A B2B Buyer’s Guide to Gf Gps: Price, Quality, and Suppliers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for gf gps
In the rapidly evolving landscape of global commerce, sourcing reliable GPS technology, specifically GF GPS systems, poses significant challenges for B2B buyers. As organizations across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek innovative solutions to enhance operational efficiency and asset management, understanding the nuances of GF GPS products becomes paramount. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the various types of GF GPS devices, their applications in diverse industries, and critical insights into supplier vetting processes.
International buyers will benefit from a detailed exploration of the features and functionalities of GF GPS systems, including performance metrics, pricing structures, and long-term value assessments. This resource aims to empower decision-makers with actionable insights to navigate the complexities of sourcing GPS technology effectively. By addressing common pain points—such as accuracy, reliability, and user experience—this guide equips businesses to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
With a focus on providing clarity and confidence in the procurement process, this guide is essential for organizations looking to leverage GF GPS technology to optimize their logistics, enhance security measures, and drive overall business growth. Whether you’re in Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, or elsewhere in the global market, understanding the intricacies of GF GPS systems will enable you to stay ahead of the competition and make strategic investments that propel your business forward.
Understanding gf gps Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
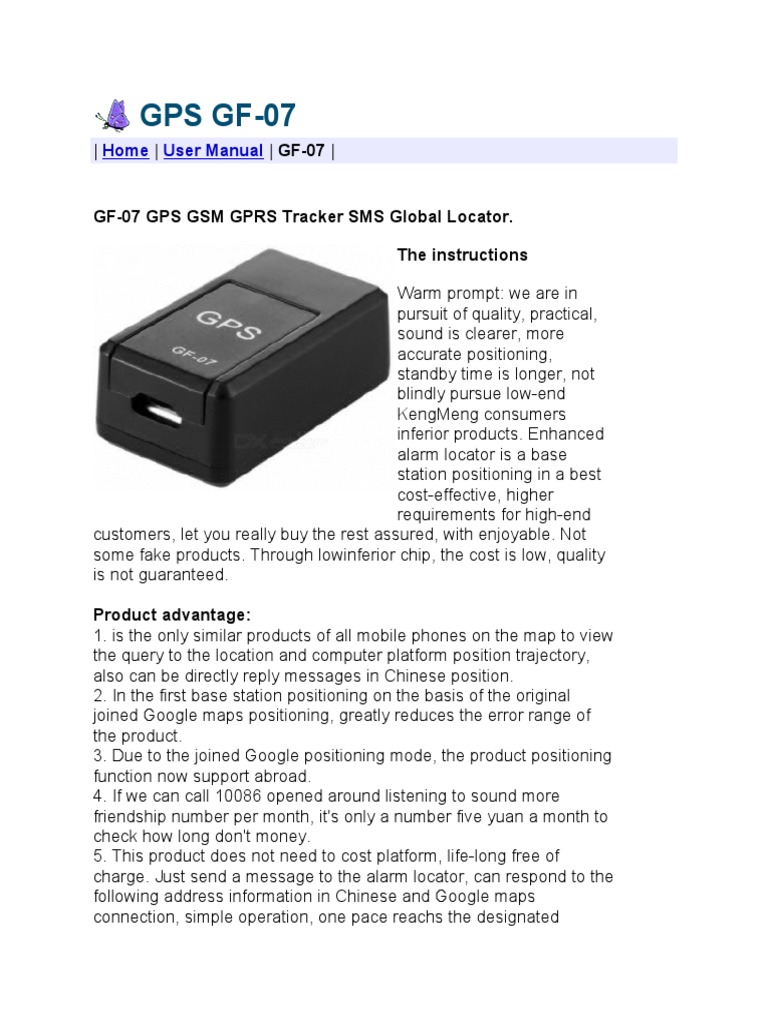
| GF-07 | Basic tracking capabilities, low cost, limited accuracy | Asset tracking, personal safety | Pros: Inexpensive, easy to use. Cons: Poor accuracy, unreliable performance. |
| GF-09 | Similar to GF-07 but includes audio monitoring feature | Vehicle tracking, security | Pros: Added audio feature, affordable. Cons: Inconsistent tracking, low battery life. |
| GF-22 | Improved location accuracy, better battery life | Fleet management, logistics | Pros: More reliable tracking, decent battery life. Cons: Higher cost, potential data privacy issues. |
| GPS-enabled Smartphones | Integrated GPS with advanced features | Emergency response, field operations | Pros: Multifunctional, high accuracy. Cons: Higher cost, may require ongoing service fees. |
| Dedicated GPS Trackers | Standalone devices with robust features | Logistics, equipment tracking | Pros: Tailored for tracking, reliable performance. Cons: Higher upfront investment, potential complexity in setup. |
What Are the Characteristics of GF-07 GPS Trackers?
The GF-07 GPS tracker is characterized by its low cost and basic tracking capabilities, making it an appealing choice for budget-conscious B2B buyers. Its primary applications include asset tracking and personal safety, particularly in industries where low-value items require monitoring. However, it suffers from significant accuracy issues, often failing to provide reliable location data. Buyers should consider the potential risks associated with its poor performance, especially in critical applications.
How Does the GF-09 Differ from Other Models?
The GF-09 offers similar features to the GF-07 but adds an audio monitoring capability, which can be beneficial for security purposes. It is often used in vehicle tracking and personal safety applications. While the audio feature may enhance its utility, the tracker still suffers from inconsistent GPS performance and short battery life. B2B buyers should weigh the added functionality against the potential drawbacks, particularly if reliable tracking is crucial to their operations.
Why Choose the GF-22 for B2B Applications?
The GF-22 stands out with improved location accuracy and battery life, making it suitable for fleet management and logistics applications. Its more reliable tracking capabilities can significantly enhance operational efficiency, particularly in industries that rely on real-time location data. However, B2B buyers should be aware of its higher cost and potential data privacy concerns. Investing in the GF-22 could be justified for businesses that prioritize accuracy and reliability in their tracking solutions.
What Are the Benefits of Using GPS-enabled Smartphones?
GPS-enabled smartphones integrate advanced tracking features, making them ideal for emergency response and field operations. Their multifunctionality allows businesses to leverage existing devices without needing additional hardware. However, the cost can be higher due to service fees and the need for robust data plans. B2B buyers should evaluate whether the benefits of using smartphones outweigh the additional expenses, especially in scenarios where dedicated tracking devices may be more effective.
When Should Businesses Consider Dedicated GPS Trackers?
Dedicated GPS trackers are tailored for tracking and provide robust features that meet specific B2B needs, such as logistics and equipment tracking. They typically offer reliable performance and greater accuracy compared to cheaper alternatives. However, they often come with a higher upfront investment and may require more complex setup processes. Businesses should consider their tracking needs, budget, and the potential return on investment when deciding whether to invest in dedicated GPS trackers.
Key Industrial Applications of gf gps
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of gf gps | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistics and Supply Chain | Fleet Management and Tracking | Enhanced operational efficiency and cost savings | Real-time tracking capabilities, battery life, and data encryption |
| Agriculture | Precision Farming and Crop Monitoring | Improved yield and resource management | Compatibility with agricultural equipment and local environmental conditions |
| Security and Surveillance | Asset Tracking for High-Value Equipment | Reduced theft risk and improved asset recovery | Accuracy in location tracking and durability in various environments |
| Transportation | Public Transportation Tracking and Management | Increased safety and improved service delivery | Integration with existing systems and user-friendly interfaces |
| Construction | Site Monitoring and Worker Safety | Enhanced project management and safety compliance | Robustness in harsh environments and compliance with local regulations |
In the Logistics and Supply Chain sector, gf gps technology is crucial for fleet management and tracking. Businesses can monitor vehicle locations in real-time, leading to enhanced operational efficiency and significant cost savings. Buyers should prioritize devices that offer long battery life and robust data encryption to protect sensitive information, especially when managing large fleets across diverse regions such as Africa and South America.
Within Agriculture, gf gps applications in precision farming enable farmers to monitor crop health and optimize resource use. This technology helps in increasing yields while minimizing waste, which is vital in resource-scarce regions. Buyers need to ensure compatibility with existing agricultural equipment and the ability to operate effectively under local environmental conditions, such as varying climates in the Middle East and Europe.
In the Security and Surveillance industry, gf gps plays a critical role in asset tracking for high-value equipment. By utilizing this technology, businesses can significantly reduce the risk of theft and enhance asset recovery processes. Buyers should look for devices that provide accurate location tracking and are durable enough to withstand various environmental challenges, particularly in regions with high theft rates.
For the Transportation sector, gf gps technology is essential for tracking and managing public transportation systems. This application improves safety and enhances service delivery by allowing for real-time updates and efficient routing. When sourcing these devices, businesses should consider their integration capabilities with existing systems and the user-friendliness of the interfaces, ensuring that they can be easily adopted by both operators and passengers.
Lastly, in Construction, gf gps is utilized for site monitoring and ensuring worker safety. This technology aids in project management by providing real-time data on site conditions and worker locations, helping to comply with safety regulations. Buyers should focus on the robustness of the devices in harsh environments and ensure that they meet local regulatory requirements, which can vary significantly across different regions.

Illustrative image related to gf gps
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘gf gps’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Language Barriers in User Interfaces
The Problem: B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and the Middle East, often encounter GPS tracking devices and applications that are solely available in Chinese or other non-local languages. This creates a significant barrier for users who are not proficient in these languages. The inability to navigate the interface can lead to frustration, improper usage, and underutilization of the technology, ultimately affecting operational efficiency and return on investment.
The Solution: To overcome language barriers, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing GPS solutions that offer multilingual support or customizable language options. When evaluating ‘gf gps’ products, ensure that you assess the software interface and confirm that it can be set to English or other relevant languages. Additionally, consider partnering with local distributors who can provide localized training and support. Investing in software solutions that allow for easy updates and user interface customization will enhance user experience and accessibility, fostering greater adoption among teams.
Scenario 2: Inaccurate Tracking Data
The Problem: A common challenge faced by businesses utilizing ‘gf gps’ technology is the inconsistency and inaccuracy of the tracking data. Reports of GPS devices providing coordinates that are significantly off from actual locations can lead to operational mishaps, such as mismanaged logistics, incorrect asset tracking, and heightened security risks. This is particularly critical for industries relying on precise location data for fleet management or asset recovery.
The Solution: To mitigate issues related to inaccurate tracking, businesses should conduct thorough research and due diligence before selecting a ‘gf gps’ device. Look for models with proven accuracy ratings, ideally those that offer real-time data updates and utilize multiple satellite systems (like GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, or Galileo) for enhanced reliability. Engage with suppliers to request performance case studies or user testimonials that validate the tracking accuracy. Additionally, implementing a rigorous testing phase, where the devices are assessed in real-world conditions, can help identify any discrepancies early on, allowing for a more informed decision before full-scale deployment.
Scenario 3: Limited Battery Life and Charging Concerns
The Problem: Many B2B buyers of GPS tracking solutions report challenges with battery life, particularly when devices need to function over extended periods without frequent recharging. This is especially pertinent for businesses operating in remote areas or regions with limited access to power sources. Poor battery performance can lead to unexpected downtimes, compromising the effectiveness of tracking solutions and causing potential financial losses.
The Solution: When considering ‘gf gps’ products, it is crucial to prioritize devices with long-lasting battery performance and efficient power management features. Research models that offer standby modes, which significantly conserve battery life when not in active use. In addition, consider the option of devices that can alert users when battery levels are low, allowing for proactive charging. It may also be beneficial to explore solar-powered or energy-efficient models tailored for outdoor applications. Collaborate with your supplier to understand the battery specifications and seek warranties or guarantees that address potential battery-related issues. Establishing a maintenance schedule for regular checks can also help in ensuring optimal device performance over time.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for gf gps
What Are the Common Materials Used in gf gps Devices?
When selecting materials for gf gps devices, it is essential to consider properties such as durability, cost, and compatibility with various environmental conditions. Here, we analyze four common materials used in gf gps applications: plastics, aluminum, stainless steel, and rubber.
How Does Plastic Perform in gf gps Applications?
Plastics, particularly polycarbonate and ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), are widely used in the casing of gf gps devices. These materials offer excellent impact resistance and can withstand a range of temperatures, typically from -40°C to 120°C. Their lightweight nature makes them ideal for portable devices.
Illustrative image related to gf gps
Pros: Plastics are generally cost-effective and can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for design flexibility. They are also resistant to corrosion, making them suitable for various environmental conditions.
Cons: While durable, plastics may not withstand extreme temperatures or prolonged exposure to UV radiation, which could lead to degradation over time. Additionally, they can be less robust than metals in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: The use of plastic is particularly beneficial for consumer-grade gps devices that require lightweight and portable designs. However, buyers should ensure that the selected plastic meets relevant standards for durability and safety.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in gf gps Devices?
Aluminum is often utilized in the structural components of gf gps devices due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for rugged applications.
Pros: Aluminum is lightweight yet strong, enhancing the durability of the device. It also has good thermal conductivity, which can aid in heat dissipation.
Cons: While it is resistant to corrosion, aluminum can be susceptible to scratches and dents, which may affect the aesthetic and functional longevity of the device. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be more complex and costly compared to plastics.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is ideal for high-performance gps devices used in outdoor or industrial applications, where durability and weight are critical factors.
Why Is Stainless Steel Chosen for gf gps Devices?
Stainless steel is another material frequently used in gf gps devices, particularly for components that require high strength and corrosion resistance. It can endure extreme temperatures and is known for its longevity.

Illustrative image related to gf gps
Pros: Stainless steel provides excellent durability and resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for harsh environments. It also offers a premium aesthetic that can enhance the marketability of the product.
Cons: The primary drawback is its weight compared to plastics and aluminum, which may be a concern for portable devices. Additionally, stainless steel can be more expensive, impacting the overall cost of the product.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is most suitable for high-end gps devices or those intended for use in severe conditions, such as marine environments.
How Does Rubber Contribute to gf gps Devices?
Rubber is often used in seals and gaskets within gf gps devices to provide protection against moisture and dust. Its flexibility and resilience make it an excellent choice for these applications.
Pros: Rubber is highly effective in creating watertight seals and can absorb shocks, protecting sensitive internal components. It is also relatively inexpensive.
Cons: Over time, rubber can degrade due to environmental factors such as UV exposure and temperature fluctuations. This degradation can compromise the integrity of seals and gaskets.
Impact on Application: Rubber is critical for ensuring the longevity and reliability of gps devices, especially those used in outdoor or rugged environments.
Summary of Material Selection for gf gps Devices
| Material | Typical Use Case for gf gps | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic | Casing for consumer-grade devices | Lightweight and cost-effective | Less durable under extreme conditions | Low |
| Aluminum | Structural components | Strong and corrosion-resistant | Susceptible to scratches | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | High-end or industrial devices | Excellent durability and aesthetics | Heavier and more expensive | High |
| Rubber | Seals and gaskets | Effective moisture protection | Can degrade over time | Low |
In conclusion, the choice of material for gf gps devices significantly impacts their performance, durability, and cost. International B2B buyers should consider these factors, along with compliance with relevant industry standards, to ensure optimal selection for their specific applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for gf gps
What Are the Main Stages of the Manufacturing Process for GF GPS Devices?
The manufacturing process for GF GPS devices typically involves several critical stages, each crucial to ensuring that the final product meets the necessary specifications and quality standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
Material Preparation: What Are the Key Components for GF GPS Devices?
The first stage involves sourcing and preparing materials, which are essential for the fabrication of GPS devices. Key components include:
-
Circuit Boards: High-quality printed circuit boards (PCBs) are crucial for the device’s electronic functionality. Manufacturers often use FR-4 material for durability and performance.
-
Sensors: GPS modules, which may include GNSS chips (GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, Galileo), are sourced from reputable suppliers. The quality of these components directly affects the accuracy of the GPS tracking.
-
Enclosures: The outer casing is typically made from durable materials such as ABS plastic or aluminum to ensure ruggedness and resistance to environmental factors.
Forming: How Are Components Shaped and Assembled?
Once materials are prepared, the forming stage begins. This includes:
-
PCB Fabrication: The circuit boards are etched and drilled according to design specifications. This process may involve surface mount technology (SMT) for placing tiny components accurately.
-
Injection Molding: For plastic components, manufacturers use injection molding techniques to shape the enclosures. This method allows for high precision and repeatability.
-
Component Assembly: The next step is assembling the components, which often involves automated pick-and-place machines for efficiency. Skilled workers may also perform manual assembly for complex parts.
Finishing: What Techniques Are Used for Final Touches?
The finishing stage focuses on enhancing the product’s aesthetics and functionality:
-
Surface Treatment: Components may undergo surface treatments such as painting, coating, or anodizing to improve durability and resistance to corrosion.
-
Quality Testing: Before packaging, devices are subjected to various quality tests to ensure they meet performance and safety standards.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for GF GPS Devices?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the manufacturing of GF GPS devices to ensure reliability and performance. Various international and industry-specific standards guide these QA processes.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For?
B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that comply with relevant international standards, such as:
-
ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is essential for ensuring consistent product quality across manufacturing processes.
-
CE Marking: For products sold in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: Particularly relevant for devices used in industrial applications, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards may be required.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are critical throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early. Key checkpoints include:

Illustrative image related to gf gps
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified requirements.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, regular checks are performed to monitor the manufacturing process and identify any deviations from quality standards.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, each device undergoes comprehensive testing, including functional tests, performance checks, and environmental simulations.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
Verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing from international markets. Here are several methods:
What Auditing Practices Should Be Implemented?
Buyers should consider conducting audits of potential suppliers. This can include:
-
On-Site Audits: Visiting the manufacturing facility allows buyers to assess the production environment, workflow, and quality control measures firsthand.
-
Supplier Self-Audits: Requesting detailed reports from suppliers can provide insights into their QC processes and adherence to standards.
What Role Do Third-Party Inspections Play?
Engaging third-party inspection services can further enhance confidence in supplier quality. These independent entities can:
-
Conduct Random Inspections: Regular inspections can ensure that the supplier maintains quality standards throughout the production cycle.
-
Provide Certification Reports: Third-party certifications can serve as a quality benchmark, providing buyers with assurance of compliance with international standards.
What Nuances Should International Buyers Consider in Quality Control?
When sourcing GF GPS devices from international suppliers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers should be aware of specific nuances:
How Do Cultural and Regulatory Differences Affect QC?
Different countries may have varying regulations regarding product quality and safety. Buyers should:
-
Understand Local Standards: Familiarize themselves with local regulations that may differ from international standards. This is particularly relevant for electronics and safety certifications.
-
Consider Language Barriers: Ensure clear communication regarding quality expectations, as language differences can lead to misunderstandings in specifications.
What Are the Risks of Sourcing from Emerging Markets?
Sourcing from emerging markets can present unique challenges, including:
-
Inconsistent Quality: While many suppliers may offer competitive pricing, quality can vary significantly. Rigorous vetting and quality checks are essential.
-
Supply Chain Reliability: Assess the reliability of the supplier’s logistics and supply chain to avoid delays and disruptions in delivery.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for GF GPS devices is essential for B2B buyers. By considering these insights and implementing robust verification practices, buyers can enhance their sourcing strategies and ensure they receive high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘gf gps’
To assist B2B buyers in sourcing GF GPS devices effectively, this guide provides a structured checklist designed to streamline the procurement process. Understanding the nuances of GPS technology and the specific requirements of your application will ensure you make informed decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before starting your search for GF GPS devices, clearly outline your technical requirements. Consider factors such as accuracy, battery life, connectivity options, and size. Establishing these parameters early will help you filter out unsuitable products and focus on those that meet your operational needs.
- Accuracy Requirements: Identify how precise the location tracking needs to be for your specific use case.
- Battery Longevity: Consider how often the device will need recharging based on its intended use.
Step 2: Research Reputable Suppliers
Finding reliable suppliers is crucial to ensuring product quality and support. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in GPS technology and positive reviews from previous clients.
- Supplier Reviews: Check online platforms and industry forums for feedback on their products and customer service.
- Certifications: Ensure the suppliers have necessary certifications to comply with international standards.
Step 3: Evaluate Product Features and Capabilities
Analyze the features of the GF GPS devices you are considering. This includes assessing their compatibility with your existing systems and their specific functionalities, such as real-time tracking and geofencing.
- User Interface: A straightforward interface can enhance usability, especially if the end-users are not tech-savvy.
- Integration Options: Ensure the device can integrate seamlessly with your software or other hardware components.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples of the GPS devices to evaluate their performance in real-world scenarios. Testing will provide insight into their reliability, accuracy, and ease of use.
- Performance Evaluation: Conduct tests in various environments to assess tracking accuracy and battery life.
- User Feedback: Gather input from team members who will be using the devices to ensure they meet operational expectations.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you’ve identified potential suppliers and tested their products, it’s time to negotiate pricing and contractual terms. This includes payment options, warranty coverage, and return policies.
- Bulk Discounts: Inquire about discounts for larger orders, which can significantly reduce overall costs.
- Warranty and Support: Ensure that the warranty period is adequate and that the supplier offers reliable customer support.
Step 6: Verify Compliance with Local Regulations
Ensure that the GF GPS devices comply with the regulatory requirements of your target market. Different regions may have specific laws governing GPS technology and data privacy.
- Data Protection Laws: Familiarize yourself with regulations regarding data collection and storage in your region.
- Import Regulations: Check for any restrictions or requirements for importing electronic devices into your country.
Step 7: Finalize the Order and Plan for Implementation
After selecting the supplier and finalizing the terms, place your order and prepare for the implementation phase. Create a detailed plan for integrating the GPS devices into your operations.
- Training: Provide training for staff on how to use the devices effectively.
- Monitoring and Feedback: Establish a system for ongoing monitoring and feedback to continuously improve usage and address any issues.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing GF GPS devices, ensuring they select the best products that meet their operational needs while minimizing risks.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for gf gps Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in GF GPS Sourcing?
When sourcing GF GPS devices, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margin.
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, such as microprocessors, antennas, and batteries, significantly impacts the final price. Higher-quality components can enhance performance and reliability but will increase initial costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and are influenced by the complexity of the manufacturing process. Countries with lower labor costs may offer attractive pricing, but this can also affect quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, utilities, and administrative functions. Efficient operations can reduce these costs, but it is essential to ensure that quality is not compromised.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for production can be substantial, especially for custom designs. Buyers should consider these costs when evaluating suppliers, as they may be passed on in the product pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are necessary to ensure the reliability of GPS devices. This adds to the overall cost but is essential for maintaining product integrity, especially in markets where performance is critical.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, including freight and insurance, can vary significantly based on the destination. For international buyers, Incoterms play a vital role in determining who bears these costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a profit margin to cover their operational costs and risks. This margin can vary widely based on market conditions and supplier reputation.
How Do Price Influencers Affect GF GPS Device Pricing?
Several factors influence the pricing of GF GPS devices, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often result in lower per-unit costs. Understanding the minimum order quantity (MOQ) can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
-
Specs/Customization: Custom features or specifications may lead to increased costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected price hikes.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly affects the pricing. Premium materials enhance durability and functionality but come with a higher price tag.
-
Quality/Certifications: Devices that meet international quality standards or certifications (e.g., CE, FCC) may command higher prices. These certifications are crucial for buyers in regions with stringent regulatory requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their track record of quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is essential for managing costs related to shipping and customs. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can significantly impact total landed costs.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in GF GPS Sourcing?
For B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective sourcing strategies can lead to significant cost savings:
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate terms with suppliers. Building a long-term relationship can lead to better pricing and terms over time.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Assess the total cost of ownership (TCO), not just the purchase price. Consider factors like maintenance, potential failures, and replacement costs.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of local market dynamics. Prices can vary based on demand, competition, and economic conditions in the supplier’s country.
-
Supplier Diversity: Engage multiple suppliers to compare pricing and quality. This not only fosters competition but also mitigates risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
-
Cultural Sensitivity: Understanding cultural differences can enhance communication and negotiations. This is particularly important in regions with diverse business practices.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
Pricing for GF GPS devices can fluctuate based on market conditions, currency exchange rates, and supplier terms. Buyers should conduct thorough market research and supplier evaluations to obtain the most accurate pricing information tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing gf gps With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to GF GPS for Tracking Solutions
In today’s competitive landscape, businesses require effective tracking solutions to safeguard assets, optimize logistics, and enhance operational efficiency. While GF GPS offers a basic tracking solution, several alternatives exist that may better suit the needs of B2B buyers, particularly in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This section compares GF GPS with two notable alternatives: the Invoxia GPS Tracker Pro and the Apple AirTag, providing insights into their respective strengths and weaknesses.
| Comparison Aspect | GF GPS | Invoxia GPS Tracker Pro | Apple AirTag |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Inconsistent accuracy; often fails to locate | Reliable with GPS; good indoor accuracy | Bluetooth-based, relies on Apple devices for location |
| Cost | Low-cost (approx. $7 – $17) | Mid-range ($150) | Moderate ($29 each) |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple setup; potential language barriers | Easy to set up via app | Seamless integration with Apple devices |
| Maintenance | Requires frequent charging; limited support | Long battery life; subscription for advanced features | No maintenance; replaceable battery |
| Best Use Case | Basic tracking for low-value items | Asset tracking for high-value goods | Item tracking in urban environments |
Invoxia GPS Tracker Pro: Pros and Cons
The Invoxia GPS Tracker Pro is a well-regarded alternative for businesses seeking a robust tracking solution. It offers reliable GPS performance with good indoor accuracy, making it suitable for tracking high-value assets. The device has a long battery life, which can last for several months without needing a recharge. However, it comes with a higher price point and may require a subscription for advanced features, which could be a deterrent for budget-conscious buyers.
Apple AirTag: Pros and Cons
Apple AirTag presents a unique solution for item tracking, particularly for businesses that utilize Apple devices. It operates on a Bluetooth-based system that leverages the vast network of Apple users for location tracking. This can provide accurate location data in urban settings. The ease of use and low maintenance are significant advantages. However, its dependency on Apple devices limits its applicability for businesses that use diverse technology ecosystems, and it is not suitable for tracking assets over long distances.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Tracking Solution?
When selecting a tracking solution, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including the specific use case, budget constraints, and technology compatibility. GF GPS may be a suitable option for organizations with minimal tracking needs or those operating on a tight budget. However, for businesses that require reliable performance and support for high-value assets, investing in alternatives like the Invoxia GPS Tracker Pro or Apple AirTag could yield better results. Ultimately, the choice hinges on balancing cost with performance requirements and the operational context in which the tracking solution will be deployed.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for gf gps
What Are the Key Technical Properties of GF GPS Devices?
In the context of GPS technology, particularly for devices like GF GPS, understanding critical technical properties is essential for B2B buyers. These specifications directly impact the performance, reliability, and suitability of the devices for various applications.
-
Accuracy and Precision
Accuracy refers to how close the GPS device’s reported location is to the actual position. Precision indicates the consistency of these measurements. For B2B applications, especially in logistics or fleet management, having a GPS device with high accuracy (within 5-10 meters) is crucial for effective tracking and operational efficiency. -
Battery Life
The longevity of a GPS device’s battery is a vital specification, particularly in applications where devices are expected to operate for extended periods without recharging. A longer battery life reduces maintenance costs and ensures uninterrupted tracking capabilities. Ideally, devices should offer at least two months of standby time to meet the needs of end-users. -
Connectivity Options
Connectivity specifications, including GSM and GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) compatibility, determine how the device communicates its location data. Devices should support multiple GNSS systems (GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, Galileo) to enhance reliability, particularly in diverse geographical regions. This connectivity is critical for ensuring real-time data transmission and effective monitoring. -
Durability and Environmental Resistance
The material grade and build quality of GPS devices are essential for ensuring longevity, especially in harsh conditions. Look for devices that are water-resistant and shock-proof, as these features enhance the reliability of the device in outdoor or industrial environments. This durability is particularly important for B2B applications in sectors such as agriculture or construction. -
Size and Weight
The compactness and weight of the GPS device are significant considerations for ease of installation and use. Lightweight and small devices are easier to integrate into various applications, from personal tracking to industrial machinery. This property is essential for businesses that prioritize unobtrusive solutions.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Associated with GF GPS Devices?
Understanding industry jargon is equally important for B2B buyers when navigating the procurement process of GPS devices. Familiarity with these terms can facilitate smoother negotiations and clarify expectations.
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products that are sold under another company’s brand. In the context of GPS devices, knowing whether a product is OEM can impact quality assurance and warranty considerations, as OEM products often have stricter quality controls. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding the MOQ is crucial for budget planning and inventory management. B2B buyers should assess their needs against the MOQ to determine the feasibility of purchasing from a supplier. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers request pricing and terms from suppliers for specific products or services. This is essential for obtaining competitive pricing and understanding the full scope of costs associated with purchasing GPS devices. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized international trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and logistics. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand shipping costs, insurance, and risk management, ensuring a smoother transaction process. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. Understanding lead times is crucial for inventory management and planning, as longer lead times can affect project timelines and operational efficiency. -
Firmware
Firmware is the software programmed into the GPS device that controls its functions. Understanding firmware specifications is essential for assessing the device’s capabilities and for troubleshooting purposes. Regular updates can enhance performance and security, making this a vital aspect of device management.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when purchasing GF GPS devices, ensuring alignment with their operational needs and strategic goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the gf gps Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the GF GPS Sector?
The global GPS market is witnessing significant growth, driven by increasing demand across various sectors, including logistics, transportation, and personal tracking. For B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the focus is on cost-effective yet reliable GPS solutions. The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies is reshaping the landscape, as businesses seek to integrate GPS capabilities into their existing systems for enhanced operational efficiency.
Emerging trends include the rise of affordable GPS trackers, like the GF series, which cater to budget-conscious consumers without compromising functionality. These devices are becoming increasingly popular for applications ranging from vehicle tracking to personal safety. Additionally, the growing emphasis on data analytics is compelling manufacturers to incorporate advanced features, such as real-time tracking and geofencing, into their products. This shift towards smart GPS technology is not only improving user experience but also providing actionable insights for businesses.
International buyers are also navigating challenges related to product quality and compliance. Many low-cost GPS devices, particularly from emerging markets, have been criticized for reliability issues, highlighting the importance of thorough supplier vetting. As the market matures, buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that demonstrate a commitment to quality assurance and customer support.

Illustrative image related to gf gps
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Be Integrated into GF GPS Procurement?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the GPS sector. As environmental concerns gain traction globally, businesses are increasingly focused on sourcing products that minimize ecological impact. For GPS devices, this involves selecting manufacturers who utilize eco-friendly materials and sustainable production methods.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers adhere to responsible labor practices and environmental regulations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and Fair Trade can serve as indicators of a manufacturer’s commitment to sustainability. Furthermore, integrating ‘green’ materials into GPS products—such as biodegradable plastics or recyclable components—can enhance brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
B2B buyers should also consider the lifecycle of GPS devices. Investing in products that are designed for longevity and easy repair can significantly reduce waste and resource consumption. By prioritizing sustainability in their sourcing strategies, companies can not only comply with regulatory requirements but also align with customer values, leading to long-term loyalty and market differentiation.
How Has the GF GPS Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the GF GPS sector reflects broader technological advancements and changing consumer needs. Initially, GPS technology was primarily utilized for navigation in vehicles and military applications. However, as the technology became more accessible, it began to permeate various sectors, including personal safety and asset tracking.
The introduction of low-cost GPS devices, such as the GF series, marked a pivotal shift, making GPS tracking feasible for a wider audience. This democratization of technology has spurred innovation and competition, with manufacturers continually enhancing features to meet diverse market demands. As the sector progresses, the focus is increasingly shifting towards integration with IoT and AI, promising even greater efficiencies and capabilities for B2B applications.
In summary, B2B buyers in the GF GPS sector must navigate a landscape characterized by rapid technological change, a growing emphasis on sustainability, and the need for reliable product sourcing. By understanding these dynamics, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and ethical standards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of gf gps
-
How do I solve GPS tracking inaccuracies in GF GPS devices?
To address GPS tracking inaccuracies, ensure that the device has a clear line of sight to the sky, as obstructions can interfere with signal reception. Regularly update the firmware to incorporate improvements and fixes released by the manufacturer. Additionally, consider testing the device in various environments to assess its performance and identify any consistent issues. If inaccuracies persist, consult the supplier for potential replacement or calibration options. -
What is the best GF GPS model for fleet management?
For fleet management, the GF-22 model stands out due to its relatively better tracking performance and ability to provide location data. It features a user-friendly interface that can integrate with existing fleet management systems. When selecting a model, also consider battery life, durability, and the availability of real-time tracking features to ensure efficient fleet operation and monitoring. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers of GF GPS devices?
When vetting suppliers, assess their experience in the GPS technology sector, including customer reviews and case studies. Verify their certifications and compliance with international quality standards. Request samples to evaluate product quality and performance. Additionally, check their after-sales support and warranty policies, as reliable support is crucial for addressing any post-purchase issues. -
What are typical payment terms when sourcing GF GPS devices internationally?
Payment terms can vary significantly based on the supplier and the buyer’s relationship. Common terms include a 30% deposit upon order confirmation, with the balance due before shipment. Some suppliers may offer letters of credit or payment upon delivery for established relationships. Always clarify these terms in writing and consider using escrow services for larger transactions to mitigate risks. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for GF GPS devices?
The MOQ for GF GPS devices typically ranges from 100 to 500 units, depending on the supplier and the specific model. Lower MOQs may be available for established buyers or during promotional periods. It’s advisable to negotiate the MOQ based on your purchasing capacity and the supplier’s willingness to accommodate smaller orders, especially for first-time buyers. -
How can I customize GF GPS devices to meet my business needs?
Customization options may include branding, firmware modifications, or hardware adjustments. Discuss your specific requirements with the supplier, who can provide insights into feasible modifications. Ensure that any changes align with the device’s technical capabilities and that you receive prototypes for testing before finalizing your order. Clear communication about your needs will help in achieving the desired customization. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing GF GPS devices?
When importing, consider shipping methods (air vs. sea), as they impact cost and delivery time. Ensure compliance with import regulations in your country, including tariffs and customs duties. It’s also wise to work with a logistics partner experienced in electronics to handle potential challenges such as customs clearance and warehousing. Tracking shipments and maintaining communication with your supplier throughout the process is essential for timely delivery. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from GF GPS suppliers?
Expect suppliers to implement strict quality assurance (QA) protocols, including pre-production samples, in-line inspections, and final product testing. Inquire about their QA certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicate adherence to international quality standards. Request documentation of testing results and warranty policies, as these ensure that the products meet your specifications and performance expectations.
Top 4 Gf Gps Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Vison Electronics – GF GPS App
Domain: play.google.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: GF GPS is an app developed by Vison Electronics Technology Ltd. that allows users to control a quadcopter equipped with a WiFi camera module. Key features include support for VGA, 720P, and 1080P video resolutions, the ability to take photos and record videos, and a 3D function. The app has a rating of 2.9 stars based on 74 reviews and has over 10,000 downloads. It is designed for everyone and was…
2. Mini GF-07 – Magnetic GPS Tracker
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “Mini GF-07 Magnetic GPS Tracker”, “features”: [“GSM”, “GPRS”, “Real-Time Vehicle Tracking”], “condition”: “Open box”, “price”: “$16.79”, “shipping”: “Free shipping”, “estimated_delivery”: “Fri, Sep 12 – Tue, Sep 16”, “seller”: {“name”: “ShopFancy”, “feedback”: “99.2% positive feedback”}, “quantity_available”: 1, “item_number”: “3761670”}
3. GF-07 – GPS Tracker
Domain: manuals.plus
Introduction: Generic GF-07 GPS Tracker Magnetic Mini Real-Time Tracking Locator; Setup Instructions: 1. Remove PIN code from SIM card; 2. Connect GPS tracker to phone by texting 000; 3. Access app by texting 102 for login info and app download link; 4. Activate GPS tracker on phone via Settings > Security & Location; 5. Connect GPS tracker to car’s OBD port and sync with app after starting the engine.
4. Uboro – GPS Tracking Solution
Domain: uboro.io
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: This company, Uboro – GPS Tracking Solution, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for gf gps
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of GF GPS products presents a unique opportunity for international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Despite the current challenges observed with some GF GPS models regarding accuracy and user experience, the potential for integrating advanced tracking technologies into various industries remains significant. Buyers must prioritize sourcing reliable, high-quality GPS solutions that can meet their specific operational needs, ensuring they conduct thorough due diligence on product performance and supplier credibility.
Strategic sourcing goes beyond mere procurement; it involves building partnerships that foster innovation and efficiency. By investing in reliable GPS technology, businesses can enhance asset management, improve safety protocols, and streamline operations. As the demand for tracking solutions continues to grow, particularly in sectors such as logistics, transportation, and security, now is the ideal time for B2B buyers to explore these technologies.
Looking ahead, we encourage buyers to engage with suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to product improvement and customer service. Embrace the evolving landscape of GPS technology to drive your business forward, ensuring you remain competitive in a rapidly changing market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.