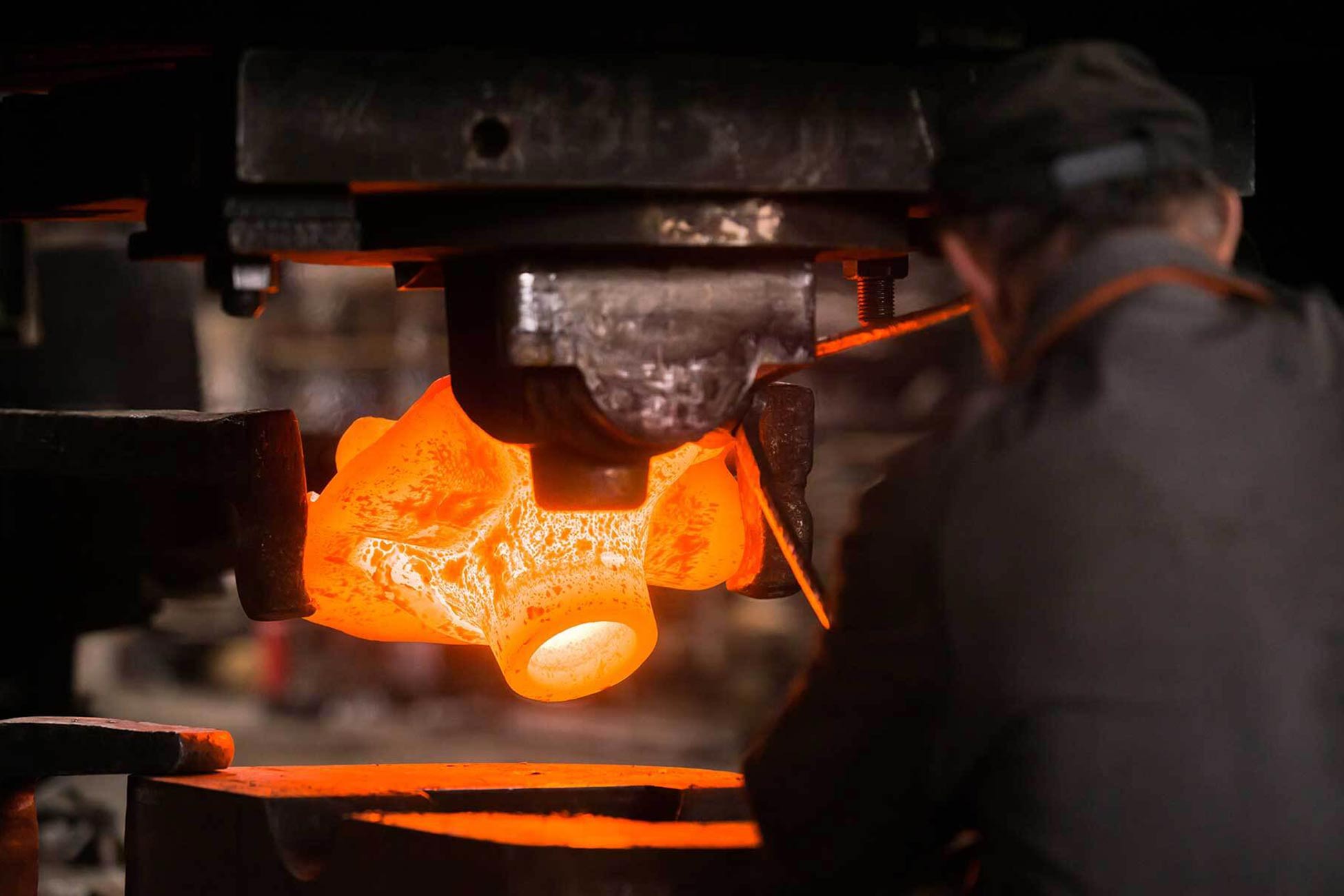
A B2B Buyer’s Guide to Die Forged Steel: Price, Quality, and Suppliers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for die forged steel
Sourcing high-quality die forged steel presents a significant challenge for international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The intricate nature of the die forging process, coupled with varying supplier standards and material specifications, can create obstacles for businesses looking to secure reliable steel products for their operations. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the global market for die forged steel, providing B2B buyers with essential insights into the different types of die forged steel, their applications, and how to effectively vet suppliers.
Throughout this guide, we will explore the nuances of die forged steel, including its manufacturing processes, quality standards, and cost considerations. By detailing the various applications across industries—from automotive to construction—we empower buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs. Additionally, we will address key factors to consider when assessing suppliers, such as certifications, production capabilities, and customer reviews, enabling buyers to establish trustworthy partnerships.
For businesses in emerging markets and established economies alike, understanding the dynamics of the die forged steel market is crucial. This guide not only facilitates better purchasing strategies but also helps mitigate risks associated with sourcing, ultimately contributing to the success and growth of your business in a competitive landscape.
Understanding die forged steel Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel Forgings | High strength, good ductility, and weldability | Automotive, construction, machinery | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile. Cons: Prone to corrosion without treatment. |
| Alloy Steel Forgings | Enhanced mechanical properties due to alloying elements | Aerospace, oil & gas, heavy machinery | Pros: Superior strength and toughness. Cons: Higher cost due to alloying materials. |
| Stainless Steel Forgings | Corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal | Food processing, medical equipment | Pros: Excellent durability, easy maintenance. Cons: Expensive and requires specialized machining. |
| Tool Steel Forgings | High hardness and wear resistance | Manufacturing tools, dies, molds | Pros: Exceptional tool longevity. Cons: Brittle, requiring careful handling. |
| High-Temperature Alloy Forgings | Retains strength at elevated temperatures | Aerospace, power generation | Pros: Ideal for extreme environments. Cons: Expensive and complex to manufacture. |
What Are the Characteristics of Carbon Steel Forgings?
Carbon steel forgings are known for their high strength, ductility, and weldability. They are primarily used in automotive, construction, and machinery applications where cost-effectiveness is crucial. Buyers should consider the potential for corrosion, which necessitates protective treatments, especially in harsh environments. The overall versatility of carbon steel makes it a popular choice for a wide range of industrial applications.
How Do Alloy Steel Forgings Stand Out?
Alloy steel forgings incorporate various alloying elements, enhancing their mechanical properties and making them suitable for demanding applications in aerospace, oil & gas, and heavy machinery. Their superior strength and toughness provide a competitive advantage in applications requiring high performance. However, buyers should be aware that the cost of alloy steel can be significantly higher than that of carbon steel, which may impact budget considerations.
Illustrative image related to die forged steel
Why Choose Stainless Steel Forgings?
Stainless steel forgings are distinguished by their corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, making them ideal for industries like food processing and medical equipment. The durability and ease of maintenance of stainless steel are compelling benefits for buyers. However, the higher cost and specialized machining requirements can be a barrier for some businesses, necessitating a careful evaluation of budget and application needs.
What Are the Benefits of Tool Steel Forgings?
Tool steel forgings are characterized by their high hardness and wear resistance, making them essential in manufacturing tools, dies, and molds. Their exceptional longevity in demanding applications is a significant advantage for B2B buyers. However, the brittleness of tool steel means it requires careful handling during production and use, making it essential for buyers to assess their operational capabilities.
When to Consider High-Temperature Alloy Forgings?
High-temperature alloy forgings are designed to maintain strength and performance in extreme conditions, making them ideal for aerospace and power generation applications. The ability to withstand high temperatures is a crucial consideration for buyers in these sectors. However, the complexity of manufacturing these alloys and their higher cost can be significant factors, necessitating a thorough cost-benefit analysis before procurement.
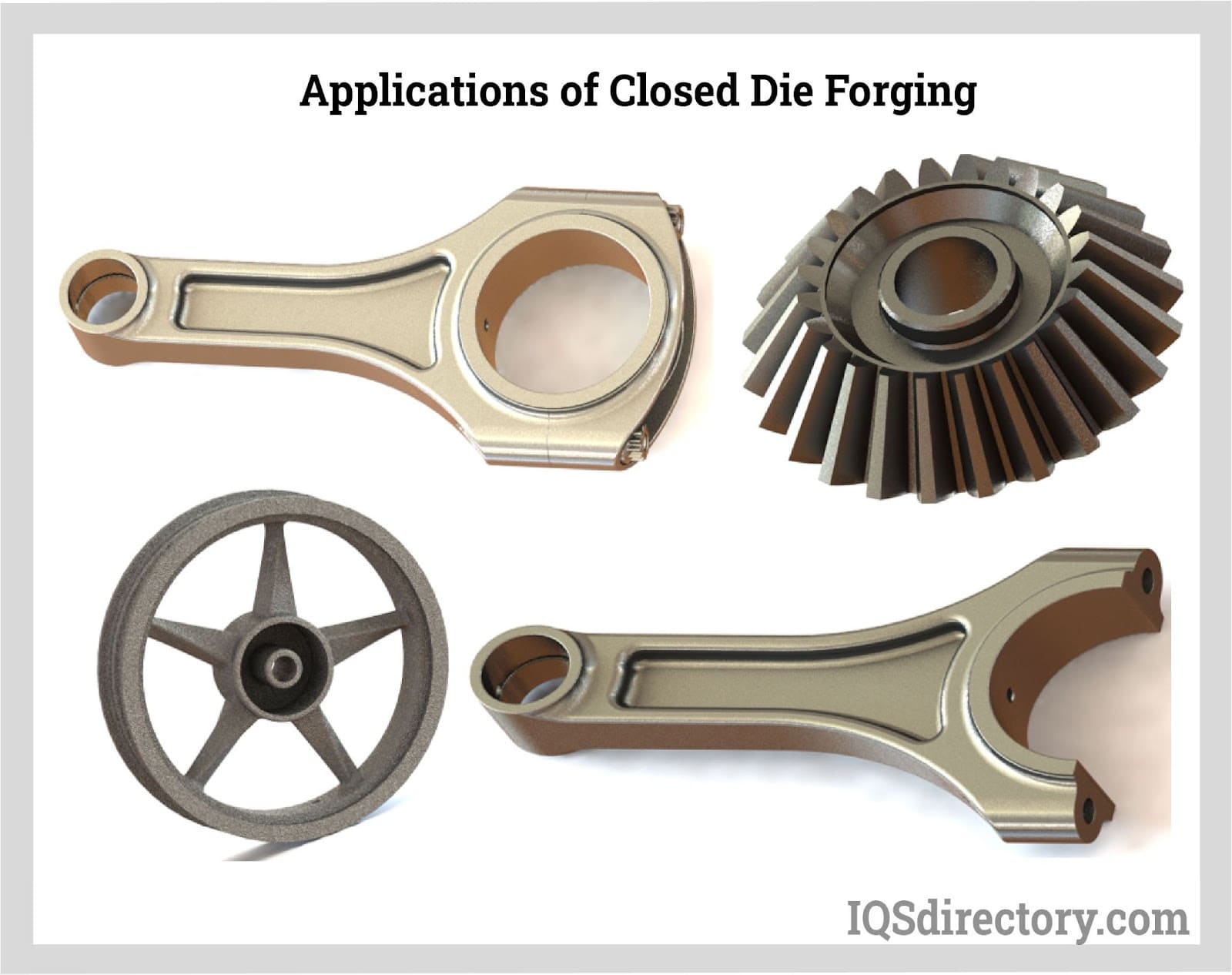
Key Industrial Applications of die forged steel
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of die forged steel | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine components manufacturing | Enhanced durability and performance | Compliance with international quality standards and certifications. |
| Aerospace | Aircraft structural components | Weight reduction with high strength | Need for precision engineering and adherence to safety regulations. |
| Oil & Gas | Drill bits and downhole tools | Improved resistance to wear and tear | Sourcing from suppliers with experience in extreme environments. |
| Construction | Heavy machinery parts | Increased lifespan and reliability | Availability of custom sizes and shapes to meet specific machinery needs. |
| Renewable Energy | Wind turbine components | Superior strength-to-weight ratio | Supplier capabilities in producing large-scale components. |
How is die forged steel used in the automotive industry?
In the automotive sector, die forged steel is crucial for manufacturing engine components such as crankshafts and connecting rods. These parts require high strength to withstand extreme conditions while maintaining weight efficiency. The use of die forged steel helps solve problems related to component failure and performance degradation, ultimately enhancing vehicle reliability and efficiency. International buyers should consider suppliers who can provide certifications for quality and precision, ensuring adherence to stringent automotive standards.
What role does die forged steel play in aerospace applications?
In aerospace, die forged steel is employed to produce structural components like landing gear and engine mounts, where weight reduction is paramount without compromising strength. This material’s inherent toughness is essential for components that endure significant stress and fatigue. Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East must prioritize suppliers who meet aerospace quality standards, including AS9100 certification, to ensure safety and performance in flight.
How does die forged steel benefit the oil and gas industry?
The oil and gas industry utilizes die forged steel for manufacturing drill bits and downhole tools that must endure harsh conditions, including extreme temperatures and pressures. The durability of die forged steel significantly reduces wear and tear, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. Buyers should seek suppliers with expertise in producing components that can withstand such demanding environments, as well as those who can provide reliable service and support.
Why is die forged steel important in construction machinery?
In the construction industry, die forged steel is used for heavy machinery parts such as gears and frames, where strength and reliability are critical. The enhanced durability of these components leads to longer equipment lifespans and reduced maintenance needs. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers can offer custom sizes and specifications to meet the unique requirements of different machinery, as well as compliance with local and international safety standards.
How is die forged steel applied in renewable energy sectors?
In renewable energy, particularly in wind turbine production, die forged steel is used for components that require a superior strength-to-weight ratio, such as turbine shafts and gearboxes. This application helps in maximizing energy efficiency and performance. Buyers in Africa and South America should focus on suppliers capable of producing large-scale components and ensuring timely delivery to meet project timelines, as well as those who adhere to sustainability practices in their manufacturing processes.

Illustrative image related to die forged steel
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘die forged steel’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Sourcing High-Quality Die Forged Steel
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face challenges in sourcing high-quality die forged steel that meets specific industry standards. This difficulty can stem from a lack of reliable suppliers, varying quality standards across regions, and the potential for miscommunication about material specifications. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America may struggle with limited access to certified manufacturers, leading to concerns about the durability and performance of the steel products they purchase. This can ultimately impact production timelines and project outcomes.
The Solution:
To overcome sourcing challenges, it is essential for buyers to conduct thorough research and establish relationships with reputable suppliers. Utilizing online platforms that specialize in industrial materials can help in identifying certified manufacturers with a proven track record in die forged steel production. Buyers should also request material test reports and certifications, such as ISO or ASTM standards, to ensure the quality of the steel. Additionally, engaging in direct communication with suppliers to clarify specifications and quality requirements can help mitigate risks associated with poor material performance. Forming partnerships with local distributors who have access to international suppliers can also enhance sourcing efficiency.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Quality in Die Forged Steel Products
The Problem:
Inconsistencies in the quality of die forged steel can lead to significant production issues, especially in sectors such as automotive or aerospace where precision is crucial. Buyers may encounter variations in strength, ductility, and finish, which can compromise the integrity of the final products. This challenge is particularly pronounced when dealing with multiple suppliers or when sourcing from regions with differing manufacturing practices and standards.
The Solution:
To ensure consistent quality, buyers should implement a robust quality assurance protocol. This includes establishing clear specifications for die forged steel products and conducting regular audits of suppliers. Collaborating closely with suppliers to develop a quality control plan that includes in-process inspections, final product testing, and adherence to specific manufacturing standards can help maintain consistency. Additionally, investing in local testing facilities to perform material tests can provide immediate feedback and prevent the use of subpar steel. Building long-term relationships with a select few suppliers who understand your quality requirements can also lead to improved consistency over time.
Illustrative image related to die forged steel
Scenario 3: High Costs Associated with Die Forged Steel
The Problem:
Cost management is a significant pain point for B2B buyers dealing with die forged steel, particularly when faced with fluctuating raw material prices and additional processing costs. Buyers may find themselves paying a premium for high-quality steel, which can strain budgets and affect overall project viability. In regions with economic instability, these fluctuations can be even more pronounced, complicating procurement strategies.
The Solution:
To combat high costs, buyers should explore bulk purchasing agreements with suppliers, which can lead to discounts and more favorable pricing structures. Additionally, leveraging long-term contracts can help stabilize costs over time, providing predictability in budgeting. Buyers should also consider alternative materials or hybrid solutions that can reduce reliance on die forged steel without sacrificing performance. Conducting a comprehensive cost analysis that includes total cost of ownership—factoring in the lifecycle, maintenance, and potential savings from increased product durability—can help justify investments in higher-quality steel. Lastly, fostering competitive bids from multiple suppliers can drive costs down while ensuring that buyers still receive quality materials.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for die forged steel
When selecting materials for die forged steel applications, it is essential to consider various factors including mechanical properties, cost-effectiveness, and compatibility with specific industry standards. This analysis focuses on four common materials used in die forged steel processes, providing insights into their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
What are the Key Properties of Carbon Steel in Die Forged Steel Applications?
Carbon steel is a widely used material in die forging due to its excellent strength and hardness. It typically exhibits high tensile strength and good wear resistance, making it suitable for applications that require durability under stress. Carbon steel can withstand high temperatures, which is crucial for forging processes. However, its corrosion resistance is limited, necessitating protective coatings or treatments in environments prone to oxidation.

Illustrative image related to die forged steel
Pros: Carbon steel is relatively inexpensive and easy to manufacture, making it a cost-effective choice for many applications. Its high strength-to-weight ratio is advantageous for industries requiring lightweight components.
Cons: The primary limitation is its susceptibility to rust and corrosion, which can lead to premature failure in harsh environments. Additionally, it may require heat treatment to achieve desired hardness levels, increasing manufacturing complexity.
How Does Alloy Steel Enhance the Performance of Die Forged Steel?
Alloy steel, which includes elements like chromium, nickel, and molybdenum, is engineered to improve specific properties such as toughness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance. This material is particularly beneficial in applications involving high-stress environments, as it can endure extreme conditions without deforming.
Pros: The enhanced properties of alloy steel make it suitable for high-performance applications, such as automotive and aerospace components. Its improved fatigue resistance prolongs the lifespan of forged parts.

Illustrative image related to die forged steel
Cons: The complexity of manufacturing alloy steel can lead to higher costs. Additionally, the specific alloying elements may require careful selection to meet precise performance criteria, which can complicate sourcing and procurement.
What Role Does Stainless Steel Play in Die Forged Steel Applications?
Stainless steel is known for its superior corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications in industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and marine environments. Its ability to maintain strength at elevated temperatures also makes it suitable for high-heat applications.
Pros: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its resistance to rust and corrosion, which reduces maintenance costs and extends the service life of components. It also offers aesthetic appeal due to its shiny finish, which can be beneficial in consumer-facing applications.
Illustrative image related to die forged steel
Cons: The major drawback is the higher cost compared to carbon and alloy steels. Additionally, the forging process can be more complex due to the material’s toughness, which may require specialized equipment.
Why is Tool Steel Essential for High-Precision Die Forging?
Tool steel is specifically designed for manufacturing tools and dies, providing exceptional hardness and wear resistance. It is often used in applications that require high precision and durability, such as molds and dies for injection molding.
Pros: Tool steel’s hardness and wear resistance make it ideal for high-precision applications where dimensional stability is critical. Its ability to withstand high temperatures without losing hardness is also advantageous in die forging processes.
Cons: Tool steel can be expensive and challenging to work with due to its hardness. The need for specialized heat treatment processes can also increase manufacturing time and costs.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Die Forged Steel
| Material | Typical Use Case for die forged steel | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | General industrial components | Cost-effective and easy to manufacture | Limited corrosion resistance | Low |
| Alloy Steel | High-performance automotive parts | Enhanced toughness and fatigue resistance | Higher manufacturing complexity and cost | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing and marine applications | Superior corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex forging process | High |
| Tool Steel | Molds and dies for precision tools | Exceptional hardness and wear resistance | Expensive and requires specialized treatment | High |
This strategic material selection guide aims to assist B2B buyers in making informed decisions when sourcing die forged steel materials, particularly in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the properties and implications of each material can lead to better procurement strategies and enhanced product performance.

Illustrative image related to die forged steel
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for die forged steel
Die forged steel is a critical material in various industries, renowned for its strength and durability. Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols is essential for B2B buyers, especially those sourcing from international markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This section delves into the key stages of die forged steel production, applicable quality control standards, and how buyers can ensure they are working with reputable suppliers.
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Die Forged Steel?
The manufacturing of die forged steel typically encompasses four primary stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is crucial to ensuring the final product meets the required specifications.
How Is Material Prepared for Die Forging?
Material preparation is the foundational step in die forging. High-quality steel billets are selected based on the desired mechanical properties. These billets are then heated to a specific temperature, typically between 1,100°C and 1,200°C, to achieve malleability. Proper temperature control is vital, as it affects the flow of steel during the forging process. Following heating, the billets are cut to size and may undergo surface cleaning to remove any contaminants that could affect the quality of the forged product.
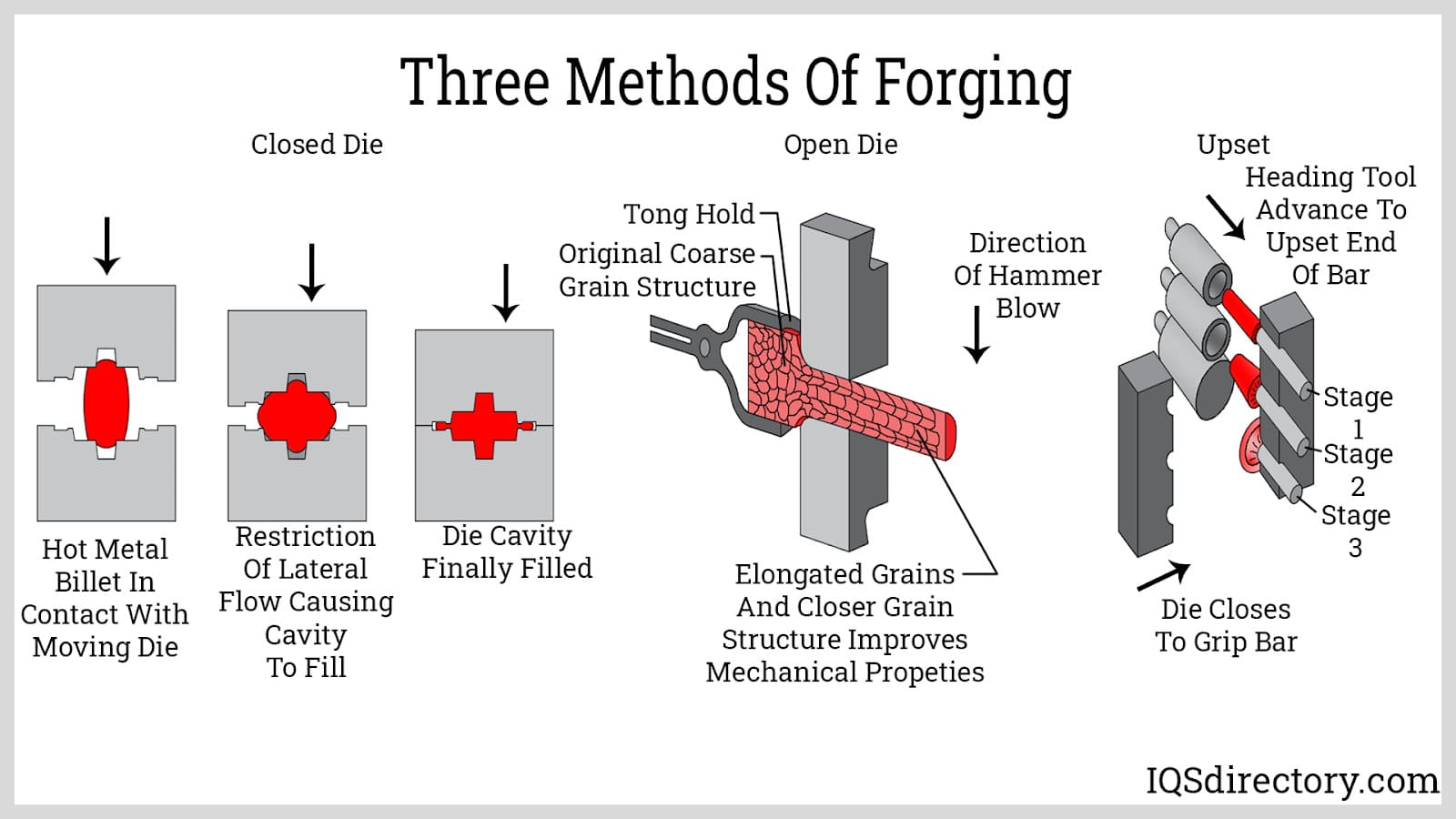
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage?
The forming process is where the actual shaping of the steel occurs. This is achieved through various forging techniques, including open-die forging and closed-die forging. Open-die forging is suitable for larger components, allowing for significant shaping through repeated hammering or pressing. Conversely, closed-die forging is ideal for producing intricate shapes with tight tolerances, as the steel is confined within a die. Each technique serves specific applications, and the choice often depends on the desired complexity and volume of production.
How Is Assembly Conducted in Die Forging?
In some cases, multiple forged components may need to be assembled. This stage involves fitting together different parts that have been forged separately. Assembly may require additional processes like welding or machining to ensure that the components fit together accurately. Precision in this stage is crucial, particularly for applications in industries like automotive and aerospace, where reliability and safety are paramount.
What Finishing Processes Are Commonly Employed?
The finishing stage involves processes that enhance the mechanical and aesthetic properties of the forged steel. Common finishing techniques include heat treatment, surface hardening, and coating applications. Heat treatment can improve toughness and reduce residual stresses, while surface hardening increases wear resistance. Coatings, such as galvanization or painting, provide additional corrosion resistance, which is critical for components exposed to harsh environments.
What Quality Control Standards Are Relevant for Die Forged Steel?
Quality assurance is a vital aspect of manufacturing die forged steel. International and industry-specific standards guide manufacturers in maintaining high-quality production processes.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized standard for quality management systems applicable across various industries. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that the manufacturer has established a systematic approach to quality management, focusing on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. For die forged steel, adherence to ISO standards ensures that the products are produced consistently and meet customer requirements.
What Industry-Specific Certifications Are Important?
In addition to ISO standards, certain industry-specific certifications may be required, depending on the application. For instance, the American Petroleum Institute (API) certification is essential for components used in the oil and gas sector, ensuring that they meet stringent safety and performance criteria. Similarly, CE marking is crucial for products sold in the European market, indicating compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection legislation.

Illustrative image related to die forged steel
How Is Quality Control Implemented During Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is integrated into every stage of the manufacturing process, with specific checkpoints to ensure that any defects are identified and rectified promptly.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Die Forged Steel Manufacturing?
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival. Billets are examined for chemical composition and physical defects to ensure they meet specifications before being used in production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, real-time monitoring is conducted. This includes checking temperatures during forging and inspecting dimensional accuracy at various stages. Any deviations from the specified parameters are addressed immediately.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the forging and finishing processes are complete, a comprehensive inspection is performed. This includes mechanical testing (tensile strength, hardness), dimensional verification, and visual inspections to ensure that the product meets all specified criteria.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
When sourcing die forged steel, particularly from international suppliers, it’s essential for B2B buyers to verify the quality control measures in place.
What Steps Can Buyers Take to Ensure Supplier Compliance?
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality management practices. Buyers should look for evidence of compliance with international standards and certifications.
-
Request Documentation: Suppliers should provide quality assurance documentation, including test reports and certifications. This information can help buyers assess the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturing processes and the final products. These inspections can be particularly beneficial for buyers unfamiliar with the local manufacturing landscape.
What Are the Nuances for International Buyers?
B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of the cultural and regulatory differences that can impact quality assurance. Understanding local manufacturing standards and practices is crucial, as they may differ from international norms. Buyers should also consider the implications of tariffs, trade agreements, and logistical challenges when sourcing die forged steel from different regions.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for die forged steel is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on the key stages of production, relevant standards, and effective verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions and build successful partnerships with suppliers in the global market.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘die forged steel’
When it comes to sourcing die forged steel, a systematic approach is essential for ensuring quality, cost-effectiveness, and timely delivery. This checklist provides B2B buyers with a clear roadmap to navigate the complexities of procurement in international markets.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing precise technical specifications is crucial before initiating the sourcing process. Clearly outline the grades of die forged steel required, including any necessary dimensions, tolerances, and mechanical properties. This clarity helps suppliers provide accurate quotes and ensures that the final product meets your operational needs.
- Considerations:
- Identify the specific applications for which the die forged steel will be used.
- Specify standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO) to ensure compatibility with international requirements.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in die forged steel. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to compile a list of candidates. This initial research phase is vital for building a network of reliable suppliers.
- Where to Look:
- Industry-specific trade publications and online marketplaces.
- Recommendations from industry peers and associations.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Before proceeding, it’s crucial to assess the capabilities of potential suppliers. This includes evaluating their production capacity, technology, and expertise in die forging. Understanding a supplier’s capabilities helps ensure they can meet your specifications and delivery timelines.
- Key Questions:
- What types of machinery and technology do they use?
- Can they accommodate custom orders or varying production volumes?
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Certification verification is a critical step in establishing supplier credibility. Ensure that suppliers possess relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific quality standards. These certifications indicate a commitment to quality control and operational excellence.
- Why It Matters:
- Certifications can significantly reduce the risk of receiving substandard materials.
- They often reflect the supplier’s adherence to international quality and safety standards.
Step 5: Request Samples and Perform Testing
Before finalizing any orders, request samples of the die forged steel. Conduct rigorous testing to verify that the samples meet your technical specifications. This step is essential for mitigating risks associated with quality and performance.
- Testing Criteria:
- Mechanical properties such as tensile strength and hardness.
- Dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Finalize Contracts
Once you’ve selected a supplier, engage in negotiations to finalize pricing, delivery schedules, and payment terms. Clear and concise contracts should outline all aspects of the agreement, including penalties for non-compliance.
- Consider Including:
- Provisions for quality assurance and inspection rights.
- Terms for returns or replacements in case of defective products.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Effective communication is key to successful procurement. Establish a clear communication plan with your supplier to facilitate updates on production status, shipping, and any potential issues. This proactive approach fosters strong supplier relationships and helps ensure smooth operations.
- Best Practices:
- Schedule regular check-ins to discuss progress and address concerns.
- Use collaborative tools for real-time updates and documentation sharing.
By following this structured checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the sourcing process for die forged steel, ensuring they obtain high-quality materials that meet their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for die forged steel Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Die Forged Steel Sourcing?
When sourcing die forged steel, understanding the cost structure is critical for making informed purchasing decisions. The main cost components include:
-
Materials: The primary raw materials for die forged steel include high-quality steel alloys. Prices can fluctuate based on market demand, availability, and geopolitical factors affecting steel production.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential in the forging process, which can influence costs significantly. Labor rates vary by region, with countries in Africa and South America often facing different wage structures compared to Europe or the Middle East.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facilities, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Overhead can vary depending on the supplier’s location and operational efficiency.
-
Tooling: The cost of dies and molds used in the forging process must be considered. Custom tooling can significantly increase initial costs but may result in better quality and efficiency for large orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that die forged steel meets specific standards involves rigorous QC processes. Costs associated with testing and certifications can add to the overall price but are crucial for maintaining product integrity.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary widely based on the distance from the supplier to the buyer and the mode of transport. International shipping also requires considerations for tariffs and customs duties.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a margin to cover their risks and ensure profitability. This can vary based on supplier reputation, market conditions, and the specific contract terms negotiated.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Die Forged Steel Pricing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of die forged steel, making it essential for buyers to understand them thoroughly:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often attract better pricing due to economies of scale. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk purchases, making it beneficial for buyers to consolidate their orders.
-
Specifications and Customization: Tailored solutions or unique specifications can lead to higher costs. Buyers should weigh the need for customization against the potential price increase.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Steel quality directly impacts performance and longevity. Certifications such as ISO or ASTM standards can increase costs but provide assurance of quality, making them worth considering.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their experience and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms affect the total landed cost, including responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs clearance. Understanding these terms can help buyers avoid unexpected costs.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Die Forged Steel Procurement?
To optimize procurement, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engaging in open dialogue with suppliers can lead to better pricing, especially for long-term contracts. Establishing a good relationship can result in favorable terms and conditions.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of focusing solely on the purchase price, consider the total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. Investing in higher-quality steel may yield lower TCO over time.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East should be aware of currency fluctuations and local economic conditions that can impact pricing. It may be beneficial to secure fixed pricing agreements to mitigate risks associated with currency volatility.
-
Research and Due Diligence: Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers, including their production capabilities, delivery timelines, and customer reviews. This knowledge can empower buyers to make more informed decisions and negotiate effectively.
Conclusion
Understanding the cost structure, price influencers, and strategic negotiation approaches for die forged steel can significantly enhance procurement efficiency for international B2B buyers. By considering all cost components and leveraging effective negotiation strategies, companies can secure the best value for their investments in die forged steel. While prices can vary widely, a comprehensive approach ensures that buyers are well-equipped to navigate the complexities of sourcing this critical material.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing die forged steel With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Die Forged Steel: A Comprehensive Comparison
In the competitive landscape of industrial manufacturing, selecting the right material or method is crucial for optimizing performance and cost-efficiency. Die forged steel is a popular choice due to its strength and durability, but several alternative solutions can also meet similar needs. This analysis compares die forged steel with two viable alternatives: cast steel and stamped metal.
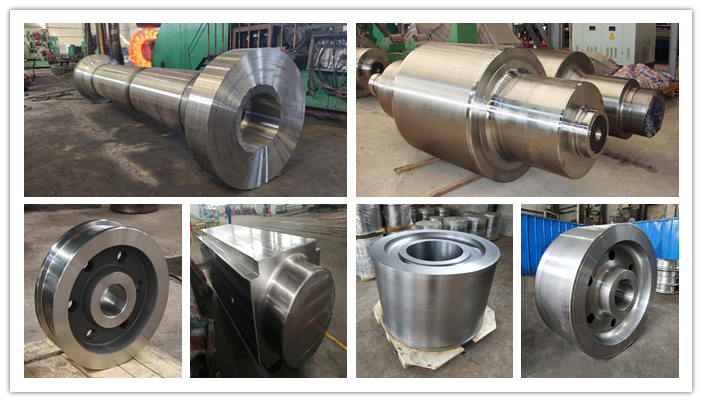

Illustrative image related to die forged steel
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Die Forged Steel | Cast Steel | Stamped Metal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High tensile strength; excellent fatigue resistance | Good strength; less fatigue resistance than forged steel | Moderate strength; limited durability |
| Cost | Higher initial cost; cost-effective for large volumes | Generally lower cost; ideal for large production runs | Lower cost; economical for high-volume projects |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized equipment and skilled labor | Easier to implement; fewer technical requirements | Simple processes; minimal skill required |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to durability | Moderate maintenance; susceptible to wear | Higher maintenance; prone to deformation |
| Best Use Case | High-stress applications (e.g., aerospace, automotive) | Structural components (e.g., bridges, machinery) | Consumer goods, automotive panels, and appliances |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
Cast Steel: A Cost-Effective Solution
Cast steel is produced by pouring molten metal into molds, allowing for complex shapes and sizes. Its lower initial cost makes it attractive for large-scale production. However, while cast steel offers good strength, it does not match the fatigue resistance of die forged steel, making it less suitable for high-stress applications. Cast steel is ideal for structural components where weight is less of an issue, but buyers should be cautious about its performance in demanding environments.
Stamped Metal: A Versatile and Economical Choice
Stamped metal is created by pressing metal sheets into desired shapes using dies. This method is highly efficient for high-volume production, leading to lower costs per unit. While stamped metal is suitable for consumer goods and automotive parts, its moderate strength and susceptibility to deformation under stress may limit its application in more demanding environments. For projects that prioritize cost and production speed over durability, stamped metal can be an excellent choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your B2B Needs
When selecting between die forged steel and its alternatives, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including the specific application, budget constraints, and production requirements. Die forged steel is ideal for high-performance applications where strength and durability are paramount, while cast steel offers a more economical solution for structural needs. Stamped metal serves well in consumer products where cost and production efficiency are key. Ultimately, the decision should align with the project’s objectives, ensuring that the chosen material or method not only meets performance standards but also adheres to budgetary considerations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for die forged steel
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Die Forged Steel?
Die forged steel is known for its superior mechanical properties and is used in various industrial applications. Understanding its technical specifications is crucial for B2B buyers, ensuring they select the right materials for their needs.

Illustrative image related to die forged steel
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of steel based on its chemical composition and mechanical properties. Common grades for die forged steel include AISI 4140 and AISI 4340, which are alloy steels known for their strength and toughness. Selecting the appropriate grade is vital as it affects the performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness of the end product.
2. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels indicate the allowable variation in dimensions and properties of the forged components. In die forging, tighter tolerances lead to better fit and function in assemblies, which can enhance product quality and reduce waste. Understanding tolerance requirements helps buyers ensure that the forged components meet their design specifications, thus minimizing the need for costly rework or adjustments.
3. Yield Strength
Yield strength is a measure of the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically. For die forged steel, high yield strength is essential for components subjected to heavy loads and stress. This property is critical for industries such as automotive and aerospace, where safety and reliability are paramount.

Illustrative image related to die forged steel
4. Hardness
Hardness measures a material’s resistance to deformation or scratching. Die forged steel typically exhibits high hardness, making it suitable for applications requiring wear resistance. This property is particularly important in manufacturing tools, dies, and high-wear components.
5. Ductility
Ductility refers to a material’s ability to undergo significant plastic deformation before rupture. In die forged steel, a good balance of ductility and strength is essential, allowing for complex shapes and designs without compromising integrity. Buyers should consider ductility when assessing the performance of components in dynamic applications.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Die Forged Steel?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B sector. Here are several key terms that are commonly used in the die forged steel industry.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of die forged steel, OEMs often require high-quality, precise components for their products. Understanding OEM relationships can influence purchasing decisions and pricing strategies.
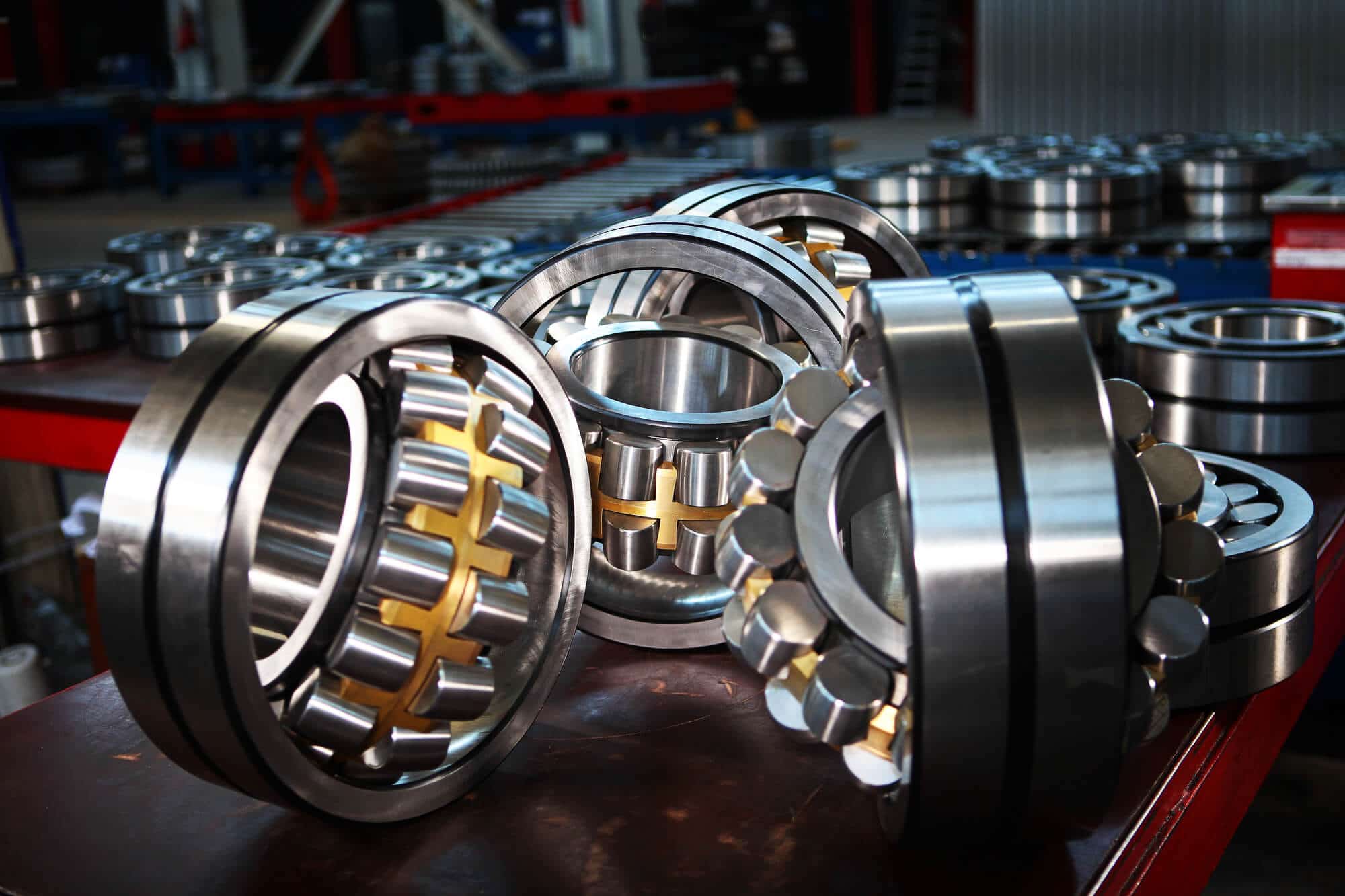

Illustrative image related to die forged steel
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. In die forged steel, MOQs can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the components. Buyers must be aware of MOQs to ensure they can meet their production needs without incurring excess inventory costs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that solicits price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. In the die forged steel market, issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare pricing and terms from different suppliers, aiding in informed decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B transactions involving die forged steel, as they dictate shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost allocation.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to delivery. In die forged steel, lead times can vary based on the complexity of the components and the supplier’s capacity. Buyers should factor in lead times when planning their production schedules to avoid delays.
In summary, being knowledgeable about the essential technical properties and trade terminology of die forged steel equips B2B buyers with the insights necessary for making informed purchasing decisions, ensuring they obtain the right materials for their industrial applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the die forged steel Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Die Forged Steel Sector?
The die forged steel market is witnessing significant growth, driven by increasing demand in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and construction. The global push for infrastructure development, particularly in emerging economies in Africa and South America, is fueling the demand for high-strength materials like die forged steel. Additionally, the rise of advanced manufacturing technologies, such as automation and Industry 4.0, is transforming sourcing strategies. Companies are increasingly leveraging digital platforms for procurement, enabling real-time tracking of materials, streamlined communication, and enhanced supplier relationships.
Emerging trends also indicate a shift towards localized sourcing, particularly in regions like the Middle East and Europe, where geopolitical factors and supply chain vulnerabilities have prompted businesses to seek domestic suppliers. This trend not only mitigates risks associated with international shipping but also supports local economies. Furthermore, the integration of data analytics and AI in supply chain management is allowing buyers to make informed decisions based on predictive insights, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency.

Illustrative image related to die forged steel
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Die Forged Steel Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become paramount in the die forged steel sector. The environmental impact of steel production, including carbon emissions and resource depletion, has led to increased scrutiny from consumers and regulatory bodies. As a result, international buyers are prioritizing suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and minimizing waste throughout the manufacturing process.
Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and ResponsibleSteel™ are becoming crucial in supplier selection. These certifications not only demonstrate a commitment to environmental stewardship but also help companies mitigate risks associated with non-compliance and potential reputational damage. Moreover, the adoption of ‘green’ materials and processes can lead to cost savings in the long run, making sustainability a key driver in sourcing decisions.
How Has the Die Forged Steel Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the die forged steel sector has been marked by significant technological advancements and shifting market demands. Initially, traditional forging methods dominated the industry, characterized by labor-intensive processes and limited precision. However, with the advent of modern engineering techniques and materials science, the sector has transitioned towards more sophisticated manufacturing processes, such as precision forging and computer numerical control (CNC) machining.
This evolution has enabled manufacturers to produce components with higher strength-to-weight ratios, essential for the increasingly stringent performance requirements in industries like aerospace and automotive. Additionally, the globalization of supply chains has opened new markets for die forged steel, allowing companies to expand their reach and enhance competitiveness. As the industry continues to adapt to changing consumer preferences and technological innovations, it remains critical for B2B buyers to stay informed about these developments to leverage opportunities effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of die forged steel
-
How do I ensure the quality of die forged steel from suppliers?
To ensure the quality of die forged steel, request certification documents such as ISO 9001 or equivalent quality management systems. Conduct supplier audits to assess their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Additionally, consider sourcing samples for testing mechanical properties and compliance with international standards. Establishing a clear quality assurance protocol in your purchase agreement will also help safeguard against subpar materials. -
What are the key specifications to consider when sourcing die forged steel?
When sourcing die forged steel, key specifications include the steel grade, tensile strength, hardness, and impact resistance. It’s also crucial to consider the dimensions and tolerances required for your application. Be aware of any industry-specific standards or certifications needed for the end-use, such as ASTM or EN standards. Communicate these specifications clearly to potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your requirements. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for die forged steel?
The minimum order quantity for die forged steel can vary significantly between suppliers and is often influenced by factors such as material type, dimensions, and production capabilities. Generally, MOQs can range from a few tons to several hundred tons. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with suppliers, as some may offer flexibility for smaller orders, especially for custom projects. -
How can I customize my die forged steel orders?
Customization of die forged steel orders typically involves specifying dimensions, grades, and treatments based on your application needs. Many suppliers offer options for tailored forging processes or additional treatments such as heat treatment or surface finishing. Engaging in detailed discussions with your supplier about your requirements will help them provide a more accurate quote and timeline for customized orders. -
What payment terms are standard in die forged steel transactions?
Standard payment terms for die forged steel transactions can include options such as advance payment, letter of credit, or net 30/60 days terms after delivery. The choice of payment terms often depends on the relationship with the supplier, order size, and country of operation. Always ensure that payment terms are clearly outlined in the purchase agreement to avoid misunderstandings. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing die forged steel?
Logistics for importing die forged steel include evaluating shipping methods, customs clearance processes, and potential tariffs. Ensure that your supplier provides necessary documentation for customs, such as certificates of origin and compliance. Additionally, consider the lead times for production and shipping to align with your project timelines. Collaborating with a logistics partner experienced in handling heavy materials can also streamline the process. -
How do I vet potential suppliers of die forged steel?
Vetting suppliers involves conducting thorough research and due diligence. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in the industry, positive customer reviews, and certifications that validate their quality standards. Request references and conduct site visits if possible to assess their facilities. Engaging in a trial order can also help evaluate their reliability and product quality before committing to larger purchases. -
What are common applications for die forged steel in various industries?
Die forged steel is widely used across several industries, including automotive, aerospace, construction, and energy. Its applications range from critical components like gears and shafts in machinery to structural elements in buildings. Understanding the specific requirements of your industry will help you select the appropriate grade and properties of die forged steel for optimal performance in your applications.
Top 6 Die Forged Steel Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. 7 Days to Die – Forged Steel
Domain: 7daystodie.fandom.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: {“name”: “Forged Steel”, “type”: “Intermediate Resource”, “category”: “Resources”, “description”: “Forged Steel is a forgeable multi-purpose resource that can be used for crafting and upgrading various items. It is easy to forge but an expensive resource to use.”, “crafting_requirements”: {“Iron”: {“amount”: 20, “source”: “Forge”}, “Clay”: {“amount”: 10, “source”: “Forge”}}, “advanced_engineering_…
2. Reddit – Forged Steel Acquisition Guide
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Forged Steel can be obtained by scrapping street lights, transformers, non-working vending machines, and weight benches. It can also be purchased from traders. To find a crucible, check traders every 3 days or invest in intelligence to unlock the schematic. For the cheapest way to get the crucible, raise intelligence to 4, wear Nerdy Glasses to increase it to 5, and get Better Barter 3 to find cru…
3. GL Forge – Alloy Steel Forgings
Domain: glforge.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: {‘product_name’: ‘Alloy Steel Forgings’, ‘manufacturing_process’: ‘Open-Dye Forging’, ‘characteristics’: ‘Strong, economical, good mechanical properties, customizable performance characteristics’, ‘alloying_elements’: [‘Manganese’, ‘Silicon’, ‘Nickel’, ‘Titanium’, ‘Copper’, ‘Chromium’, ‘Aluminum’], ‘forged_alloy_steel_grades’: [{‘grade’: ‘4130’, ‘description’: ‘Excellent weldability and high stren…
4. Fremont Cutting Dies – Forged Die Solutions
Domain: fremontcuttingdies.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Forged Dies are constructed using special forged rule, 4140, S7, and Stainless Steel. Die wall thickness is normally .25″(6.35mm) to .50″(12.7mm) with almost unlimited heights. Cutting edges are typically center bevel, Straight Inside Wall (SIW) or Straight Outside Wall (SOW). Investment: Moderate. Size Options: Small – Medium/Large. Die Life: High (100,000+ Impressions). Tolerance: 0.015″ (.38mm)…
5. Steam Community – Forged Steel Crafting Issues
Domain: steamcommunity.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Forged Steel in 7 Days to Die requires 31 iron and 15 clay to craft 1 ingot. Players have reported issues with crafting limits, where they can only select a maximum of 200 forged steel to craft at a time, despite having sufficient materials. This issue is linked to the Advanced Engineering skill, which reduces the material cost for crafting but causes the game to initially check against the base c…
6. Cornell Forge – Forging Services
Domain: cornellforge.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Cornell Forge offers a range of forging services including Closed Die Hot Forging, Microalloy Forging, Stainless Steel Forgings, Forged Alloys, and Custom Forged Steel Parts. The forging process involves forming raw metal without melting it, utilizing techniques such as hammering, rolling, or pressing. Key advantages of forged parts include higher tensile strength (26% greater than comparable cast…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for die forged steel
How Can Strategic Sourcing Transform Your Business in Die Forged Steel?
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of die forged steel is pivotal for businesses aiming to enhance operational efficiency and product quality. By leveraging strong supplier partnerships, companies can access high-grade materials that not only meet international standards but also offer cost efficiencies through bulk purchasing and reduced wastage. Understanding the local market dynamics in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe enables buyers to optimize their supply chains and negotiate better terms.
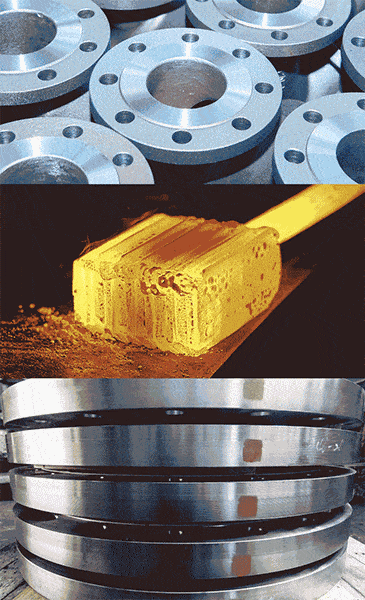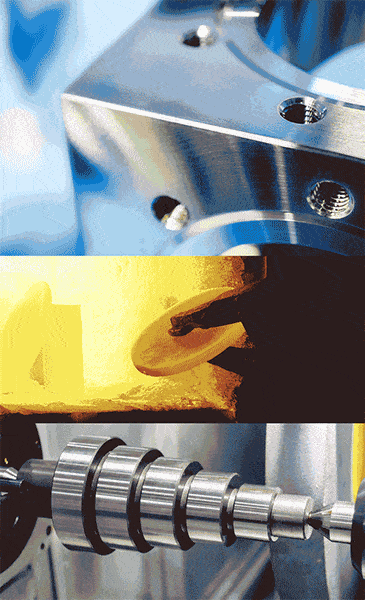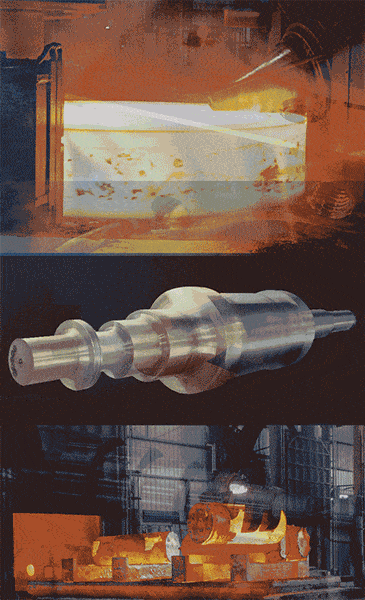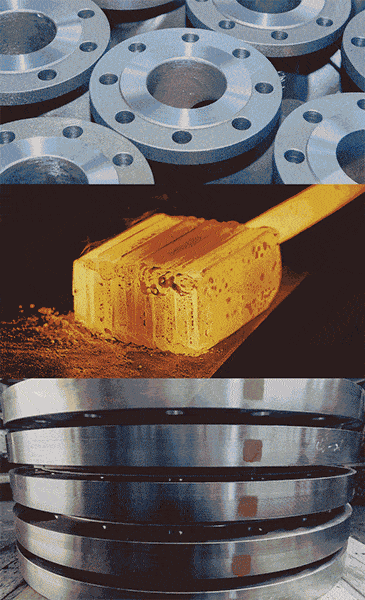
Illustrative image related to die forged steel
Furthermore, as industries increasingly demand sustainability and innovation, sourcing die forged steel from suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices can significantly enhance your brand’s reputation. Engaging with suppliers that focus on advanced engineering techniques will not only improve product offerings but also ensure compliance with evolving regulations.
As we look to the future, the global demand for die forged steel is set to grow. International buyers are encouraged to take proactive steps in their sourcing strategies today. By doing so, they position themselves to capitalize on market opportunities and foster resilience against supply chain disruptions. Embrace strategic sourcing to drive your business forward in this competitive landscape.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

Illustrative image related to die forged steel