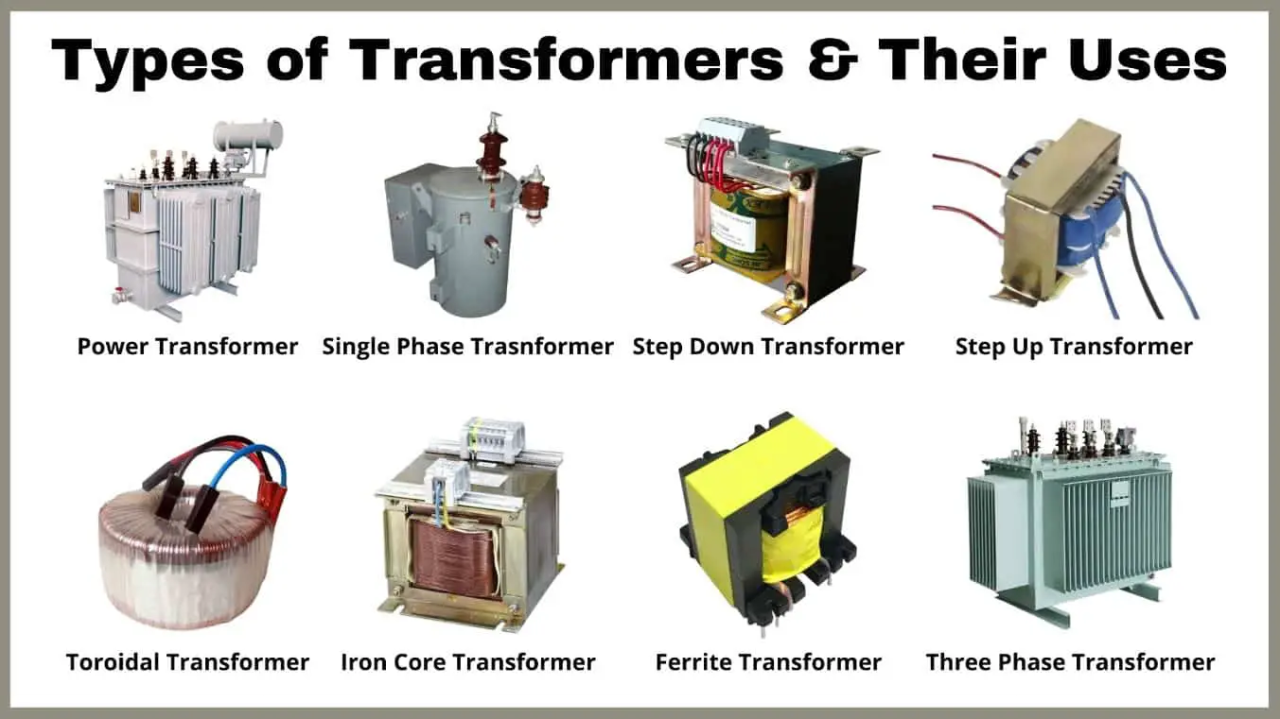
A B2B Buyer’s Guide to Different Types Of Transformers: Price, Quality, and Suppliers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for different types of transformers
In today’s interconnected global economy, sourcing the right types of transformers can be a daunting challenge for B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With varying regional demands and specific application needs, understanding the nuances of transformer types—from liquid-filled to dry-type, and substation to padmount—becomes crucial. This guide provides an in-depth exploration of different transformer types, their unique applications, and considerations for effective supplier vetting.
As you navigate the complexities of transformer procurement, this comprehensive resource will empower you with insights into cost factors, performance metrics, and the technological advancements shaping the industry. Whether you’re in Saudi Arabia seeking reliable substation transformers or in Germany exploring energy-efficient dry-type options, this guide will help you make informed purchasing decisions that align with your operational requirements.
Additionally, we delve into the key attributes to look for when selecting suppliers, ensuring that you not only find the right products but also establish partnerships with manufacturers who prioritize quality and reliability. By leveraging this guide, you can confidently approach your procurement strategy, minimizing risks while maximizing value in your transformer investments.
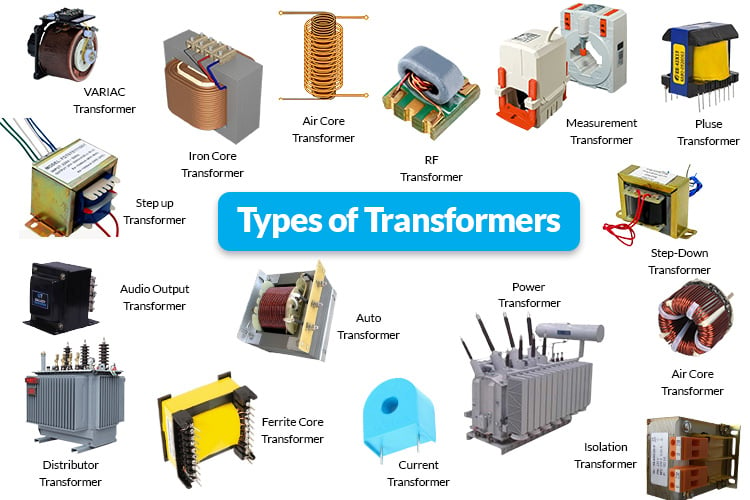
Understanding different types of transformers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid-Filled Transformers | Contains dielectric fluid for cooling and insulation | Outdoor applications, substations, industrial settings | Pros: Better heat dissipation; durable in overloads. Cons: Requires containment; more complex maintenance. |
| Dry-Type Transformers | Air-cooled, no fluids; designed for indoor use | Commercial buildings, data centers, manufacturing | Pros: No fluid leaks; easier installation. Cons: Less effective in overloads; more heat generation. |
| Padmount Transformers | Tamper-proof, compact design for outdoor areas | Public facilities, urban environments | Pros: Economic and space-efficient; safe for public use. Cons: Limited to lower voltage applications. |
| Substation Transformers | Rugged design, external monitoring devices | Heavy industrial areas, power distribution networks | Pros: High capacity; suitable for harsh environments. Cons: Larger footprint; higher installation costs. |
| Autotransformers | Single coil design for voltage adjustment | General purpose, applications needing slight voltage changes | Pros: Cost-effective; compact size. Cons: No electrical isolation; limited voltage change range. |
What Are Liquid-Filled Transformers and Their B2B Relevance?
Liquid-filled transformers utilize a dielectric fluid for cooling and insulation, making them ideal for outdoor applications and environments with high electrical loads. Their robust design allows them to handle overload scenarios more effectively than dry-type transformers. For B2B buyers, the choice of liquid-filled transformers is beneficial in settings such as substations and industrial plants where durability and heat management are critical. However, they require careful maintenance and containment systems to manage potential leaks, which can increase operational complexity.
How Do Dry-Type Transformers Benefit Indoor Applications?
Dry-type transformers are designed for indoor use and rely on air for cooling, making them suitable for commercial buildings, data centers, and manufacturing facilities. They are easier to install and maintain since they do not contain any liquid, reducing the risk of leaks. However, they generate more heat and are less capable of handling overload situations, which may necessitate additional cooling solutions. B2B buyers should consider the specific heat generation and load requirements of their applications when selecting dry-type transformers.
What Makes Padmount Transformers Ideal for Urban Settings?
Padmount transformers are characterized by their compact, tamper-proof design, which allows for safe installation in public areas like airports and campuses. These transformers are typically used for lower voltage applications and are favored for their economic advantages and minimal footprint. B2B buyers in urban environments can benefit from their ease of installation and operational safety. However, the limitation to lower voltage applications may necessitate complementary solutions for larger power distribution needs.
Why Choose Substation Transformers for Heavy Industrial Use?
Substation transformers are built with a rugged design to support high-capacity operations, often found in heavy industrial areas. They feature external monitoring devices and are capable of handling significant electrical loads, making them essential for power distribution networks. B2B buyers in sectors like manufacturing and energy should prioritize these transformers for their reliability and capacity. However, they come with a larger footprint and higher installation costs, which are important considerations for budget-conscious projects.
What Advantages Do Autotransformers Offer for Voltage Adjustments?
Autotransformers feature a single coil design that allows for cost-effective voltage adjustments, making them suitable for applications requiring minor voltage changes. Their compact size and efficiency make them attractive for general-purpose applications. However, the lack of electrical isolation between primary and secondary windings may limit their use in sensitive applications. B2B buyers should assess their specific voltage conversion needs and the potential risks associated with using autotransformers in their electrical systems.

Illustrative image related to different types of transformers
Key Industrial Applications of different types of transformers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of different types of transformers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Medium Voltage Dry-Type Transformers in production lines | Enhances operational efficiency by ensuring stable voltage for machinery | Compatibility with existing equipment and local standards |
| Renewable Energy | Substation Transformers in solar and wind farms | Facilitates efficient energy distribution and grid integration | Compliance with environmental regulations and durability in harsh conditions |
| Telecommunications | Dry-Type Transformers for data centers | Provides reliable power supply, minimizing downtime and data loss | Size and power capacity to match data center requirements |
| Mining | Liquid-Filled Transformers for remote operations | Ensures reliable power supply in harsh, isolated environments | Robust design to withstand extreme weather and operational demands |
| Commercial Buildings | Padmount Transformers for urban development | Space-saving solution that blends with surroundings while providing reliable power | Accessibility for maintenance and integration with city infrastructure |
How Are Different Types of Transformers Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, medium voltage dry-type transformers are crucial for production lines. They step down high voltage electricity to levels suitable for machinery operation, ensuring a consistent power supply. This reliability enhances operational efficiency and reduces downtime. For international buyers, compatibility with existing systems and adherence to local electrical standards are vital considerations when sourcing these transformers.
What Role Do Transformers Play in Renewable Energy?
Substation transformers are essential in renewable energy projects, such as solar and wind farms. They manage the transition of power generated at variable voltages to a stable output suitable for grid integration. This capability maximizes energy efficiency and supports sustainable practices. Buyers should consider the durability of these transformers, ensuring they can withstand environmental challenges while complying with local regulations.
Why Are Transformers Important for Telecommunications?
In the telecommunications industry, dry-type transformers are commonly employed in data centers to provide a reliable power supply. These transformers ensure that sensitive equipment operates smoothly, minimizing the risk of downtime and data loss. When sourcing transformers for this application, businesses must evaluate the size and power capacity to ensure they meet the specific energy demands of their facilities.
How Do Transformers Support Mining Operations?
Liquid-filled transformers are often used in mining operations, particularly in remote and harsh environments. They provide a stable power supply essential for operating heavy machinery and processing equipment. The robust design of these transformers allows them to endure extreme weather conditions. Buyers should prioritize sourcing transformers that can handle the operational demands of mining while ensuring reliability in isolated locations.
What Are the Benefits of Using Transformers in Commercial Buildings?
Padmount transformers are increasingly popular in urban developments for commercial buildings. Their compact and aesthetically pleasing design allows them to blend into the environment while delivering reliable power. This is especially important in densely populated areas where space is limited. When sourcing padmount transformers, businesses should consider accessibility for maintenance and how well the transformers integrate with existing city infrastructure to ensure optimal performance.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘different types of transformers’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Ensuring Efficient Power Distribution in Diverse Environments
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in regions with variable climates, such as Africa and the Middle East, face challenges in selecting transformers that can operate efficiently across diverse environmental conditions. The wrong choice can lead to equipment failures, increased maintenance costs, and operational downtime. For instance, liquid-filled transformers, while excellent for cooling in hot climates, may be prone to leaks or damage in extreme cold. Buyers may struggle to find a reliable supplier who understands the unique demands of their specific environment and can offer tailored solutions.
The Solution: To address these challenges, buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their operational environment and specify transformers that are designed for such conditions. Engaging with manufacturers who have a deep understanding of regional requirements is crucial. Buyers can benefit from selecting transformers that feature robust construction, such as encapsulated or cast coil designs, which offer enhanced protection against moisture and dust. Additionally, implementing regular maintenance schedules and environmental monitoring systems can help ensure that the transformers continue to operate efficiently regardless of external conditions. Working closely with suppliers to customize transformers according to local climate and operational needs is essential to avoid costly failures.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Sizing and Load Capacity Issues
The Problem: In many commercial and industrial applications, particularly in South America and Europe, B2B buyers often struggle with accurately sizing transformers to match their load requirements. An undersized transformer can lead to overheating and system failures, while an oversized unit may result in unnecessary capital expenditure and inefficiencies. This issue is exacerbated in industries with fluctuating power demands, where buyers may not have a clear understanding of their peak and average load requirements.
The Solution: To combat sizing issues, buyers should start by conducting a comprehensive load analysis that takes into account both current and anticipated power needs. Utilizing tools like load calculators can help provide a clearer picture of the required transformer capacity. Buyers should also consider working with engineering consultants who specialize in transformer applications to ensure accurate specifications. Additionally, choosing transformers with flexible configurations, such as autotransformers or multi-winding units, can provide the adaptability needed to handle varying load conditions effectively. Regular performance assessments and adjustments based on operational data will further enhance the efficiency and reliability of power distribution systems.
Scenario 3: Navigating Compliance and Regulatory Standards
The Problem: In Europe and parts of the Middle East, B2B buyers are often confronted with stringent regulations regarding electrical equipment, including transformers. Compliance with local and international safety standards can be daunting, particularly for businesses that lack in-house expertise in electrical engineering. Failure to adhere to these regulations can result in costly fines, project delays, and even legal repercussions. Buyers may find themselves overwhelmed by the complexity of regulations, particularly when sourcing transformers from different countries.

Illustrative image related to different types of transformers
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize engaging with suppliers who are well-versed in local regulations and can provide transformers that meet all necessary compliance standards. Conducting thorough due diligence when selecting suppliers, including reviewing their certifications and past compliance records, is vital. Additionally, buyers can benefit from establishing a compliance checklist that outlines all regulatory requirements specific to their location and industry. Collaborating with local authorities or industry associations can also provide valuable insights and resources. By ensuring that their transformers are compliant from the outset, buyers can mitigate risks and ensure smooth project execution. Regular training for staff on compliance issues can further reinforce the importance of adhering to regulations, ultimately leading to safer and more efficient operations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for different types of transformers
What Are the Key Materials Used in Different Types of Transformers?
When selecting materials for transformers, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and how they align with specific applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in transformer construction: copper, aluminum, silicon steel, and epoxy resin.
How Does Copper Perform in Transformer Applications?
Key Properties: Copper is known for its high electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity, making it an excellent choice for transformer windings. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 200°C and exhibits good corrosion resistance, especially when properly treated.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, which allows for smaller wire sizes and reduced energy losses. However, copper is relatively expensive compared to other materials, which can increase the overall cost of the transformer. Additionally, its weight can be a consideration in applications where weight is a critical factor.
Illustrative image related to different types of transformers
Impact on Application: Copper is particularly effective in high-performance applications where efficiency is paramount, such as in power distribution and industrial transformers. Its compatibility with various insulating materials ensures reliable operation under a range of conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the standards governing copper quality, such as ASTM B170 or DIN 17440. In regions like Europe and the Middle East, compliance with these standards is crucial for ensuring product reliability and performance.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Transformer Design?
Key Properties: Aluminum has a lower density than copper and is also a good conductor of electricity, though not as effective as copper. It typically has a temperature rating of around 150°C, with decent corrosion resistance, especially in non-humid environments.

Illustrative image related to different types of transformers
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its cost-effectiveness, as it is significantly cheaper than copper. Additionally, its lightweight nature makes it easier to handle and install. However, aluminum’s lower conductivity means that larger wire sizes are often required, which can offset some of the cost savings. Its susceptibility to oxidation can also affect performance if not adequately managed.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is commonly used in lower voltage transformers and applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in portable transformers. Its compatibility with various cooling methods makes it versatile for different environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that aluminum components meet relevant standards, such as ASTM B233 or JIS H 3100. In regions like Africa and South America, where humidity can be high, proper treatment against corrosion is vital.
Why Is Silicon Steel Important for Transformer Cores?
Key Properties: Silicon steel is a magnetic material that enhances the efficiency of transformers by reducing energy losses due to hysteresis and eddy currents. It typically has a saturation flux density of around 1.6 T and is available in various thicknesses.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of silicon steel is its ability to improve transformer efficiency, which is crucial for reducing operational costs. However, it is more brittle than other materials, making it more challenging to work with during manufacturing. Additionally, its higher cost compared to standard steel can impact the overall budget.
Impact on Application: Silicon steel is essential in both liquid-filled and dry-type transformers, where efficient magnetic performance is required. Its properties make it suitable for high-frequency applications, such as in industrial transformers.

Illustrative image related to different types of transformers
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A677 or DIN EN 10106 is crucial for ensuring quality. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should prioritize suppliers who adhere to these standards for reliable performance.
How Does Epoxy Resin Enhance Transformer Durability?
Key Properties: Epoxy resin is used as an insulating material in transformers, providing excellent dielectric strength and thermal stability, with a temperature rating often exceeding 180°C. It is also resistant to moisture and chemicals.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of epoxy resin is its ability to protect transformer components from environmental factors, enhancing durability and reliability. However, the manufacturing process can be complex and time-consuming, which may increase production costs.
Impact on Application: Epoxy resin is particularly beneficial in harsh environments, such as those found in submersible transformers or outdoor applications where exposure to moisture is a concern. Its compatibility with various materials allows for flexibility in design.

Illustrative image related to different types of transformers
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the epoxy resin used complies with international standards like ASTM D638 or ISO 527. In regions with extreme climates, such as parts of Africa and the Middle East, selecting high-quality epoxy can significantly impact transformer longevity.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Transformers
| Material | Typical Use Case for different types of transformers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Windings in high-efficiency transformers | Superior conductivity | Higher cost, heavier weight | High |
| Aluminum | Windings in lower voltage transformers | Cost-effective, lightweight | Lower conductivity, oxidation risk | Medium |
| Silicon Steel | Transformer cores in both liquid-filled and dry-type | Improved efficiency | Brittle, higher cost than standard steel | Medium |
| Epoxy Resin | Insulation in harsh environment transformers | Excellent durability and moisture resistance | Complex manufacturing process | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with critical insights into the materials used in transformer construction, helping them make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance with international standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for different types of transformers
What are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Transformers?
The manufacturing process of transformers involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the reliability and efficiency of the final product. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed purchasing decisions.
How is Material Preparation Conducted in Transformer Manufacturing?
The first step in transformer manufacturing is material preparation. This involves sourcing high-quality raw materials such as copper or aluminum for windings, silicon steel for cores, and dielectric fluids for liquid-filled transformers. Each material must meet specific international standards to ensure performance. For instance, copper is often preferred for its conductivity, while aluminum offers a lighter and more cost-effective option.
Once materials are sourced, they undergo rigorous inspection to verify quality. This initial quality control (IQC) is crucial as it sets the foundation for the entire manufacturing process. Suppliers can provide certificates of compliance or material test reports, allowing buyers to verify the quality of the materials used.
What Techniques are Used in the Forming Stage of Transformer Manufacturing?
The forming stage includes processes such as cutting, winding, and stacking. For the core, silicon steel sheets are cut to size and assembled into a laminated structure to minimize energy loss due to eddy currents.
Winding is a critical step where copper or aluminum wire is wound around the core to form the primary and secondary coils. Depending on the transformer type, different winding techniques are employed, such as continuous winding for large transformers or layer winding for smaller units. The winding process must be precise to ensure optimal performance and reduce the risk of failures.
How Does the Assembly Process Work for Different Types of Transformers?
The assembly stage involves integrating the core and windings into a complete unit. This may vary depending on the transformer type:
- Liquid-Filled Transformers: These units require careful sealing to prevent fluid leaks. The assembly must ensure that all components are securely fastened and that the tank is properly welded.
- Dry-Type Transformers: These transformers are generally easier to assemble since they do not contain liquid. However, they require proper ventilation to ensure efficient cooling.
During assembly, manufacturers conduct in-process quality checks (IPQC) to identify any defects early on. This includes verifying the integrity of connections and ensuring that the insulation meets specified standards.
What Finishing Processes Are Involved in Transformer Manufacturing?
The finishing stage includes painting, labeling, and packaging the transformers. A protective coating is applied to enhance durability and resistance to environmental factors, especially for outdoor applications. Proper labeling is essential for easy identification and compliance with safety regulations.

Illustrative image related to different types of transformers
Packaging is also a critical aspect, particularly for international shipments. Transformers must be securely packaged to prevent damage during transit. Manufacturers often provide detailed packaging specifications, which can be crucial for B2B buyers who need to ensure products arrive in perfect condition.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential in Transformer Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to transformer manufacturing, ensuring that products meet both industry standards and customer expectations.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Manufacturers typically adhere to international quality management standards, such as ISO 9001, which ensures a consistent quality management system. In addition to ISO certifications, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) may also be relevant, depending on the application and geographic region.
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these standards can help in evaluating suppliers. Compliance with international standards not only ensures product quality but also facilitates easier cross-border transactions.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Transformer Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection focuses on raw materials and components. Suppliers provide test reports and certificates to confirm compliance with specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during the manufacturing process help identify defects early. This may include visual inspections, electrical testing, and measurements of physical dimensions.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, transformers undergo thorough testing to ensure they meet performance specifications. Common tests include insulation resistance, power factor testing, and thermal imaging to detect hotspots.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of their suppliers:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits can help assess a supplier’s adherence to quality standards and manufacturing practices. Buyers can request audit reports as part of their due diligence.
-
Request Quality Control Documentation: Suppliers should provide detailed documentation of their quality control processes, including inspection reports and testing results.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspection Services: For added assurance, buyers may engage third-party inspection services to evaluate the quality of transformers before shipment. These services can verify compliance with international standards and provide an unbiased assessment.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
B2B buyers from diverse regions may face unique challenges regarding quality control. For example, differing standards and regulations across countries can complicate the procurement process. Buyers should be aware of local regulations and how they align with international standards.
Additionally, language barriers and cultural differences may impact communication regarding quality expectations. It is essential for buyers to establish clear lines of communication with suppliers, ensuring mutual understanding of quality requirements.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for transformers is vital for B2B buyers. By familiarizing themselves with these aspects, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and ensure they acquire reliable, high-quality transformers.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘different types of transformers’
When sourcing transformers, it’s essential to follow a structured approach to ensure you select the right type for your application. This checklist provides actionable steps for international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, to facilitate a successful procurement process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly outlining the technical requirements for the transformer you need. This includes voltage ratings, power capacity (in kVA or MVA), and application type (e.g., indoor or outdoor use). Understanding these specifications is crucial as it directly influences the type of transformer you will source.
- Voltage Needs: Specify whether you require a step-up or step-down transformer.
- Environment Considerations: Determine if you need a dry-type transformer for indoor use or a liquid-filled transformer for outdoor applications.
Step 2: Research Available Transformer Types
Familiarize yourself with the various types of transformers and their applications. Different transformers serve specific purposes, such as distribution transformers for residential use or substation transformers for industrial applications.
- Liquid-Filled vs. Dry-Type: Understand the cooling and insulation methods to select the appropriate design for your needs.
- Specialty Transformers: Identify if you need specialized transformers like autotransformers or drive-isolation transformers based on your application requirements.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers to ensure they meet your quality and reliability standards. Request company profiles, certifications, and references from previous clients.
- Experience in Your Region: Choose suppliers with a proven track record in your geographical area to ensure they understand local regulations and market conditions.
- Quality Assurance: Verify that suppliers adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO certifications.
Step 4: Request Detailed Proposals
After narrowing down your list of suppliers, request detailed proposals that outline pricing, delivery timelines, and warranty options. This will help you compare offerings effectively.
- Cost Breakdown: Look for transparency in the pricing structure, including installation and maintenance costs.
- Delivery Schedules: Ensure that the proposed timelines align with your project needs to avoid delays.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Services
Evaluate the after-sales support provided by your potential suppliers. A reliable supplier should offer comprehensive support, including installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting services.
- Technical Assistance: Check if they provide technical support during installation and operation.
- Spare Parts Availability: Ensure that the supplier can quickly provide spare parts to minimize downtime in case of issues.
Step 6: Review Contracts Carefully
Before finalizing your purchase, thoroughly review the contract terms and conditions. Pay close attention to warranty details, service agreements, and return policies.
- Warranty Coverage: Confirm the duration and extent of warranty coverage for the transformer.
- Liability Clauses: Understand the terms related to liability in case of product failure or defects.
Step 7: Finalize Purchase and Arrange Logistics
Once you have selected a supplier and agreed on the terms, finalize the purchase. Coordinate logistics for delivery, ensuring that the installation site is prepared and compliant with safety regulations.
- Installation Planning: Schedule the installation to coincide with your project timeline.
- Compliance Checks: Ensure that all local regulations regarding electrical installations are met before proceeding.
By following this structured approach, you can confidently source the appropriate transformers for your needs, minimizing risks and maximizing operational efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for different types of transformers Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Transformer Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure of different types of transformers is essential for effective budgeting and procurement. Key components that contribute to the total cost include:
Illustrative image related to different types of transformers
-
Materials: The primary materials used in transformers, such as copper or aluminum for windings, silicon steel for cores, and dielectric fluids for liquid-filled units, significantly impact costs. High-quality materials typically lead to higher prices but can enhance performance and longevity.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and are influenced by the complexity of the transformer design. Skilled labor is required for manufacturing and assembly, particularly for custom or high-spec transformers.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, utilities, and indirect labor. Overhead can fluctuate based on local economic conditions and the scale of production.
-
Tooling: Specialized tools and equipment for manufacturing transformers can be costly, particularly for custom designs. The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, affecting overall pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous testing and quality assurance processes are essential to ensure reliability and compliance with international standards. These costs are often embedded in the overall pricing of transformers.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs, especially for international buyers, can add a significant amount to the overall price. Factors such as distance, weight, and shipping method play crucial roles in logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin that can vary based on market conditions, competition, and negotiation outcomes.
What Influences Transformer Pricing for B2B Buyers?
Several factors can influence transformer pricing, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom transformers tailored to specific applications may incur additional costs. Clearly defining specifications can help avoid unexpected charges.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Transformers with higher quality materials or specific certifications (e.g., ISO, IEC) may carry premium pricing. Buyers should assess whether these certifications are necessary for their applications.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and service levels can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better service and support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international transactions, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in terms of shipping, insurance, and tariffs. This can significantly affect the total landed cost of transformers.
What Are Some Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Transformer Prices?
To maximize cost-efficiency and ensure favorable purchasing outcomes, B2B buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions to explore pricing flexibility. Leverage factors like order volume and long-term relationships to negotiate better terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the long-term costs associated with the transformers, including maintenance, energy efficiency, and potential downtime. A lower upfront cost may not always be the best value if TCO is high.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and trade regulations that can affect pricing. Engaging with local experts or consultants can provide valuable insights into these complexities.
-
Research and Benchmarking: Conduct market research to understand standard pricing for different types of transformers. This knowledge can empower buyers during negotiations and help identify competitive offers.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
While this analysis provides a framework for understanding the cost structure and pricing influences for transformers, actual prices may vary based on market conditions, supplier agreements, and specific project requirements. It is advisable to obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing and value.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing different types of transformers With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Different Types of Transformers
In the energy sector, transformers play a critical role in voltage regulation and distribution. However, there are alternative technologies and methods that can fulfill similar objectives. This section compares various types of transformers with two viable alternatives—power electronics solutions and energy storage systems—highlighting their respective strengths and weaknesses to help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
Comparison Table of Transformers and Alternative Solutions
| Comparison Aspect | Different Types of Transformers | Power Electronics Solutions | Energy Storage Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency in voltage conversion; reliable for long-term use. | Excellent for rapid response and dynamic control of power quality. | Effective for load leveling and demand response. |
| Cost | Generally high upfront costs; long-term ROI through efficiency. | Moderate costs; can vary significantly based on technology. | Initial investment can be high, but savings on energy costs can be substantial. |
| Ease of Implementation | Installation can be complex, especially for large units; requires skilled labor. | Easier to implement in existing systems; often requires less space. | Can be integrated with renewable energy systems but requires careful planning. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed; potential for oil leaks in liquid-filled units. | Minimal maintenance; often relies on software updates. | Requires regular checks; battery replacement can be costly over time. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for stable, high-capacity power distribution in urban and industrial settings. | Best for environments requiring rapid response to load changes, such as data centers. | Suitable for renewable energy applications and peak demand management. |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
What Are Power Electronics Solutions and Their Benefits?
Power electronics solutions, including devices like inverters and converters, are designed to manage and control electrical energy flow efficiently. Their primary advantage lies in their ability to react quickly to changes in demand, making them ideal for applications that require dynamic load management, such as data centers or electric vehicle charging stations. However, they may not be as effective for high-capacity voltage regulation compared to traditional transformers, and their performance can be sensitive to the quality of the electrical grid.
How Do Energy Storage Systems Operate and What Are Their Pros and Cons?
Energy storage systems, such as batteries, are increasingly being integrated into electrical networks to provide backup power and enhance grid stability. They excel in applications where energy needs to be stored during low demand and released during peak times. This capability can help reduce energy costs and improve efficiency in renewable energy systems. However, the initial capital investment can be significant, and the longevity of storage solutions often requires careful consideration of maintenance and replacement costs.
Making the Right Choice: How Can B2B Buyers Select the Best Solution?
When considering the right electrical solution, B2B buyers should assess their specific needs, such as the scale of their operations, the nature of their electrical loads, and long-term sustainability goals. If the primary requirement is stable voltage regulation over large areas, different types of transformers may be the best choice. Conversely, if rapid response and flexibility are critical, power electronics may be more suitable. Energy storage systems can be a strategic addition for businesses looking to integrate renewable energy and manage peak demand effectively. Ultimately, understanding the unique strengths and weaknesses of each option will guide buyers toward the most effective solution for their operational requirements.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for different types of transformers
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Different Types of Transformers?
Understanding the technical specifications of transformers is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when making investment decisions. Here are some critical properties to consider:
1. Voltage Rating
The voltage rating indicates the maximum voltage the transformer can handle on both the primary and secondary sides. It’s essential for ensuring compatibility with the electrical systems in use. Buyers must select transformers with voltage ratings that match their operational requirements to avoid equipment failure or safety hazards.
2. Power Rating (kVA)
Expressed in kilovolt-amperes (kVA), the power rating determines the maximum load the transformer can handle without overheating. Selecting a transformer with an appropriate power rating is vital for operational efficiency and longevity, as underloading or overloading can lead to premature failure or wasted energy.
3. Insulation Class
Transformers are classified based on their insulation materials and the maximum temperature they can withstand. Common classes include A, B, F, and H, with H being the highest at 180°C. Understanding the insulation class is essential for ensuring that the transformer can operate in the intended environment without degrading over time, particularly in regions with extreme temperatures.
4. Efficiency Rating
Efficiency ratings indicate how much of the input power is converted to output power, with losses occurring primarily as heat. A higher efficiency rating is critical for reducing operational costs, particularly in large-scale installations where energy expenses can significantly impact the bottom line.
5. Cooling Method
Transformers are cooled either by air (dry-type) or by oil (liquid-filled). The choice of cooling method affects the transformer’s application suitability, installation requirements, and maintenance needs. Understanding the cooling method helps buyers select transformers that best fit their environmental conditions and operational demands.
6. Harmonic Distortion Rating
This rating indicates the transformer’s ability to handle non-linear loads that generate harmonics. Transformers designed for higher harmonic distortion ratings are essential in applications with variable frequency drives (VFDs) or other equipment that may introduce harmonics into the system. Choosing the right transformer can help mitigate issues related to power quality.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Transformers?
Familiarity with industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in the transformer market. Here are some commonly used terms:
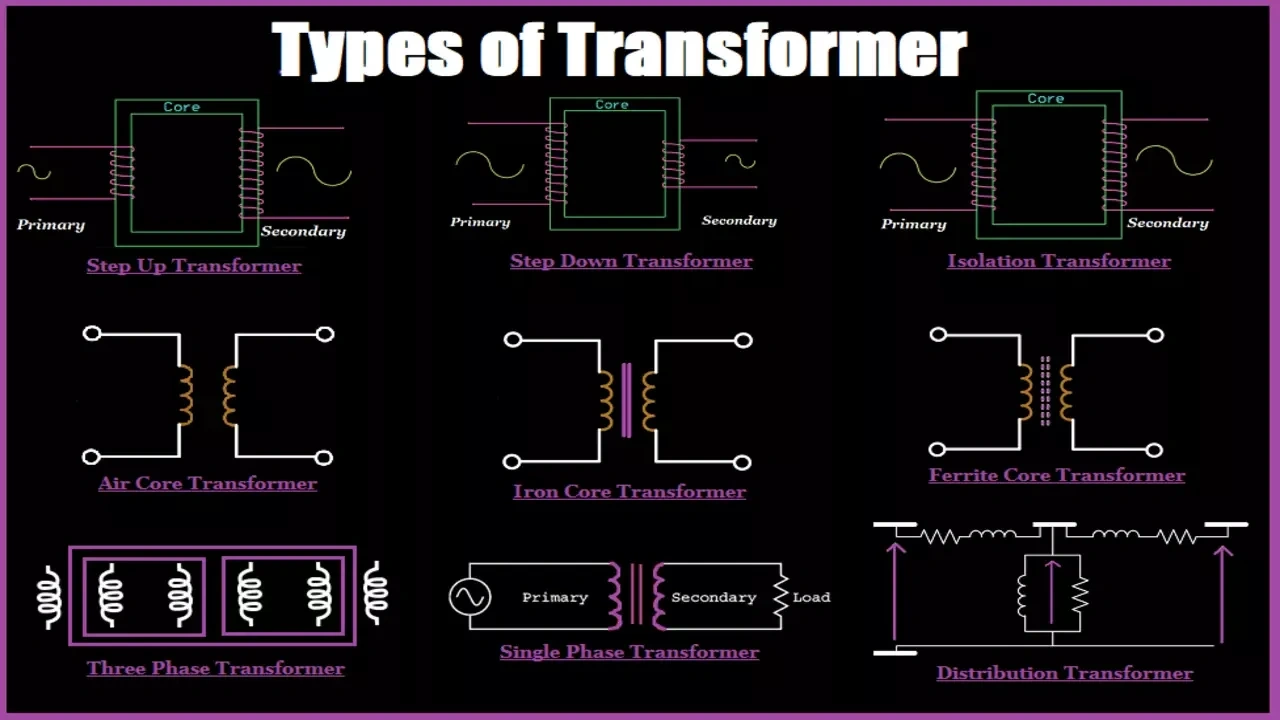
Illustrative image related to different types of transformers
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce components that are used in another company’s end products. In the transformer industry, OEMs provide transformers that meet specific specifications for various applications. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and products.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers, as it can affect inventory costs and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their purchases effectively to meet operational demands without overcommitting resources.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers asking for pricing and terms for specific products. In the transformer market, RFQs are essential for comparing offers from different manufacturers, ensuring that buyers receive competitive pricing and favorable terms.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that delineate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers to understand shipping costs, risks, and delivery obligations when sourcing transformers from different regions.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period between placing an order and receiving the product. In the context of transformers, understanding lead times is vital for project planning, especially for large installations where delays can significantly impact operations.
6. Certification Standards
These are industry standards that transformers must meet to ensure safety, efficiency, and reliability. Common standards include IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) and ANSI (American National Standards Institute). Knowing the certification standards relevant to a specific market can help buyers ensure compliance and performance expectations.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting transformers that best meet their operational needs and market conditions.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the different types of transformers Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Impacting the Transformers Sector?
The global transformer market is poised for significant growth, driven by increasing energy demands, urbanization, and the transition toward renewable energy sources. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are witnessing a surge in demand for various transformer types, including liquid-filled and dry-type transformers. Emerging markets are investing heavily in infrastructure development, necessitating reliable power distribution systems. The rise of smart grids and energy-efficient technologies is further influencing sourcing trends, as businesses seek transformers that not only meet current energy demands but also align with future sustainability goals.

Illustrative image related to different types of transformers
Furthermore, technological advancements are transforming the transformer landscape. Innovations such as digital monitoring systems and enhanced insulation materials are becoming essential. These technologies enable real-time performance tracking, predictive maintenance, and improved operational efficiency, making them attractive to international buyers seeking long-term reliability. In regions like Saudi Arabia and Germany, regulatory frameworks are also tightening, prompting companies to prioritize compliance with energy efficiency standards and invest in advanced transformer solutions.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Transformers Market?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the transformer sector. The environmental impact of transformer production and operation is under scrutiny, pushing manufacturers to adopt greener practices. Ethical sourcing of materials, such as recycled metals and eco-friendly insulation, is gaining traction. This shift not only reduces the carbon footprint but also appeals to environmentally conscious buyers looking to enhance their corporate social responsibility profiles.
Green certifications are increasingly important in the procurement process. Buyers are now more inclined to select suppliers with recognized sustainability certifications, such as ISO 14001, which ensures that environmental management systems are in place. Additionally, the use of low-impact manufacturing processes and materials that minimize waste and energy consumption is becoming a standard expectation. For international buyers, aligning with suppliers who prioritize sustainability not only helps meet regulatory requirements but also strengthens brand reputation in a competitive market.
What Is the Historical Context of Transformers in B2B Markets?
The evolution of transformers dates back to the late 19th century, marking a significant turning point in electrical engineering. Originally designed for industrial applications, transformers have transformed into essential components of modern electrical infrastructure. Over the decades, advancements in materials and technology have led to the development of specialized transformers, such as dry-type and liquid-filled units, tailored for diverse applications ranging from residential power distribution to large industrial setups.
As global energy consumption continues to rise, the transformer industry has adapted by innovating designs and improving efficiency. The shift towards renewable energy sources and smart grid technologies has further accelerated this evolution, compelling manufacturers to focus on sustainability and reliability. For B2B buyers, understanding this historical context can inform sourcing decisions, highlighting the importance of choosing suppliers who are not only experienced but also forward-thinking in terms of technology and environmental responsibility.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of different types of transformers
-
How do I choose the right transformer for my application?
Choosing the right transformer depends on several factors, including voltage requirements, load capacity, and environmental conditions. Start by assessing the voltage input and output needed for your specific application. Consider the type of transformer—liquid-filled for outdoor use or dry-type for indoor settings. Evaluate your load requirements and any potential overload scenarios. It’s advisable to consult with suppliers who can provide insights based on their experience with similar applications, ensuring you select a transformer that meets your technical specifications and operational needs. -
What is the best transformer type for outdoor installations?
For outdoor installations, liquid-filled transformers, particularly padmount and substation types, are ideal. They are designed to withstand harsh weather conditions and have effective heat dissipation properties due to the dielectric fluid used for cooling. Their sealed tank design makes them tamper-proof and suitable for public areas. If your application requires a transformer to be placed in an urban environment or in densely populated areas, consider submersible transformers, which are engineered for subsurface installations and can handle flooding. -
What should I consider when sourcing transformers internationally?
When sourcing transformers internationally, consider the supplier’s reliability, product certifications, and compliance with local regulations in your region. Verify the manufacturer’s experience and reputation in the industry. Additionally, assess logistics and shipping capabilities, ensuring they can meet your delivery timelines. Look into import duties and tariffs that may apply to your purchase, and be mindful of currency fluctuations that could impact pricing. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for transformers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for transformers can vary significantly based on the type and supplier. Generally, larger manufacturers may have higher MOQs due to production costs, while smaller suppliers may offer more flexibility. It’s essential to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies. If your requirements do not meet the MOQ, consider negotiating a trial order or exploring options for custom transformers that align with your project scope. -
What payment terms should I expect when buying transformers?
Payment terms for transformer purchases can vary by supplier and region. Common arrangements include partial upfront payments (e.g., 30-50%) with the balance due upon delivery or installation. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment terms for larger orders. Always clarify payment expectations early in negotiations and review the payment methods accepted, such as bank transfers, letters of credit, or online payment platforms, to ensure they align with your financial processes. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when purchasing transformers?
To ensure quality assurance, request product certifications and compliance documentation from your supplier, such as ISO or IEC standards. Inquire about their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and testing protocols. It’s beneficial to conduct factory visits or audits if feasible. Additionally, consider third-party testing for critical components to validate performance and reliability before final acceptance. Establishing clear quality expectations in your contract can also safeguard your interests. -
What customization options are available for transformers?
Customization options for transformers vary by supplier but can include modifications to voltage ratings, enclosure types, cooling methods, and specific features like built-in monitoring systems. If you have unique operational requirements or environmental considerations, discuss these with your supplier to see how they can tailor a transformer to meet your needs. Custom solutions may come with additional costs and longer lead times, so factor these into your planning. -
What are the logistics considerations for transporting transformers?
Transporting transformers requires careful planning due to their size and weight. Discuss logistics with your supplier, focusing on shipping methods (e.g., road, rail, sea) and packaging solutions to prevent damage during transit. Ensure that you have the necessary permits for oversized loads if applicable. Additionally, consider the timeline for delivery and any potential delays related to customs clearance. Collaborating with logistics experts familiar with heavy equipment transport can help streamline the process and mitigate risks.
Top 7 Different Types Of Transformers Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Maddox – Types of Transformers
Domain: maddox.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Types of Transformers: 1. Padmount Transformers: 3-Phase Padmount Transformer, 1-Phase Padmount Transformer. 2. Polemount Transformers. 3. Substation Transformers. 4. Dry-Type Transformers: Low Voltage Dry-Type Transformers, Medium Voltage Dry-Type Transformers, Cast Coil Transformers. 5. Mini Power Centers. 6. Switchgear: Metal-Enclosed Switchgear, Pad-Mounted Switchgear.
2. Meta Power Solutions – Pad Mount Transformers
Domain: metapowersolutions.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Types of Transformers: Single Phase Pad Mount Transformers (25 kVA, 50 kVA, 75 kVA, 100 kVA, 125 kVA, Clam-Shell 150 kVA), Three Phase Pad Mount Transformers (50 kVA, 80 kVA, 100 kVA, 160 kVA, 200 kVA, 250 kVA, 315 kVA, 500 kVA, 630 kVA, 800 kVA, 1000 kVA, 1500 kVA, 2000 kVA, 2500 kVA, 3000 kVA, 3750 kVA, 5000 kVA), Substation Transformers (76 MVA, 1000 kVA, 1500 kVA, 2000 kVA, 2500 kVA, 3000 kVA,…
3. Transformers – Types of Characters
Domain: screenrant.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: The Transformers movie franchise features seven types of Transformers: 1. Autobots – The main heroes, ruled by the Primes, including Optimus Prime and Bumblebee. They protect Earth from threats. 2. Decepticons – The main villains, led by Megatron, seeking to defeat the Autobots. 3. Constructicons – A sub-type of Decepticons that can combine to form Devastator. 4. Dinobots – A subgroup of Autobots …
4. Vietnam Transformer – Types of Transformers
Domain: vietnamtransformer.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Types of transformers include: 1. Based on core design: a. Core Type Transformer – Two cylinders with a square magnetic core. b. Shell Type Transformer – Center cylinder with HV and LV coils on the center column. c. Berry Type Transformer – Magnetic circuit resembling a wheel, filled with oil. 2. Based on voltage conversion: a. Step-Up Transformer – Increases voltage on output side. b. Step-Down T…
5. IQS Directory – Electric Transformers
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Electric transformers are devices that change electrical currents into necessary voltage levels, utilizing electromagnetic coupling to transmit electrical energy between circuits. They come in various sizes, from small units for electronics to large systems for power stations. Types include low voltage transformers for small electronics and dimmer switches, and high voltage transformers for electr…
6. Elprocus – Types of Transformers
Domain: elprocus.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Types of Transformers: Step-Up Transformer, Step-Down Transformer, Air-Core Transformer, Iron Core Transformer, Two Winding Transformer, AutoTransformer, Power Transformer, Distribution Transformer, Measuring Transformer, Protection Transformer. Applications: Power generation, distribution, transmission, and utilization of electrical power.
7. PCB Hero – Transformers Explained
Domain: pcb-hero.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Different types of transformers and their applications include: 1. Step-Down Transformer: Converts high primary voltage (e.g., 230V AC) to lower secondary voltage (e.g., 5V, 12V, 24V). Used in power adapters, cell phone chargers, and electrical distribution systems. 2. Step-Up Transformer: Increases low primary voltage to high secondary voltage. Used in stabilizers, inverters, and electrical power…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for different types of transformers
In navigating the landscape of transformer procurement, understanding the diverse types available—such as liquid-filled, dry-type, padmount, and substation transformers—enables B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific operational needs. Each transformer type presents unique advantages that can enhance efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness in power distribution.
Strategic sourcing is critical; it not only allows for the selection of the most suitable transformers but also fosters relationships with reputable suppliers who can provide ongoing support and innovation. By evaluating factors such as application environment, load capacity, and installation requirements, buyers can optimize their energy solutions while ensuring compliance with local regulations and standards.

Illustrative image related to different types of transformers
As the global market evolves, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for advanced transformer technologies will continue to rise. Forward-thinking companies should seize opportunities to engage with manufacturers and distributors who are at the forefront of innovation.
Take action today—assess your transformer needs, explore partnerships with trusted suppliers, and position your business for sustainable growth in an increasingly electrified world.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to different types of transformers
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.