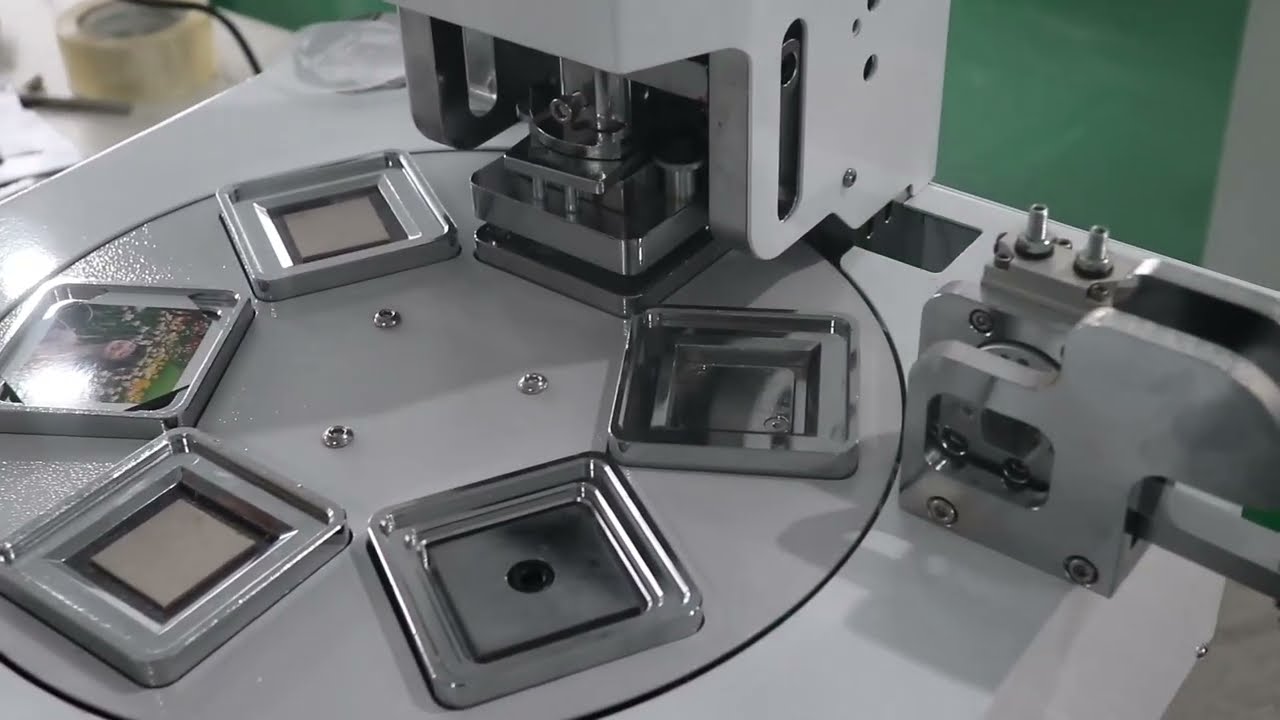
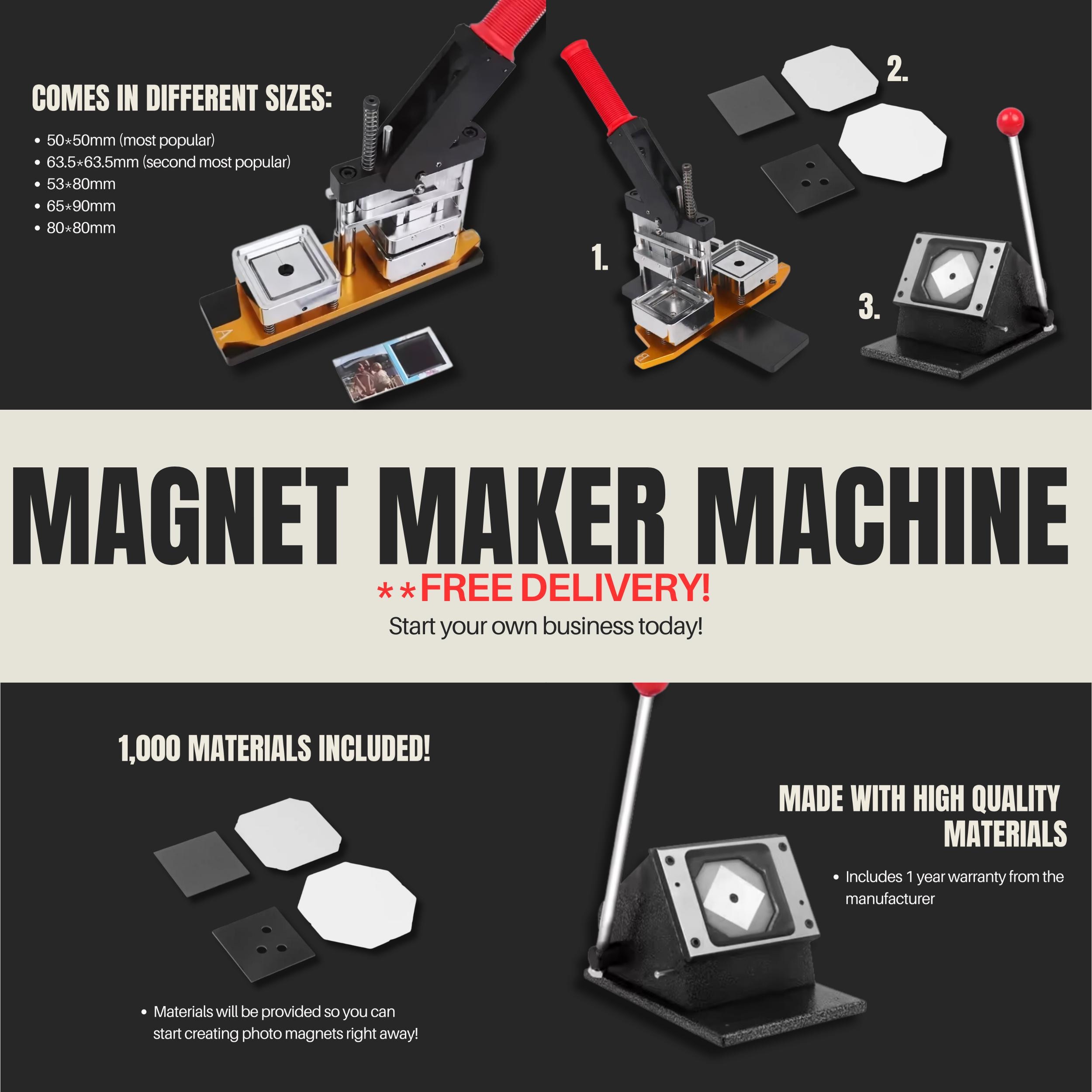
A B2B Buyer’s Guide to Magnet Making Machine: Price, Quality, and Suppliers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for magnet making machine
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing the right magnet making machine can be a daunting task for B2B buyers, especially when navigating the diverse global market. With a wide array of options available, from manual to electric machines, buyers must assess their unique production needs, quality expectations, and budget constraints. This comprehensive guide aims to simplify the purchasing process by offering insights into the various types of magnet making machines, their applications across different industries, and essential tips for vetting suppliers effectively.
Understanding the intricacies of magnet making machinery is crucial for businesses looking to enhance their product offerings, whether for promotional items, crafts, or industrial applications. This guide will delve into the specific functionalities of different machines, the cost implications of various models, and the potential return on investment for your operations. Moreover, we will provide strategies for evaluating suppliers to ensure quality and reliability, which is particularly important for international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including markets like Vietnam and Brazil.
By empowering B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions, this guide serves as a valuable resource for those seeking to enhance their production capabilities while minimizing risks associated with sourcing machinery. Let’s explore the world of magnet making machines and unlock the potential for your business growth.
Understanding magnet making machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Magnet Making Machines | Operated manually; various shapes and sizes available | Small businesses, craft fairs | Pros: Cost-effective, portable. Cons: Slower production rate. |
| Electric Magnet Making Machines | High-volume production; automated operation | Large-scale manufacturing, promotional items | Pros: Faster output, consistent quality. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Button-Making Machines | Specialized for making button magnets; various sizes | Events, promotions, custom branding | Pros: User-friendly, versatile. Cons: Limited to button shapes. |
| Specialty Magnet Machines | Customizable for unique magnet types (e.g., photo magnets) | Niche markets, personalized products | Pros: Tailored solutions, unique offerings. Cons: Potentially higher costs. |
| Industrial Magnet Machines | Heavy-duty, designed for large production runs | Manufacturing, retail displays | Pros: Durable, high efficiency. Cons: Requires significant space and resources. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Manual Magnet Making Machines?
Manual magnet making machines are ideal for small businesses or craft enthusiasts looking to produce customized magnets without a large upfront investment. They are versatile, accommodating various shapes and sizes, which makes them perfect for personalized gifts or promotional items. B2B buyers should consider factors such as ease of use, portability, and the speed of production when selecting manual machines, as these can significantly influence operational efficiency.
How Do Electric Magnet Making Machines Benefit Large-Scale Production?
Electric magnet making machines are designed for high-volume output, making them suitable for businesses that require rapid production of promotional items or merchandise. These machines automate the magnet-making process, ensuring consistent quality and reducing labor costs. When purchasing, B2B buyers should evaluate the machine’s production capacity, energy consumption, and maintenance requirements to ensure they meet their operational needs efficiently.
What Makes Button-Making Machines Unique for Custom Products?
Button-making machines specifically cater to the production of button magnets, which are popular in events and promotional contexts. Their user-friendly design allows businesses to create custom buttons quickly, making them an excellent choice for craft fairs or marketing campaigns. Buyers should consider the machine’s size options, ease of use, and available templates to maximize their creative potential while ensuring a smooth production process.
Why Should Businesses Consider Specialty Magnet Machines?
Specialty magnet machines offer customizable options for unique magnet types, such as photo magnets or fridge magnets with intricate designs. These machines cater to niche markets, allowing businesses to differentiate themselves with personalized products. B2B buyers should assess the customization capabilities, production speed, and material compatibility of these machines to ensure they align with their specific product offerings and market demands.
What are the Advantages of Industrial Magnet Machines for High-Demand Environments?
Industrial magnet machines are built for heavy-duty use, ideal for manufacturers or retailers needing large quantities of magnets for displays or products. Their robust construction ensures longevity and efficiency in high-demand environments. B2B buyers should consider the machine’s footprint, output capacity, and integration with existing production lines to optimize their investment and enhance productivity in their operations.
Key Industrial Applications of magnet making machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Magnet Making Machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Promotional Products | Custom magnets for events and branding | Enhances brand visibility and customer engagement | Quality of magnets, machine efficiency, and customization options |
| Automotive Manufacturing | Production of magnetic components for vehicle assembly | Improves assembly accuracy and efficiency | Durability of magnets, machine precision, and production capacity |
| Electronics | Manufacturing of magnetic parts for devices like speakers | Ensures high performance and reliability of electronic products | Compatibility with electronic components and material specifications |
| Arts and Crafts | Creation of custom art magnets and craft supplies | Fosters creativity and supports local artisans | Variety of sizes, ease of use, and availability of supplies |
| Education and Training | Production of educational magnets for schools | Enhances interactive learning experiences for students | Safety standards, machine reliability, and educational value |
How is the Magnet Making Machine Used in Promotional Products?
In the promotional products industry, magnet making machines are essential for producing custom magnets that serve as marketing tools at events or for branding purposes. Businesses can create unique designs that resonate with their audience, enhancing brand visibility. The ability to produce high-quality, durable magnets quickly addresses issues related to outsourcing and quality control. International buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, should consider sourcing machines that offer customization options and reliable output to meet diverse market demands.

Illustrative image related to magnet making machine
What Role Does Magnet Making Machinery Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive sector, magnet making machines are utilized to manufacture magnetic components that are crucial in vehicle assembly, such as sensors and motors. These machines ensure precision in the production of parts that contribute to the overall functionality and safety of vehicles. By investing in high-quality magnet making machines, automotive manufacturers can improve assembly efficiency and reduce production costs. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should focus on sourcing machines that adhere to international quality standards and can handle high-volume production.
How is Magnet Making Equipment Used in Electronics?
The electronics industry relies heavily on magnet making machines to produce various magnetic components used in devices like speakers, motors, and sensors. These machines enable manufacturers to create parts that meet strict performance and reliability requirements. Sourcing considerations for international buyers include ensuring compatibility with electronic components, compliance with safety standards, and the ability to produce magnets in various sizes. Understanding the specific needs of electronic applications is critical to optimizing manufacturing processes.
What Applications Exist for Arts and Crafts?
In the arts and crafts sector, magnet making machines are employed to create custom art magnets, which serve as unique products for artists and crafters. These machines enable the production of personalized items that can be sold at craft fairs or online, fostering creativity among local artisans. Buyers should look for machines that are user-friendly and offer a variety of sizes and shapes to accommodate different artistic visions. Availability of supplies and ease of operation are crucial for those entering the market.
How are Magnet Making Machines Beneficial for Education and Training?
Magnet making machines find applications in educational settings, where they are used to create educational magnets that enhance learning experiences. These magnets can be utilized in classrooms for interactive teaching methods, making complex concepts more tangible for students. When sourcing machines for educational purposes, buyers should prioritize safety standards, reliability, and the potential for engaging students in hands-on learning activities. The educational value of the products produced plays a significant role in their marketability.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘magnet making machine’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Ensuring Consistent Quality of Magnets
The Problem: One of the most significant challenges faced by B2B buyers in the magnet-making industry is achieving consistent quality in their products. Buyers may experience fluctuations in magnet strength, durability, and finish quality due to varying materials, equipment performance, or operator skill levels. This inconsistency can lead to customer dissatisfaction and potential loss of business, particularly in competitive markets where quality is paramount.

Illustrative image related to magnet making machine
The Solution: To combat quality issues, buyers should invest in high-quality magnet-making machines known for their precision and reliability. It’s crucial to source machines from reputable manufacturers that offer warranties and robust customer support. Additionally, establishing standard operating procedures (SOPs) for machine operation can help maintain consistency. Training staff on these SOPs will ensure that every operator understands the importance of adhering to quality checks during production. Regular maintenance of the machines, including calibration and parts inspection, can further enhance output quality. Implementing a quality control system that includes sampling and testing of finished magnets will allow businesses to catch and rectify issues before they reach customers.
Scenario 2: High Initial Investment and Operational Costs
The Problem: Many B2B buyers are deterred by the high initial investment required to purchase magnet-making machines. This is especially true for startups and smaller businesses in regions like Africa or South America, where capital availability can be limited. Coupled with ongoing operational costs for materials and maintenance, buyers may find it challenging to justify the investment, particularly if they are uncertain about their return on investment (ROI).
The Solution: To address the cost barrier, buyers should consider leasing options or financing plans offered by manufacturers. Many companies provide flexible payment structures, allowing businesses to spread out the cost over time. Moreover, buyers can explore starter kits or used machines, which can significantly reduce the initial outlay. When assessing ROI, it’s essential to calculate not just the direct profit from magnet sales but also the potential savings from reduced outsourcing and improved production speed. Additionally, buyers should focus on creating a diverse product line that can tap into different market segments, thus spreading risk and enhancing revenue opportunities.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Sourcing Quality Materials
The Problem: Sourcing high-quality materials for magnet production is a common pain point, particularly for businesses in regions with less established supply chains. Inconsistent material quality can lead to defects in the final product, affecting performance and customer satisfaction. Buyers often struggle to find reliable suppliers that can provide the necessary materials consistently and at competitive prices.
The Solution: To overcome sourcing challenges, buyers should build strong relationships with multiple suppliers to create a diversified supply chain. This strategy mitigates the risk of relying on a single source, which can be detrimental if that supplier faces issues. Buyers should conduct thorough research to identify suppliers known for quality assurance and reliability. Participating in industry trade shows or networking events can also help buyers connect with reputable suppliers. Additionally, buyers can implement a supplier evaluation process that includes assessments of quality, delivery timelines, and pricing. Establishing long-term contracts with preferred suppliers can also ensure a steady flow of quality materials while securing better pricing terms.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for magnet making machine
What Are the Key Materials Used in Magnet Making Machines?
When selecting materials for magnet making machines, it is crucial to consider factors that affect performance, durability, and cost. Below are analyses of four common materials used in the manufacturing of these machines, each with unique properties and implications for international B2B buyers.
1. Steel
Key Properties:
Steel is known for its high tensile strength and durability. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 300°C and offers good resistance to wear and tear, making it suitable for the mechanical components of magnet making machines.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of steel is its robustness, which ensures longevity and reliability in high-volume production settings. However, steel can be prone to corrosion if not properly treated, which may require additional coatings or finishes, increasing manufacturing complexity and cost.
Illustrative image related to magnet making machine
Impact on Application:
Steel is compatible with various media, including those used for button-making and magnet production. Its strength allows for the efficient handling of high-pressure applications during the magnet pressing process.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Steel products must comply with international standards such as ASTM A36 or DIN 10130 for structural steel. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure that suppliers provide corrosion-resistant options, especially in humid environments.
2. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight, with excellent corrosion resistance and a melting point around 660°C. It is also non-magnetic, which is advantageous in applications where magnetic interference must be minimized.

Illustrative image related to magnet making machine
Pros & Cons:
The lightweight nature of aluminum facilitates easier handling and transportation of machines, reducing shipping costs. However, it is generally less durable than steel, making it less suitable for heavy-duty applications. The higher cost of aluminum compared to steel can also be a drawback for budget-conscious buyers.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum’s corrosion resistance makes it ideal for environments where moisture is a concern, such as coastal regions. Its non-magnetic properties ensure that it does not interfere with the magnet-making process.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with standards like ASTM B221 for aluminum alloys is essential. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe often prefer aluminum for its aesthetic appeal and lightweight characteristics, particularly in portable machines.
3. Plastic Composites
Key Properties:
Plastic composites are versatile materials that offer excellent resistance to chemicals and moisture, with a temperature rating typically around 60-80°C. They are lightweight and can be molded into complex shapes.

Illustrative image related to magnet making machine
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of plastic composites is their resistance to corrosion and chemicals, making them ideal for various applications. However, they may not withstand high temperatures or pressures as well as metals, limiting their use in some components of magnet making machines.
Impact on Application:
These materials are often used in non-load-bearing parts, such as housings or covers, where weight savings are beneficial. Their compatibility with various adhesives and coatings allows for flexibility in design.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that plastic composites meet relevant standards, such as ISO 9001 for quality management. In regions like Brazil and Vietnam, where humidity can be high, selecting high-quality composites that resist moisture is crucial.
4. Rubber
Key Properties:
Rubber is known for its excellent elasticity and shock-absorbing properties. It can withstand a temperature range of -40°C to 120°C, making it suitable for various applications in magnet making machines.
Pros & Cons:
Rubber’s flexibility and durability make it ideal for gaskets and seals, ensuring airtight and watertight connections. However, its susceptibility to degradation from UV exposure and certain chemicals can limit its lifespan in some applications.

Illustrative image related to magnet making machine
Impact on Application:
Rubber components are essential in reducing vibrations and ensuring smooth operation of machines. Their compatibility with various media makes them suitable for diverse magnet-making processes.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers should look for rubber materials that comply with standards such as ASTM D2000 for rubber materials. In the Middle East, where high temperatures can affect rubber performance, selecting high-quality, heat-resistant rubber is vital.
Summary Table of Material Selection
| Material | Typical Use Case for magnet making machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Structural components and frames | High durability and strength | Prone to corrosion without treatment | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight machine bodies | Corrosion resistance and lightweight | Less durable than steel | High |
| Plastic Composites | Non-load-bearing parts (covers, housings) | Excellent chemical resistance | Limited temperature and pressure tolerance | Medium |
| Rubber | Gaskets and seals | Flexibility and shock absorption | Susceptible to UV degradation | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides actionable insights for international B2B buyers, ensuring they make informed decisions tailored to their specific operational needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for magnet making machine
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Magnet Making Machines?
The manufacturing process of magnet making machines involves several critical stages that ensure the machines operate effectively and produce high-quality magnets. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting a supplier.
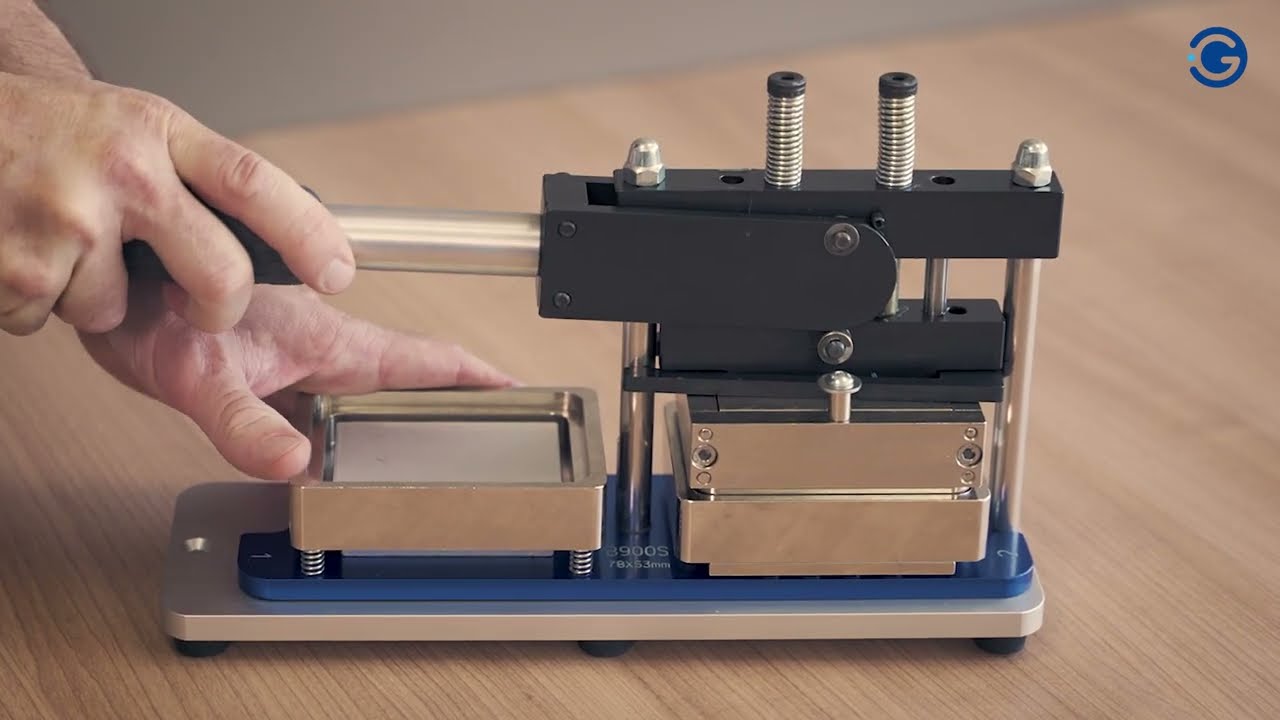
Illustrative image related to magnet making machine
1. Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Magnet Making Machines?
The first stage involves sourcing and preparing the materials required for the machine’s construction. Common materials include:
- Metal Alloys: Primarily used for the machine’s framework and components, ensuring durability and stability.
- Plastics: Often utilized for non-load-bearing parts and housings due to their lightweight and cost-effectiveness.
- Magnets: Depending on the type of machine, different magnet types (e.g., neodymium, ferrite) are sourced for production.
Suppliers should provide documentation on material specifications and origin to ensure compliance with international standards.
2. Forming: How Are the Components Shaped?
Once materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. This can involve various techniques, including:
- CNC Machining: Precision machining is used to create intricate parts that fit together seamlessly.
- Injection Molding: For plastic components, injection molding allows for high-volume production with consistent quality.
- Stamping: Metal parts may be stamped to achieve specific shapes and dimensions.
Each technique must be chosen based on the specific requirements of the machine and the intended end-use of the magnets.
3. Assembly: What is the Process of Assembling Magnet Making Machines?
After forming, the components move to the assembly stage. This involves:
- Component Integration: Parts are assembled according to engineered specifications, ensuring that all components fit correctly.
- Electronics Installation: For electric machines, wiring and control systems are installed, requiring precision to ensure safety and functionality.
- Calibration: Each machine is calibrated to ensure it operates within specified tolerances.
A rigorous assembly process is critical as it directly affects the performance and longevity of the machine.
4. Finishing: How is Quality and Aesthetics Achieved?
The finishing stage enhances both the functionality and appearance of the machines. This can include:
- Surface Treatment: Processes like powder coating or anodizing are employed to protect metal surfaces and improve aesthetics.
- Quality Checks: Before the machines are packaged, they undergo a series of quality checks to ensure they meet all specifications.
This stage is essential for the durability of the machine, particularly in diverse operational environments.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Commonly Used in Magnet Making Machine Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that the machines meet international standards and customer expectations.
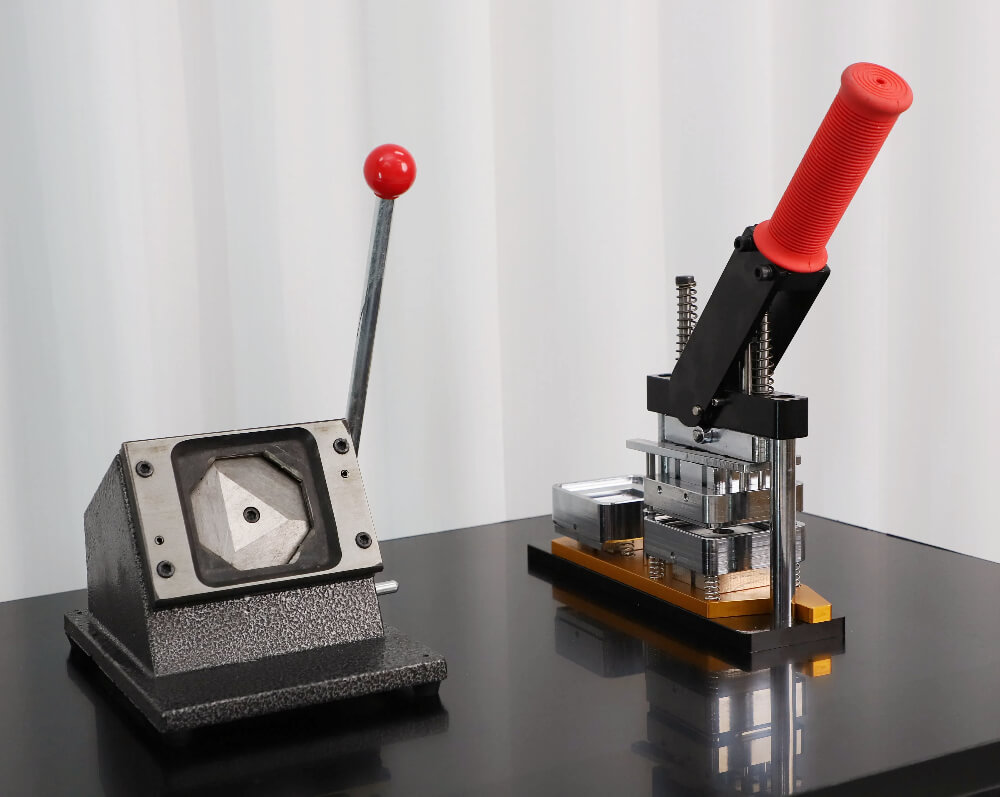
Illustrative image related to magnet making machine
International Standards: Which Certifications Should B2B Buyers Look For?
B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers adhere to internationally recognized quality standards. Key certifications include:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems, ensuring that suppliers consistently produce quality products.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold within the European Economic Area, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For machines used in industrial applications, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards may be relevant.
These certifications provide a level of assurance regarding the supplier’s commitment to quality.
Quality Control Checkpoints: What Should Buyers Expect?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints during the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials are inspected upon receipt to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring occurs during manufacturing to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Completed machines undergo thorough inspections and testing to ensure they meet all operational and safety standards.
These checkpoints help mitigate risks and ensure the final product is reliable.
What Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Magnet Making Machine Quality?
Common testing methods employed during the QC process include:
- Functional Testing: Machines are operated under normal conditions to ensure they perform as expected.
- Durability Testing: Stress tests are conducted to assess the machine’s resilience under extreme conditions.
- Safety Testing: Ensures that machines meet safety standards, particularly important for electric models.
B2B buyers should request documentation of these tests to verify the machine’s reliability.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
Buyers can take several steps to verify a supplier’s QC practices:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to see firsthand the manufacturing processes and quality control measures in place.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed QC reports can provide insights into the supplier’s testing methods and results.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can add an extra layer of assurance, especially for international transactions.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, understanding the nuances of QC can be critical:
- Cultural Differences: Be aware that quality expectations may differ by region, which could impact the manufacturing process and final product.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the machines comply with local regulations in the buyer’s country, which may differ significantly from the supplier’s country.
- Shipping and Handling: Quality assurance doesn’t end at manufacturing; consider how machines are packaged and shipped, as this can affect their condition upon arrival.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing and quality assurance processes for magnet making machines, B2B buyers can make informed choices and select suppliers that meet their operational needs and standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘magnet making machine’
In the competitive landscape of magnet production, sourcing the right magnet making machine is critical for optimizing operations and ensuring product quality. This guide offers a systematic approach to assist B2B buyers in making informed decisions when procuring magnet making machines.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly outline your requirements. This includes the types of magnets you plan to produce (e.g., round, square, or custom shapes), production volume, and whether you need manual or electric machines. Defining these specifications will streamline your search and help suppliers provide tailored solutions.

Illustrative image related to magnet making machine
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers, focusing on their reputation and experience in the industry. Look for established manufacturers with a history of serving clients similar to your business. Consider using platforms like LinkedIn or industry-specific directories to find credible suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
It’s essential to ensure that the suppliers you consider have the necessary certifications and comply with international standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 indicate a commitment to quality management systems. This step is vital for guaranteeing that the machines meet safety and quality benchmarks.
Step 4: Request Product Samples
Before making a significant investment, request product samples or demonstrations of the machines. This allows you to assess the quality of the output firsthand. Pay attention to the ease of operation and the durability of the materials used in the machine’s construction.

Illustrative image related to magnet making machine
Step 5: Inquire About After-Sales Support
Reliable after-sales support can be a game-changer for your operations. Verify what kind of support is available, including maintenance services, warranty terms, and training for your staff. Good support can minimize downtime and ensure that you get the most out of your investment.
Step 6: Compare Pricing and Terms
Once you’ve narrowed down your options, compare the pricing and payment terms offered by different suppliers. Take into account not only the upfront costs but also any potential hidden fees related to shipping, installation, or training. Ensure that the total cost aligns with your budget without compromising on quality.
Step 7: Check for Customer Reviews and Testimonials
Finally, look for reviews and testimonials from previous customers. This feedback can provide insights into the machine’s performance and the supplier’s reliability. Reach out to current users if possible to gather firsthand information about their experiences and any challenges they faced.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and long-term goals in the magnet manufacturing industry.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for magnet making machine Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Magnet Making Machines?
When evaluating the cost structure of magnet making machines, several components contribute to the final pricing. The primary elements include:
-
Materials: The quality of raw materials directly affects the machine’s performance and longevity. High-grade metals and durable plastics typically increase costs but offer better durability and efficiency.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for the assembly and quality control of machines. Labor costs can vary significantly based on the region, with countries in Europe and North America generally incurring higher wages compared to regions in Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory maintenance, utilities, and other indirect costs associated with production. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overheads, impacting the overall pricing.
-
Tooling: Specialized tools and dies used in the manufacturing process also represent a significant cost. Custom tooling for unique machine specifications will further increase expenses.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that machines meet specified standards involves rigorous testing and inspection processes. Investing in robust QC can reduce defects but adds to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are crucial, especially for international buyers. These costs can fluctuate based on shipping method, distance, and the weight of the machines.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a markup to cover their operational costs and profit margin. This margin can vary widely based on the supplier’s market position and brand reputation.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Magnet Making Machine Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of magnet making machines, particularly for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher order volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to maximize cost-efficiency.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features, such as machine size or additional functionalities, can significantly increase prices. Buyers should assess whether these customizations are essential for their operations.
-
Materials: The choice of materials can vary based on the intended use of the machines. Premium materials may increase initial costs but can lead to lower maintenance and replacement costs over time.
-
Quality and Certifications: Machines that comply with international quality standards may come at a higher price but provide assurance of reliability and performance. Certifications can also impact resale value.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and customer service can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their perceived value and support services.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) involved in the transaction is crucial. Terms that dictate responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs can affect the total cost of ownership.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Costs When Sourcing Magnet Making Machines?
To navigate the complexities of pricing and ensure cost-effectiveness, buyers should consider the following strategies:

Illustrative image related to magnet making machine
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing and terms. Leverage your purchasing power, especially if you are placing a large order, to secure discounts.
-
Cost-Efficiency Analysis: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including purchase price, maintenance, and operational costs. Sometimes a higher upfront investment can result in lower long-term costs.
-
Research Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have unique pricing structures based on local market conditions, tariffs, and regulations. Understanding these nuances can help in negotiating better deals.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: Sourcing from local manufacturers can reduce shipping costs and lead times. Additionally, local suppliers may offer better after-sales support and service.
-
Request Samples: Before committing to a large purchase, request samples to assess quality. This ensures that the machine meets your expectations and reduces the risk of unsatisfactory purchases.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
All prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on current market conditions, supplier pricing strategies, and specific buyer requirements. It is advisable for buyers to obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing and favorable terms.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing magnet making machine With Other Solutions
When considering the production of magnets, businesses often explore various solutions beyond the conventional magnet making machine. While these machines provide a streamlined approach to magnet production, alternative methods can also serve specific needs and contexts. This analysis compares the magnet making machine to two viable alternatives: outsourcing magnet production and using manual hand-cutting techniques.
| Comparison Aspect | Magnet Making Machine | Outsourcing Magnet Production | Manual Hand-Cutting Techniques |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-volume, consistent output | Variable quality, dependent on supplier | Low volume, labor-intensive |
| Cost | Initial investment required; cost-effective over time | Variable costs; may be cheaper short-term | Low initial cost, but high labor costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires setup and training | Quick implementation; relies on supplier expertise | Simple tools needed; no training required |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed; durable | No maintenance; dependent on supplier | Minimal maintenance; tools may wear out |
| Best Use Case | High-demand production; customization | Short-term projects; limited quantities | Prototyping; low-volume custom orders |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Outsourcing Magnet Production?
Outsourcing magnet production can be an attractive option for businesses looking to minimize upfront investments. This approach allows companies to leverage the expertise of specialized manufacturers who can produce magnets to high specifications. However, the downsides include a lack of control over quality and longer turnaround times, which can be problematic for businesses requiring quick delivery or custom designs. Additionally, reliance on external suppliers can create vulnerabilities in supply chain management.
How Do Manual Hand-Cutting Techniques Compare?
Manual hand-cutting techniques involve using basic tools to create magnets from raw materials. This method is highly accessible, requiring minimal investment and no specialized machinery. It is ideal for low-volume production and unique custom projects. However, the labor-intensive nature of this approach can lead to inconsistencies in quality and longer production times. Additionally, it may not be feasible for businesses aiming for high-volume output, as the workforce may struggle to meet increasing demand without significant time and labor investment.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
In selecting the right magnet production method, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific requirements, including volume, budget, and desired quality. Companies anticipating high production volumes and a need for consistent quality will likely benefit from investing in a magnet making machine, which offers automation and efficiency. Conversely, businesses looking for flexibility in low-volume projects or custom designs may find outsourcing or manual techniques more suitable. Ultimately, understanding the trade-offs associated with each option will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for magnet making machine
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Magnet Making Machines?
When considering the purchase of a magnet making machine, it is crucial to understand its technical properties to ensure optimal performance and suitability for your business needs. Here are several key specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade of a magnet making machine refers to the quality and type of materials used in its construction, including the frame, components, and tools. High-grade materials, such as stainless steel or reinforced aluminum, enhance durability and reduce wear over time. For B2B buyers, investing in machines made from quality materials means fewer maintenance issues and longer lifespans, ultimately resulting in lower total cost of ownership.
2. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels indicate the precision with which the machine can produce magnets. This specification is critical in applications where exact dimensions are necessary, such as in automotive or aerospace industries. Machines with tighter tolerances lead to higher quality products, reducing waste and ensuring consistency. For businesses focused on high-volume production, understanding tolerance levels can be a deciding factor in choosing the right equipment.
3. Production Capacity
Production capacity refers to the number of magnets a machine can produce within a given timeframe, often measured in units per hour. This property is vital for B2B buyers looking to meet demand and scale operations. Higher production capacity machines allow businesses to fulfill larger orders quickly, improving turnaround times and customer satisfaction.
4. Electrical Specifications
For electric magnet making machines, electrical specifications such as voltage, power consumption, and phase type (single or three-phase) are essential. These specifications determine the machine’s energy efficiency and compatibility with existing electrical systems. Understanding these details helps businesses assess operational costs and ensure compliance with local electrical standards, particularly in regions with specific energy regulations.
5. Automation Features
Automation features, such as programmable controls and integration with design software, enhance the efficiency of magnet production. Machines equipped with advanced automation can reduce manual labor, minimize errors, and streamline the production process. For B2B buyers, investing in automation can lead to significant labor cost savings and improved production efficiency.
What Are Common Trade Terminology and Jargon in the Magnet Making Industry?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology is crucial for effective communication and negotiation. Here are several common terms that B2B buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce components or equipment that are marketed by another company under its brand name. In the context of magnet making machines, buyers may source machines or components from OEMs to ensure quality and compatibility. Understanding OEM relationships helps buyers identify reliable suppliers and negotiate better terms.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is particularly relevant in B2B transactions as it can impact purchasing decisions and inventory management. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their orders efficiently, especially when dealing with large machines or specialized components.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer submits to suppliers to request pricing and other details for specific products. For magnet making machines, submitting an RFQ can help businesses gather competitive quotes and make informed purchasing decisions. Understanding the RFQ process is essential for effective supplier negotiation.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and delivery. Familiarity with Incoterms helps businesses clarify shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, which is especially important when importing machines from other countries. This knowledge can prevent misunderstandings and ensure smooth transactions.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is critical for businesses that rely on timely deliveries to meet production schedules. Knowing the expected lead time for magnet making machines allows companies to plan their operations more effectively and avoid disruptions.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when investing in magnet making machines, ensuring that they meet their operational needs and market demands.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the magnet making machine Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Magnet Making Machine Sector?
The magnet making machine sector is experiencing significant growth driven by various global factors. The rise in demand for customized promotional products, particularly in the advertising and crafting industries, is a primary driver. Additionally, the increasing emphasis on local manufacturing and supply chain resilience, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, is reshaping sourcing dynamics. International B2B buyers are now more inclined to invest in high-quality machines that offer versatility and efficiency, reflecting a shift towards quality over cost.
Emerging technologies, such as automation and digital printing capabilities, are also influencing sourcing trends. Manufacturers are integrating advanced features into magnet making machines, enabling faster production rates and improved precision. For instance, electric machines are gaining popularity due to their ability to handle high-volume orders with minimal labor, appealing to businesses looking to scale operations. Furthermore, the trend towards customization is pushing companies to seek machines that can produce various sizes and shapes of magnets, catering to diverse customer preferences.
Buyers from regions like Vietnam and Brazil are increasingly sourcing from established manufacturers who provide robust customer support and warranties, ensuring reliability in machine performance. This growing focus on after-sales service reflects a broader trend where businesses prioritize partnerships with suppliers that can provide ongoing assistance and training, thereby enhancing operational efficiency.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Magnet Making Machine Industry?
Sustainability has emerged as a critical consideration for international B2B buyers in the magnet making machine sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, prompting companies to seek out machines that minimize waste and energy consumption. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who utilize eco-friendly materials and processes, such as recyclable components and non-toxic adhesives, in their machines and production supplies.
Ethical sourcing is also becoming a priority. Businesses are evaluating their supply chains to ensure that materials are sourced responsibly, avoiding suppliers that exploit labor or harm the environment. Certifications such as ISO 14001, which focuses on effective environmental management systems, and other ‘green’ labels are gaining traction among buyers who wish to align their operations with sustainable practices.
Moreover, the demand for transparency in the supply chain is driving manufacturers to adopt practices that demonstrate their commitment to ethical standards. B2B buyers are more inclined to partner with companies that can provide clear documentation of their sourcing practices and environmental impact. This shift not only enhances brand reputation but also meets the growing consumer demand for socially responsible products.
How Has the Magnet Making Machine Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the magnet making machine sector can be traced back to the early days of manual production, where craftsmen used rudimentary tools to create magnets. Over the decades, technological advancements have transformed the industry, leading to the development of more sophisticated machines capable of producing high-quality magnets at scale.
The introduction of electric machines marked a significant milestone, allowing for increased efficiency and reduced labor costs. As industries expanded, the need for customization grew, prompting manufacturers to innovate and offer machines that could accommodate various sizes and shapes. Today, the sector stands at a crossroads where automation and digital technology are paving the way for even greater advancements, making it essential for international B2B buyers to stay informed about these trends to maintain a competitive edge.
In summary, understanding the current market dynamics, prioritizing sustainability, and recognizing the historical context of the magnet making machine sector will empower international B2B buyers to make informed sourcing decisions that align with their business objectives and values.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of magnet making machine
-
How do I solve common issues with magnet making machines?
Common issues with magnet making machines include misalignment, jamming, and inconsistent quality. To resolve misalignment, ensure that all components are correctly assembled and regularly maintained. For jamming, check for debris in the feeding mechanism and ensure that the materials used are compatible with the machine. Inconsistent quality may stem from variations in raw materials; therefore, sourcing high-quality supplies is essential. Regular maintenance and following the manufacturer’s guidelines can also help prevent these problems. -
What is the best type of magnet making machine for small businesses?
For small businesses, a manual magnet making machine often proves to be the best choice due to its lower initial investment and ease of use. These machines can produce a variety of magnet sizes and styles, making them versatile for custom orders. If your business anticipates high demand, consider an electric model that offers greater speed and efficiency, though it requires a higher upfront cost. Assess your production volume and budget to determine the best fit for your needs. -
How can I vet a supplier for magnet making machines?
When vetting a supplier for magnet making machines, prioritize their reputation and experience in the industry. Look for reviews and testimonials from previous clients, and inquire about their product warranties and support services. Request samples of their machines to evaluate quality and performance. Additionally, verify their compliance with international standards and certifications, especially if you are sourcing from overseas. Establishing clear communication and understanding their after-sales support is crucial for a long-term partnership. -
What customization options are available for magnet making machines?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for magnet making machines, allowing you to tailor features to meet your specific production needs. Customizations can include machine size, type of magnet produced, and additional accessories such as printing templates or electric upgrades. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to explore available options and ensure that the machine aligns with your business goals. Keep in mind that custom orders may have longer lead times. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for magnet making machines?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for magnet making machines varies by supplier and can depend on several factors, including the type of machine and customization requirements. Some manufacturers may offer single units for trial purposes, while others may set an MOQ for bulk orders to optimize production costs. It’s advisable to discuss your purchasing plans with suppliers to understand their MOQ policies and explore options for negotiating smaller orders if needed. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing a magnet making machine internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of magnet making machines typically include options like advance payment, letter of credit, or payment upon delivery. Many suppliers require a deposit before production, especially for custom orders. Understanding the supplier’s payment policies, including currency options and potential financing, is crucial. It’s also wise to clarify any additional fees, such as shipping or customs duties, to avoid unexpected costs during the transaction. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for magnet making machines?
To ensure quality assurance (QA) for magnet making machines, start by selecting suppliers who adhere to international quality standards and possess relevant certifications. Request detailed specifications and testing results for the machines you are considering. Establish a QA process that includes inspection upon delivery, regular maintenance checks, and feedback loops with your supplier for any issues encountered during operation. Engaging in open communication about quality expectations can also foster a stronger partnership. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing magnet making machines?
When importing magnet making machines, logistics considerations include shipping methods, import regulations, and customs clearance processes. Evaluate the most efficient shipping options based on cost, delivery time, and the machine’s weight. Ensure compliance with local regulations and tariffs that may apply to industrial machinery. Collaborating with a reputable freight forwarder can streamline the logistics process, as they can assist with documentation and navigating customs requirements, ensuring a smooth import experience.
Top 6 Magnet Making Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. MPRO – Professional Magnet Machines and Supplies
Domain: mprousa.com
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
Introduction: Professional Magnet Machines and Supplies – MPRO offers a variety of manual and electric button machines and supplies. Key products include: 1. Manual Kits: – Square 2 x 2″ Manual Kit – $2,225.00 – Square 2.5 x 2.5″ Manual Kit – $3,257.00 – Square 3 x 3″ Manual Kit – $3,257.00 – Round 2.25″ Manual Kit – $602.00 – Rectangle 2 x 3″ Manual Kit – $2,479.00 – Round 1.25″ Manual Kit – $582.00 – Round 3….
2. Tecre – Button Maker Machines
Domain: tecre.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Tecre’s button maker machine is made in the U.S.A. and comes in a variety of shapes, sizes, and price ranges. It includes a manual button maker machine that is heavy-duty but lightweight, allowing users to pick from 24 shapes and sizes. Tecre also offers two electric button maker machines for high-speed, high-volume button making, accommodating up to 23 different shapes and sizes. Additionally, th…
3. MyButtonMachine – Custom Button Makers
Domain: mybuttonmachine.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Product Size: 115*40 mm, 120*50 mm, 127*41.5 mm, 170*50 mm, 50*50 mm, 63.5*63.5 mm, 80*53 mm, 80*80 mm, 90*65 mm; Product Shape: Oval (1), Rectangle (16), Square (10); Product Type: Electric (1), Manual (18), Pneumatic (1); Product Style: Magnet (14), Manual (1), Pin Button (2); Price Range: $265.00 to $4,550.00; Complete Kits Available.
4. Button Making Machine – Key Supplies and Tools
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: – Button making machine (2.5*2.5 size, brand undecided)
– Supplies needed: cellophane/mylar, backing
– Recommended supplier: chibuttons.com
– Types of cutters available: hand presses, standing punch presses, simple blade tools
– Suggested cutting tools: ceramic tip paper cutter, rotary fabric cutter, stencil and scissors
– Magnets: blank magnets available at dollar or craft stores, flat …
5. Titan Press – 2×2 Magnet Making Bundle
Domain: titanpress.co
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
Introduction: Titan Press offers a 2×2″ Magnet Making Bundle priced at $1,650.18 (regular price $1,750.18) with free shipping and a lifetime warranty. This bundle includes professional square magnet and button making equipment, designed for creating custom fridge magnets and pins. The starter pack contains all necessary materials to begin making personalized magnets immediately. Available supplies include: 100 …
6. American Button Machines – 2×2 Magnet Sets
Domain: americanbuttonmachines.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “2×2 Magnet Sets”, “price”: “$130.95”, “sku”: “#1362-500”, “quantity_options”: [{“quantity”: “500 Sets”, “price”: “$130.95”}, {“quantity”: “1000 Sets”, “price”: “$225.95”}], “included_items”: [“2×2 Shell”, “plastic back”, “mylar”, “self adhesive peel and stick magnet (1-3/4″ x 1-3/4″ x 0.060″ thick)”]}
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for magnet making machine
In the competitive landscape of magnet production, strategic sourcing plays a crucial role in enhancing operational efficiency and product quality. By investing in high-quality magnet making machines, businesses can significantly improve their manufacturing processes, ensuring consistent output and superior end products. The diverse range of machines available, from manual to electric models, allows businesses across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to select equipment that best fits their specific needs and production volumes.

Illustrative image related to magnet making machine
As international buyers explore options, understanding the importance of supplier reliability and the potential for long-term partnerships can greatly influence purchasing decisions. High-quality machines not only reduce the risk of operational disruptions but also enhance the overall value proposition to end customers, leading to increased satisfaction and loyalty.
Looking ahead, the demand for customized and high-quality magnets is expected to grow, driven by industries ranging from advertising to manufacturing. Now is the ideal time for B2B buyers to leverage strategic sourcing to capitalize on market opportunities. Engage with trusted suppliers, evaluate your production requirements, and invest in technology that will propel your business forward. Your journey towards operational excellence in magnet production starts today.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.