A B2B Buyer’s Guide to Diagram Of A Coil: Price, Quality, and Suppliers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for diagram of a coil
In the fast-paced landscape of global commerce, sourcing a reliable diagram of a coil can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. Understanding the intricacies of coil types—such as induction coils and ignition coils—along with their varied applications is essential for making informed decisions. This guide aims to illuminate the complexities involved in selecting the right coil diagram, addressing critical factors such as supplier vetting, cost implications, and industry standards.
With a focus on empowering businesses from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia—this resource serves as a comprehensive roadmap. It will help buyers navigate the multifaceted market, ensuring they can confidently choose the right products that meet their operational needs.
By delving into the different types of coils, their functions, and the technical specifications detailed in the diagrams, this guide equips purchasers with the knowledge necessary to optimize their supply chains. Whether you’re looking for cost-effective solutions or high-performance components, our insights will facilitate informed purchasing decisions, ultimately enhancing your competitive edge in the global market.
Understanding diagram of a coil Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Induction Coil | Utilizes mutual induction; generates high-voltage pulses | Automotive ignition systems, spark generation | Pros: High voltage output; compact design. Cons: Requires careful handling; potential overheating. |
| Air-Core Coil | Uses air as the core material; lightweight and efficient | RF applications, antennas | Pros: Lightweight; low cost. Cons: Limited inductance; lower efficiency at high frequencies. |
| Toroidal Coil | Doughnut-shaped design; minimizes electromagnetic interference | Power supplies, transformers | Pros: High efficiency; low electromagnetic noise. Cons: Complex manufacturing; may require specialized equipment. |
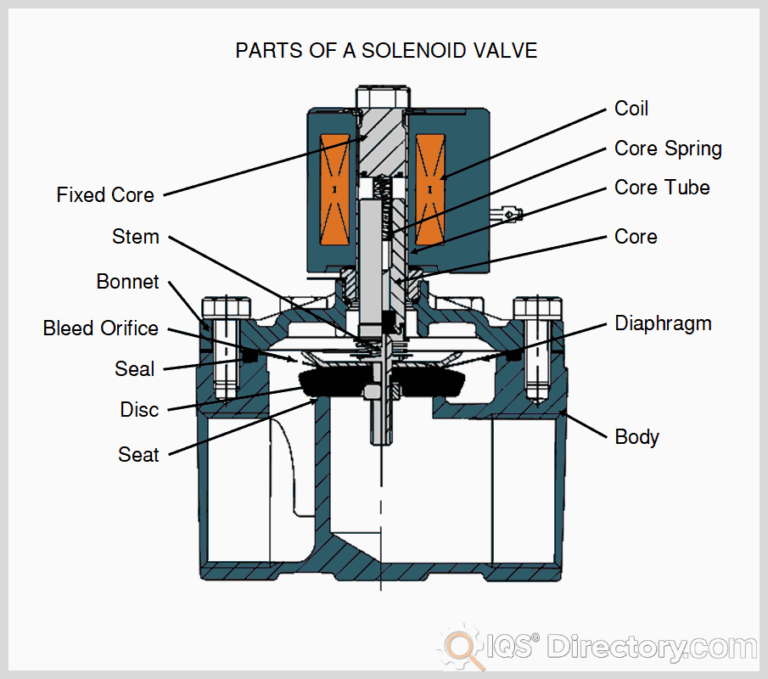
| Solenoid Coil | Cylindrical shape; produces magnetic fields when energized | Electromechanical devices, relays | Pros: Simple design; versatile applications. Cons: Limited to linear motion; can be bulky. |
| Choke Coil | Designed to block high-frequency AC while allowing low-frequency signals | Audio equipment, power supply circuits | Pros: Effective noise filtering; enhances signal integrity. Cons: Can be large; may introduce distortion at high frequencies. |
What Are the Characteristics of Induction Coils and Their Suitability for B2B Buyers?
Induction coils are essential components that utilize the principle of mutual induction to generate high-voltage pulses from low-voltage direct current. They are commonly used in automotive ignition systems and spark generation applications. B2B buyers should consider the coil’s voltage output, size, and heat management capabilities, as these factors directly affect performance in demanding environments, such as automotive or industrial applications.
How Do Air-Core Coils Differ and Where Are They Most Applicable?
Air-core coils are characterized by their use of air as the core material, making them lightweight and cost-effective. They are particularly suitable for radio frequency (RF) applications and antennas, where weight and efficiency are crucial. Buyers should evaluate the coil’s inductance and frequency response to ensure compatibility with their specific RF needs, especially in sectors like telecommunications or broadcasting.
What Advantages Do Toroidal Coils Offer for B2B Applications?
Toroidal coils are designed in a doughnut shape, which significantly reduces electromagnetic interference and enhances efficiency. They are often found in power supplies and transformers, where low electromagnetic noise is a priority. When purchasing toroidal coils, B2B buyers should assess the manufacturing capabilities of suppliers, as the complexity of these coils can affect lead times and costs.
Why Choose Solenoid Coils for Electromechanical Applications?
Solenoid coils, with their cylindrical shape, are widely used in electromechanical devices and relays due to their ability to produce magnetic fields when energized. They offer a straightforward design and versatile applications. However, buyers should consider the physical dimensions and operational requirements, as solenoids can be bulky and may only provide linear motion, which could limit their use in compact systems.
How Do Choke Coils Function and What Are Their Key Considerations?
Choke coils are specifically designed to block high-frequency AC signals while allowing lower-frequency signals to pass through, making them ideal for audio equipment and power supply circuits. They effectively filter out noise, enhancing signal integrity in various applications. Buyers should keep in mind the choke’s size and potential impact on signal quality, as larger coils may introduce distortion at higher frequencies, necessitating careful selection based on the application.
Key Industrial Applications of diagram of a coil
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of diagram of a coil | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Ignition systems in internal combustion engines | Enhanced engine performance and reliability | Quality of materials, compatibility with engine types |
| Telecommunications | Induction coils for signal transmission | Improved signal clarity and range | Compliance with industry standards, durability under conditions |
| Manufacturing | Induction heating processes | Increased efficiency in metal processing | Energy consumption, safety features, and precision |
| Medical Devices | MRI and diagnostic equipment | Accurate imaging and diagnostics | Regulatory compliance, precision engineering, and reliability |
| Energy Sector | Transformer systems for power distribution | Stable energy supply and reduced losses | Voltage ratings, efficiency, and environmental conditions |
How is the diagram of a coil utilized in the automotive industry?
In the automotive sector, the diagram of a coil is crucial for designing ignition systems in internal combustion engines. These coils convert low-voltage current from the battery into high-voltage pulses that ignite the fuel-air mixture in the engine cylinders. This process enhances engine performance, increases fuel efficiency, and ensures reliable operation. B2B buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing high-quality coils that meet specific voltage and durability standards to withstand varying environmental conditions, particularly in regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia.
What role does the diagram of a coil play in telecommunications?
In telecommunications, coils are utilized in induction systems to enhance signal transmission. The diagram illustrates how these coils facilitate the transfer of electrical signals with minimal loss, improving clarity and range. This application is vital for maintaining robust communication networks, especially in remote areas of Africa and South America, where reliable connectivity is essential. Buyers should consider sourcing coils that comply with international telecommunications standards, ensuring durability and performance in diverse environmental conditions.
How does the diagram of a coil contribute to manufacturing efficiency?
The manufacturing industry employs induction coils in heating processes, such as metal forging and welding. The diagram highlights how these coils generate heat through electromagnetic induction, allowing for precise temperature control and efficient processing of materials. This method significantly reduces energy consumption and enhances production speed. For international buyers, especially from Europe, it’s important to source coils that are energy-efficient and designed for high-volume operations, ensuring compliance with local regulations and sustainability goals.
In what ways is the diagram of a coil essential for medical devices?
In the medical field, the diagram of a coil is integral to the functioning of MRI machines and other diagnostic equipment. These coils generate the necessary magnetic fields for imaging, providing accurate diagnostics critical for patient care. The reliability and precision of these coils are paramount, making it essential for B2B buyers to ensure their suppliers meet rigorous regulatory standards. Buyers should also focus on sourcing coils that offer long-term performance and minimal maintenance to support continuous operations in healthcare settings.
How does the diagram of a coil support the energy sector?
In the energy sector, coils are fundamental components in transformer systems used for power distribution. The diagram illustrates how these coils manage voltage levels and facilitate the efficient transfer of electricity across long distances. This application is vital for ensuring a stable energy supply and reducing transmission losses. International buyers should consider factors such as voltage ratings, efficiency metrics, and environmental compatibility when sourcing coils to ensure optimal performance in diverse geographical regions, including the Middle East and Europe.
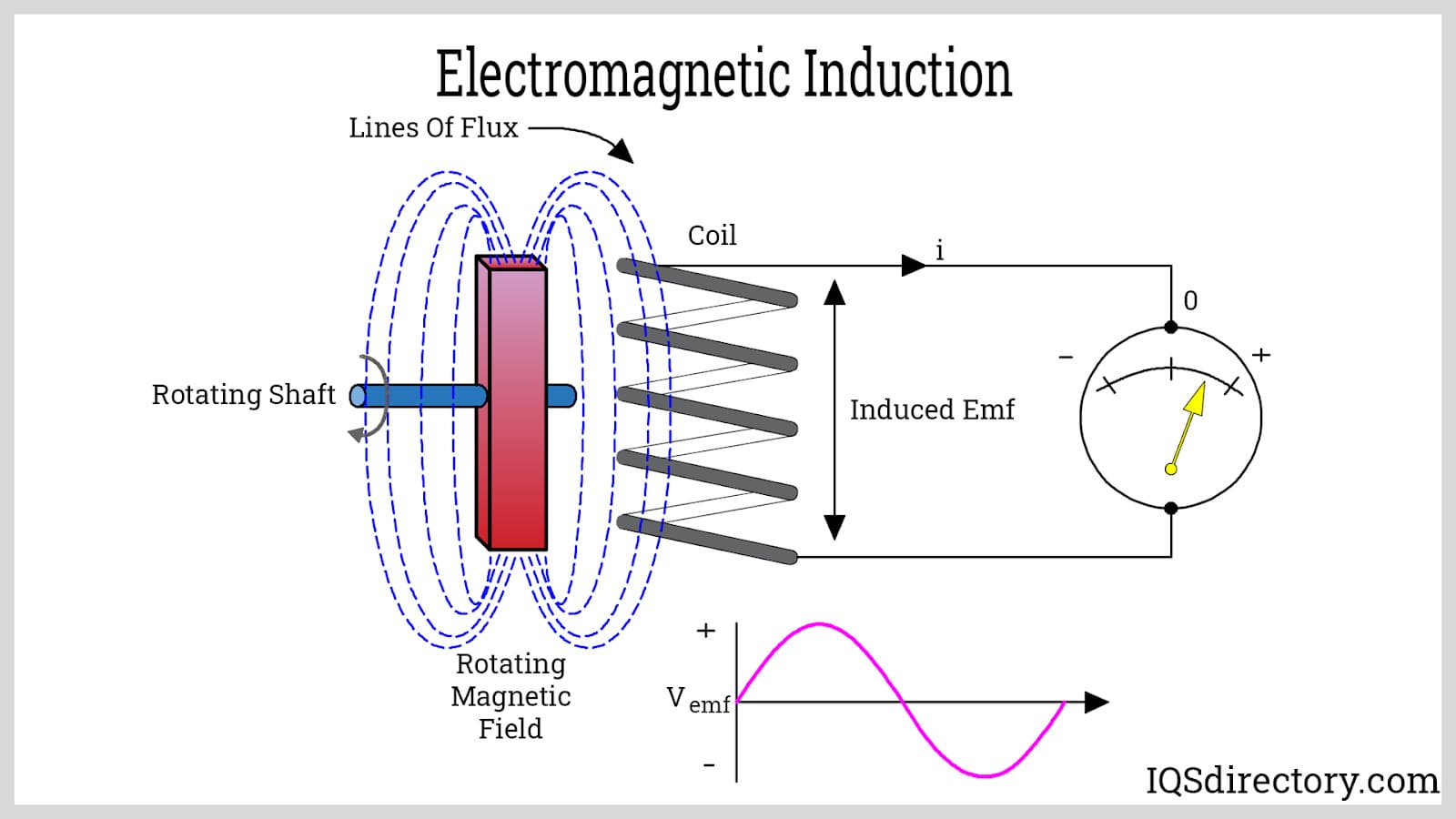
Illustrative image related to diagram of a coil
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘diagram of a coil’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Understanding Complex Coil Diagrams
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, especially those new to electrical engineering or purchasing components for manufacturing, struggle with interpreting complex diagrams of coils. This challenge can lead to miscommunications with suppliers, incorrect orders, and ultimately, production delays. For instance, a buyer in Nigeria may receive a coil with specifications that do not match their machinery requirements simply because they misinterpreted the diagram.
The Solution: To overcome this issue, it is crucial for buyers to enhance their understanding of coil diagrams. Engaging with technical support from suppliers can provide clarity on essential components such as the primary and secondary coils, as well as the make-and-break arrangements. Additionally, investing in training sessions or workshops that focus on electrical components can empower teams to read and utilize these diagrams effectively. Buyers should also request simplified versions of complex diagrams from suppliers, ensuring that they receive visual aids that highlight critical features without overwhelming detail.
Scenario 2: Sourcing Quality Components for Specific Applications
The Problem: International B2B buyers often face challenges in sourcing high-quality induction coils that meet specific application requirements, particularly in regions where access to reliable suppliers is limited. For example, a manufacturer in Saudi Arabia may find it difficult to determine whether a supplier’s coil diagram accurately represents the quality and performance needed for their automotive ignition systems.
The Solution: To address this sourcing challenge, buyers should establish strong relationships with multiple suppliers and conduct thorough due diligence. This includes reviewing technical specifications, certifications, and customer testimonials. Additionally, requesting sample coils along with their corresponding diagrams can allow buyers to verify quality firsthand before placing larger orders. Utilizing industry-specific platforms or networks to connect with reputable suppliers can also streamline the sourcing process, ensuring that buyers receive components that meet their exacting standards.
Scenario 3: Inadequate Technical Support Post-Purchase
The Problem: After purchasing coils based on diagrams, many B2B buyers experience inadequate technical support when integrating these components into their systems. This is particularly true for companies in South America, where local technical expertise may be limited. A buyer may find themselves struggling to troubleshoot issues arising from incorrect installation or unexpected performance discrepancies due to a lack of guidance.
Illustrative image related to diagram of a coil
The Solution: To mitigate this pain point, buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer robust post-purchase technical support. This can include detailed installation manuals, access to online troubleshooting resources, and direct lines of communication with technical experts. Suppliers should be encouraged to provide training sessions or webinars that delve into the operational intricacies of their products. Moreover, creating a feedback loop where customers can report issues and receive tailored advice can significantly enhance the integration process, ensuring that coils perform optimally in their intended applications. By selecting suppliers who prioritize customer support, buyers can foster a more seamless operational experience.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for diagram of a coil
When selecting materials for the construction of coils, particularly in applications such as ignition coils or induction coils, it is essential to consider several factors that affect performance, durability, and cost. The choice of material can significantly influence the efficiency and effectiveness of the coil in its intended application. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in coil manufacturing, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Copper for Coil Manufacturing?
Copper is one of the most widely used materials for coil windings due to its excellent electrical conductivity. It has a high melting point (1,984°F or 1,085°C) and can withstand significant thermal stress, making it suitable for high-temperature applications. Additionally, copper has good corrosion resistance, especially when coated, which enhances its longevity.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, which leads to efficient energy transfer. However, it is relatively expensive compared to other metals and can be prone to oxidation if not properly treated, which may affect performance over time.
Impact on Application: Copper coils are ideal for applications requiring high efficiency and low resistance, such as in transformers and inductors. They are compatible with various media, including air and oil, making them versatile.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM B170 for copper wire. Additionally, they should consider local availability and cost fluctuations due to market demand.
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Material for Coils?
Aluminum is another popular choice for coil manufacturing due to its lightweight and cost-effectiveness. It has a lower electrical conductivity than copper but is often used in applications where weight savings are critical. Aluminum coils can operate at temperatures up to 1,221°F (660°C) and are resistant to corrosion, especially when anodized.
Illustrative image related to diagram of a coil
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its lower cost and weight, which can reduce overall system costs. However, its lower conductivity means that aluminum coils may require more material to achieve the same performance level as copper, potentially increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Aluminum coils are suitable for applications where weight is a concern, such as in automotive and aerospace industries. They are compatible with various media but may require additional considerations for thermal management.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum wire. Additionally, they should be aware of local market conditions that may affect the availability of aluminum.
What Are the Benefits of Using Steel in Coil Applications?
Steel, particularly stainless steel, is utilized in coil applications where strength and durability are paramount. It offers excellent mechanical properties and can withstand high pressures and temperatures, making it suitable for harsh environments. Stainless steel also provides good corrosion resistance, which is essential in many industrial applications.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of steel coils is their robustness and resistance to deformation. However, the downside is that steel is heavier and less conductive than copper or aluminum, which may limit its use in certain electrical applications.
Impact on Application: Steel coils are often used in applications requiring structural integrity, such as in industrial machinery and heavy equipment. They are compatible with fluids and gases, making them versatile in various industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel. Additionally, they should consider the weight implications and potential shipping costs associated with steel products.
Why Choose Plastic or Composite Materials for Coils?
Plastic and composite materials are increasingly being used in coil applications, particularly for insulation and housing. These materials are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and can be engineered to withstand a range of temperatures. They also provide excellent electrical insulation properties.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of plastic materials is their versatility and low weight, which can lead to reduced manufacturing costs. However, they may not be suitable for high-temperature applications and can degrade over time when exposed to UV light or certain chemicals.
Impact on Application: Plastic coils are ideal for applications requiring insulation and protection from environmental factors. They are compatible with various media but should be evaluated for specific chemical resistances.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with relevant standards such as ASTM D638 for plastics. Additionally, they should assess the environmental impact and recyclability of plastic materials.
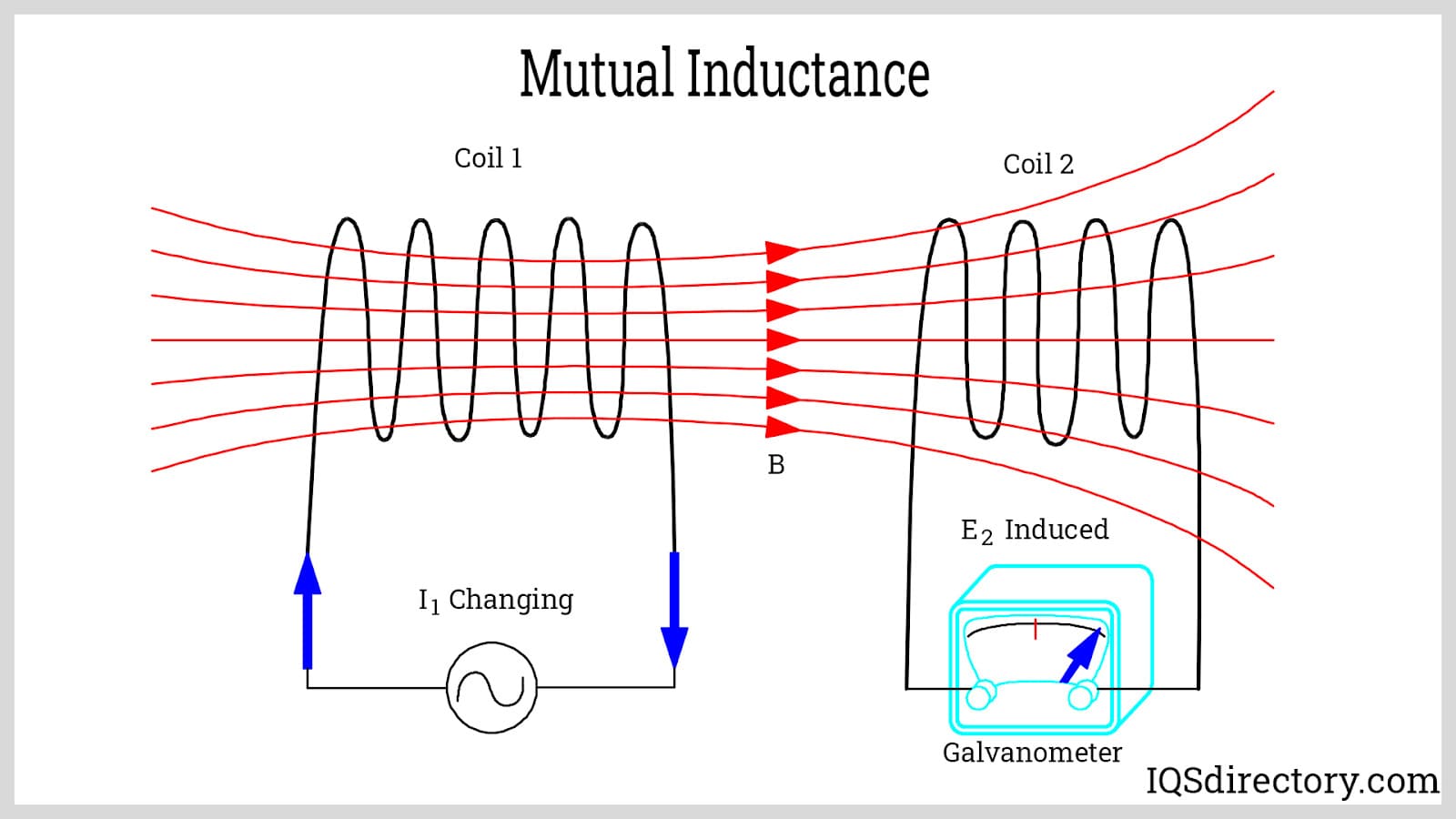
Illustrative image related to diagram of a coil
Summary Table of Material Selection for Coils
| Material | Typical Use Case for diagram of a coil | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Electrical coils in transformers | Superior conductivity | Higher cost and oxidation | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight coils in automotive | Cost-effective and lightweight | Lower conductivity | Medium |
| Steel | Structural coils in machinery | High strength and durability | Heavier and less conductive | Medium |
| Plastic/Composite | Insulation and housing for coils | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Limited temperature tolerance | Low |
In conclusion, selecting the right material for coil manufacturing requires careful consideration of the specific application, performance requirements, and regional market conditions. By understanding the properties and implications of each material, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for diagram of a coil
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing a Coil?
Manufacturing coils involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the required specifications and quality standards. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Coil Manufacturing?
The first stage in coil manufacturing is material preparation, where raw materials such as copper or aluminum wire are selected based on the coil’s intended application. The wire is often drawn to the desired diameter and must meet specific electrical and mechanical properties. Additionally, any insulation materials, such as enamel or plastic coatings, are prepared to ensure that the coil can operate safely and effectively under the intended conditions.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of Coil Production?
The forming stage involves winding the prepared wire around a core or mandrel. This process can be done manually or through automated machinery, depending on the complexity and volume of production. Precision winding techniques are critical to achieving the desired inductance and resistance values. Advanced CNC (computer numerical control) machines may be used to ensure consistency and accuracy in the winding process.
How Is Assembly Conducted in Coil Manufacturing?
Once the winding is complete, the assembly stage begins. This may involve adding components such as terminals, connectors, or additional insulation layers. For induction coils, a make-and-break mechanism may be integrated to facilitate the creation of high-voltage pulses. The assembly process must be carried out with care to avoid damaging the coil and to ensure that all components fit together seamlessly, which is vital for functionality and reliability.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Applied to Coils?
Finishing techniques in coil manufacturing include processes such as curing, coating, and testing. Curing involves applying heat or other methods to solidify any adhesives or coatings used in the assembly process. Coatings may provide additional insulation or protection against environmental factors. Finally, testing is performed to ensure that the coil meets the required specifications, including electrical resistance, inductance, and physical dimensions.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Coil Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is crucial in coil manufacturing to ensure that products meet international and industry-specific standards. The implementation of robust QA processes helps B2B buyers mitigate risks associated with subpar products and enhances trust in suppliers.
Which International Standards Should Be Followed in Coil Manufacturing?
Manufacturers of coils should adhere to various international standards, with ISO 9001 being one of the most recognized quality management standards globally. ISO 9001 outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS) that enhances customer satisfaction through consistent product quality. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking (for compliance with European safety standards) and API standards (for the oil and gas industry) may be relevant depending on the coil’s application.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Coil Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are critical throughout the manufacturing process. These typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing stages to identify and rectify any issues in real-time.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection of the finished product to verify that all specifications have been met before shipping.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify a supplier’s quality control practices.
-
Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can help buyers assess compliance with quality standards and manufacturing processes. This can include reviewing production methods, quality documentation, and employee training protocols.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports that outline inspection results, testing methods, and any non-conformance issues can provide transparency into the supplier’s processes.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspectors to evaluate the manufacturing facility and processes can offer an unbiased view of quality practices.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Coils?
Testing methods for coils are vital for ensuring performance and reliability. Common testing methods include:
- Electrical Testing: This includes measuring resistance, inductance, and insulation resistance to ensure the coil operates effectively within its designated parameters.
- Thermal Testing: Evaluating how the coil performs under varying temperature conditions can help predict its longevity and reliability in real-world applications.
- Mechanical Testing: Assessing the physical integrity of the coil, including tensile strength and fatigue resistance, ensures that the product can withstand operational stresses.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of several nuances when it comes to quality control in coil manufacturing.
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding the cultural context of suppliers can help buyers navigate communication and negotiation processes effectively.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Buyers must ensure that suppliers comply with both local and international regulations, which can vary significantly from one region to another.
-
Supply Chain Considerations: Geographic and logistical factors can impact delivery times and product quality. Buyers should consider these elements when selecting suppliers.
-
Risk Management: Establishing clear quality expectations and contractual obligations can help mitigate risks associated with international sourcing.
By focusing on these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing coils, ensuring that they receive products that meet their specifications and industry standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘diagram of a coil’
To assist B2B buyers in the procurement of diagrams of coils, this practical sourcing guide outlines essential steps to ensure a successful purchase. This checklist aims to enhance your decision-making process and minimize risks associated with sourcing technical diagrams.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is critical when sourcing a diagram of a coil. This includes determining the type of coil (e.g., induction coil, ignition coil) and its intended application. Providing detailed requirements will help suppliers understand your needs and offer tailored solutions.
- Key Considerations:
- Voltage ratings and current specifications.
- Dimensions and material requirements.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reputable suppliers who specialize in coil diagrams. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to gather a list of potential candidates. This foundational step is vital to ensure you are considering experienced and capable suppliers.
- Effective Strategies:
- Look for suppliers with a strong portfolio of similar projects.
- Check their industry reputation through reviews and testimonials.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Before making a commitment, assess the capabilities of potential suppliers. Request samples of previous work, including diagrams and technical drawings, to gauge their quality and precision. This evaluation ensures that the supplier can meet your specific needs.
- Important Aspects:
- Confirm their expertise in the type of coil you require.
- Evaluate their design and engineering resources.
Step 4: Verify Compliance and Certifications
Ensure that the suppliers comply with relevant industry standards and possess the necessary certifications. Compliance with international standards, especially for electrical components, is crucial for safety and reliability.
- What to Look For:
- ISO certifications or other relevant quality assurance certifications.
- Evidence of adherence to local and international regulations.
Step 5: Request Detailed Proposals
After narrowing down your options, request detailed proposals from your shortlisted suppliers. These proposals should include pricing, delivery timelines, and any additional services offered, such as revisions or support.
- Critical Elements:
- Compare pricing structures and total costs, including potential hidden fees.
- Assess the proposed timeline for delivery and any guarantees.
Step 6: Engage in Direct Communication
Establish direct communication with suppliers to clarify any doubts regarding their proposals. This engagement can provide deeper insights into their operational processes and customer service quality.
- Communication Tips:
- Prepare specific questions related to your project.
- Gauge their responsiveness and willingness to collaborate.
Step 7: Finalize Contracts and Agreements
Once you’ve selected a supplier, ensure that all agreements are documented in a formal contract. This contract should outline all terms, including deliverables, payment schedules, and dispute resolution mechanisms.
- Key Contract Elements:
- Clearly define the scope of work.
- Include clauses for quality assurance and warranties.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the procurement process for coil diagrams, ensuring they select the right suppliers and achieve their technical goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for diagram of a coil Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing a Diagram of a Coil?
When sourcing a diagram of a coil, understanding the cost structure is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margin.
-
Materials: The type of materials used, such as copper for winding or specialized insulation materials, significantly impacts costs. Higher-quality materials may lead to a higher initial price but can result in better performance and longevity.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the region and the complexity of the coil design. Skilled labor is often required for precision manufacturing, which can increase overall costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses associated with the production process. Efficient manufacturing operations can help reduce these costs.
-
Tooling: The investment in specialized tools and machinery necessary for producing specific coil designs can be substantial. Buyers should consider whether the supplier has the appropriate tooling already in place or if new tooling will be needed.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures that the coils meet specifications and performance standards. While this may add to the upfront costs, it can prevent costly returns and replacements.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary significantly based on distance, shipping method, and the Incoterms agreed upon. Buyers should factor in these costs when assessing overall pricing.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and profit. Understanding the margin expectations within different regions can help buyers negotiate better prices.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Coils?
Several factors influence the pricing of coils, particularly in an international B2B context.
-
Volume/MOQ: The minimum order quantity (MOQ) can affect pricing. Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom designs or specifications can increase costs. Buyers should assess whether standard designs meet their needs to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials: Fluctuations in raw material prices can impact overall costs. Buyers should stay informed about market trends to anticipate price changes.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products with specific certifications (e.g., ISO, RoHS) may carry a premium. However, these certifications can also enhance product reliability and marketability.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and financial stability can influence pricing. Establishing a relationship with reputable suppliers can lead to better pricing and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for determining who bears the shipping costs and risks during transit. This can significantly affect the total landed cost of the product.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Coil Prices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation strategies can yield significant cost savings.
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in transparent discussions about pricing. Leverage bulk purchasing and long-term partnerships to negotiate better terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Assess the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not only the purchase price but also maintenance, operational costs, and disposal. This holistic approach can lead to better purchasing decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing trends. For example, suppliers in Europe may have different pricing structures compared to those in the Middle East or Africa due to varying operational costs and market conditions.
-
Research and Benchmarking: Conduct market research to understand competitive pricing and ensure you are receiving fair offers. Use benchmarking against similar products to gauge value.
Disclaimer
Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough due diligence and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing diagram of a coil With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to the Diagram of a Coil: A Comprehensive Analysis
In the realm of electrical engineering and applications requiring high-voltage generation, various solutions are available to meet specific operational needs. While the diagram of a coil, particularly induction coils, has been a traditional choice for many applications, it’s essential to consider alternative technologies. These alternatives may offer distinct advantages depending on the context of their use, such as performance efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and ease of maintenance.
| Comparison Aspect | Diagram of a Coil | Capacitor-Based Solutions | High-Frequency Transformers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-voltage pulses | Moderate energy storage | High efficiency at high frequencies |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost | Low to moderate cost | Higher initial investment |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires careful setup | Simple circuit integration | Complex setup and tuning |
| Maintenance | Moderate maintenance needs | Low maintenance required | Regular maintenance required |
| Best Use Case | Spark generation, ignition systems | Power supply smoothing | RF applications, transmission systems |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Capacitor-Based Solutions?
Capacitor-based solutions store electrical energy and release it rapidly when needed. They are typically less expensive than coil systems, making them attractive for applications where budget constraints are a primary concern. Their integration into circuits is generally straightforward, allowing for quick deployment. However, the performance is limited in terms of energy output compared to induction coils, which can generate higher voltage pulses. Capacitor systems are ideal for applications like power supply smoothing and energy storage but may not suffice for high-voltage requirements.
How Do High-Frequency Transformers Compare to the Diagram of a Coil?
High-frequency transformers are designed to operate efficiently at elevated frequencies, making them suitable for applications in radio frequency (RF) transmission and other high-frequency scenarios. They offer superior efficiency and can handle larger power loads, which is advantageous in industrial applications. However, the initial investment for high-frequency transformers is usually higher, and their setup can be complex, requiring specialized knowledge. Maintenance can also be more demanding, as they may need periodic checks to ensure optimal performance. They are best utilized in systems where efficiency at high frequencies is paramount, such as in telecommunications.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the appropriate technology for high-voltage applications, B2B buyers must consider their specific requirements, including budget, application type, and desired performance. The diagram of a coil remains a robust option for applications needing high-voltage pulses, particularly in ignition systems. However, for buyers seeking cost-effective and simpler alternatives, capacitor-based solutions can be effective for energy storage and smoothing. On the other hand, those in need of efficient power handling at high frequencies should explore high-frequency transformers despite the higher costs and complexity. Ultimately, understanding the unique characteristics of each solution will enable buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
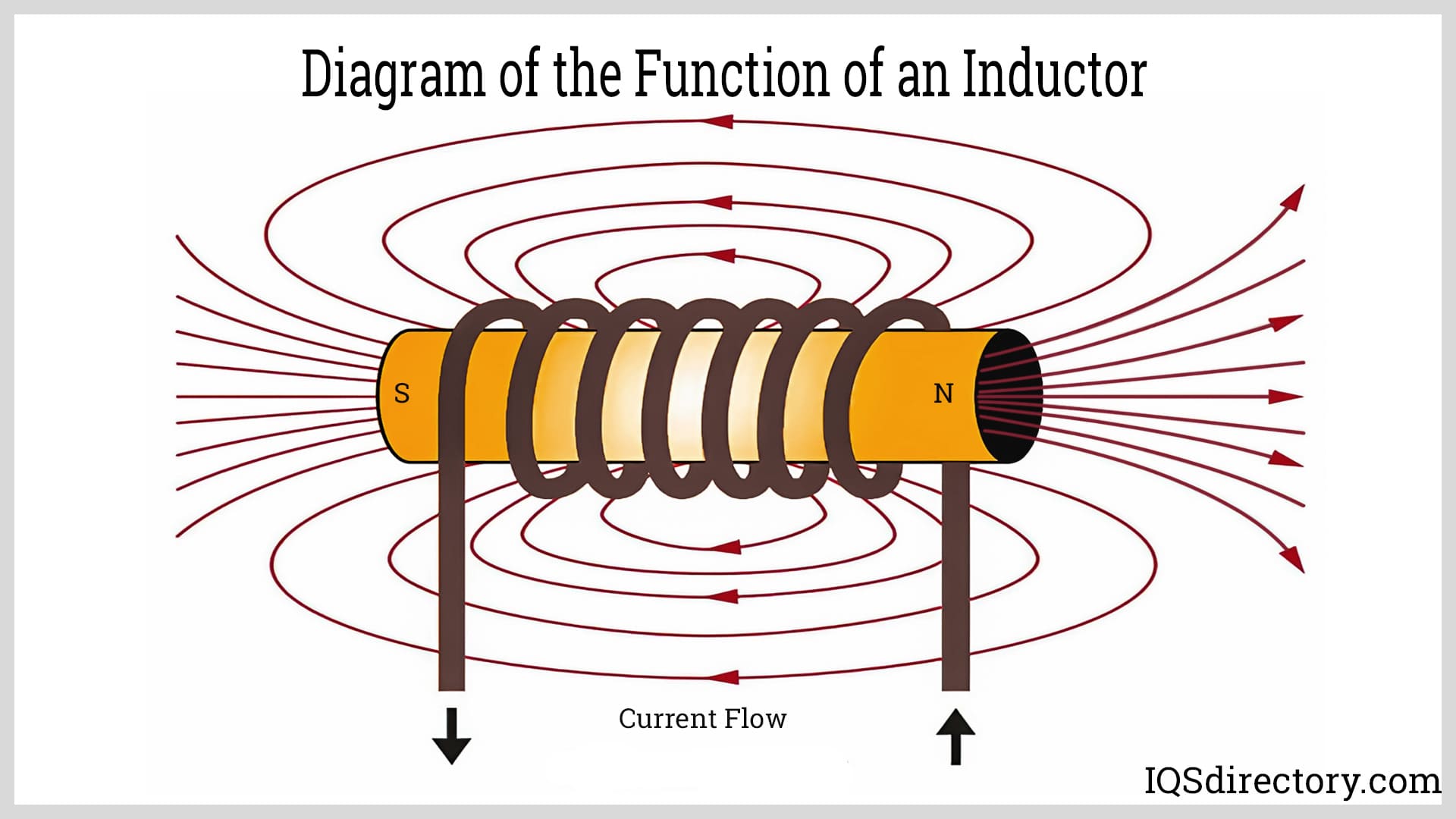
Illustrative image related to diagram of a coil
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for diagram of a coil
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Coil Diagram?
Understanding the essential technical properties of a coil diagram is crucial for B2B buyers involved in electrical components and systems. Here are some of the most critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material used in the coil, such as copper or aluminum, significantly affects its conductivity and resistance. High-grade copper is preferred for its superior electrical conductivity, ensuring optimal performance in various applications. For B2B buyers, selecting the right material grade can enhance efficiency and longevity, reducing maintenance costs. -
Inductance Value
Measured in henries (H), inductance indicates how effectively the coil can store energy in a magnetic field. A higher inductance value typically translates to a stronger magnetic field, essential in applications like transformers and inductors. B2B buyers should assess inductance requirements based on the specific application to ensure compatibility and efficiency. -
Winding Configuration
The winding configuration refers to how the wire is arranged around the core. Common configurations include solenoid, toroidal, and bifilar. Each type has distinct characteristics affecting inductance, resistance, and overall performance. Buyers should consider the specific needs of their application when selecting a winding configuration to achieve optimal results. -
Tolerance
Tolerance indicates the allowable deviation from specified dimensions or performance characteristics. For coils, tighter tolerances ensure consistent performance, which is critical in precision applications. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who can provide coils with the necessary tolerances to meet their operational standards and minimize the risk of failure. -
Temperature Rating
The temperature rating specifies the maximum operating temperature of the coil. High-temperature ratings are essential for applications in harsh environments, ensuring reliability and preventing breakdown. Buyers must evaluate the operational environment to select coils with appropriate temperature ratings, ensuring durability and performance.
What Are the Common Trade Terms in Coil Manufacturing?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and better communication between B2B buyers and suppliers. Here are some common terms to know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is vital for B2B buyers to ensure they source components that meet their quality and performance standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is essential for B2B buyers to understand their purchasing limits and manage inventory effectively. Negotiating MOQ can lead to cost savings and more efficient supply chain management. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent by a buyer to suppliers requesting pricing information for specific products or services. In the context of coils, submitting an RFQ can help buyers compare costs and terms, facilitating informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and delivery. Understanding these terms helps B2B buyers clarify shipping costs, insurance, and risk management, ensuring a smooth transaction process. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to its delivery. In coil manufacturing, understanding lead times is crucial for project planning and inventory management. Buyers should account for lead times to avoid disruptions in their operations. -
Customs Clearance
Customs clearance is the process of passing goods through customs so they can enter a country. For international B2B transactions, understanding customs procedures and requirements is vital to ensure timely delivery and compliance with regulations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, optimize their supply chains, and foster successful partnerships in the coil manufacturing industry.
Illustrative image related to diagram of a coil
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the diagram of a coil Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing the Coil Sector?
The global coil market is witnessing significant transformation driven by technological advancements and evolving buyer preferences. Key trends include the integration of smart technologies, such as IoT and AI, which are enhancing the functionality and efficiency of coil applications across various industries, from automotive to renewable energy. Additionally, there is a growing demand for high-performance coils that can withstand extreme conditions, particularly in regions like Africa and the Middle East, where environmental factors play a crucial role in product selection.
International B2B buyers are increasingly focused on sourcing coils that offer not only superior performance but also cost-effectiveness. The rise of e-commerce platforms and digital marketplaces has simplified procurement processes, enabling buyers from diverse regions, including South America and Europe, to access a wider range of suppliers and products. Furthermore, the emphasis on customization is becoming more pronounced, as businesses seek coils tailored to specific operational needs.
Another important market dynamic is the shift towards localized sourcing. Factors such as trade regulations, tariffs, and the desire for reduced lead times are prompting companies to explore suppliers closer to their operational bases. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers in developing regions like Nigeria, where local sourcing can enhance supply chain resilience and support economic growth.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Coil Industry?
Sustainability has emerged as a critical consideration in the coil sector, influencing both manufacturing processes and sourcing decisions. The environmental impact of coil production, particularly regarding energy consumption and waste generation, is prompting companies to seek out ‘green’ materials and practices. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials or adhering to energy-efficient manufacturing standards.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction, with a focus on ensuring fair labor practices and transparency within supply chains. This is particularly significant for international buyers who operate in regions with varying regulatory frameworks. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to attract global clientele.
Incorporating sustainable materials into coil production not only mitigates environmental impact but also enhances brand reputation among consumers who are increasingly environmentally conscious. As a result, B2B buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who can provide verifiable sustainability credentials, thereby aligning their procurement strategies with broader corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals.
What Is the Historical Context Behind the Development of Coils in B2B Markets?
The evolution of coils dates back to the late 19th century when they were first utilized in electromagnetic applications. Initially used in telegraphy and radio transmission, coils have since diversified into various applications, including automotive ignition systems and industrial machinery. This historical progression has been marked by continual improvements in design and materials, driven by the increasing demand for efficiency and performance.
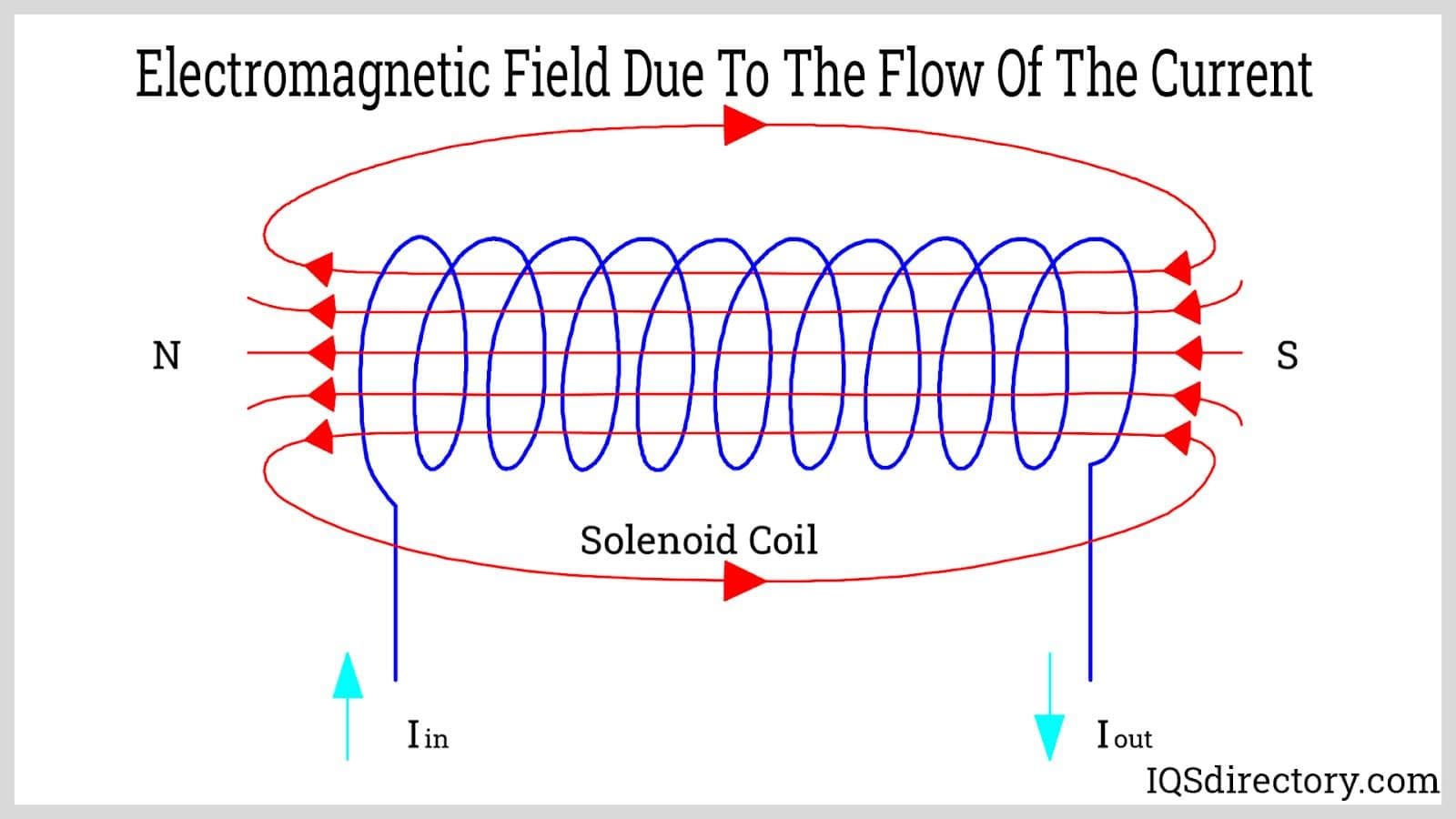
Illustrative image related to diagram of a coil
In the modern context, coils are pivotal in the transition towards renewable energy, particularly in wind and solar technologies. The advancement of coil technology has facilitated the development of more efficient energy conversion systems, further integrating them into everyday applications. As the coil sector continues to evolve, understanding this historical backdrop provides B2B buyers with insights into the potential future developments and innovations that may shape their sourcing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of diagram of a coil
-
How do I ensure the quality of the coils I am sourcing?
To guarantee the quality of coils, it is essential to conduct thorough supplier vetting. Request samples to assess the product firsthand and verify certifications that align with international standards. Additionally, consider third-party quality assurance audits to evaluate the manufacturing process. Establish clear quality specifications and criteria in your purchase agreements to hold suppliers accountable. Engaging in regular communication and feedback can also foster a quality-centric partnership. -
What is the best type of coil diagram for my application?
The optimal coil diagram depends on your specific application requirements. For ignition systems, an induction coil diagram is typically preferred, while transformer applications might require a different configuration. Assess the voltage and current specifications, as well as the intended use (e.g., automotive, industrial, etc.). Collaborating with engineers or technical experts can help you select the most suitable design and ensure it meets your operational needs. -
How can I customize the coil diagram for my specific needs?
Customization options for coil diagrams often depend on the supplier’s capabilities. Discuss your requirements for dimensions, materials, and any specific electrical characteristics with potential suppliers. Many manufacturers offer tailored solutions, but be prepared to provide detailed specifications and possibly engage in design iterations. Ensure that the supplier can accommodate your customizations within the required time frame and budget. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for coils?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among suppliers and depend on factors such as the complexity of the coil design and the materials used. Typically, larger orders can reduce unit costs, while smaller orders might incur higher prices. When negotiating with suppliers, inquire about flexibility in MOQs and explore potential discounts for bulk orders. Understanding the trade-offs between MOQ and pricing is crucial for effective budgeting. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing coils internationally?
Payment terms for international orders can vary widely based on supplier policies and your negotiating power. Common terms include upfront deposits, net 30, or even letters of credit for larger transactions. Clarify these terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings. Consider the potential impact of currency exchange rates on your costs, and explore payment methods that offer security and convenience, such as PayPal or escrow services. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing coils?
When importing coils, it’s important to factor in shipping costs, customs duties, and potential delays in transit. Work with logistics providers experienced in international shipping to navigate regulations and ensure compliance with local import laws. Establish a clear timeline for delivery and consider the impact of logistics on your overall supply chain. Keep communication open with both your supplier and logistics partner to anticipate any issues. -
How can I effectively communicate my technical requirements to suppliers?
To effectively communicate your technical requirements, prepare detailed specifications that outline dimensions, materials, electrical characteristics, and performance criteria. Utilize visual aids, such as diagrams or prototypes, to clarify your expectations. Regularly engage with suppliers through meetings or technical discussions to address any questions they may have. Establishing a collaborative relationship can facilitate better understanding and alignment on project goals. -
What certifications should I look for in coil manufacturers?
When sourcing coils, look for manufacturers that hold relevant certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and CE marking for compliance with European safety standards. Additional certifications, like RoHS for hazardous substances or UL for safety in North America, may also be important depending on your market. These certifications not only ensure product quality but also demonstrate the manufacturer’s commitment to regulatory compliance and industry standards.
Top 4 Diagram Of A Coil Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Pinterest – Ignition Coil Wiring Diagram
Domain: pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Ignition Coil Wiring Diagram, used to wire an ignition coil in a car’s spark plug to ignite fuel.
2. Facebook – Ignition System Diagram
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: A wiring diagram illustrating the ignition system of a vehicle, including the ignition coil, distributor, spark plug, battery, and related components.
3. Scribd – Ignition Coil Troubleshooting Guide
Domain: scribd.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: This document provides troubleshooting steps for ignition coil primary/secondary circuit DTC codes P0351 through P0354. It describes checking the ignition coil circuits one by one according to the specific DTC, and includes steps to inspect the coil assembly power source and harness connections. The diagnostic procedure involves clearing codes, shuffling coil arrangements to check if the code foll…
4. Mad Teddy – Old Sparky Ignition Coil Circuit
Domain: madteddy.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Mad Teddy’s ignition coil circuit, named “Old Sparky”, is based on an auto ignition coil, which is a type of induction coil. It operates by being activated at the right moment by the engine’s rotation, using a distributor to deliver the output to the appropriate spark plug. The circuit includes a capacitor (0.1 microfarad) to ensure a powerful spark for igniting the fuel/air mixture. The ignition …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for diagram of a coil
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of coils, particularly ignition and induction coils, presents a significant opportunity for international B2B buyers. Understanding the intricate design and functionality of these components, as illustrated in the accompanying diagrams, enables businesses to make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and product performance. By prioritizing quality sourcing from reputable suppliers, companies can mitigate risks associated with component failure and ensure compliance with industry standards.
The value of strategic sourcing extends beyond immediate cost savings; it fosters long-term partnerships that can drive innovation and adaptability in a rapidly changing market. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, leveraging local and global supply chains can enhance competitive advantage, ensuring access to the latest technology and expertise.
Illustrative image related to diagram of a coil
As you look ahead, consider the critical role that coils play in your applications, from automotive to industrial uses. Engage with suppliers who not only understand your specific needs but also offer robust support and solutions tailored to your market. Take the next step in enhancing your sourcing strategy—connect with trusted manufacturers today to secure the quality components your business requires for future growth.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.