A B2B Buyer’s Guide to High Shear Homogenizer: Price, Quality, and Suppliers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for high shear homogenizer
Navigating the complex landscape of sourcing a high shear homogenizer can be a daunting task for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As industries demand more efficient and consistent mixing solutions, understanding the intricacies of high shear homogenizers becomes essential. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, addressing key challenges such as identifying suitable types of homogenizers, understanding their applications across various sectors—including pharmaceuticals, food processing, and cosmetics—and effectively vetting suppliers.
In today’s global market, where quality and efficiency are paramount, selecting the right high shear homogenizer can significantly impact product consistency and operational success. This guide empowers international B2B buyers by providing actionable insights into the latest technologies, cost considerations, and best practices for supplier evaluation. Whether you’re a manufacturer in Saudi Arabia seeking to enhance product quality or a supplier in Nigeria looking to streamline your operations, our detailed analysis will equip you with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions.
By leveraging the information presented here, buyers can confidently navigate the global market, ensuring that they not only meet their production needs but also maintain a competitive edge in their respective industries.
Understanding high shear homogenizer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batch High Shear Mixer | Suitable for single or multiple vessels; flexible design | Food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals | Pros: Versatile, easy to clean. Cons: Slower for large batches. |
| Inline High Shear Mixer | Continuous processing; quick product changeover | Adhesives, paints, chemicals | Pros: Efficient for multiple products. Cons: Requires precise flow control. |
| High-Speed Disperser | Handles medium to high viscosities; effective for dispersions | Plastics, inks, coatings | Pros: Fast processing. Cons: Limited to specific viscosity ranges. |
| SLIM (Solids Injection) | Instant wetting of powders; integrates solids directly | Food, pharmaceuticals, chemicals | Pros: Reduces processing time. Cons: May require additional setup. |
| High Pressure Homogenizer | Utilizes high pressure for micro and nano-emulsions | Pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, food | Pros: Produces fine emulsions. Cons: Larger footprint, complex maintenance. |
What Are the Characteristics of Batch High Shear Mixers?
Batch high shear mixers are known for their versatility in processing different materials in either benchtop or production sizes. Their design allows for permanent or suspended mounting over a vessel, enabling manufacturers to use a single mixer for multiple applications. This type of mixer is particularly suited for industries such as food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals where the need for uniformity in emulsification and dispersion is critical. Buyers should consider the potential slower processing speed for larger batches, but appreciate the ease of cleaning and flexibility this type offers.
How Do Inline High Shear Mixers Improve Production Efficiency?
Inline high shear mixers are engineered for continuous processing, making them ideal for industries that frequently change products, such as adhesives and paints. They feature a design that allows for seamless transition from one product to another, streamlining operations and reducing downtime. The ability to maintain precise flow control is crucial for achieving consistent results. While they offer efficiency and adaptability, buyers should be aware that operational precision is necessary to prevent inconsistencies in product quality.
What Advantages Do High-Speed Dispersers Offer?
High-speed dispersers are designed to handle medium to high viscosity materials, making them suitable for applications in plastics, inks, and coatings. They deliver rapid processing times, allowing manufacturers to meet tight production schedules. However, their effectiveness is limited to specific viscosity ranges, which buyers must consider when evaluating their suitability for particular applications. The speed and efficiency of high-speed dispersers can significantly enhance productivity, but careful assessment of material compatibility is essential.
What Is the SLIM Technology and Its Benefits?
SLIM (Solids Injection) technology revolutionizes the way powders are integrated into liquid mixtures by allowing for instant wetting and dispersion directly in the high shear rotor-stator. This innovative approach is particularly beneficial in food, pharmaceuticals, and chemical industries where time efficiency is paramount. While SLIM technology can significantly reduce processing times, buyers should note that it may require additional setup and training for optimal use.
How Do High Pressure Homogenizers Function?
High pressure homogenizers are specialized equipment that utilizes high pressure to create micro and nano-emulsions, making them a staple in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and food industries. They are capable of producing highly uniform mixtures, which is critical for product stability and quality. However, their larger footprint and complexity in maintenance can be a concern for some buyers. Understanding the operational requirements and the scale of production is crucial for businesses considering this investment.
Key Industrial Applications of high shear homogenizer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of high shear homogenizer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Emulsification of sauces and dressings | Achieves uniform consistency and improved shelf life | Equipment must comply with food safety regulations and be easy to clean. |
| Pharmaceutical | Creation of stable emulsions for creams | Ensures product efficacy and patient safety | Requires precise control over shear rates and temperature management. |
| Cosmetics | Mixing of pigments and oils | Enhances product texture and color uniformity | Must accommodate varying viscosities and be suitable for small batch sizes. |
| Adhesives and Sealants | Dispersion of fillers and resins | Improves adhesion properties and product performance | Equipment should allow for quick changeovers and efficient cleaning. |
| Chemicals and Coatings | Particle size reduction in paints | Ensures consistent color and finish quality | Must handle high-viscosity materials and offer scalability for production. |
How is a High Shear Homogenizer Used in the Food and Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage sector, high shear homogenizers are pivotal for emulsifying sauces and dressings. These machines create stable emulsions by breaking down fat globules, resulting in a uniform texture that enhances flavor and shelf life. For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, sourcing equipment that meets stringent food safety standards is crucial. Additionally, ease of cleaning and maintenance is essential to ensure compliance with health regulations.
What Role Does a High Shear Homogenizer Play in Pharmaceuticals?
High shear homogenizers are extensively used in the pharmaceutical industry to create stable emulsions for creams and ointments. This ensures that active ingredients are evenly distributed, enhancing product efficacy and patient safety. For buyers in the Middle East and Europe, it’s important to consider equipment that offers precise control over shear rates and temperature to maintain the integrity of sensitive formulations. Compliance with regulatory standards is also a key factor in the selection process.
How Do Cosmetics Manufacturers Benefit from High Shear Homogenizers?
In the cosmetics industry, high shear homogenizers are utilized for mixing pigments and oils, resulting in products with improved texture and color consistency. This technology is particularly beneficial for manufacturers looking to produce high-quality skincare and makeup products. Buyers from regions like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria should focus on machines that can handle varying viscosities and are designed for small batch production, ensuring flexibility and quality in their offerings.
Why are High Shear Homogenizers Important for Adhesives and Sealants?
High shear homogenizers play a vital role in the adhesives and sealants industry by dispersing fillers and resins to improve adhesion properties. This process not only enhances product performance but also ensures consistency in the final output. For businesses sourcing equipment in Africa and South America, it is essential to choose homogenizers that allow for quick changeovers and efficient cleaning to minimize downtime and enhance productivity.
How are High Shear Homogenizers Used in Chemicals and Coatings?
In the chemicals and coatings industry, high shear homogenizers are essential for reducing particle size in paints and coatings, ensuring consistent color and finish quality. This technology aids in achieving uniform dispersion, which is crucial for product performance. International buyers, particularly in Europe and the Middle East, should consider equipment that can handle high-viscosity materials and offers scalability to meet production demands, ensuring efficiency and effectiveness in manufacturing processes.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘high shear homogenizer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Achieving Consistent Emulsification in Viscous Materials
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, especially in industries such as cosmetics and food production, face challenges when trying to emulsify high-viscosity materials. These products, which often contain oils, waxes, and other thick substances, can be particularly difficult to mix uniformly. Buyers may find that traditional mixing equipment fails to produce a stable emulsion, leading to separation of ingredients, inconsistent product quality, and ultimately customer dissatisfaction.
The Solution: To tackle this issue, B2B buyers should invest in a high shear homogenizer specifically designed for handling viscous materials. When selecting equipment, it’s crucial to consider features such as adjustable shear rates and the ability to customize rotor-stator configurations. High shear homogenizers with variable speed settings allow operators to fine-tune the mixing process, optimizing shear energy to achieve the desired emulsification without overheating sensitive ingredients. Additionally, conducting thorough testing with sample batches in a manufacturer’s development center can help identify the right equipment for specific formulations, ensuring consistent results and reducing waste.
Scenario 2: Inefficient Cleaning Processes Leading to Downtime
The Problem: Another common pain point for businesses using high shear homogenizers is the time-consuming cleaning process required after each use. This is particularly problematic for companies producing multiple products with different formulations, as cross-contamination can lead to product recalls and financial losses. Buyers often experience significant downtime while cleaning, resulting in reduced productivity and delayed time-to-market.
The Solution: To mitigate these challenges, buyers should consider selecting high shear homogenizers with easy-clean designs, such as those featuring quick-disconnect components and smooth surfaces that reduce residue build-up. Investing in inline high shear mixers can also help, as they allow for continuous production without the need for extensive cleaning between batches. Additionally, implementing a robust cleaning protocol that includes the use of automated cleaning systems can significantly reduce manual labor and downtime. Buyers can consult with equipment manufacturers for recommendations on best practices and cleaning agents that effectively remove residues while maintaining equipment integrity.
Scenario 3: High Energy Consumption and Operating Costs
The Problem: Many B2B buyers are increasingly concerned about the energy consumption and overall operating costs associated with high shear homogenizers. These machines often require significant energy input, especially when processing large volumes or high-viscosity materials. As operational costs continue to rise, businesses may find themselves searching for ways to improve efficiency without sacrificing product quality.
The Solution: To address energy consumption concerns, buyers should explore high shear homogenizers that are designed with energy efficiency in mind. Look for models that feature advanced motor technology, which can provide the same or better performance while consuming less energy. Additionally, incorporating process optimization strategies, such as batch size adjustments and proper equipment sizing, can lead to significant energy savings. Regular maintenance and calibration of machines will also ensure optimal performance and longevity, further reducing costs over time. Buyers should work closely with suppliers to assess their specific needs and identify energy-efficient solutions tailored to their production processes.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for high shear homogenizer
What Materials Are Commonly Used in High Shear Homogenizers?
When selecting materials for high shear homogenizers, it is crucial to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. The choice of material can significantly impact the performance, durability, and efficiency of the homogenizer, especially in diverse applications across various industries. Below, we analyze four common materials used in high shear homogenizers: stainless steel, ceramic, plastic, and titanium.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in High Shear Homogenizers?
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high tensile strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. Common grades like 304 and 316 are often used in food and pharmaceutical applications due to their hygienic properties.
Pros & Cons: The durability of stainless steel makes it a preferred choice for high shear homogenizers. It is relatively easy to clean, which is essential in industries requiring strict hygiene standards. However, stainless steel can be more expensive compared to other materials and may not be suitable for highly abrasive substances, which can lead to wear over time.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including corrosive substances, making it ideal for food, pharmaceutical, and chemical applications. Buyers must ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and FDA regulations.
What Role Does Ceramic Play in High Shear Homogenizers?
Key Properties: Ceramic materials are highly resistant to wear and corrosion and can withstand high temperatures. They are often used in applications involving abrasive materials due to their hardness.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of ceramics is their exceptional durability and resistance to chemical attack. However, they can be brittle, making them susceptible to cracking under mechanical stress. Additionally, ceramic components can be more expensive and complex to manufacture.
Impact on Application: Ceramics are particularly suitable for applications involving abrasive or highly corrosive materials. Buyers in regions with stringent quality standards, such as Europe, should consider the certifications required for ceramic components in their homogenizers.
How Do Plastics Compare in High Shear Homogenizers?
Key Properties: Various plastics, such as polypropylene and PTFE (Teflon), offer good chemical resistance and can handle a wide range of temperatures. They are lightweight and can be molded into complex shapes.

Illustrative image related to high shear homogenizer
Pros & Cons: Plastics are generally less expensive than metals and ceramics, making them an attractive option for cost-sensitive applications. However, they may not withstand high pressures as effectively as metals or ceramics, and their durability is often lower, leading to a shorter lifespan.
Impact on Application: Plastics are suitable for applications involving non-abrasive and less aggressive media. Buyers should be aware of the specific chemical compatibility and temperature limits of the plastic materials used in their homogenizers.
What Advantages Does Titanium Offer for High Shear Homogenizers?
Key Properties: Titanium is known for its high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures and pressures. It is often used in specialized applications requiring high durability.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of titanium is its superior strength and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for harsh environments. However, titanium is significantly more expensive than other materials and can be challenging to machine, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Titanium is particularly beneficial in industries such as aerospace and pharmaceuticals, where high performance is critical. Buyers must consider the cost implications and ensure that the benefits justify the investment.
Summary Table of Material Selection for High Shear Homogenizers
| Material | Typical Use Case for high shear homogenizer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Food and pharmaceutical applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | More expensive, wear over time | High |
| Ceramic | Abrasive and corrosive material applications | Exceptional durability | Brittle, higher manufacturing cost | High |
| Plastic | Non-abrasive media applications | Cost-effective, lightweight | Lower pressure resistance, durability | Low |
| Titanium | Harsh environments in aerospace and pharma | Superior strength and corrosion resistance | High cost, complex manufacturing | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on the specific needs of their applications and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for high shear homogenizer
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of High Shear Homogenizers?
The manufacturing of high shear homogenizers involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets industry standards and performance expectations. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to invest in high-quality mixing and homogenizing equipment.
Material Preparation: How Are Components Selected and Processed?
The first stage in manufacturing high shear homogenizers is the careful selection and preparation of raw materials. Typically, stainless steel is used for components in contact with the product due to its corrosion resistance and durability. Suppliers often provide certificates of compliance to verify material quality.
Once the materials are selected, they undergo a series of processes, including cutting, machining, and surface treatment. Machining processes, such as milling and turning, are employed to achieve precise dimensions and surface finishes. Surface treatments like passivation enhance corrosion resistance, which is crucial for maintaining hygiene in food and pharmaceutical applications.
What Forming Techniques Are Used to Create High Shear Homogenizers?
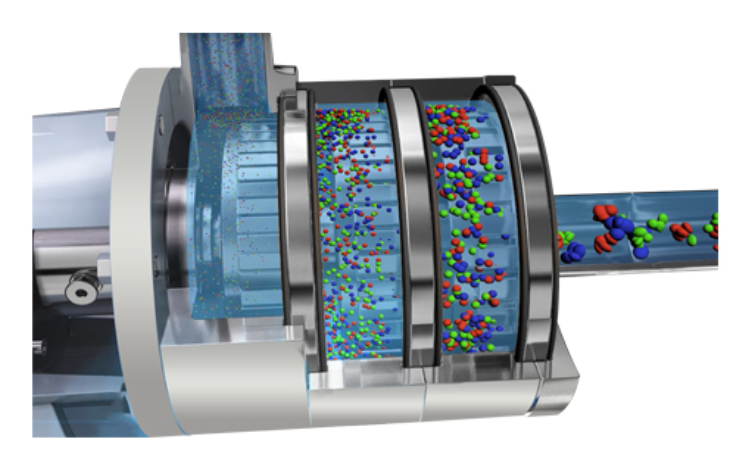
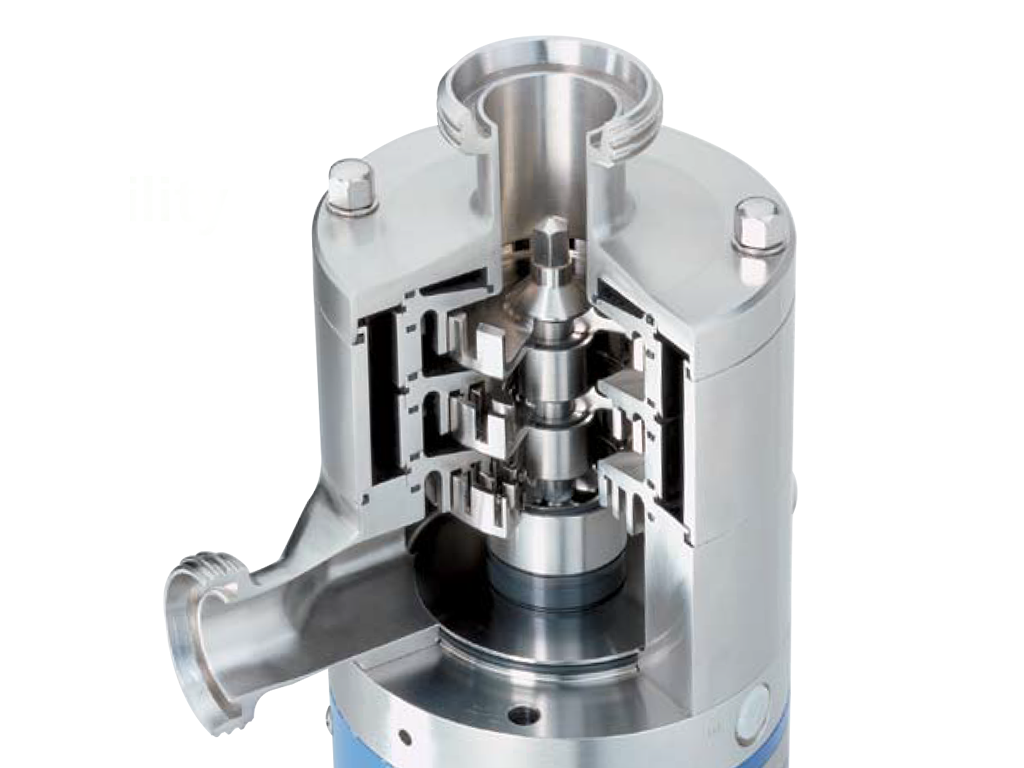
After material preparation, the next step is forming the components. Various techniques, including casting, forging, and precision machining, are utilized. High-precision machining is particularly important for the rotor-stator assembly, which is critical in achieving the desired shear rates and mixing efficiency.
In some cases, advanced techniques like 3D printing may be employed for prototyping or producing complex geometries. This innovative approach allows for rapid development and testing of new designs, which can be especially beneficial for companies looking to customize their equipment.
How Is the Assembly Process Conducted for High Shear Homogenizers?
Assembly is a vital stage that combines all the individual components into a functional unit. During this phase, manufacturers often adopt modular assembly techniques, allowing for flexibility and efficiency. The rotor and stator are carefully aligned and assembled to ensure optimal performance.
Quality assurance begins even at this stage, with checks for alignment, fit, and finish. Any deviations are addressed immediately, as they can impact the homogenizer’s performance and longevity. Additionally, manufacturers often implement cleanroom environments during assembly, particularly for equipment intended for pharmaceutical or food applications, to minimize contamination risks.
What Finishing Processes Enhance the Performance of High Shear Homogenizers?
The final manufacturing stage involves various finishing processes that enhance the performance and aesthetic appeal of the homogenizer. These processes include polishing, coating, and cleaning. Polishing is essential for achieving a smooth surface finish, which reduces friction and enhances flow characteristics.
Coatings may also be applied to specific components to enhance wear resistance or provide additional protection against corrosion. Finally, a thorough cleaning process ensures that all residues from manufacturing are removed, preparing the equipment for operational use.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Implemented in High Shear Homogenizer Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of the manufacturing process, ensuring that high shear homogenizers meet international standards and customer expectations. B2B buyers must understand these QA measures to evaluate potential suppliers effectively.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Look for?
Manufacturers of high shear homogenizers typically adhere to various international quality standards, such as ISO 9001. This standard outlines a framework for a quality management system, ensuring consistent product quality and continuous improvement.
In addition to ISO 9001, industry-specific certifications may apply. For example, equipment intended for the pharmaceutical sector may require compliance with the FDA’s Current Good Manufacturing Practices (CGMP) or the European Medicines Agency (EMA) guidelines. In the food industry, equipment may need to meet standards set by the Food Safety Authority or be CE marked to indicate compliance with European safety directives.
Illustrative image related to high shear homogenizer
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process, ensuring that each phase meets the established standards. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials and components upon delivery to ensure they meet specifications before they enter the production line.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During assembly and manufacturing, operators conduct regular checks to monitor process parameters and product quality. This includes verifying the alignment of the rotor and stator and measuring shear rates.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the homogenizer is fully assembled, it undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it meets performance specifications. This may involve running the equipment under simulated conditions to verify its effectiveness in mixing and homogenizing.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Product Quality?
Manufacturers employ various testing methods to validate the performance of high shear homogenizers. Common techniques include:
-
Shear Rate Testing: This assesses the homogenizer’s ability to create the desired shear rates, which is crucial for effective emulsification and particle size reduction.
-
Viscosity Testing: Measuring viscosity before and after processing helps determine the efficiency of the homogenization process.
-
Durability Testing: This involves subjecting the equipment to stress tests to simulate long-term usage and identify potential failure points.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
To ensure they are selecting a reputable supplier, B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of potential manufacturers.
What Steps Should Buyers Take to Conduct Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to assess a manufacturer’s quality management system. Buyers should request access to the manufacturer’s facilities and review their QA processes. Key areas to focus on during an audit include:
-
Documentation: Verify the existence of quality control documentation, including process maps, SOPs, and inspection records.
-
Certifications: Check for relevant certifications that indicate adherence to international and industry-specific standards.
-
Equipment and Technology: Assess the tools and technologies used in the manufacturing and testing processes to ensure they are up-to-date and capable of producing high-quality products.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Buyer Confidence?
Engaging third-party inspection services can further enhance buyer confidence. These independent organizations can provide objective assessments of a manufacturer’s quality control processes and product performance. Buyers should consider arranging for third-party inspections at various stages of the manufacturing process, from material sourcing to final product testing.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification can significantly impact purchasing decisions.
How Do Regional Standards Affect Equipment Selection?
Different regions may have specific standards and regulations that apply to high shear homogenizers. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should familiarize themselves with local regulations, such as the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) standards in the Middle East or the European Union’s CE marking requirements.
What Should Buyers Consider Regarding After-Sales Support and Documentation?
Finally, B2B buyers should ensure that suppliers provide comprehensive after-sales support, including maintenance services and spare parts availability. Additionally, documentation such as user manuals, maintenance guides, and compliance certificates should be provided to facilitate smooth operations and adherence to local regulations.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures of high shear homogenizers is crucial for B2B buyers seeking reliable equipment. By focusing on supplier quality control, certifications, and regional standards, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regulatory requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘high shear homogenizer’
In the competitive landscape of B2B procurement, sourcing a high shear homogenizer requires careful consideration to ensure you meet your operational needs while maximizing your investment. This guide provides a structured checklist to help you navigate the complexities of selecting the right high shear homogenizer for your business.
1. Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your technical requirements is the first step in sourcing a high shear homogenizer. Consider the material types you will be processing, including their viscosity and particle size. This information will help you determine the necessary shear rates and mixing capabilities required for your applications.
- Key Considerations:
- Viscosity range of materials.
- Desired particle size reduction.
- Batch versus continuous processing needs.
2. Identify Your Application Needs
Different industries and applications have unique requirements. Establish whether your focus is on emulsification, dispersion, or particle size reduction, as this will influence the type of high shear homogenizer you need.
- Application Examples:
- Food and beverage emulsions.
- Cosmetic creams and lotions.
- Pharmaceutical formulations.
3. Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it is crucial to conduct a thorough evaluation. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from other buyers in your industry or region. This will ensure you select a reputable supplier who understands your specific needs.
- What to Look For:
- Industry experience and expertise.
- Customer testimonials and case studies.
- Support and service offerings post-purchase.
4. Request Equipment Demonstrations
Seeing the high shear homogenizer in action can provide invaluable insights into its performance and suitability for your needs. Many suppliers offer testing facilities where you can evaluate the equipment with your actual materials.
- Benefits of Demonstrations:
- Assess mixing efficiency and speed.
- Understand the machine’s operation and maintenance requirements.
- Identify potential challenges with your specific formulations.
5. Verify Compliance and Certifications
Ensure that the homogenizer complies with relevant industry standards and certifications. This is particularly important in regulated industries such as pharmaceuticals and food production, where compliance can affect product safety and quality.
- Key Certifications:
- ISO certifications.
- CE marking for equipment sold in Europe.
- Industry-specific certifications (e.g., FDA for food and pharmaceuticals).
6. Consider After-Sales Support and Maintenance
A high shear homogenizer is a significant investment, and ongoing support is essential. Evaluate the supplier’s after-sales service, including warranty, spare parts availability, and technical support.

Illustrative image related to high shear homogenizer
- What to Ask:
- Warranty duration and coverage.
- Availability of local service technicians.
- Training programs for your staff on equipment operation.
7. Compare Pricing and Financing Options
Finally, gather quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing. Look beyond just the initial purchase price; consider total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential financing options.
- Cost Factors to Consider:
- Initial purchase price versus long-term savings.
- Costs associated with installation and training.
- Financing options that may be available to spread out the investment.
By following this structured approach, you will be better equipped to source a high shear homogenizer that meets your operational needs, ensuring efficiency and quality in your production processes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for high shear homogenizer Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for High Shear Homogenizers?
When sourcing high shear homogenizers, understanding the cost structure is vital for B2B buyers. The main components contributing to the overall cost include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margins.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the price. High-quality stainless steel is commonly used for its durability and resistance to corrosion, especially in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Specialized materials, like those resistant to high temperatures or chemicals, will increase costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs involve both skilled and unskilled workers in manufacturing and assembly processes. High shear homogenizers often require precision engineering, which demands skilled labor, thereby raising the overall cost.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation associated with the production process. A sophisticated manufacturing setup for high shear mixers may lead to higher overhead costs.
-
Tooling: The cost of tools required for production can vary significantly based on the complexity of the homogenizer design. Custom tooling will increase initial costs but can lead to efficiencies in production.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous quality control measures ensures product reliability and compliance with industry standards. This can add to the overall cost but is crucial for minimizing returns and maintaining customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on the destination, shipping method, and customs duties. International buyers must be aware of these costs, particularly when sourcing from manufacturers in different regions.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their operational costs and profit. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s brand reputation and market positioning.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sourcing Decisions?
Several factors influence the pricing of high shear homogenizers, and understanding these can help buyers negotiate better deals.
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities often leads to discounts due to economies of scale. Buyers should evaluate their production needs to determine the optimal order quantity.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customization can significantly impact pricing. Unique specifications may require specialized production processes, which can increase costs. Buyers should assess whether standard models meet their needs to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials and Quality/Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) often come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the importance of these factors against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but often provide better support and warranty options, reducing long-term costs.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers. They dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process, affecting logistics costs and potential risks.
What Are Essential Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency?
B2B buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider the following strategies to enhance cost-efficiency when sourcing high shear homogenizers.
-
Negotiation: Engage in active negotiation with suppliers. Understanding the cost structure can empower buyers to negotiate better terms and discounts.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but the total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime. This holistic view can lead to more informed purchasing decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be mindful of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local taxes that can affect the final cost. Establishing clear communication with suppliers regarding pricing terms can mitigate unexpected expenses.
-
Research and Compare: Conduct thorough research on different suppliers and their offerings. Comparing multiple quotes can provide insights into the market and help identify the best value for money.
Disclaimer
Prices for high shear homogenizers can vary widely based on specifications, materials, and supplier factors. The information provided here is indicative and should be verified through direct consultation with suppliers to obtain accurate and current pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing high shear homogenizer With Other Solutions
In the quest for efficient mixing and homogenization, businesses often consider multiple solutions to meet their specific needs. High shear homogenizers are renowned for their ability to create uniform mixtures, but other technologies may also provide viable alternatives depending on the application. This section explores and compares high shear homogenizers with two alternative solutions: high-pressure homogenizers and traditional paddle mixers.
| Comparison Aspect | High Shear Homogenizer | High-Pressure Homogenizer | Paddle Mixer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent for emulsification and particle size reduction; accommodates various viscosities. | Superior for micro and nano-emulsions; provides consistent results across different materials. | Suitable for low-viscosity applications; slower and less efficient for emulsification. |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment; operational costs depend on energy usage and maintenance. | High initial cost; ongoing maintenance can be expensive due to complex parts. | Low initial cost; minimal operational costs, but limited in capability. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires some technical knowledge for optimal setup; can be integrated into existing processes with relative ease. | Complex setup; may require specialized training for operators. | Simple to use; minimal training needed, making it accessible for most operators. |
| Maintenance | Moderate maintenance; requires regular cleaning and occasional part replacements. | High maintenance due to complexity; requires thorough cleaning after each use. | Low maintenance; easy to clean and operate. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for industries requiring fine emulsification, such as cosmetics and food. | Best suited for applications needing high-pressure processing, like pharmaceuticals. | Effective for mixing dry powders or low-viscosity liquids, such as in construction materials. |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of High-Pressure Homogenizers?
High-pressure homogenizers excel in creating micro and nano-emulsions, making them particularly valuable in industries such as pharmaceuticals and food processing. Their ability to break down particles using high pressure leads to a uniform product that is stable and consistent. However, the initial investment is considerably higher than that of high shear homogenizers, and the complexity of operation and maintenance can be daunting. Additionally, they may not be the best choice for high-viscosity materials, as these can lead to clogging.
When Should You Consider Paddle Mixers?
Paddle mixers are a cost-effective solution for blending low-viscosity liquids and dry powders. They are straightforward to operate and require minimal maintenance, making them an attractive option for businesses with limited budgets or less complex mixing needs. However, paddle mixers fall short in applications requiring emulsification or particle size reduction, making them less suitable for industries that demand high-quality homogenization.
How Should B2B Buyers Select the Right Mixing Solution?
Choosing the right mixing solution depends on specific operational requirements, including the materials being processed, desired outcomes, and budget constraints. High shear homogenizers are versatile and effective for a wide range of applications, particularly where emulsification and particle size reduction are critical. In contrast, high-pressure homogenizers may be better suited for specialized applications requiring consistent micro and nano-emulsions, while paddle mixers may suffice for simpler tasks. Buyers should evaluate their unique needs, including production volume, product characteristics, and available resources, to make an informed decision that will enhance operational efficiency and product quality.

Illustrative image related to high shear homogenizer
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for high shear homogenizer
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of High Shear Homogenizers?
When evaluating high shear homogenizers, understanding their technical properties is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in your specific applications. Here are key specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade of a homogenizer significantly impacts its durability and suitability for various industries. Common materials include stainless steel (often 316L) for its corrosion resistance and compatibility with food and pharmaceutical products. Selecting the right material ensures longevity and compliance with industry standards, which is vital in regions with stringent regulations.
2. Shear Rate
Shear rate refers to the speed at which the homogenizer can apply force to the materials being mixed. A higher shear rate results in more effective emulsification and particle size reduction, which is critical for applications in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals. Understanding the shear rate helps buyers choose a homogenizer that meets their specific viscosity and consistency requirements.

Illustrative image related to high shear homogenizer
3. Flow Rate
Flow rate, measured in liters per minute (LPM), indicates the volume of material the homogenizer can process within a given time frame. A higher flow rate is essential for large-scale operations, ensuring efficiency and productivity. For B2B buyers, assessing flow rate against production needs can prevent bottlenecks in manufacturing processes.
4. Viscosity Range
High shear homogenizers are designed to handle materials of varying viscosities, typically specified in centipoise (cP). Knowing the viscosity range your homogenizer can accommodate is crucial for applications involving thick pastes or thin liquids. This specification allows buyers to select equipment that can effectively process their specific formulations.
5. Power Rating
The power rating, usually expressed in horsepower (HP), indicates the energy required to operate the homogenizer effectively. A higher power rating can enhance mixing efficiency, especially for challenging materials. Buyers should align the power rating with their operational demands to ensure optimal performance without overloading the equipment.
6. Cleaning and Maintenance Requirements
Understanding the cleaning and maintenance requirements of a high shear homogenizer is vital for operational efficiency. Equipment that allows for easy disassembly or features self-cleaning capabilities can save time and reduce downtime between batches. For B2B buyers, this translates to lower operational costs and improved productivity.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to High Shear Homogenizers?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms relevant to high shear homogenizers:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of high shear homogenizers, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers ensure they receive reliable and high-quality equipment that meets specific industry standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers, as it can affect inventory management and pricing strategies. Understanding MOQs can help businesses plan their purchasing effectively, especially in regions with varying demand.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotations for specific products or services. For buyers of high shear homogenizers, submitting an RFQ can facilitate competitive pricing and ensure that potential suppliers meet their technical specifications.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Knowing these terms helps B2B buyers understand shipping responsibilities, risk transfer, and cost allocation, which is particularly important for companies operating across different regions.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving the product. Understanding lead times is essential for B2B buyers to manage production schedules effectively. This knowledge can also aid in supply chain planning, particularly in regions with longer shipping durations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when investing in high shear homogenizers, ensuring that they select the right equipment for their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the high shear homogenizer Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in High Shear Homogenizers?
The high shear homogenizer market is currently experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for advanced mixing solutions across various industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and chemicals. One of the primary global drivers is the rising need for product consistency and quality. As industries continue to prioritize efficiency and scalability, high shear mixers are becoming indispensable for achieving homogeneous mixtures, especially in applications involving complex formulations.
Emerging B2B technology trends are shaping the sourcing landscape. Innovations such as inline high shear mixers and batch high shear mixers provide greater flexibility and efficiency, allowing manufacturers to adapt quickly to changing product requirements. The integration of automation and IoT capabilities in mixing equipment is also gaining traction, enabling real-time monitoring and control of mixing processes. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers who need to optimize production in diverse environments, such as those found in Africa and South America.
Moreover, as competition intensifies, there is a growing emphasis on cost-efficiency and reduced lead times. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who can provide not just equipment but also comprehensive support, including laboratory testing services and customized solutions. This shift is indicative of a broader trend towards partnership-driven sourcing, where suppliers are viewed as strategic allies rather than mere vendors.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Affecting the High Shear Homogenizer Market?
Sustainability is becoming a crucial factor for B2B buyers in the high shear homogenizer sector. The environmental impact of production processes is under scrutiny, leading to a demand for energy-efficient and environmentally friendly mixing equipment. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on developing high shear homogenizers that minimize waste and energy consumption, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Ethical sourcing is equally important in this context. Buyers are more inclined to collaborate with suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to ethical labor practices and sustainable materials. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other green certifications are becoming essential criteria in supplier selection. These certifications not only enhance the credibility of suppliers but also assure buyers that they are investing in equipment that aligns with their corporate social responsibility (CSR) objectives.
Moreover, the push for greener materials is influencing the design and manufacturing of high shear homogenizers. Companies are exploring the use of recyclable or biodegradable components, which can contribute to a more sustainable lifecycle for their products. As a result, B2B buyers are encouraged to evaluate their suppliers not just on performance but also on their commitment to sustainability and ethical practices.
What Is the Evolution of High Shear Homogenizers in the B2B Context?
The evolution of high shear homogenizers can be traced back to the early 20th century when mechanical mixing methods were primarily employed. As industries expanded, the demand for more efficient and effective mixing solutions grew. The introduction of high shear mixers revolutionized the field by enabling the emulsification and dispersion of challenging materials that traditional methods could not achieve.
Over the decades, technological advancements have led to the development of sophisticated rotor-stator designs, allowing for higher shear rates and better control over particle size reduction. The ongoing innovation in materials and designs has resulted in equipment that is not only more efficient but also easier to clean and maintain, addressing some of the operational challenges faced by B2B buyers.
Today, the market is characterized by a diverse range of high shear homogenizers, each tailored to meet specific industry needs. This evolution highlights the importance of selecting the right equipment based on application requirements, emphasizing the need for B2B buyers to engage with suppliers who can provide expert guidance and tailored solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of high shear homogenizer
-
How do I choose the right high shear homogenizer for my application?
Selecting the appropriate high shear homogenizer depends on factors such as the viscosity of your materials, the desired particle size, and the type of mixing required (emulsification, dispersion, or homogenization). Consider the production scale—batch or inline mixers are available for different needs. It’s also beneficial to conduct laboratory tests to assess how different models perform with your specific materials, which can help you make an informed choice. -
What are the advantages of high shear mixing over other methods?
High shear mixing is particularly effective for achieving uniform mixtures of materials that are difficult to blend, such as solids in liquids. This method allows for variable speeds, enabling customization of shear energy tailored to specific applications. High shear mixers are versatile and can handle a wide range of viscosities, making them suitable for industries like food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. Additionally, they can often produce a more consistent product than traditional mixing methods. -
What customization options are available for high shear homogenizers?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for high shear homogenizers, including rotor-stator configurations, blade designs, and sizes that cater to specific industry requirements. You can also customize features like speed settings, batch sizes, and additional functionalities such as heating or cooling systems. Engaging with suppliers to discuss your unique needs can lead to a tailored solution that optimizes your production process. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for high shear homogenizers?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on the type of equipment being purchased. Generally, high shear homogenizers may have MOQs ranging from one unit for standard models to larger quantities for customized solutions. It’s advisable to inquire directly with manufacturers or distributors to understand their specific MOQs and negotiate terms that align with your operational needs. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing high shear homogenizers internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of high shear homogenizers typically vary by supplier and can include options such as upfront payments, net 30/60/90 days, or letters of credit. Some suppliers may require a deposit before manufacturing, particularly for custom orders. It’s essential to clarify these terms early in the negotiation process and ensure they align with your cash flow and financial planning. -
How can I ensure the quality of high shear homogenizers before purchase?
To ensure product quality, consider sourcing from reputable manufacturers with a track record of reliability in your industry. Request certifications such as ISO or CE, which indicate adherence to international quality standards. Additionally, ask for references or case studies from similar companies in your sector. If possible, arrange for a factory visit or a product demonstration to evaluate the equipment firsthand. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing high shear homogenizers?
Logistics for importing high shear homogenizers involve several key factors, including shipping methods, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Verify the supplier’s capabilities regarding packaging and freight forwarding, and understand the associated costs. Additionally, be aware of any import regulations specific to your country, including tariffs and duties. Collaborating with a logistics partner experienced in international trade can help streamline this process. -
What after-sales support should I expect from high shear homogenizer suppliers?
Reliable suppliers typically offer comprehensive after-sales support, which may include installation assistance, training for your staff, and ongoing maintenance services. Ensure that the supplier provides a warranty period during which repairs or replacements are covered. It’s also beneficial to inquire about the availability of spare parts and technical support, as this can minimize downtime and maintain operational efficiency in your facility.
Top 4 High Shear Homogenizer Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. PRO Scientific – High Shear Lab Homogenizers
Domain: proscientific.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: High shear lab homogenizers from PRO are ideal for various applications in Life Sciences, Food, Pharmaceutical, Cosmetic, Industrial, and Environmental fields. They are rotor-stator disperser homogenizers designed for high-speed shearing to disperse, homogenize, lyse, emulsify, mix, or blend samples efficiently. Key features include:
– Precision-designed generator probes for fast processing of va…
2. Admix – High Shear Dispersers
Domain: admix.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: High Shear Dispersers by Admix include the Rotosolver® mixer, Rotostat emulsifier, and Benchmix benchtop lab mixer. These mixers are designed for in-tank sanitary applications across various industries, including food, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, chemicals, and adhesives. Key features include CIP and 3-A compliant designs, enhanced efficiency for rapid dispersion and homogenization, cost savings t…
3. Texas Process Technologies – High Shear Mixer Homogenizer
Domain: texasprocesstechnologies.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: High Shear Mixer Homogenizer 3 Stages (In Stock)\n- Original Price: $20,419.75\n- Current Price: $19,837.80 (10HP WEG TEFC General Purpose Motor)\n- Availability: Low stock\n- Shipping Limitation: Mixers do not qualify for free shipping.\n- Shipping Time: Ships in 1-2 weeks if in stock.\n- Features: 10HP Motor, 3 phase 460V (Baldor Stainless Steel Motor), 316 SS product contact parts, Tri-clamp Co…
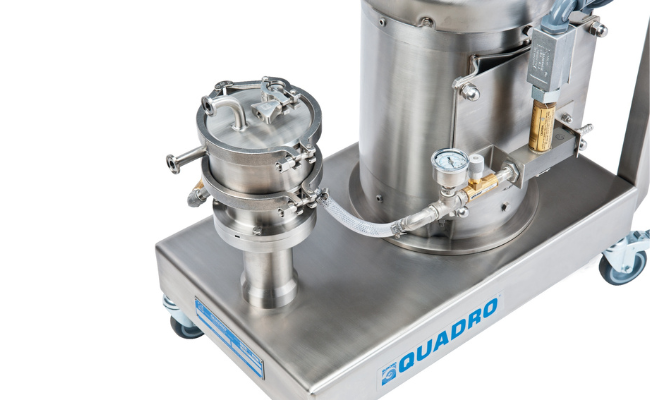
4. Quadro – High Shear Homogenizer Wet Mill
Domain: quadroliquids.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: High Shear Homogenizer Wet Mill; Designed for high shear mixing and wet milling; Suitable for a variety of applications including emulsification, homogenization, and particle size reduction; Features include adjustable rotor speed, easy cleaning, and compact design; Ideal for food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries; Available in different sizes and configurations to meet specific production …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for high shear homogenizer
In today’s competitive landscape, strategic sourcing of high shear homogenizers is essential for businesses aiming to enhance product quality and operational efficiency. By understanding the nuances between high shear mixing and homogenization, buyers can select equipment that aligns with their specific processing needs, whether for food, pharmaceuticals, or industrial applications. Key considerations include the viscosity of materials, scalability, and cleaning requirements, all of which can significantly impact production timelines and costs.
Investing in the right high shear homogenizer not only optimizes product consistency but also minimizes waste, thus contributing to sustainable practices. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to grow, the demand for advanced mixing solutions will rise.
International buyers should prioritize establishing partnerships with reputable manufacturers who offer tailored solutions and robust support. Embrace the opportunity to elevate your production capabilities by engaging with suppliers who can provide equipment suited to your specific requirements. The future of high shear homogenization is bright—seize the potential today to drive your business forward.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.