A B2B Buyer’s Guide to Die Cutting Process: Price, Quality, and Suppliers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for die cutting process
In the dynamic landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing the right die-cutting process can be a pivotal challenge for international B2B buyers. The die-cutting process is essential for converting a wide array of materials—such as rubber, plastics, and foams—into precise shapes that meet specific industry needs. As businesses from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including Brazil and Vietnam) expand their operations, understanding the nuances of die-cutting becomes crucial for enhancing product quality and operational efficiency.
This comprehensive guide will delve into various types of die-cutting methods, including rotary and overhead die-cutting, and explore their applications across multiple industries. Additionally, we will discuss critical factors like tooling options, cost considerations, and best practices for supplier vetting. By equipping B2B buyers with in-depth knowledge about these processes, this guide aims to empower informed purchasing decisions, ensuring that you select the most suitable die-cutting solutions for your unique requirements.
Navigating the complexities of die-cutting not only aids in improving production outcomes but also fosters better supplier relationships. As you engage with this guide, you will gain actionable insights to streamline your sourcing process and enhance your competitive edge in the global market.
Understanding die cutting process Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rotary Die-Cutting | High-speed production using cylindrical dies | Labels, gaskets, adhesive tapes | Pros: Cost-effective for high volumes; precise cuts. Cons: Limited to certain material thicknesses. |
| Overhead Die-Cutting | Utilizes steel rule dies for low-volume production | Large parts, custom shapes | Pros: Versatile for larger, thicker materials. Cons: Slower run rates lead to higher labor costs. |
| Kiss-Cutting | Cuts through the top layer, leaving a liner intact | Stickers, labels, foam parts | Pros: Maintains the integrity of the backing material. Cons: Not suitable for all material types. |
| Steel Rule Dies | Customizable blades for various shapes and thicknesses | Packaging, automotive parts | Pros: Good for medium volumes; can be re-ruled. Cons: Slower production rates; higher labor costs. |
| Magnetic Tooling | Utilizes magnets for quick tool changes | High-speed rotary presses | Pros: Reduces setup time significantly. Cons: Typically requires specialized equipment. |
What Are the Characteristics of Rotary Die-Cutting and Its Suitability for B2B Buyers?
Rotary die-cutting is characterized by its use of cylindrical dies that allow for high-speed production, making it ideal for large-scale applications such as labels and adhesive tapes. This method excels in delivering precise cuts with minimal waste, which is crucial for cost-efficiency in high-volume manufacturing. B2B buyers should consider rotary die-cutting when they require rapid turnaround times and consistent quality, particularly in industries like packaging and automotive.
How Does Overhead Die-Cutting Differ from Other Methods for B2B Applications?
Overhead die-cutting employs steel rule dies to cut through materials, making it particularly suitable for low-volume production or larger parts. This method is versatile and can handle thicker materials, which is beneficial for custom shapes. However, the slower run rates can lead to increased labor costs, making it less ideal for high-volume needs. B2B buyers should evaluate their production scale and material specifications when considering overhead die-cutting.
Why Choose Kiss-Cutting for Specific Applications in B2B Transactions?
Kiss-cutting is distinct in that it cuts only through the top layer of a material while leaving the liner intact. This technique is highly effective for producing stickers and labels, where the backing material is essential for product integrity. B2B buyers should opt for kiss-cutting when they require intricate designs or shapes that need to be easily peeled away from a carrier. It is essential to ensure that the materials used are compatible with this cutting method.
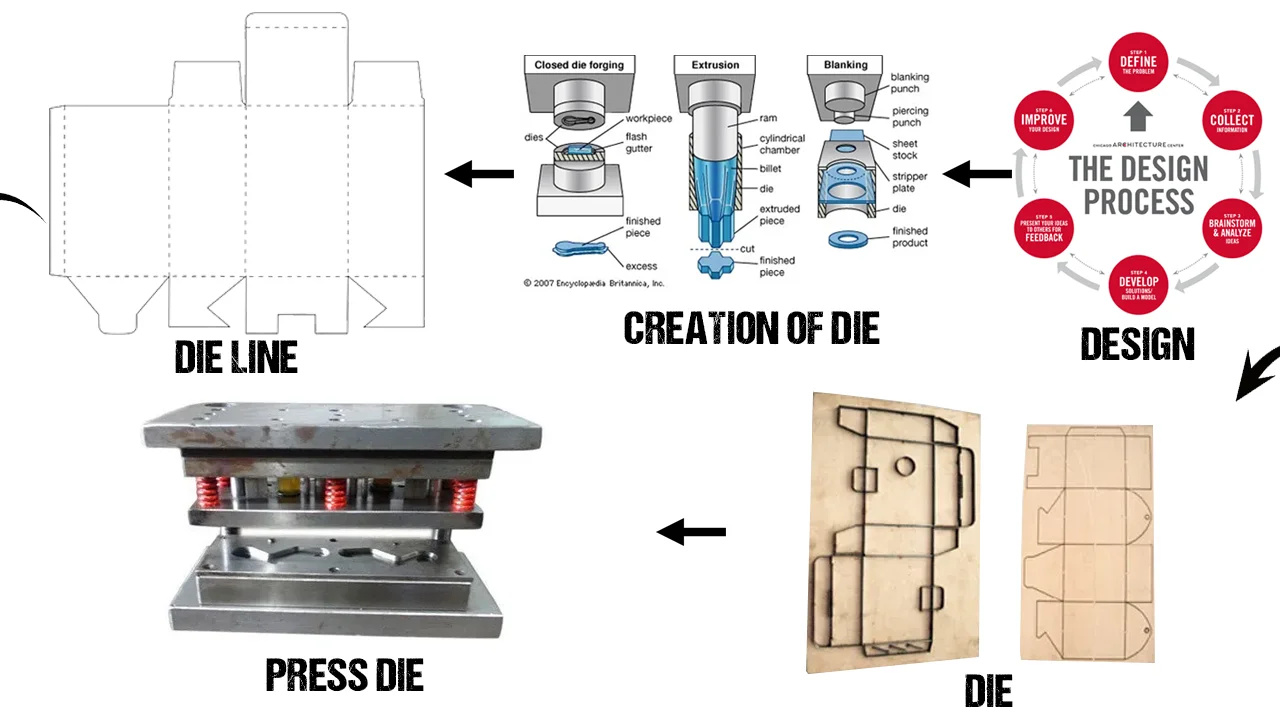
Illustrative image related to die cutting process
What Are the Advantages of Using Steel Rule Dies in B2B Manufacturing?
Steel rule dies are known for their customizable blades, which can accommodate various shapes and thicknesses. This method is advantageous for producing medium-volume items, such as packaging and automotive components. While steel rule dies can be re-ruled, resulting in extended usability, their slower production rates may lead to higher labor costs. B2B buyers should assess their volume needs and budget constraints when considering this option.
How Do Magnetic Tooling Solutions Enhance Die-Cutting Efficiency for B2B Buyers?
Magnetic tooling leverages powerful magnets to secure flexible tooling dies, significantly speeding up setup times during the die-cutting process. This method is particularly beneficial in high-speed rotary presses, where quick changes can enhance overall production efficiency. However, it typically requires specialized equipment, which may entail additional costs. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of increased efficiency against the initial investment in magnetic tooling when planning their die-cutting strategies.
Key Industrial Applications of die cutting process
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of die cutting process | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Production of gaskets and seals | Enhanced sealing performance, reduced leakage | Material compatibility, thickness specifications, lead times |
| Electronics | Custom insulation and shielding components | Improved product reliability, thermal management | Material properties, precision cuts, regulatory compliance |
| Packaging | Creation of custom packaging solutions | Cost efficiency, enhanced product presentation | Design complexity, material durability, environmental impact |
| Medical Devices | Manufacturing of adhesive components and labels | Improved patient safety, ease of application | Biocompatibility, sterilization requirements, precision accuracy |
| Construction | Production of insulation and soundproofing materials | Enhanced energy efficiency, reduced noise pollution | Material specifications, fire safety standards, compliance with local regulations |
How is Die Cutting Used in the Automotive Sector for Gaskets and Seals?
In the automotive industry, die cutting is essential for producing gaskets and seals that ensure proper sealing in engines, transmissions, and other components. This process addresses challenges such as leakage and wear, which can lead to costly repairs and reduced vehicle performance. Buyers in this sector must consider material compatibility with automotive fluids, thickness specifications for effective sealing, and lead times to align with production schedules. Ensuring that suppliers can meet these requirements is critical for maintaining operational efficiency.
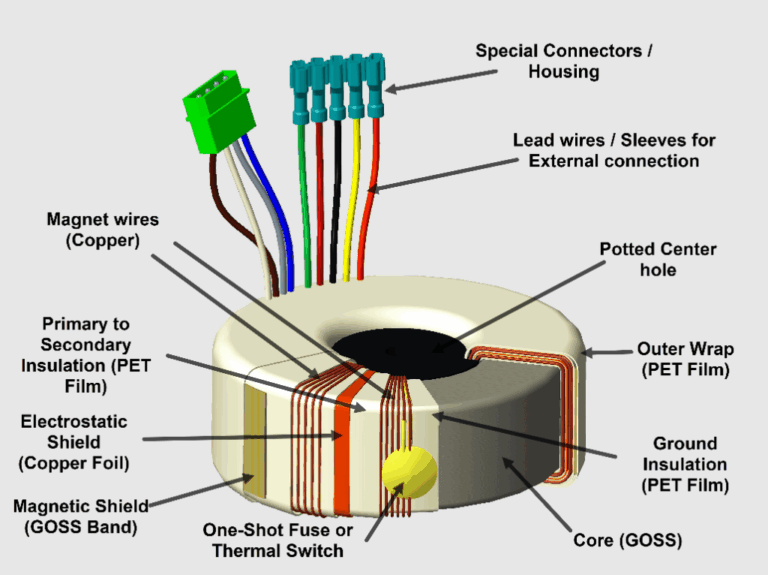
What Role Does Die Cutting Play in Electronics Manufacturing?
Die cutting is widely used in the electronics sector to create custom insulation and shielding components, which protect sensitive electronic parts from environmental factors and electromagnetic interference. This process helps resolve issues related to overheating and signal disruption, thereby enhancing product reliability. International buyers should focus on sourcing materials with specific thermal and electrical properties, ensuring precision cuts that meet stringent quality standards, and verifying compliance with regulatory requirements to avoid supply chain disruptions.
How Can Die Cutting Improve Packaging Solutions?
In packaging, die cutting is leveraged to create custom solutions that enhance product presentation while optimizing material usage. This method not only reduces costs but also allows for unique designs that attract consumer attention. Buyers should consider the complexity of the design, the durability of the materials used, and the environmental impact of packaging choices. It’s essential to collaborate with suppliers who can provide sustainable options that comply with local regulations, especially in regions with strict environmental guidelines.
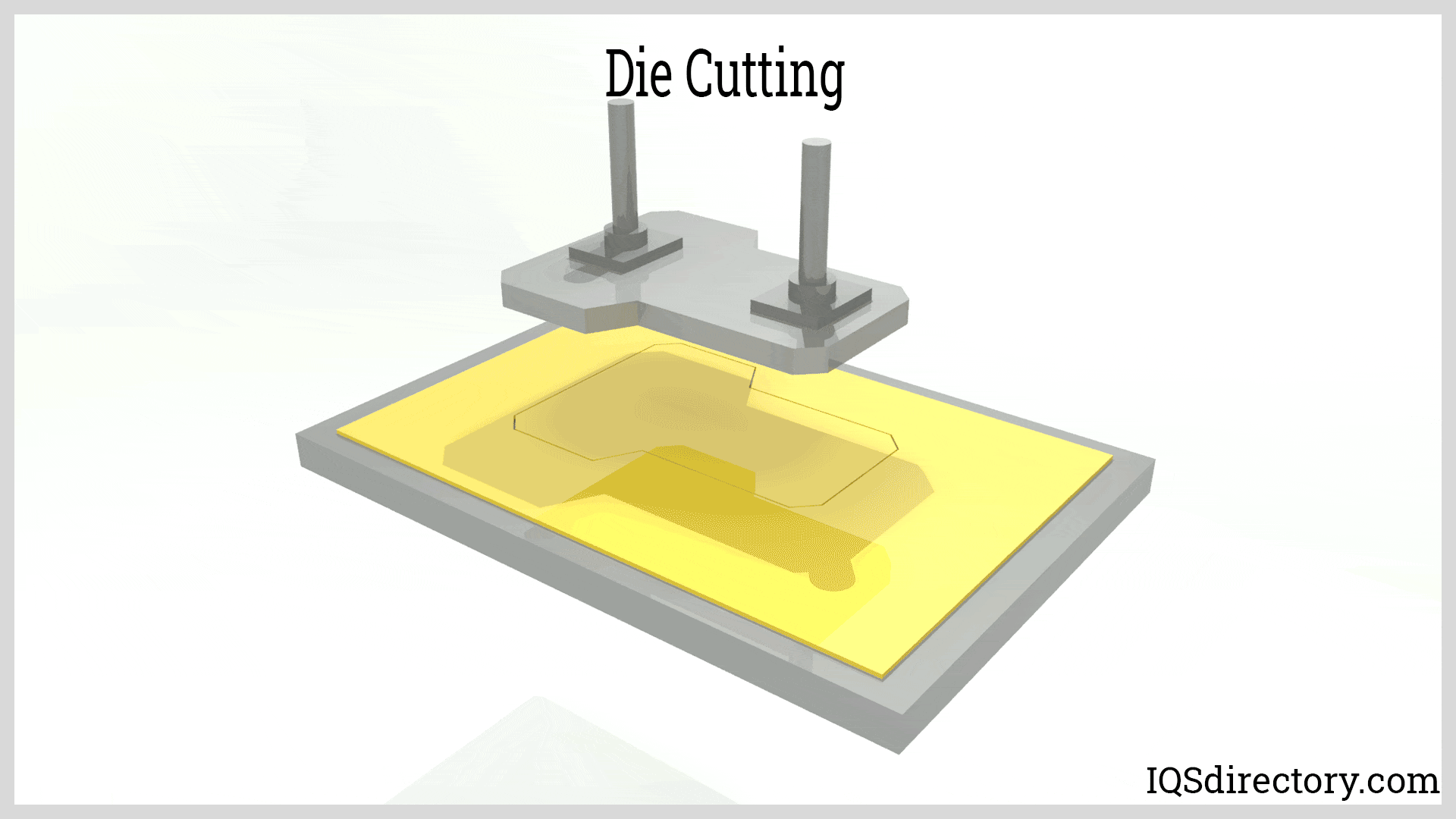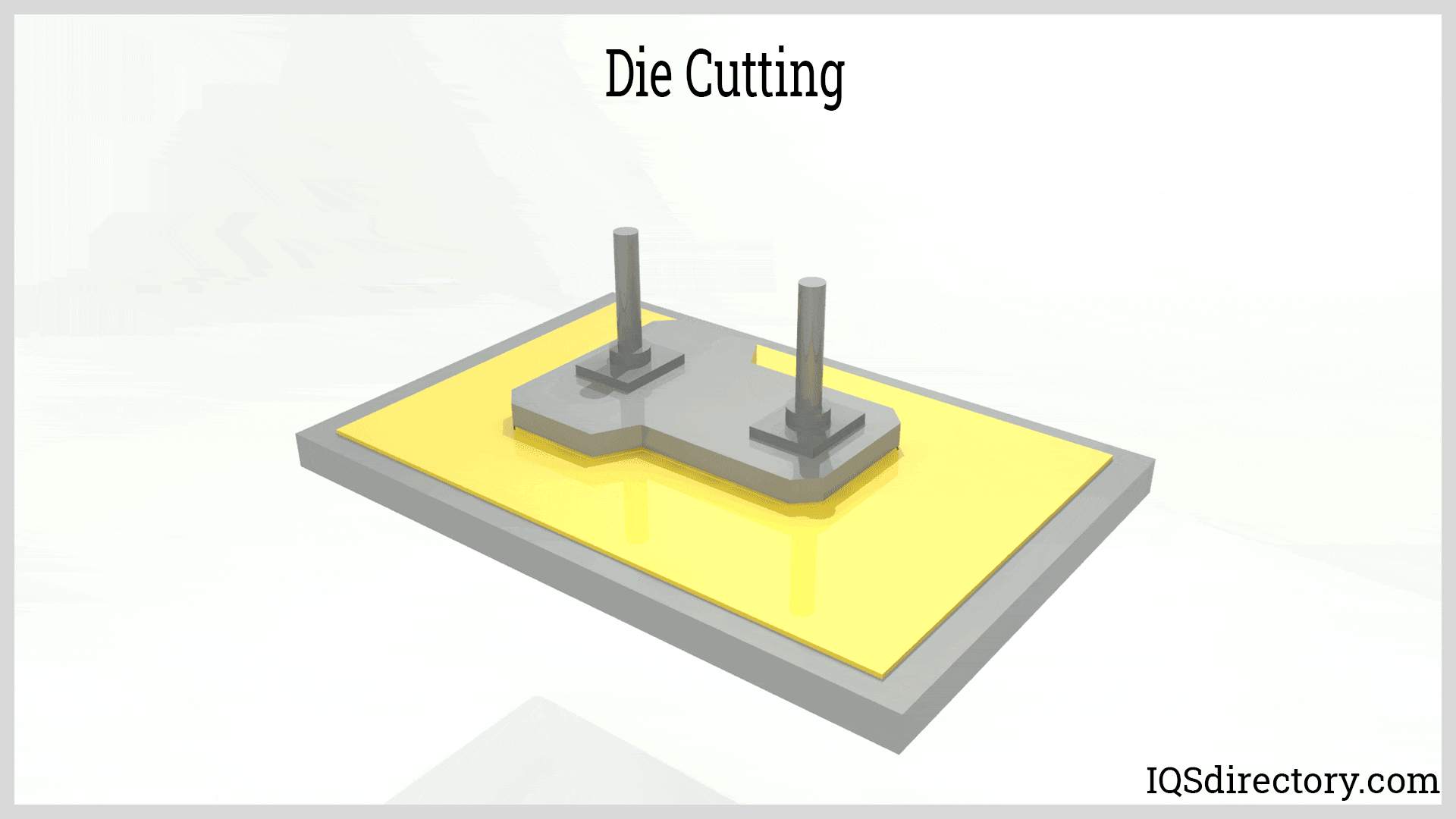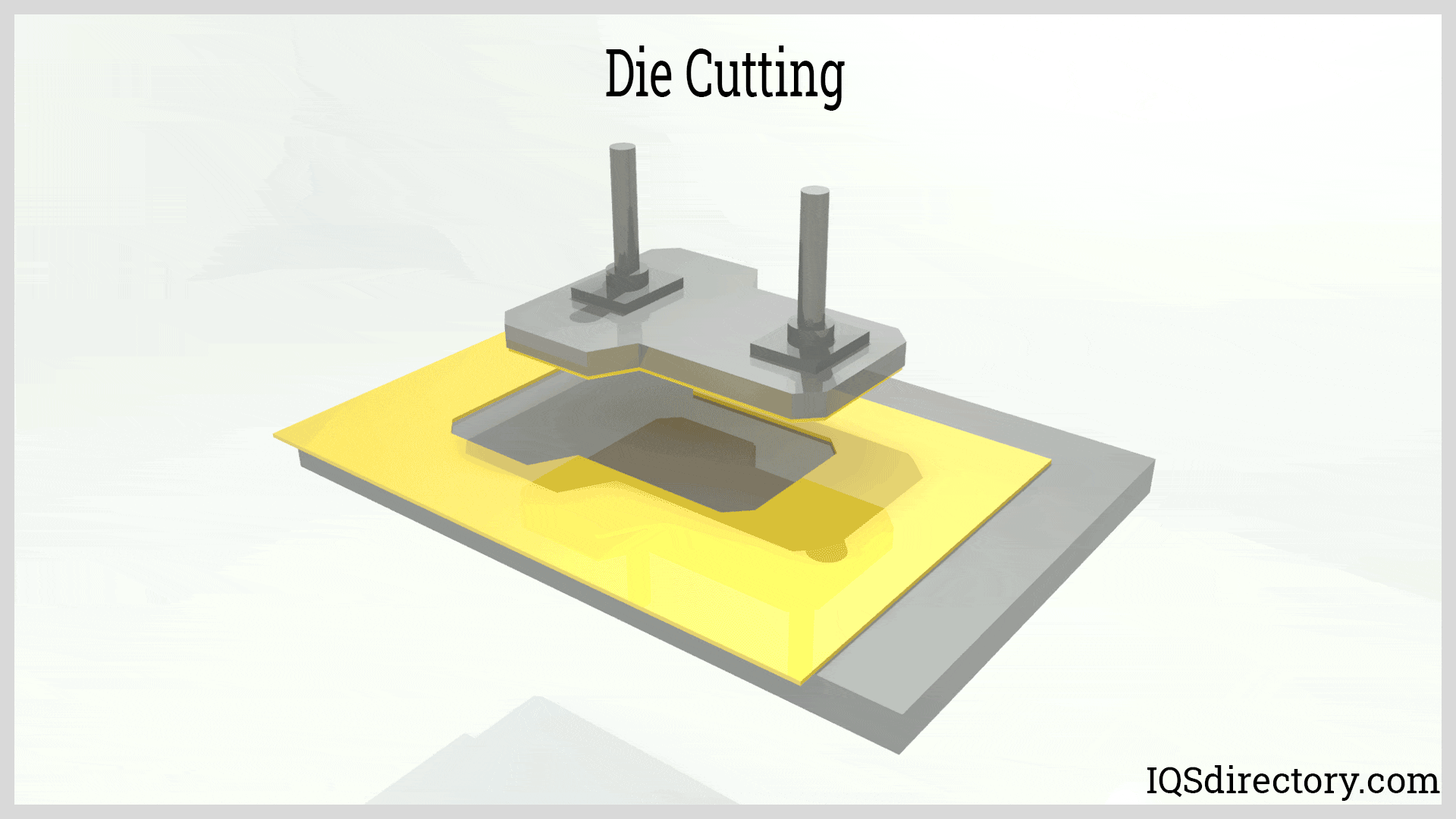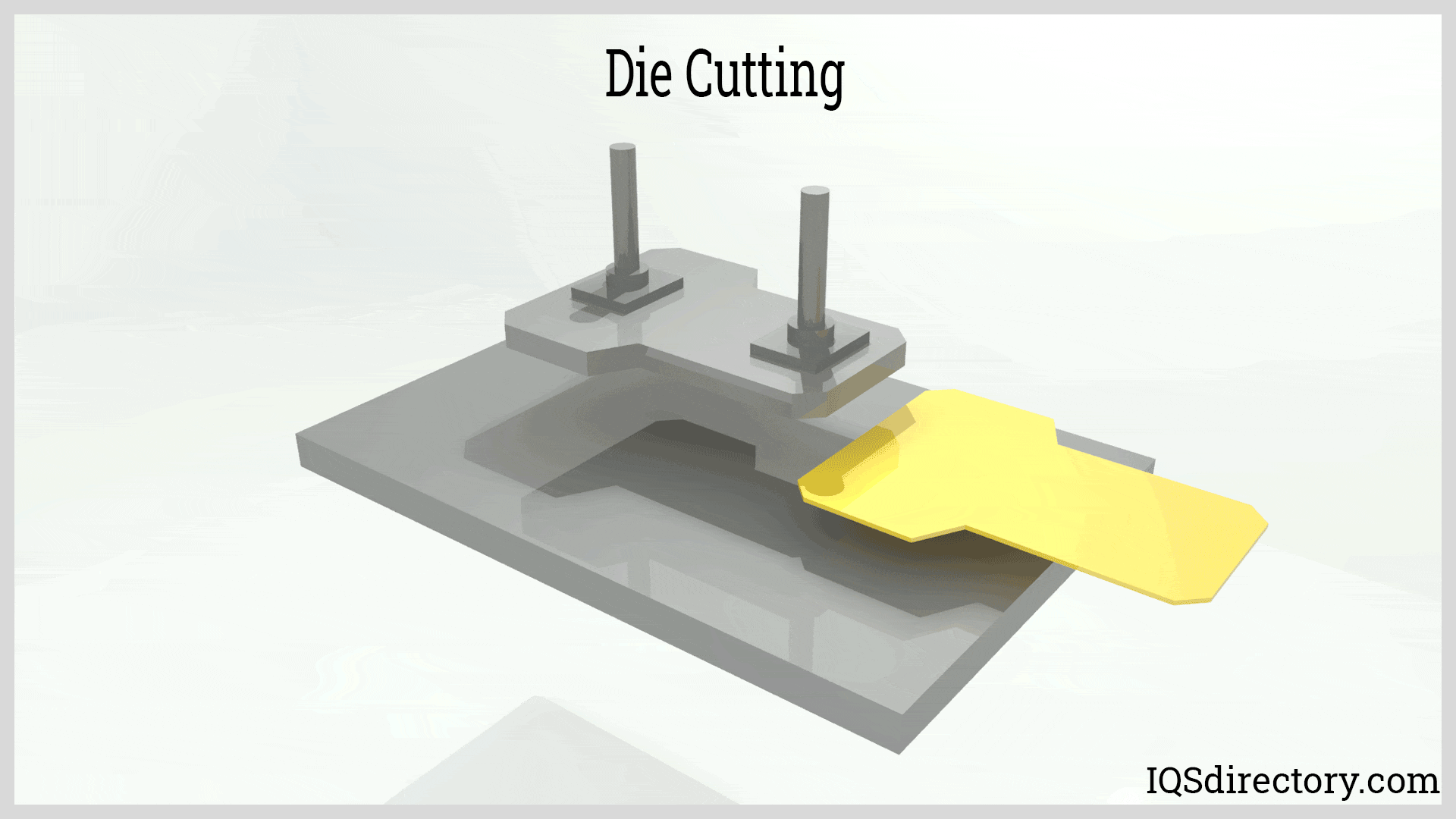
Illustrative image related to die cutting process
Why is Die Cutting Important for Medical Device Manufacturing?
Die cutting plays a critical role in the medical device industry, particularly in the production of adhesive components and labels used in various applications, from bandages to surgical tools. This process ensures improved patient safety and ease of application, addressing concerns about contamination and effectiveness. Buyers must prioritize sourcing materials that meet biocompatibility standards, consider sterilization requirements, and demand precision accuracy to guarantee product reliability. Working with experienced suppliers can facilitate compliance with stringent industry regulations.
How Does Die Cutting Enhance Construction Materials?
In the construction sector, die cutting is utilized to produce insulation and soundproofing materials that contribute to energy efficiency and noise reduction in buildings. This application addresses the growing demand for sustainable construction practices and improved living conditions. Buyers in this market should focus on sourcing materials that meet fire safety standards, comply with local building regulations, and provide the necessary insulation properties. Collaborating with suppliers who understand these requirements is vital for successful project execution.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘die cutting process’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Quality of Die-Cut Products
The Problem: A B2B buyer in the packaging industry faces significant challenges with inconsistent quality in die-cut products, leading to high rejection rates and increased production costs. Variations in cut precision and material defects can result in unusable products, causing delays in fulfilling customer orders and damaging the company’s reputation. The buyer struggles to find a reliable supplier who can consistently deliver high-quality die-cut components that meet their specifications.
The Solution: To mitigate quality issues, it is essential to establish a thorough supplier evaluation process. Begin by requesting samples from potential suppliers, focusing on their die-cutting capabilities, material handling, and precision. Specify your exact requirements, including material type, thickness, and tolerances, to ensure the supplier understands your quality standards. Implement regular quality control checks on incoming materials and establish a feedback loop with your supplier to address any discrepancies promptly. Additionally, consider suppliers with certifications in quality management systems, such as ISO 9001, which can provide assurance of their commitment to quality.
Scenario 2: High Production Costs Due to Inefficient Die-Cutting Methods
The Problem: A manufacturer specializing in automotive parts discovers that their die-cutting process is leading to excessive production costs. They rely on traditional overhead die-cutting methods that are slow and labor-intensive, resulting in high labor costs and longer lead times. This inefficiency hampers their competitiveness in a market that demands quick turnaround times and cost-effective solutions.
The Solution: To enhance efficiency and reduce costs, the manufacturer should evaluate transitioning to rotary die-cutting technology. Rotary die-cutting is known for its speed and precision, making it ideal for high-volume production runs. Collaborate with a die-cutting expert to assess your current processes and identify opportunities for automation. Investing in advanced die-cutting machinery can drastically reduce production time and waste, ultimately lowering overall costs. Additionally, consider implementing lean manufacturing principles to streamline workflows and eliminate unnecessary steps in the die-cutting process.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Sourcing the Right Die-Cutting Tools for Diverse Applications
The Problem: A B2B buyer in the electronics sector often encounters challenges in sourcing appropriate die-cutting tools that cater to the diverse range of materials and designs they require for their products. The buyer finds themselves overwhelmed by the variety of tooling options available, from solid dies to flexible tooling, and is uncertain about which type will best suit their specific applications.

Illustrative image related to die cutting process
The Solution: To effectively navigate the die-cutting tooling landscape, the buyer should start by conducting a comprehensive assessment of their material types and product specifications. Create a detailed matrix that outlines the characteristics of each material, such as thickness, flexibility, and the desired cut type (complete or kiss-cut). This matrix will serve as a guide when discussing tooling options with suppliers. Seek advice from experienced die-cutting professionals who can provide insights into the most suitable tooling for your applications. Additionally, consider suppliers that offer prototyping services, allowing you to test different tooling options before committing to larger production runs. This approach not only helps in selecting the right tools but also minimizes the risk of costly mistakes during full-scale production.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for die cutting process
What Materials Are Commonly Used in the Die Cutting Process?
In the die cutting process, the selection of materials is crucial for ensuring product performance and suitability for specific applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in die cutting, providing insights into their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Rubber
Key Properties: Rubber is known for its excellent elasticity, resilience, and ability to withstand a wide range of temperatures. It also offers good abrasion resistance and can be formulated to provide varying levels of hardness.
Pros & Cons: The durability of rubber makes it ideal for gaskets and seals, where flexibility is essential. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may require complex manufacturing processes, especially when custom formulations are needed.
Impact on Application: Rubber is compatible with various media, including oils and chemicals, making it suitable for automotive and industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM for rubber materials. Additionally, understanding the specific rubber grades that meet regional requirements is essential, especially in markets like Brazil and Vietnam.
2. Pressure-Sensitive Adhesive Tapes
Key Properties: These tapes feature a sticky surface that adheres upon contact without the need for heat or solvents. Their performance can vary based on the adhesive formulation, which affects temperature resistance and shear strength.
Pros & Cons: Pressure-sensitive adhesive tapes are versatile and easy to apply, making them ideal for packaging and bonding applications. However, their performance can degrade under extreme temperatures or in humid environments, which may limit their use in certain conditions.
Impact on Application: The compatibility of these tapes with various substrates is critical for applications in electronics, automotive, and construction.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with international standards such as JIS for adhesive products, especially in regions like the Middle East where environmental conditions can impact adhesive performance.
3. Foams
Key Properties: Foams can be made from various polymers, providing excellent cushioning, insulation, and sound-dampening properties. They can be tailored for specific applications, with varying densities and thicknesses.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of foam makes it cost-effective for shipping and handling. However, some foam types may not be as durable under mechanical stress, which can limit their use in high-impact applications.
Impact on Application: Foams are commonly used in automotive interiors, packaging, and insulation, where their properties can enhance user experience and product protection.
Illustrative image related to die cutting process
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the environmental regulations regarding foam materials, especially in Europe where there are stringent guidelines on the use of certain chemicals in foams.
4. Plastics
Key Properties: Plastics are versatile and can be engineered to provide specific characteristics such as clarity, flexibility, and chemical resistance. Common types include PVC, PET, and polycarbonate.
Pros & Cons: Plastics offer a wide range of applications due to their customizable properties. However, they may have limitations in terms of temperature resistance and can be more expensive than other materials like paper.
Illustrative image related to die cutting process
Impact on Application: Plastics are widely used in packaging, automotive, and consumer goods due to their durability and aesthetic appeal.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with global standards such as DIN for plastic materials is essential, particularly for buyers in Africa and South America, where local regulations may vary.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Die Cutting
| Material | Typical Use Case for die cutting process | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber | Gaskets and seals | Excellent durability and flexibility | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Pressure-Sensitive Adhesive Tapes | Packaging and bonding | Versatile and easy to apply | Performance degradation in extreme conditions | Medium |
| Foams | Automotive interiors and insulation | Lightweight and cost-effective | Limited durability under mechanical stress | Medium |
| Plastics | Packaging and consumer goods | Customizable properties | Potentially higher cost and temperature limitations | Medium |
This material selection guide provides B2B buyers with critical insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of common die-cutting materials, facilitating informed decision-making for their specific applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for die cutting process
What Are the Main Stages of the Die Cutting Manufacturing Process?
The die cutting manufacturing process involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure efficiency, precision, and quality. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers who seek to partner with reliable suppliers.

Illustrative image related to die cutting process
1. Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Die Cutting?
The first step in the die cutting process is selecting and preparing the materials. Common materials include rubber, plastics, foam, paper, and pressure-sensitive adhesives. Each material requires specific handling and preparation to ensure optimal cutting results.
- Material Selection: Choose materials based on the final application and performance requirements. For instance, rubber is typically used for gaskets and seals, while paper may be preferred for packaging solutions.
- Quality Checks: Before proceeding, materials undergo inspections for defects such as inconsistencies in thickness or surface quality. This step is crucial for preventing issues during the cutting process.
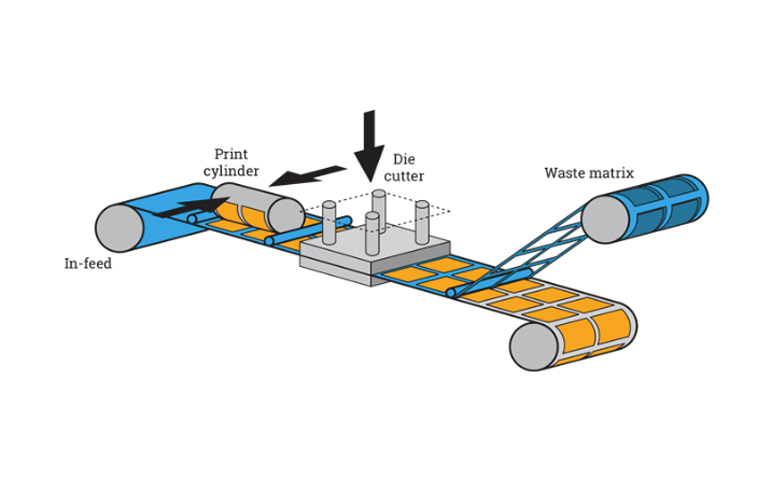
2. Forming: How Is Die Cutting Executed?
The forming stage involves the actual die cutting, where the prepared materials are shaped using a die. There are two primary methods of die cutting: rotary and flatbed (overhead) die cutting.
- Rotary Die Cutting: This technique utilizes cylindrical dies to perform high-speed, continuous cuts. It is particularly effective for large production runs and materials that require kiss-cutting, where only the top layer is cut.
- Flatbed Die Cutting: Ideal for lower volume runs or larger parts, this method employs a flat die that presses down on the material, cutting through it completely. It is often used for more complex shapes and thicker materials.
3. Assembly: How Are Die-Cut Components Assembled?
After die cutting, the next stage is assembly, which may involve additional processes such as laminating, stacking, or packaging the die-cut parts.
- Laminating: In some applications, layers of materials are bonded together to enhance durability or functionality.
- Stacking: Die-cut pieces are often stacked for easy handling and transportation. This requires careful consideration to prevent damage or misalignment.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential in Die Cutting?
Quality assurance is a vital aspect of the die cutting process, ensuring that the final products meet the required standards and specifications. B2B buyers should be aware of various quality control checkpoints and methods.
International Standards: Which Standards Should Be Followed?
Compliance with international quality standards is essential for maintaining consistency and reliability. Common standards include:
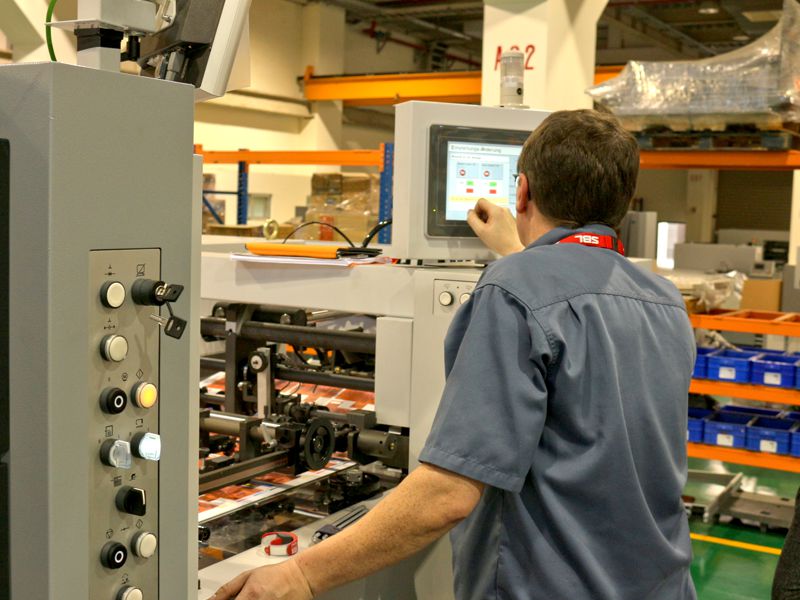

Illustrative image related to die cutting process
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines a framework for quality management systems, emphasizing continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: Particularly relevant for products sold in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For industries such as oil and gas, adhering to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards ensures that products meet rigorous performance and safety criteria.
Quality Control Checkpoints: What Are the Key QC Stages?
Quality control in die cutting typically involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of raw materials upon arrival at the facility. Materials that do not meet specifications are rejected.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the die cutting process, operators monitor key parameters such as cutting speed, pressure, and die wear. This proactive approach helps identify issues before they affect the final product.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, finished products undergo thorough inspections to ensure they meet all specified requirements. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspections, and functional tests.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Die Cutting Quality Assurance?
To ensure that die-cut products meet quality standards, various testing methods can be employed:
- Dimensional Analysis: Measuring the physical dimensions of die-cut parts to ensure they conform to specifications.
- Adhesion Testing: For adhesive products, tests are conducted to evaluate the bond strength and performance of the adhesive under various conditions.
- Material Testing: This may include tensile strength tests, elongation tests, and hardness tests to verify material properties.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to ensure that their suppliers adhere to strict quality control standards. Here are several effective strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their quality control processes and adherence to international standards. This can include reviewing their production capabilities, quality certifications, and adherence to safety regulations.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should request detailed quality assurance reports, including inspection results and any corrective actions taken. This transparency helps build trust between buyers and suppliers.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. This is especially valuable for international transactions where on-site inspections may not be feasible.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control:
- Understanding Regional Standards: Different regions may have varying standards for quality and safety. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and ensure that their suppliers comply with these requirements.
- Logistical Considerations: Transporting die-cut products across international borders can introduce risks such as damage or delays. Ensuring that suppliers have robust packaging and shipping processes is vital to maintaining product integrity.
- Cultural Differences: Communication styles and business practices can vary significantly across regions. Building strong relationships with suppliers and understanding their operational contexts can enhance collaboration and ensure quality compliance.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in die cutting is essential for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers. By familiarizing themselves with the main stages of the manufacturing process, quality control checkpoints, and international standards, buyers can make informed decisions and establish successful partnerships that meet their production needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘die cutting process’
Introduction
This guide provides a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure die-cutting services. Understanding the nuances of the die-cutting process and the criteria for selecting a supplier is vital for ensuring quality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in your production needs. Following these steps will help you make informed decisions and establish fruitful partnerships in the die-cutting industry.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clearly outline your project requirements, including material types, thickness, dimensions, and volume. Defining these specifications helps you communicate effectively with potential suppliers and ensures they can meet your unique needs. Consider including details on tolerances and application requirements to avoid misunderstandings later.
Step 2: Research Different Die-Cutting Methods
Familiarize yourself with the various die-cutting techniques available, such as rotary and overhead die-cutting. Understanding these methods will allow you to select the most appropriate one based on your production volume and material characteristics. For instance, rotary die-cutting is ideal for high-speed production, while overhead die-cutting may be better for larger, lower-volume parts.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. This due diligence helps ensure that the supplier has a proven track record and can deliver on quality and timelines.
- Look for certifications: Verify any industry certifications or standards compliance that the supplier holds, as this can indicate reliability and quality assurance.
- Assess capabilities: Ensure the supplier has the necessary equipment and expertise to handle your specific requirements, including tooling options and production capabilities.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request samples or prototypes of their work. This step is critical for assessing the quality of the die-cut products and their adherence to your specifications. Evaluate the samples based on accuracy, material handling, and overall finish to make an informed choice.
Step 5: Discuss Lead Times and Production Capacity
Engage suppliers in discussions about their lead times and production capacity. Understanding their ability to meet your deadlines is essential, especially if you have a tight schedule. Inquire about their processes for scaling production and handling rush orders, as this can impact your supply chain.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, negotiate terms and conditions that benefit both parties. Discuss pricing structures, payment terms, and delivery schedules to align expectations. Be clear about penalties for delays or quality issues to protect your interests.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Lastly, set up a communication plan to ensure seamless collaboration throughout the project lifecycle. Determine key points of contact and establish regular check-ins to address any challenges or changes promptly. Effective communication fosters a strong partnership and can lead to better outcomes in your die-cutting projects.
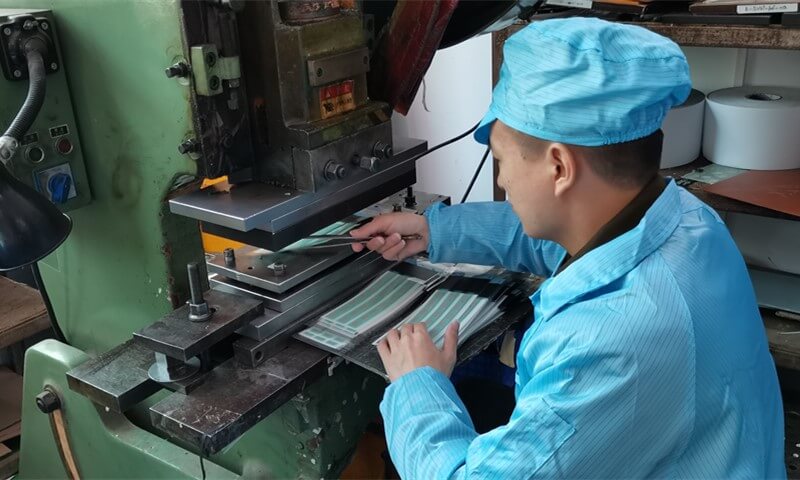

Illustrative image related to die cutting process
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the die-cutting procurement process with confidence, ensuring they select the right suppliers and achieve their project objectives efficiently.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for die cutting process Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in the Die Cutting Process?
Understanding the cost structure in the die-cutting process is essential for B2B buyers seeking to optimize their sourcing strategies. The primary components influencing the cost include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The type of material significantly impacts cost. Common materials for die cutting include rubber, plastics, and paper. Prices can fluctuate based on market conditions and the quality of the material. For instance, specialized or high-performance materials typically command higher prices.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both direct and indirect labor involved in the die-cutting process. This includes skilled technicians who operate machinery and oversee production. Labor costs can vary widely by region, with lower costs in emerging markets such as Africa and South America compared to Europe.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes the indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs. Effective management of overhead can enhance profitability and should be factored into overall pricing.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can vary based on the complexity of the die and the type of tooling used (solid, flexible, or steel rule dies). Solid tooling often has a higher upfront cost but offers durability, while flexible tooling is more cost-effective for low-volume runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality is vital, especially for industries with stringent standards. QC processes add to the overall cost but can save money in the long run by reducing waste and rework.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs are influenced by the distance to delivery points and the mode of transport. International buyers should consider Incoterms, which define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin on top of the cost of production. Understanding the market dynamics and competitive landscape can help buyers negotiate better prices.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Die Cutting Process?
Several factors influence pricing in the die-cutting process, which can vary based on regional markets and specific project requirements.
-
Volume/MOQ: The minimum order quantity (MOQ) often plays a significant role in pricing. Higher volumes usually lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale.
-
Specifications and Customization: Unique specifications or custom designs can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their needs to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: The choice of materials, particularly specialized ones, can significantly influence pricing. Understanding the trade-offs between cost and performance is crucial.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that require specific certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) may come at a premium. Buyers should evaluate the necessity of these certifications based on their end-use.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, experience, and production capabilities can affect pricing. Established suppliers may offer higher quality but at a higher price point.
-
Incoterms: Knowing the terms of shipping can help buyers anticipate additional costs. For example, choosing DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) means the supplier covers all shipping and customs costs, simplifying the purchasing process.
What Are the Best Practices for Buyers in the Die Cutting Market?
For international B2B buyers, especially from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, navigating the die-cutting landscape requires strategic approaches.
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing, particularly for large orders. Building long-term relationships can often lead to better terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Focus on the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the initial price. Consider factors like durability, maintenance, and potential waste when evaluating offers.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations and regional economic conditions that may impact pricing. Establishing contracts with fixed prices can mitigate these risks.
-
Supplier Diversity: Consider multiple suppliers from different regions to compare pricing and quality. This can also reduce risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
-
Research and Due Diligence: Conduct thorough research on suppliers, including checking references and certifications. This ensures that you choose a partner that aligns with your quality and pricing expectations.
Conclusion
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of the cost structure, price influencers, and best practices in die cutting can empower B2B buyers to make informed sourcing decisions. By evaluating the various components and negotiating effectively, businesses can achieve a balance between cost and quality that meets their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing die cutting process With Other Solutions
When evaluating manufacturing processes, understanding the available alternatives to die cutting can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions. Die cutting is a popular method for converting various materials into specific shapes, but there are other technologies that may suit different needs, such as laser cutting and waterjet cutting. This analysis compares these alternatives to help businesses identify the best solution for their production requirements.
Illustrative image related to die cutting process
| Comparison Aspect | Die Cutting Process | Laser Cutting | Waterjet Cutting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-speed, precise cuts for mass production | Excellent precision, versatile materials | Can cut thick materials, good for complex shapes |
| Cost | Moderate upfront costs, lower operational costs in high volumes | Higher initial investment, lower for small runs | High operational cost due to water and abrasive material |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific tooling and setup | Minimal tooling, quick to set up | Requires specialized equipment and training |
| Maintenance | Moderate maintenance, tooling resharpening needed | Low maintenance, but requires optics care | High maintenance due to wear on abrasive materials |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for high-volume runs of consistent shapes | Best for intricate designs and varied materials | Suitable for thick materials and complex geometries |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Laser Cutting as an Alternative to Die Cutting?
Laser cutting utilizes focused light beams to melt or vaporize material. One of the significant advantages of laser cutting is its precision, allowing for intricate designs and tight tolerances. It is particularly effective for materials like metals, plastics, and wood. However, the initial investment in laser cutting technology can be high, making it less cost-effective for smaller production runs. Additionally, while setup is relatively quick, ongoing costs for maintenance and the consumables required (like lenses) can add up.
How Does Waterjet Cutting Compare to Die Cutting?
Waterjet cutting employs a high-pressure jet of water, often mixed with abrasives, to cut through materials. This method is known for its ability to handle thicker materials and is particularly effective for complex shapes without thermal distortion. Waterjet cutting is highly versatile, as it can be used on materials ranging from metals to glass. However, it tends to have higher operational costs due to the need for specialized equipment and the ongoing cost of abrasive materials. Maintenance can also be more intensive compared to die cutting, as the equipment is subject to wear and tear.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Cutting Solution?
Choosing the right cutting solution depends on various factors, including the specific requirements of the project, budget constraints, and production volume. Die cutting is an excellent choice for businesses that require high-speed production of consistent shapes at moderate costs. In contrast, laser cutting may be more suitable for projects requiring high precision and versatility, while waterjet cutting excels in handling thicker materials and complex designs. By assessing these aspects and aligning them with project goals, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance efficiency and profitability in their manufacturing processes.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for die cutting process
What Are the Key Technical Properties of the Die Cutting Process?
Understanding the technical properties involved in the die cutting process is crucial for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize their manufacturing needs. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the quality and type of substrate used in die cutting, including rubber, plastics, paper, and metals. Selecting the appropriate material grade is vital as it impacts the durability and performance of the finished product. For example, using high-grade materials can enhance the longevity of gaskets or seals, reducing the need for frequent replacements and thus lowering overall costs.
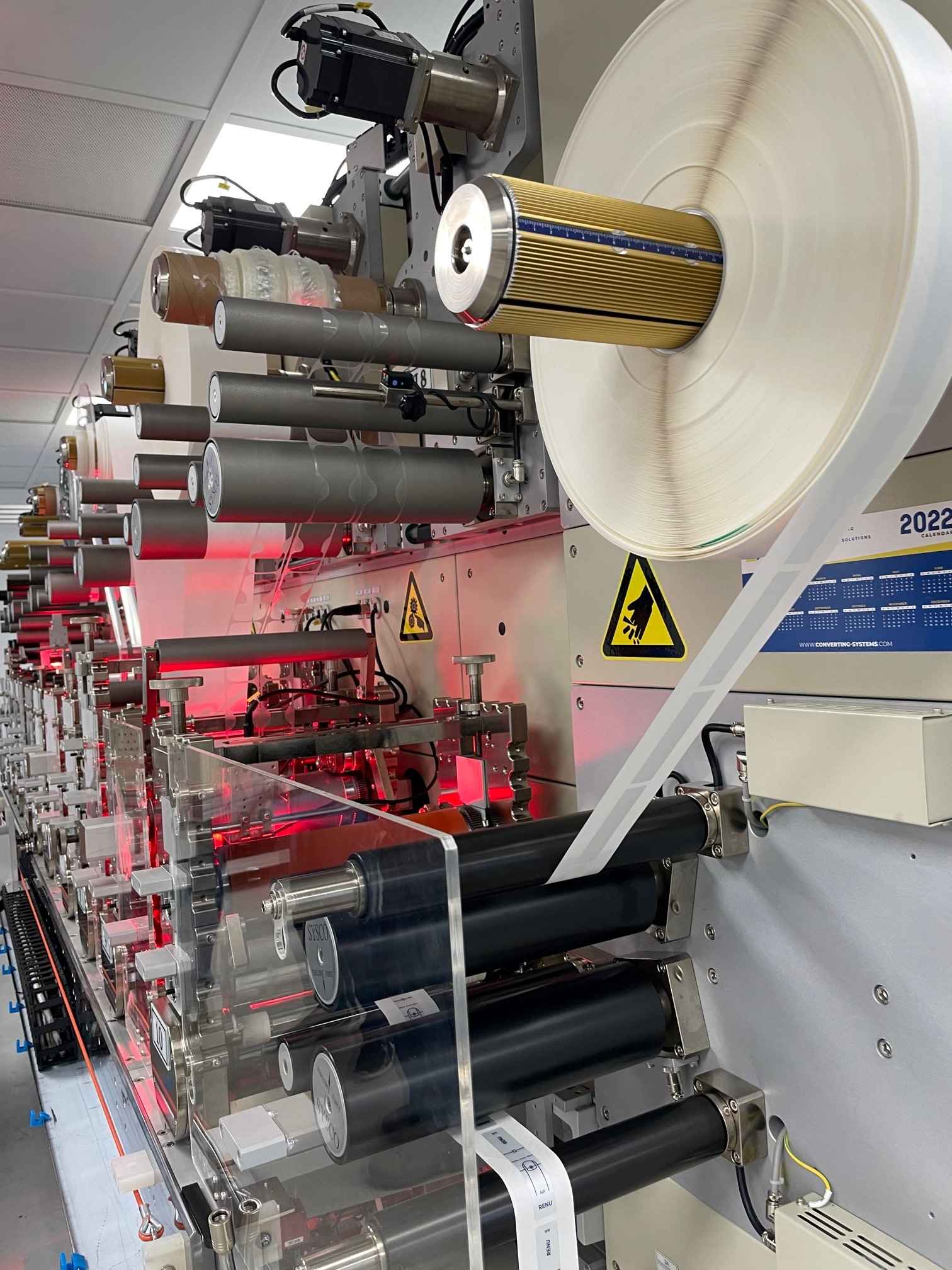

Illustrative image related to die cutting process
2. Tolerance
Tolerance denotes the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. In die cutting, this specification is crucial for ensuring that parts fit together correctly in assemblies. Tight tolerances may be required for precision applications, such as automotive or aerospace components. Understanding tolerance levels helps buyers avoid costly reworks and ensures product reliability.
3. Die Life
Die life measures how long a die can be effectively used before it requires replacement or maintenance. The choice between solid tooling and flexible tooling can significantly influence die life. High die life is particularly important for large-volume production runs, as it minimizes downtime and keeps manufacturing processes efficient.
4. Thickness
Thickness refers to the measurement of the material being cut. Different die cutting methods accommodate various thicknesses, impacting the choice of tooling and the type of cut that can be achieved. For instance, rotary die cutting is often preferred for thinner materials, while overhead die cutting is suitable for thicker substrates. Understanding thickness specifications ensures that the right process is chosen for the desired outcome.
5. Cut Type
The type of cut—complete or kiss-cut—determines the final product’s usability and application. A complete cut goes through the entire substrate, while a kiss-cut only penetrates the top layer, leaving a liner intact. Knowing the desired cut type is essential for meeting specific application requirements, such as ease of use or waste management.
Illustrative image related to die cutting process
Which Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know in the Die Cutting Industry?
Familiarizing oneself with industry jargon can streamline communication and enhance negotiations in the die cutting sector. Here are several key terms that buyers should understand:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In die cutting, OEMs are critical partners for sourcing custom components tailored to specific applications. Recognizing OEM relationships can help buyers ensure they are receiving high-quality, reliable products.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for B2B buyers, as it affects inventory management and production costs. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production needs to avoid excess inventory or stockouts.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a standard business process in which a buyer requests pricing and terms from suppliers. For die cutting projects, submitting an RFQ helps clarify specifications, timelines, and costs, allowing buyers to make informed decisions. A well-prepared RFQ can lead to better pricing and terms.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms, such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), is crucial for managing shipping costs and responsibilities in the die cutting supply chain. Understanding these terms helps mitigate risks associated with international shipping.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period from placing an order to receiving the finished product. In die cutting, lead time is influenced by tooling complexity, material availability, and production schedules. Buyers should consider lead times when planning projects to ensure timely delivery and avoid disruptions in their supply chain.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, optimize their procurement processes, and foster stronger supplier relationships in the die cutting industry.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the die cutting process Sector
What Are the Key Trends Shaping the Die Cutting Process Market?
The die cutting process sector is currently experiencing significant shifts driven by technological advancements and evolving market demands. A major global driver is the increasing need for customization across industries such as packaging, automotive, and electronics. This demand is pushing suppliers to adopt innovative die-cutting technologies that enhance precision and speed. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there is a growing emphasis on automation and digitalization in production processes. Technologies like CAD/CAM integration are becoming essential for streamlining operations and improving design accuracy.
Additionally, the rise of Industry 4.0 is fostering a more connected and data-driven manufacturing environment. This trend allows for real-time monitoring and optimization of die-cutting processes, ultimately leading to improved efficiency and reduced waste. Buyers should also be aware of the shift towards sustainable materials and practices, as consumers increasingly prefer eco-friendly products. As a result, suppliers that can provide materials with lower environmental impacts are gaining a competitive edge.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the Die Cutting Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of sourcing strategies in the die cutting process sector. As environmental regulations tighten globally, B2B buyers are under pressure to ensure their supply chains are ethically sound and environmentally responsible. This involves selecting suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials or adopting energy-efficient manufacturing processes.

Illustrative image related to die cutting process
Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and FSC certification for paper products are becoming critical benchmarks for assessing suppliers’ sustainability efforts. Furthermore, the use of biodegradable and recyclable materials in die cutting not only meets regulatory standards but also appeals to environmentally conscious consumers. For buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where sustainability initiatives are still developing, aligning with suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to ethical sourcing can significantly enhance brand reputation and marketability.
How Has the Die Cutting Process Evolved Over Time?
The die cutting process has evolved considerably since its inception, transitioning from manual techniques to highly automated systems. Initially used for basic shapes in textiles and paper industries, die cutting has expanded into a versatile manufacturing solution across various sectors. The introduction of rotary die cutting in the mid-20th century marked a significant advancement, enabling higher production speeds and more complex shapes.
As technology progressed, the integration of CNC machinery and computer-aided design (CAD) systems revolutionized the industry, allowing for precise and customizable die-cutting solutions. Today, the focus is on continuous improvement, with innovations such as flexible tooling and magnetic dies enhancing efficiency and reducing waste. This evolution not only reflects technological advancements but also aligns with changing market demands for speed, quality, and sustainability, making it an essential consideration for international B2B buyers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of die cutting process
-
How do I choose the right die-cutting method for my project?
Choosing the right die-cutting method depends on several factors, including the material type, the complexity of the design, production volume, and cost constraints. For high-volume runs, rotary die-cutting is often more efficient and cost-effective, while overhead die-cutting is suitable for lower volumes or larger parts. Assess your project requirements, including material thickness and tolerances, to determine which method aligns best with your objectives. -
What materials can be effectively die-cut?
Die-cutting can be applied to a variety of materials, including rubber, paper, plastics, foams, and pressure-sensitive adhesive tapes. Each material requires specific tooling and techniques; for example, kiss-cutting is ideal for adhesive-backed materials, while complete cuts are better for thicker substrates like rubber gaskets. Discuss your material options with suppliers to ensure they can meet your specifications. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for die-cutting services?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly by supplier and the specific die-cutting method used. Generally, rotary die-cutting has higher MOQs due to the initial setup costs, while overhead die-cutting may accommodate smaller orders. It’s essential to communicate your needs with potential suppliers and inquire about flexibility in MOQs to align with your production plans. -
How can I ensure the quality of die-cut products?
Quality assurance in die-cutting involves several steps: selecting a reputable supplier, specifying quality standards, and implementing a thorough inspection process. Request samples before committing to large orders to assess the die-cutting precision and material integrity. Additionally, consider suppliers who adhere to international quality standards, as this can provide greater assurance of consistent quality. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by die-cutting suppliers?
Payment terms can vary widely based on supplier policies, order size, and the buyer’s creditworthiness. Common terms include advance payment, net 30/60/90 days, or payment upon delivery. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that work for both parties and consider the implications of each option on cash flow. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can also lead to more favorable terms over time. -
How do logistics and shipping affect die-cutting projects?
Logistics play a critical role in die-cutting projects, especially for international shipments. Factors such as shipping times, customs clearance, and transportation costs must be considered when planning your project timeline. Work closely with your supplier to understand their shipping capabilities and ensure you factor in lead times for production and delivery to avoid delays. -
What customization options are available for die-cut products?
Customization in die-cutting can range from adjusting shapes and sizes to selecting specific materials and finishes. Suppliers often offer options for blade angles, die designs, and even specialized coatings. Clearly communicate your customization needs early in the design process to ensure the supplier can accommodate them and provide the best solutions for your application. -
How can I effectively vet die-cutting suppliers?
Vetting die-cutting suppliers involves assessing their experience, capabilities, and customer feedback. Start by checking their portfolio to see previous work that aligns with your needs. Request references and inquire about their quality assurance processes and certifications. Additionally, consider visiting their facility if possible, or conducting virtual audits to gain confidence in their operations and reliability.
Top 4 Die Cutting Process Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. IQS Directory – Die Cutting Solutions
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Die cutting is a bulk production technique used to cut materials like paper, chipboard, fabrics, rubber, fiberglass, metal sheets, foam, wood, and plastics into specific shapes using a custom-crafted die. The process is applicable in various industries including packaging, consumer goods, automotive, and medical device manufacturing. Key methods include flatbed die cutting, rotary die cutting, and…
2. Maxcess International – Rotary Dies & Coatings
Domain: maxcessintl.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Rotary Dies: Solid Dies (RD90M, RD100, RD200, RD250, RD300, Challenger), Flexible Dies (SmartFlex Series, Prime Series, UltraFilm Dura Series, GoldLine, Special MicroBlade), Coatings and Treatments (RotoRepel™ & RotoRepel™ RX), Die Rebuilding & Repair, Die Quality Assurance & Compliance Support, Die Product Evaluation, Custom Rotary Die Design.
3. Interwell – Die Cutting Solutions
Domain: interwell.cn
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Die cutting is a process used in various industries, including metalworking, printing, and packaging, to cut, shape, and shear sheets of stock material into unique designs. It utilizes a specialized tool called a die to produce high volumes of identical items quickly. Key types of dies include nesting dies, corner dies, and edgeable dies. Die-cutting machines vary from manual and digital options f…
4. PrintArts – Die Cutting and Scoring Solutions
Domain: printarts.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Die Cutting and Scoring can happen in one pass; Die cutting uses sharp steel dies to cut irregular shapes; Die scoring creates channels for easier folding; Substrates affect blade life; Ejection rubber cushions blades and controls cut depth; The cutting board is called a platen, often made from birch; Grain direction is crucial for proper folding; Blanking simplifies die cut projects; Nicks hold f…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for die cutting process
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers in Die Cutting?
In the dynamic landscape of die cutting, understanding the nuances of the process is paramount for international B2B buyers. Key considerations include the selection between rotary and overhead die-cutting methods, which can significantly impact production efficiency and costs. Emphasizing the importance of material selection, tooling options, and cut types will enable buyers to optimize their sourcing strategies and meet their unique project requirements.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Business Operations?
Strategic sourcing not only streamlines procurement but also fosters long-term partnerships with suppliers who understand your specific needs. By leveraging the right die-cutting technologies and methods, businesses can achieve significant cost savings, reduce lead times, and improve product quality. This approach is particularly vital for companies in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where competitive advantage is crucial.
Illustrative image related to die cutting process
What Does the Future Hold for Die Cutting in Global Markets?
As the die-cutting industry continues to evolve with advancements in technology and materials, now is the time for international buyers to engage proactively with suppliers. Embrace innovation and seek out collaborative opportunities to enhance your product offerings. Reach out today to explore how strategic partnerships can elevate your business in the global marketplace.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.