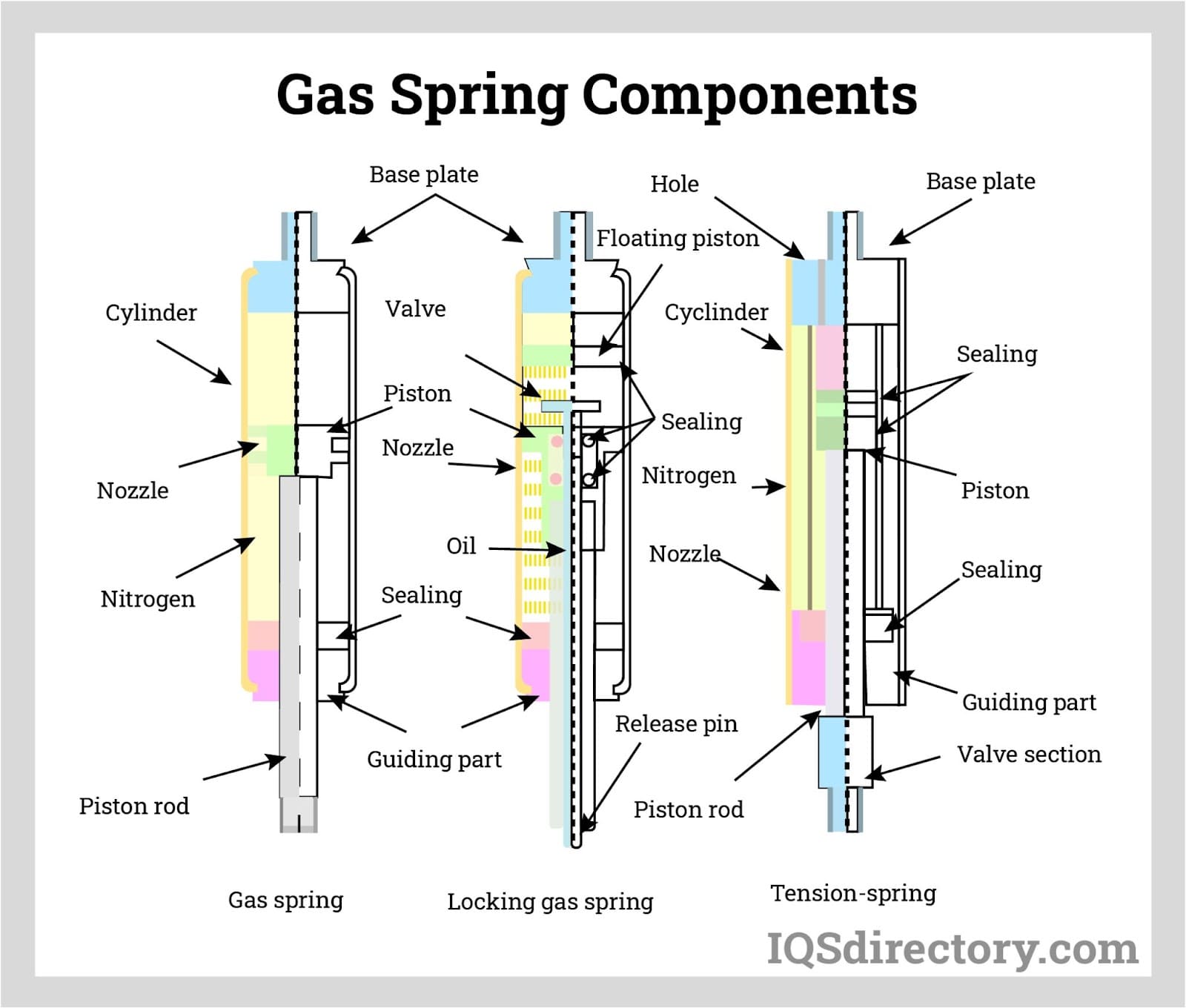
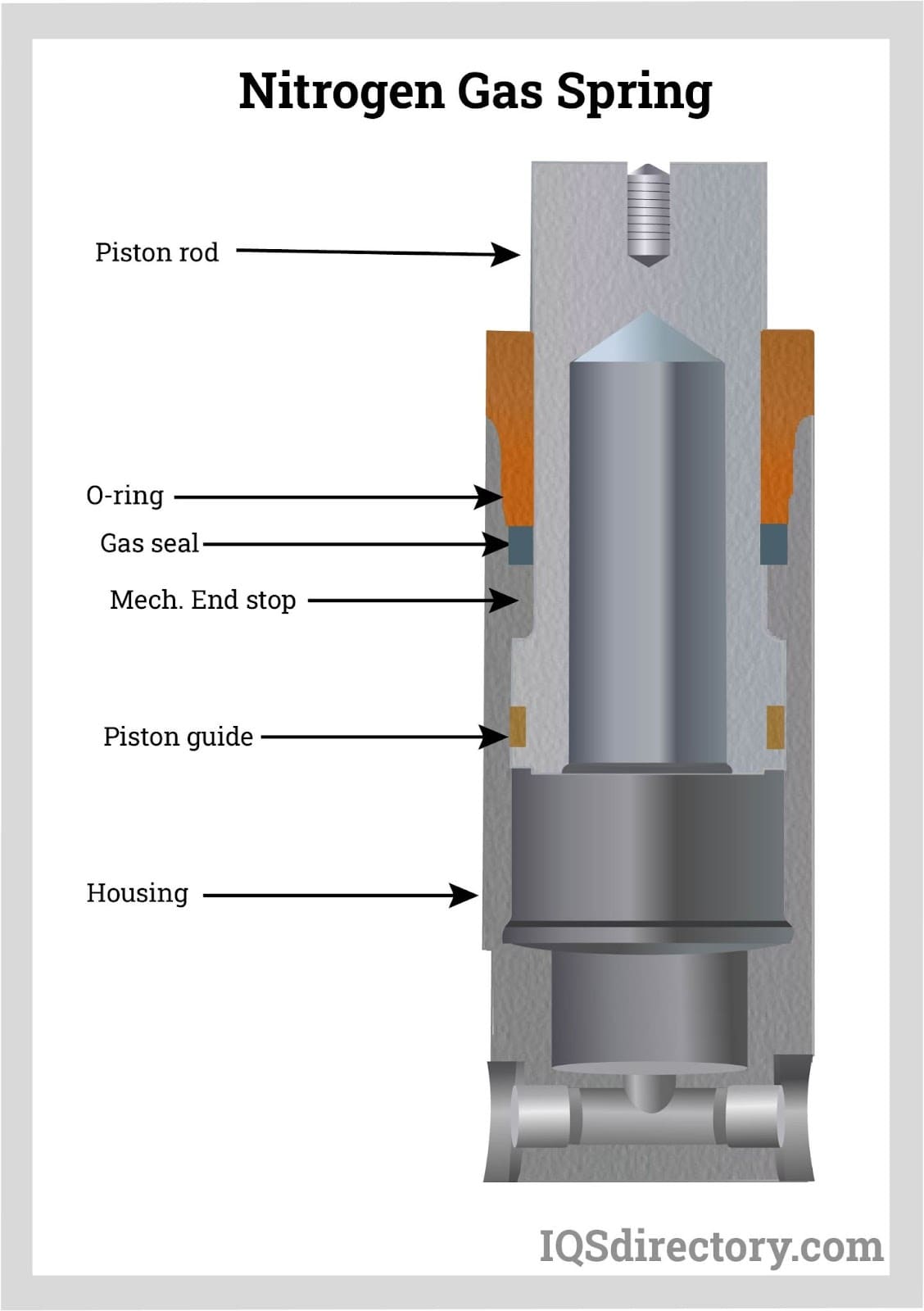
A B2B Buyer’s Guide to How Do Gas Springs Work: Price, Quality, and Suppliers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how do gas springs work
In the competitive landscape of international manufacturing and design, understanding how gas springs work is crucial for B2B buyers seeking efficient and reliable solutions. Whether you’re sourcing components for automotive applications or ergonomic furniture, knowing the mechanics behind gas springs can significantly enhance your product offerings and operational efficiency. This guide delves into the intricacies of gas springs, from their types and applications to supplier vetting and cost considerations.
Gas springs are vital in providing controlled motion and support in a variety of products, ensuring safety and ease of use. As B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe face challenges in sourcing high-quality components, this comprehensive resource empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions. By exploring the functional principles of gas springs, assessing their versatility across different industries, and understanding the factors that influence pricing, you can streamline your procurement process.
Additionally, the guide highlights best practices for supplier evaluation, ensuring you partner with reputable manufacturers who meet international standards. Whether you’re in Saudi Arabia, Vietnam, or elsewhere, navigating the global market for gas springs has never been easier. Equip yourself with the knowledge to optimize your supply chain and enhance your product development with this essential B2B guide.
Understanding how do gas springs work Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Gas Springs | Utilizes pressurized gas for lifting and supporting loads. | Automotive, furniture, industrial machinery | Pros: Cost-effective, reliable; Cons: Limited customizability. |
| Adjustable Gas Springs | Features adjustable pressure settings for varying load needs. | Office furniture, aerospace, packaging | Pros: Versatile, customizable; Cons: Higher initial costs. |
| Locking Gas Springs | Includes a mechanism to lock in place at specific heights. | Medical equipment, automotive, heavy machinery | Pros: Enhanced safety, stability; Cons: Complexity may increase maintenance. |
| Twin-Tube Gas Springs | Consists of two tubes for improved damping and stability. | Automotive, heavy-duty applications | Pros: Better performance under dynamic loads; Cons: Bulkier design. |
| Mini Gas Springs | Compact design for limited spaces, with lower force outputs. | Electronics, small machinery, automotive interiors | Pros: Space-efficient; Cons: Limited load capacity. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Standard Gas Springs?
Standard gas springs operate using a sealed cylinder filled with pressurized gas, typically nitrogen, which allows for smooth lifting and lowering of loads. They are widely used in automotive applications, such as trunk lids and hoods, as well as in office chairs and various industrial machinery. Buyers should consider their load requirements and space constraints, as these springs are often available in various sizes but may lack the customizability of more specialized options.
How Do Adjustable Gas Springs Cater to Diverse Needs?
Adjustable gas springs allow users to modify the internal pressure, enabling them to accommodate a range of weights and applications. This adaptability makes them particularly valuable in sectors like aerospace and packaging, where load requirements can vary significantly. When purchasing, B2B buyers should evaluate the ease of adjustment and whether the spring can withstand the operational conditions, such as temperature and frequency of use.
Why Choose Locking Gas Springs for Safety and Stability?
Locking gas springs incorporate a mechanism that secures the spring at specific heights, making them ideal for applications requiring enhanced safety, such as in medical equipment or heavy machinery. Their ability to maintain a fixed position under load is a significant advantage. Buyers must consider the complexity of these systems, as they may require more maintenance and could be more expensive than standard options.
What Benefits Do Twin-Tube Gas Springs Offer for Heavy Loads?
Twin-tube gas springs feature a dual-tube design that improves damping capabilities and stability, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications, including automotive and industrial uses. Their enhanced performance under dynamic loads is a key selling point. However, buyers should be aware that these springs can be bulkier, which might limit their application in compact spaces.
How Are Mini Gas Springs Designed for Space Efficiency?
Mini gas springs are designed for applications where space is at a premium, such as in electronics and automotive interiors. They provide adequate force for lighter loads while maintaining a compact footprint. B2B buyers should evaluate their specific load requirements, as mini gas springs typically have lower force outputs and may not be suitable for heavier applications.
Key Industrial Applications of how do gas springs work
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how do gas springs work | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Trunk and hatch support systems | Enhances user convenience and safety during loading/unloading | Durability, weight capacity, and resistance to environmental factors |
| Furniture | Adjustable office chairs and ergonomic furniture | Improves employee comfort and productivity | Customization options, gas pressure ratings, and warranty terms |
| Aerospace | Access panels and cargo doors in aircraft | Ensures safe and easy access while maintaining structural integrity | Compliance with aviation standards and reliability under varying conditions |
| Machinery and Equipment | Lifting and lowering mechanisms in industrial machines | Increases operational efficiency and safety | Load capacity, response time, and compatibility with existing systems |
| Medical Devices | Adjustable hospital beds and examination tables | Enhances patient comfort and ease of use for healthcare staff | Compliance with health regulations, ease of cleaning, and durability |
How Are Gas Springs Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, gas springs are crucial for supporting trunk lids and hatches, allowing for effortless opening and secure holding during loading and unloading. This functionality not only enhances user convenience but also prevents accidents caused by sudden closures. Buyers in this sector must consider factors such as durability, weight capacity, and resistance to temperature fluctuations, especially in regions like the Middle East where extreme heat can affect performance.
What Role Do Gas Springs Play in Furniture Design?
In the furniture industry, gas springs are commonly found in adjustable office chairs and ergonomic furniture, enabling smooth height adjustments. This feature significantly improves employee comfort and productivity by allowing users to customize their seating position. When sourcing gas springs for furniture, businesses should focus on customization options, gas pressure ratings, and warranty terms to ensure long-lasting performance.
How Are Gas Springs Essential in Aerospace Applications?
In aerospace, gas springs are used in access panels and cargo doors, providing safe and easy access while maintaining the structural integrity of the aircraft. These springs must operate reliably under a range of conditions, including pressure changes at high altitudes. Buyers in this sector need to prioritize compliance with aviation standards and the springs’ reliability to ensure safety and operational efficiency.
Why Are Gas Springs Important for Machinery and Equipment?
Gas springs are integral to lifting and lowering mechanisms in various industrial machines, contributing to increased operational efficiency and safety. By providing controlled motion, they help prevent accidents and equipment damage. When sourcing gas springs for machinery, businesses should consider load capacity, response time, and compatibility with existing systems to ensure seamless integration.
How Do Gas Springs Improve Medical Devices?
In the medical field, gas springs are utilized in adjustable hospital beds and examination tables, enhancing patient comfort and facilitating ease of use for healthcare staff. This adaptability is essential in providing optimal care. Buyers must ensure compliance with health regulations, ease of cleaning, and durability, particularly in regions with varying healthcare standards and practices, such as South America and Africa.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how do gas springs work’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Gas Spring for Specific Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle to identify the appropriate gas spring for their unique applications. This challenge can arise from a lack of understanding of the various specifications, such as force ratings, stroke lengths, and installation orientations. For instance, a manufacturer might require gas springs for a new product design but may not know how the pressure of the gas, the size of the piston, or the type of damping will affect the performance. This can lead to costly mistakes, such as purchasing the wrong type of gas spring that does not meet the required load-bearing capacity or operational smoothness.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should engage in a thorough needs assessment before sourcing gas springs. Start by clearly defining the application’s requirements, including the load weight, desired movement speed, and environmental factors (like temperature and humidity). Once you have this information, consult with manufacturers or suppliers who can provide detailed product specifications and recommendations. Utilize tools such as force calculators, which many suppliers offer, to match the spring’s output force to your specific needs. Additionally, consider requesting prototypes or samples to test in real-world conditions before making bulk purchases. This approach minimizes risks and ensures that the selected gas springs will function optimally in the intended application.
Scenario 2: Lack of Understanding of Gas Spring Maintenance Requirements
The Problem: Many B2B buyers underestimate the importance of maintenance for gas springs, leading to premature failure or suboptimal performance. Buyers may be unaware that gas springs require regular checks for leaks, pressure loss, and the condition of seals. For example, in an industrial setting, a gas spring that has not been properly maintained can lead to equipment downtime or even safety hazards when it fails unexpectedly, resulting in costly repairs and operational disruptions.
The Solution: To address maintenance issues, it is crucial to establish a proactive maintenance schedule that includes regular inspections and servicing of gas springs. Buyers should educate their teams on the indicators of wear and tear, such as unusual noises or inconsistent movement. Additionally, collaborating with the gas spring supplier for training sessions can provide invaluable insights into proper maintenance protocols. Suppliers may also offer service contracts that include regular inspections and replacements as needed. By prioritizing maintenance, businesses can extend the life of their gas springs, enhance safety, and reduce unexpected downtimes, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency.
Illustrative image related to how do gas springs work
Scenario 3: Misunderstanding the Operational Mechanism of Gas Springs
The Problem: A significant pain point for B2B buyers is the lack of knowledge regarding how gas springs operate, which can lead to improper usage or integration into products. For instance, a company designing a new piece of machinery might misunderstand the mechanics of gas springs, thinking they function similarly to traditional metal springs. This misunderstanding can result in incorrect installation, inadequate support, or the failure of the spring to perform its intended function, potentially jeopardizing the entire project.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should invest in comprehensive training and educational resources about gas springs. Manufacturers often provide technical documentation, videos, and user manuals that explain the principles of operation, including how gas springs store and release energy and how they generate force. Attending workshops or industry conferences focusing on gas spring technology can also provide hands-on learning opportunities. Additionally, engaging in direct discussions with technical representatives from suppliers can clarify any uncertainties and provide insights into best practices for integration and use. By fostering a deeper understanding of gas spring mechanics, buyers can ensure that they select and implement these components correctly, thereby enhancing product reliability and performance.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how do gas springs work
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Gas Springs and How Do They Perform?
Gas springs are integral components in various applications across multiple industries, and the materials used in their construction significantly influence their performance. Below, we analyze four common materials utilized in gas springs, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Steel Affect Gas Spring Performance?
Key Properties: Steel is renowned for its high tensile strength, excellent fatigue resistance, and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. It typically offers a corrosion resistance rating that can be enhanced through coatings or treatments.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of steel is its durability, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, it can be relatively heavy, which may not be ideal for lightweight applications. Manufacturing complexity can also be higher due to the need for precision machining and finishing processes.
Impact on Application: Steel gas springs are compatible with a variety of media, including oil and gas, making them versatile across different sectors. However, the potential for corrosion in certain environments (e.g., coastal areas) necessitates careful consideration of protective coatings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like the Middle East and South America should ensure compliance with local standards (e.g., ASTM or DIN) for steel grades. The availability of high-quality steel may vary, impacting sourcing decisions.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Gas Springs?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and possesses good thermal conductivity. It typically has a lower pressure rating than steel but is effective in applications where weight savings are critical.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum gas springs is their reduced weight, making them ideal for applications in automotive and aerospace sectors. However, they may not provide the same level of strength and durability as steel, particularly under extreme conditions.
Impact on Application: Aluminum gas springs are often used in applications where weight reduction is paramount, such as in automotive hoods or lightweight machinery. Their compatibility with various media is generally good, but care must be taken in corrosive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and Africa should be aware of the varying quality standards for aluminum materials. Ensuring compliance with JIS or EN standards can help mitigate risks associated with material performance.
Why Is Plastic an Emerging Choice for Gas Springs?
Key Properties: Engineering plastics, such as nylon or polycarbonate, are lightweight and can offer good chemical resistance. They typically have lower temperature and pressure ratings compared to metals.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of plastics is their lightweight nature and lower manufacturing costs, making them suitable for low-load applications. However, they may not withstand high temperatures or heavy loads, limiting their use in demanding environments.
Impact on Application: Plastic gas springs are often used in consumer products and lightweight machinery. Their compatibility with various chemicals can vary, necessitating careful selection based on the specific application.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like South America and Africa should consider the availability of high-quality engineering plastics that meet international standards. Ensuring compliance with local regulations regarding material safety is also essential.
How Do Composite Materials Enhance Gas Spring Functionality?
Key Properties: Composite materials, such as carbon fiber or fiberglass, offer high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent corrosion resistance. They can be engineered to meet specific performance requirements.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of composites is their ability to provide high performance while being lightweight. However, they can be more expensive than traditional materials and may require specialized manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: Composites are suitable for high-performance applications, such as aerospace and high-end automotive sectors, where weight and strength are critical. Their chemical compatibility can be tailored to specific applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should be aware of the advanced manufacturing techniques required for composites. Compliance with specific industry standards is crucial to ensure product reliability.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Gas Springs
| Material | Typical Use Case for how do gas springs work | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty applications (e.g., automotive) | High durability and strength | Heavier weight, higher manufacturing complexity | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight automotive and aerospace parts | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength under extreme conditions | Medium |
| Plastic | Consumer products and lightweight machinery | Low cost and lightweight | Limited temperature and load capacity | Low |
| Composite | High-performance aerospace and automotive | High strength-to-weight ratio | Higher cost and specialized manufacturing | High |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with a comprehensive understanding of material options for gas springs, enabling informed decisions that align with their specific application needs and regional considerations.

Illustrative image related to how do gas springs work
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how do gas springs work
What Are the Main Stages of the Gas Spring Manufacturing Process?
The manufacturing of gas springs is a complex process that involves several critical stages. Each stage plays a vital role in ensuring that the final product meets the necessary performance and safety standards. Here are the main stages involved:
1. Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used and How Are They Prepared?
Gas springs are primarily made from high-grade steel, which provides the necessary strength and durability. The steel is often sourced from suppliers who meet international standards. The preparation phase includes cutting the steel into precise lengths, followed by processes such as annealing to relieve stress and improve machinability. Additionally, specialized alloys may be used for specific applications, particularly in industries that require enhanced corrosion resistance.
2. Forming: How Are Gas Springs Shaped and Assembled?
The forming stage involves several techniques to shape the components of the gas spring. Key processes include:
- Deep Drawing: This method is used to create the cylindrical body of the gas spring. Sheets of steel are drawn into a die to form the desired shape.
- Machining: Precision machining techniques, such as turning and milling, are employed to create the piston rod and any internal components. Tolerances are kept tight to ensure proper functioning.
- Welding: In cases where components are joined, welding processes are used to ensure strong and durable connections.
After forming, the components are often subjected to heat treatment to enhance strength and fatigue resistance.
3. Assembly: What Steps Are Involved in Putting Together a Gas Spring?
The assembly stage is where the individual components come together to create a functional gas spring. This process typically includes:
- Sealing: Each gas spring must be completely sealed to prevent gas and oil leakage. This is often done using O-rings or other sealing methods that withstand high pressure.
- Filling: The cylinder is filled with nitrogen gas and oil under controlled conditions. This is a critical step, as the pressure must be precisely calibrated to ensure optimal performance.
- Testing: Each assembled gas spring undergoes initial testing to verify that it meets pressure and force specifications before moving on to quality control.
What Are the Quality Assurance Measures in Gas Spring Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in ensuring that gas springs meet both performance and safety standards. Various international and industry-specific standards guide these QA measures.
International Standards: What Certifications Should Buyers Look For?
ISO 9001 is the most recognized international quality management standard and is applicable to gas spring manufacturers. Compliance with this standard indicates that the manufacturer has established a quality management system that meets customer and regulatory requirements. Other relevant certifications may include:
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, indicating compliance with safety standards.
- API Certification: Important for manufacturers supplying industries such as oil and gas, ensuring adherence to specific industry standards.
Quality Control Checkpoints: How Are Gas Springs Monitored Throughout Production?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during manufacturing to catch any deviations from quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of the finished product, including pressure testing, force measurement, and leak testing.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Gas Springs?
Several testing methods are employed to ensure the functionality and reliability of gas springs. Common testing procedures include:
- Pressure Testing: Assessing the gas spring’s ability to hold pressure without leakage.
- Force Measurement: Evaluating the output force to confirm it meets specified requirements.
- Durability Testing: Subjecting gas springs to repeated cycles of compression and extension to assess fatigue resistance.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
Verifying a supplier’s quality control is crucial for B2B buyers, especially in international markets where standards may vary. Here are some actionable steps:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into the manufacturing processes and quality control measures in place. This is particularly important for buyers from regions like Africa and South America, where local standards may differ.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation that details their quality assurance processes, testing results, and certifications. Regular reports on quality metrics can also be beneficial.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality standards. This is especially useful in regions with less stringent regulatory oversight.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of the nuances in quality control that can affect their purchasing decisions. These include:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have varying regulations regarding product safety and quality. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local requirements and ensure their suppliers are compliant.
- Cultural Considerations: Understanding the cultural context of quality expectations can help buyers communicate effectively with suppliers. This may include recognizing the importance of personal relationships in business dealings, particularly in regions like the Middle East and Africa.
- Logistics and Supply Chain: Quality assurance doesn’t end at the factory. Buyers should consider the entire supply chain, including shipping and handling, to ensure that products remain within quality standards upon arrival.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with gas springs, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and quality expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how do gas springs work’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed for B2B buyers looking to procure gas springs. Understanding how gas springs work is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions, ensuring that the selected products meet your technical requirements and operational needs. Follow this step-by-step checklist to streamline your procurement process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the specifications required for your gas springs. Consider parameters such as load capacity, stroke length, and dimensions.
– Load Capacity: Determine the weight the gas spring needs to support, as this will influence the pressure and size of the spring.
– Stroke Length: Identify how far the piston needs to travel; this affects the design and functionality of the gas spring.
Step 2: Research Different Types of Gas Springs
Familiarize yourself with the various types of gas springs available in the market.
– Variants: Learn about different designs, such as standard gas springs, locking gas springs, and adjustable gas springs, as each serves specific applications.
– Applications: Consider the context in which the gas springs will be used, as this will guide you toward the most suitable type.
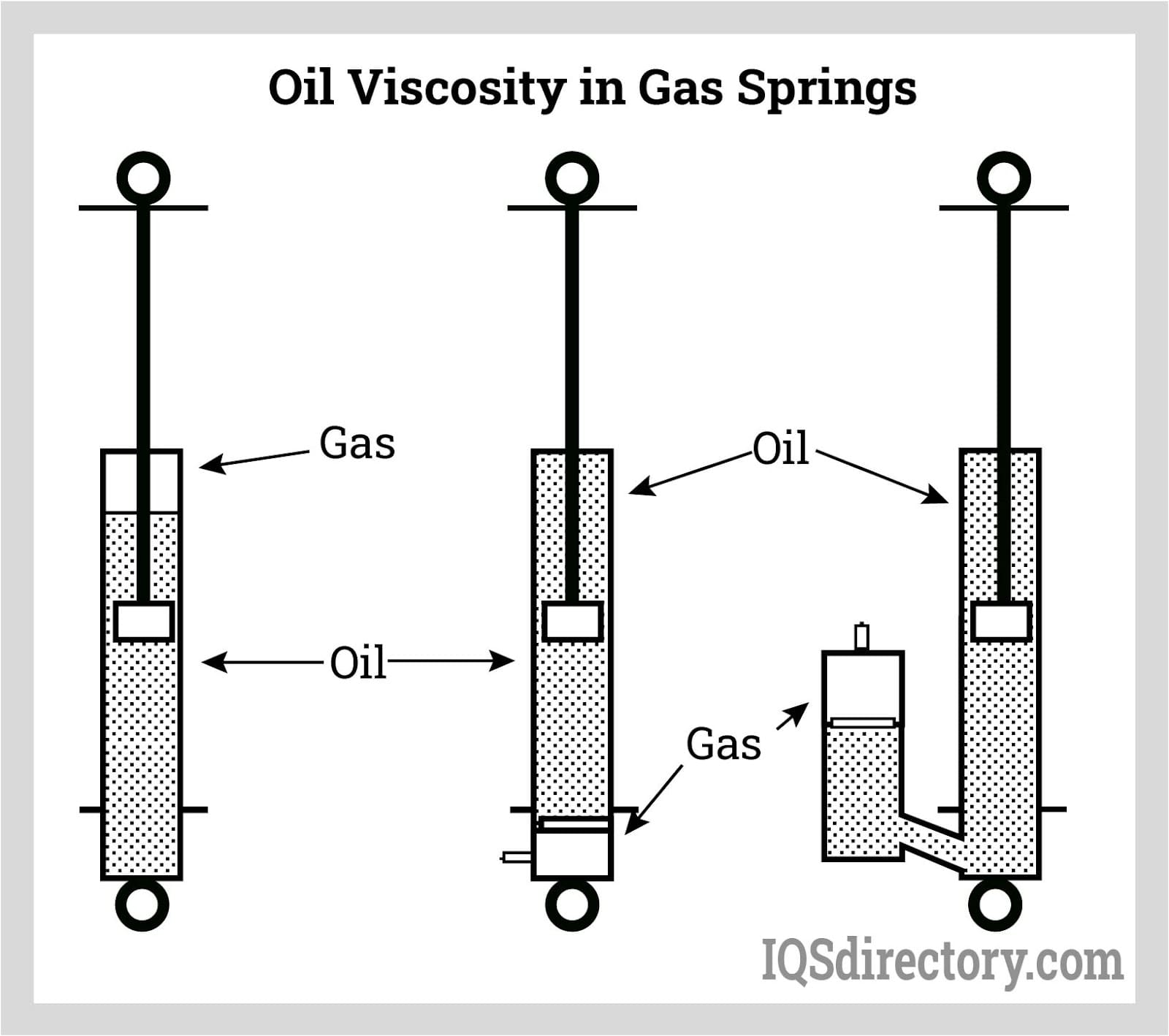
Illustrative image related to how do gas springs work
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a purchase, thoroughly vet potential suppliers.
– Company Profiles: Request detailed profiles and product catalogs to assess their range and capabilities.
– References: Ask for case studies or testimonials from other businesses in your industry to understand their reliability and service quality.
Step 4: Verify Quality and Compliance Standards
Ensure that the gas springs comply with relevant industry standards and regulations.
– Certifications: Check for ISO certifications or any specific quality management systems the supplier adheres to.
– Testing Procedures: Inquire about their quality control processes and whether the products undergo rigorous testing before shipment.
Step 5: Assess Pricing and Payment Terms
Compare pricing models from different suppliers while considering the total cost of ownership.
– Pricing Structure: Evaluate whether the costs are competitive and transparent, including shipping and handling fees.
– Payment Terms: Review payment options and terms, including any discounts for bulk purchases or early payments.
Step 6: Request Samples for Testing
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the gas springs you’re considering.
– Functionality Testing: Use the samples to test compatibility and performance in your specific applications.
– Quality Assessment: This step allows you to inspect the build quality and ensure the product meets your specifications.
Step 7: Establish a Long-Term Relationship
Consider establishing a long-term partnership with your chosen supplier.
– Communication: Maintain open lines of communication for future needs or adjustments in specifications.
– Support: A reliable supplier should provide ongoing support, including technical assistance and warranty options.
By following this checklist, you can make informed decisions when sourcing gas springs, ensuring they meet your operational requirements and contribute positively to your business processes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how do gas springs work Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Gas Springs?
When considering the procurement of gas springs, international B2B buyers must analyze a comprehensive cost structure that encompasses several essential components:
-
Materials: The primary materials used in gas springs include high-grade steel for the cylinder, specialized seals, and gas (typically nitrogen). The quality of these materials directly impacts the durability and performance of the gas springs. Buyers should consider sourcing from suppliers who can provide high-quality materials that meet industry standards.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly depending on the region and the manufacturing process employed. Skilled labor is essential for precision assembly, particularly in maintaining the integrity of seals and pressure systems. Buyers should evaluate suppliers based on their labor practices and workforce skill levels.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead costs, which may be passed on to buyers in the form of competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be required for specific gas spring designs, particularly for unique applications. This upfront investment can affect the overall cost, but it often results in higher quality and precision in the final product.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC measures ensures that gas springs perform reliably under pressure. Costs associated with QC can vary, but investing in quality assurance can prevent costly returns and warranty claims.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs, including shipping and handling, are crucial considerations. The choice of Incoterms can significantly influence logistics expenses, impacting the total landed cost for international buyers.
-
Margin: Suppliers will apply a margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. Understanding the supplier’s pricing strategy can help buyers negotiate better terms.
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Cost of Gas Springs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of gas springs, which buyers should carefully consider:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk orders typically lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their requirements to take advantage of volume discounts.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom-engineered solutions can drive up costs, particularly if they require specialized tooling or materials. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against budget constraints.
-
Quality Certifications: Gas springs that meet specific industry certifications may come at a premium. However, these certifications can enhance product reliability and marketability, particularly in regulated industries.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and location of the supplier can affect pricing. Suppliers with established quality records may command higher prices, but their reliability can justify the investment.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects responsibilities related to shipping, insurance, and customs duties. Understanding these terms can help buyers avoid unexpected costs and streamline procurement processes.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for International B2B Buyers?
To optimize procurement costs, buyers should employ effective negotiation strategies:
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Focus on the long-term costs associated with gas springs, including maintenance, reliability, and warranty considerations. A slightly higher upfront cost may result in lower overall expenditures.
-
Research Market Pricing: Understanding market rates for gas springs can empower buyers during negotiations. This knowledge allows for informed discussions and the ability to challenge unjustified pricing.
-
Explore Multiple Suppliers: Engaging with several suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations. It also opens opportunities for competitive bidding, leading to better pricing.
-
Consider Local vs. International Suppliers: While international suppliers may offer lower prices, local suppliers can provide advantages in terms of logistics and support. Assessing these trade-offs can lead to cost efficiencies.
-
Timing and Economic Conditions: Be mindful of economic conditions, such as currency fluctuations and material shortages, which can affect pricing. Timing purchases strategically can mitigate these risks.
Disclaimer
Prices for gas springs can vary significantly based on the factors outlined above. Buyers should seek quotations from multiple suppliers to obtain the most accurate and competitive pricing for their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how do gas springs work With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Gas Springs: A Comparative Analysis
In various industrial and automotive applications, gas springs serve as a reliable solution for providing controlled force and motion. However, businesses often explore alternative methods to achieve similar results based on specific requirements, budget constraints, and operational contexts. This section examines two prominent alternatives to gas springs: mechanical springs and hydraulic cylinders. Each alternative presents unique advantages and disadvantages that can influence a buyer’s decision.
| Comparison Aspect | How Do Gas Springs Work | Mechanical Springs | Hydraulic Cylinders |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Smooth, adjustable force; effective in limited space | Limited to linear force; may vary in performance | High force output; effective in heavy-duty tasks |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment | Generally low-cost; varies by type | Higher initial cost; maintenance can be expensive |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple installation; requires minimal adjustments | Easy to install; may require space for expansion | More complex setup; requires additional components |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; seals prevent leakage | Low maintenance; durable under normal conditions | Higher maintenance; potential for leaks and repairs |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for applications needing adjustable support | Suitable for general load-bearing applications | Best for heavy lifting and precise control tasks |
Understanding Mechanical Springs as an Alternative
Mechanical springs, including compression and extension springs, are widely used in various applications. They are known for their simplicity and cost-effectiveness. The primary advantage of mechanical springs lies in their low initial investment and straightforward installation. However, they can be limited in terms of performance, particularly when it comes to providing smooth and adjustable force. Additionally, mechanical springs may require more space for extension or compression, which can be a drawback in compact environments.
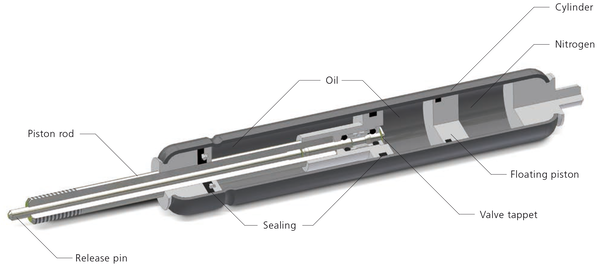
Illustrative image related to how do gas springs work
Evaluating Hydraulic Cylinders as an Alternative
Hydraulic cylinders are another alternative that can deliver a significant amount of force, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. They utilize pressurized fluid to generate movement, which can be precisely controlled. While hydraulic systems offer exceptional power, they come with higher initial costs and more complex installation processes. Maintenance can also be a concern, as hydraulic systems are prone to leaks and require regular monitoring. Their best use cases include industrial machinery and automotive applications where substantial lifting and force are necessary.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the right solution for your application, B2B buyers should consider specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. Gas springs provide a unique combination of adjustability and ease of use, making them ideal for applications where space and smooth operation are crucial. However, for those seeking lower initial costs, mechanical springs may be more appealing. Conversely, hydraulic cylinders are optimal for applications requiring significant force, albeit with higher complexity and maintenance demands. Ultimately, understanding the distinct advantages and limitations of each option will empower buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific operational needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how do gas springs work
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Gas Springs?
Understanding the technical specifications of gas springs is essential for B2B buyers to ensure they select the right products for their applications. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Gas springs are typically constructed from high-strength steel or aluminum alloys. The material grade affects the spring’s durability, corrosion resistance, and overall performance. High-grade materials are crucial for applications in harsh environments, such as automotive or aerospace, where safety and longevity are paramount.
2. Pressure Rating
The internal pressure of a gas spring is a vital specification, often ranging from 20 to 170 bar (290 to 2,465 psi). This rating indicates the force the spring can exert when compressed. Understanding the pressure rating is essential for ensuring that the gas spring can handle the load requirements of specific applications, such as automotive hoods or office chairs.
3. Stroke Length
Stroke length refers to the distance the piston can travel within the cylinder. It is critical to match the stroke length with the intended application to ensure proper functionality. For instance, a gas spring used in a vehicle trunk must have a stroke length sufficient to support the trunk’s opening and closing smoothly.
4. Force Output
The force output of a gas spring, measured in Newtons (N) or pounds (lbs), is determined by the piston area and the internal pressure. This specification is essential for determining the spring’s suitability for specific tasks, such as supporting heavy lids or providing counterbalance in ergonomic chairs.
5. Temperature Range
Gas springs must operate effectively within specified temperature ranges, typically from -30°C to +80°C (-22°F to +176°F). The temperature range affects the gas pressure and, consequently, the force output. Buyers should consider this specification to ensure the gas springs will perform reliably in their intended environments.
6. Damping Characteristics
Damping refers to the ability of the gas spring to control the speed of movement when the piston is extended or compressed. Different designs allow for varying degrees of damping, which can be crucial in applications requiring smooth motion, such as in furniture or automotive components.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Gas Springs?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B space. Here are several common trade terms relevant to gas springs:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products that are sold under another company’s brand. In the context of gas springs, OEMs might produce components for automotive or industrial applications, making it essential for buyers to ensure compatibility with existing systems.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding the MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers to manage inventory effectively and avoid overstocking or understocking components that are essential for their operations.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. For gas springs, submitting an RFQ can help buyers compare prices, lead times, and specifications to make informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is vital for B2B buyers, as they clarify who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and risk during transport. This knowledge helps in budgeting and ensures compliance with international trade regulations.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order until it is delivered. For businesses relying on timely production schedules, understanding lead times for gas springs is essential for planning and ensuring that projects stay on track.
6. Certification Standards
Certification standards, such as ISO or ASTM, indicate that a product meets specific quality and safety benchmarks. For gas springs, compliance with these standards assures buyers of the product’s reliability and performance, which is critical in industries like automotive and aerospace.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terminology empowers B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing gas springs, ensuring that they select products that meet their operational needs and standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how do gas springs work Sector
What Are the Global Drivers Shaping the Gas Springs Market?
The gas springs market is experiencing robust growth, driven by several global factors. Increasing automation in manufacturing and automotive sectors is elevating the demand for gas springs, as they provide reliable support and ease of operation in various applications. Additionally, the growing emphasis on enhancing user experience in consumer products, such as office furniture and automotive components, is pushing manufacturers to integrate gas springs that offer smooth and controlled movements.
Emerging technologies, including IoT and smart manufacturing, are influencing sourcing trends. Companies are investing in advanced gas spring solutions that can be monitored and adjusted in real-time, leading to enhanced operational efficiency and reduced downtime. Furthermore, the expansion of e-commerce platforms is facilitating easier access to suppliers and diversified product offerings, allowing B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to source gas springs more efficiently.
Market dynamics are also being shaped by regional variations in manufacturing capabilities. For instance, countries like Vietnam are becoming manufacturing hubs due to lower labor costs and favorable trade agreements, attracting international buyers looking for competitive pricing without sacrificing quality. However, buyers must navigate the complexities of international logistics and customs regulations, which can affect sourcing timelines and costs.
How Is Sustainability Influencing the Sourcing of Gas Springs?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration in the gas springs market. As environmental concerns grow, B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices. This includes sourcing materials that are recyclable or derived from renewable resources, as well as implementing energy-efficient manufacturing processes.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, with companies being urged to ensure that their supply chains are free from exploitation and environmental harm. Buyers are looking for manufacturers who hold certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management, which indicates a commitment to reducing their ecological footprint.
Moreover, innovations in the production of gas springs are leading to the development of ‘green’ materials that can replace traditional components without compromising performance. For instance, the use of lightweight composites not only reduces the overall weight of gas springs but also minimizes energy consumption during transportation and installation. By aligning purchasing decisions with sustainability goals, B2B buyers can enhance their brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
How Has the Gas Springs Industry Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of gas springs dates back to the mid-20th century, when engineers began to explore the potential of pressurized gas for energy storage and controlled movement. Initially used in automotive applications, gas springs quickly gained traction in various industries due to their versatility and efficiency.
As technology advanced, the design and functionality of gas springs improved significantly. Innovations such as adjustable damping mechanisms and enhanced sealing techniques have led to more reliable and durable products, catering to a broader range of applications.
Today, gas springs are integral components in industries such as aerospace, furniture manufacturing, and industrial machinery. The ongoing demand for customization and advanced features is driving continuous innovation, ensuring that the gas spring sector remains dynamic and responsive to the needs of international B2B buyers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how do gas springs work
-
How do gas springs work to support heavy loads?
Gas springs operate by utilizing pressurized gas, typically nitrogen, and hydraulic oil within a sealed cylinder. When the piston rod is pushed into the cylinder, it compresses the gas, creating a difference in pressure that generates an upward force. This force assists in lifting heavy items, such as car trunks or office chairs, with minimal manual effort. The precise force generated can be customized based on the specific requirements of the application, ensuring that it effectively supports the intended load. -
What factors should I consider when selecting gas springs for my application?
When selecting gas springs, consider the load capacity, stroke length, mounting options, and environmental conditions. It’s essential to choose a spring that provides the appropriate output force while accommodating the specific movement range needed for your application. Additionally, evaluate the working environment—temperature extremes or exposure to chemicals may require specialized materials or designs. Consulting with suppliers about customization options can help ensure optimal performance. -
What are the common applications of gas springs in B2B industries?
Gas springs are widely used across various industries, including automotive, furniture manufacturing, and industrial machinery. In automotive applications, they support trunk lids and hoods, while in furniture, they enable adjustable height mechanisms in office chairs and tables. Additionally, they are utilized in medical equipment, aerospace components, and even packaging machinery, demonstrating their versatility in providing controlled motion and support in diverse settings. -
How can I ensure the quality of gas springs when sourcing from international suppliers?
To ensure quality, conduct thorough research on potential suppliers by checking their certifications, such as ISO standards, and reviewing customer testimonials. Request samples to evaluate performance, and inquire about their quality assurance processes, including testing methods and materials used. Establishing clear communication regarding specifications and performance expectations is crucial to avoid discrepancies. Partnering with suppliers who provide transparent documentation can further enhance confidence in product quality. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for gas springs?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on factors such as the complexity of the gas spring design and the supplier’s production capabilities. Generally, MOQs range from 50 to several hundred units. It’s advisable to discuss your needs with potential suppliers, as some may offer flexibility for smaller orders, especially for custom designs. Understanding your projected usage can also help negotiate better terms. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing gas springs internationally?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and region, but common practices include upfront payments, letter of credit, or partial payments with the balance due upon delivery. It’s essential to clarify payment options early in negotiations to avoid misunderstandings. Many suppliers may also accept secure online payment methods, which can facilitate smoother transactions. Be mindful of currency fluctuations and consider using a fixed exchange rate if applicable. -
How do I handle logistics and shipping for gas springs from international suppliers?
When sourcing gas springs internationally, consider logistics factors such as shipping costs, delivery timelines, and customs regulations. Work closely with your supplier to determine the best shipping method—air freight is faster but more expensive than sea freight. Ensure that all documentation, including invoices and packing lists, is accurate to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Partnering with a reliable freight forwarder can help streamline the shipping process and mitigate potential delays. -
Can gas springs be customized for specific applications?
Yes, gas springs can be customized to meet specific requirements such as force output, stroke length, and mounting configurations. Many manufacturers offer design modifications to suit unique applications, allowing for tailored solutions that enhance performance. When discussing customization options, provide detailed specifications and any specific performance criteria you have in mind. This collaborative approach can lead to a more effective product that meets your operational needs.
Top 2 How Do Gas Springs Work Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Explain That Stuff – Gas Springs
Domain: explainthatstuff.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Gas springs, also known as gas dampers, are piston-like devices that support heavy objects like car trunk lids with minimal effort. They are filled with pressurized nitrogen gas and oil, allowing them to store energy and dampen movement. Gas springs work by compressing gas when the piston is pushed into the cylinder, generating force due to the difference in area on either side of the piston. They…
2. IQS Directory – Gas Springs
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Gas springs are hydro-pneumatic devices that store potential energy by compressing gas inside a sealed cylinder, regulated by a moving piston. They operate as self-contained units filled with inert nitrogen, requiring no additional gas. Key terms include stroke (maximum range of motion), extended length (total length), closed length (fully closed length), and beadroll section (protects seal packag…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how do gas springs work
What Are the Key Takeaways on Gas Springs for B2B Buyers?
In summary, gas springs are essential mechanical components that enhance efficiency and ease of use across various applications, from automotive to office furniture. Their ability to store and release energy provides significant advantages, allowing for smoother operations and reduced physical strain. For international B2B buyers, understanding how gas springs work is crucial in selecting the right products that meet operational needs while ensuring safety and reliability.
How Does Strategic Sourcing Enhance Gas Spring Procurement?
Strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in optimizing the procurement process for gas springs. By focusing on quality, supplier reliability, and cost-effectiveness, businesses can secure the best components that align with their production goals. Engaging with reputable suppliers from diverse regions—such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—can also foster innovation and adaptability in supply chains.
What’s Next for International B2B Buyers?
As you navigate the complexities of sourcing gas springs, consider the long-term implications of your purchasing decisions. Seek partnerships with manufacturers who prioritize sustainability and quality, ensuring that your operations remain competitive in a global marketplace. Embrace the future of engineering solutions by investing in high-quality gas springs that not only meet current demands but also adapt to evolving industry standards.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.