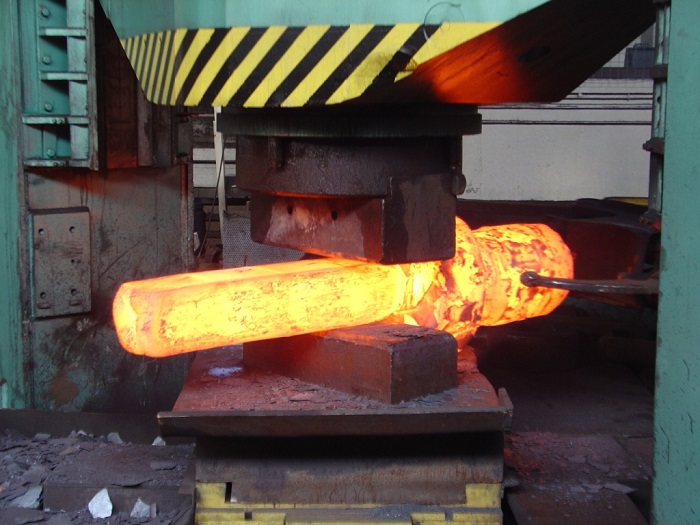
A B2B Buyer’s Guide to Open Die Forge: Price, Quality, and Suppliers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for open die forge
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing reliable open die forging solutions can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe strive for innovation and efficiency, understanding the nuances of open die forging becomes paramount. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, delving into the various types of open die forging processes, their applications, and the essential criteria for vetting suppliers. With insights into cost considerations and quality assurance, we aim to empower businesses to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their specific needs.
Open die forging, characterized by its versatility and ability to produce large components, is crucial for sectors such as oil and gas, aerospace, and manufacturing. By highlighting the strengths and limitations of this method, the guide equips buyers with the knowledge necessary to assess potential suppliers effectively. Whether you are navigating complex supply chains or seeking high-quality forged parts tailored to your specifications, this resource will enhance your understanding of open die forging and its significance in the global market. Ultimately, it aims to facilitate strategic partnerships that drive operational success and foster growth in your industry.
Understanding open die forge Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flat Die Forging | Uses flat dies for simple shapes; high versatility. | Bars, plates, and simple components. | Pros: Low tooling costs, quick setup. Cons: Limited to simpler geometries. |
| Swaging | Involves reducing the diameter of a workpiece by radial compressive forces. | Manufacturing shafts and tubes. | Pros: Efficient material use, precise dimensions. Cons: More complex setup. |
| V-Dies Forging | Utilizes V-shaped dies for specific contouring needs. | Specialized components in automotive. | Pros: Enhanced shape definition, good for medium runs. Cons: Limited to specific shapes. |
| Mandrel Forging | Employs mandrels to create hollow shapes and tubes. | Oil and gas pipelines, aerospace parts. | Pros: Produces complex hollow forms, strong structures. Cons: Requires precise alignment. |
| Custom Open Forging | Tailored processes for unique specifications and designs. | Aerospace, defense, and heavy machinery. | Pros: High customization, improved mechanical properties. Cons: Potentially higher costs for low volumes. |
What Are the Characteristics of Flat Die Forging?
Flat die forging is characterized by its use of flat dies, allowing for the production of simple, larger components such as bars and plates. This method is particularly suitable for applications requiring basic shapes with minimal complexity. B2B buyers should consider flat die forging for projects with lower budgets and shorter lead times, as it incurs little tooling cost and offers flexibility in production.
How Does Swaging Differ in Open Die Forging?
Swaging is a unique open die forging technique that reduces the diameter of a workpiece through radial compressive forces. This method is commonly employed in the manufacturing of shafts and tubes, making it ideal for industries like automotive and aerospace. Buyers should evaluate swaging when precision and material efficiency are priorities, although they may encounter slightly more complex setups compared to traditional flat die forging.
What Advantages Do V-Dies Forging Offer?
V-dies forging utilizes V-shaped dies to create specific contours, making it particularly advantageous for producing specialized components in sectors such as automotive and machinery. This method strikes a balance between shape definition and production efficiency, appealing to B2B buyers who need medium runs of parts with unique geometries. However, its limitation to certain shapes may restrict its application for more versatile projects.
Why Choose Mandrel Forging for Hollow Shapes?
Mandrel forging is designed to produce hollow shapes and tubes, which is essential for industries like oil and gas and aerospace. This technique allows for the creation of complex hollow forms with enhanced structural integrity. When considering mandrel forging, B2B buyers should weigh its ability to deliver strong, lightweight components against the need for precise alignment during production, which can complicate the process.

Illustrative image related to open die forge
How Does Custom Open Forging Enhance B2B Solutions?
Custom open forging is tailored for unique specifications, offering high levels of customization and the ability to improve mechanical properties. This method is particularly beneficial for industries such as aerospace and defense, where specialized parts are required. B2B buyers should consider custom open forging for projects demanding specific designs, although they may face higher costs for low-volume production runs compared to standard processes.
Key Industrial Applications of open die forge
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of open die forge | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oil & Gas | Production of large flanges and fittings | Enhanced strength and durability for harsh environments | Ensure high-quality materials and compliance with industry standards |
| Mining | Manufacturing of heavy-duty shafts | Ability to withstand extreme operational conditions | Seek suppliers with experience in high-volume production and quality assurance |
| Aerospace | Custom forging of engine components | Lightweight yet strong parts for improved efficiency | Look for manufacturers with precision capabilities and certifications |
| Power Generation | Creation of turbine components | High-performance parts that meet stringent safety standards | Verify sourcing of high-grade alloys and reliable supply chains |
| Construction & Infrastructure | Production of structural beams and supports | Cost-effective solutions with reduced lead times | Assess the flexibility of suppliers in adapting to project specifications |
How is Open Die Forging Used in the Oil & Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas sector, open die forging is critical for producing large flanges, fittings, and other components that must withstand extreme pressures and corrosive environments. The process allows for the creation of robust parts that enhance the integrity of pipelines and drilling equipment. International buyers should consider sourcing from manufacturers who can provide high-quality materials that comply with industry standards, ensuring durability and reliability in challenging conditions.
What Role Does Open Die Forging Play in Mining Applications?
Mining operations require heavy-duty shafts and components that can endure rigorous use. Open die forging is utilized to manufacture these parts, providing enhanced strength and fatigue resistance. Buyers in this sector should prioritize suppliers who have a proven track record in high-volume production and stringent quality assurance processes, as these factors are crucial for maintaining operational efficiency and safety in mining environments.
How is Open Die Forging Beneficial for Aerospace Components?
In aerospace, open die forging is employed to create custom engine components that are lightweight yet strong, essential for optimizing fuel efficiency and performance. This method allows for the production of complex shapes while maintaining tight tolerances. Buyers should seek manufacturers with advanced precision capabilities and relevant certifications to ensure that the components meet the rigorous safety and performance standards required in the aerospace industry.
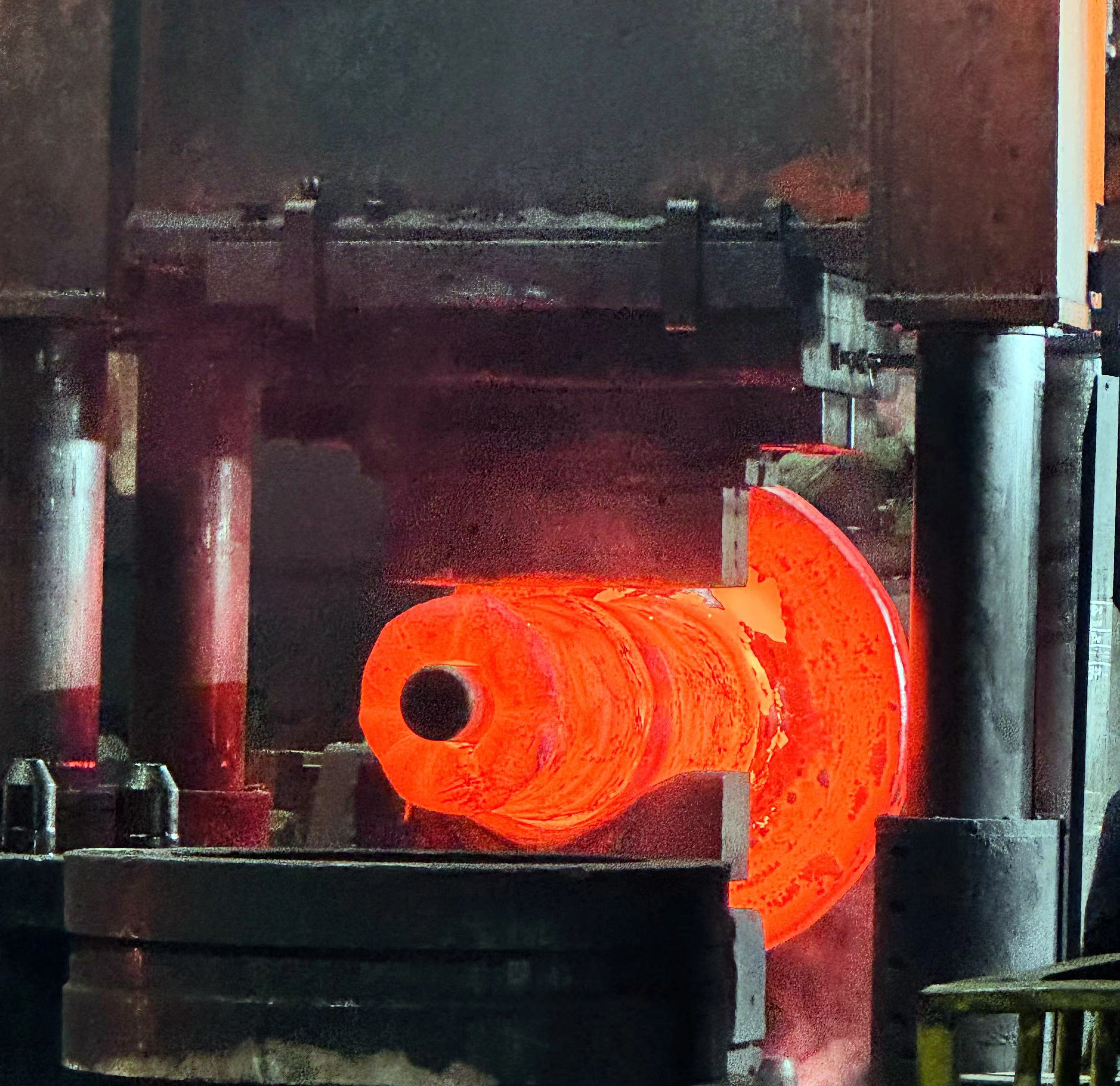

Illustrative image related to open die forge
What Advantages Does Open Die Forging Offer in Power Generation?
Open die forging is vital in the power generation industry for the creation of turbine components that must perform reliably under high-stress conditions. The process enables the production of high-performance parts that meet stringent safety and operational standards. When sourcing, companies should verify that suppliers utilize high-grade alloys and have reliable supply chains, as these factors significantly impact the quality and longevity of the components.
How is Open Die Forging Utilized in Construction & Infrastructure Projects?
In construction and infrastructure, open die forging is commonly used to produce structural beams and supports that require both strength and versatility. This method is advantageous for its cost-effectiveness and reduced lead times, making it suitable for large-scale projects. Buyers should evaluate suppliers based on their ability to adapt to specific project requirements and their capacity to deliver high-quality forged products in a timely manner.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘open die forge’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Quality in Open Die Forgings
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face challenges with the inconsistency in quality when sourcing open die forgings. This inconsistency can stem from variations in the forging process, including temperature control during heating, hammering techniques, and the skill level of operators. In industries such as aerospace and oil and gas, where precision is crucial, any deviation in quality can lead to significant operational issues, increased downtime, and financial losses.
The Solution: To mitigate these quality issues, buyers should prioritize suppliers that implement strict quality control measures and standardized processes. Request detailed information about the supplier’s quality assurance protocols, including their use of non-destructive testing (NDT) methods to identify flaws in the material. Additionally, consider suppliers that utilize advanced technologies, such as automated temperature monitoring and programmable forging machines, to ensure consistency in production. Establishing a collaborative relationship with the supplier can also facilitate better communication regarding quality expectations and allow for adjustments in the production process based on feedback.
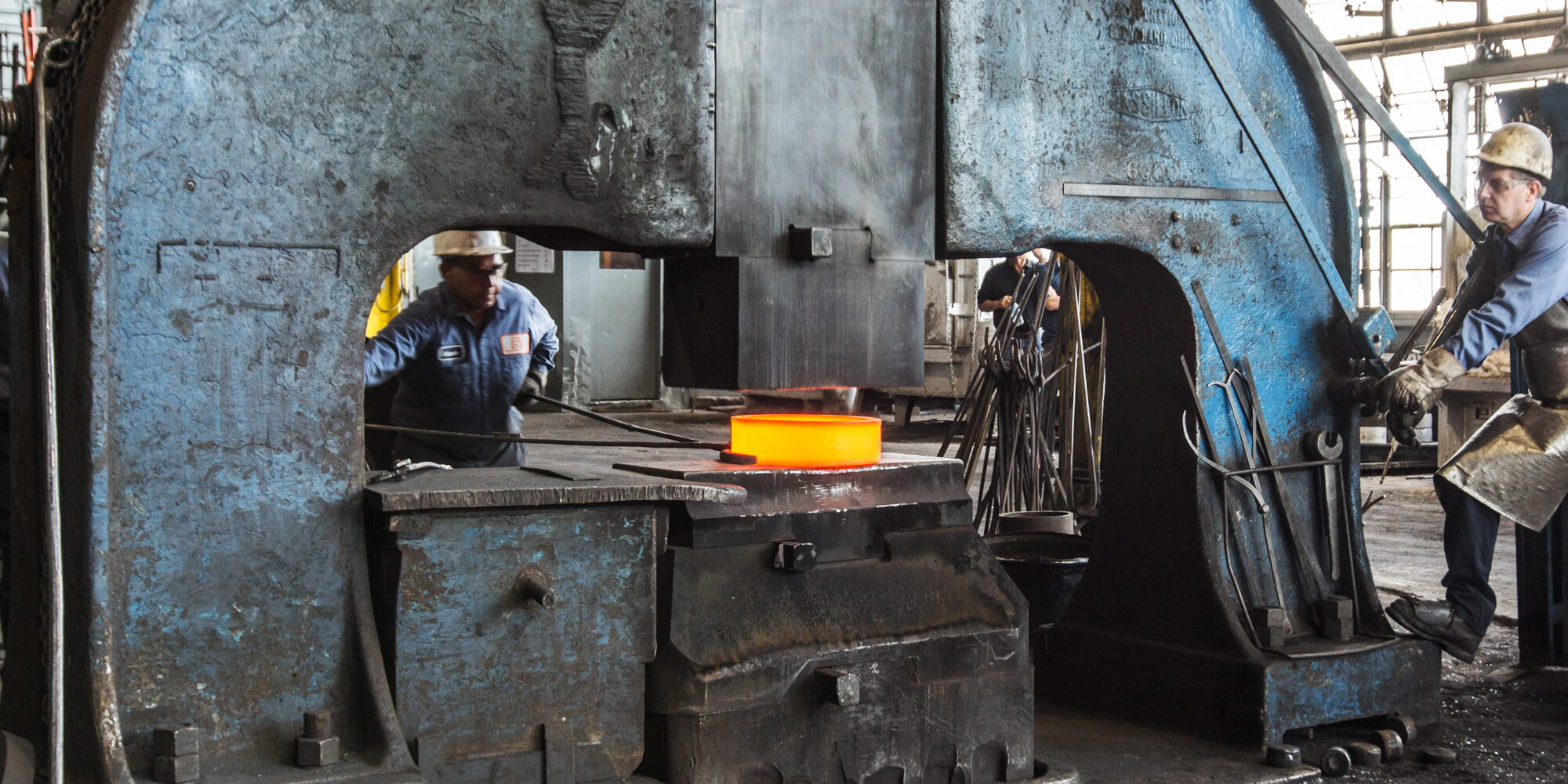

Illustrative image related to open die forge
Scenario 2: Limited Customization Options for Unique Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter limitations when seeking custom solutions through open die forging. Many manufacturers may not offer the flexibility required for unique designs or specific material requirements, resulting in parts that do not meet the buyer’s precise needs. This limitation can hinder innovation and the ability to respond effectively to market demands, especially for businesses involved in niche markets or specialized applications.
The Solution: To overcome these customization challenges, buyers should look for open die forging suppliers that specialize in bespoke manufacturing solutions. Engage in discussions about the specific requirements of your projects, including dimensions, tolerances, and material specifications. Suppliers with extensive experience in open die forging often have the capability to accommodate custom designs without the need for complex tooling, thereby reducing lead times and costs. Additionally, consider leveraging computer-aided design (CAD) tools to present your designs clearly to potential suppliers, ensuring that your vision is accurately conveyed and understood.
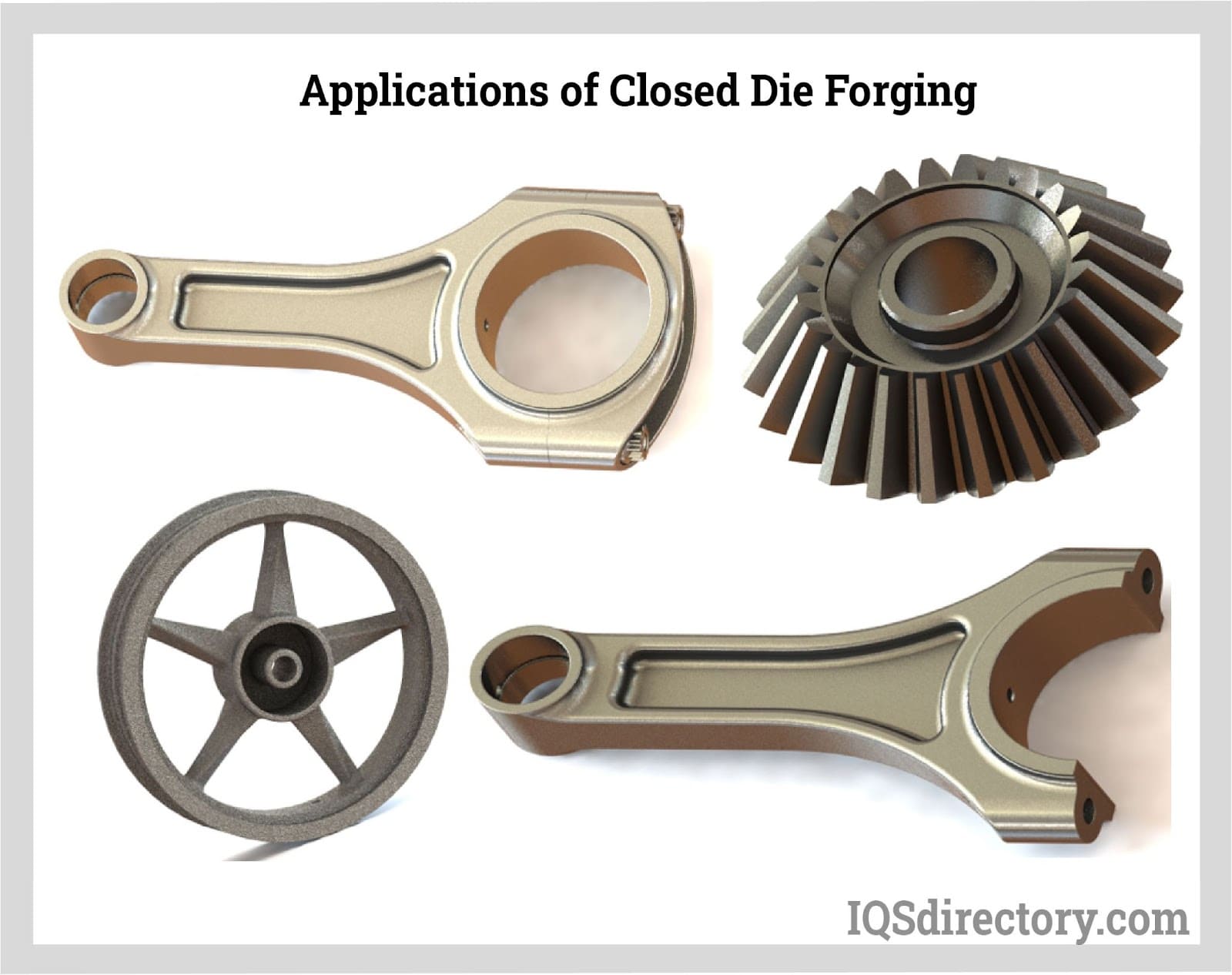
Scenario 3: High Production Costs and Inefficient Lead Times
The Problem: High production costs and inefficient lead times can be significant barriers for B2B buyers utilizing open die forging. Factors such as the need for additional machining, long setup times, and fluctuating material costs can drive up expenses and delay project timelines. This situation is particularly problematic for companies that require rapid prototyping or short production runs to remain competitive.
Illustrative image related to open die forge
The Solution: To address these issues, buyers should seek suppliers that offer integrated services combining open die forging with in-house machining capabilities. This integration can streamline the production process, reducing the need for outsourcing and minimizing lead times. Additionally, establishing a long-term partnership with a reliable supplier can lead to cost savings through negotiated pricing based on consistent order volumes. Buyers should also inquire about the supplier’s inventory management practices to ensure they can accommodate fluctuating demands without incurring unnecessary costs. By collaborating closely with the supplier on production planning, buyers can optimize their supply chain and enhance overall efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for open die forge
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Open Die Forging?
Open die forging is a versatile manufacturing process that allows for the shaping of various metals into custom components. The choice of material significantly influences the performance, durability, and overall suitability of the forged products. Here, we analyze four common materials used in open die forging: carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, and titanium.
How Does Carbon Steel Perform in Open Die Forging Applications?
Carbon steel is one of the most widely used materials in open die forging due to its excellent balance of strength, ductility, and cost-effectiveness. Key properties include high tensile strength and good wear resistance, making it suitable for applications that require durability under stress. However, carbon steel has limited corrosion resistance, which can be a drawback in corrosive environments.
Pros: Carbon steel is relatively inexpensive and easy to machine, making it ideal for large production runs. Its versatility allows for a wide range of applications, from automotive components to structural parts.
Cons: The primary limitation is its susceptibility to rust and corrosion, necessitating protective coatings or treatments for certain applications. Additionally, it may require post-forging machining to achieve precise dimensions.
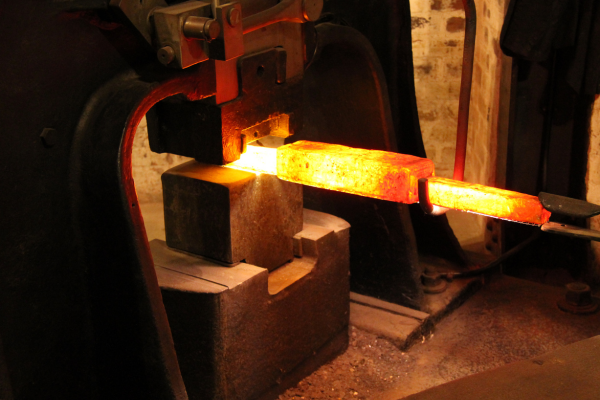

Illustrative image related to open die forge
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is commonly used in industries such as construction and automotive, where strength is critical. However, in humid or corrosive environments, buyers must consider additional protective measures.
What Advantages Does Alloy Steel Offer in Open Die Forging?
Alloy steel is engineered to enhance specific properties, such as toughness, hardness, and wear resistance. The addition of elements like chromium, nickel, and molybdenum improves its performance in high-stress applications. Alloy steel typically exhibits higher temperature and pressure ratings compared to carbon steel.
Pros: The enhanced mechanical properties make alloy steel suitable for high-performance applications, such as aerospace and oil and gas industries. It also provides better fatigue resistance and can be heat-treated for improved strength.
Cons: The complexity of alloy steel manufacturing can lead to higher costs. Additionally, certain alloys may require specialized forging techniques or equipment, increasing production complexity.
Impact on Application: Alloy steel is often preferred in applications that demand high performance and durability, particularly in harsh environments. B2B buyers should consider compliance with international standards, as specific alloy compositions may be required for certain applications.
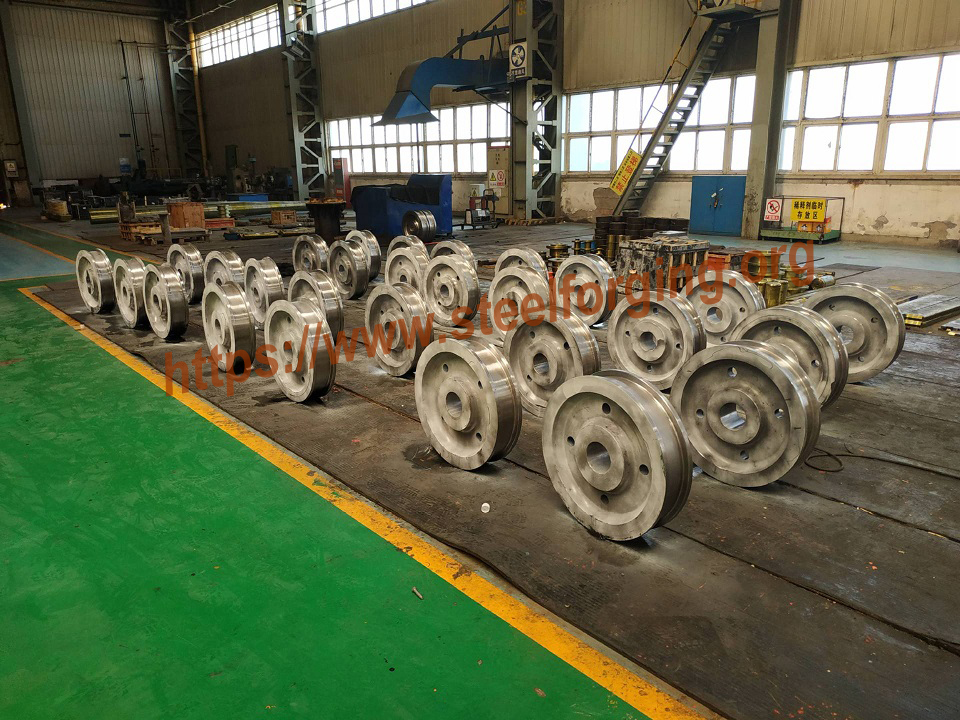

Illustrative image related to open die forge
How Does Stainless Steel Compare in Open Die Forging?
Stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, making it a popular choice for applications where hygiene and appearance are critical. Key properties include excellent resistance to oxidation and scaling at elevated temperatures, which enhances its longevity in various environments.
Pros: Stainless steel offers superior durability and is less prone to rust, making it ideal for food processing, medical devices, and marine applications. Its strength-to-weight ratio is also favorable, providing robust performance without excessive weight.
Cons: The primary drawback is the higher cost compared to carbon and alloy steels. Additionally, stainless steel can be more challenging to machine, which may require specialized tools and processes.
Impact on Application: In industries such as food processing and pharmaceuticals, compliance with hygiene standards is crucial. Buyers from regions with stringent regulations, such as Europe, must ensure that the selected stainless steel grades meet relevant standards.
What Role Does Titanium Play in Open Die Forging?
Titanium is a lightweight, high-strength material known for its exceptional corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, making it ideal for specialized applications like aerospace and medical implants. Key properties include a high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent resistance to extreme temperatures.
Illustrative image related to open die forge
Pros: Titanium’s unique properties allow for the production of components that can withstand harsh environments, including high temperatures and corrosive media. Its biocompatibility makes it suitable for medical applications.
Cons: The main limitation is the high cost of titanium, which can be prohibitive for large-scale production runs. Additionally, titanium forging requires specialized equipment and expertise, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: B2B buyers in aerospace or medical sectors must consider the stringent quality standards and certifications required for titanium components. Compliance with international standards like ASTM and ISO is essential for successful procurement.
Summary of Material Selection for Open Die Forging
| Material | Typical Use Case for open die forge | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Automotive components, structural parts | Cost-effective and versatile | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Alloy Steel | Aerospace, oil and gas applications | Enhanced mechanical properties | Higher manufacturing complexity | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, medical devices | Superior corrosion resistance | Higher cost and machining difficulty | High |
| Titanium | Aerospace, medical implants | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | High cost and complex manufacturing | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of common materials used in open die forging. Understanding these factors will enable B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific application needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for open die forge
What Are the Key Stages of the Open Die Forging Manufacturing Process?
Open die forging is a versatile manufacturing process that involves several key stages to transform raw materials into high-quality forged components. Understanding these stages is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure they are making informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
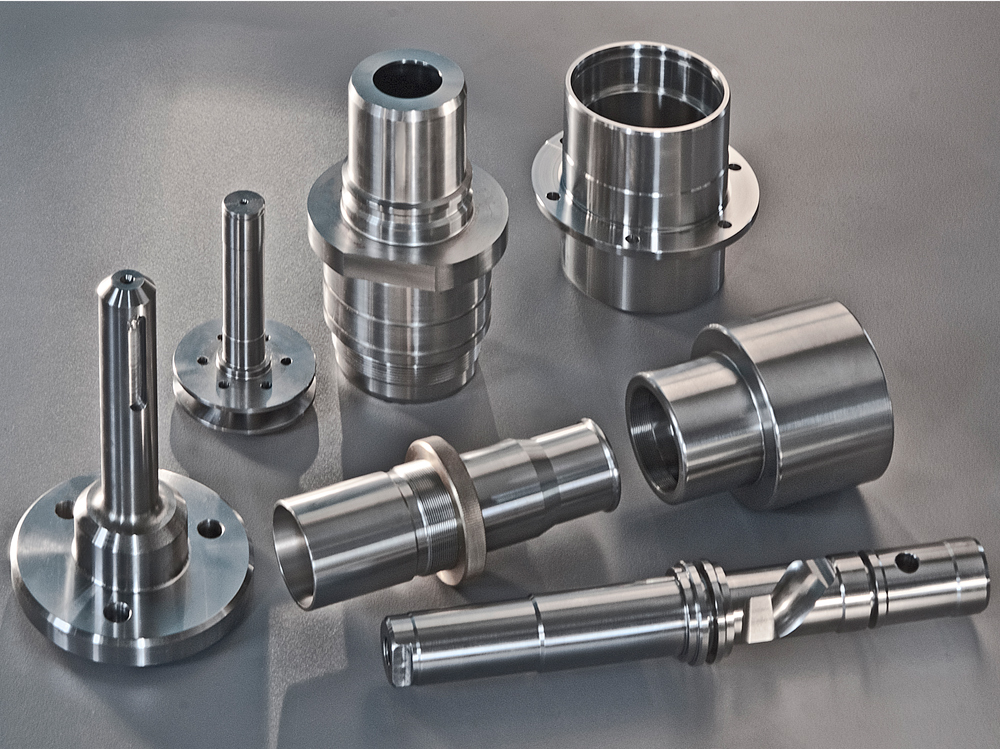

Illustrative image related to open die forge
Material Preparation: How Is Raw Material Readied for Forging?
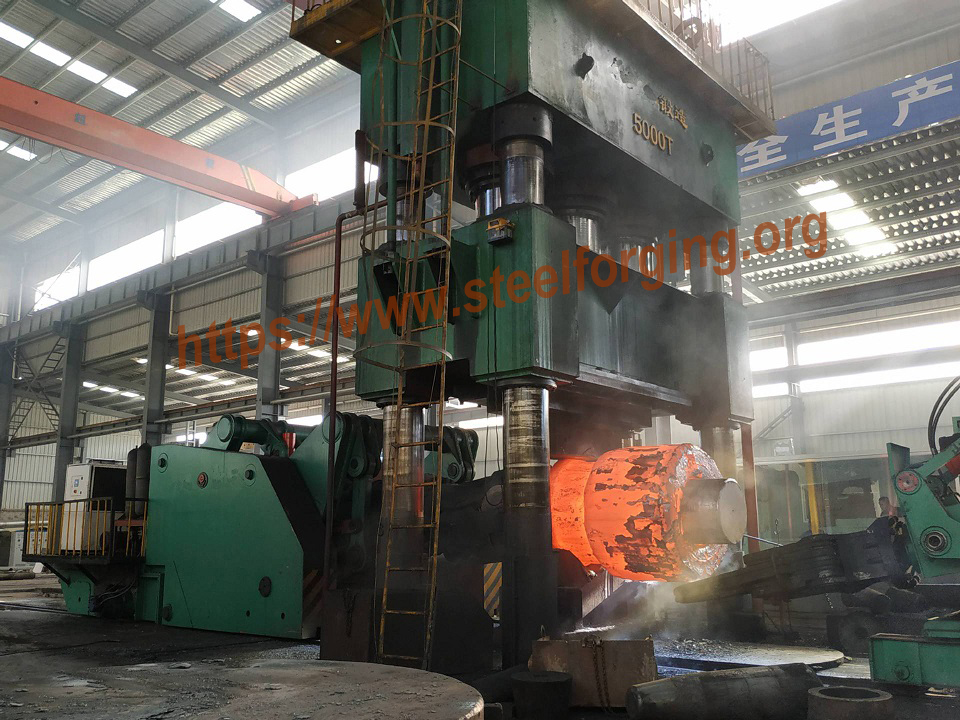
The first stage of the open die forging process involves selecting and preparing the raw material, typically in the form of cast ingots or billets. These materials are carefully chosen based on their chemical composition and mechanical properties, which can significantly affect the performance of the final product.
Once selected, the material is heated to a temperature suitable for deformation, usually between 1,100°C to 1,300°C for carbon steel. This heating process is critical, as it ensures that the metal becomes malleable enough to be shaped without cracking. The heating is often conducted in gas-fired or induction furnaces, which allows for uniform temperature distribution.
What Techniques Are Commonly Used in Open Die Forging?
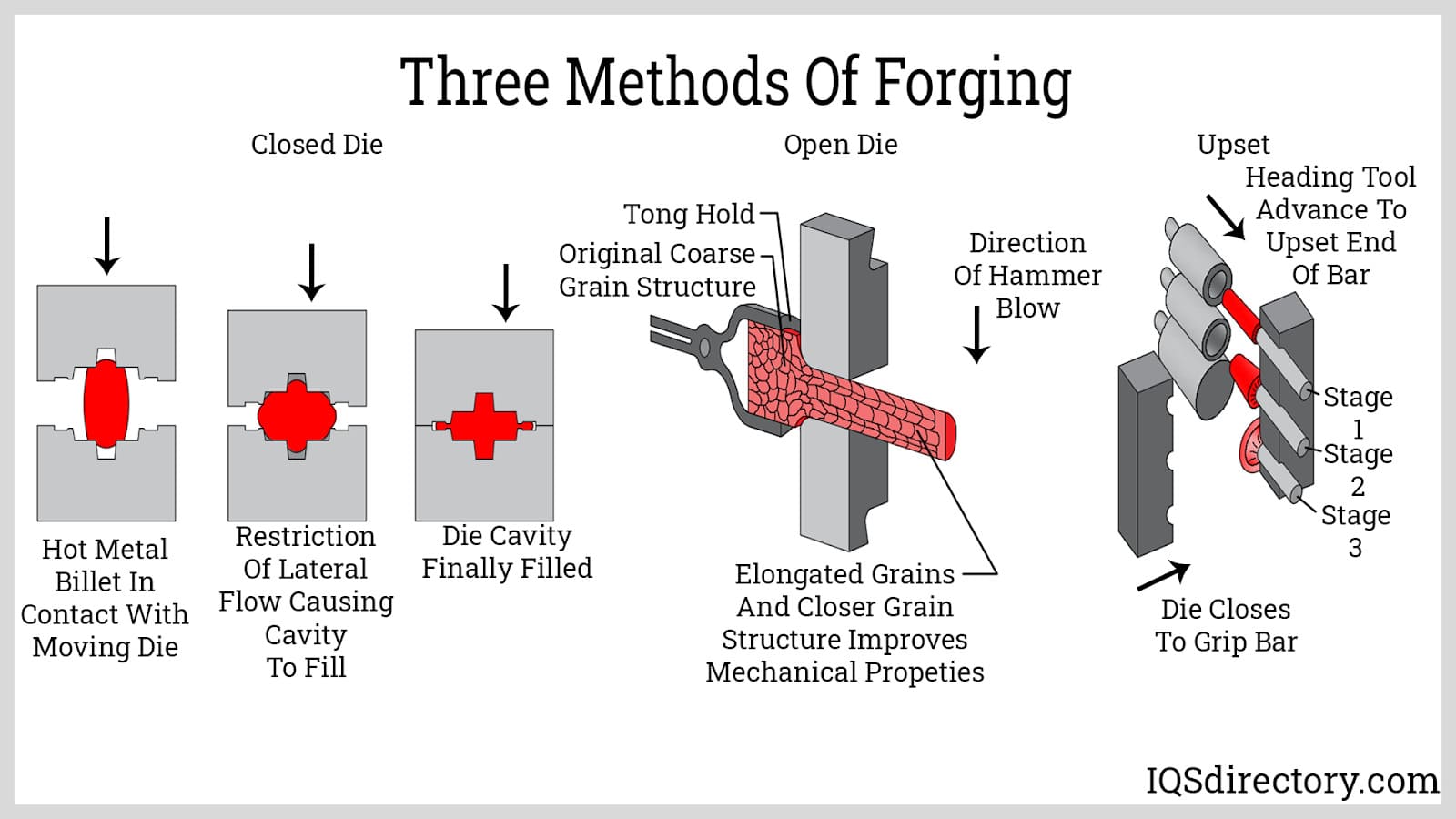
Forming: What Are the Main Techniques for Shaping Metal?
After the material is adequately heated, it undergoes the forming stage, where various techniques can be employed. The most common methods include hammering and pressing.
-
Hammering: This traditional method involves striking the heated metal with a hammer, either manually or using mechanized hammers, to deform the metal into the desired shape. This technique is particularly effective for achieving specific grain flow patterns that enhance the mechanical properties of the final product.
-
Pressing: In this method, the heated metal is placed between flat or shaped dies, and a hydraulic press applies force to mold the material. This technique is often used for larger components that require a more uniform shape and size.
The choice between these techniques often depends on the complexity and dimensions of the desired part, as well as the production volume.
How Does the Finishing Process Enhance the Quality of Open Die Forged Parts?
Once the metal has been formed, it goes through a finishing stage, which may involve several processes such as machining, heat treatment, and surface finishing.

Illustrative image related to open die forge
-
Machining: Although open die forging can produce rough shapes, machining is typically required to achieve precise dimensions and surface finishes. This involves using CNC machines to remove excess material and create features such as holes or grooves.
-
Heat Treatment: Post-forging heat treatments, such as quenching and tempering, are often applied to enhance the mechanical properties of the forged parts. These treatments improve hardness, strength, and ductility, making the parts suitable for demanding applications.
-
Surface Finishing: Techniques like shot blasting or polishing may be employed to improve the surface finish and remove any oxidation or scale formed during the forging process. A better surface finish not only enhances aesthetic appeal but also increases resistance to corrosion.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Essential for Open Die Forging?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of the open die forging process, particularly for B2B buyers who require reliable and consistent products. Understanding relevant international standards and industry-specific certifications can help buyers assess potential suppliers effectively.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Look For?
ISO 9001 is the most widely recognized international standard for quality management systems. Compliance with this standard indicates that a supplier has established procedures to ensure consistent product quality and customer satisfaction. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate ISO 9001 certification, as it reflects a commitment to quality.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications may also be relevant. For instance, the API (American Petroleum Institute) certification is crucial for suppliers serving the oil and gas sector, while CE marking is important for products destined for the European market. These certifications assure buyers that the products meet specific regulatory and safety standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Open Die Forging?
How Do QC Checkpoints Ensure Product Integrity?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated throughout the open die forging process to ensure that each stage meets established standards. These checkpoints typically include:
Illustrative image related to open die forge
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting the raw materials to confirm they meet the specified chemical and mechanical properties before they are processed.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the forging and machining stages, operators conduct real-time inspections to monitor dimensional accuracy and surface quality. This proactive approach helps identify and address any issues before they escalate.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the parts are completed, they undergo a final inspection that includes dimensional checks, surface finish evaluations, and mechanical property testing. This stage is crucial for verifying that the finished products meet customer specifications and industry standards.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Open Die Forging Quality Assurance?
Which Testing Methods Can Validate the Quality of Forged Parts?
Several testing methods are employed to ensure the quality of open die forged components:
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing, radiographic testing, and magnetic particle inspection are used to identify internal defects without damaging the parts. These methods provide valuable insights into the integrity of the forged components.
-
Destructive Testing: Mechanical tests, including tensile, impact, and fatigue testing, are conducted to evaluate the material properties of the forged parts. These tests provide definitive data on how the components will perform under operational conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Assurance Practices?
What Steps Should Buyers Take to Ensure Supplier Compliance?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify a supplier’s quality assurance practices:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide firsthand insight into a supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control systems. This allows buyers to assess compliance with international standards and industry-specific certifications.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask suppliers for detailed quality reports that outline inspection results, testing methods, and compliance with relevant standards. This documentation is essential for making informed decisions.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality assurance practices. This adds an extra layer of confidence in the supplier’s capabilities.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
How Do Regional Differences Affect Quality Assurance Practices?
For B2B buyers operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding regional differences in quality assurance practices is vital. Buyers should be aware that regulatory standards can vary significantly across countries. Engaging local representatives or consultants who understand the specific requirements and certifications in each region can facilitate smoother transactions and ensure compliance.
Additionally, cultural differences may affect communication and expectations regarding quality. Establishing clear agreements and expectations upfront can help mitigate misunderstandings and foster successful supplier relationships.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures involved in open die forging, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring they partner with suppliers that meet their rigorous standards for quality and reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘open die forge’
In the competitive landscape of B2B procurement, sourcing open die forge services requires careful consideration and strategic planning. This guide serves as a step-by-step checklist to ensure that you make informed decisions that align with your business objectives and technical requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Start by clearly outlining your technical requirements. This includes the type of material (e.g., carbon steel, stainless steel) and the dimensions of the components you need. Having precise specifications ensures you communicate effectively with potential suppliers and helps them determine if they can meet your needs.
- Consider the weight and size of the parts to ensure the supplier has the necessary equipment.
- Assess the complexity of the shapes required, as open die forging is best suited for simpler designs.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in open die forging. Look for companies with a strong reputation and experience in your industry.
- Utilize online resources like industry directories and trade associations to find qualified suppliers.
- Check for customer reviews and testimonials to gauge their reliability and quality of service.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Don’t just rely on their website.
- Inquire about their forging capacity, including the maximum size and weight they can handle.
- Assess their technology and equipment to ensure they can produce the quality and specifications you require.
Step 4: Verify Certifications and Standards
Confirm that potential suppliers meet industry standards and possess relevant certifications. This step is essential for ensuring quality and compliance with international regulations.
- Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management.
- Check for compliance with industry-specific standards that may be applicable to your sector, such as ASTM or ASME.
Step 5: Request Samples and Prototypes
Before making a large order, ask for samples or prototypes. This allows you to evaluate the quality of the forgings and the supplier’s ability to meet your specifications.
- Assess the physical properties of the samples, including strength and finish.
- Test the components in real-world applications, if possible, to ensure they meet your performance requirements.
Step 6: Discuss Lead Times and Production Capacity
Understanding the supplier’s lead times is critical for planning your production schedule. Discuss their current workload and production capabilities to ensure they can meet your deadlines.
- Inquire about their typical lead times for different sizes and types of forgings.
- Ask about their flexibility in scaling production up or down based on your needs.
Step 7: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, negotiate pricing and terms. This includes not only the cost per unit but also payment terms, warranties, and service agreements.
- Be clear about your budget while being open to discussing value-added services they may offer.
- Ensure that all terms are documented to prevent misunderstandings later in the process.
By following this checklist, you can streamline your procurement process and select the right open die forge supplier to meet your business needs effectively.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for open die forge Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Open Die Forging?
When sourcing open die forgings, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type of metal used significantly influences costs. Common materials like carbon steel or stainless steel vary in price based on market demand and availability. Specialty alloys may incur higher costs due to their unique properties.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential in the forging process, affecting the overall cost. Labor rates can differ widely between regions, with countries in Africa and South America often presenting lower labor costs than European counterparts.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the operational costs of running a forging facility, including utilities, equipment maintenance, and indirect labor. Buyers should inquire about a supplier’s overhead costs as they can impact the final pricing.
-
Tooling: While open die forging requires less complex tooling than closed-die methods, there are still costs associated with maintaining and replacing dies. Custom tooling can also increase expenses.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous quality assurance processes ensure that the final product meets specifications. The costs associated with QC processes should be factored into pricing, especially for critical applications in industries such as aerospace or oil and gas.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary significantly based on the destination and logistics provider. Factors like Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) will determine who bears the costs and risks during transport.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the competitive landscape can help buyers gauge if margins are reasonable.
How Do Volume and Specifications Affect Pricing?
Volume and minimum order quantities (MOQ) play a pivotal role in determining pricing. Suppliers often offer tiered pricing models, where larger orders yield lower per-unit costs. International buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production needs to maximize cost efficiency.
Moreover, the complexity of specifications and customization can lead to increased prices. Custom parts with intricate designs or specific material requirements will generally cost more than standard offerings. Buyers should clearly communicate their needs to avoid unexpected costs.
What Are the Price Influencers for Open Die Forging?
Several factors influence the price of open die forgings:
-
Materials: Prices fluctuate based on global supply chains. For example, a surge in demand for steel can drive costs up, impacting the overall pricing structure.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that require specific industry certifications (like ISO 9001) may incur additional costs. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers can meet these requirements without compromising quality.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, location, and production capabilities can all affect pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may command higher prices, but they often provide better reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping and delivery is vital. Different Incoterms can shift costs and responsibilities between the buyer and supplier, impacting the total cost.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for International Buyers?
When negotiating with suppliers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, consider the following:
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate all costs associated with the procurement, including logistics, customs duties, and potential tariffs. This holistic view can inform better negotiation strategies.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If your organization has the capacity for larger orders, use this as leverage to negotiate lower prices.
-
Be Clear on Specifications: Provide detailed specifications upfront to minimize the risk of miscommunication, which can lead to costly rework.
-
Research Local Market Conditions: Familiarize yourself with local economic conditions and labor costs to better understand what constitutes a fair price.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for open die forging can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. This analysis provides indicative insights, but actual costs will depend on specific project requirements, supplier negotiations, and prevailing market conditions. Always conduct thorough due diligence and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing open die forge With Other Solutions
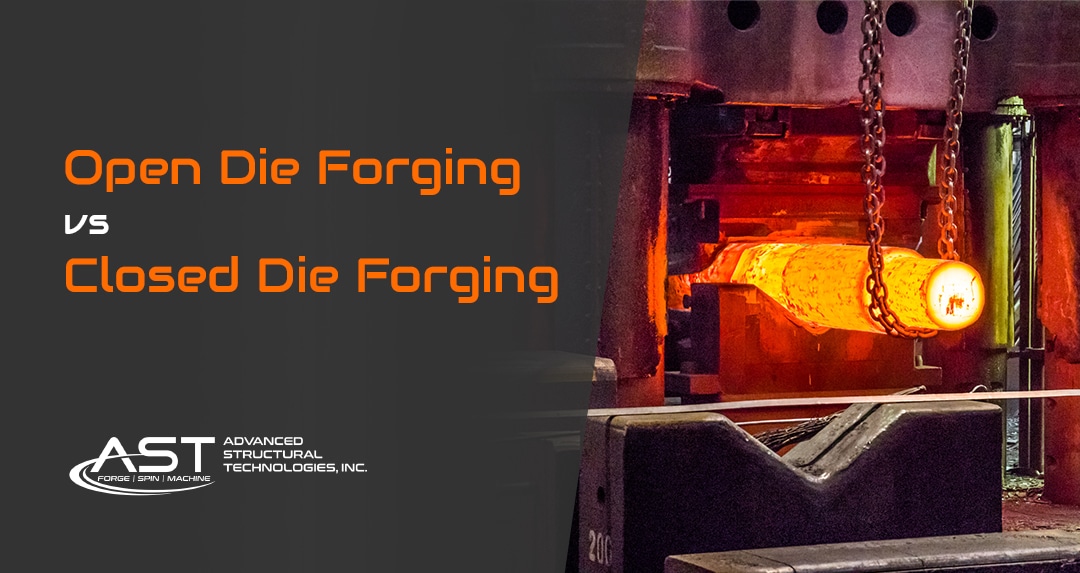
When evaluating manufacturing processes for metal components, it’s essential to consider various alternatives to open die forging. Each method has unique advantages and disadvantages, which can significantly impact production efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and product quality. Below, we compare open die forging with closed die forging and casting, two common alternatives in metalworking.
| Comparison Aspect | Open Die Forge | Closed Die Forging | Casting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Suitable for large, simple shapes; provides good strength | Produces complex shapes with high precision | Excellent for intricate designs and high-volume production |
| Cost | Low tooling costs; economical for short runs | Higher initial setup costs due to die fabrication | Generally lower cost for large volumes; tooling can be expensive |
| Ease of Implementation | Flexible and quick setup; minimal tooling required | More complex setup; requires custom dies | Requires detailed molds; longer lead time for setup |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance as equipment is simpler | Higher maintenance due to complex machinery | Maintenance varies; mold integrity is crucial |
| Best Use Case | Large parts, custom shapes, low to medium production | High-volume runs with tight tolerances | High-volume production of intricate shapes |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Closed Die Forging?
Closed die forging, also known as impression-die forging, utilizes custom-shaped dies to confine the metal during the forging process. This method excels in producing intricate designs with tighter tolerances, making it ideal for high-volume production runs. The mechanical properties of closed-die forged parts are generally superior, requiring little to no post-processing. However, the initial costs are significantly higher due to die manufacturing, which may not be economical for smaller production runs. Additionally, the complexity of the setup can lead to longer lead times.
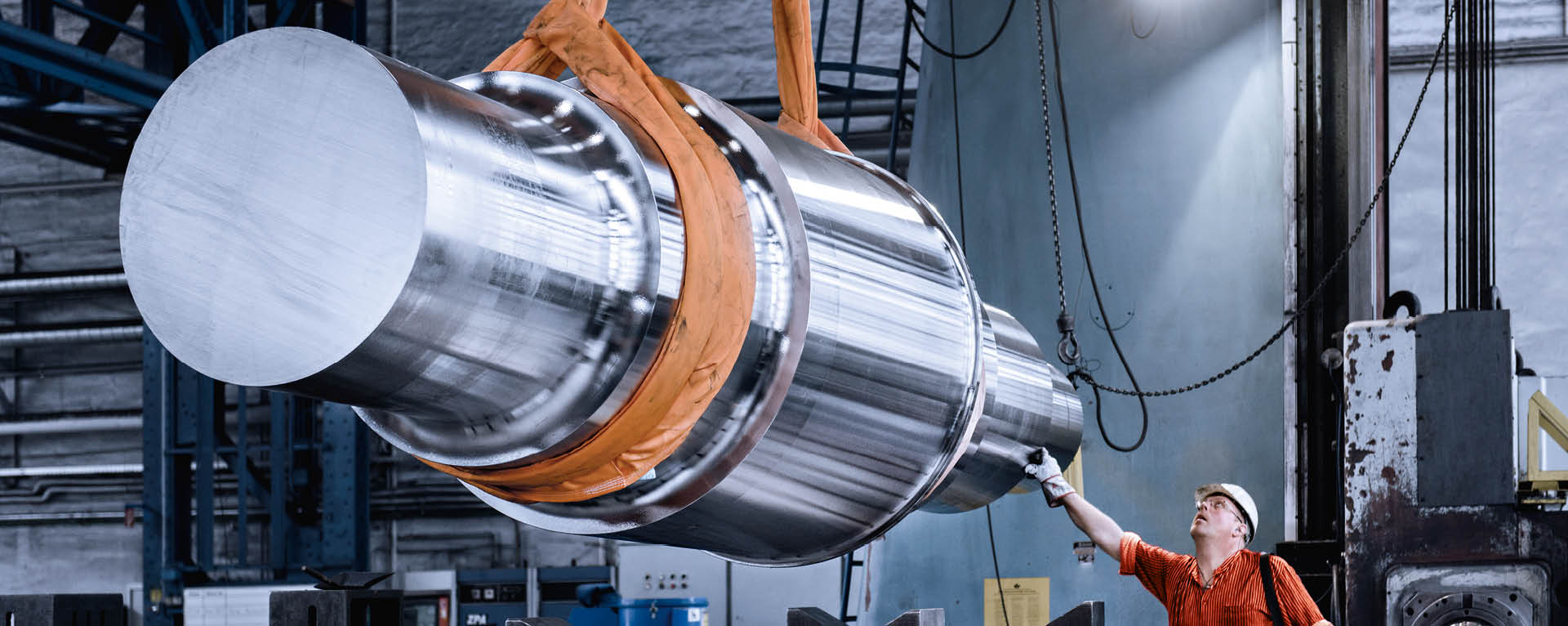

Illustrative image related to open die forge
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Casting?
Casting involves pouring molten metal into a mold to create the desired shape. This method is highly effective for producing complex geometries and is often more cost-efficient for large production volumes. Casting can accommodate a wide range of materials and is suitable for intricate designs. However, the mechanical properties of cast components may not match those of forged products, and the process can introduce defects such as porosity. Additionally, the need for detailed molds can extend lead times and increase upfront costs.
How Should B2B Buyers Decide on the Right Metalworking Solution?
For B2B buyers evaluating metalworking solutions, the choice between open die forging, closed die forging, and casting depends largely on the specific requirements of their projects. If the goal is to produce large, robust components with a quick turnaround and lower costs, open die forging may be the best option. On the other hand, for projects requiring high precision and intricate designs, closed die forging or casting might be more appropriate. Buyers should also consider production volume, material properties, and budget constraints when making their decision, ensuring that the chosen method aligns with their operational needs and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for open die forge
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Open Die Forging?
In the open die forging process, several critical technical properties play a significant role in determining the quality and suitability of the forged products for various industrial applications. Understanding these specifications is crucial for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions.
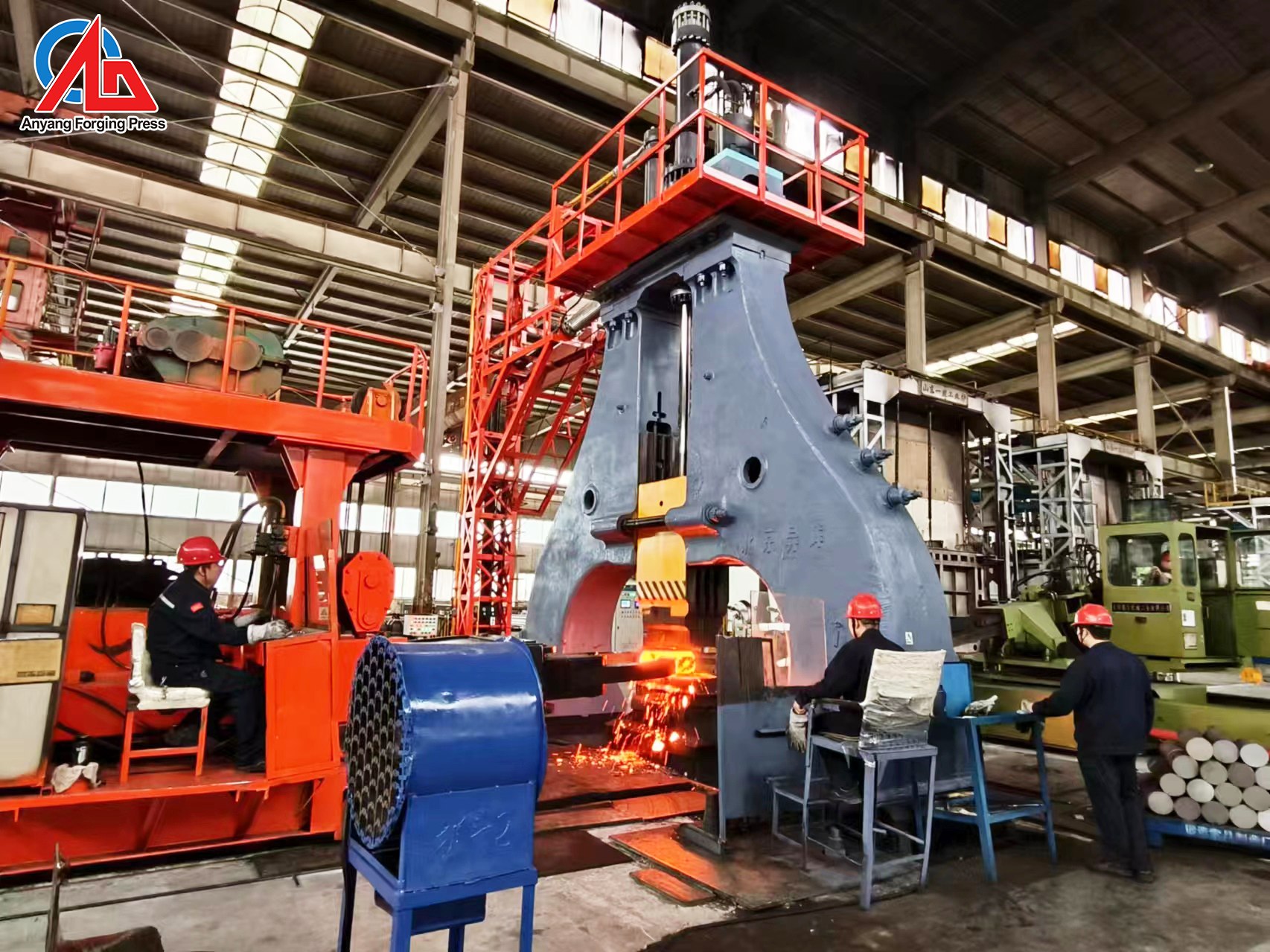

Illustrative image related to open die forge
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific composition and characteristics of the metal used in forging, such as carbon steel, stainless steel, or alloy steel. Different grades offer varying mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and strength levels. For example, 316 stainless steel is ideal for applications requiring high corrosion resistance, while carbon steel may be preferable for structural applications. Knowing the material grade helps buyers select the right metal for their specific needs, ensuring durability and performance.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance indicates the permissible limits of variation in a forged part’s dimensions. In open die forging, achieving tight tolerances can be challenging due to the nature of the process. Typically, tolerances in open die forging may range from ±0.5 mm to ±2 mm, depending on the part’s complexity and size. Understanding tolerance specifications is essential for buyers, as it impacts the need for subsequent machining processes and the overall fit and function of the component in its intended application.
3. Grain Structure
The grain structure of a forged part refers to the arrangement and size of the metal’s internal grains. Open die forging refines the grain structure, resulting in finer and more uniform grains compared to cast components. This enhancement leads to improved mechanical properties, such as strength, toughness, and fatigue resistance. Buyers should consider grain structure when assessing the performance characteristics of forged components, particularly in high-stress applications.
4. Weight Capacity
Weight capacity denotes the maximum weight that can be effectively forged using open die techniques. Open die forging allows for larger parts, ranging from a few pounds to several tons. Understanding the weight capacity is critical for buyers looking to manufacture large components, as it influences the design and feasibility of the forging process.
5. Surface Finish
Surface finish refers to the texture and smoothness of the forged product. Open die forging can produce a variety of surface finishes, from rough to polished, depending on the post-forging treatment. A good surface finish is vital for applications where aesthetics or friction characteristics are important. Buyers must communicate their surface finish requirements clearly to ensure that the final product meets their specifications.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Open Die Forging?
Familiarity with industry-specific jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and better communication between buyers and suppliers. Here are some essential terms related to open die forging:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that manufactures products that are then sold under another company’s brand. In open die forging, OEMs often require custom parts to meet specific design criteria. Understanding OEM relationships helps buyers identify reliable suppliers who can deliver quality components tailored to their needs.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. In open die forging, MOQs can vary significantly based on the complexity of the part and the production process. Buyers need to be aware of MOQs to plan their procurement strategies effectively and avoid excess inventory or stockouts.
3. RFQ (Request for Quote)
An RFQ is a document sent by a buyer to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. In the context of open die forging, submitting an RFQ enables buyers to gather competitive quotes and evaluate potential suppliers based on pricing, lead times, and capabilities.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. They specify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers engaged in global sourcing of forged components, as they impact cost calculations and risk management.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving the finished product. In open die forging, lead times can vary based on production schedules, tooling requirements, and material availability. Buyers should factor in lead times when planning their projects to ensure timely delivery and avoid delays in production.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can enhance their decision-making processes when sourcing open die forged components, ultimately leading to more successful procurement outcomes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the open die forge Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Open Die Forge Sector?
The global open die forging market is witnessing significant growth driven by a surge in demand across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and oil and gas. Factors such as the need for high-strength components that can withstand extreme conditions are propelling this trend. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the increasing focus on localized manufacturing is reshaping sourcing strategies. International buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who can offer customized solutions that meet specific technical requirements, particularly for larger, simpler components.
Illustrative image related to open die forge
Emerging technologies are also influencing the open die forging landscape. The integration of advanced manufacturing technologies like CNC machining and automation is enhancing precision and efficiency. Furthermore, digital platforms are facilitating better communication and collaboration between suppliers and buyers, streamlining the sourcing process. The trend toward adopting Industry 4.0 practices is promoting real-time data sharing and predictive maintenance, which can significantly reduce downtime and improve production efficiency.
With the global supply chain still recovering from disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, buyers are increasingly focusing on sourcing from reliable partners who can ensure timely delivery and consistent quality. This shift is prompting a reevaluation of traditional supplier relationships and an increased emphasis on strategic partnerships that can offer flexibility and innovation.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Open Die Forge Sector?
As businesses worldwide increasingly recognize the importance of sustainable practices, the open die forge sector is not exempt from this trend. The environmental impact of traditional forging processes—such as energy consumption and waste generation—has prompted many manufacturers to adopt greener technologies. This includes the use of energy-efficient furnaces and recycled materials, which not only reduce the carbon footprint but also lower production costs.
Ethical sourcing is becoming a critical consideration for international B2B buyers. Companies are now more than ever scrutinizing their supply chains to ensure they align with corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals. This involves evaluating suppliers based on their labor practices, environmental policies, and commitment to ethical sourcing. Buyers are increasingly seeking partnerships with manufacturers that hold certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other green certifications that reflect a commitment to sustainable practices.
The emphasis on sustainability is not just a trend; it is becoming a competitive differentiator. Suppliers who can demonstrate their commitment to environmentally friendly practices and ethical sourcing are likely to attract more business, particularly from regions where consumers are increasingly conscious of sustainability issues.
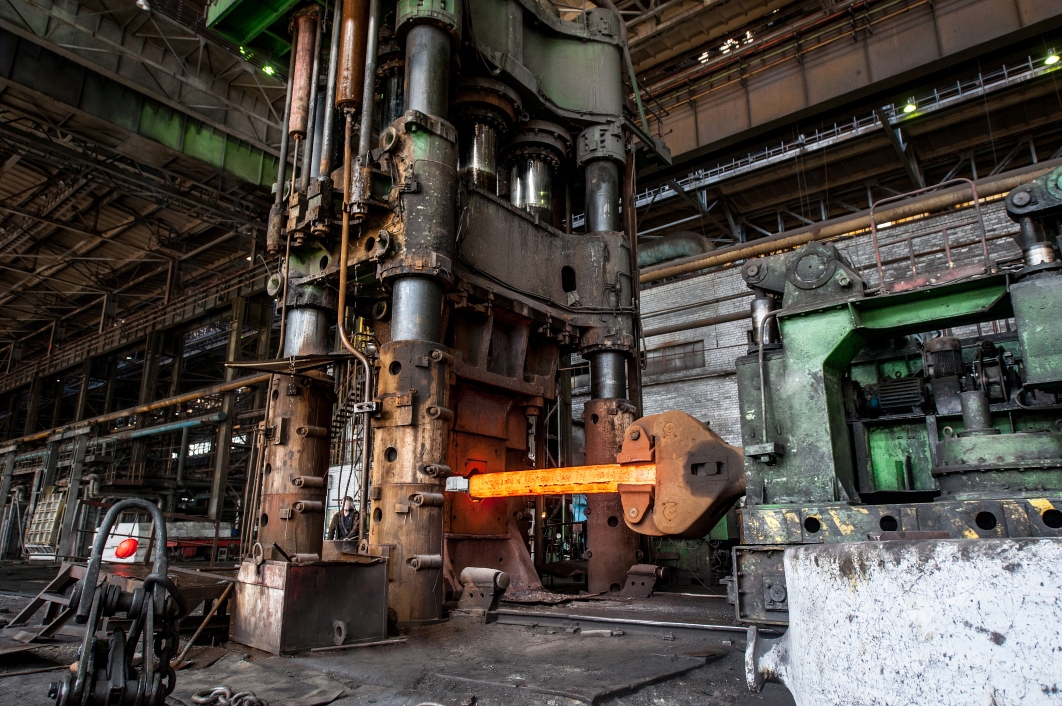

Illustrative image related to open die forge
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Open Die Forging?
Open die forging has its roots in ancient metalworking techniques, evolving from simple hammering methods used by blacksmiths to complex industrial processes. Initially employed for crafting tools and weapons, the technique has expanded significantly over the centuries. The Industrial Revolution marked a pivotal shift, as mechanization and steam power allowed for larger-scale production and the ability to forge heavier and more complex components.
In recent decades, advancements in metallurgy and forging technology have further refined open die processes, enabling manufacturers to produce high-strength, low-weight components that meet the demands of modern applications. As industries increasingly seek tailored solutions for specific applications, open die forging continues to evolve, blending traditional craftsmanship with cutting-edge technology. This evolution positions open die forging as a vital component of contemporary manufacturing, particularly for sectors requiring robust and reliable metal parts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of open die forge
-
How do I choose the right open die forging supplier?
Selecting the right supplier involves evaluating their experience, capabilities, and certifications. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in open die forging, particularly in your industry. Request case studies or references to assess their reliability and quality. Additionally, consider their technological capabilities and production capacity to ensure they can meet your specific requirements. It’s also wise to conduct a site visit if possible, to gauge their operational standards and quality control processes firsthand. -
What factors should I consider when sourcing open die forgings internationally?
When sourcing internationally, consider factors such as compliance with local regulations, tariffs, and import/export restrictions. Evaluate the supplier’s quality assurance practices and certifications, as these can vary by region. Logistics and shipping costs are also critical; ensure that the supplier can handle shipping to your location efficiently. Finally, cultural differences in communication and negotiation styles can impact the relationship, so it’s essential to approach discussions with cultural sensitivity. -
What is the typical lead time for open die forgings?
Lead times for open die forgings can vary significantly based on factors such as the complexity of the design, material availability, and the supplier’s production capacity. Generally, you can expect lead times to range from a few weeks to several months. For custom orders, it’s advisable to discuss specific timelines with your supplier upfront. Establishing clear communication about your deadlines can help ensure that your project stays on track. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for open die forgings?
Minimum order quantities can vary by supplier and depend on the complexity and size of the forgings. Some suppliers may have low MOQs for standard shapes, while custom designs might require larger quantities to be economically viable. Always clarify MOQs with potential suppliers to ensure they align with your production needs. If you have specific constraints, discuss them openly to explore possible solutions. -
What are common payment terms for international open die forging transactions?
Payment terms can differ widely between suppliers. Common terms include advance payments, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. For larger orders, suppliers may offer installment payments tied to production milestones. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that protect both parties, considering factors such as currency fluctuations and transaction fees. Always ensure that the payment method is secure and acceptable to both parties. -
How does quality assurance work in open die forging?
Quality assurance in open die forging typically involves rigorous testing and inspection processes throughout production. This includes material testing, dimensional verification, and surface quality checks. Suppliers should follow established standards such as ISO certification to ensure consistency and reliability. Discuss the quality control measures with potential suppliers to understand their processes and how they handle defects or non-conformities. -
What customization options are available for open die forgings?
Open die forging offers a high degree of customization, allowing for various shapes, sizes, and material types. Common customization options include specific dimensions, surface finishes, and mechanical properties tailored to your application. You can also request particular heat treatments or alloy compositions to enhance performance. Work closely with your supplier to define your requirements and explore their capabilities for producing customized solutions. -
What industries typically use open die forgings, and what are their applications?
Open die forgings are used across a wide range of industries, including oil and gas, aerospace, automotive, and construction. Applications often include large components like shafts, rings, and blocks that require high strength and durability. The flexibility of the open die forging process makes it ideal for producing both standard and custom parts that meet specific engineering requirements. Understanding the typical applications in your industry can help you make informed sourcing decisions.
Top 7 Open Die Forge Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Canton Drop Forge – Open Die Forging
Domain: cantondropforge.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Open Die Forging:
– Also known as free forging or smith forging.
– Involves striking a hammer to deform metal on a stationary anvil or using compression between simple dies.
– Dies are typically flat, semi-round, or V-shaped.
– Not completely encased in the process.
– Pros: Little or no tooling cost, reduced lead time, variety of size options (from a few centimeters to nearly 100 feet).
– Co…
2. GL Forge – Custom Open Die Forgings
Domain: glforge.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Custom Open Die Forgings, Open Die Forging Capabilities, Custom Forged Parts including Forged Blocks, Rectangles & Flats, Custom Forged Rounds, Discs & Sleeves, Forged Hubs, Spindles & Step Shafts, Forged Stainless Steel Blocks, Custom Forged Crankshafts, Forged Stainless Steel Fluid Ends, Custom Forged Steel & Stainless Steel Shaft Manufacturing Services. Services Offered: Custom Open Die Forging…
3. WHEMCO – Open Die Forgings
Domain: whemco.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Open Die Forgings from WHEMCO include custom, complex components made from ferrous and nonferrous materials. Key specifications include: 1. Largest Heavy Forge Facility in the Western Hemisphere. 2. Forging capabilities with ingots up to 285 tons and ship weights exceeding 165 tons using a 10,000 ton hydraulic press. 3. Smaller forgings starting at 10 tons produced by a 3,000 ton press. 4. Power G…
4. Cornell Forge – Forging Solutions
Domain: cornellforge.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Cornell Forge Company specializes in various forging processes including Open Die Forging, Impression Die Forging (Closed Die Forging), Cold Forging, and Seamless Rolled Ring Forging. Open Die Forging is used for larger components like cylinders and shafts, producing minimal waste and high fatigue resistance. Impression Die Forging is suitable for precision parts in automotive and oil industries, …
5. Philadelphia Forgings – Open Die Forging Solutions
Domain: philadelphiaforgings.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Open Die Forging Capabilities at Philadelphia Forgings:
– Type: Open Die Forging (hot forging process)
– Weight Range: Up to 80,000 pounds
– Materials Used: Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel, Stainless Steel, Tool Steel, Aluminum, Copper, Titanium, Inconel®, Invar®, Monel®, Nickel Alloys, Superalloys
– Benefits: High strength, long service life, decreased porosity, aligned grain flow, fine grain struc…
6. Ferralloy – Open Die Forging
Domain: ferralloy.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Open die forging, also known as free forging, is a metalworking process that involves heating metal and compressing it between two dies. The metal is worked at temperatures ranging from 500°F to 2400°F and shaped through hammering or pressing. This method uses geometrically simple dies that are moved relative to the piece, allowing for the production of strong, durable parts in sizes ranging from …
7. Anderson Shumaker – Open Die Forging Solutions
Domain: andersonshumaker.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Anderson Shumaker specializes in open die forging, offering a variety of forged products including forged blocks, forged discs & gear blanks, forged flat bars, forged rings, and forged round bars. The company works with a range of materials such as alloy steel, aluminum (2014, 6061), carbon steel, nickel-based alloys (Inconel 718), and various stainless steels (303, 304, 347, 410, 431, 440-C, 2205…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for open die forge
In summary, open die forging presents a versatile and cost-effective solution for international B2B buyers seeking to enhance their manufacturing capabilities. Its ability to produce large, custom-designed components without the need for complex tooling is a significant advantage, particularly for industries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By employing open die forging, companies can achieve superior mechanical properties and structural integrity while reducing material waste.
Strategic sourcing is essential in navigating the global supply chain landscape, enabling businesses to identify reliable partners who can deliver high-quality forged products tailored to their unique specifications. As industries evolve and demand for customized solutions grows, forging partnerships with established open die forging manufacturers can provide a competitive edge.
Looking ahead, international buyers are encouraged to leverage open die forging’s strengths to meet their operational needs. By exploring diverse supplier options and prioritizing quality and flexibility, companies can position themselves for success in an increasingly dynamic market. Engage with trusted forging experts today to discover how open die forging can transform your production capabilities.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to open die forge
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.