes a higher upfront investment leads to lower long-term expenses.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Understand regional differences in pricing, especially in markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Currency fluctuations, local tariffs, and import duties can all affect final costs.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Gathering quotes from several suppliers allows buyers to compare prices and services. This can also provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Be Aware of Market Trends: Stay informed about industry trends and pricing fluctuations, as these can impact supplier pricing strategies and availability.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for overhead conveyor systems can vary widely based on customization, supplier, and regional factors. The information provided here is meant to serve as a guideline and should not be considered definitive. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough research and obtain specific quotes tailored to their unique operational needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing overhead conveyor design With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Overhead Conveyor Design
In the realm of material handling and production logistics, selecting the most efficient conveyor system can significantly impact operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. While overhead conveyor systems are widely recognized for their ability to optimize vertical space and streamline workflows, it’s essential to evaluate alternative solutions that may better suit specific operational requirements. This section compares overhead conveyor design with two viable alternatives: Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and Roller Bed Conveyors.
| Comparison Aspect | Overhead Conveyor Design | Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) | Roller Bed Conveyors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High throughput; ideal for continuous production. | Flexible routing; can adapt to changing layouts. | Efficient for heavy and bulk items; limited vertical movement. |
| Cost | Higher initial setup cost; long-term savings on labor. | Moderate cost; requires investment in navigation technology. | Lower initial cost; maintenance can add up over time. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires significant planning and structural support. | Easier to integrate into existing layouts; minimal structural changes needed. | Simple installation; can be set up quickly. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; high durability when properly installed. | Moderate maintenance; battery and software updates needed. | Higher maintenance due to wear and tear on rollers. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for assembly lines and processes requiring overhead space. | Best for warehouses and facilities with dynamic layouts. | Suitable for handling heavy loads in a linear flow. |
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)?
AGVs represent a modern solution for material handling, utilizing sensors and software to navigate autonomously within a facility. One of the primary advantages of AGVs is their flexibility; they can be easily reprogrammed to accommodate changing layouts, making them ideal for dynamic environments such as warehouses and distribution centers. Additionally, AGVs can integrate with other technologies, such as warehouse management systems, to optimize inventory flow. However, the initial investment in navigation technology and potential software complexities can be a downside for some businesses, especially those with limited budgets.
How Do Roller Bed Conveyors Compare to Overhead Systems?
Roller bed conveyors are another alternative that excels in handling heavy and bulky items. They are particularly effective in environments where items need to be moved horizontally and can easily accommodate large loads without the need for complex infrastructure. The installation process for roller bed conveyors is relatively straightforward, allowing for quick deployment. However, they lack the vertical movement capabilities of overhead systems and can require more maintenance due to wear on the rollers. This could lead to increased operational downtime if not managed properly.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Conveyor Solution?
When selecting a conveyor solution, B2B buyers must consider their specific operational needs, including the types of materials handled, the facility layout, and budget constraints. Overhead conveyor systems are particularly suited for environments that benefit from vertical space utilization, while AGVs offer flexibility for changing workflows. Roller bed conveyors present a cost-effective option for transporting heavy items along a flat plane. By evaluating the performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance requirements, and best use cases of each option, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and enhance overall efficiency.

Illustrative image related to overhead conveyor design
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for overhead conveyor design
What Are the Key Technical Properties for Overhead Conveyor Design?
When designing an overhead conveyor system, several technical properties are essential to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Here are some critical specifications:
-
Material Grade
The choice of material for the conveyor system significantly affects durability and performance. Common materials include carbon steel for structural components and stainless steel for environments requiring corrosion resistance. Selecting the appropriate material grade can impact operational longevity and maintenance costs, making it a vital consideration for B2B buyers. -
Load Capacity
This specification defines the maximum weight that the conveyor can safely transport. Load capacity varies by system type and configuration, with common limits ranging from 250 pounds per trolley in enclosed track systems to several tons in heavy-duty I-beam systems. Understanding load capacity is crucial for ensuring that the conveyor meets production demands without risking failure. -
Speed and Tolerance
Conveyor speed is typically measured in feet per minute (FPM) and is essential for synchronizing with production processes. Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation in dimensions, which is critical for ensuring that components fit together seamlessly. These specifications are important for optimizing throughput and ensuring the efficiency of operations. -
Support Centers and Structural Integrity
Support centers are the distances between support structures for the conveyor track. This affects load distribution and stability. Proper calculation of support centers ensures that the conveyor maintains structural integrity, preventing sagging or failure under load. Buyers must consider the engineering requirements to ensure safe and effective installation. -
Drive and Control Systems
The drive system, which includes motors and gearboxes, is crucial for determining conveyor speed and load handling capabilities. Control systems, including variable frequency drives (VFDs), allow for speed adjustments and operational flexibility. Understanding these components helps buyers assess the suitability of the system for their specific applications.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Overhead Conveyor Design?
In addition to technical properties, familiarity with industry-specific terminology is essential for effective communication between buyers and suppliers. Here are some key terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers ensure they are sourcing components from reputable manufacturers that meet industry standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for B2B buyers, as it affects purchasing decisions, inventory management, and overall project budgeting. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document soliciting price bids from suppliers for specific products or services. It is a vital tool for buyers to compare costs and terms from different vendors, facilitating informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers to clarify shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost allocation. -
Trolley Attachments
Trolley attachments are components that connect the load to the conveyor chain. They come in various designs to accommodate different types of loads and operational needs. Knowing about trolley attachments helps buyers customize their systems effectively. -
Take-Up Units
These are mechanisms used to maintain tension in the conveyor chain, ensuring smooth operation. Proper selection and installation of take-up units are essential for the longevity and reliability of the conveyor system, making this term significant for buyers.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when designing or purchasing overhead conveyor systems, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and productivity.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the overhead conveyor design Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics in Overhead Conveyor Design?
The overhead conveyor design sector is witnessing significant growth, propelled by the ongoing evolution of manufacturing processes and logistics in various industries. Key drivers include the increasing need for automation in production facilities and the optimization of space utilization. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are actively seeking efficient solutions that not only enhance operational productivity but also reduce labor costs. The rise of Industry 4.0 technologies, including IoT and AI, is further transforming how overhead conveyors are designed and integrated into manufacturing systems, allowing for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance.
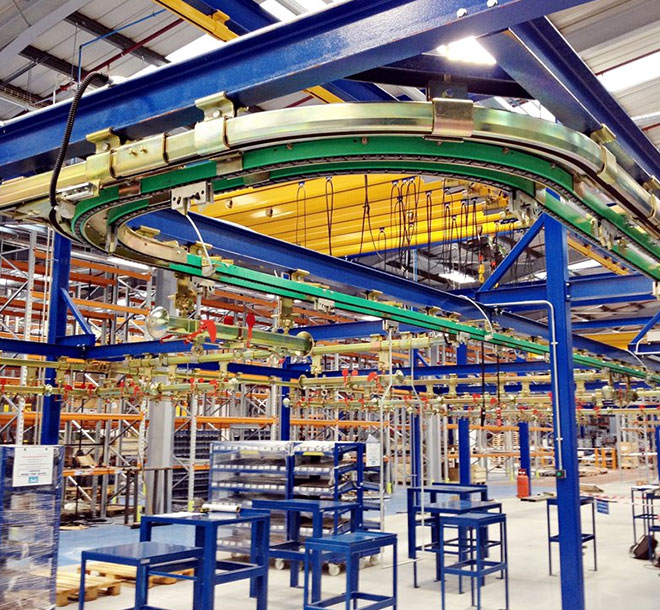

Illustrative image related to overhead conveyor design
Emerging trends in sourcing for overhead conveyor systems include a shift towards modular designs that facilitate easy scalability and customization. Buyers are increasingly interested in solutions that allow for the integration of advanced robotics and automated guided vehicles (AGVs), enhancing the overall efficiency of material handling processes. Moreover, the focus on digital twin technologies enables manufacturers to simulate and optimize conveyor system performance before actual implementation, reducing risks and improving ROI.
As global supply chains continue to evolve, B2B buyers must navigate complexities such as fluctuating raw material costs and varying lead times. The recent disruptions caused by geopolitical tensions and the COVID-19 pandemic have underscored the importance of building resilient supply chains. Buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers that offer transparency in their sourcing processes and can adapt to changing market conditions.
How is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Trends in Overhead Conveyor Design?
Sustainability has become a crucial consideration in the sourcing of overhead conveyor systems. As environmental regulations tighten globally, manufacturers are compelled to adopt sustainable practices throughout their supply chains. This includes minimizing waste, reducing energy consumption, and utilizing eco-friendly materials. For B2B buyers, selecting suppliers that prioritize sustainability is not just a compliance issue but also a strategic advantage that can enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty.
The use of ‘green’ certifications and materials is gaining traction in the overhead conveyor design sector. Buyers should look for products that incorporate recycled materials or are manufactured using energy-efficient processes. Additionally, suppliers that adhere to internationally recognized sustainability standards, such as ISO 14001, can provide assurance of their commitment to environmental stewardship.
Moreover, the shift towards a circular economy is influencing sourcing decisions. B2B buyers are increasingly seeking manufacturers that offer solutions for the entire lifecycle of their products, including end-of-life recycling and refurbishment services. By investing in sustainable conveyor systems, companies can reduce their carbon footprint while also achieving long-term cost savings through energy efficiency and reduced material waste.
What is the Historical Context of Overhead Conveyor Systems in B2B?
The evolution of overhead conveyor systems dates back to the early 20th century, with the first modern designs developed for assembly line production. The introduction of the rivetless conveyor chain by Jervis B. Webb marked a significant milestone, enabling efficient mass production techniques exemplified by the Ford Model T assembly line. Over the decades, advancements in materials and technology have led to the development of more versatile and robust conveyor systems, capable of handling various loads and integrating seamlessly with automated processes.
Today, overhead conveyors are an integral part of manufacturing and warehousing operations across multiple sectors, including automotive, food and beverage, and pharmaceuticals. As industries continue to innovate, the design and functionality of overhead conveyors are expected to evolve further, driven by the need for enhanced efficiency and sustainability. For international B2B buyers, understanding this historical context can inform sourcing decisions and highlight the importance of selecting suppliers with a proven track record of innovation and reliability.

Illustrative image related to overhead conveyor design
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of overhead conveyor design
-
How do I solve issues with overhead conveyor system compatibility?
To ensure compatibility in your overhead conveyor system, start by assessing the existing equipment and layout of your facility. Consider factors such as load capacity, track type, and operational workflow. Consult with suppliers who provide detailed design guides, layout tools, and technical specifications to tailor a solution that meets your requirements. Engaging with an experienced manufacturer can also facilitate a seamless integration of new components into your current setup, minimizing downtime and enhancing operational efficiency. -
What is the best overhead conveyor type for high-volume production?
For high-volume production, a motorized power and free overhead conveyor system is often the best choice. This system allows for independent movement of carriers, providing flexibility in operations such as assembly lines and sorting processes. It can handle heavier loads and is capable of navigating complex layouts with curves and elevation changes. Additionally, it offers the ability to pause individual carriers without stopping the entire system, which is crucial for maintaining productivity in busy environments. -
What customization options are available for overhead conveyor systems?
Customization options for overhead conveyor systems are extensive and can include modifications in track design, load capacity, and operational features. Buyers can opt for enclosed track systems for cleaner operations or I-beam systems for heavier loads. Additional features such as variable speed drives, specific trolley attachments, and even automated controls can be integrated. Discussing your specific needs with manufacturers will help ensure that the conveyor system is tailored to optimize your production processes. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for overhead conveyor systems?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for overhead conveyor systems can vary widely based on the manufacturer and the complexity of the design. Generally, MOQs may range from a few units for standard systems to larger quantities for customized solutions. To secure the best pricing and lead times, it is advisable to communicate your requirements early in the sourcing process. Engaging with multiple suppliers can also provide leverage in negotiating MOQs that align with your project needs. -
How should I vet suppliers for overhead conveyor systems?
Vetting suppliers for overhead conveyor systems involves several steps. Start by checking their experience in the industry and reviewing customer testimonials or case studies. Assess their technical capabilities, including design flexibility and after-sales support. Ensure they comply with international standards and certifications relevant to your market. Request references from previous clients and consider conducting site visits if feasible, to gain firsthand insight into their manufacturing processes and product quality. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing conveyor systems internationally?
Payment terms when sourcing overhead conveyor systems internationally can vary depending on the supplier and transaction size. Common terms include a deposit upfront (typically 30-50%) with the balance due before shipment or upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment terms for larger orders. It’s essential to discuss and agree on payment terms clearly in the contract to avoid misunderstandings and ensure a smooth transaction. -
What quality assurance processes should I look for in conveyor system suppliers?
Quality assurance processes are critical when selecting suppliers for overhead conveyor systems. Look for suppliers that have established quality management systems, such as ISO 9001 certification. Inquire about their testing procedures, including load testing and durability assessments, to ensure that products meet specified standards. Additionally, check if they provide warranties and guarantees, which can be indicators of their commitment to quality and customer satisfaction. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing conveyor systems?
When importing overhead conveyor systems, logistics considerations are paramount. Ensure you understand customs regulations, duties, and taxes that may apply to your import. Coordinate with suppliers to determine shipping methods that balance cost and delivery time. It’s also advisable to work with experienced freight forwarders who can navigate international shipping complexities and provide reliable tracking and insurance options. Proper logistics planning will help mitigate delays and additional costs, ensuring a smooth delivery process.
Top 5 Overhead Conveyor Design Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Rapid Industries – Overhead Conveyor Systems
Domain: rapidindustries.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Overhead Conveyor Systems: Rapid Flex (enclosed track), Rapid Flow Q (Power + Free), Rapid Flow 3×3 (Power + Free), Rapid Flow 4×4 (Power + Free). System Integration, Floor Conveyors, Conveyor Systems Components including Take Ups, Drives, Track, IBeam. Services offered: Fabrication, Engineering, Installation, Support. Design Guides available: Design Guide (technical details and spec drawings), La…
2. Ultimation – Overhead Conveyors
Domain: ultimationinc.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Overhead conveyors are commonly used in production facilities to move parts, utilizing vertical space above work areas. They can pass through areas inaccessible to humans, like ovens and robot work cells. Ultimation classifies overhead conveyors by movement system (hand pushed, motorized, power and free), track style (I-beam or Unibilt enclosed track), and installation orientation (overhead or inv…
3. PAC-LINE™ – Enclosed Track Conveyors
Domain: pacline.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: PAC-LINE™ enclosed track conveyor, PAC-MAX™ heavy duty conveyor, Power and Free conveyor system, PAC-BEAM™ monorail conveyor, PAC-TRAK™ towline system, PAC-RAK™ vertical conveyor. PAC-LINE™: medium-capacity, 50 lbs. per pendant; PAC-MAX™: heavy-duty, 220 lbs. per trolley; Power and Free: asynchronous conveying; I-Beam conveyor: heavy loads, available in 3″, 4″, and 6″ track heights. Customization …
4. Overhead Conveyor Systems – Key Features
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Overhead conveyor systems utilize a drive system that typically includes a motor connected to a gearbox, which reduces the RPM and rotates a sprocket. This sprocket is linked to a chain. The discussion also mentions the use of an I-beam conveyor for heavier loads, indicating a preference for this design over an enclosed beam.
5. Webb-Stiles – Overhead Conveyor Systems
Domain: webb-stiles.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Overhead Conveyor Systems by Webb-Stiles are material handling systems that move products along a suspended track, allowing items to travel above ground-level operations. They utilize trolleys mounted to an I-beam or enclosed track to transport parts through various workstations without interrupting activity below. Key types include Monorail Conveyors, Enclosed Track Conveyors, Power & Free Convey…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for overhead conveyor design
Why is Strategic Sourcing Essential for Overhead Conveyor Systems?
In today’s competitive landscape, the strategic sourcing of overhead conveyor systems is paramount for optimizing operational efficiency and ensuring cost-effectiveness. By leveraging comprehensive design guides and understanding the nuances of various conveyor types, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific needs. Key factors such as load capacity, installation orientation, and modularity should be carefully considered to maximize productivity while minimizing downtime.
How Can International Buyers Benefit from Custom Overhead Conveyor Solutions?
Investing in tailored overhead conveyor solutions not only enhances workflow but also capitalizes on the often-overlooked vertical space in manufacturing environments. Regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe stand to gain significantly by adopting advanced conveyor technologies that integrate seamlessly with emerging automation trends. This adaptability is crucial for businesses looking to maintain a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market.
What’s Next for Businesses Looking to Implement Overhead Conveyors?
As industries continue to innovate, the demand for efficient, reliable overhead conveyor systems will only increase. We encourage B2B buyers to engage with reputable suppliers and leverage their expertise to explore the best options for their unique operational challenges. The future of overhead conveyor design is bright, and now is the ideal time to invest in solutions that will propel your business forward.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
Illustrative image related to overhead conveyor design
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.